Every brand or business wants to become a market leader. For that, it needs to attract the maximum customers out there. To achieve the same, it needs to have an unbeatable marketing strategy. The Marketing Mix model helps marketers plan a solid product or service offering that hits all the right notes with the target audience.
Marketing mix refers to the strategies or plan that a company formulates to increase awareness about its products or services. It is also known as the 4Ps of marketing- Product, Price, Place and Promotion since the marketing mix strategy is a mixture of these four elements. In case of a service, the marketing mix becomes 7Ps of Marketing with other three Ps being- Physical Evidence, People and Process.
Download the 4 Ps of Marketing Mix (Slide 4 of Complete Deck)
Knowledge of these Ps is a must for every marketer to develop a successful marketing strategy. Let’s look at each in detail:
4 Ps of Marketing: Product Marketing Mix
Product Marketing Mix, as we discussed above, is a combination of these 4 Ps:
1) Product: The product being sold is the most important element in the marketing mix. What is the functional value of the product? What customer needs and wants does it fulfill? What is its unique selling proposition (USP)? Without the sound knowledge of this, other Ps in the mix won’t be able to add much punch to the marketing strategy. All attributes of the product come under this element:
- Functionality / Features
- Appearance
- Quality
- Packaging
- Brand
- Warranty
- Service/Support
2) Price: Refers to the value you put for your product. Formulating the right pricing strategy depends upon a number of factors such as the cost of production, competitor’s pricing strategy, ability of the target market to pay, supply-demand, brand personality, and so on. It covers the following aspects:
- List Price
- Discounts
- Allowances
- Financing
- Leasing Options
Pricing Strategies:
Broadly speaking, there are three approaches to pricing a product:
- Cost-oriented Pricing: The profit margin is added on top of the cost of production
- Customer-based Pricing: Pricing is decided on the basis of what the market segment can pay for the product
- Competitor Pricing: The prices set by competitors influence the company’s pricing strategy
Download Product Pricing Strategies (Slide 13 of Complete Deck)
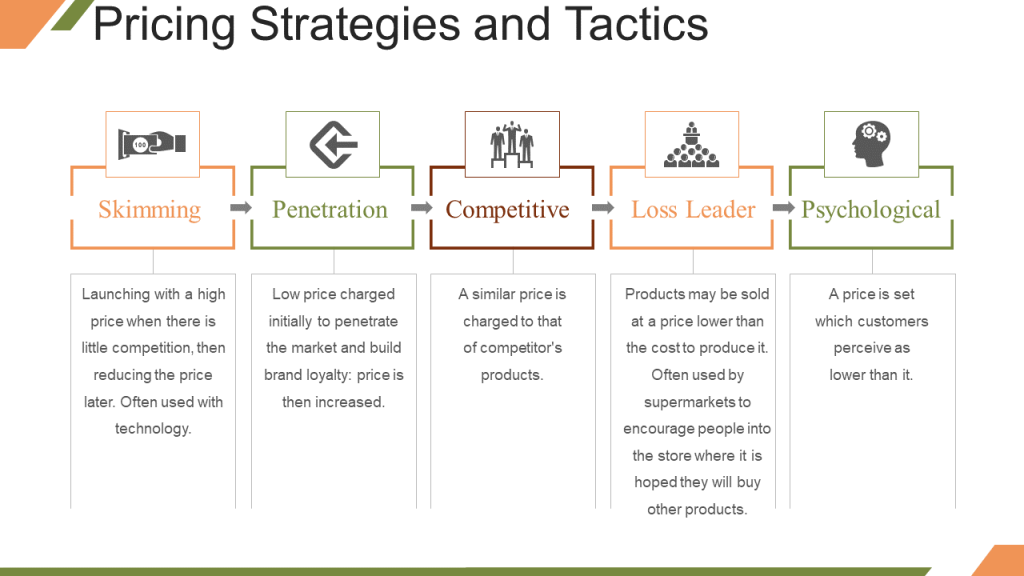
Let’s look at the pricing tactics in some detail:
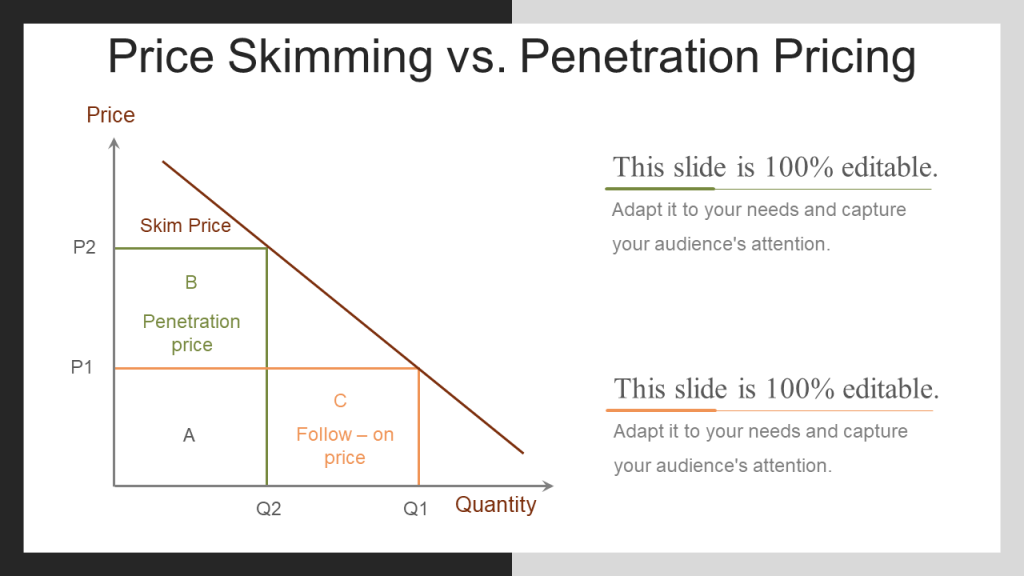
#1- Skimming Pricing: If you are the first to launch a product in the market, you can initially charge a high price and later skim it down as more competitors join the market. This is a short-term strategy since eventually competitors will enter your market with similar products. This strategy caters to a category of buyers known as “early adopters” and “innovators” who are quick to purchase new products in the market without worrying about their cost.
#2- Penetration Pricing: This strategy is the opposite of skimming pricing. Here you enter the market with a lower product price and later increase the price once the market share is established. This strategy is usually followed in a price-sensitive market and is done to attract customers of rivals and make them switch to your product. Although this strategy yields lesser profits than skimming pricing, it can be profitable in the long run as you have established a big market share which you can nurture for repeat sales. The “special offer for new customers” “first time purchase offers” are an example of this strategy.
#3- Loss Leader: Using this strategy, the business decides to offer a low priced product at an even lower price thereby incurring loss. The reason behind this is to attract customers into your store and encourage them to also buy other profitable goods. This is a sales promotion technique to boost up sales.
#4- Psychological Pricing: A very common strategy employed by marketing team. The pricing is perceived to be lower than it actually is. For example, a product is delivered at $9.99 instead of $10. The customers are tricked into considering the price as low even though it is the same as $10. Customers can see through this but still fall for it!
#5- Competitor Pricing (Price Takers)- When there are several businesses offering a similar product at similar prices, that becomes the “going-rate” of that product and your business has little option but to take that price for its product. You then have to build a competitive advantage using other Ps in the marketing mix.
3) Place: Refers to the dynamics of location. The advent of internet has added a new dimension to the “place” parameter. A product no longer needs to think about close proximity to target customers to get more reach. For many products, however, the right location and the right placement of products is still a key winning factor. The retail sector places great importance on placing products closer to the eye level and near the entry point to increase the probability of more purchases. Marketing team ensures POP (Point of Purchase) materials and display advertising are put at strategic locations to target more customers and increase their market share. The place element covers:
- Channel Members
- Channel Motivations
- Marketing Converge
- Locations, Logistics
- Service Levels
4) Promotion: Refers to all promotional activities undertaken to make people aware about the product. Advertising, public relations, word of mouth, personal selling and other forms of communication come under this element. To sump up:
- Advertising
- Personal Selling
- Public Relations
- Message
- Media
- Budget
Download Promotion Strategies (Slide 17 of Complete Deck)
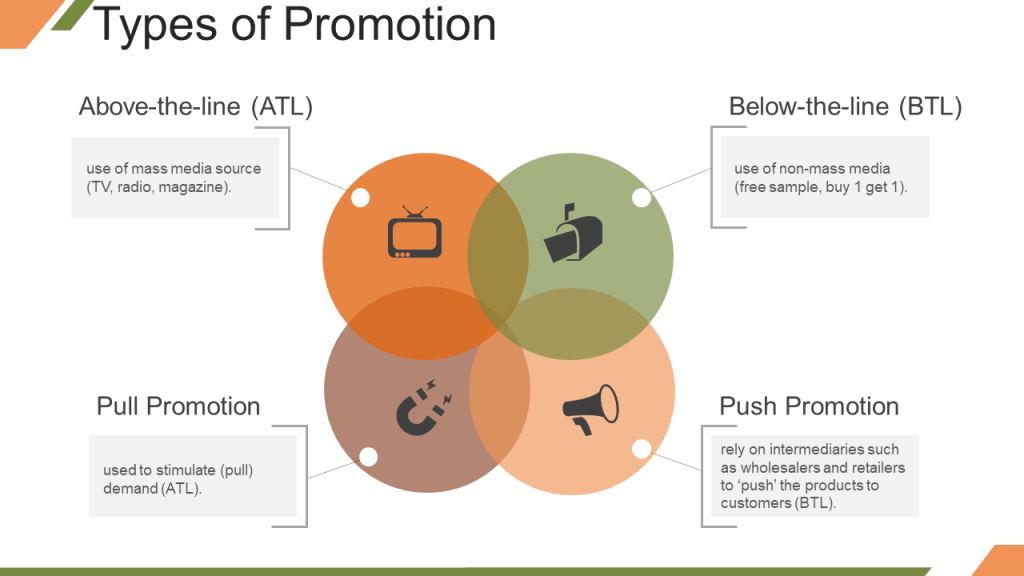
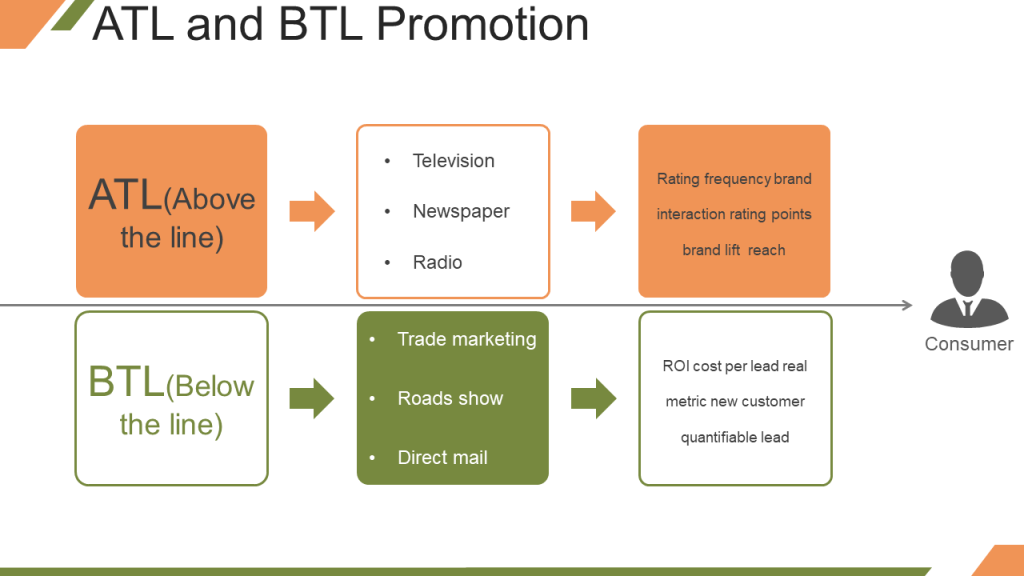
The promotional activities can be divided into- Above the Line (ATL) Promotion and Below the Line (BTL) Promotion. ATL involves the use of mass media such as print ads, television commercials, and radio ads to increase awareness about the product amongst mass audience. Below the Line advertising is use of non-mass media to target specific customers. It includes product demos at malls or other public places, roadshows, distribution of pamphlets and brochures, and other non-conventional methods of promotion.
Download Types of Promotion Diagram (Slide 18 of Complete Deck)
7 Ps of Marketing: Service Marketing mix
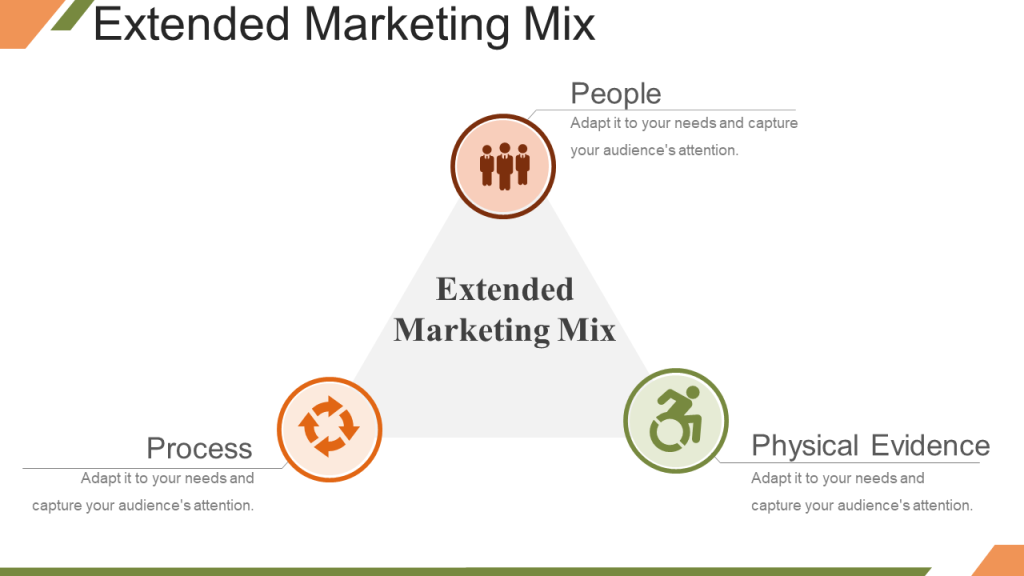
Apart from the 4 Ps of the product marketing mix, the marketing mix of a service has three additional Ps, namely People, Process and Physical Evidence.
5) People - The internal as well as the external audience come under people. Knowledge of the company’s staff as well as its customers can be useful for the marketing team in creating better strategies. Marketers should know about the preferences of the businesses’ target audience. That will help them mould their message accordingly.
People working in your organization are the ones providing service to your customers. Their training, motivation and communication skills have to be top class so that your service is the best in the market. The customer support should be ready to help the customers around the clock. Live chat and support through social media should also be made available. The behavior of salespeople and customer support team towards customers can be a strong factor in the success of your service.
6) Process - Process includes the systems and mechanisms by which the service is executed and delivered to the end customer. Quick and efficient delivery can be the USP of a service. Companies keep expanding its delivery network to aid faster delivery of their services. The marketing team can utilize the process strategy by attracting customers with one-day delivery offers if the company has the capabilities to achieve that.
7) Physical Evidence - Intangible services can be enhanced with tangible services. First and foremost, the physical environment where the service is delivered plays a huge role in influencing customer’s perception of the service. For example, the ambience and the furniture used in a cafe will make the service look modern, classic or plain boring. The sound, colors, smell of a place evoke emotions that become associated with the brand. The signs, symbols, brochures, staff uniform, logos, etc. contribute in brand building and a marketing team employs all these physical evidences to enhance brand experience and attract more customers.
4 Ps to 4 Cs:
An extension of marketing mix model was proposed by Robert F. Lauterborn. Since customer is the king in a business, four Ps is replaced by 4 Cs which are:
- Customer Value - replaces product with focus on how the product satisfies customer wants and needs
- Cost - replaces price and includes opportunity cost also
- Communication - replaces promotion with focus on an open dialogue with customers
- Convenience - replaces location with focus on the ease of purchasing a product
Marketers must have learnt about all these marketing strategies during their course. How so ever simple they might seem, they are the foundations of a successful marketing strategy and should be kept in mind at all times by the marketing team.
“Marketing is no longer about the stuff that you make, but about the stories you tell.”- Seth Godin




 Customer Reviews
Customer Reviews