Role And Importance Of Prioritization In Time Management Training Ppt
This training module on the Role and Importance of Prioritization in Time Management comprehensively covers the concept of prioritization, its importance, and the process people follow while prioritizing tasks. In detail, it also covers prioritization techniques Eisenhower Matrix, ABC Prioritization, Ivy Lee Method, MoSCow Prioritization, and Impact-Effort Prioritization. Further, it discusses task prioritization tips, challenges individuals and organizations and distractions internal and external to prioritization, and CEOs task prioritization approach. It also contains key takeaways, exercises, and discussion questions related to the topic. The deck has PPT slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, and training completion certificate. It contains energizer activities to engage the coaching session audience. It also includes a client proposal and assessment form for training evaluation.
This training module on the Role and Importance of Prioritization in Time Management comprehensively covers the concept of ..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Role and Importance of Prioritization in Time Management. This presentation deck contains 111 well-researched and uniquely designed slides. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon, and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 5
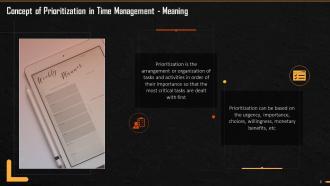
This slide explains the meaning and concept of prioritization in time management. It says that Prioritization is the arrangement or organization of tasks and activities in order of their importance so that the most important tasks can be dealt with first. Prioritization can be based on the urgency, importance, choices, willingness, and monetary benefits, etc.
Slide 6
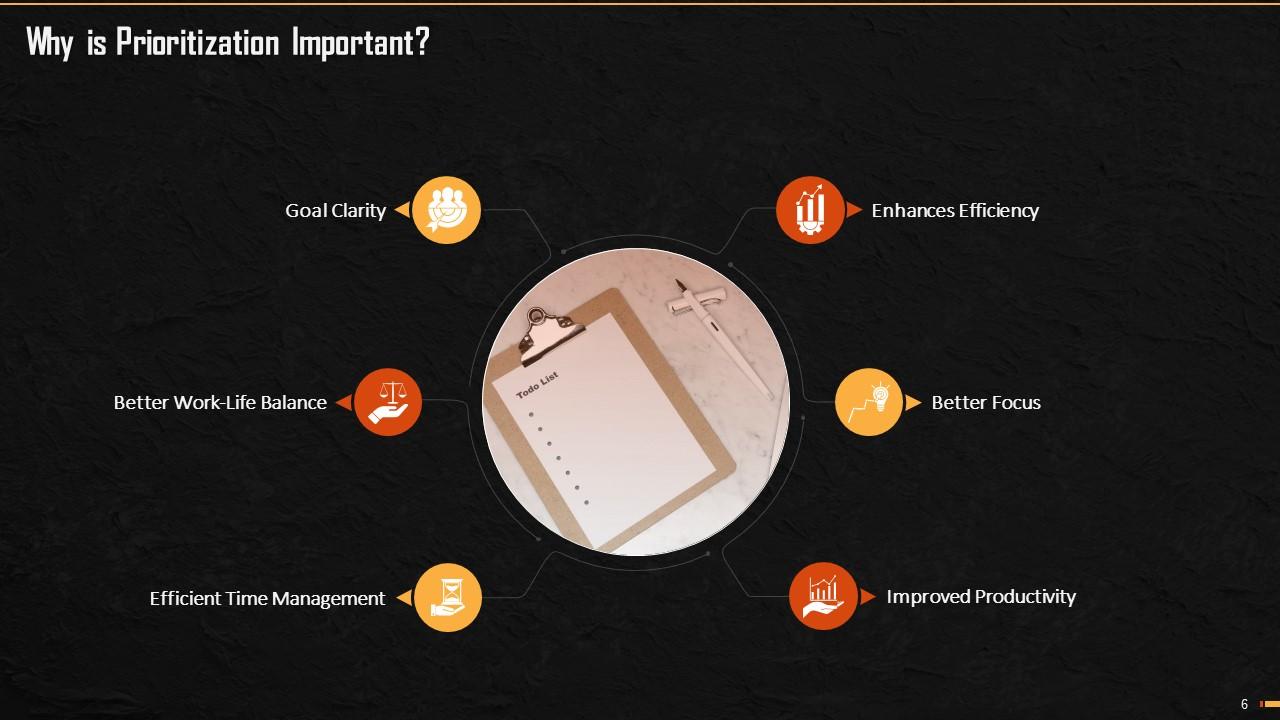
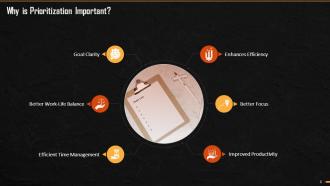
This slide explains the reasons for prioritizing tasks in normal life and workplace. Prioritization is crucial as it improves efficiency, leads better focus, improves productivity, helps in time management, offers work-life balance, and provides clarity in goals.
Slide 7
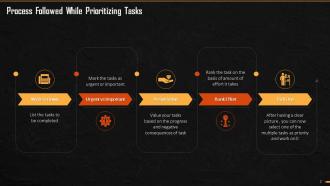
This slide illustrates the process to be followed to prioritize tasks. It states that for accurate prioritization of tasks, the individual must focus five things before taking a decision. The five activities are - writing down the tasks to be completed, categorizing the tasks as urgent or important, assigning value to tasks, ranking the amount of effort required for each task, and then pick the one that has the highest ranking for execution.
Slide 8
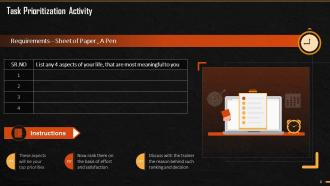
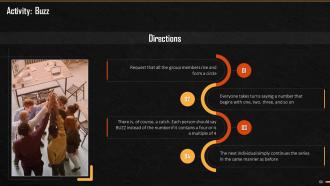
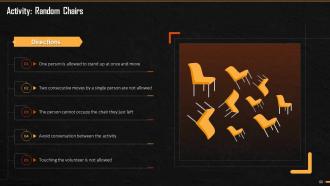
This slide mentions the activity that can be conducted by the trainer to briefly give overview to the trainees about how tasks can be managed and prioritized.
Slide 11
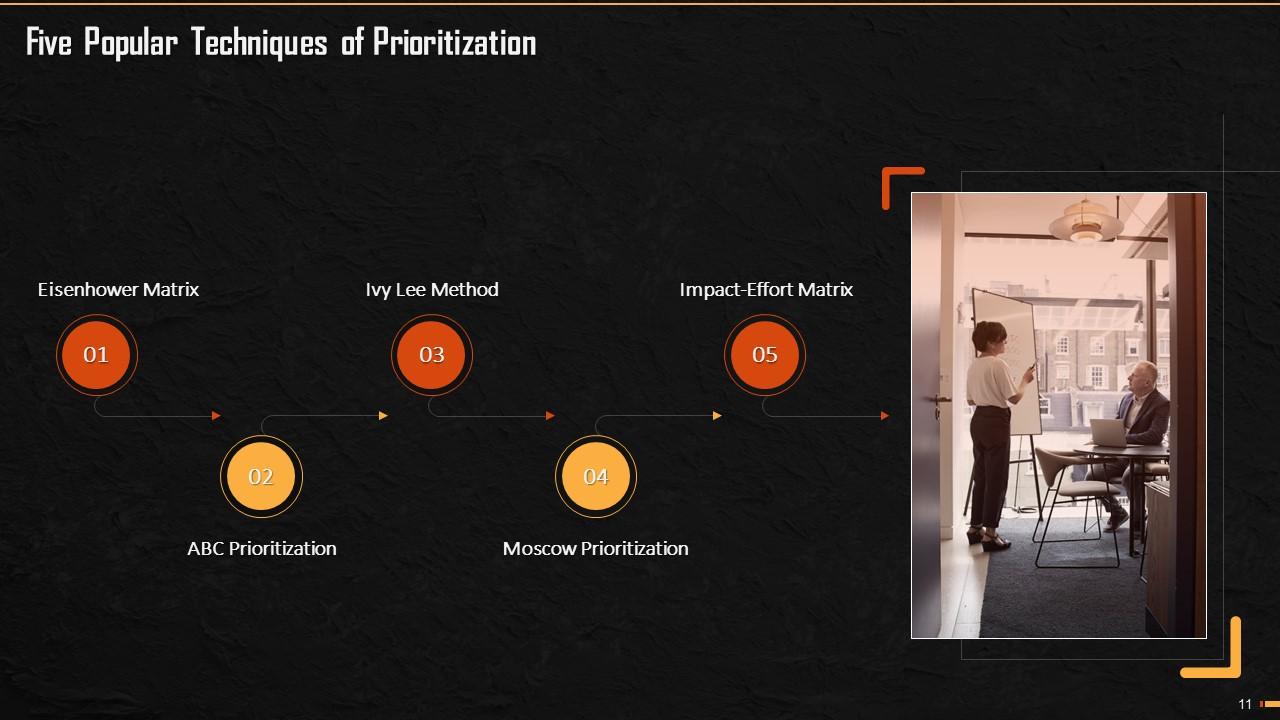
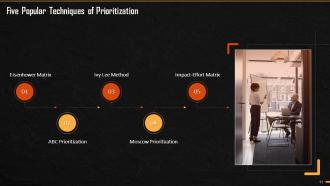
This slide lists techniques used in prioritizing tasks. These are Eisenhower Matrix, ABC Prioritization, Ivy Lee Method, MoSCowPrioritization, and Impact-Effort Matrix.
Slide 12
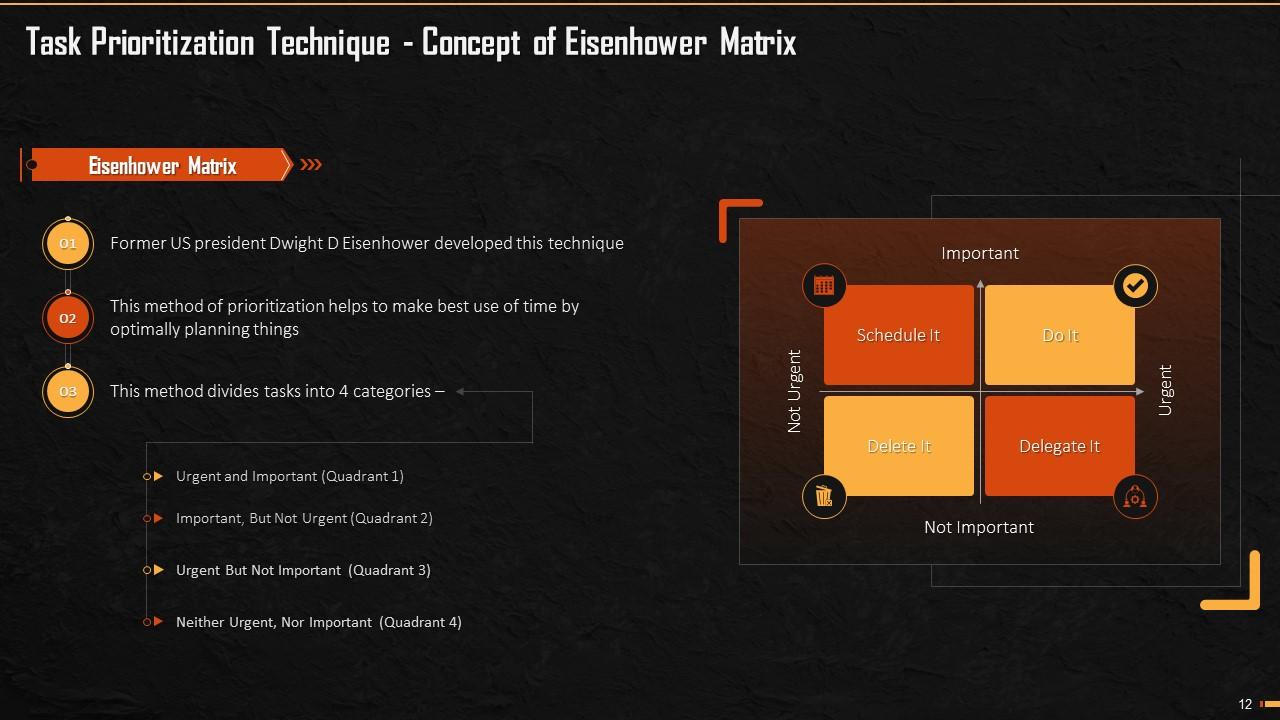
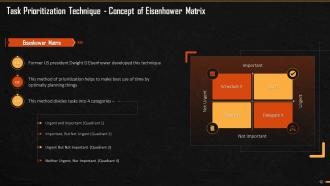
This slide explains the Eisenhower Matrix of Prioritization. Ex-US President Dwight D. Eisenhower developed it. The technique helps to optimally manage time and plan things. This method divides tasks into four main quadrants – Urgent and Important; Important, but not Urgent; Urgent but not Important, and Neither Urgent Nor Important.
Slide 13
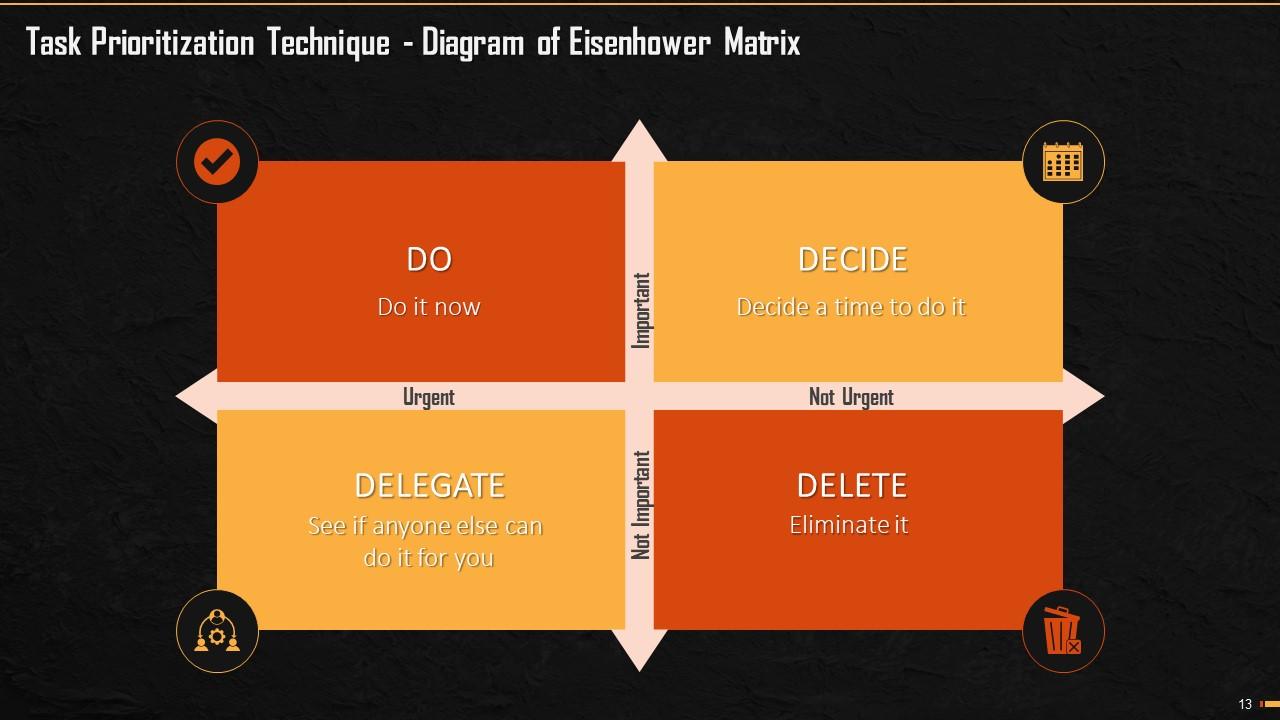
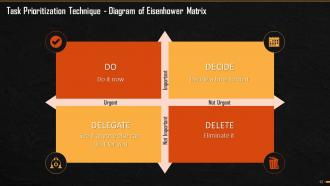
This slide mentions how Eisenhower matrix is prepared and what each quadrant means. This method divides the tasks into 4four main quadrants of Urgent and Important; Important, but not Urgent; Urgent, but not Important and Neither Urgent Nor Important.
Slide 14
This slide explains the examples for each quadrant of the Eisenhower matrix that is the tasks that are Urgent and Important; Important, but not Urgent; Urgent, but not Important and Neither Urgent Nor Important.
Slide 15
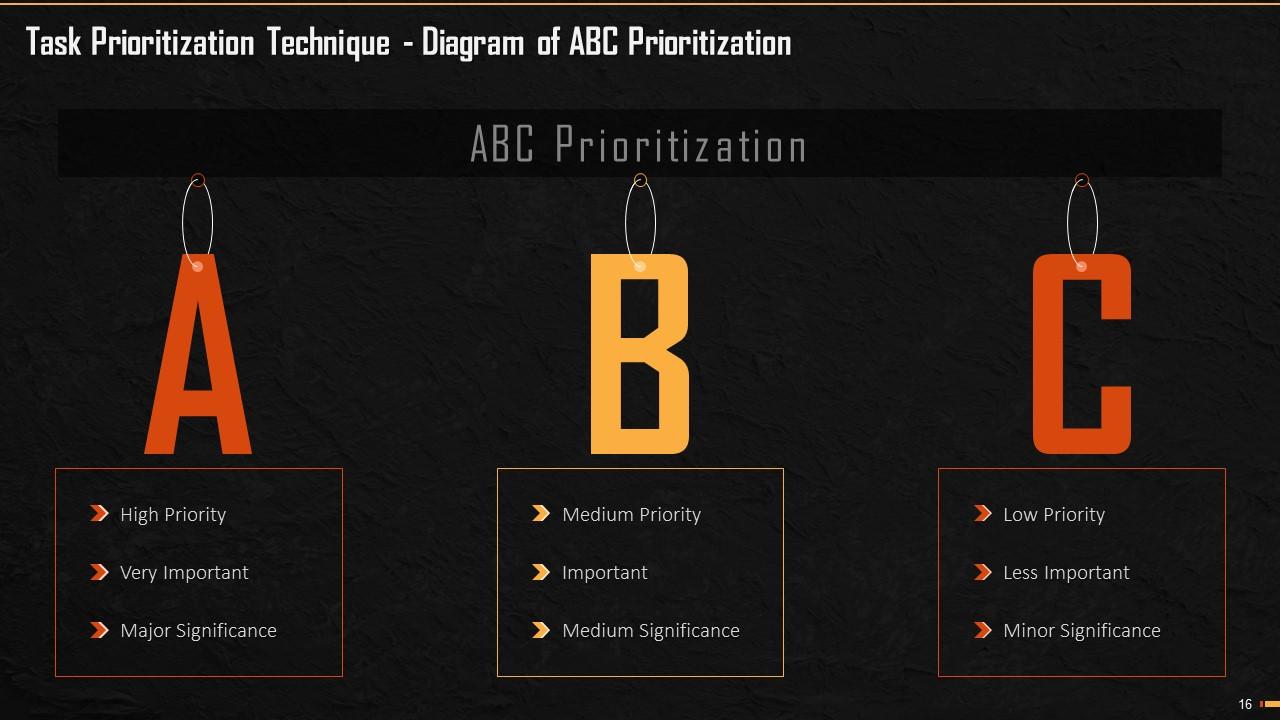
This slide explains the ABC Prioritization Technique of Prioritization. Alan Lakeindeveloped it and the technique uses the first three letters of the alphabet to set the priorities.
Slide 16
This slide explains the ABC Prioritization Technique of Prioritization. It uses the three alphabets on the basis of urgency and importance.
Slide 17
This slide explains the A element of ABC Prioritization Technique. The tasks under this category go under the critical and urgent section of Eisenhower Matrix. These tasks should be done, and if not done, there are consequences to it. The example is not being able to finish a task that your senior needs by the next day.
Slide 18
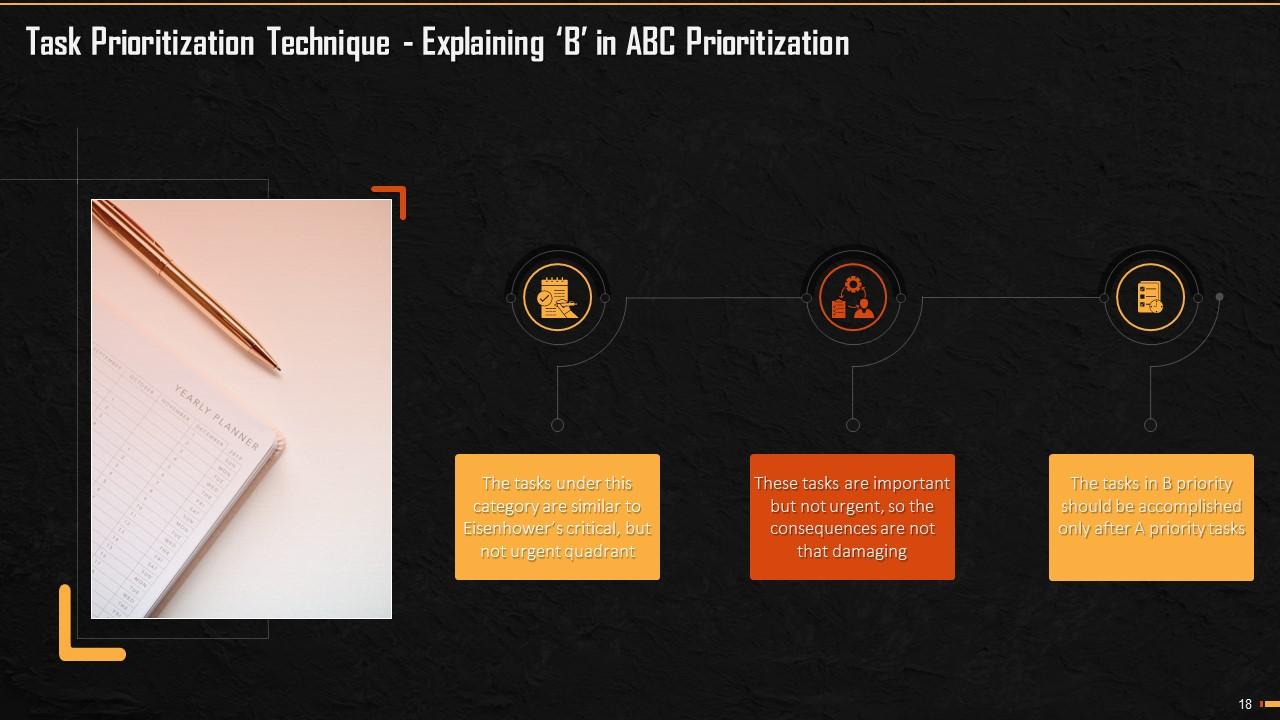
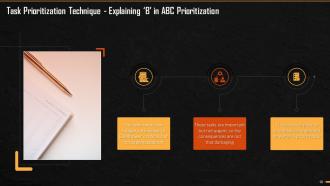
This slide explains the B element of ABC Prioritization Technique. The tasks under this category are similar to Eisenhower’s ‘critical, but not urgent’ quadrant. These tasks are important but not urgent, so the consequences are not that severe.
Slide 19
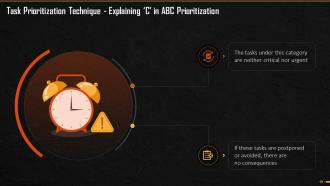
This slide explains the C element of ABC Prioritization Technique. The tasks under this category are neither critical nor urgent. If these tasks are postponed or avoided, there are no consequences.
Slide 20
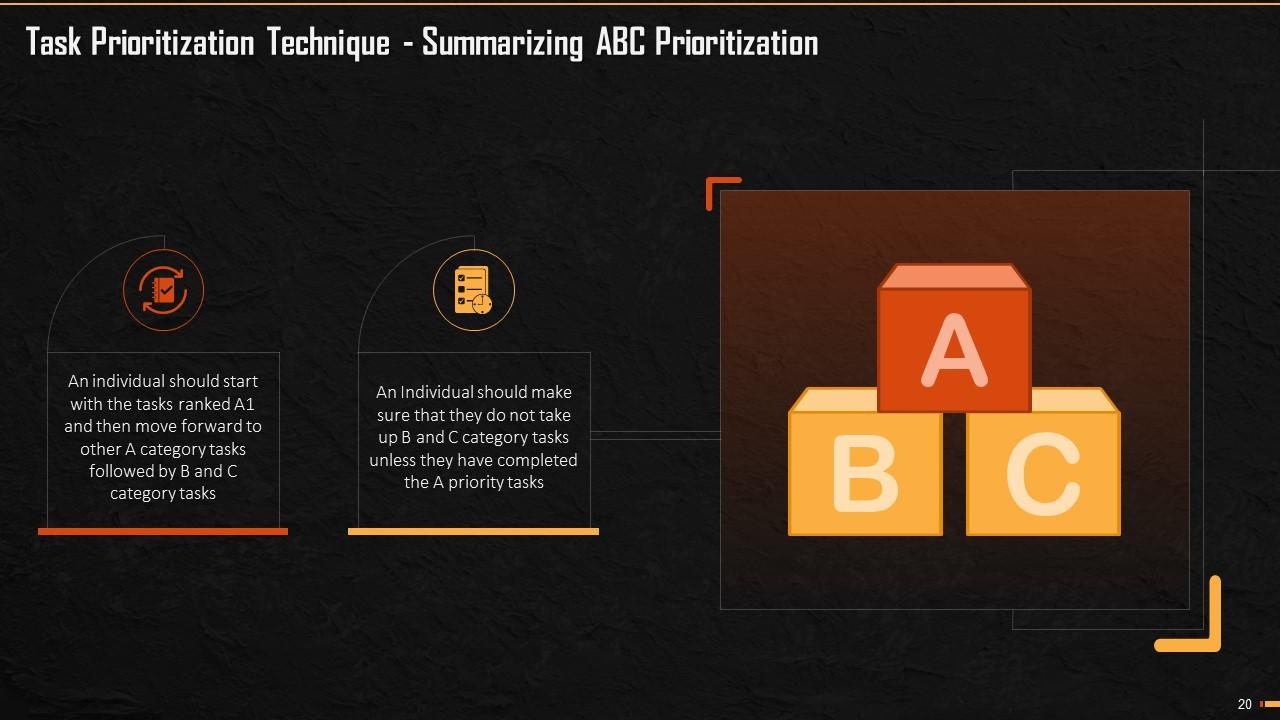
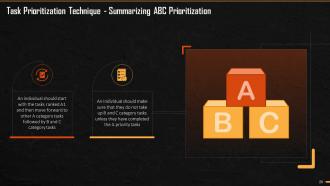
This slide summarizes the ABC Prioritization Technique. It says that an individual should start with the tasks ranked A1 and then move forward to other A category tasks followed by B and C category tasks. An Individual should make sure that they do not move to B and C category tasks unless they have completed the A priority tasks.
Slide 21
This slide mentions the activity that a trainer can conduct during a session. This exercise is based on the ABC technique of prioritization and will help the trainees plan their day better.
Slide 23
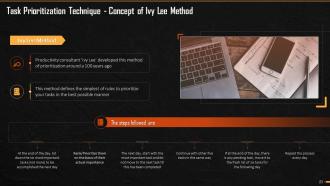
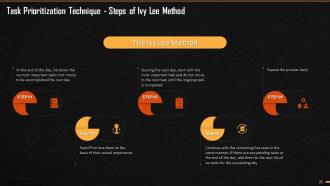
This slide explains the Ivy Lee Method and the steps followed in this method for prioritization of tasks. It says that this method was developed 100 years ago by productivity consultant ‘Ivy Lee’. This is one of the simplest methods to prioritize your tasks in the best possible manner.
Slide 24
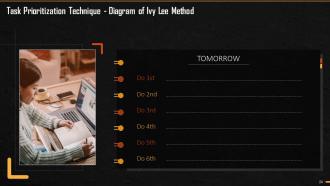
This slide illustrates the Ivy Lee Method of Prioritization. In this slide, the diagram explains how priorities are listed and considered in this method.
Slide 25
This slide explains the steps followed in the Ivy Lee Method of Prioritization. There are five steps to be followed- At the end of the day, list down the six most important tasks (not more) to be accomplished the next day, Rank/Prioritize them on the basis of their actual importance. The next day, start with the most important task and do not move to the next task till this is done, Continue with other five tasks in the same way. If at the end of the day, there is any pending task, move it to the fresh list of six tasks for the following day. Repeat the process daily.
Slide 26
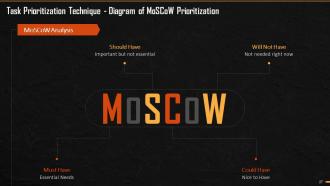
This slide explains the meaning and concept of MoSCoW method of Prioritization. It says Software development expert Dai Clegg created it. It is also known as MoSCoW method or MoSCoW analysis. It includes four main categories – Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, and Will Not Have.
Slide 27
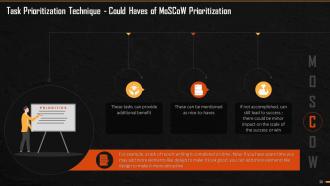
This slide depicts the diagram for MoSCoW Method of Prioritization. It mentions the major elements of MoSCoW method and their meaning in prioritizing tasks.
Slide 28
This slide explains the first head of MoSCoW analysis that is ‘Must Have’. These are high priority tasks that contribute to the overall growth and success. These tasks when not performed to a high degree of satisfaction, can cause overall failure.
Slide 29
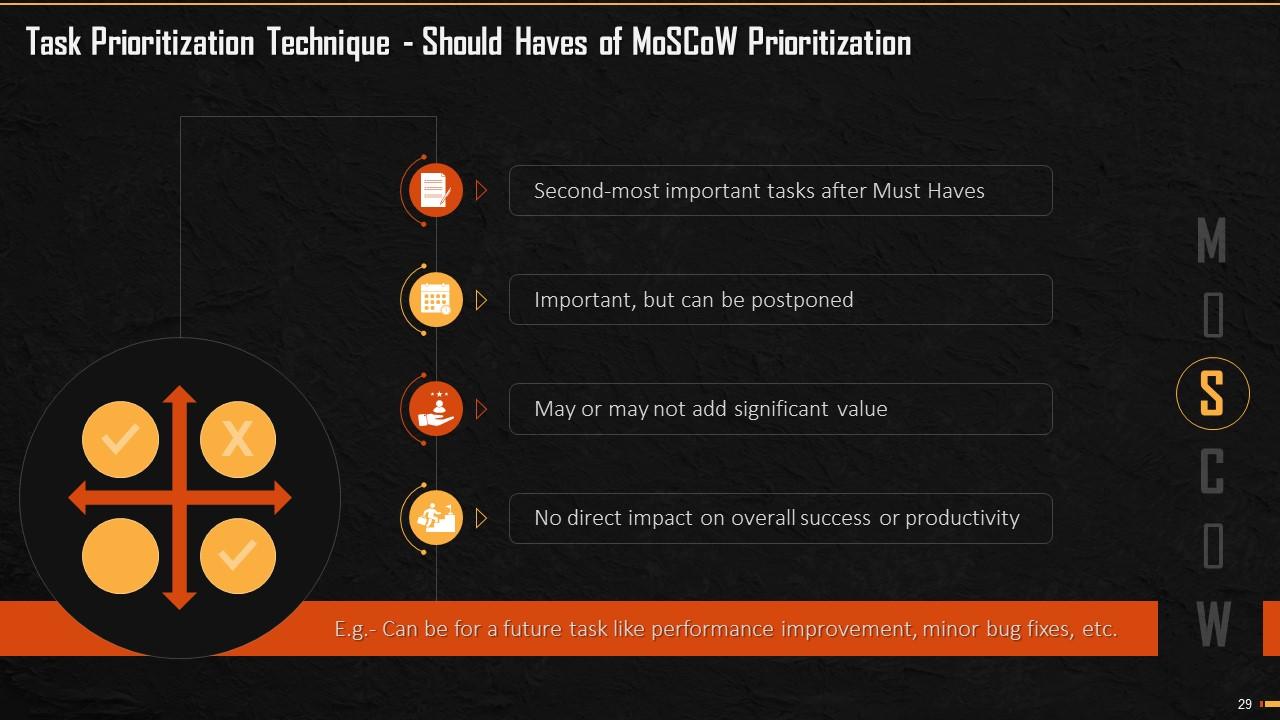
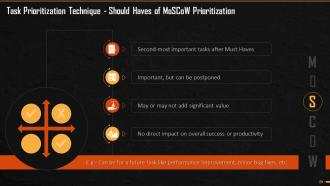
This slide explains the second head of MoSCoW analysis that is ‘Should Have’. These are the second priority tasks after the Must Haves. These tasks are important but can be postponed. These tasks do not add significant value to productivity and do not have direct impact on overall success.
Slide 30
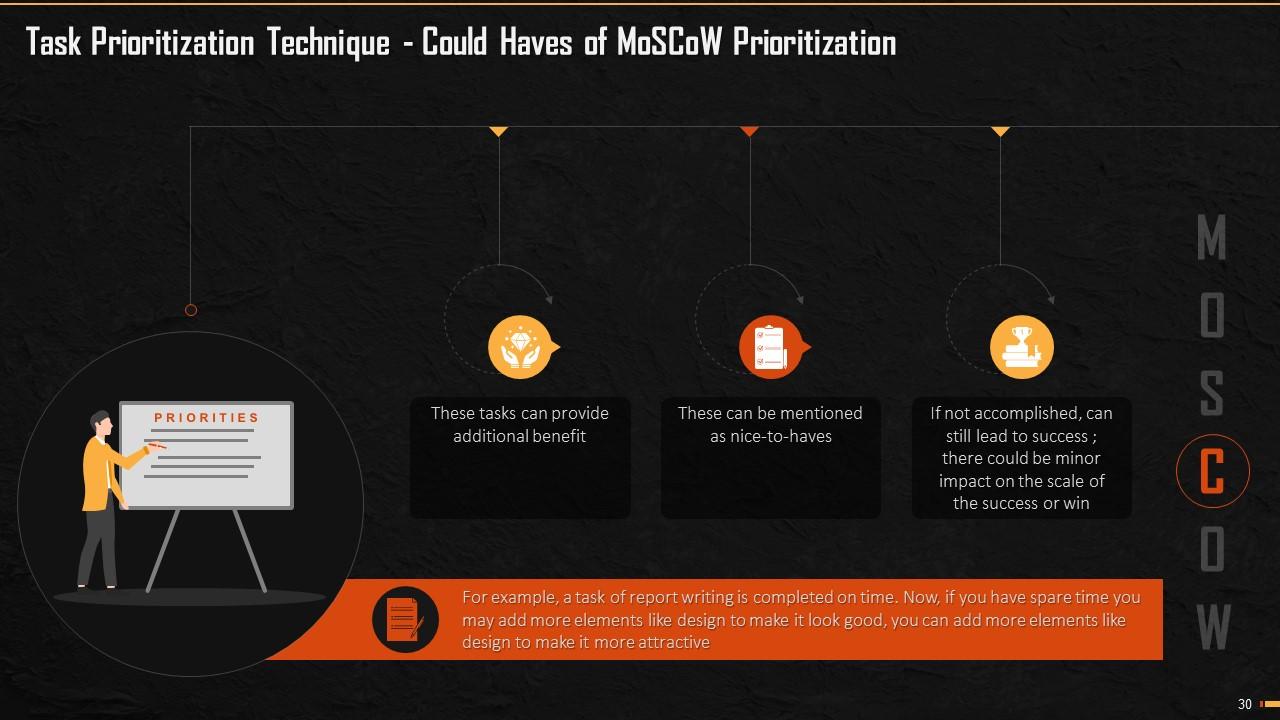
This slide explains the third head of MoSCoW analysis that is ‘Could Haves’. These tasks provide additional or add-on benefit to the ongoing performance. These tasks, even if skipped, do not pose any hindrance to the achievement of successful results.
Slide 31
This slide explains the fourth head of MoSCoW analysis that is’ Will Not Haves’. These are tasks that cannot be immediately and are, usually, pushed to a future date. These are the least important tasks that need to be completed only if you get free time, after all the important and urgent tasks have been addressed.
Slide 32
This slide explains the meaning and concept of priority matrix. It is a powerful time and task management tool that helps an individual focus on tasks that matters the most and keeps the crucial tasks on track. As mentioned, it categorizes tasks on the basis of effort these require and the impact they will have on performance and productivity. There are four quadrants in priority matrix. The Quadrant 1 is Quick Wins, followed by three other quadrants that are Major Projects, Fill-Ins and Thankless Tasks, etc.
Slide 33
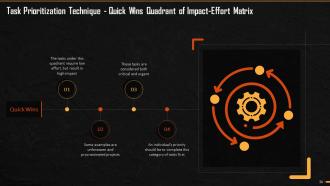
This slide explains the Priority Matrix, how is it built, and the quadrants in it.
Slide 34
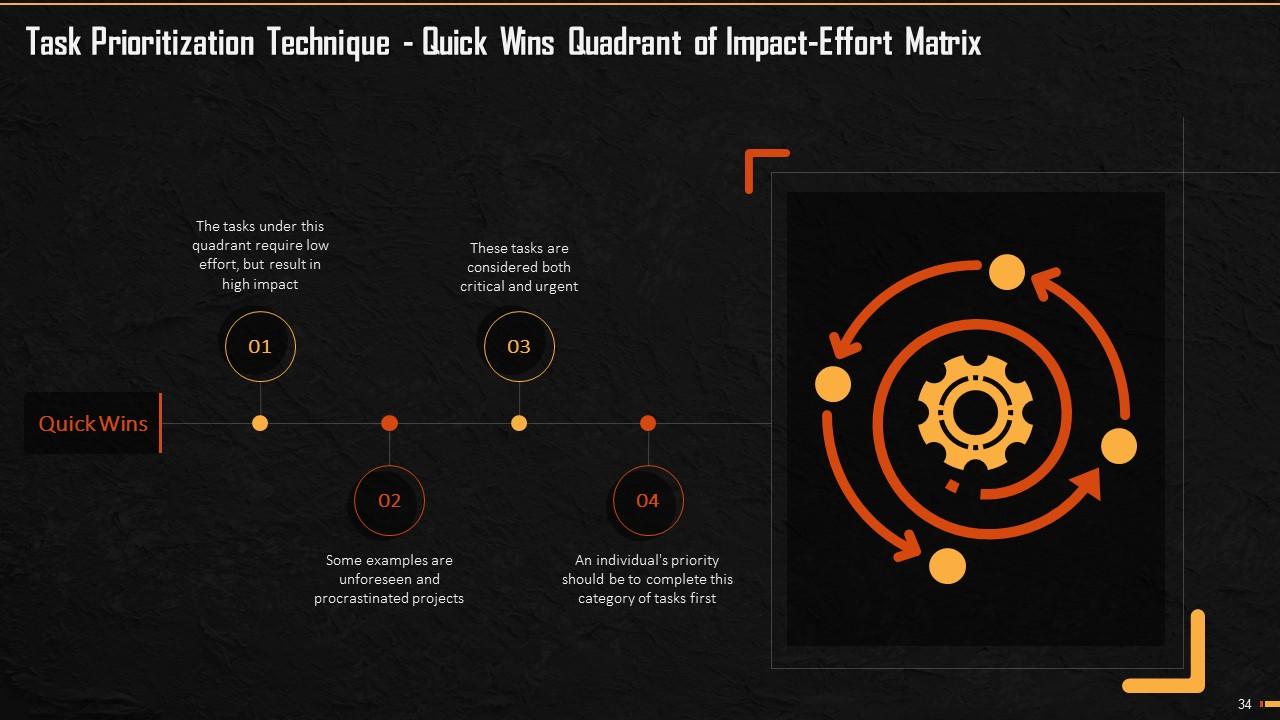
This slide explains the first quadrant of priority matrix that is quick wins. It says that the tasks under this quadrant require low effort but have high impact. An individual's priority should be to complete this category of tasks first.
Slide 35
This slide explains the second quadrant of priority matrix that is major projects. It says that the tasks under this under this category require high effort and have a very high impact. Individual should set deadlines for such tasks and build checkpoints into the schedule.
Slide 36
This slide explains the third quadrant of priority matrix that is fill-ins. It says that the tasks under this under this category require low-effort and have low impact. Individuals can delegate or decline such tasks.
Slide 37
This slide explains the fourth quadrant of priority matrix that is thankless tasks. It says that the tasks in this quadrant require a lot of effort, but have little impact on productivity. Individual should try to postpone or eliminate such tasks so as to not get distracted from high-impact tasks.
Slide 38
This slide exhibits a picture related to organization and prioritization. The trainer can show this slide only if he wants to add some humor to the session.
Slide 40
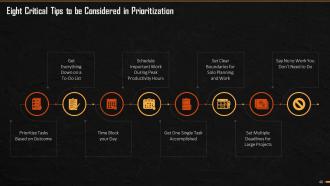
This slide explains the eight tips that must be followed while prioritizing tasks at the workplace or in personal life. The tips are prioritize tasks based on outcome; time block your day; prepare a to-do list; get tasks accomplished in a sequential order; say no to low value tasks; schedule important work during peak productivity hours; set a clear boundary for solo planning and work, and set multiple deadline for large projects.
Slide 41
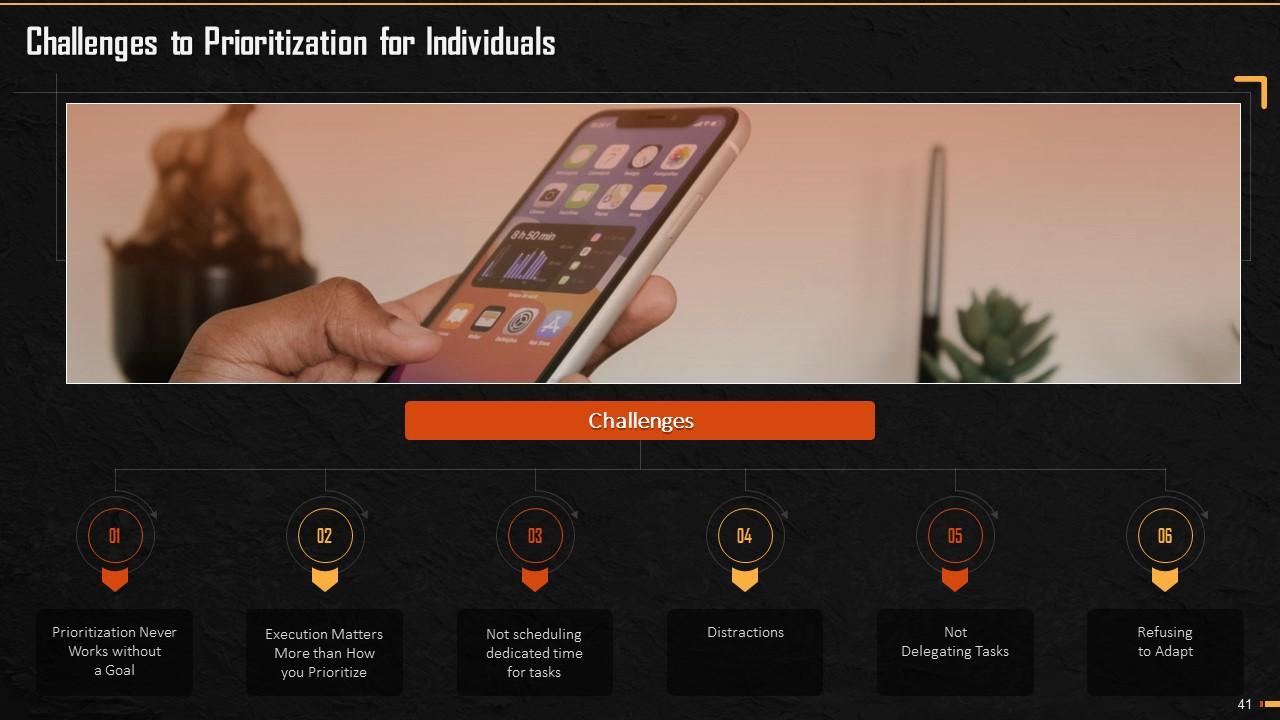
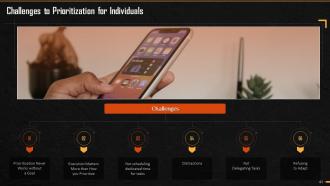
This slide mentions challenges that individuals have to be wary of, as they prioritize. It states challenges like prioritization never works without a specified goal, its execution matters more than how it is prioritized, not scheduling dedicated time for important tasks, not delegating tasks in an appropriate manner, and refusing to adapt to a dynamic environment.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Prioritization Never Works Without a Goal: Prioritization can be done only when there is a clear goal or a motive. You cannot prioritize without knowing where to reach or what to attain. Unless and until there is a clear goal behind prioritization, a person might end up nowhere
- Execution Matters More than How You Prioritize: The simpler the process, the more effective it is. Prioritization focuses more on proper execution than just formulating plans on how to do it. One of the prioritization frameworks suggested to avoid challenges and properly execute the plan is – Define a goal, Eliminate tasks not related to the defined goal, Define a Matrix that suits your needs, and a Clear agreement/expectation of what work will be executed and what will not be done
- Not scheduling dedicated time for tasks: Not dedicating the required amount of time and effort your task requires can cause ineffectiveness in prioritization. A person should take 15-20 minutes before starting the process to evaluate tasks and sort these sort
- Distractions: Getting distracted by unimportant things or things that are not a priority, like phone calls, not urgent emails, etc. might cause the non-completion of priority tasks on time. These unimportant tasks unnecessarily compete with prioritized tasks and should be ignored. Before starting, a person should set everything else aside, disconnect from the crowd, social media, and mobile phones, for the time being
- Not Delegating Tasks: Focusing on work that someone else can handle can distract you from your primary goal. A person should be aware of what they can do best and should demonstrate trust in peers/employees by delegating non-urgent and non-essential tasks to them
- Refusing to Adapt: Setting priorities should be a thoughtful, irreversible process. Once finalized, the priority list is not to be tinkered with on whims and fancies. Change in priorities can cause chaos and inefficiency in tasks. In case, any new information arises that requires your attention it should be considered an emergency and taken care of then and there
Slide 42
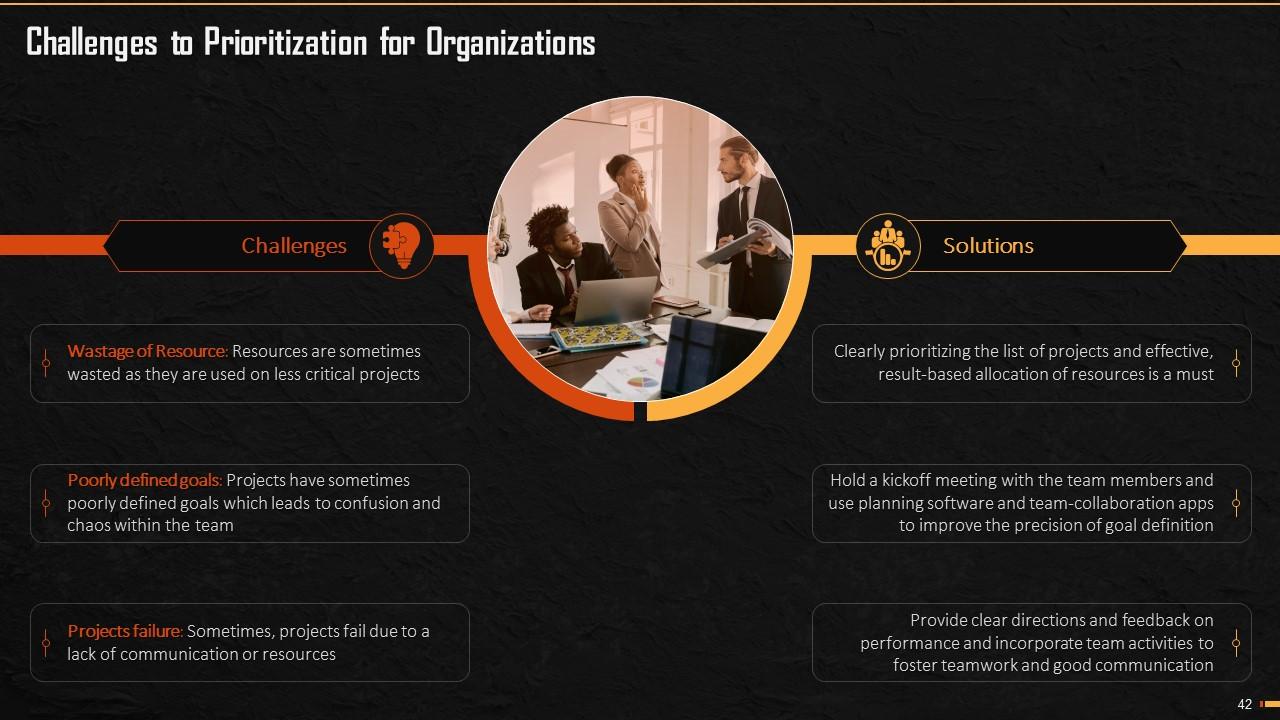
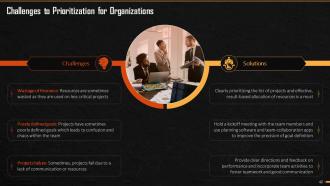
This slide showcases challenges and solutions to problems that organizations face during the prioritization. It illustrates challenges like wastage of resources, poorly defined goals, lack of communication, etc.
Slide 43
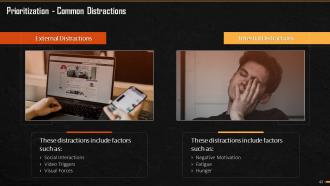
This slide mentions the distractions that arise while prioritizing things. It mentions that there are two kinds of distractions in prioritization, which are external and internal distractions. External distractions include factors like social interactions, social triggers, etc. Internal distractions include factors like negative motivation, fatigue, hunger, etc.
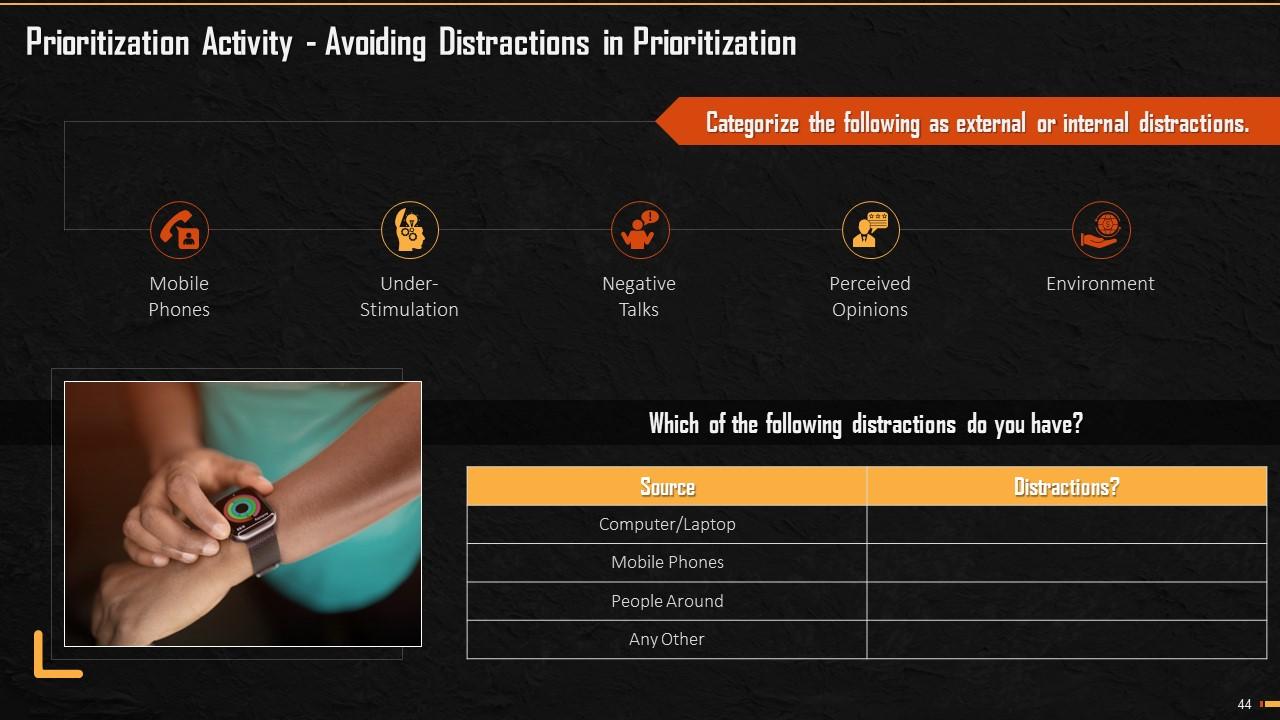
Slide 44
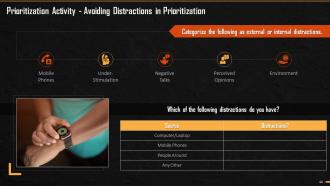
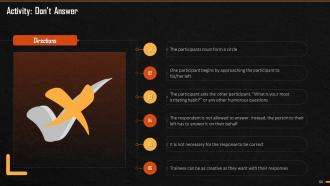
This slide illustrates an exercise that the trainees must conduct during the session. The aim is to help them figure out distractions that arise, during the prioritizing of tasks and how these distractions should be identify, evaluated, and avoided.
Slide 45
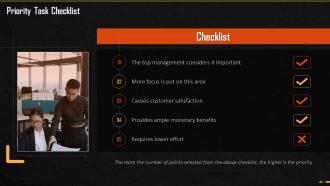
This slide introduces a Priority Task Checklist illustrating significant considerations that need consideration before preparing a priority list. The considerations are importance of task, focus of people towards it, customer satisfaction offered, monetary benefits provided, and effort required.
Slide 46
This slide is a compendium of the best practices that CEOs of big companies follow as a credo. It says that to prioritize and manage tasks effectively, a CEO should figure out the following: Whether it exists on the dashboard of his/her 5/6 main key drivers or not; Will it add any value to his/her task; Should he/she be dealing with it; Is it the right time to start the job, and is the required information available to execute the task.
Instructor’s Notes:
The five key questions that CEOs need to ask before taking up a task are:
- Does it exist on my dashboard of 5/6 key drivers of business?CEOs of companies do not have time to go into details of every aspect of the business. Therefore, they need to focus on being on the top of things in general; this requires monitoring the five-six key drivers that determine the success of their business
- Does it add value to my task?CEOs engage themselves only in those tasks that will add substantial value to the business. If it is not providing any additional benefit or is not differentiating them from others, they will ignore it
- Should I be dealing with it?High-performers are experts at recognizing whether they are the right person to perform that task or should they delegate it. This avoids the wastage of time at the end of CEOs and also helps build trust among other team members
- Is it the right time to deal with it?Before starting, CEOs sort out their tasks and figure out whether it is the right time to deal with these or can they push some of these to a later date. It is very important to figure out whether the task is urgent or important or both
- Do I have all the necessary information to deal with it?It becomes almost impossible to complete the task if information required is not available. Instead of wasting time, CEOs find it productive to leave the task for now and move ahead with it only when complete information becomes available
Slide 48
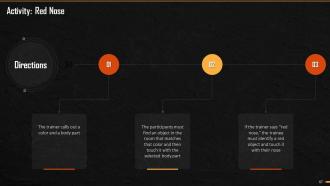
This slide mentions an activity that the trainer can conduct to explain the concept of prioritization. The trainer can add this if he/she wants to practically explain them the concept of prioritization. Using this activity, members can understand and compare ways people prioritize and manage their tasks.
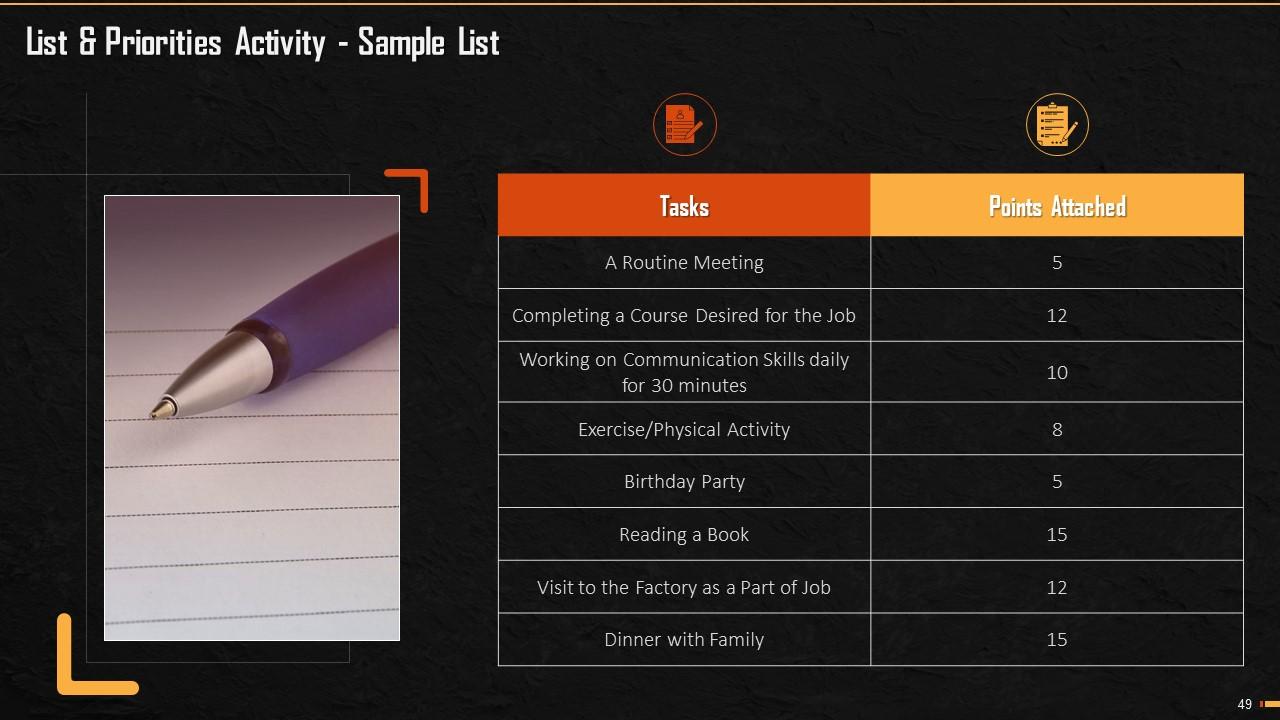
Slide 49
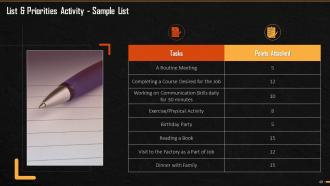
This slide mentions the sample list of tasks that trainer can use to conduct the activity.
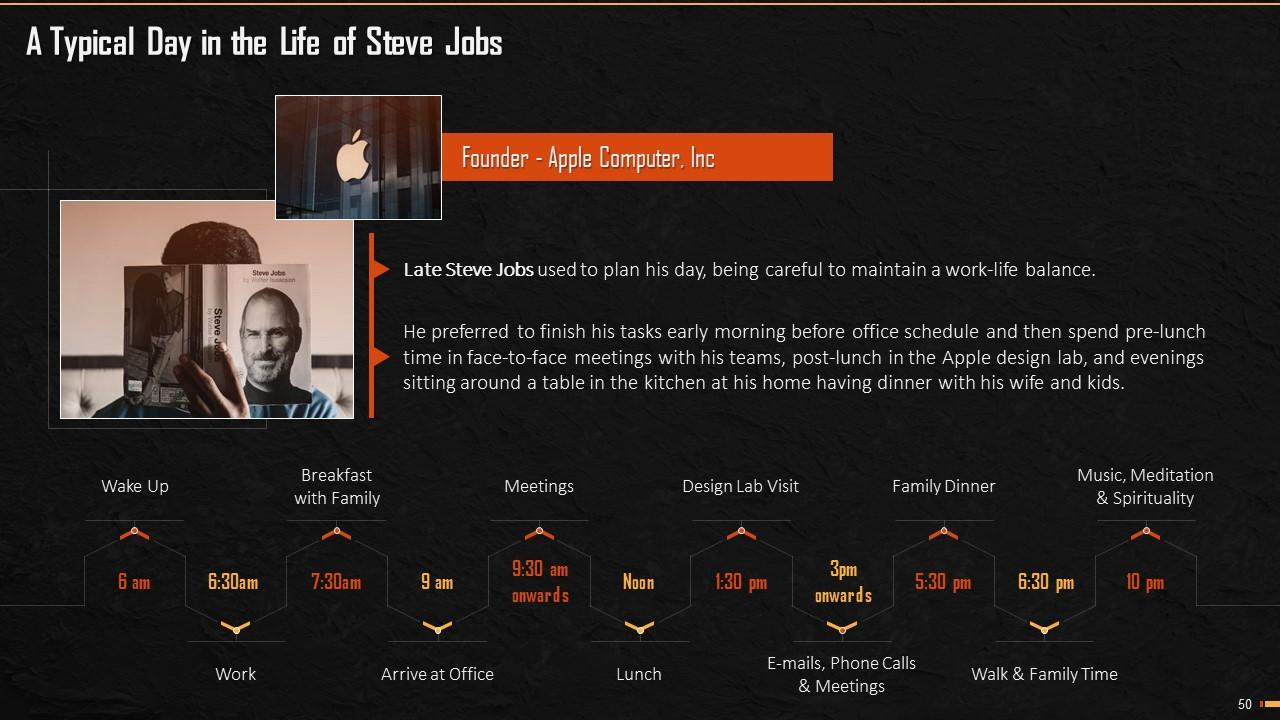
Slide 50
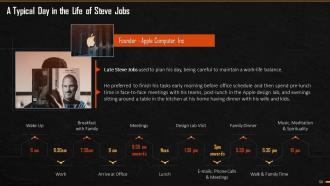
This slide mentions how the late Steve Jobs managed his day and prioritized his tasks. The slide depicts a full day routine starting from 6am till the legend wrapped up his day with successful completion of all his tasks.
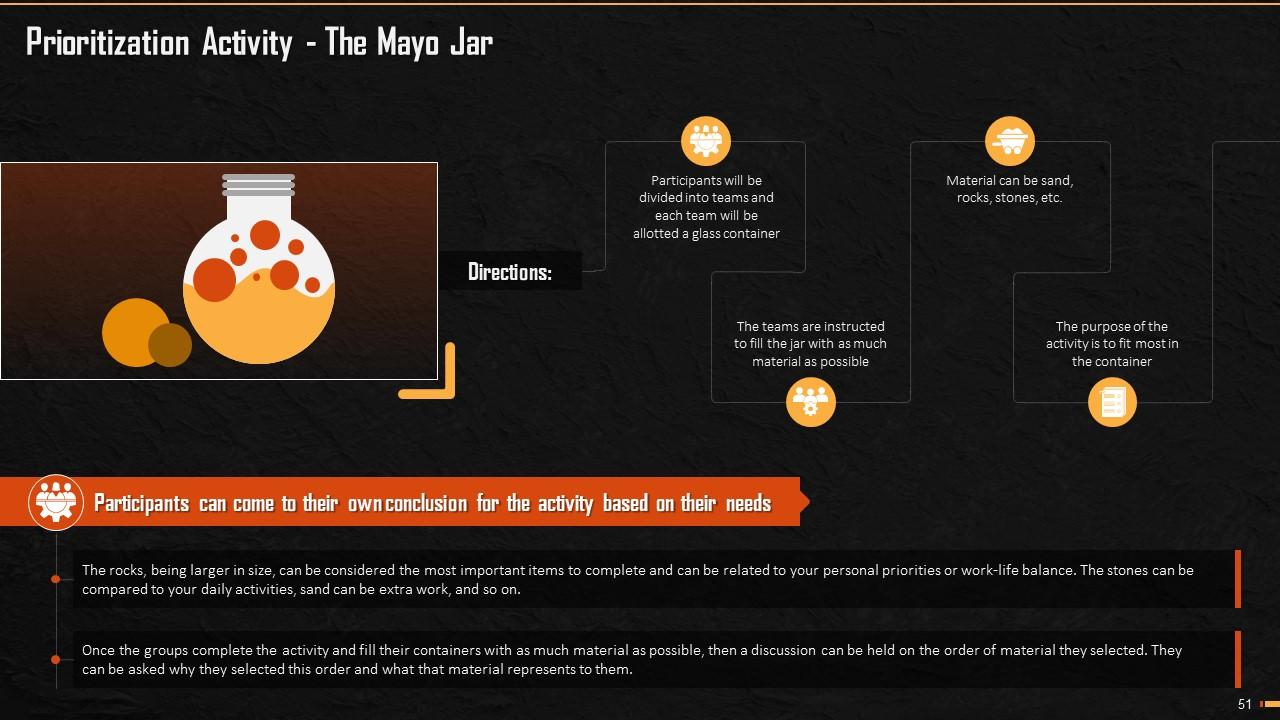
Slide 51
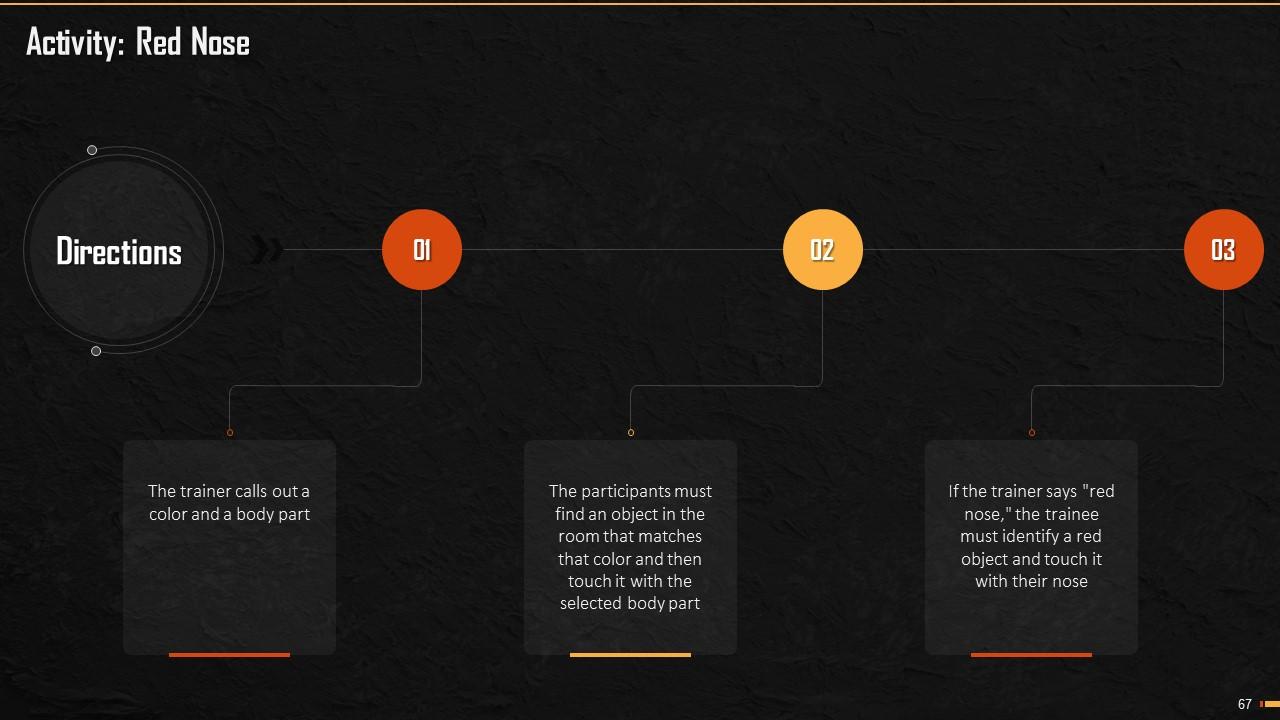
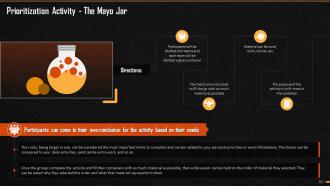
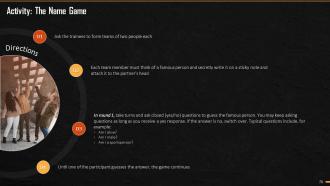
This slide mentions an activity which the trainer can conduct while explaining the training module prioritization to the trainees. The trainer can add this only if you want to energize the crowd and practically explain the concept of prioritization.
Instructor Notes:
The correct way to effectively and efficiently fill the jar is:
- First of all, fill the jar with the bigger bricks or objects, that means that all essential tasks are to be completed on priority
- Then, we can add pebbles that represent the necessary tasks but not urgent or important
- As we near the end of time allotted, we can fill the jar with sand which represents less critical work or non-essential tasks
- In this way, an individual will be able to maximize productivity with a similar level of effort
Slide 52
This slide mentions the key takeaways from the session on role and importance of prioritization in time management.
Slide 53
This slide presents some thought-provoking discussion questions that a trainer can ask the hall of trainees to start a fruitful discussion.
Slide 65 to 80
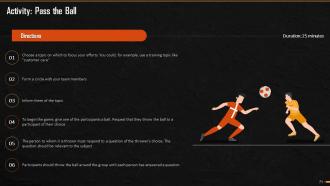
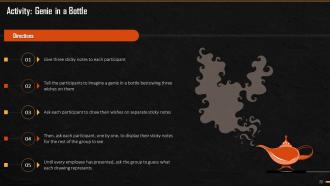
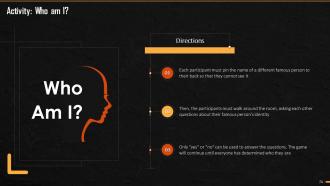
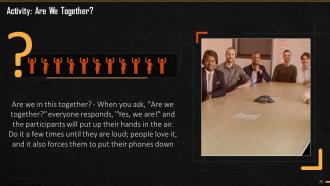
These slides depict energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 81 to 108
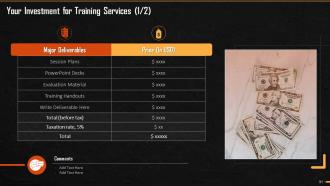
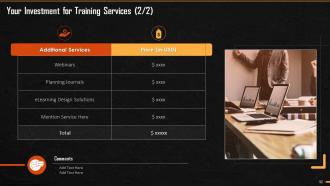
These slides consist of a client training proposal highlighting what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
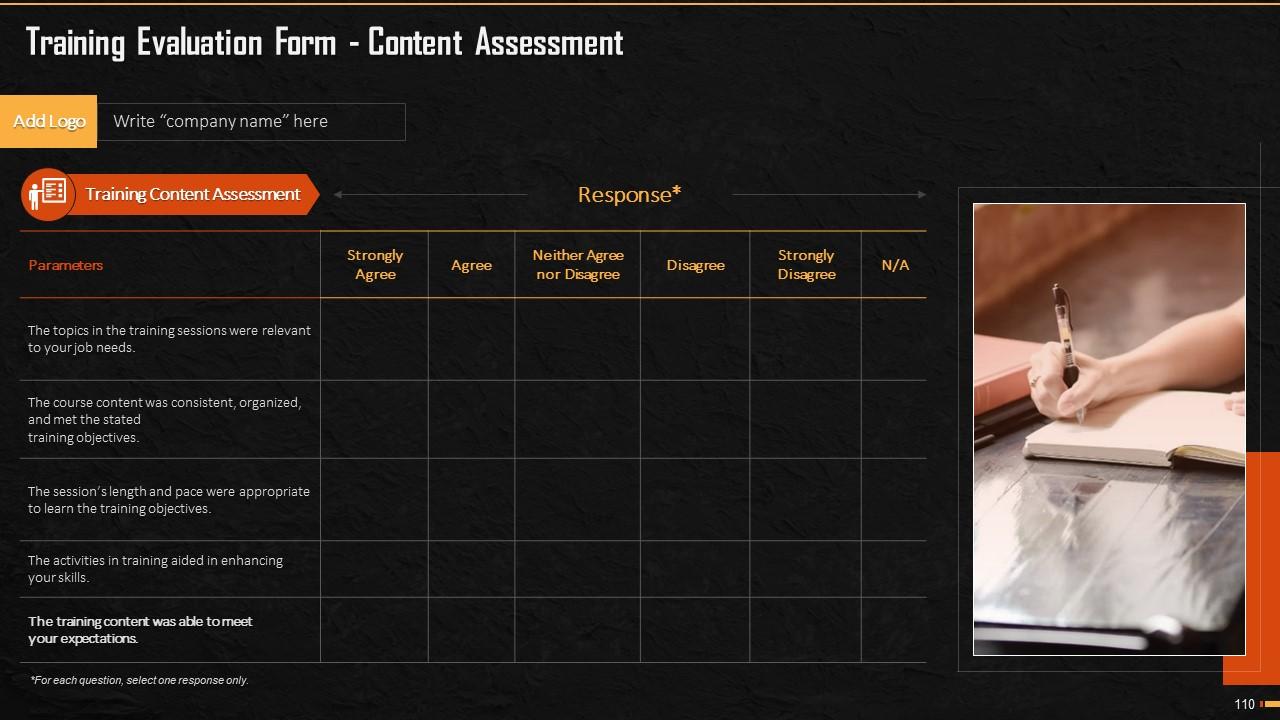
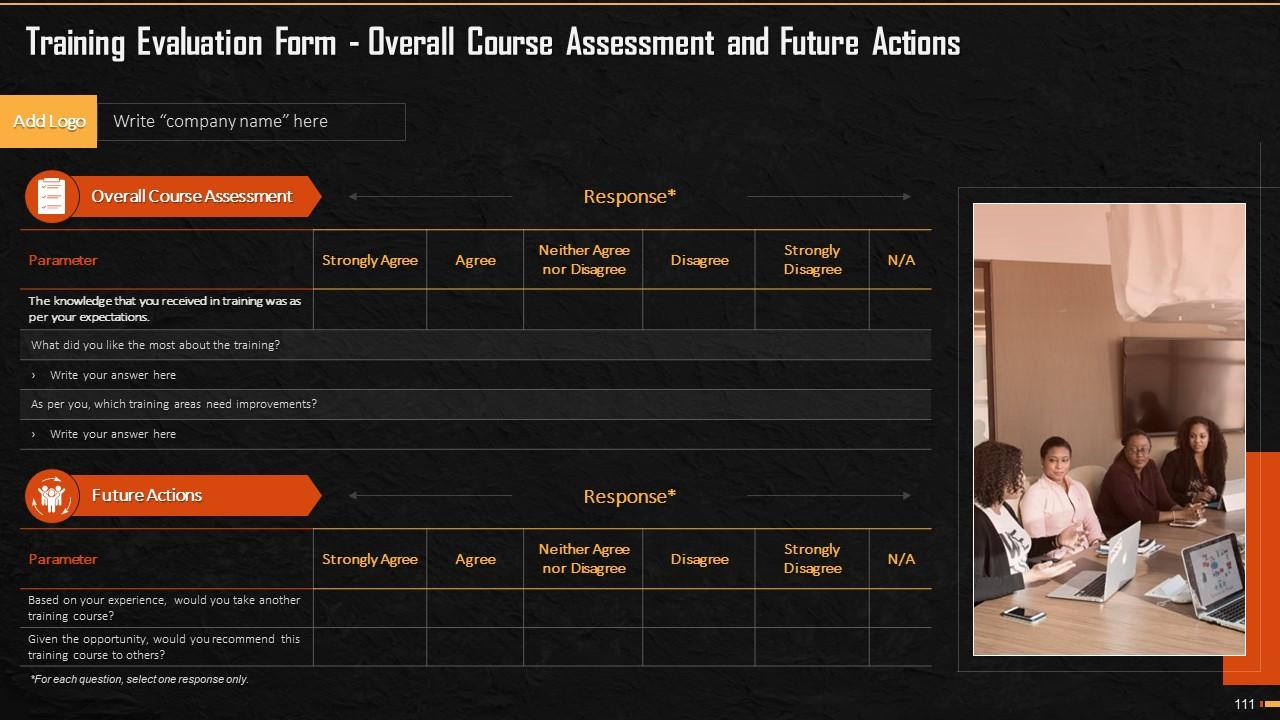
Slide 109 to 111
These slides highlight the training evaluation form for instructor, content, and course assessment.
Role And Importance Of Prioritization In Time Management Training Ppt with all 116 slides:
Use our Role And Importance Of Prioritization In Time Management Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Great product with highly impressive and engaging designs.
-
Editable, diversified, compatible with MS PPT and Google Slides, and on top of that finest graphics!! I mean in the words of the famous Ross Geller, “What more do you want!”