Comprehensive Training Curriculum on Blockchain Technology and its Applications Training Ppt
What is it
- EduDecks are professionally-created comprehensive decks that provide complete coverage of the subject under discussion
- These are also innovatively-designed for a powerful learning experience and maximum retention
Who is it for?
- EduDecks are for Trainers who want to add punch and flair to program and leave a lasting impact on their trainees
- They are also for Teachers who want to win over their students with content as well design
Why EduDecks?
- EduDecks provide an A-Z coverage of courses on any topic and covers it in both great depth and wide scope
- These slides are also professionally-designed to deliver a punch to your programs
Create an Immersive Training Experience
Created by Subject Matter Experts
Professionally Designed Slides
Structured Sessions
Comprehensive Curriculum
Detailed Teaching Notes
Real-Life Case Studies
Assessment Questions
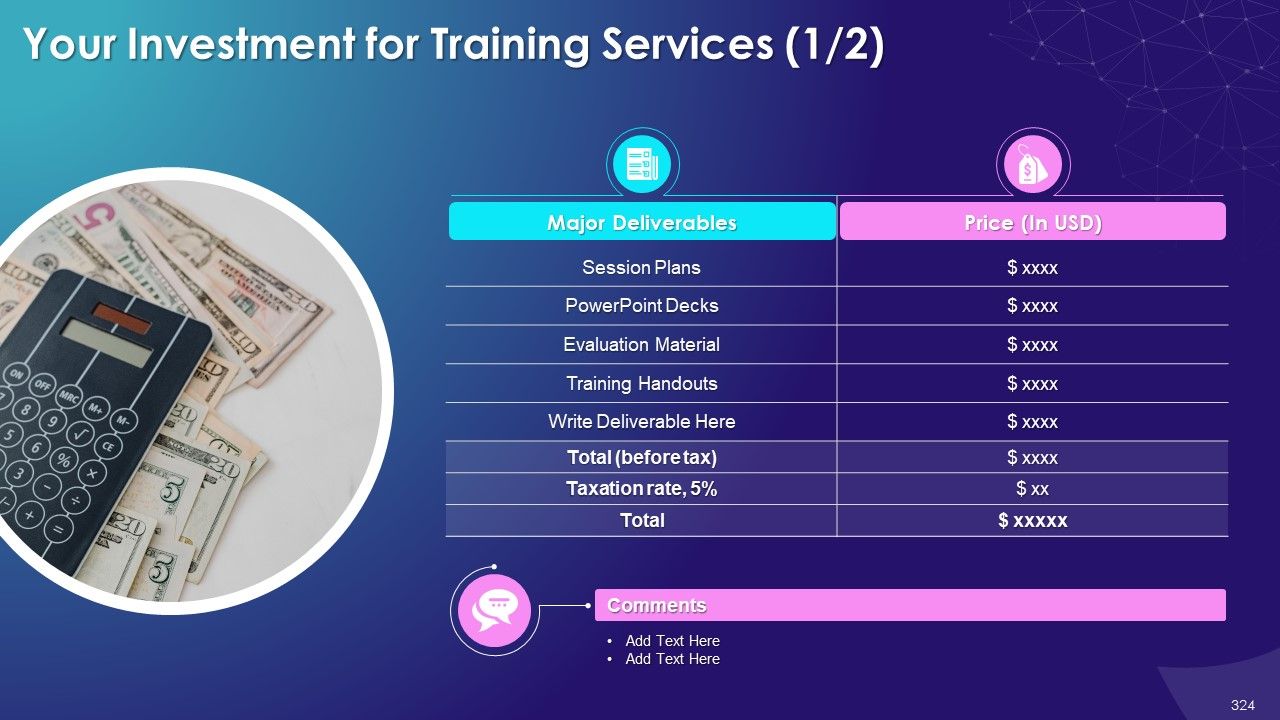
Client Proposal
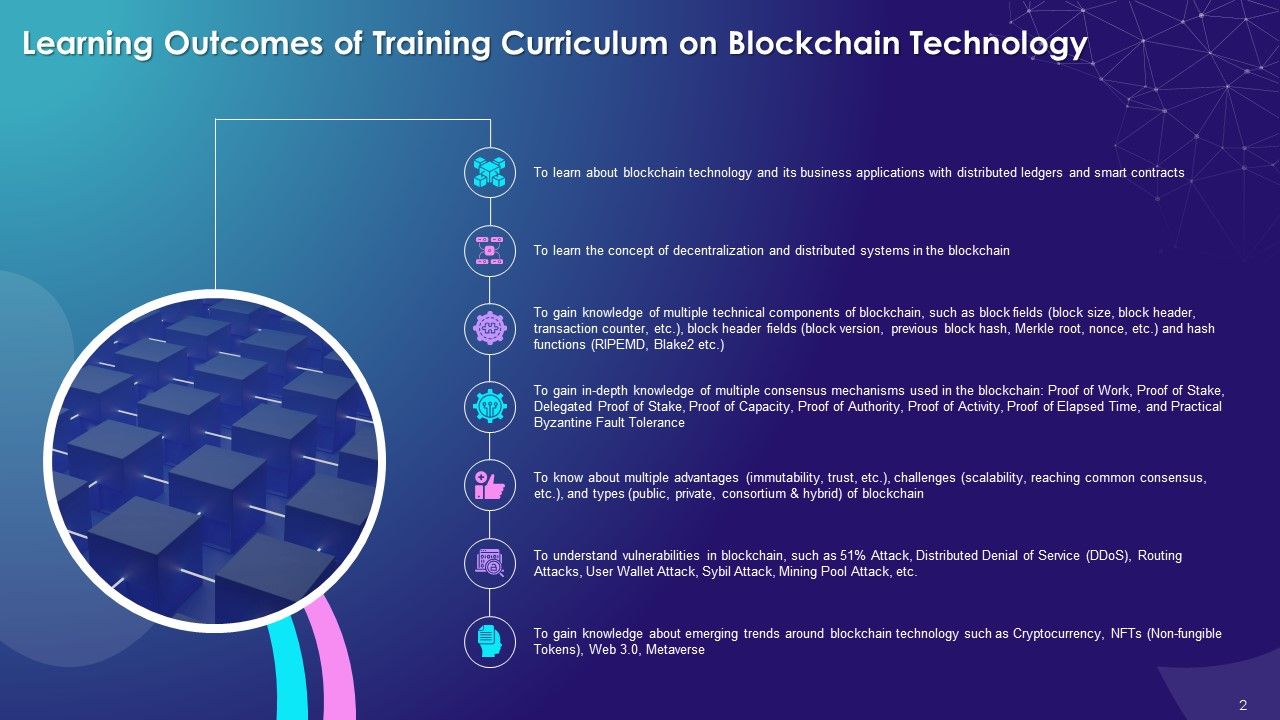
Complete Curriculum
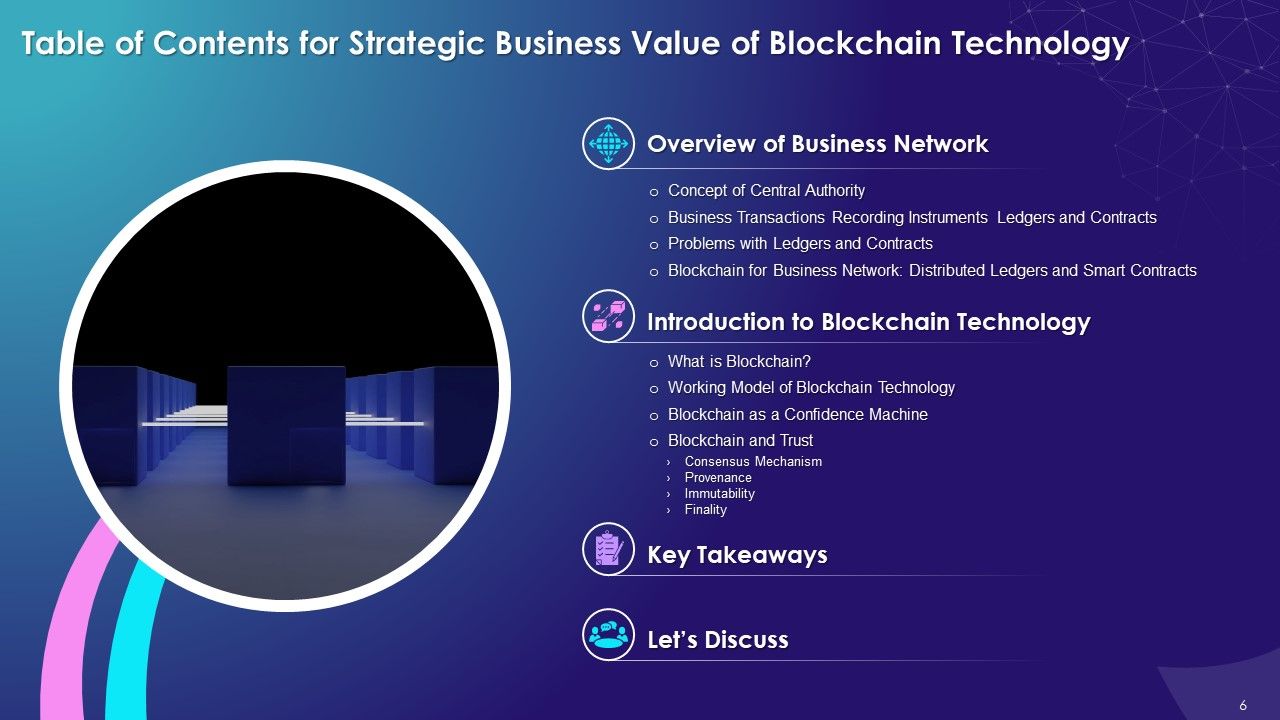
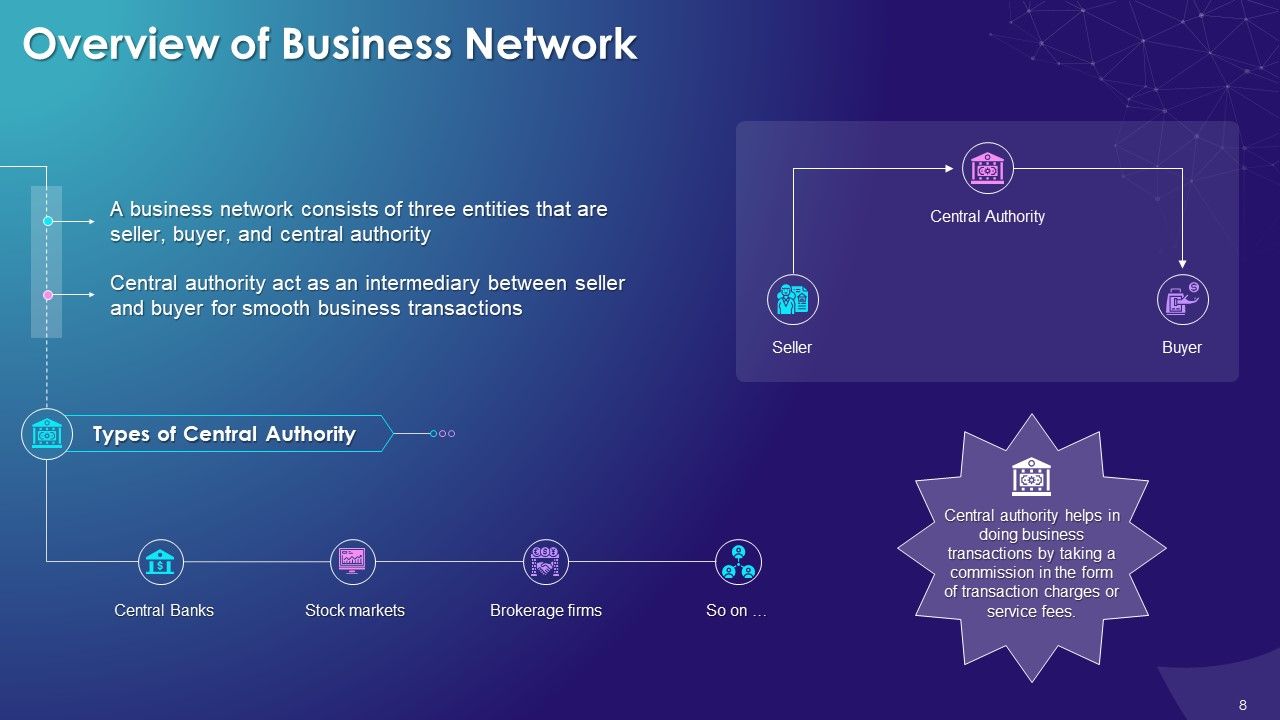
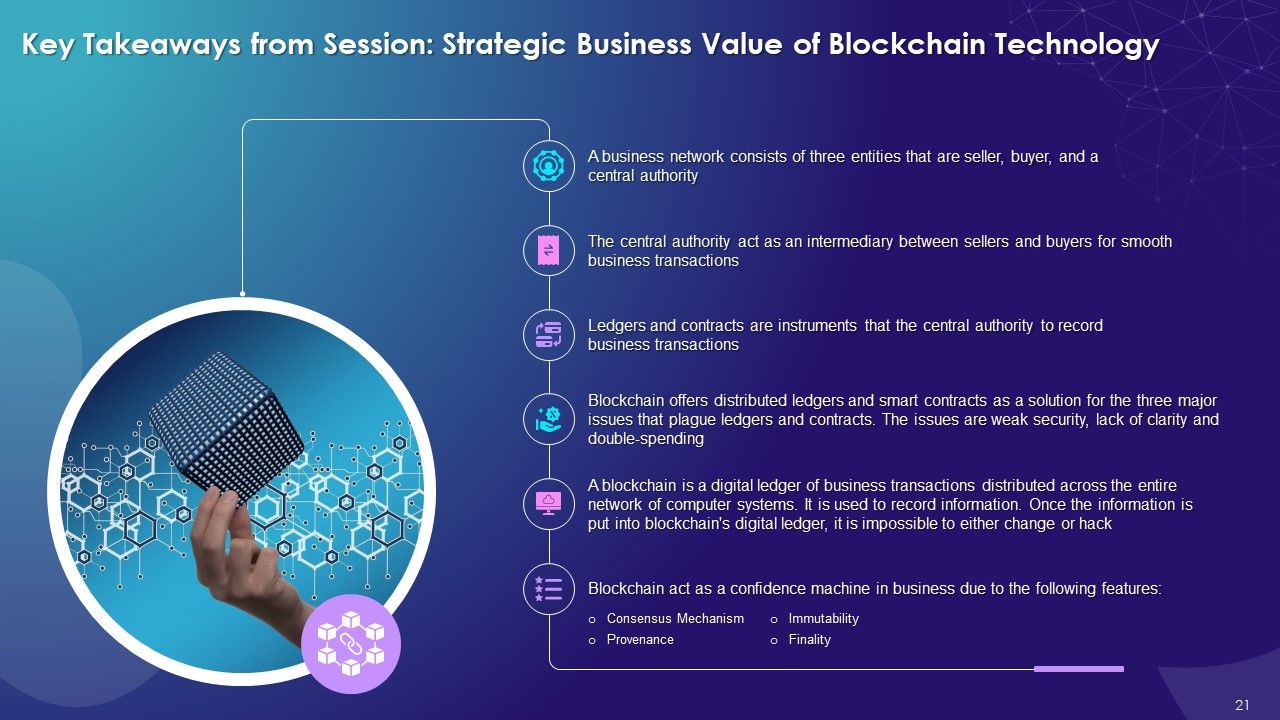
- Overview of Business Network
- Concept of Central Authority
- Business Transactions Recording Instruments: Ledgers and Contracts
- Problems with Ledgers and Contracts
- Blockchain for Business Network: Distributed Ledgers and Smart Contracts
- Introduction to Blockchain Technology:
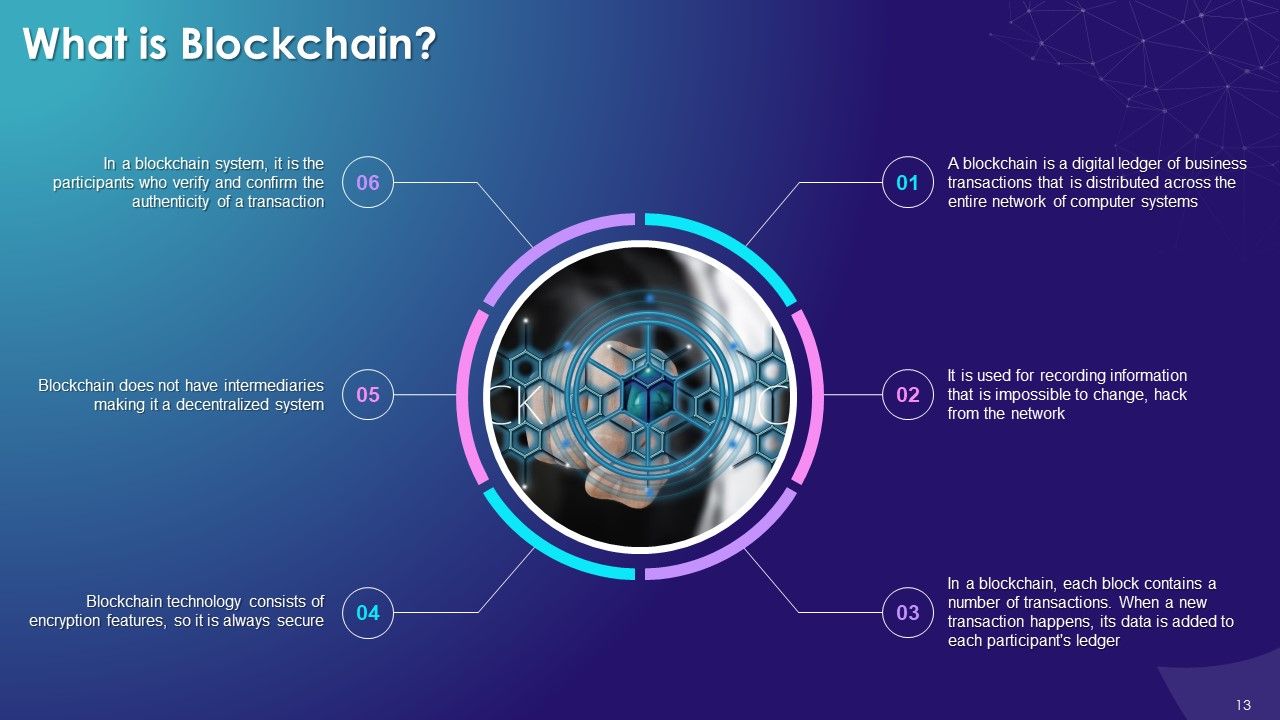
- What is Blockchain?
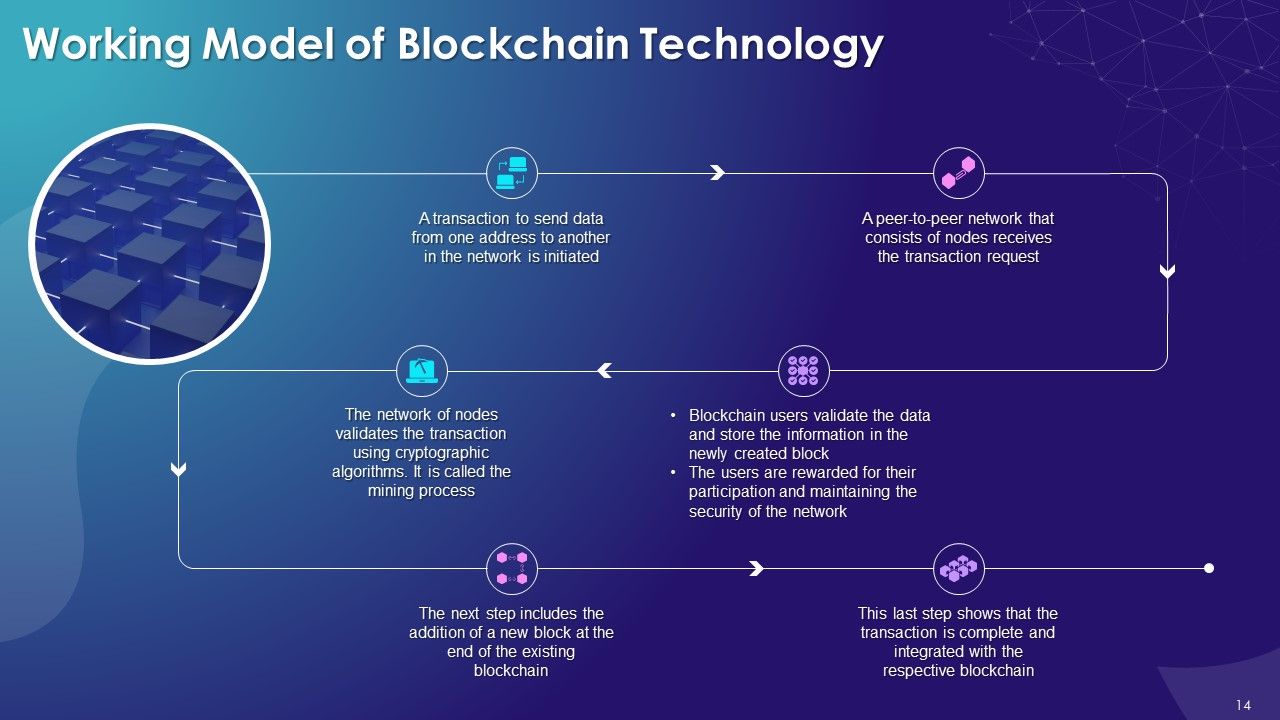
- Working Model of Blockchain Technology
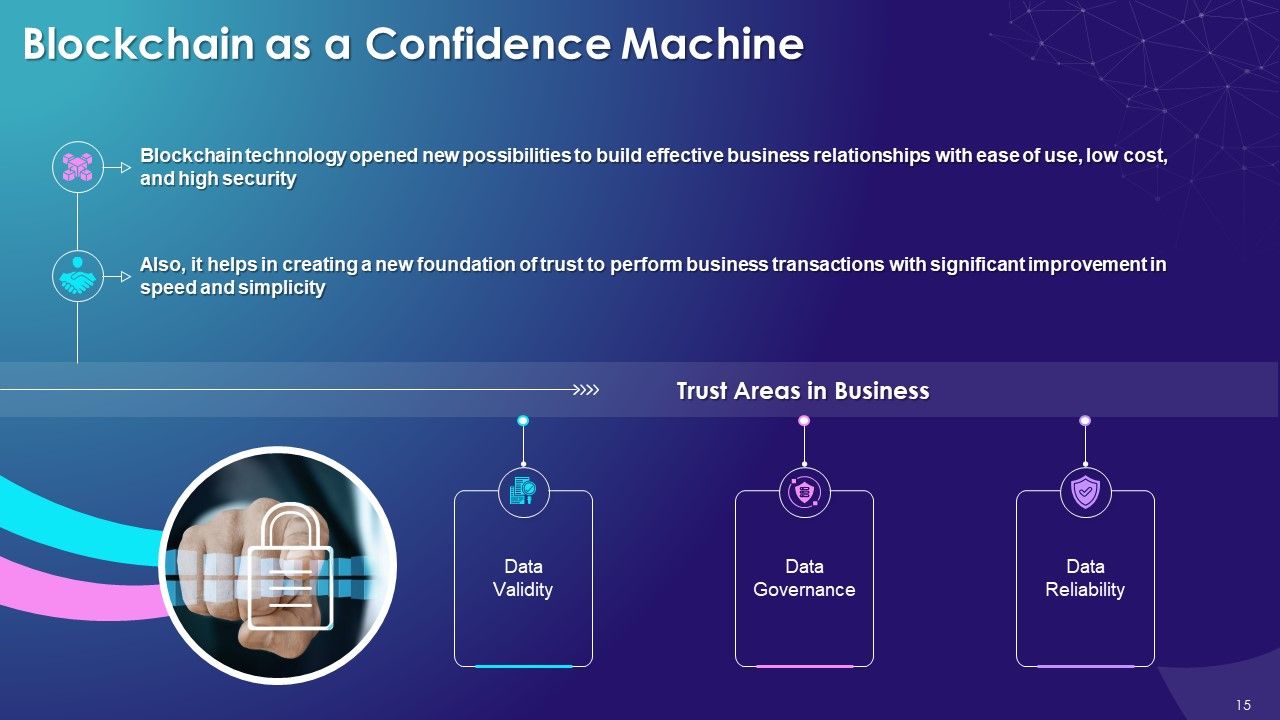
- Blockchain as a Confidence Machine
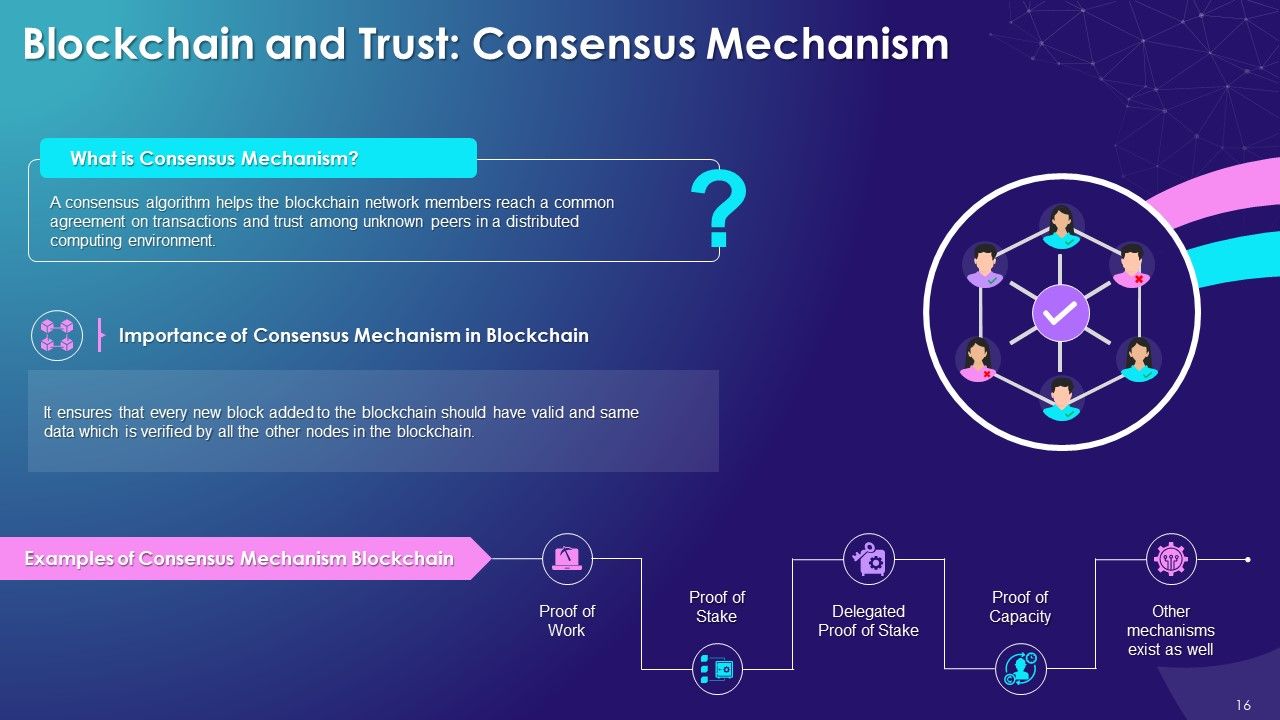
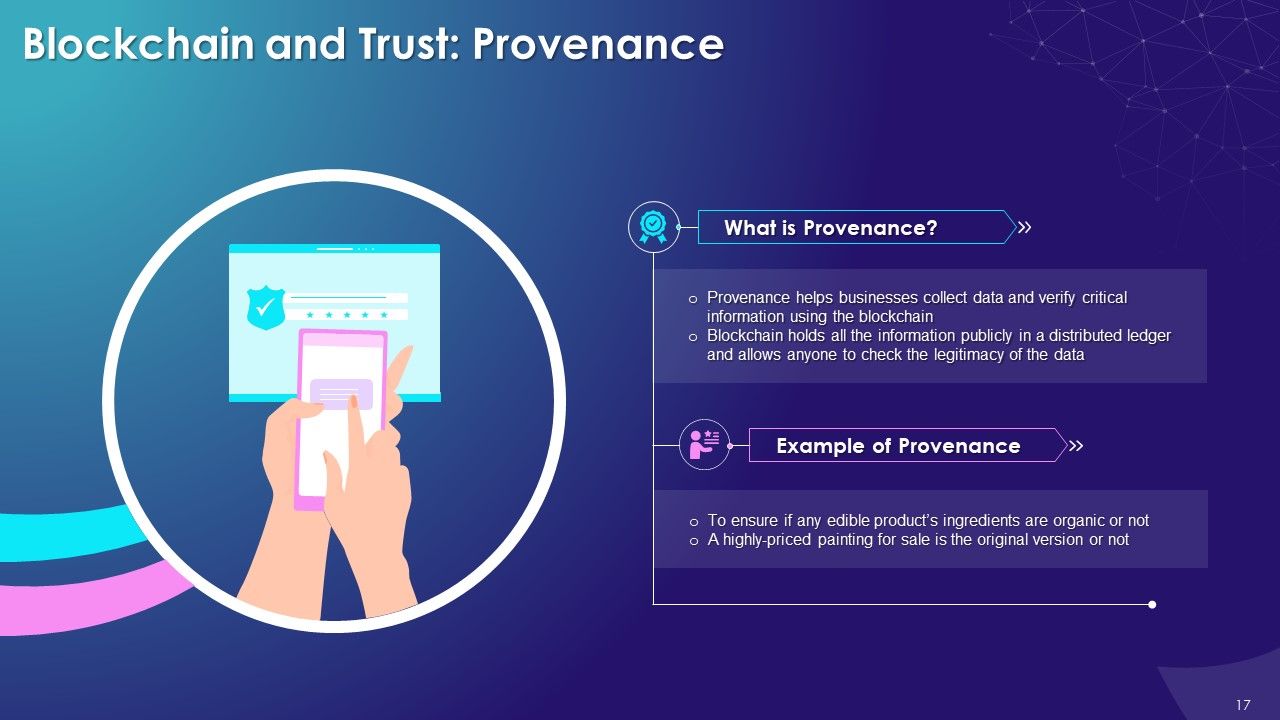
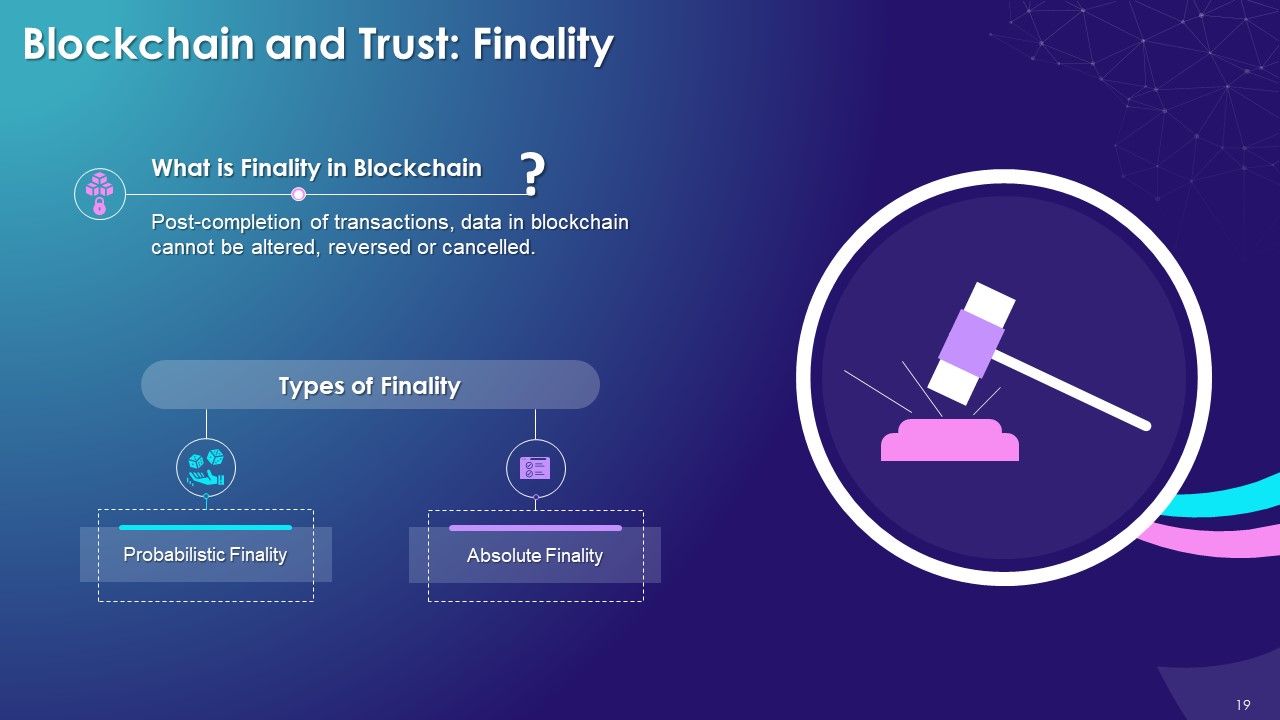
- Blockchain and Trust: Consensus Mechanism, Provenance, Immutability, and Finality
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
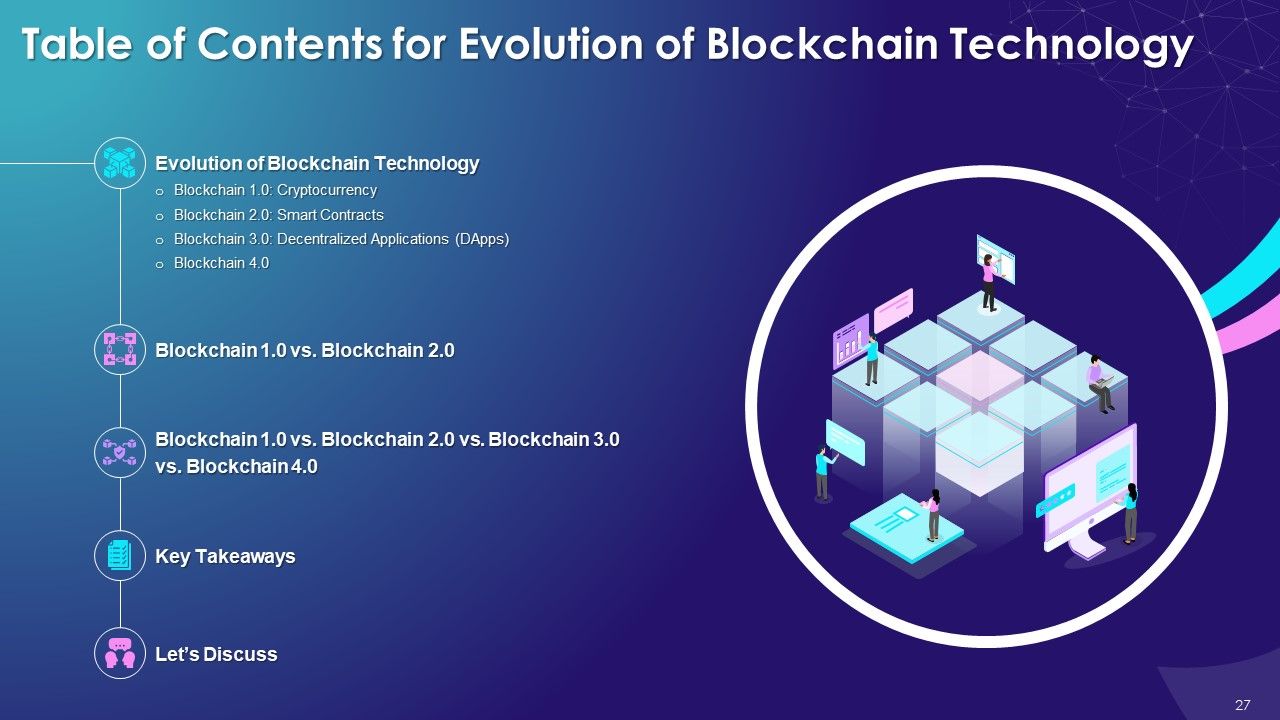
- Evolution of Blockchain Technology
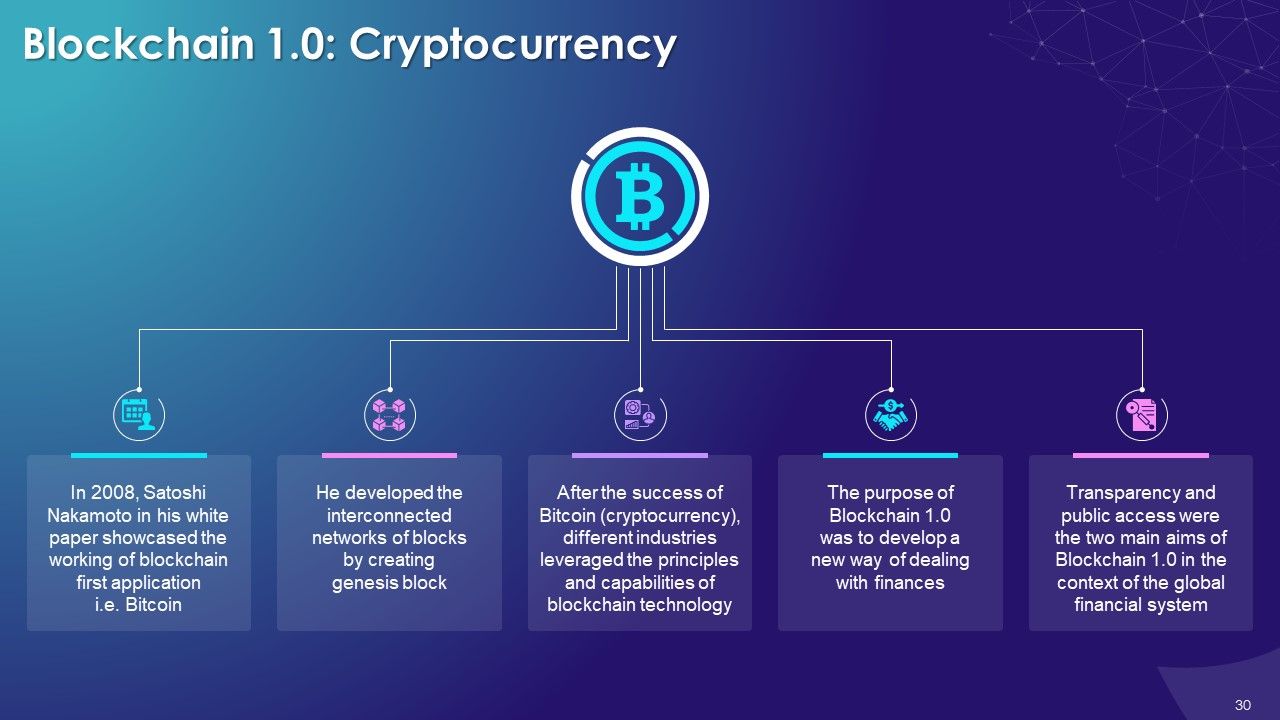
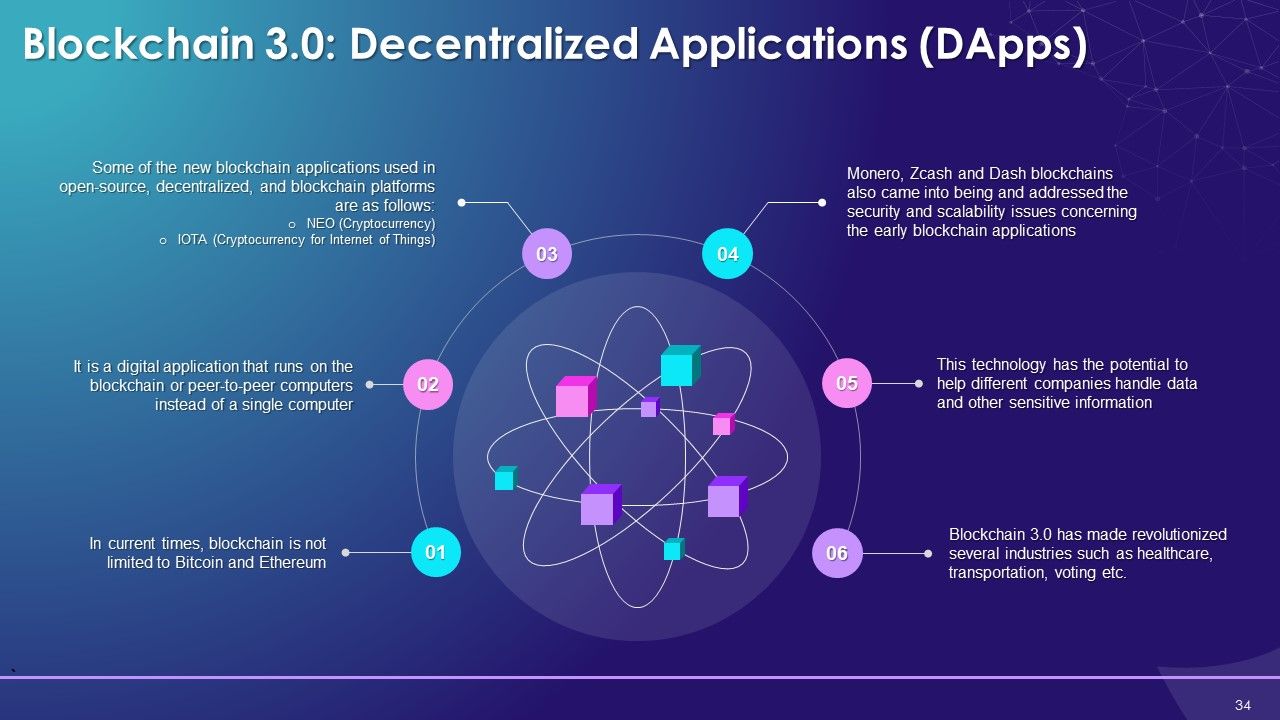
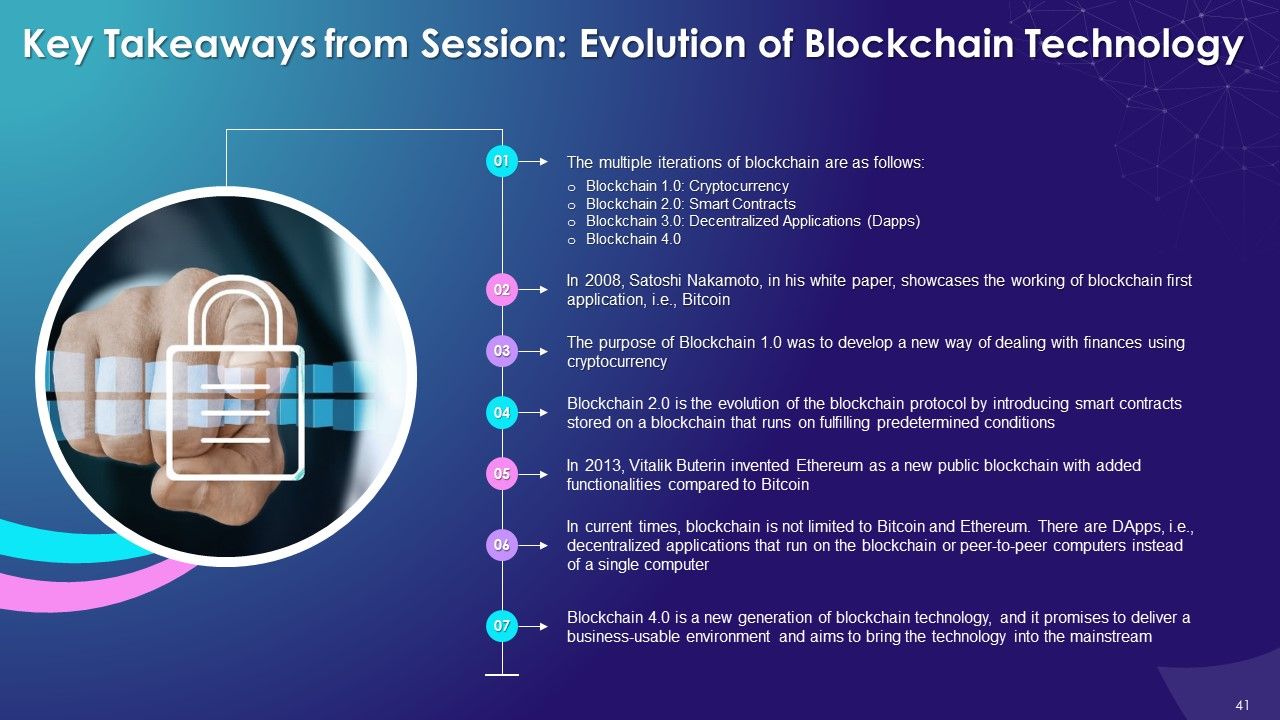
- Blockchain 1.0: Cryptocurrency
- Blockchain 2.0: Smart Contracts
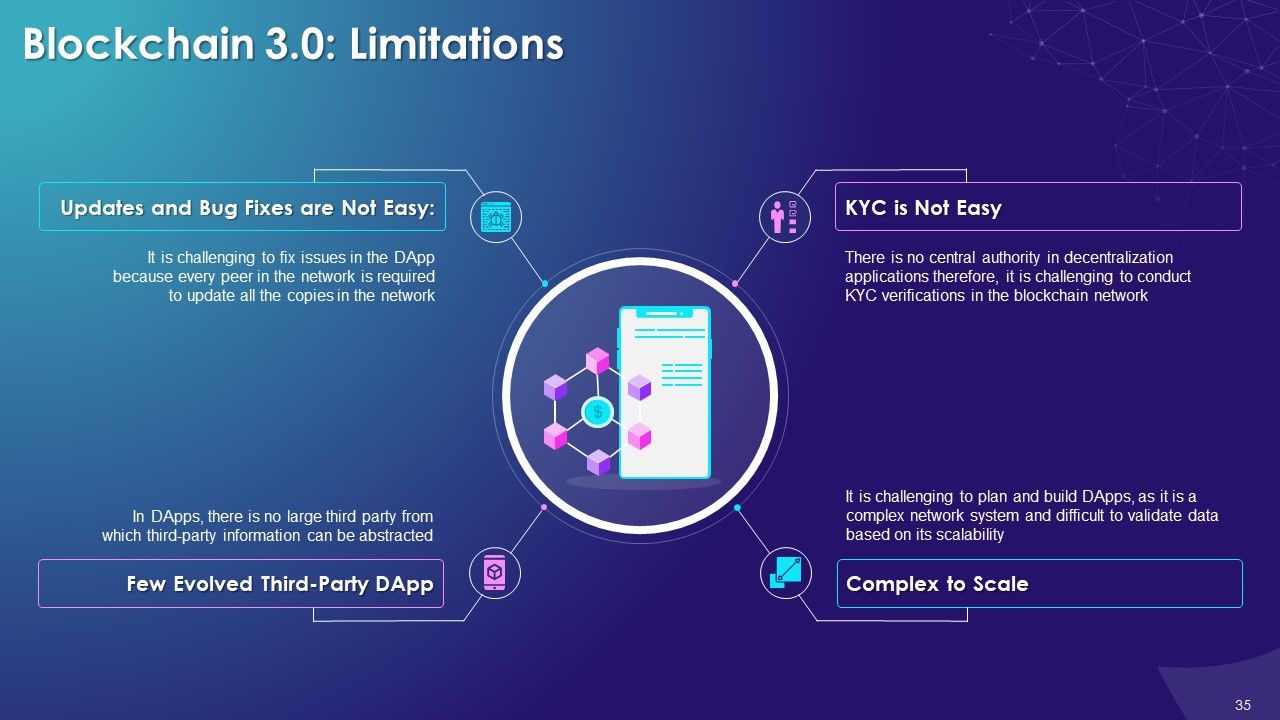
- Blockchain 3.0: Decentralized Applications (DApps)
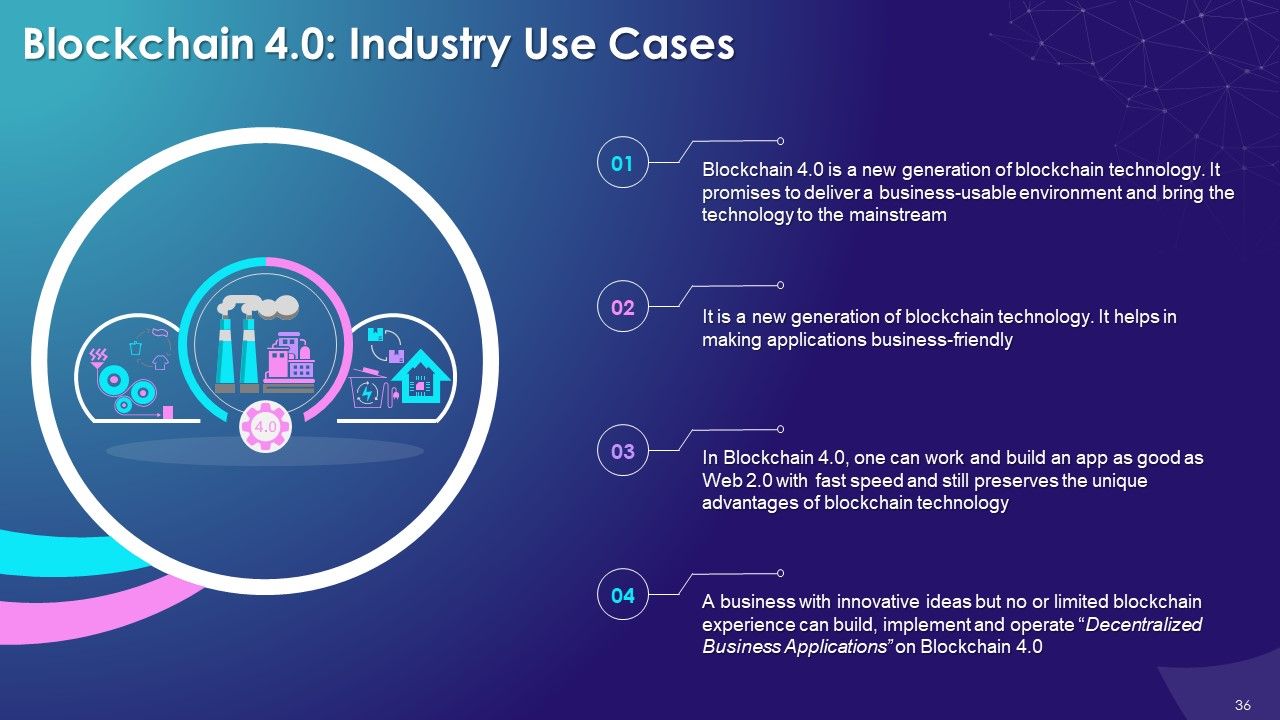
- Blockchain 4.0
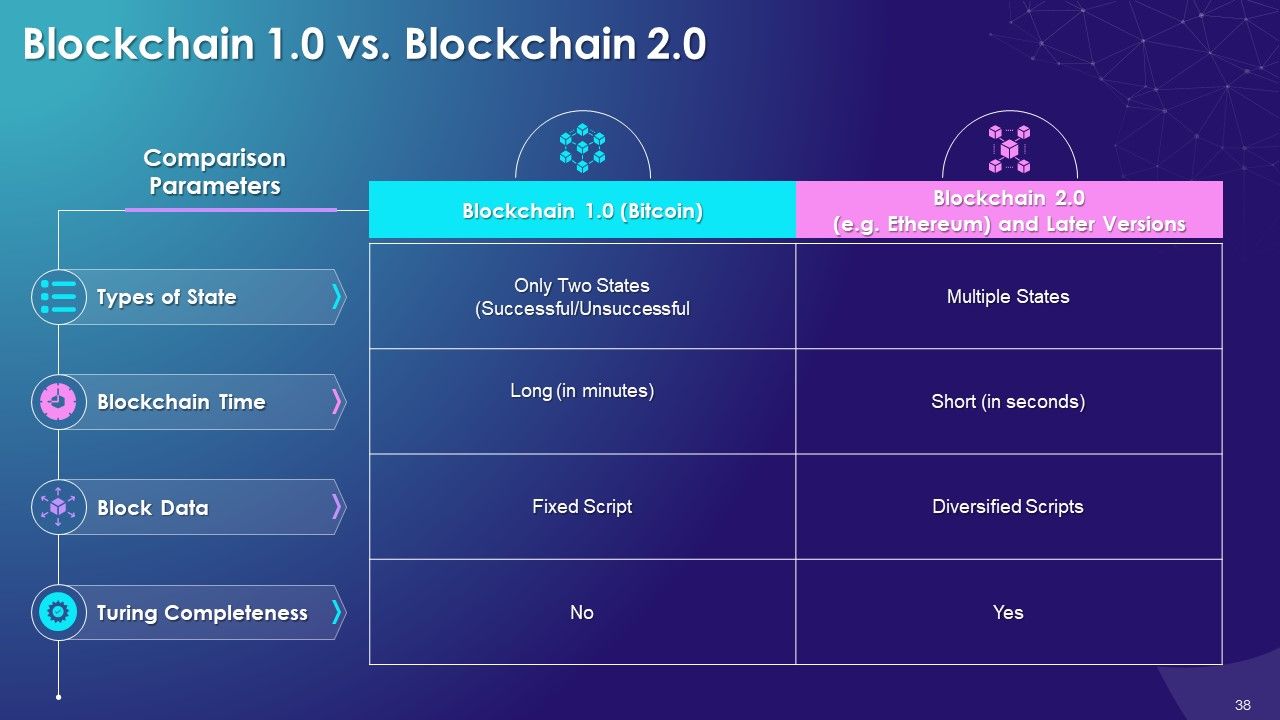
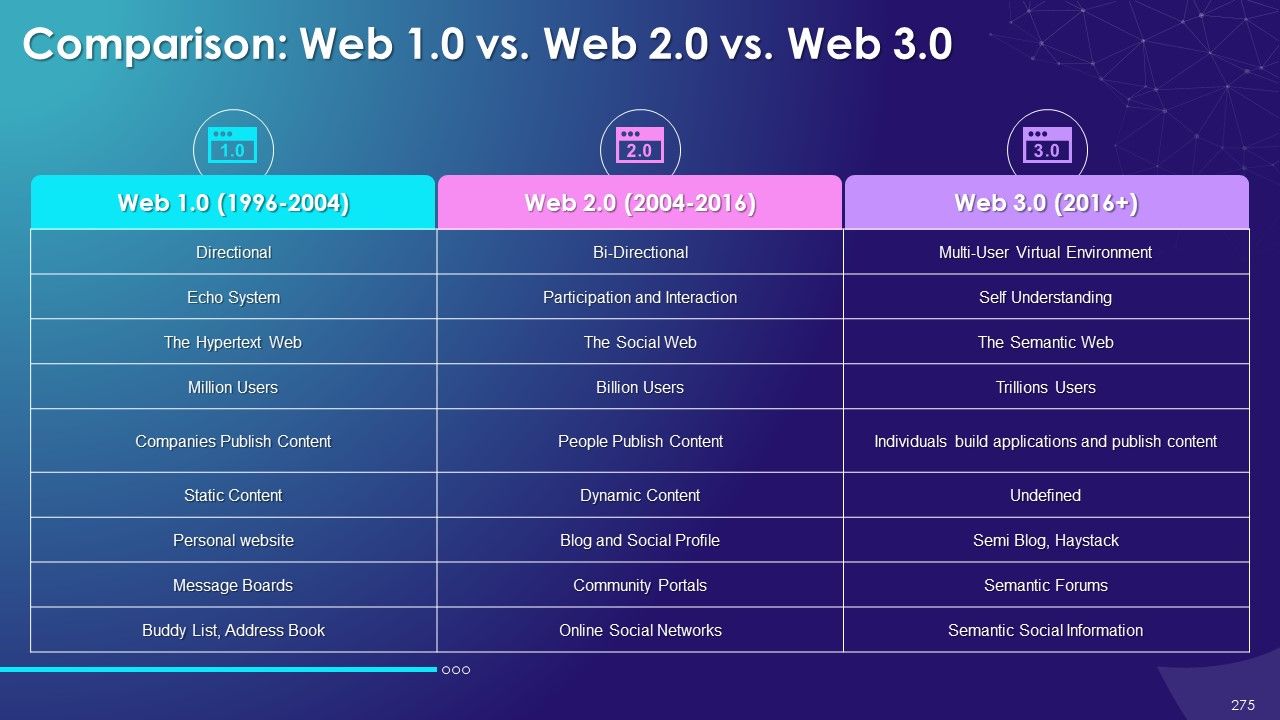
- Blockchain 1.0 vs. Blockchain 2.0
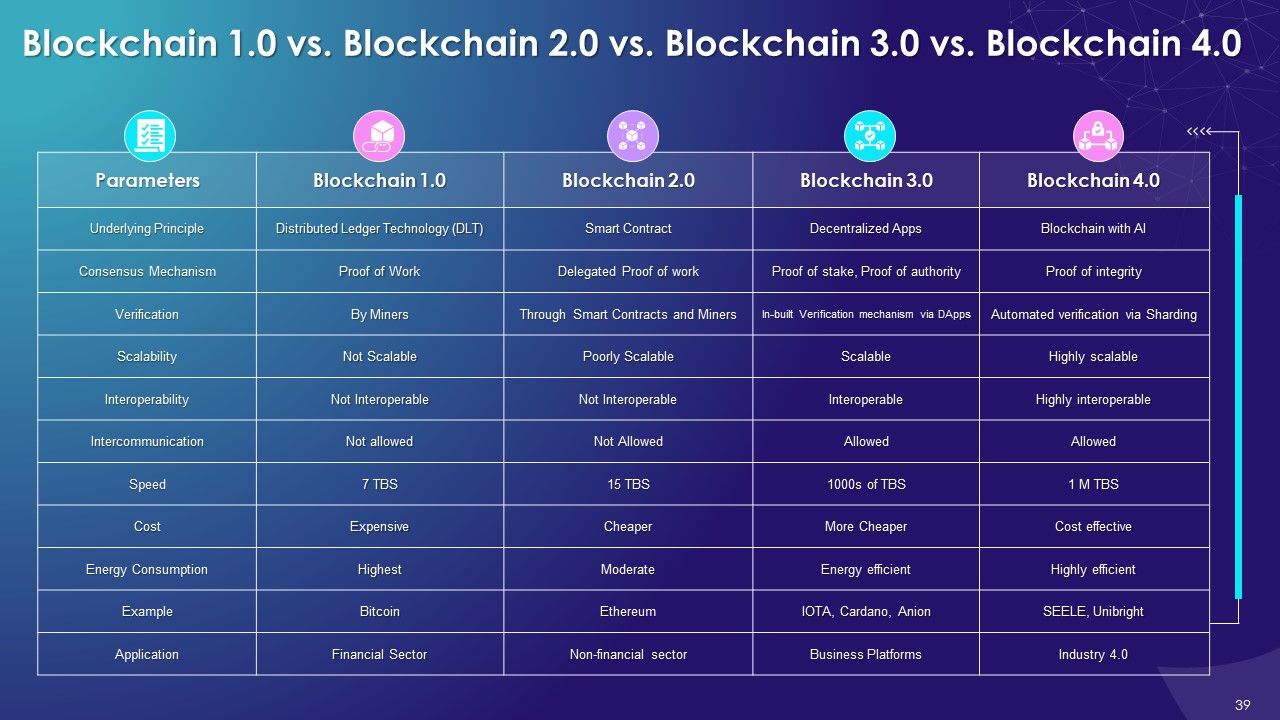
- Blockchain 1.0 vs. Blockchain 2.0 vs. Blockchain 3.0 vs. Blockchain 4.0
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Blockchain Technology Statistics
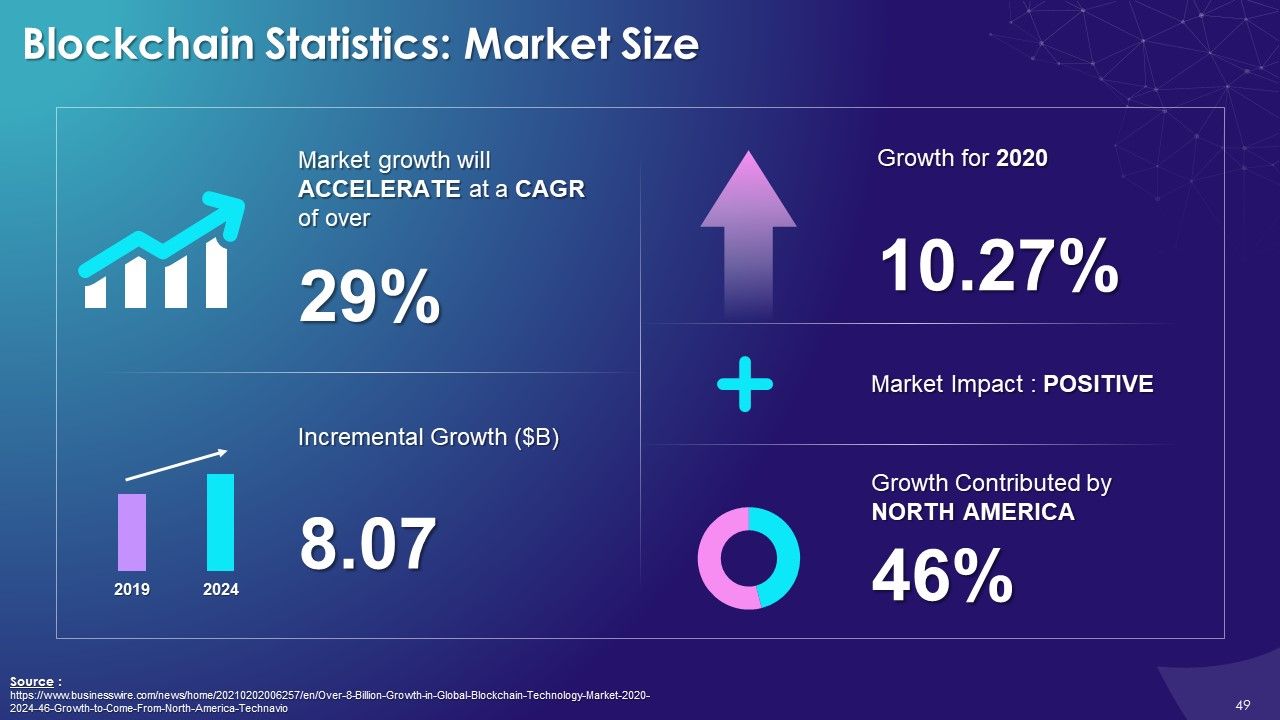
- Market Size
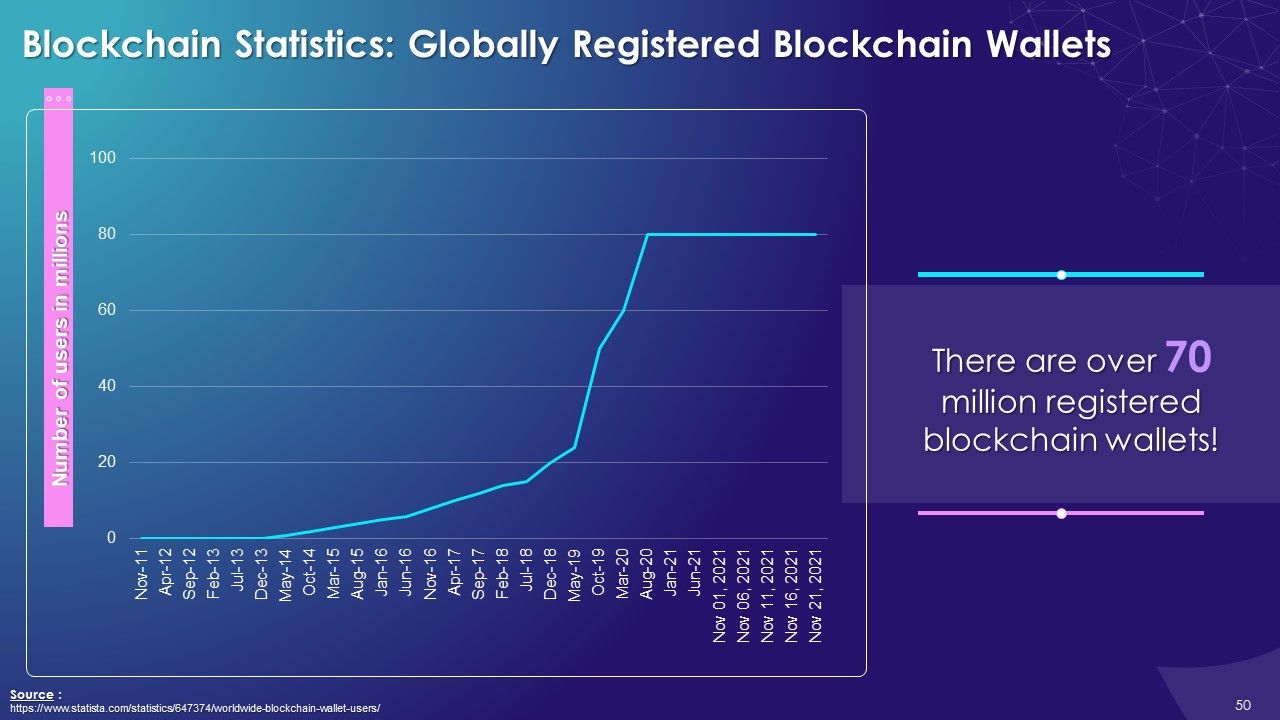
- Registered Wallets Globally
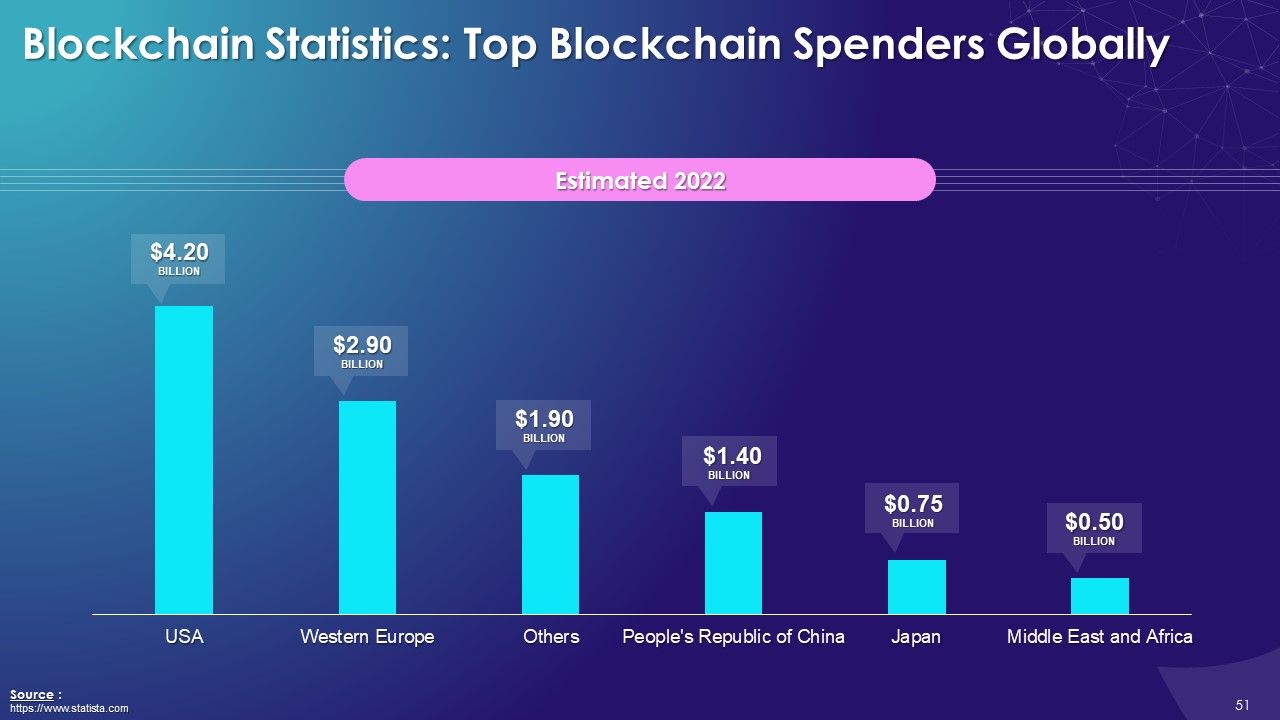
- Top Spenders Globally
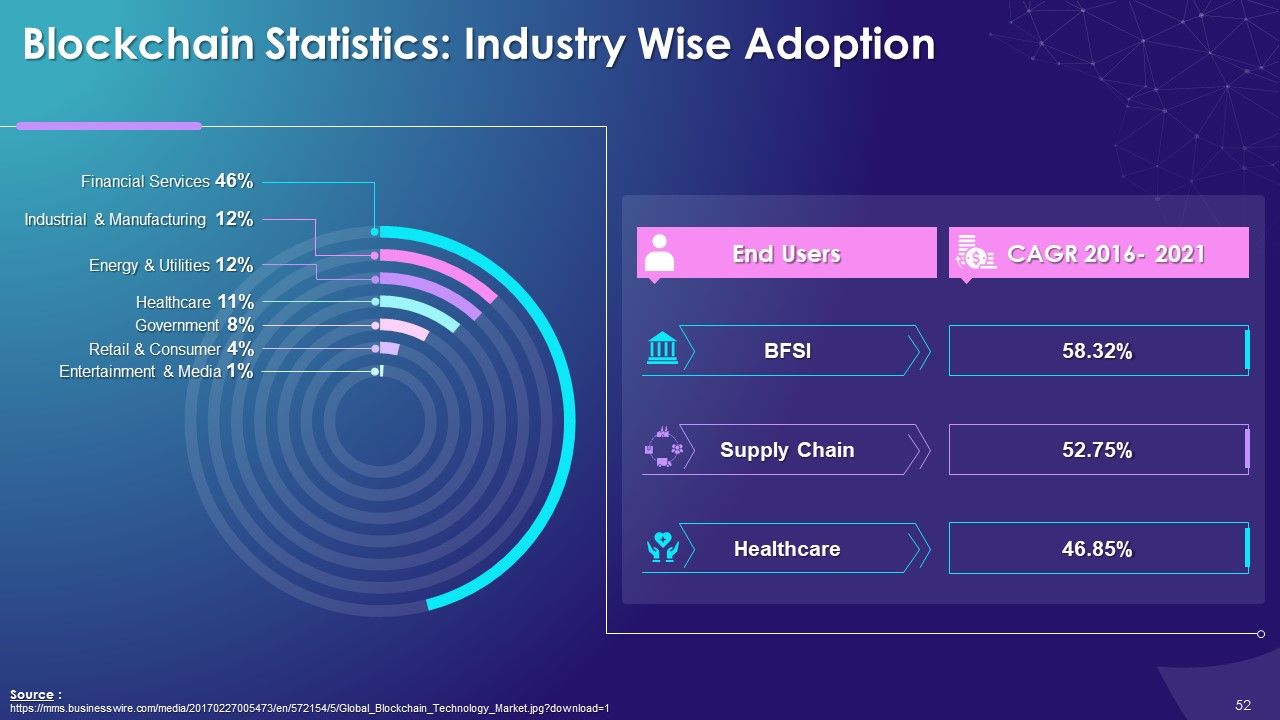
- Industry Wise Adoption
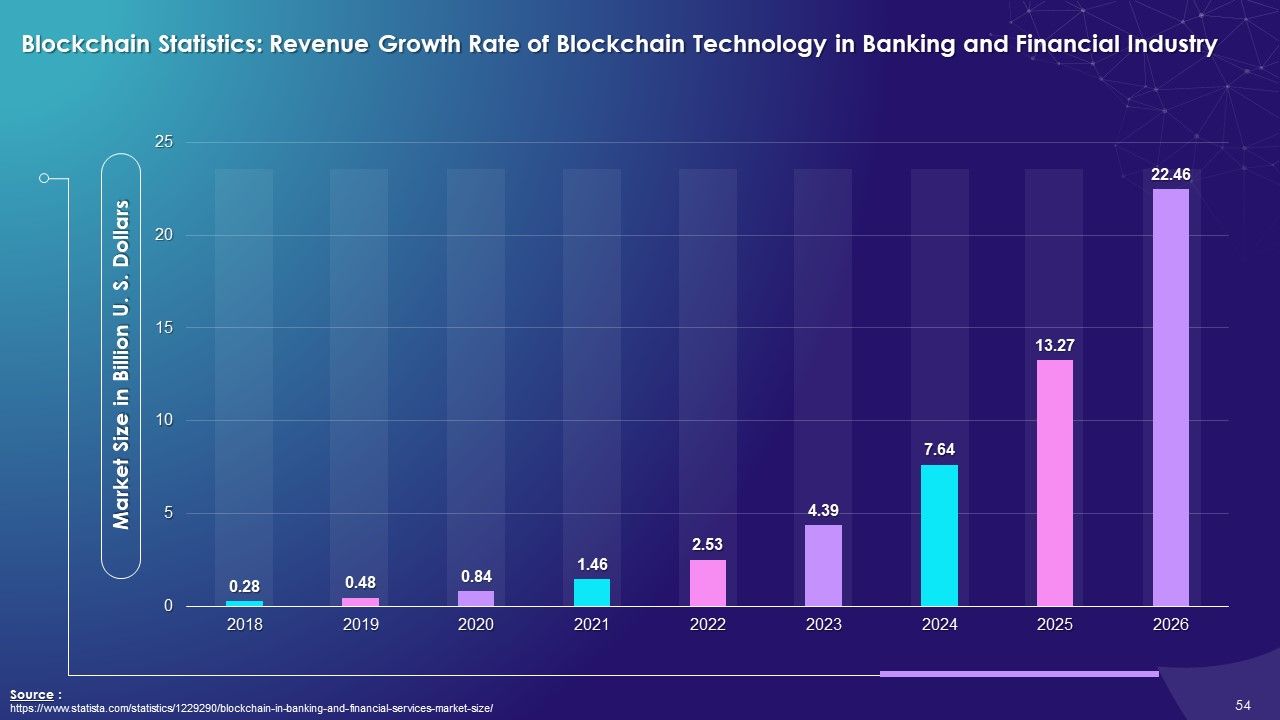
- Revenue Growth Rate in Banking and Financial Industry
- Future Trends
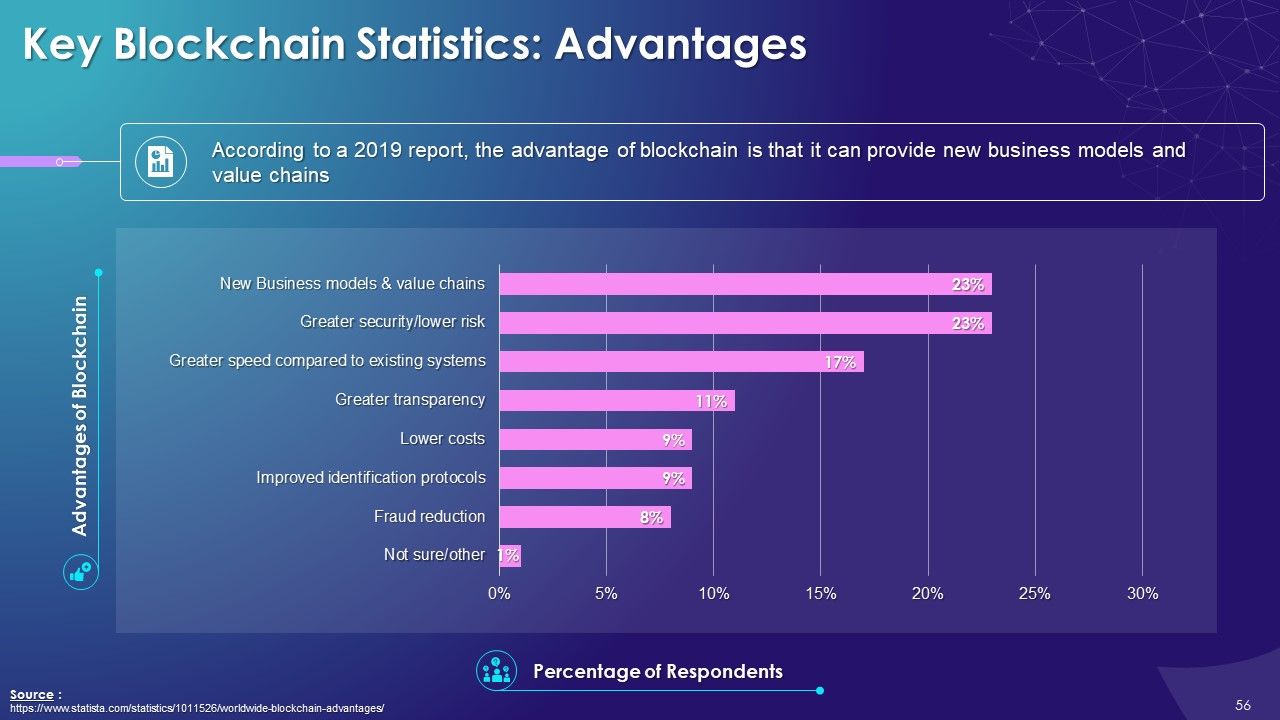
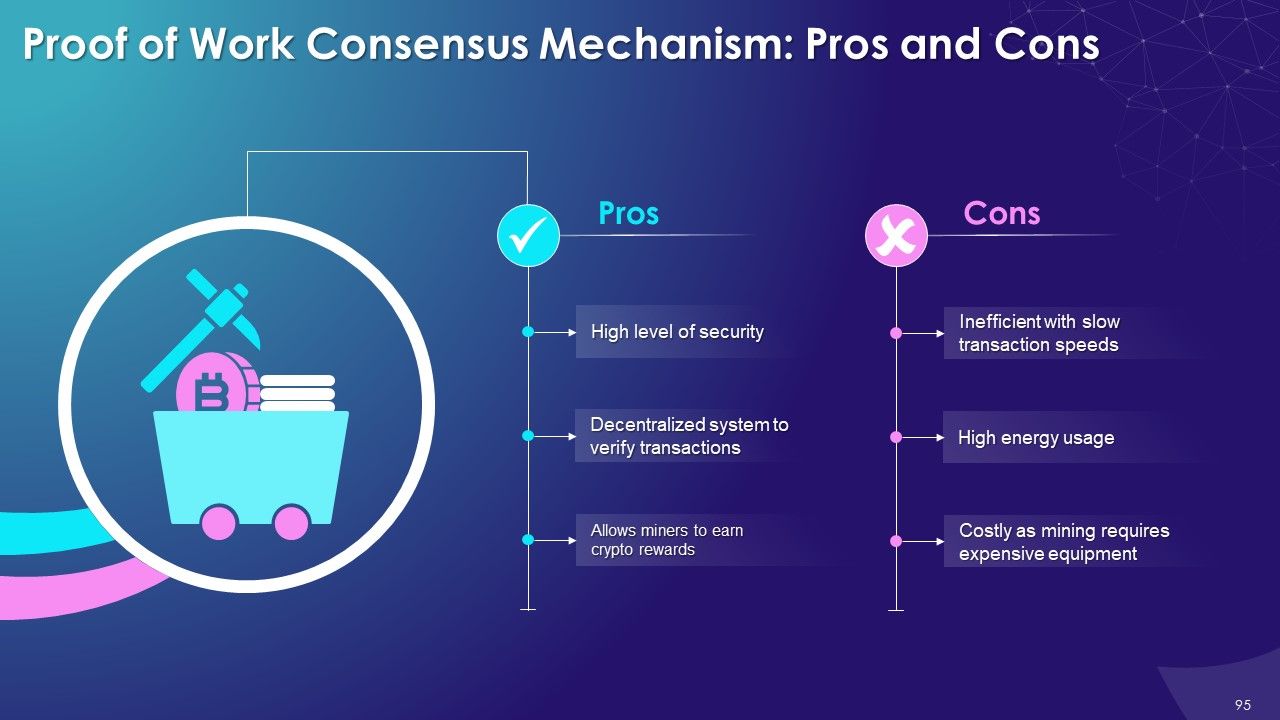
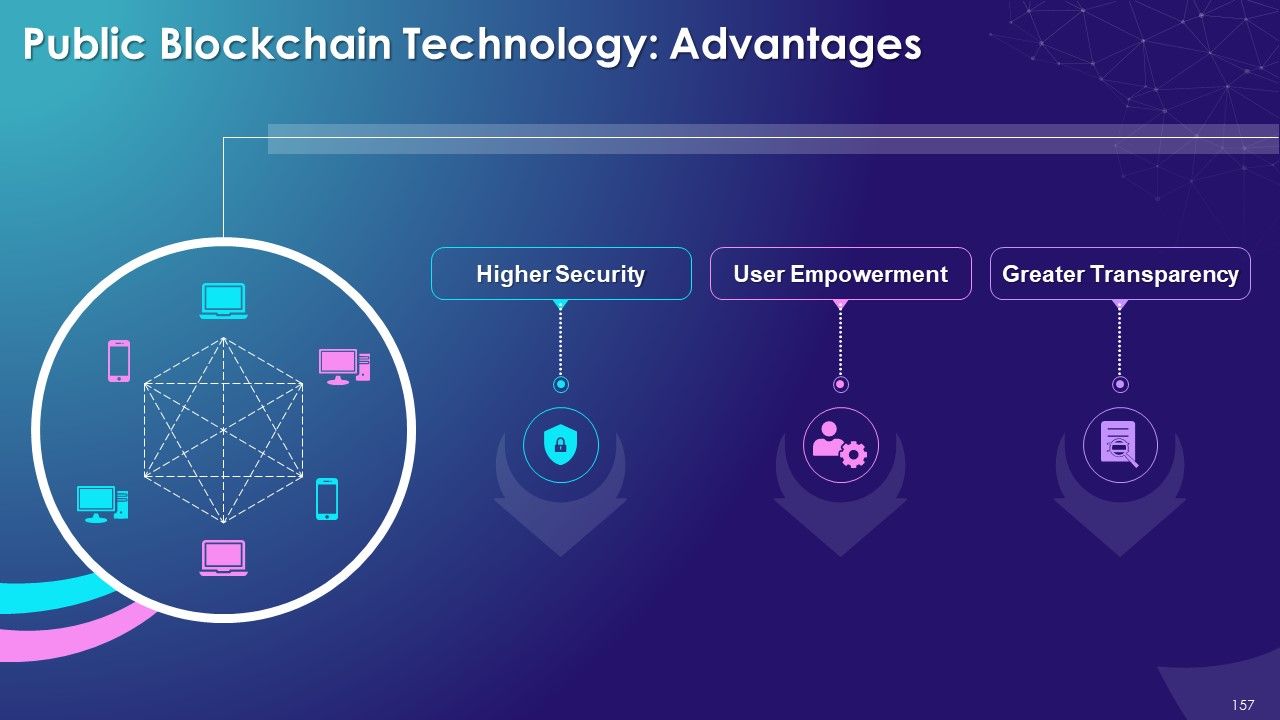
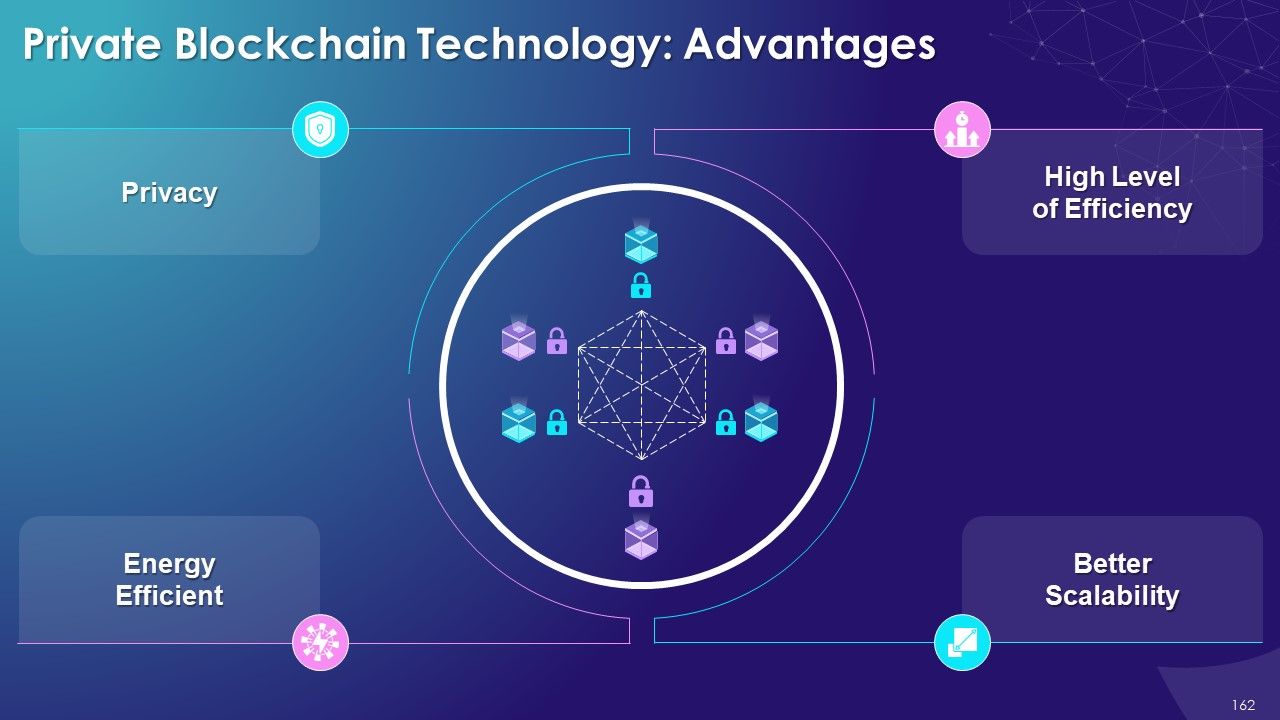
- Advantages
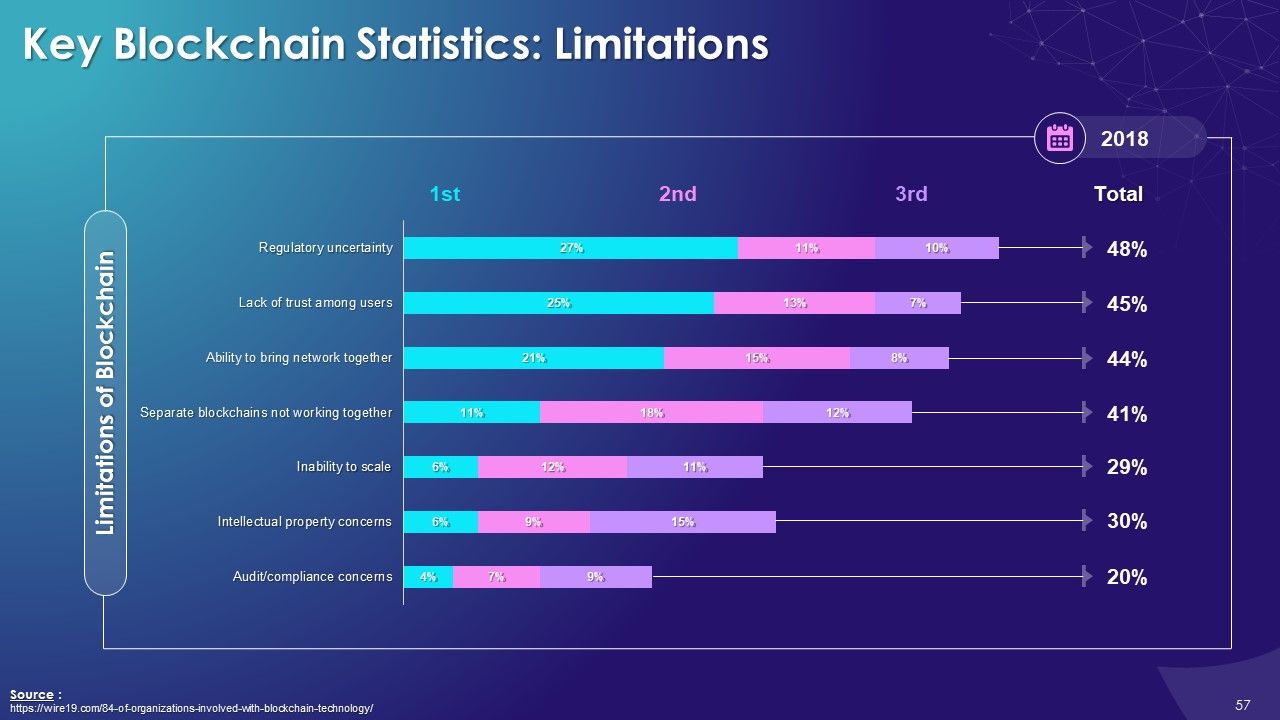
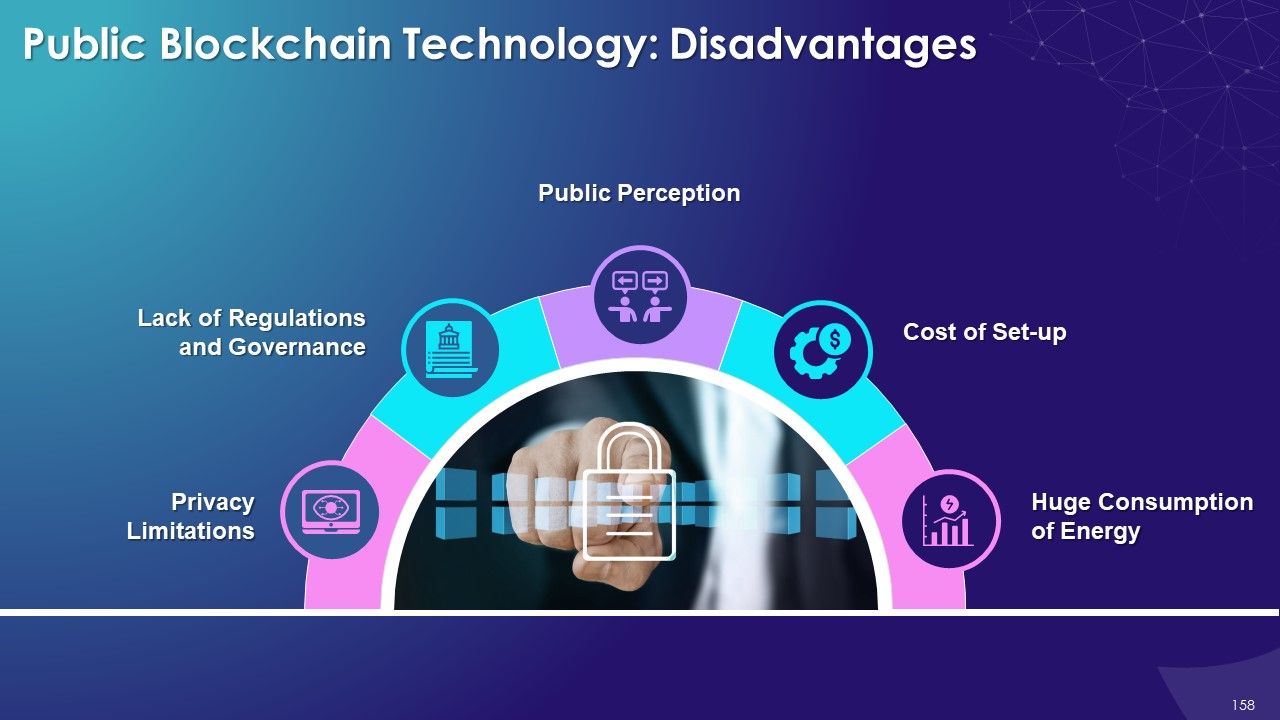
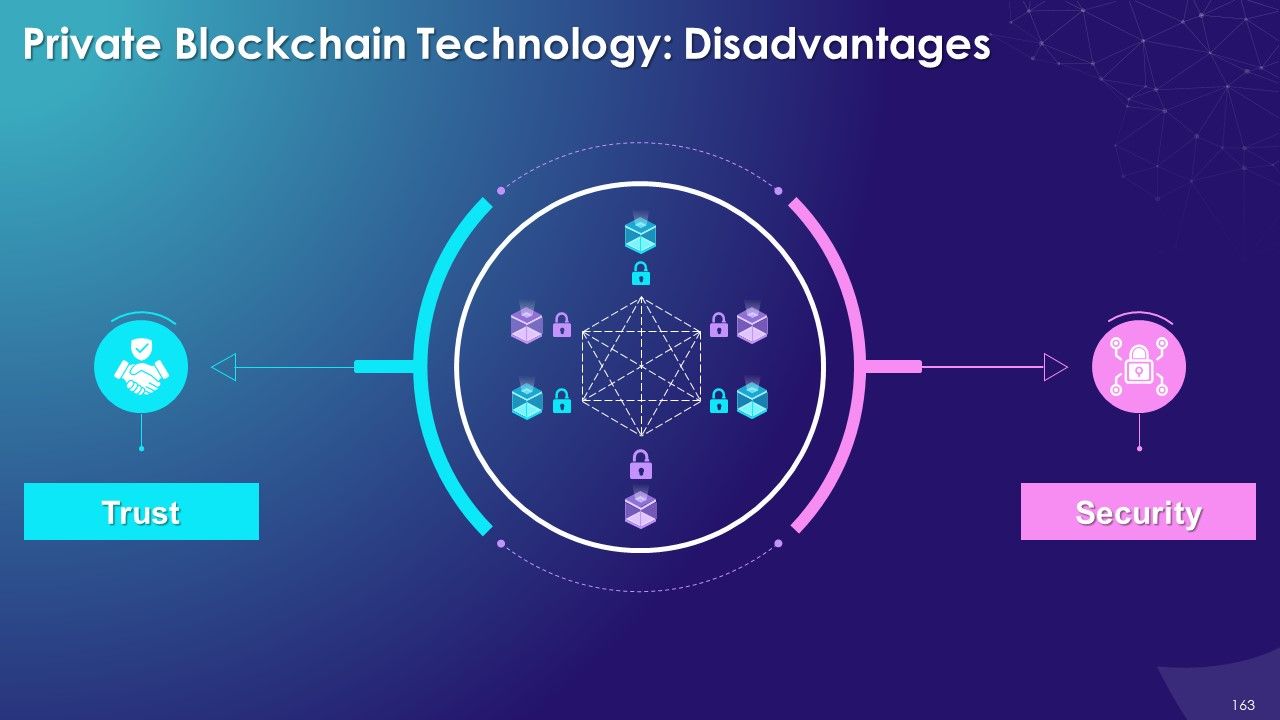
- Limitations
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
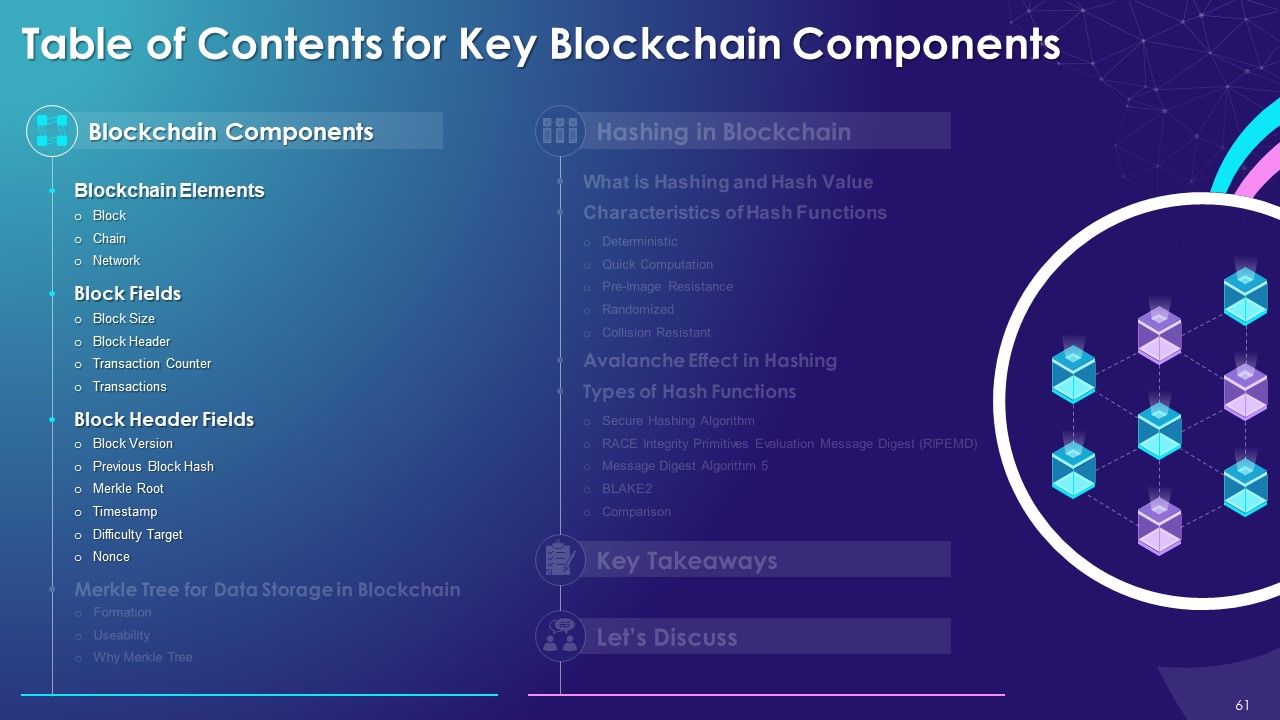
- Blockchain Components
- Blockchain Elements
- Block
- Chain
- Network
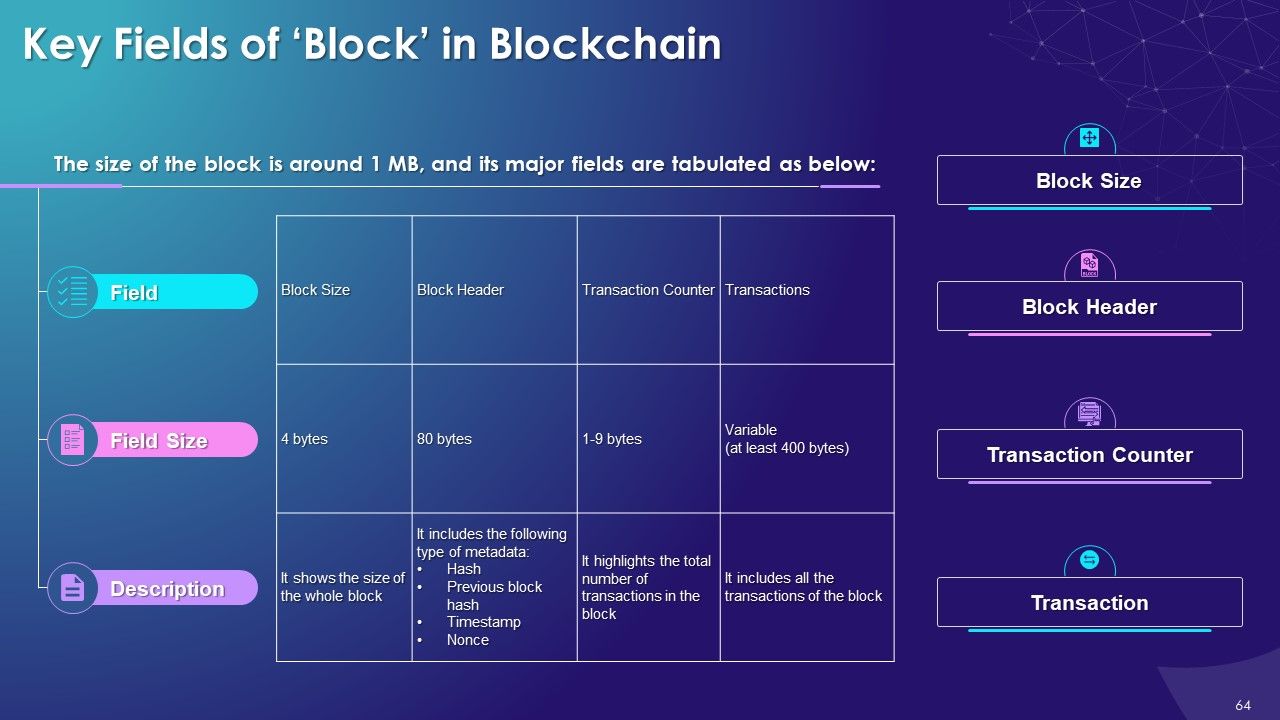
- Block Fields
- Block Size
- Block Header
- Transaction Counter
- Transactions
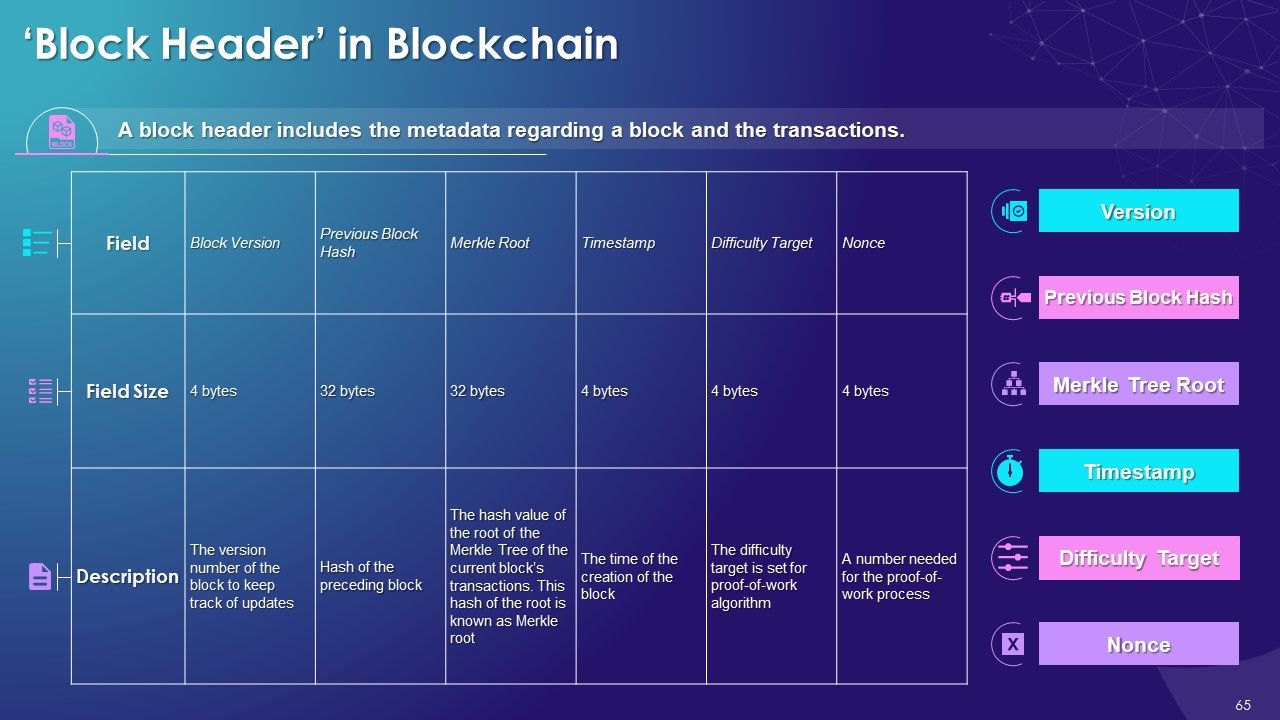
- Block Header Fields
- Block Version
- Previous Block Hash
- Merkle Root
- Timestamp
- Difficulty Target
- Nonce
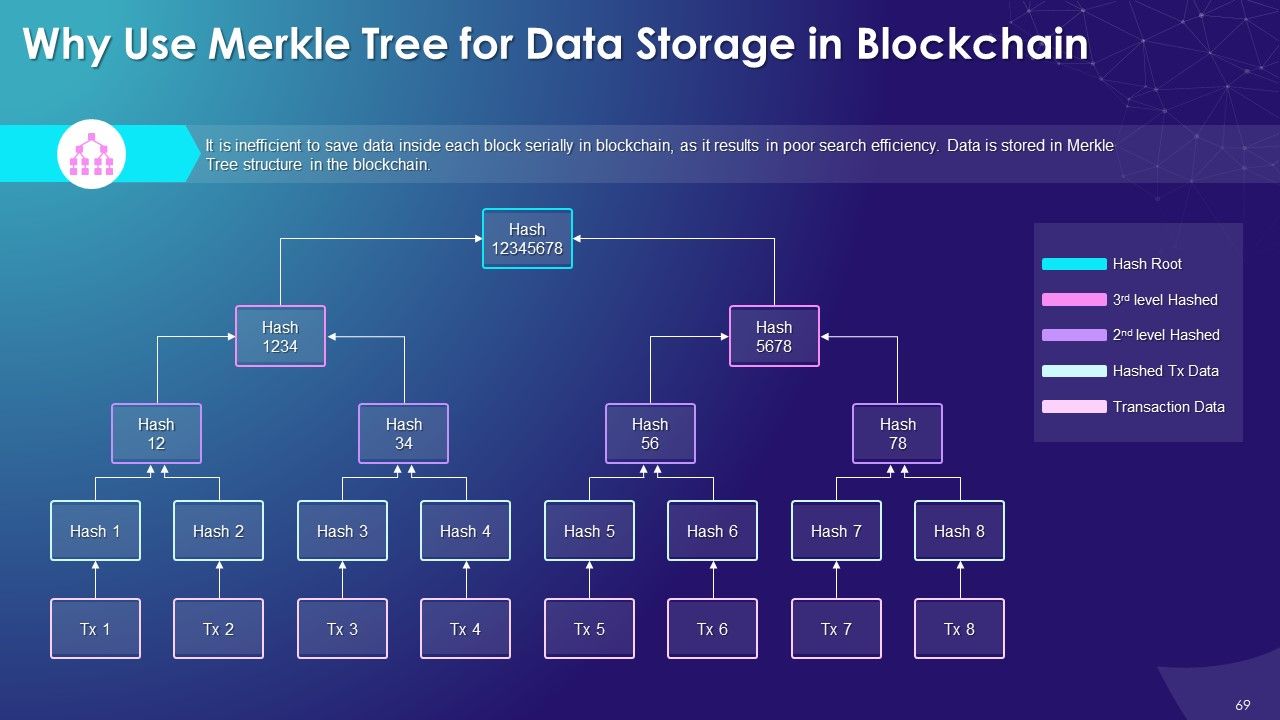
- Merkle Tree for Data Storage in Blockchain
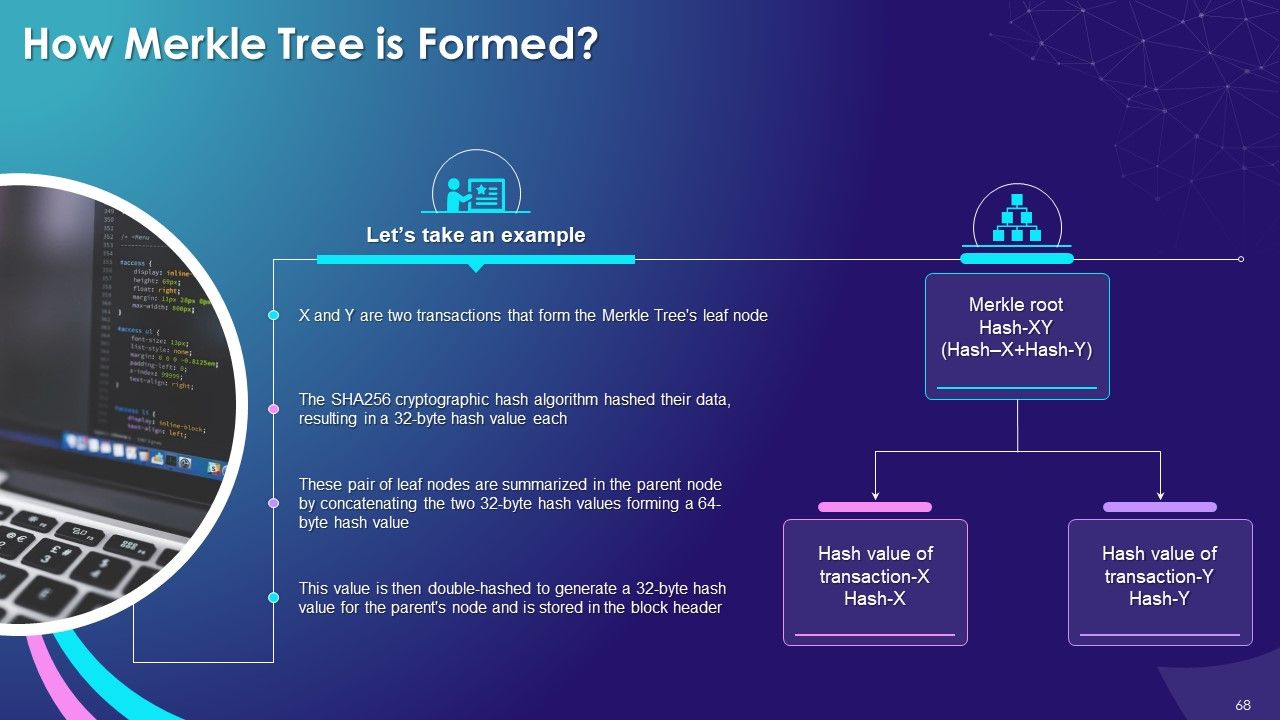
- Formation
- Useability
- Why Merkle Tree
- Blockchain Elements
- Hashing in Blockchain
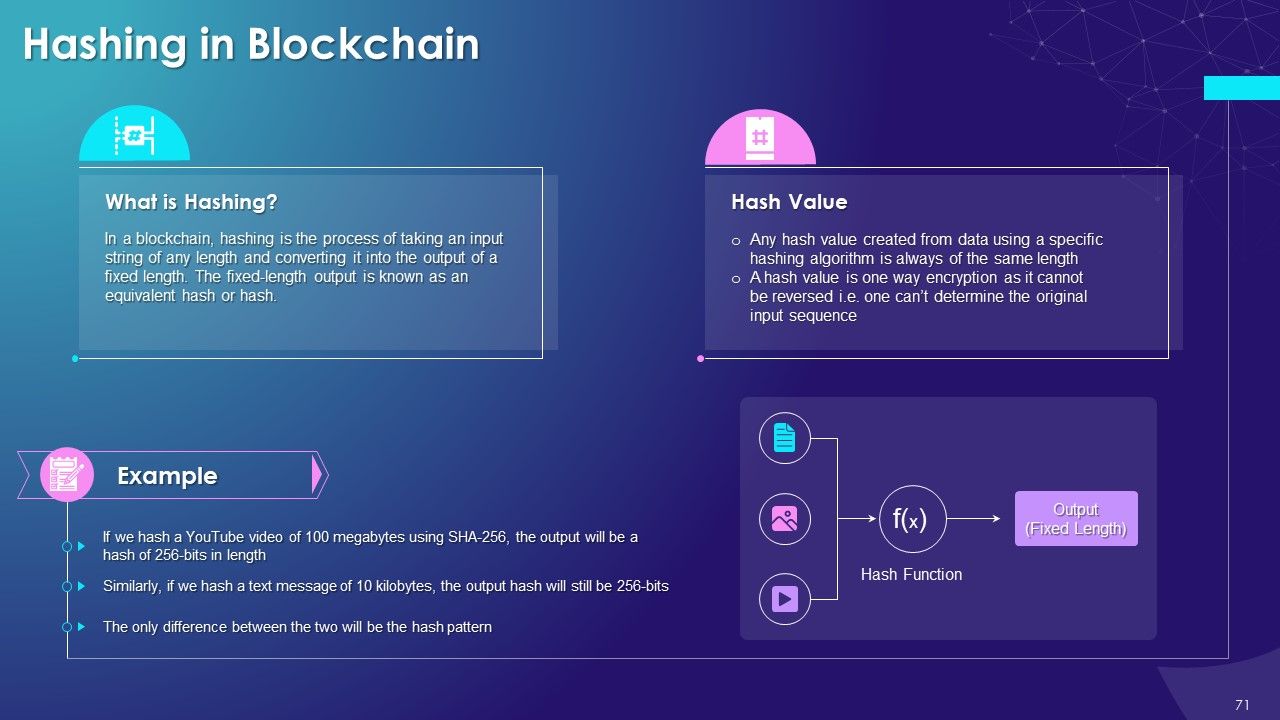
- What is Hashing and Hash Value
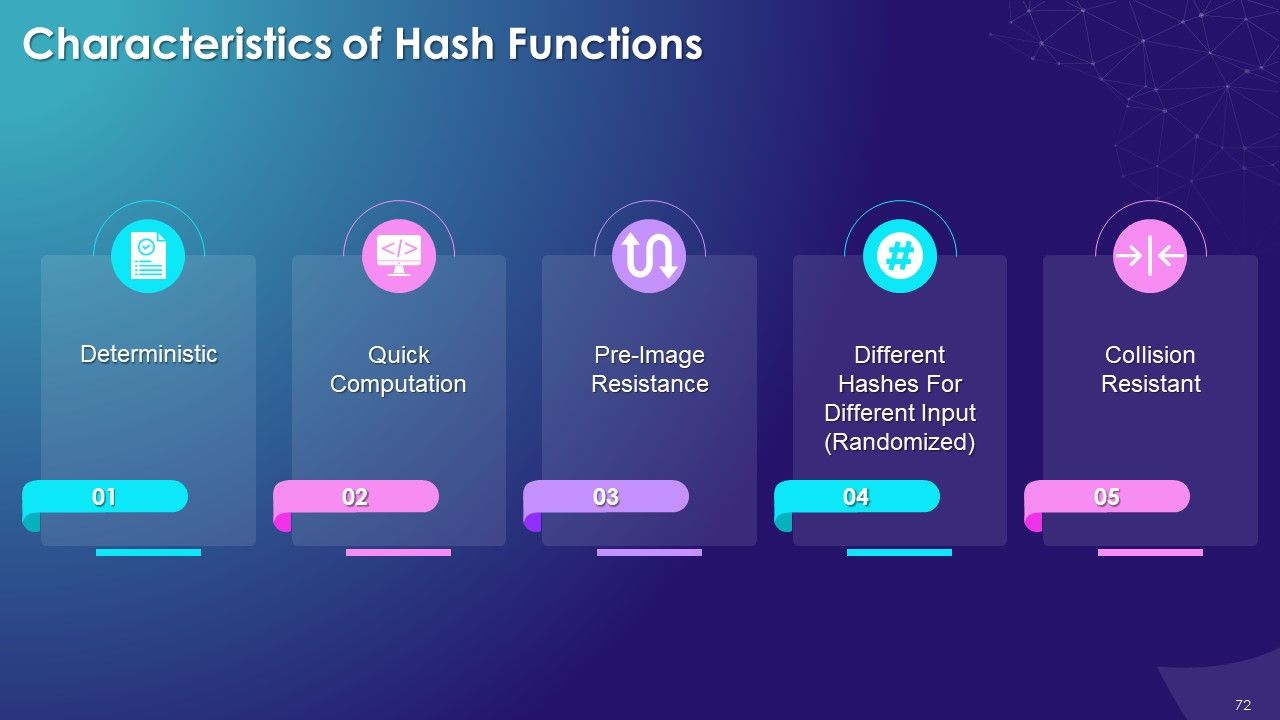
- Characteristics of Hash Functions
- Deterministic
- Quick Computation
- Pre-Image Resistance
- Randomized
- Collision Resistant
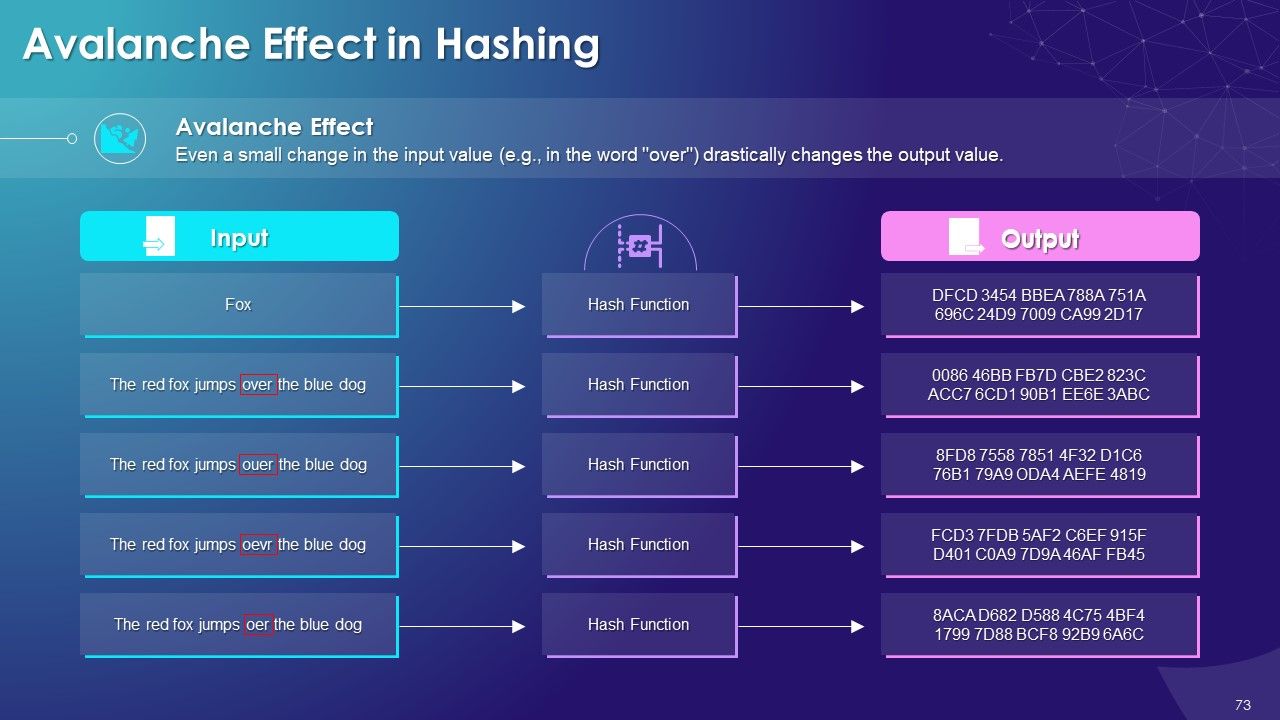
- Avalanche Effect in Hashing
- Types of Hash Functions
- Secure Hashing Algorithm
- RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation Message Digest (RIPEMD)
- Message Digest Algorithm 5
- BLAKE2
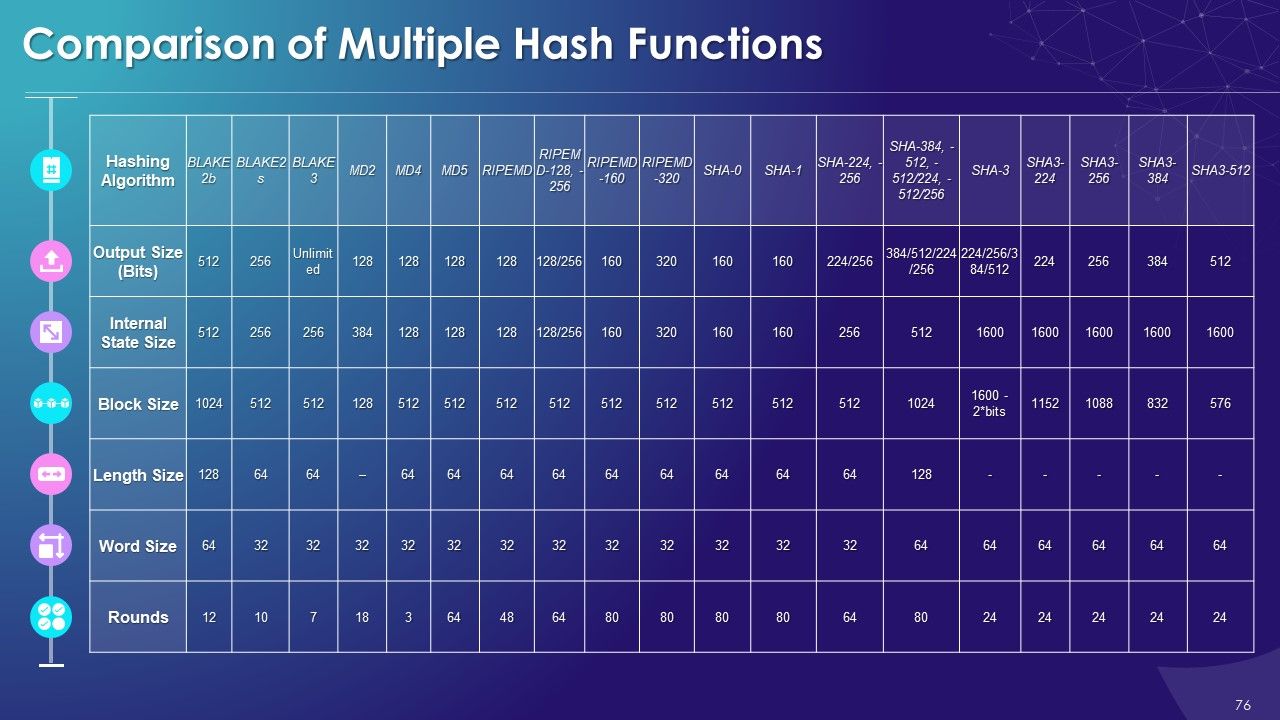
- Comparison
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- What is Mining in Blockchain?
- Mining Types: Individual, Pool, and Cloud
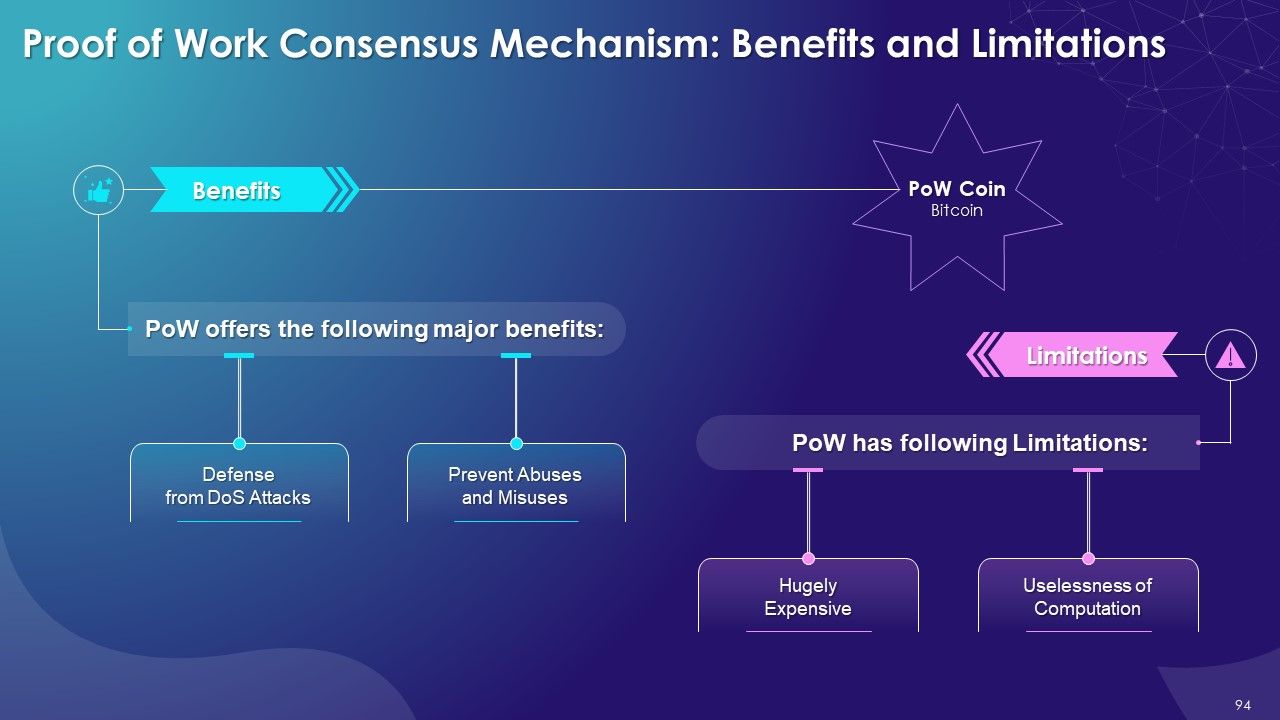
- Mining Uses
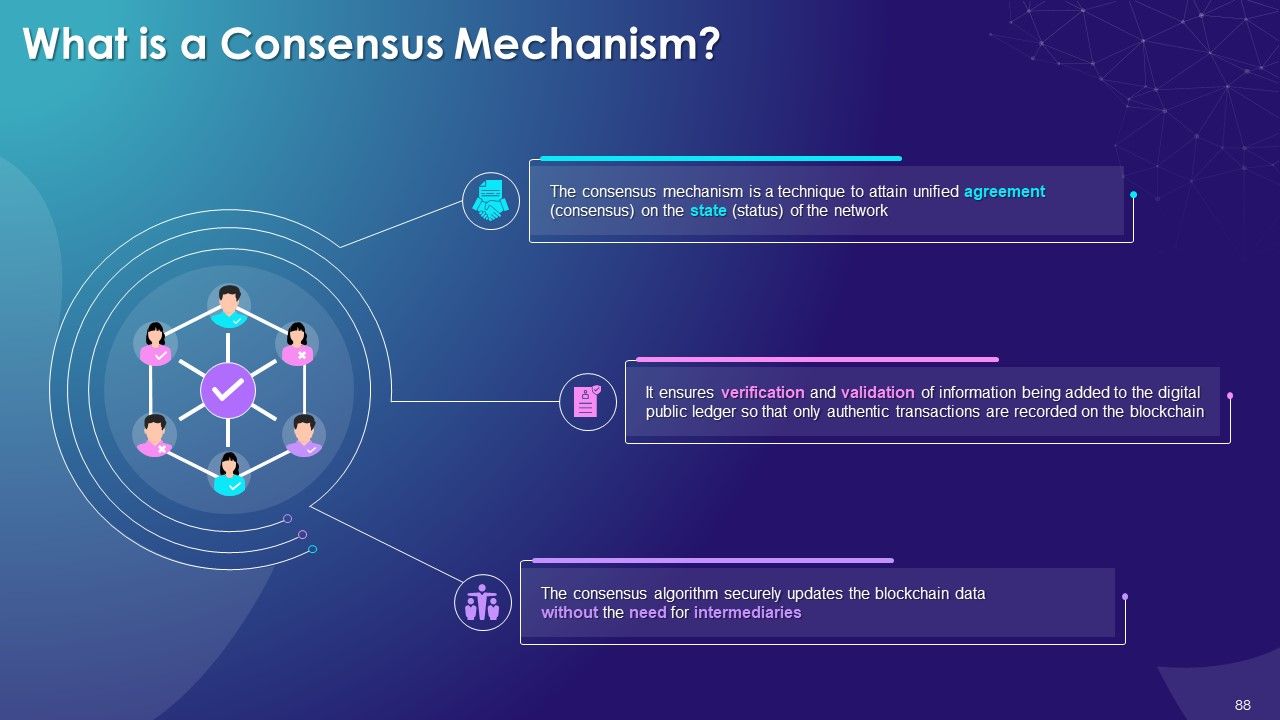
- What is a Consensus Mechanism?
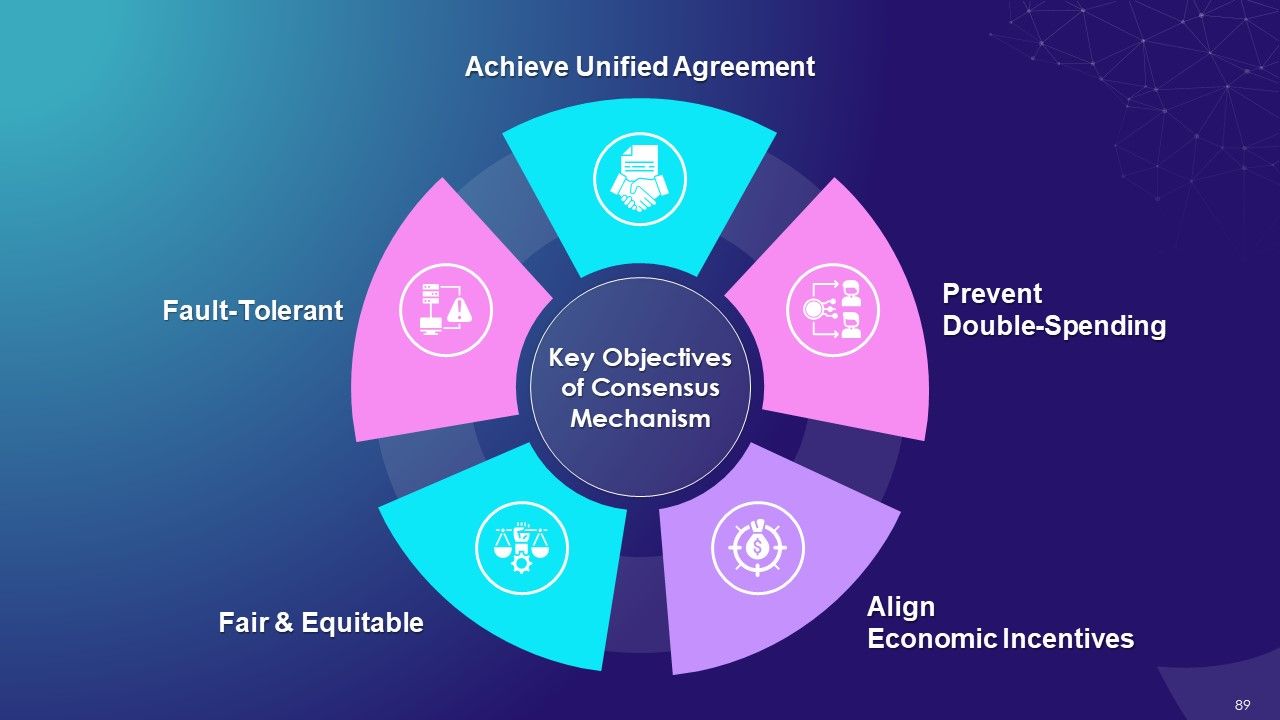
- Key Objectives of Consensus Mechanism
- Achieve Unified Agreement
- Prevent Double-Spending
- Align Economic Incentives
- Fair & Equitable
- Fault-Tolerant
- Consensus Mechanism Types
- Proof of Work
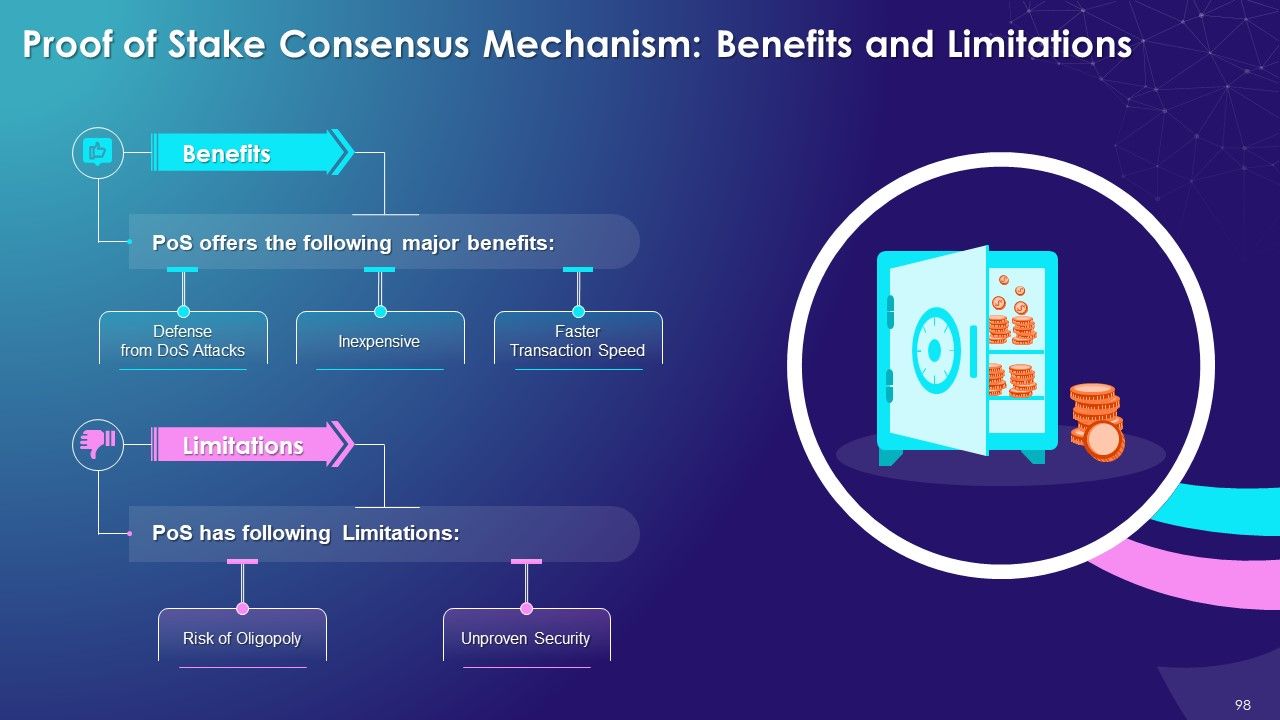
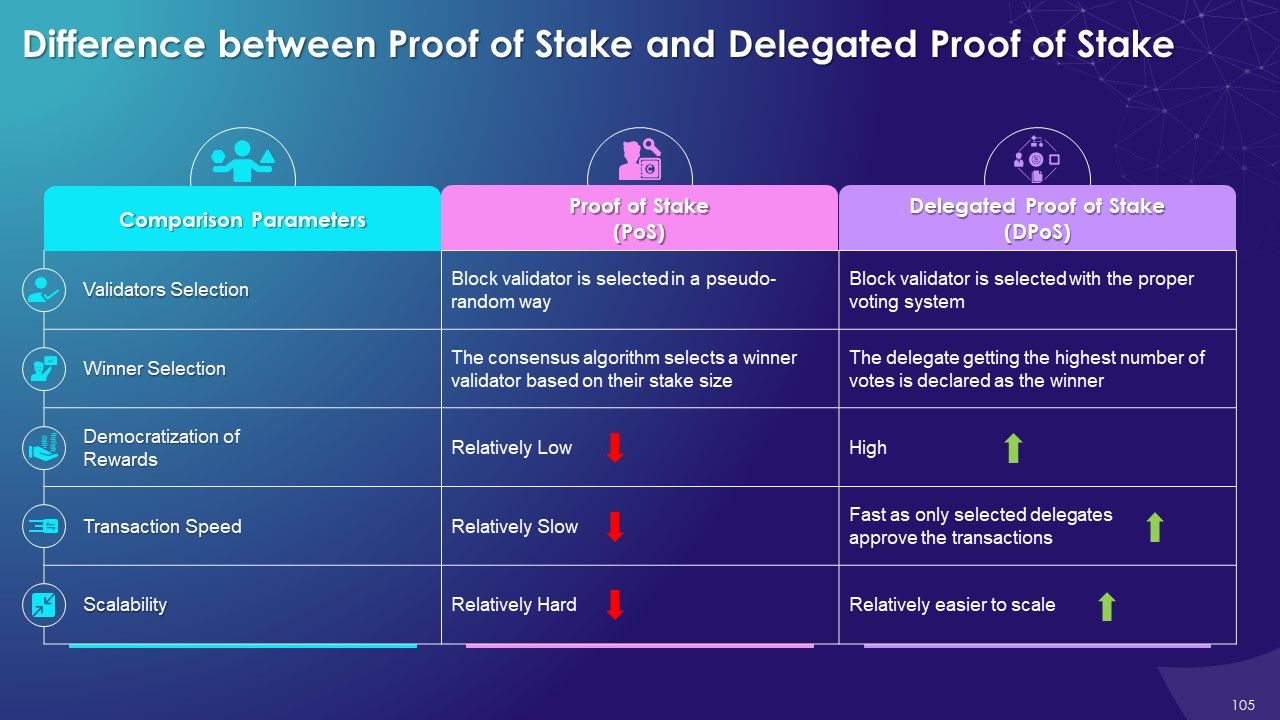
- Proof of Stake
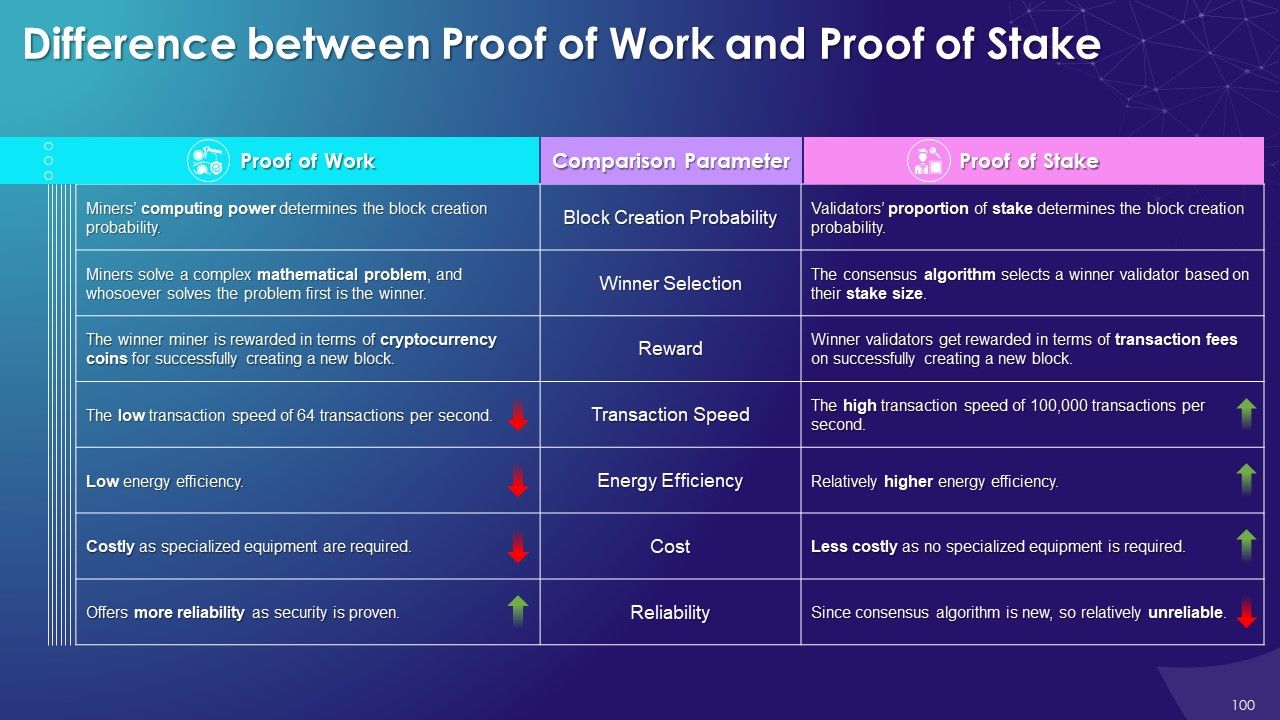
- Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
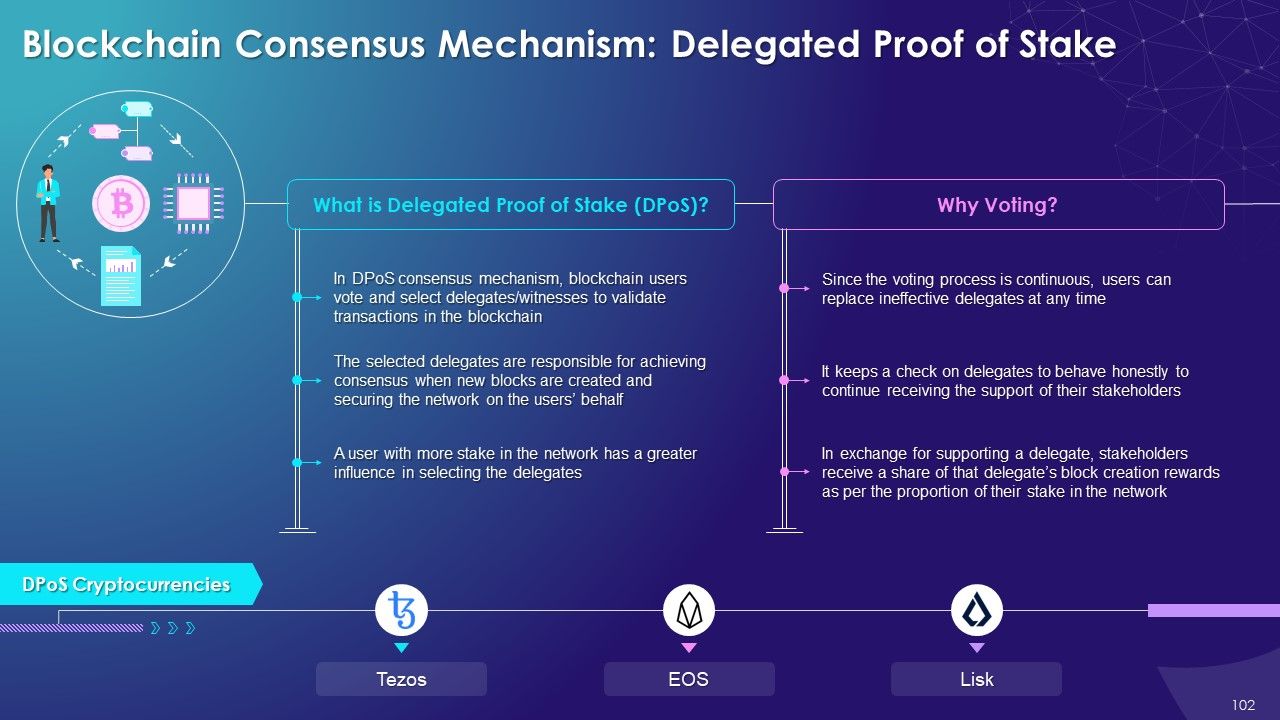
- Delegated Proof of Stake
- Proof of Stake vs. Delegated Proof of Stake
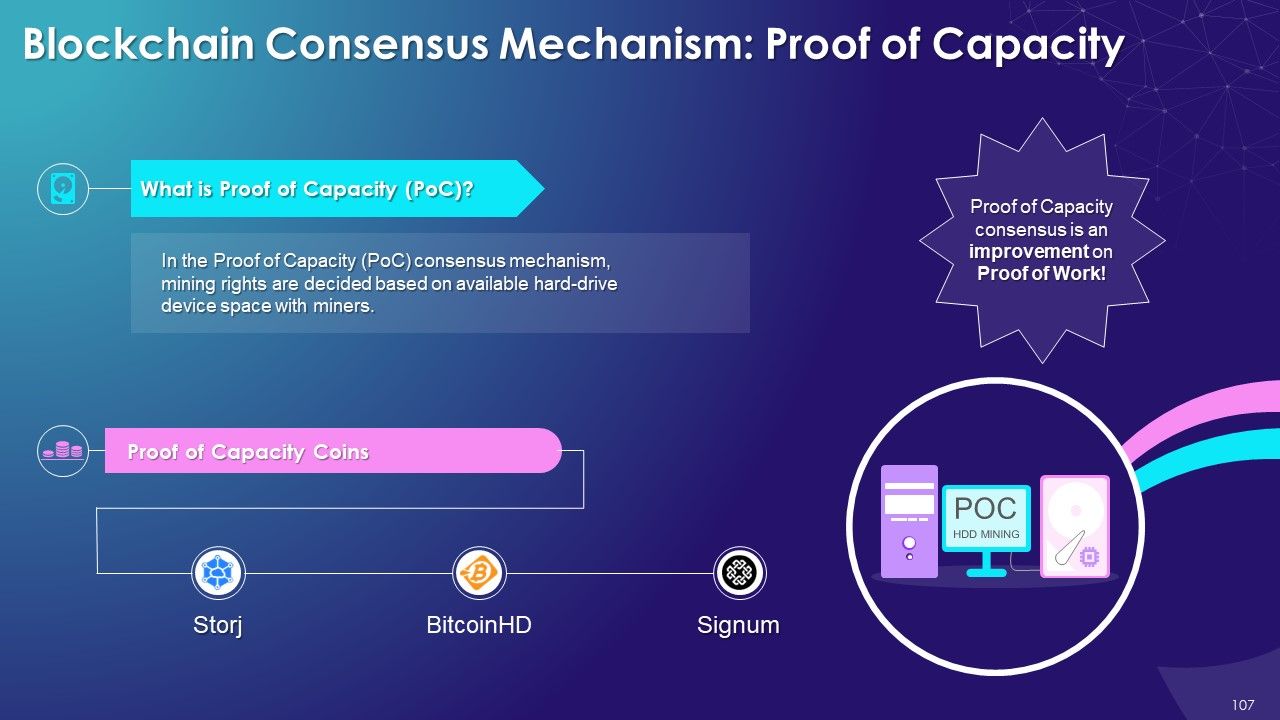
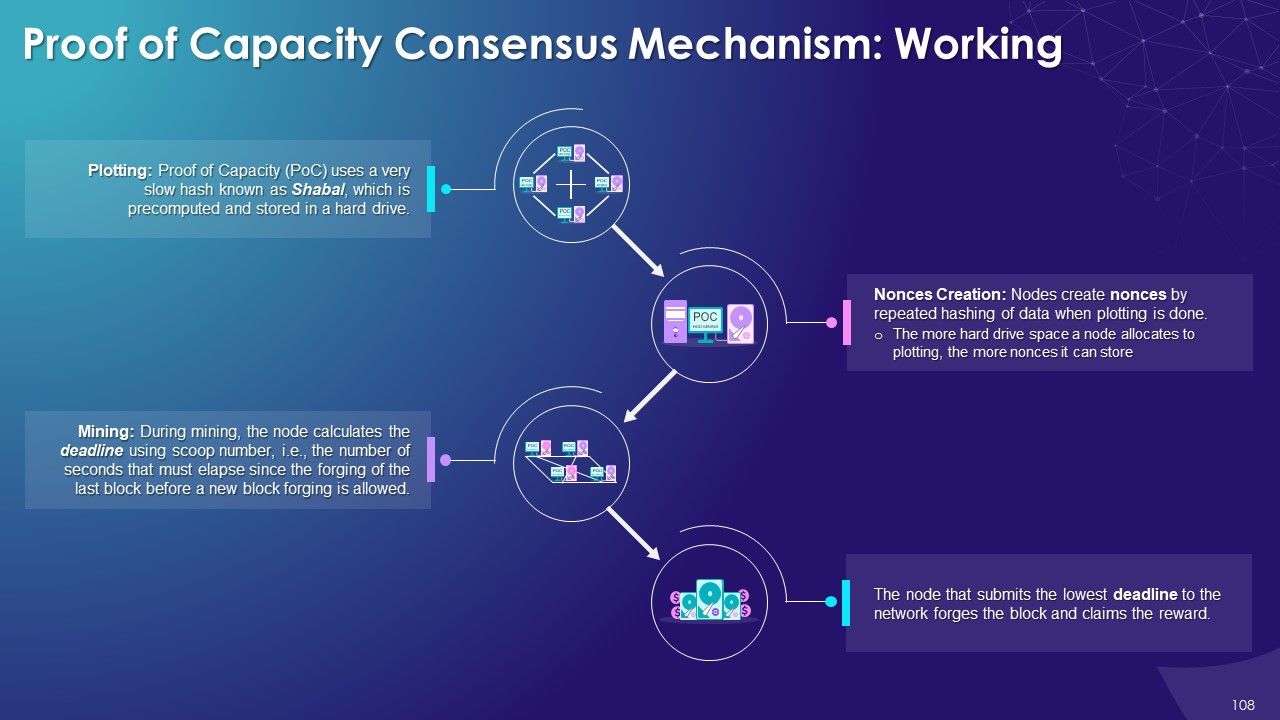
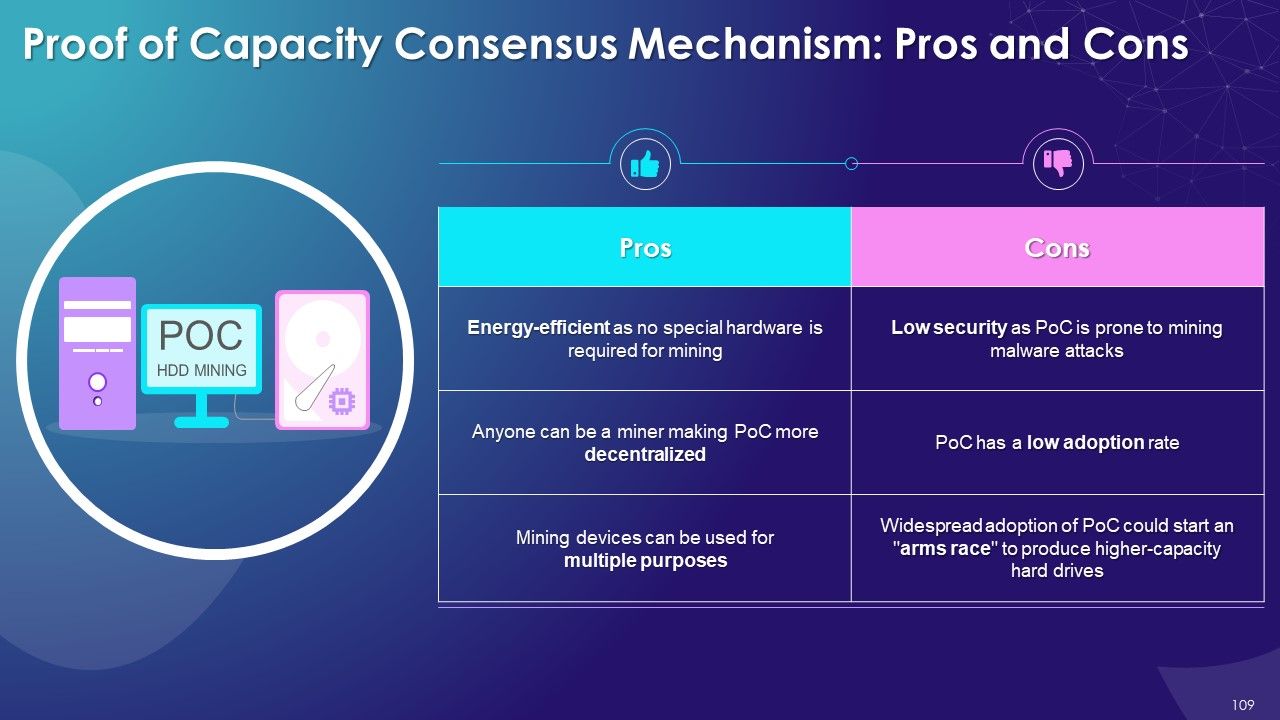
- Proof of Capacity
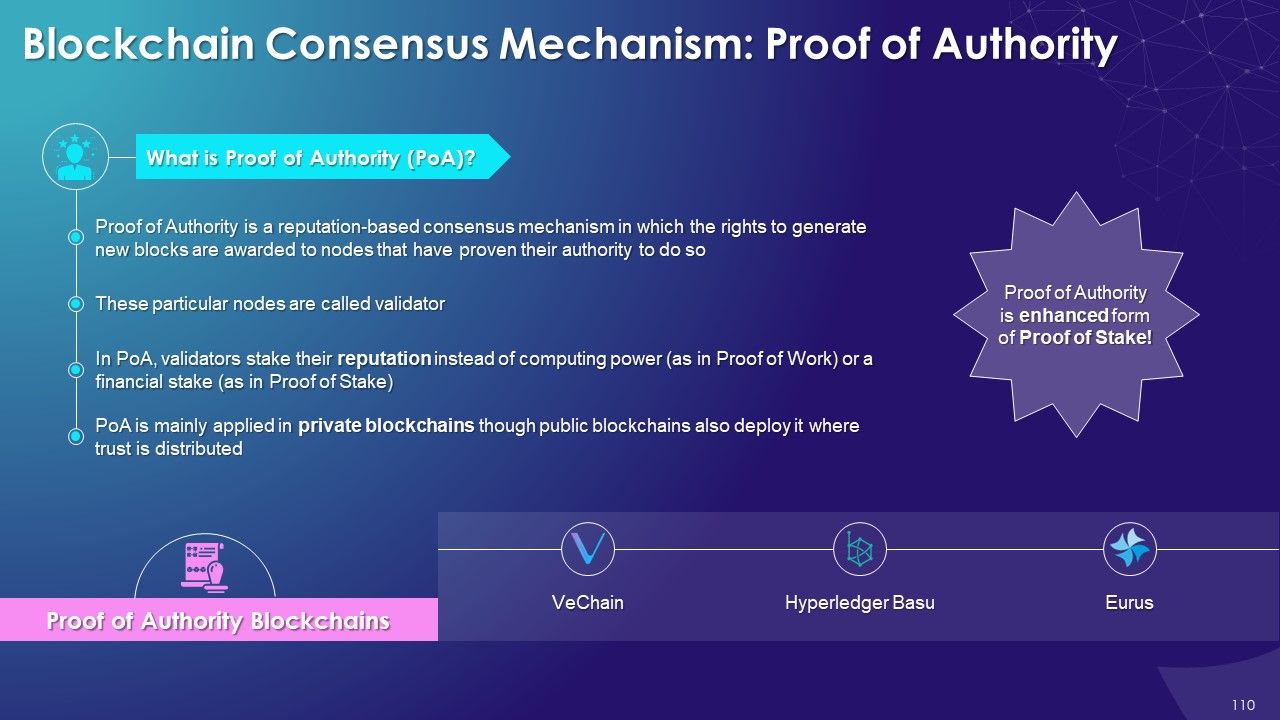
- Proof of Authority
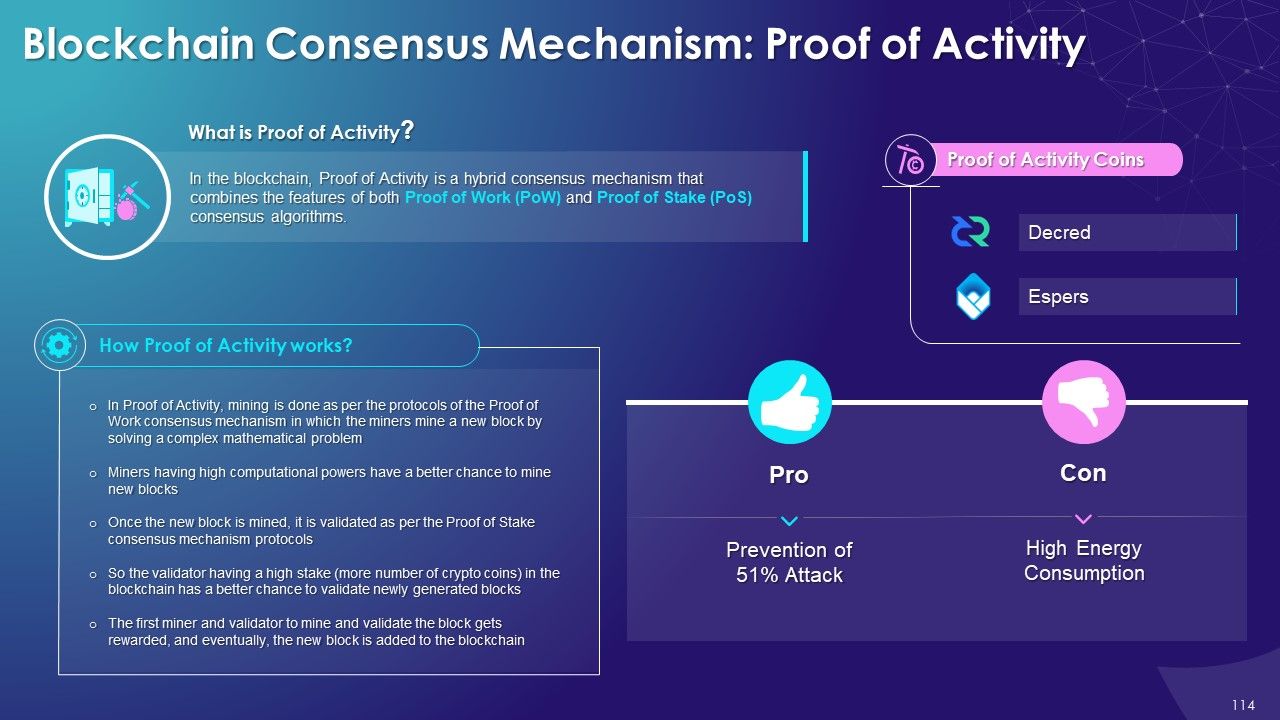
- Proof of Activity
- Proof of Elapsed Time
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Comparison
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
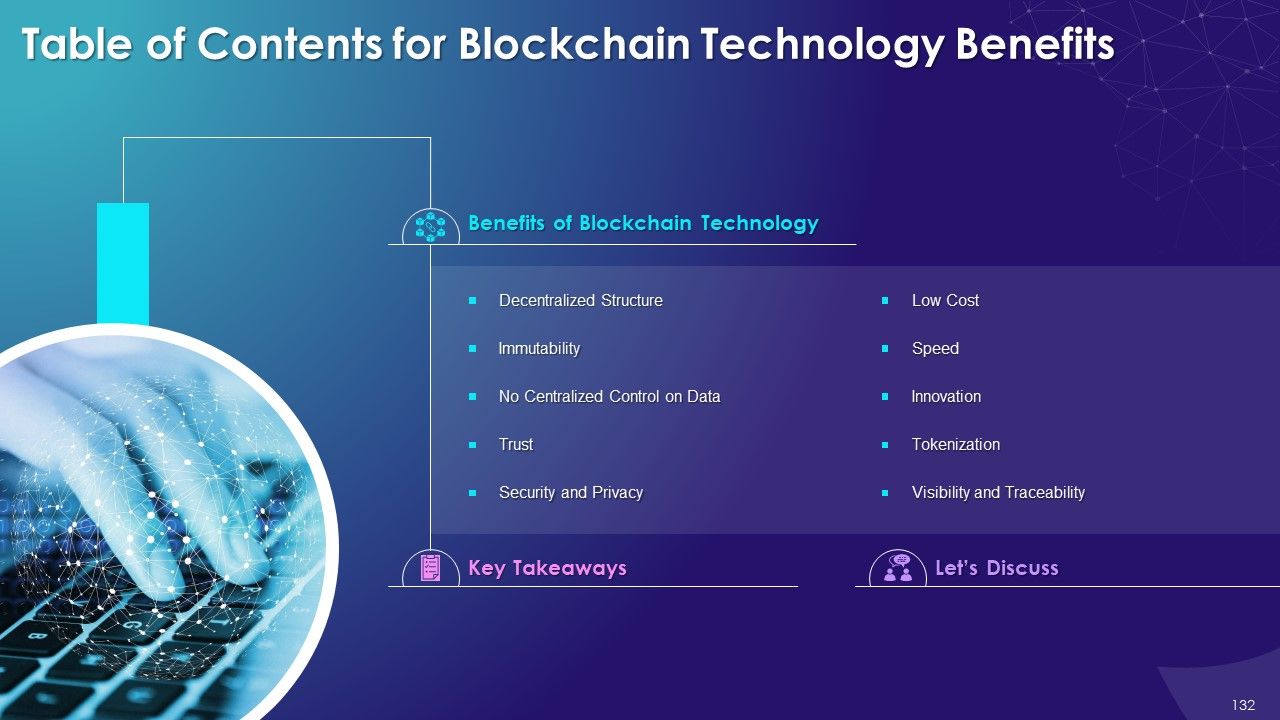
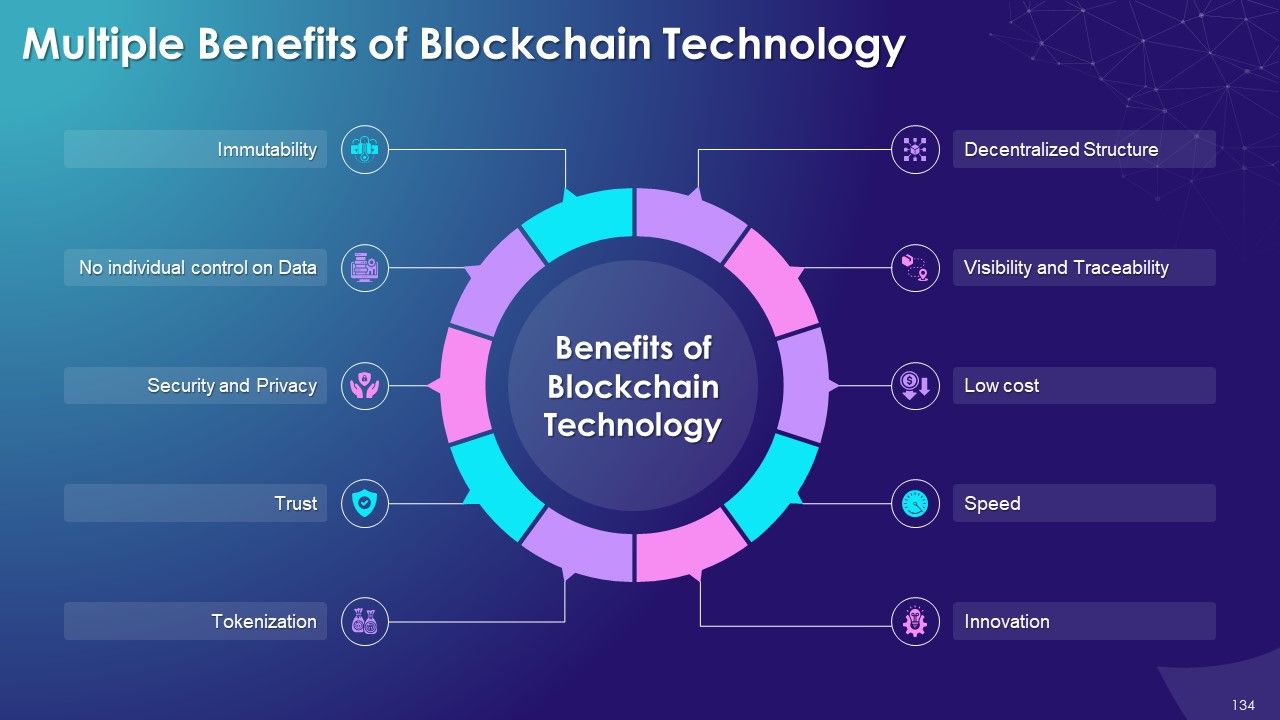
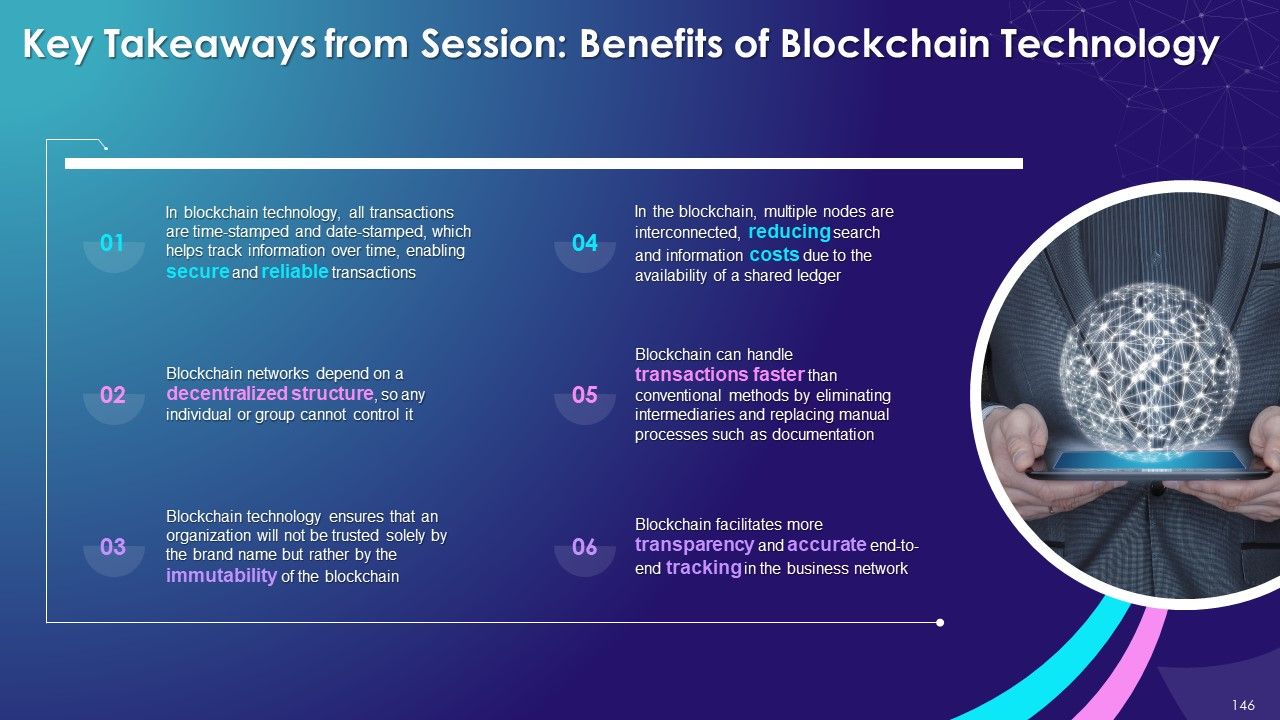
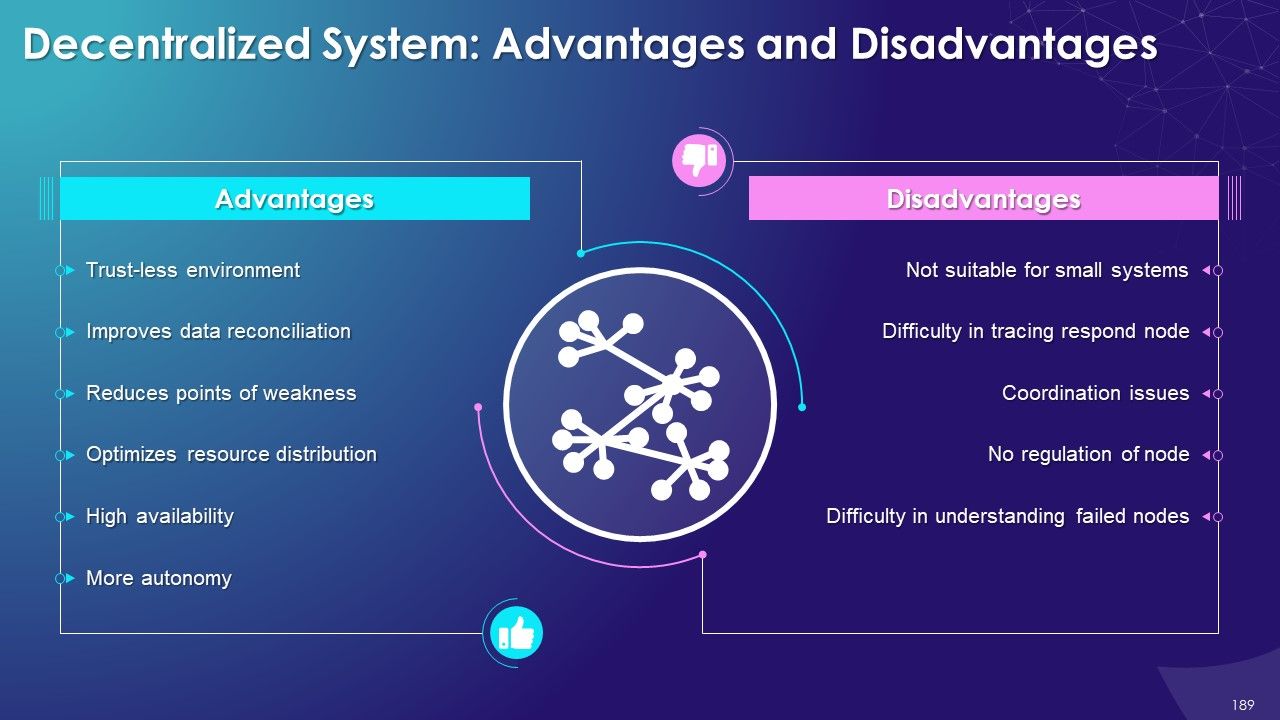
- Benefits of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralized Structure
- Immutability
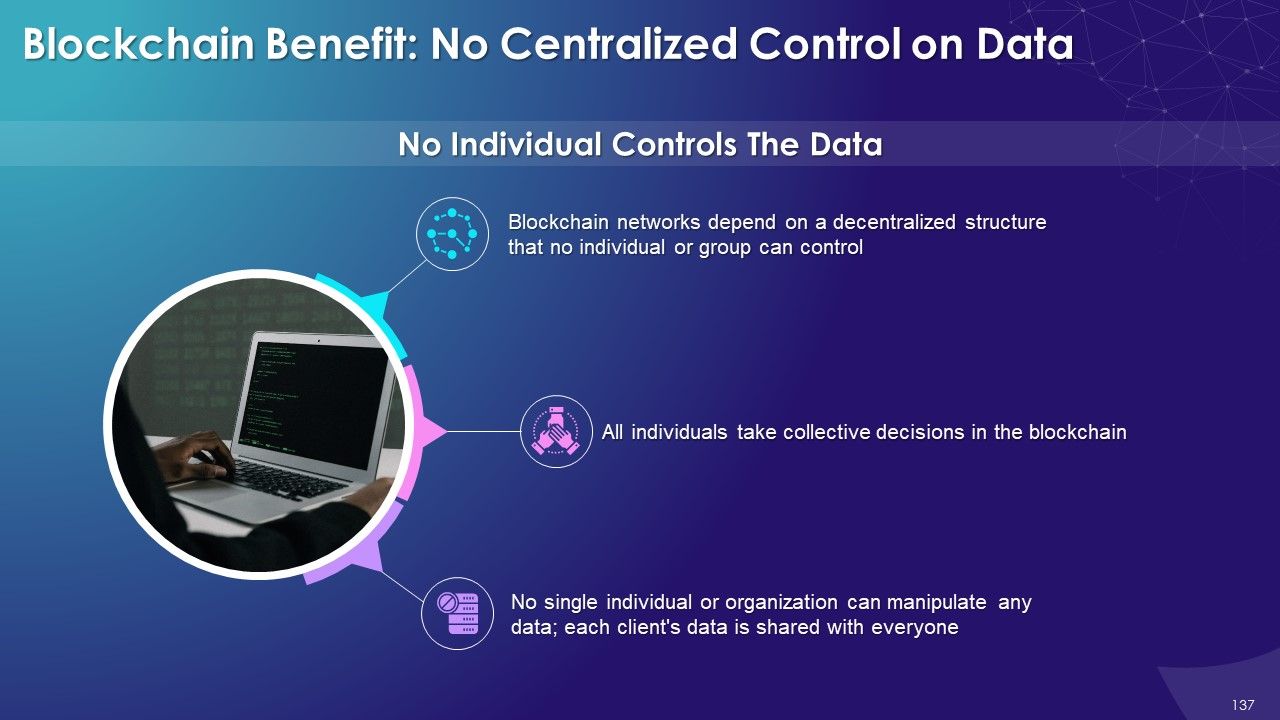
- No Centralized Control on Data
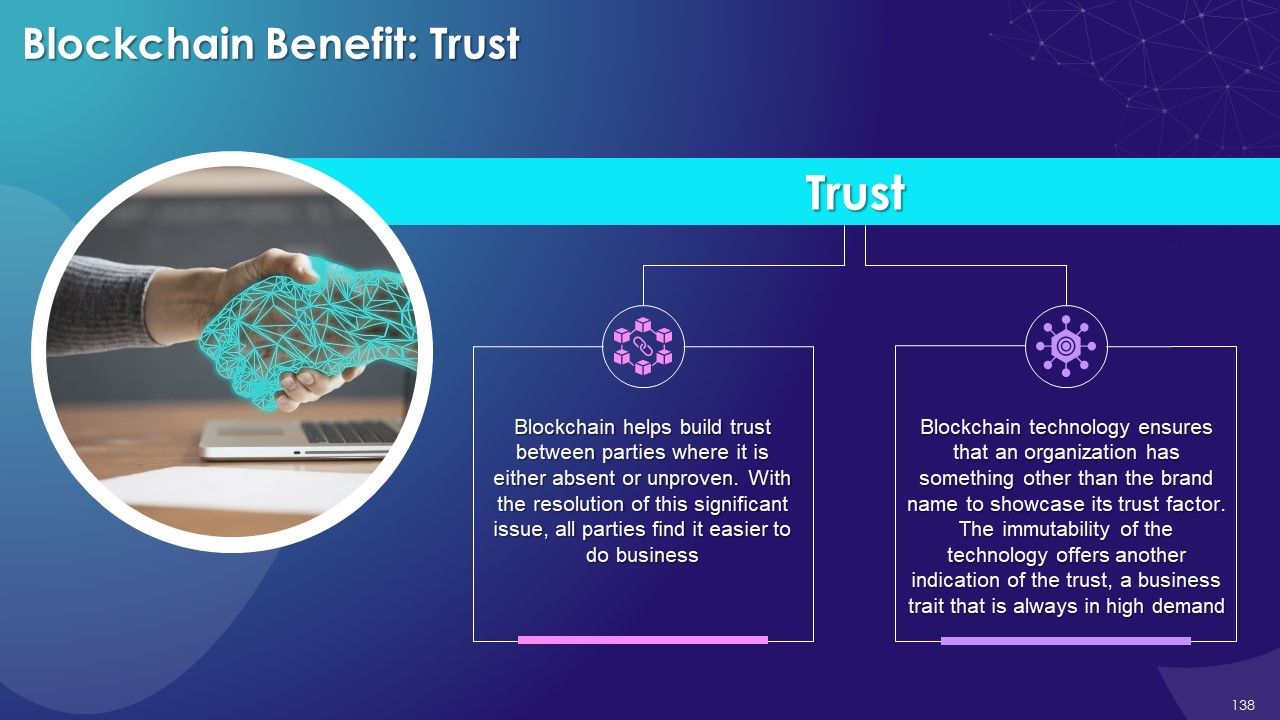
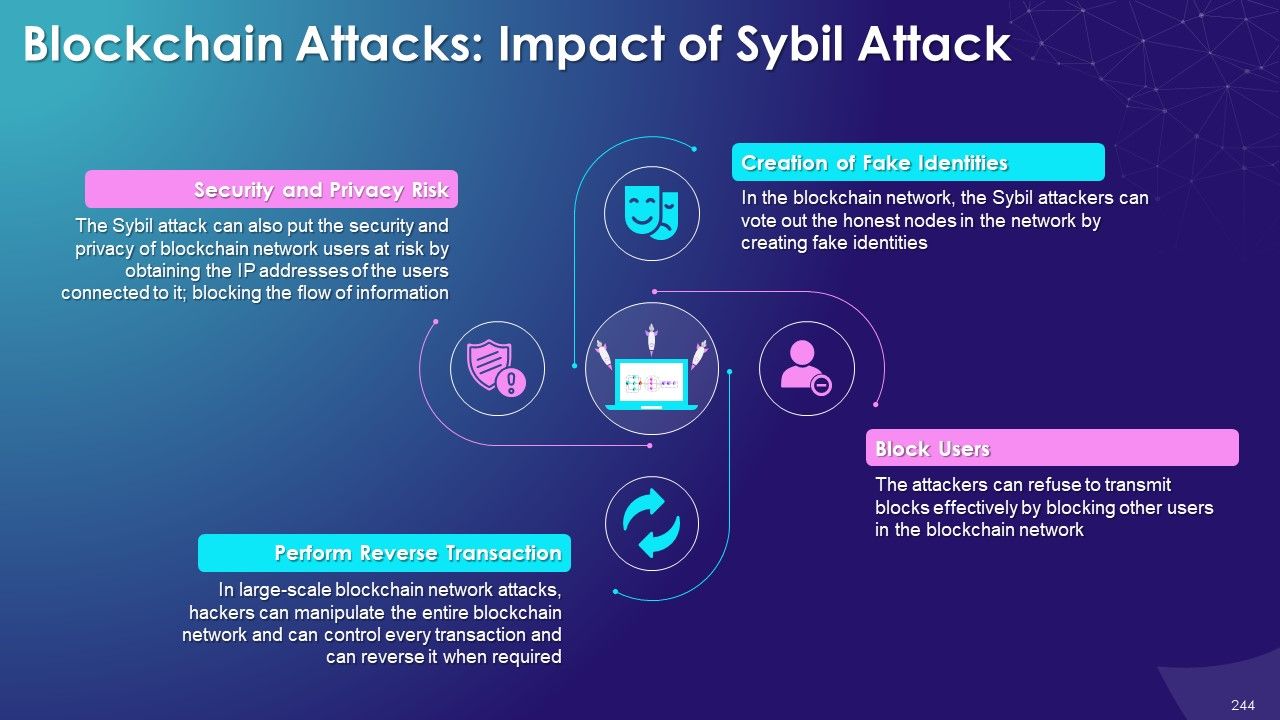
- Trust
- Security and Privacy
- Less Cost
- Speed
- Innovation
- Tokenization
- Visibility and Traceability
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
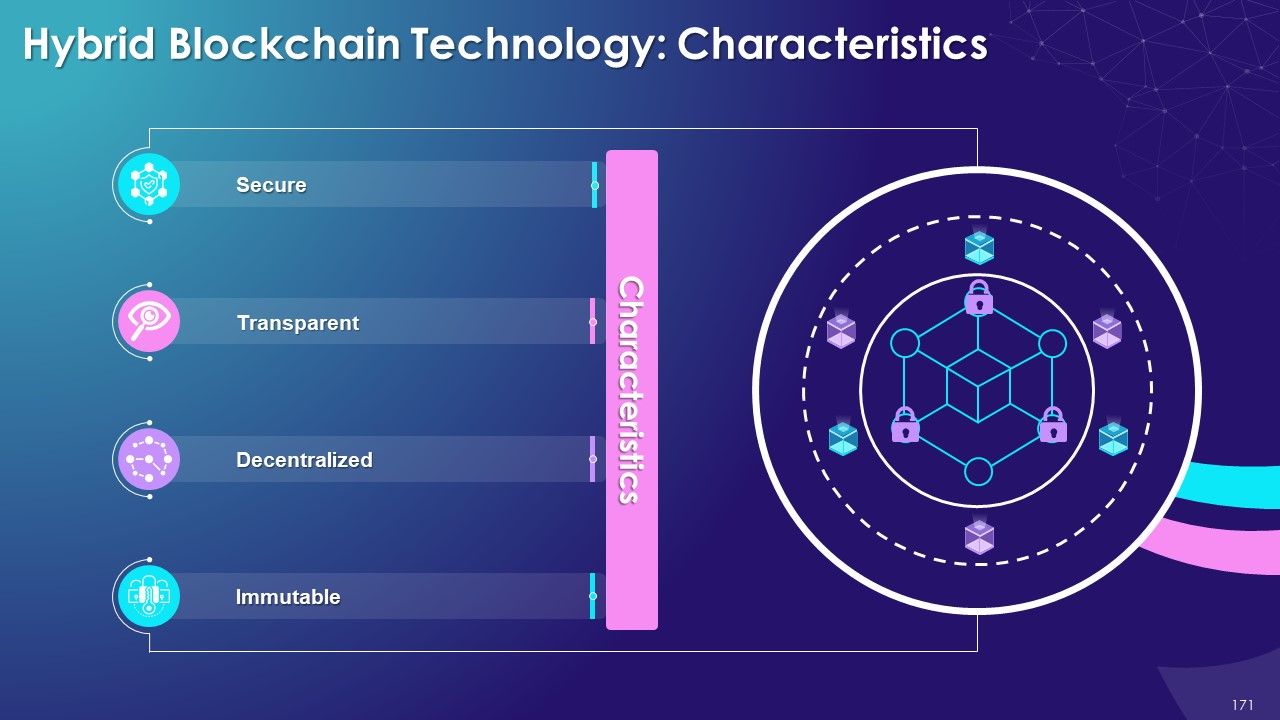
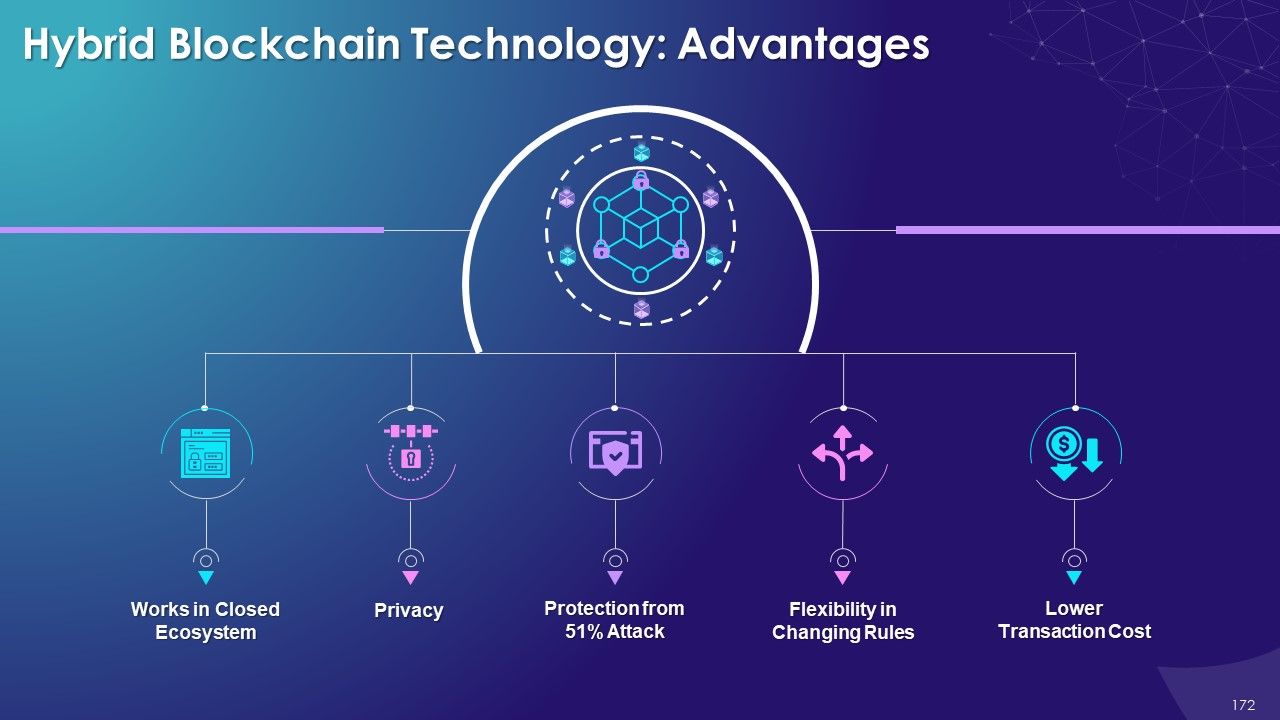
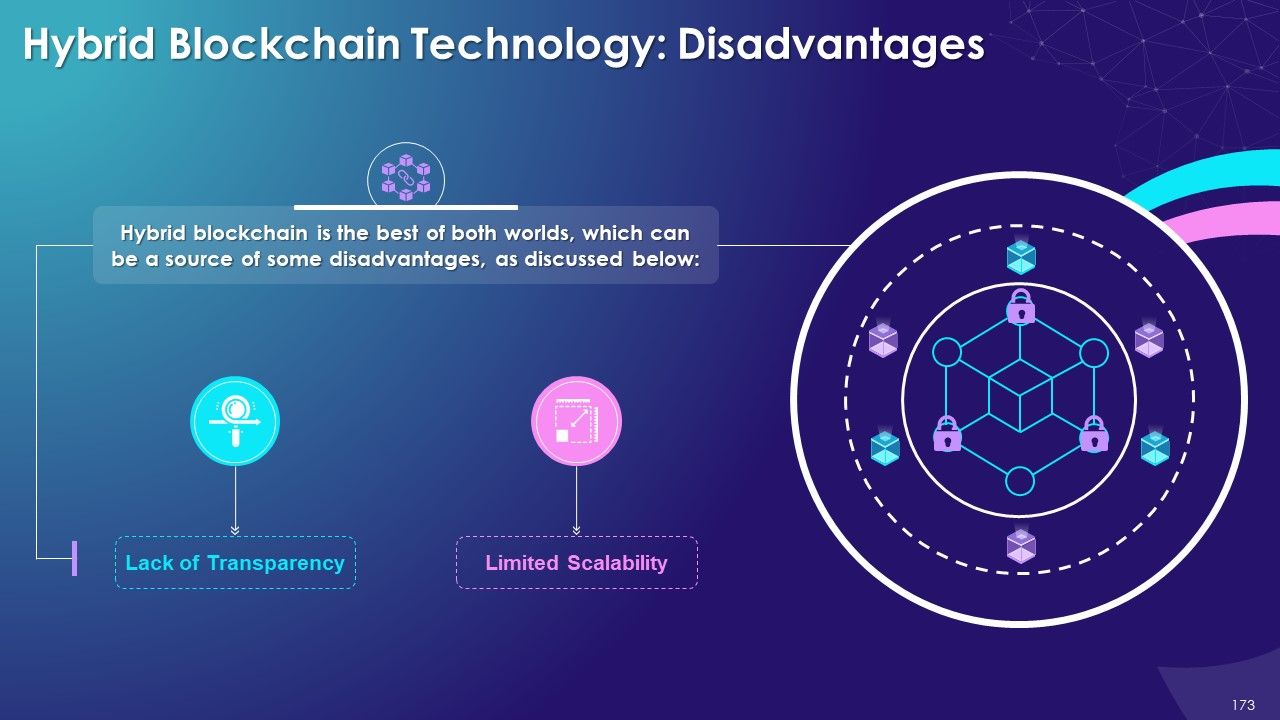
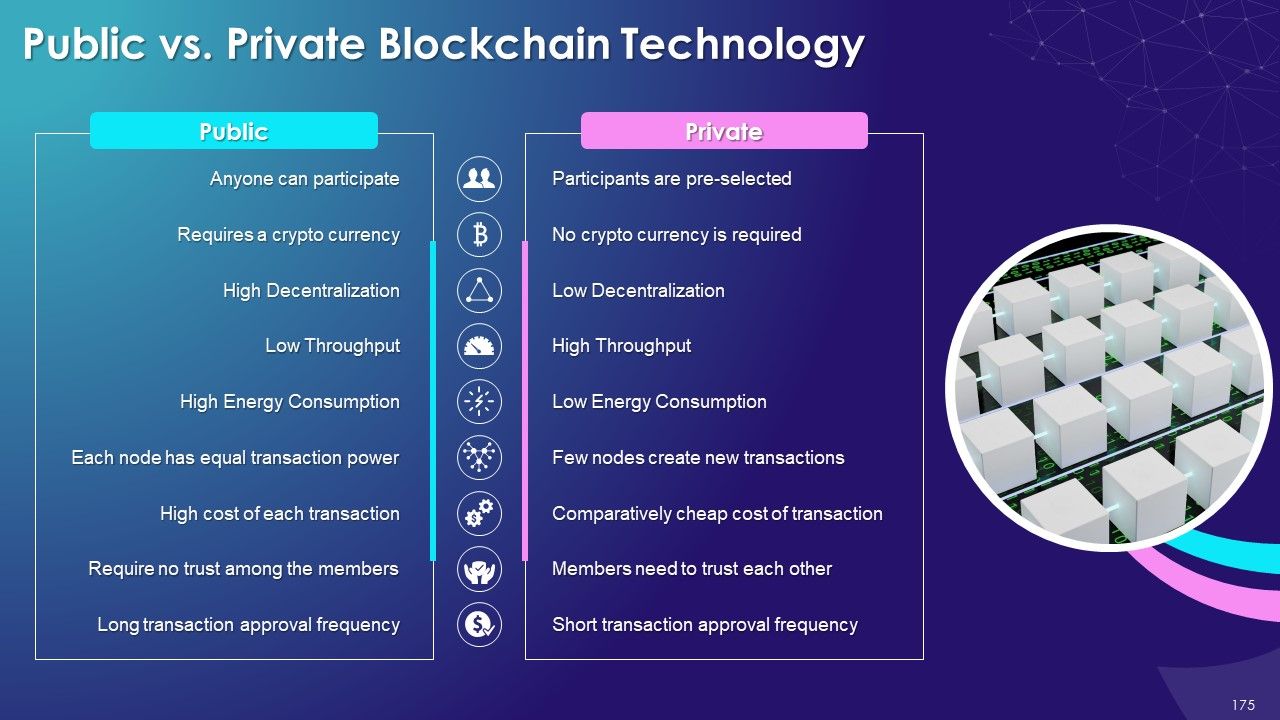
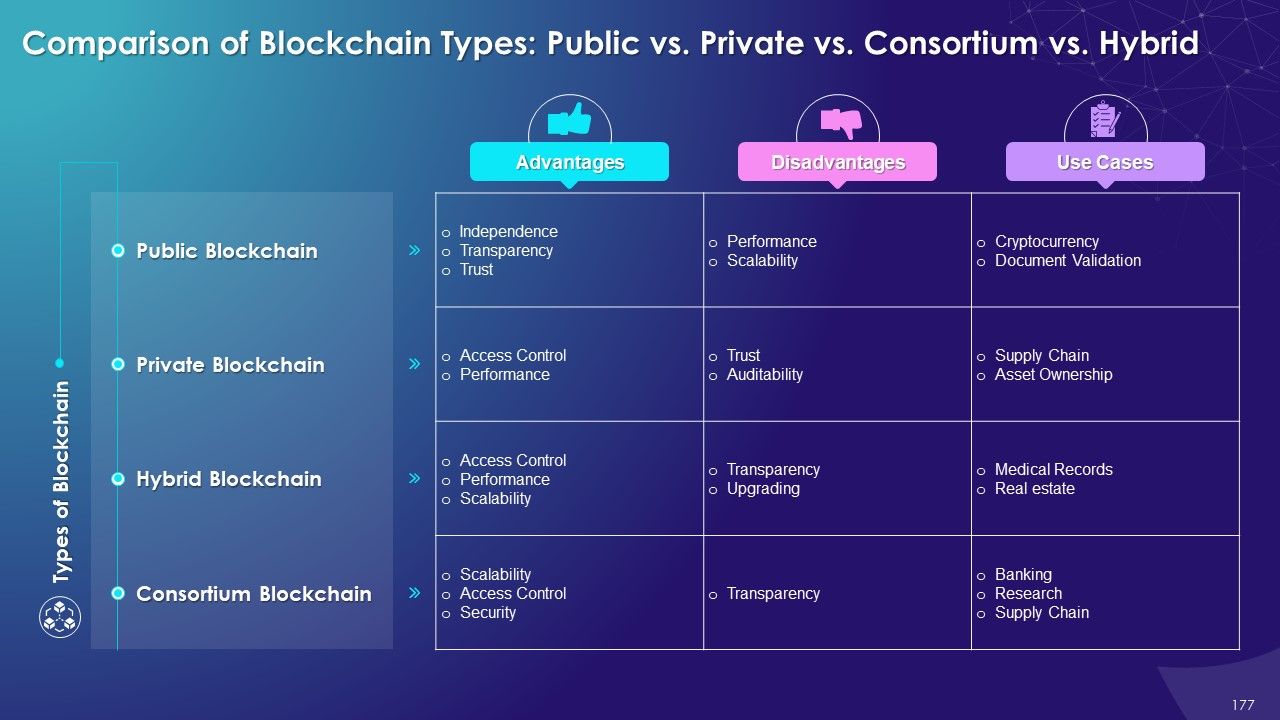
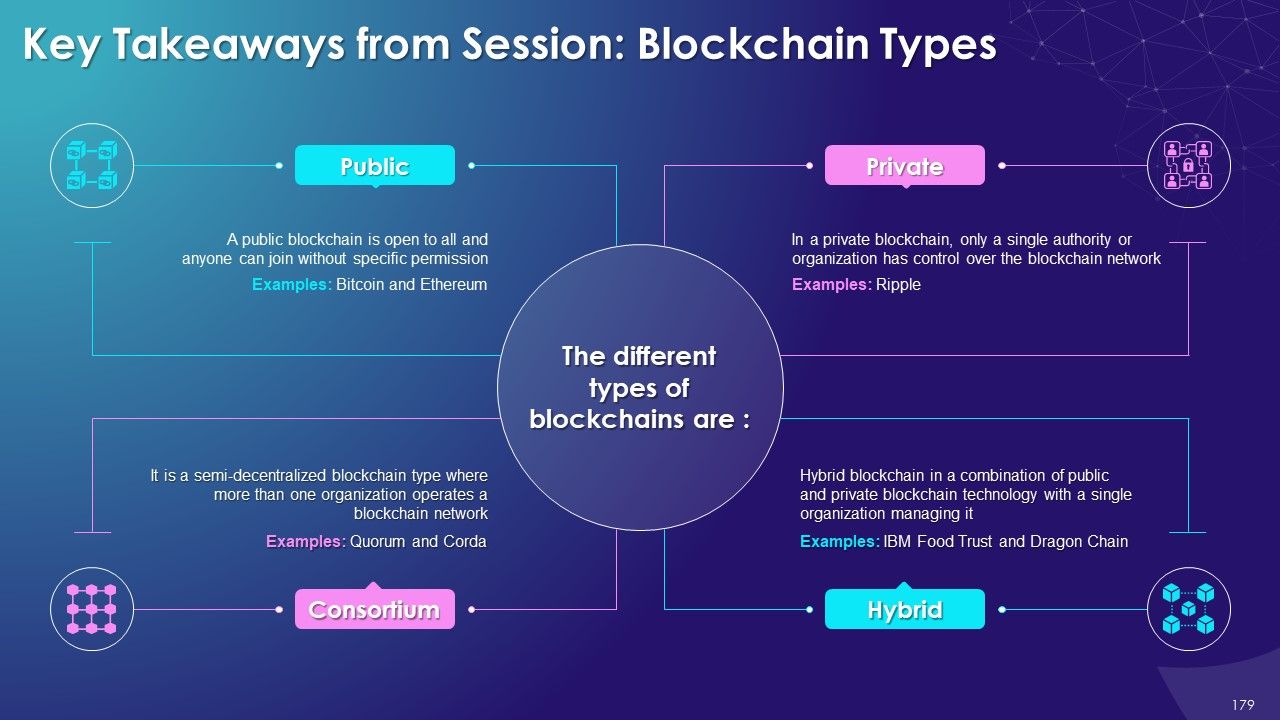
- Types of Blockchain
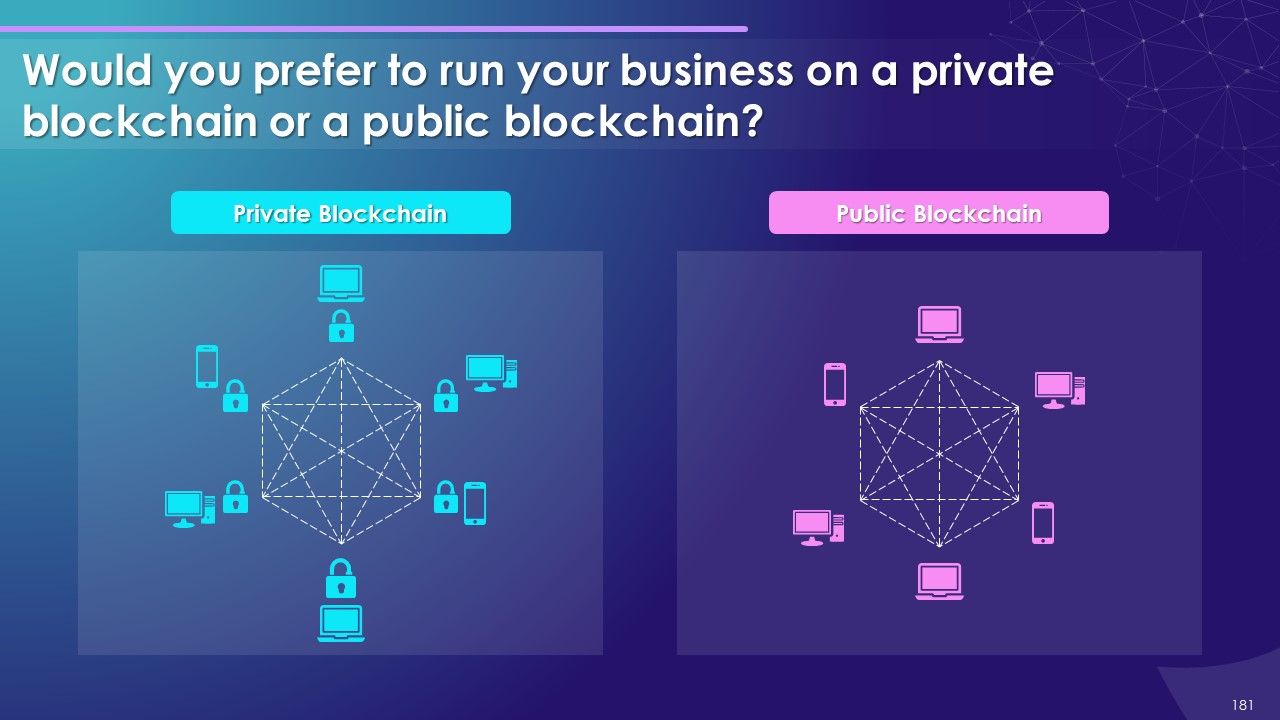
- Public
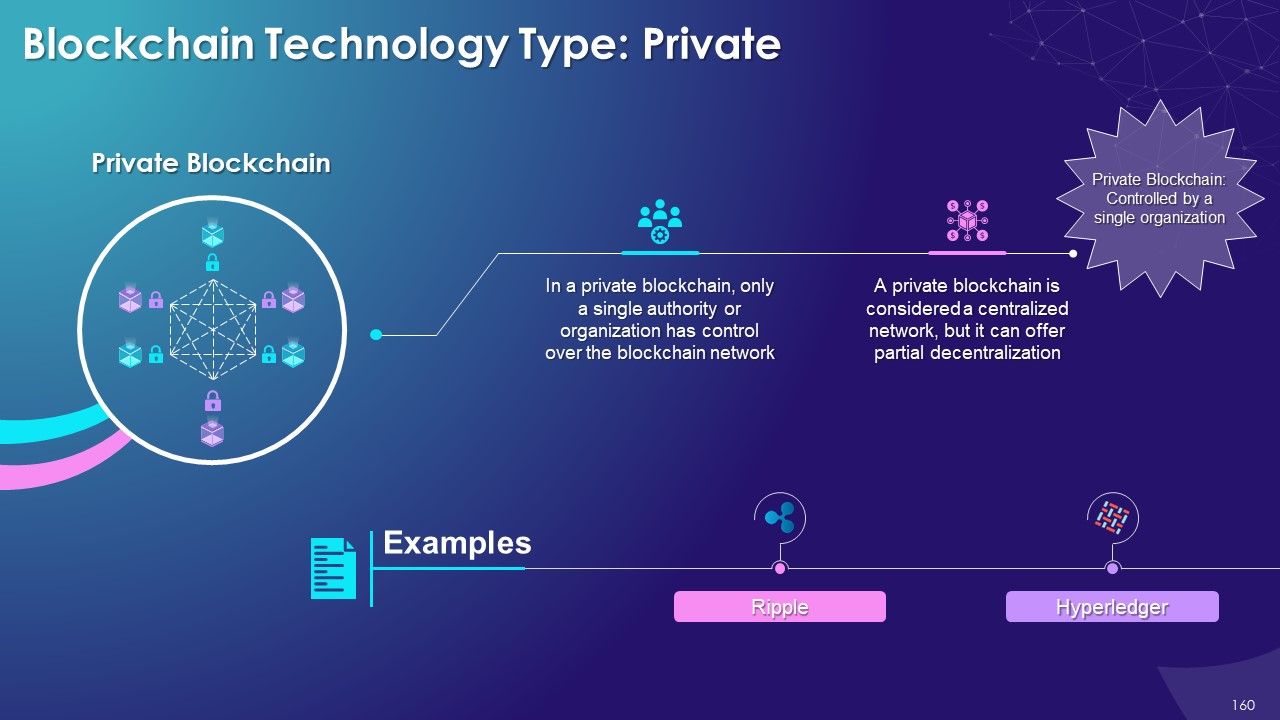
- Private
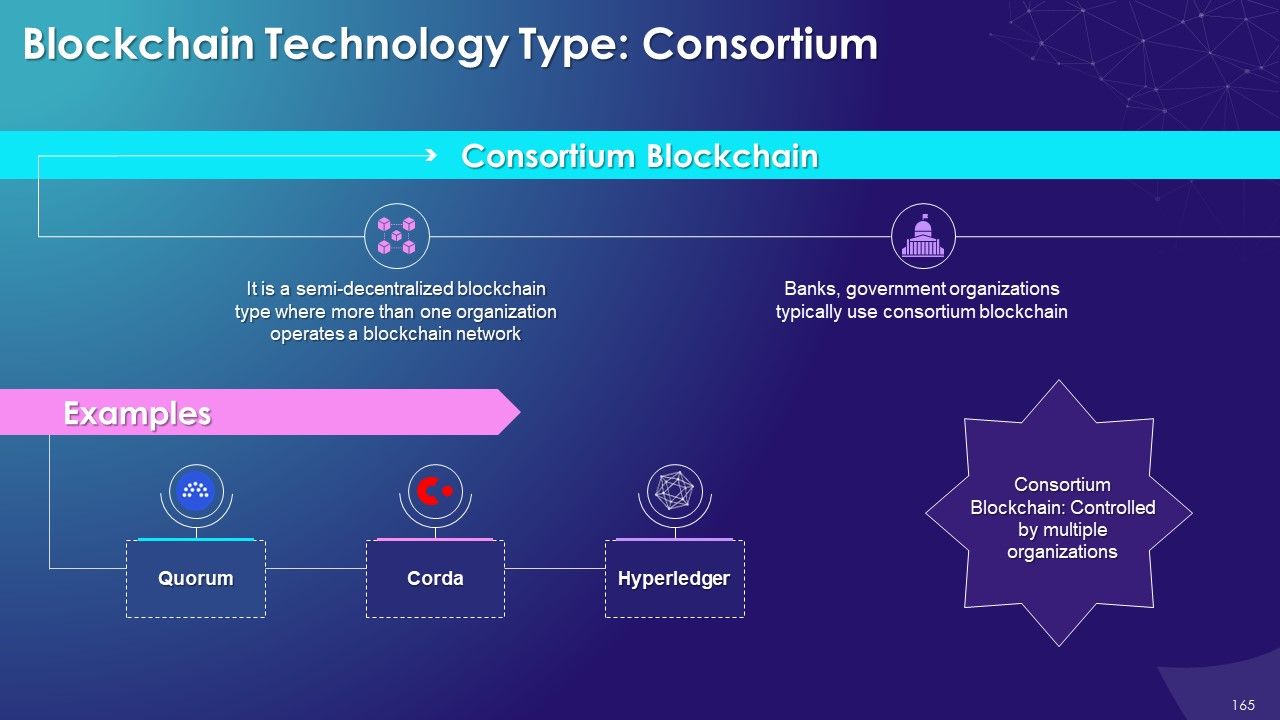
- Consortium
- Hybrid
- Public vs. Private Blockchain
- Public vs. Private vs. Consortium
- Public vs. Private vs. Consortium vs. Hybrid
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
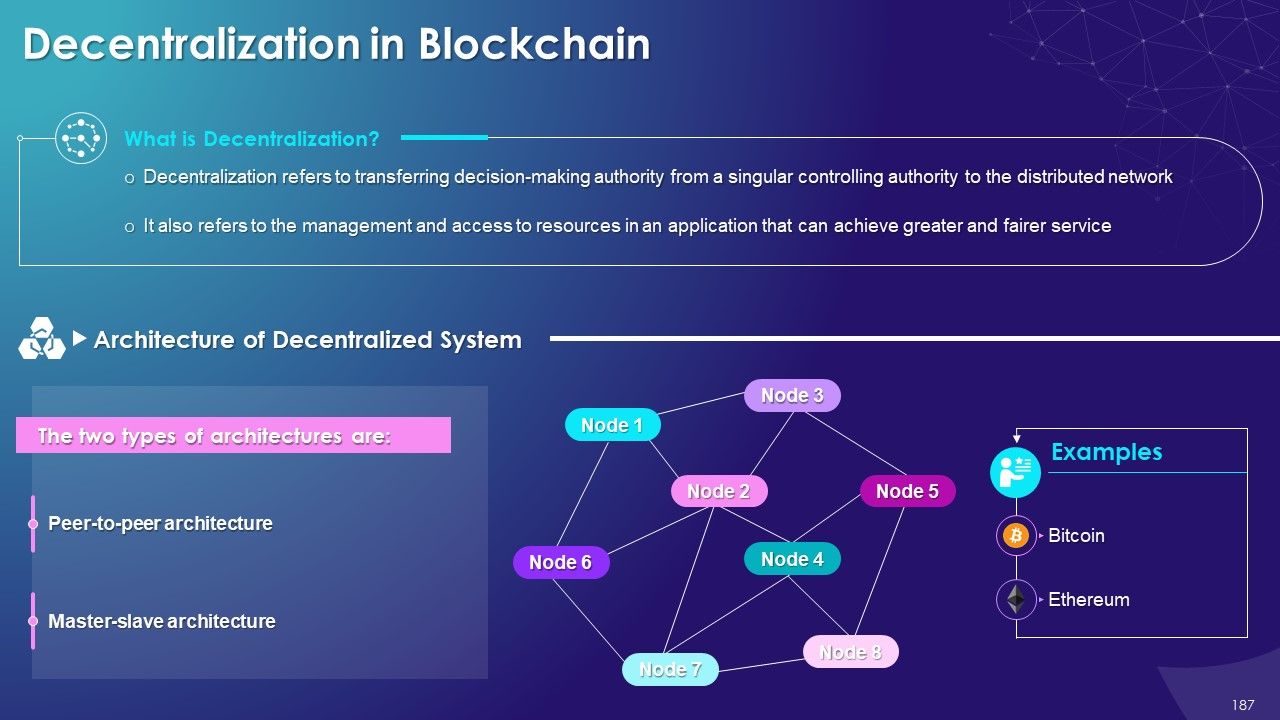
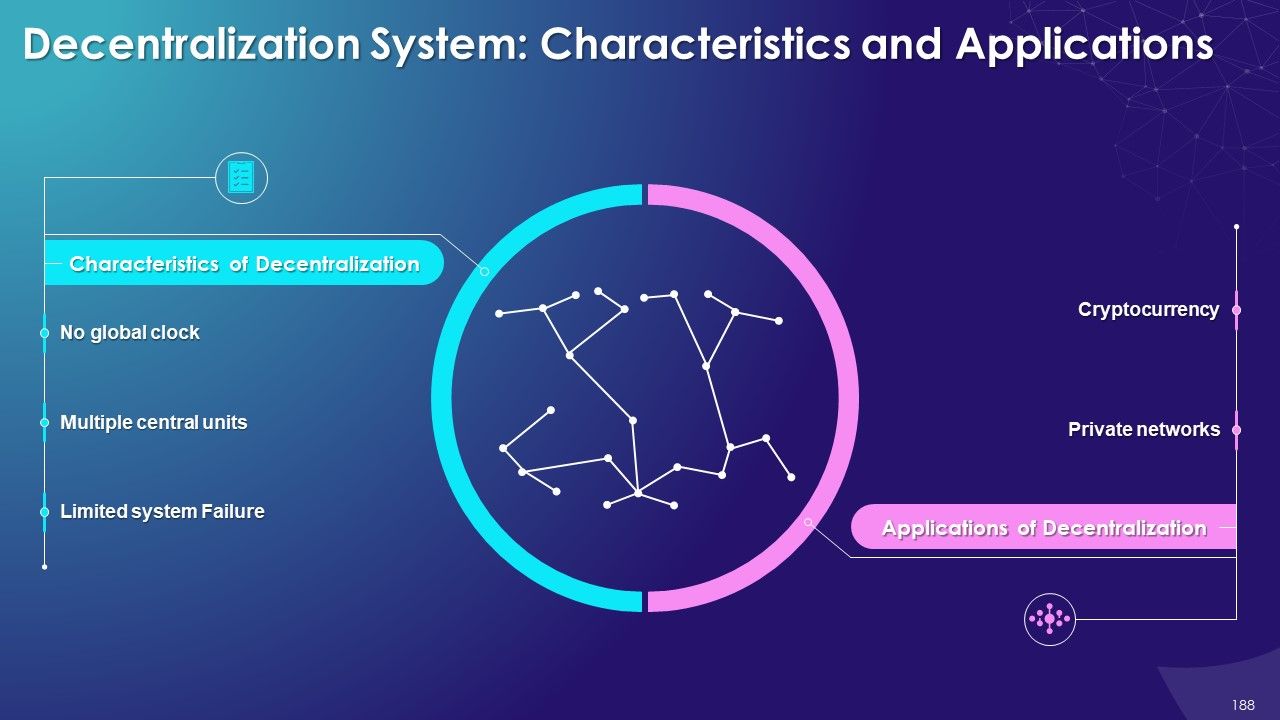
- Decentralization in Blockchain
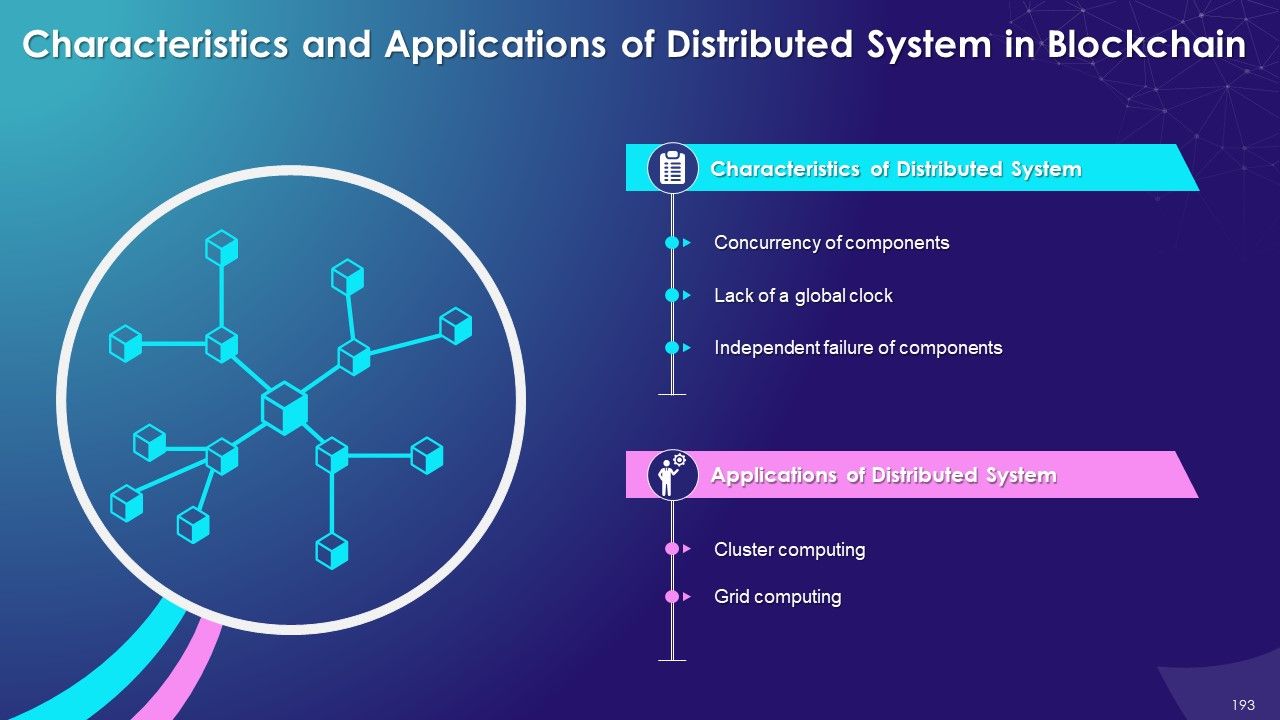
- Characteristics and Applications
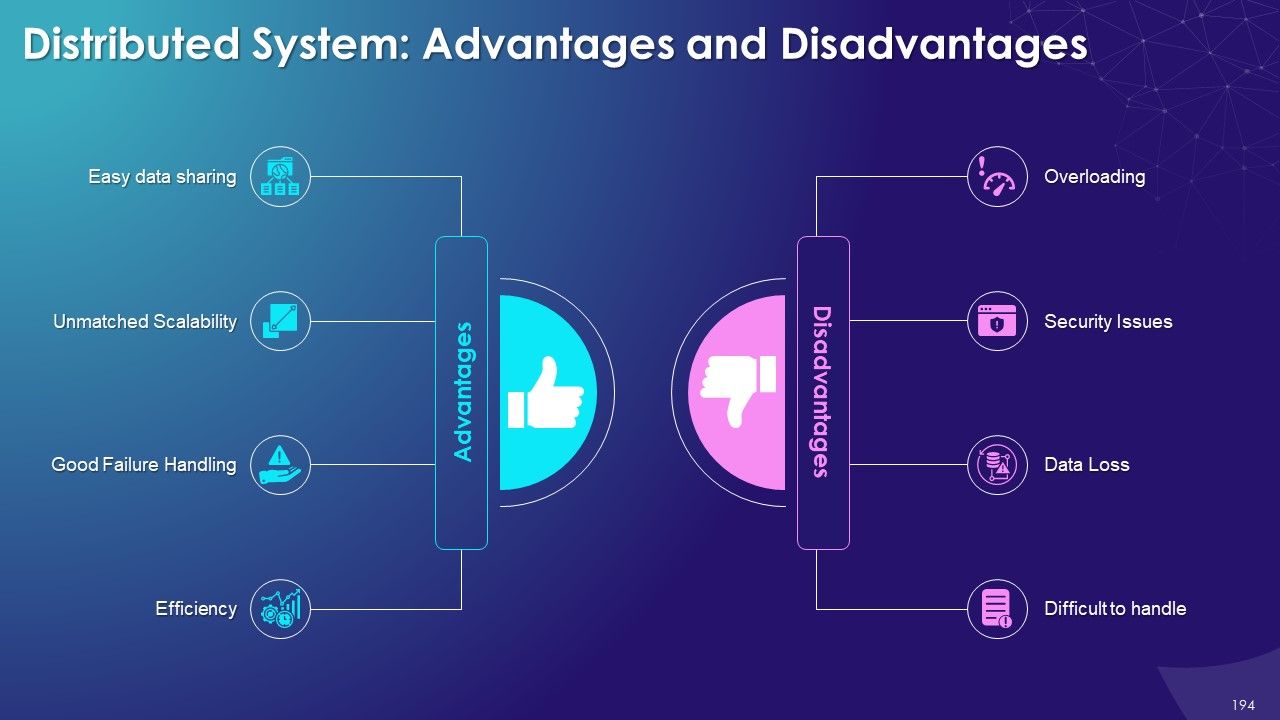
- Advantages and Disadvantages
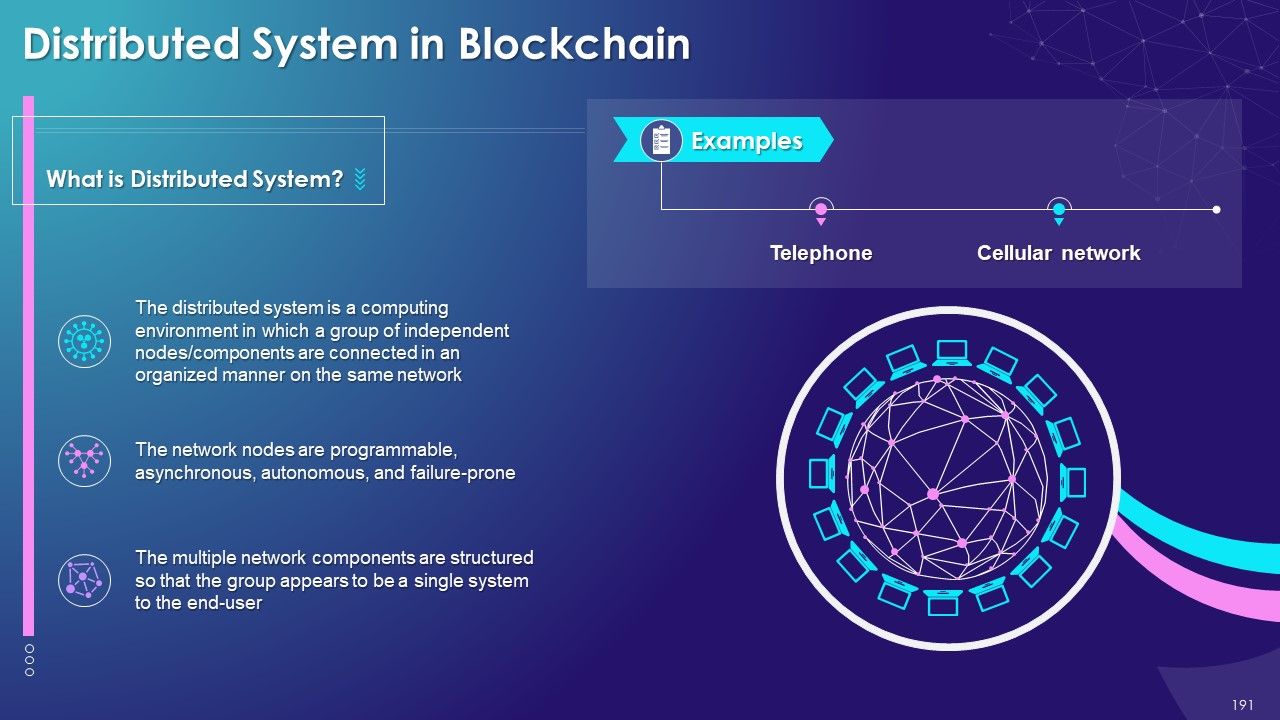
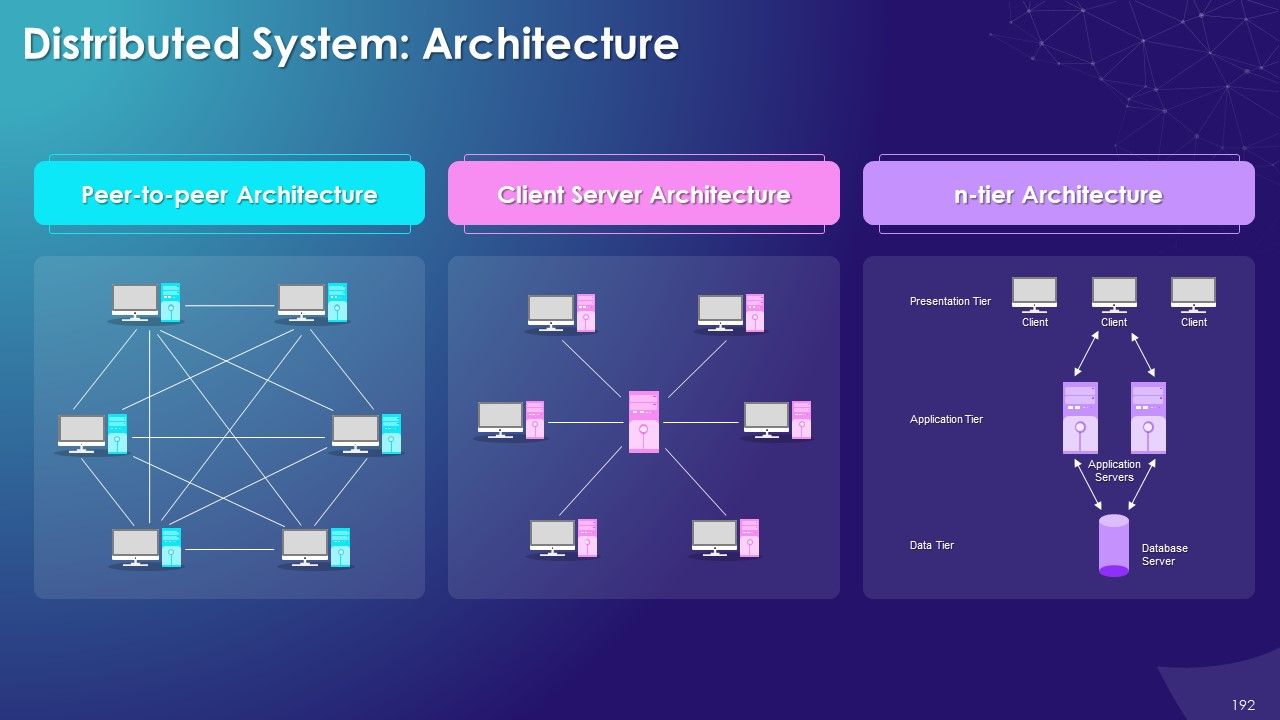
- Distributed System in Blockchain
- Architecture: Peer-to-peer, Client Server and n-tier
- Characteristics and Applications
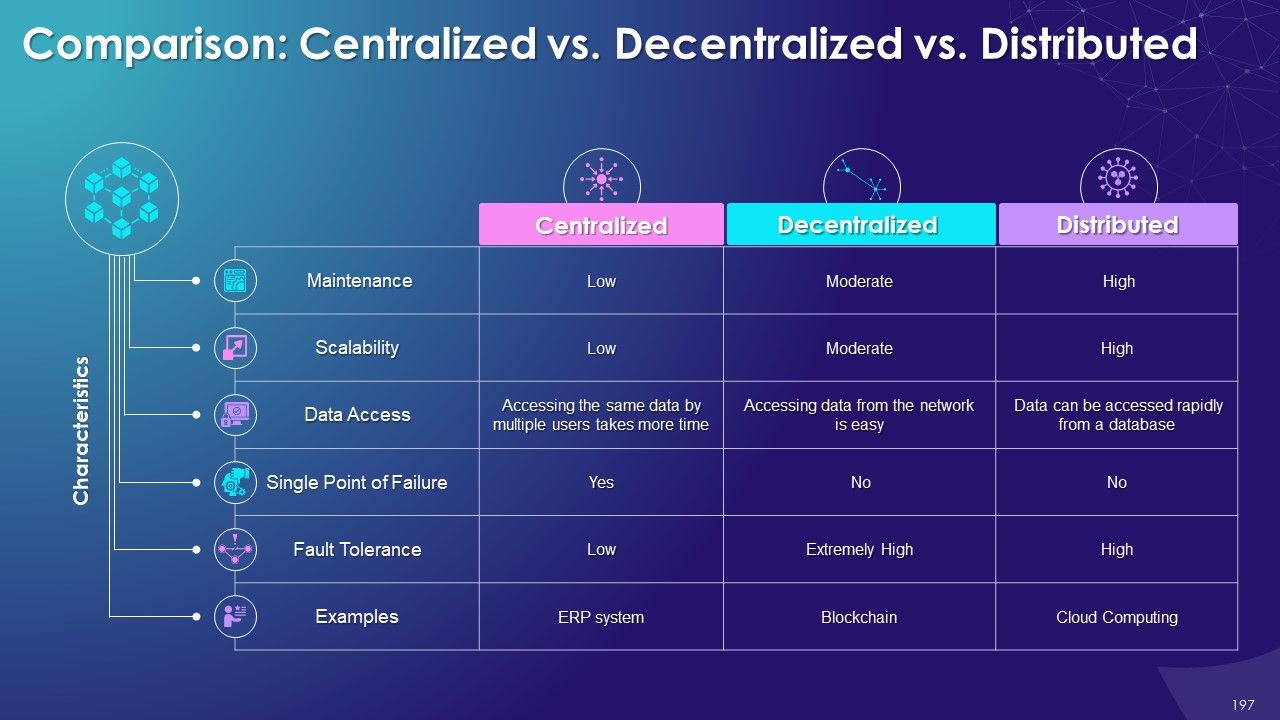
- Centralized vs. Decentralized
- Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Distributed
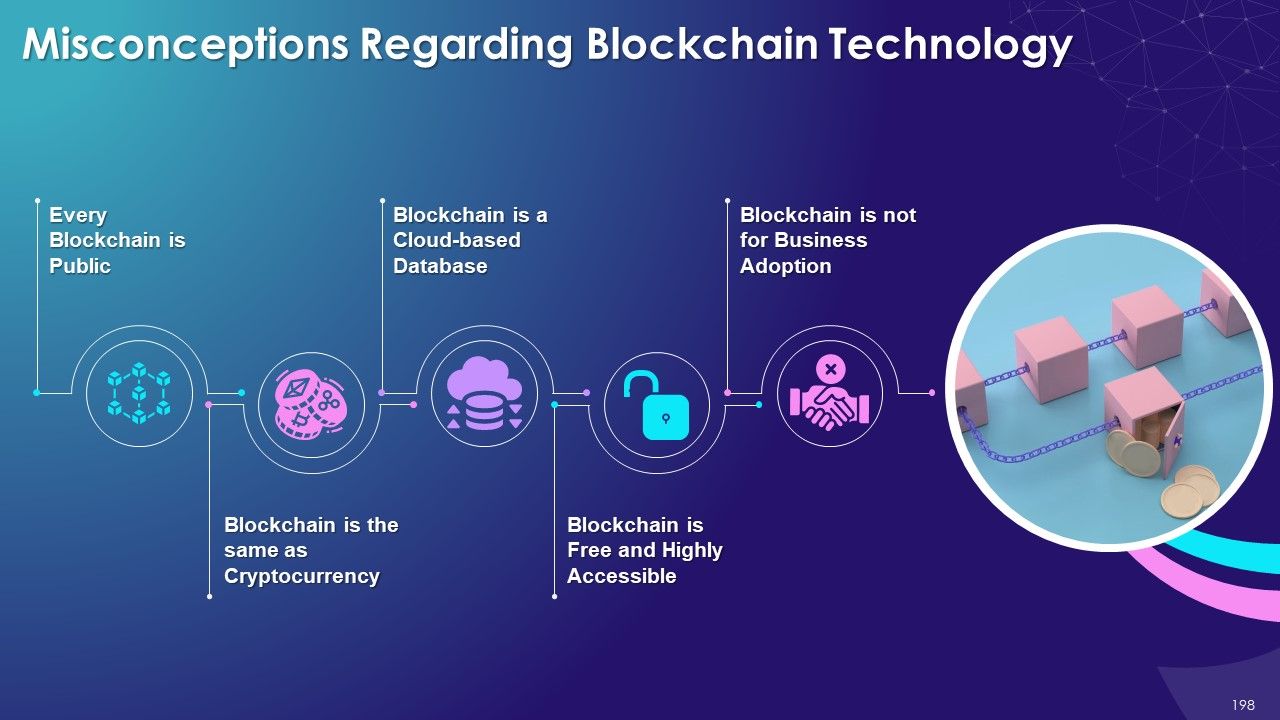
- Misconceptions Regarding Blockchain Technology
- Key Takeaways
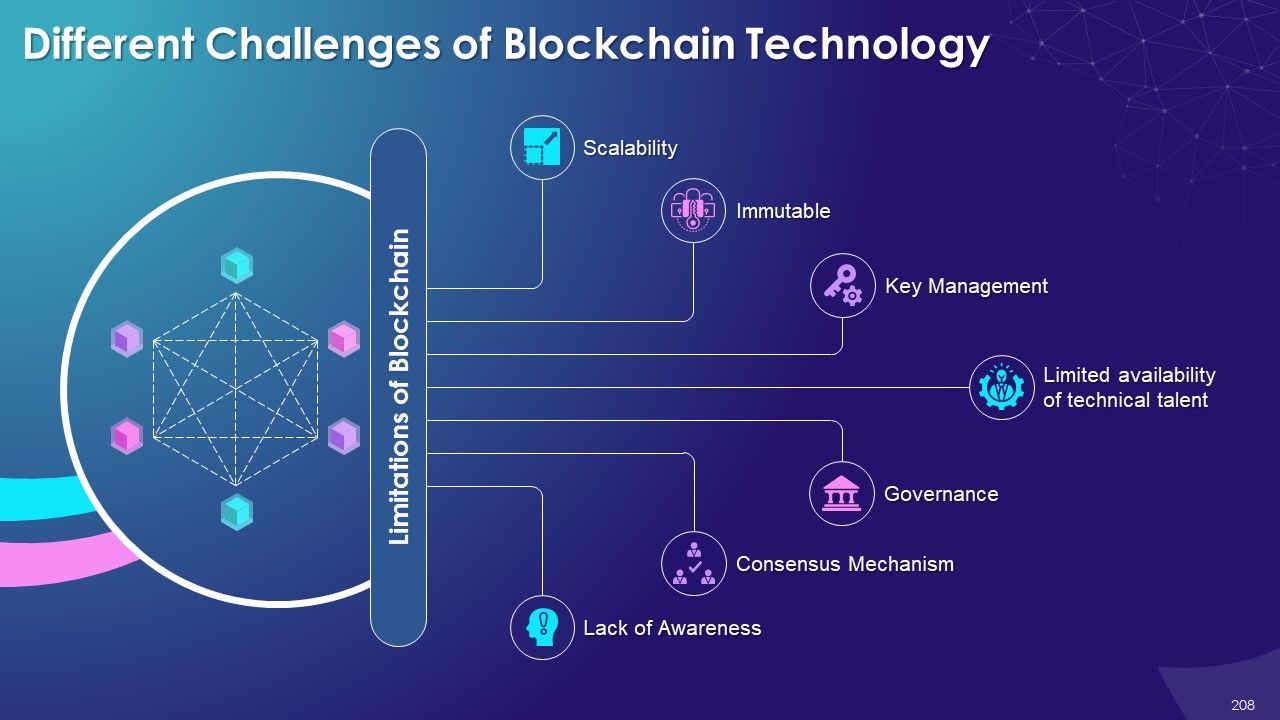
- Challenges of Blockchain Technology
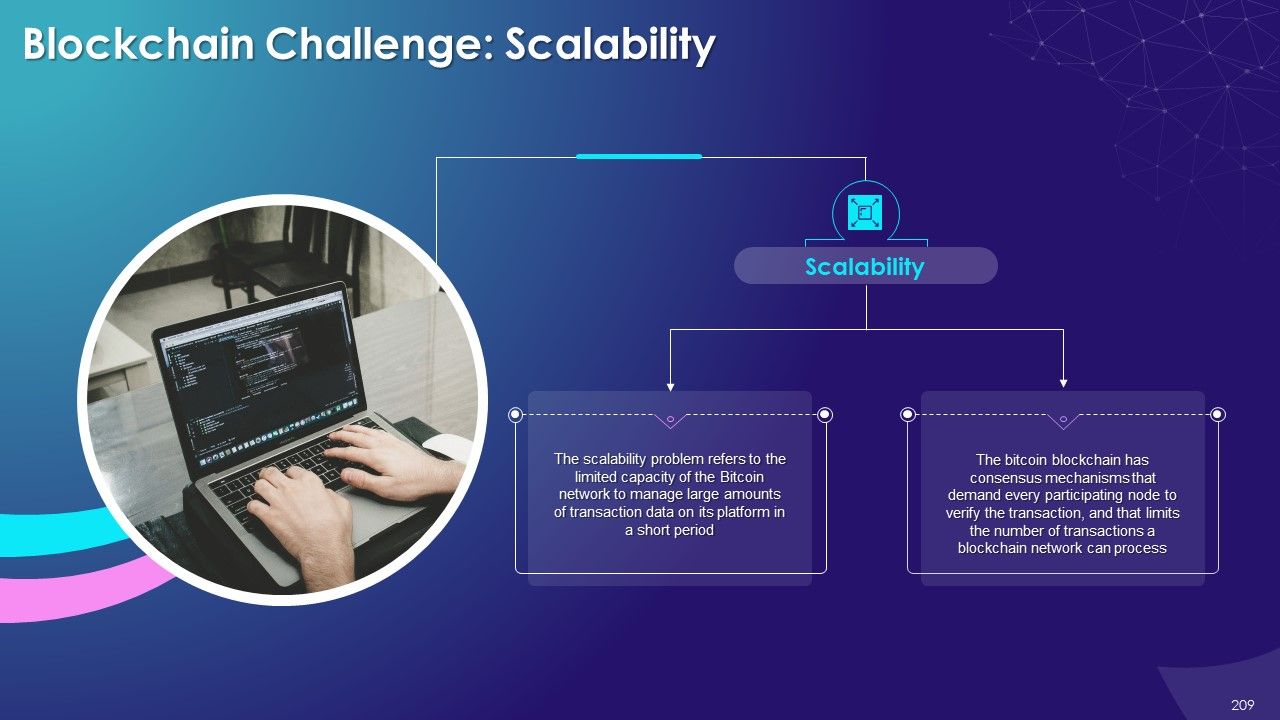
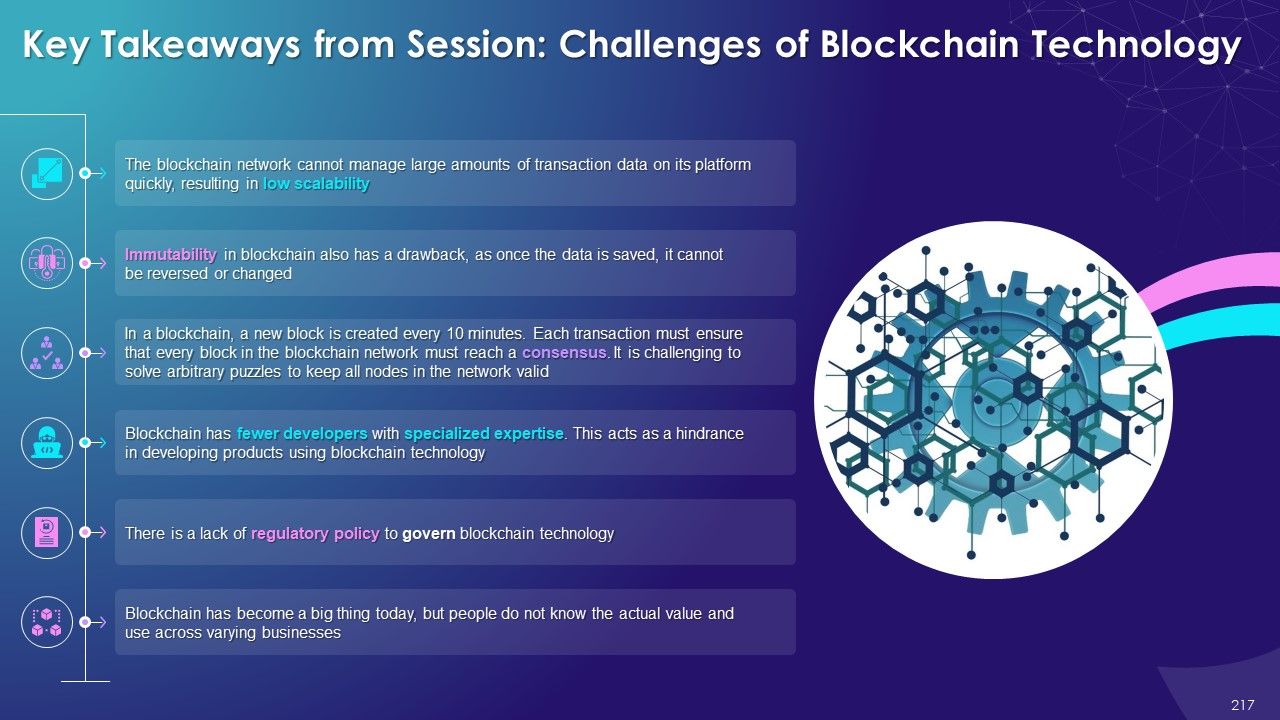
- Scalability
- Immutable
- Key Management
- Limited Availability of Technical Talent
- Reaching Common Consensus
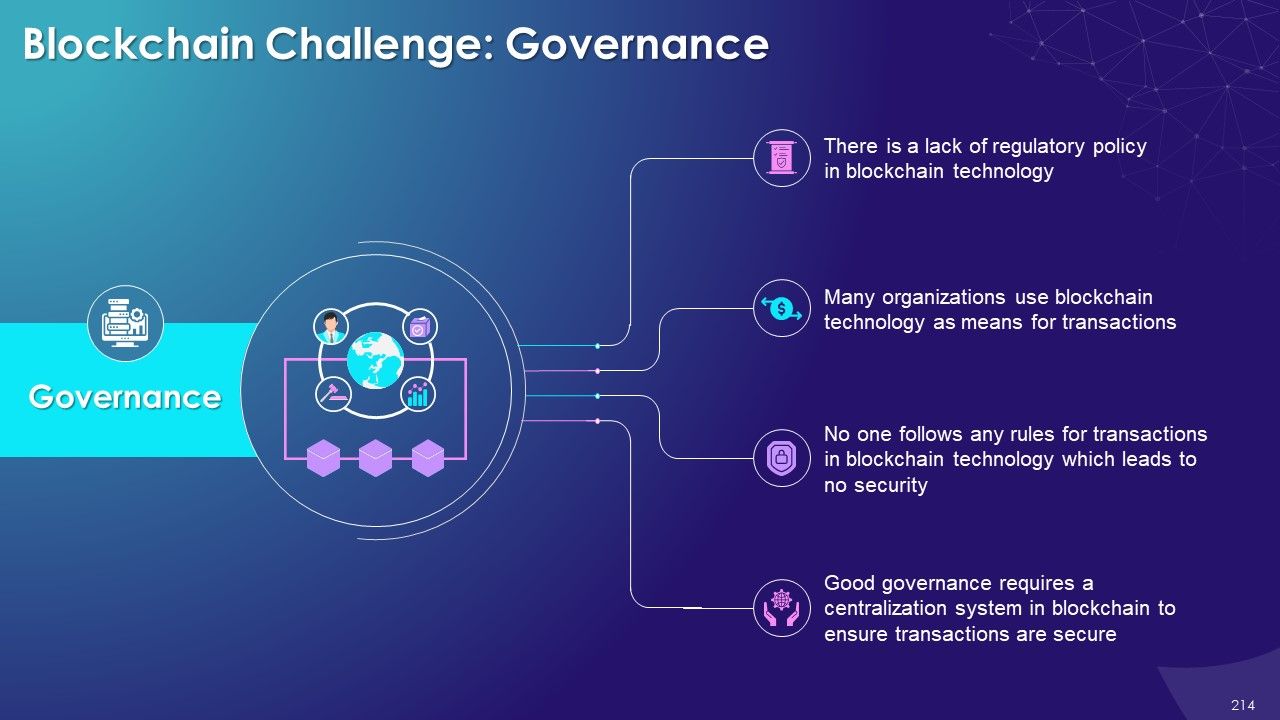
- Governance
- Lack of Awareness
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Types of Attacks
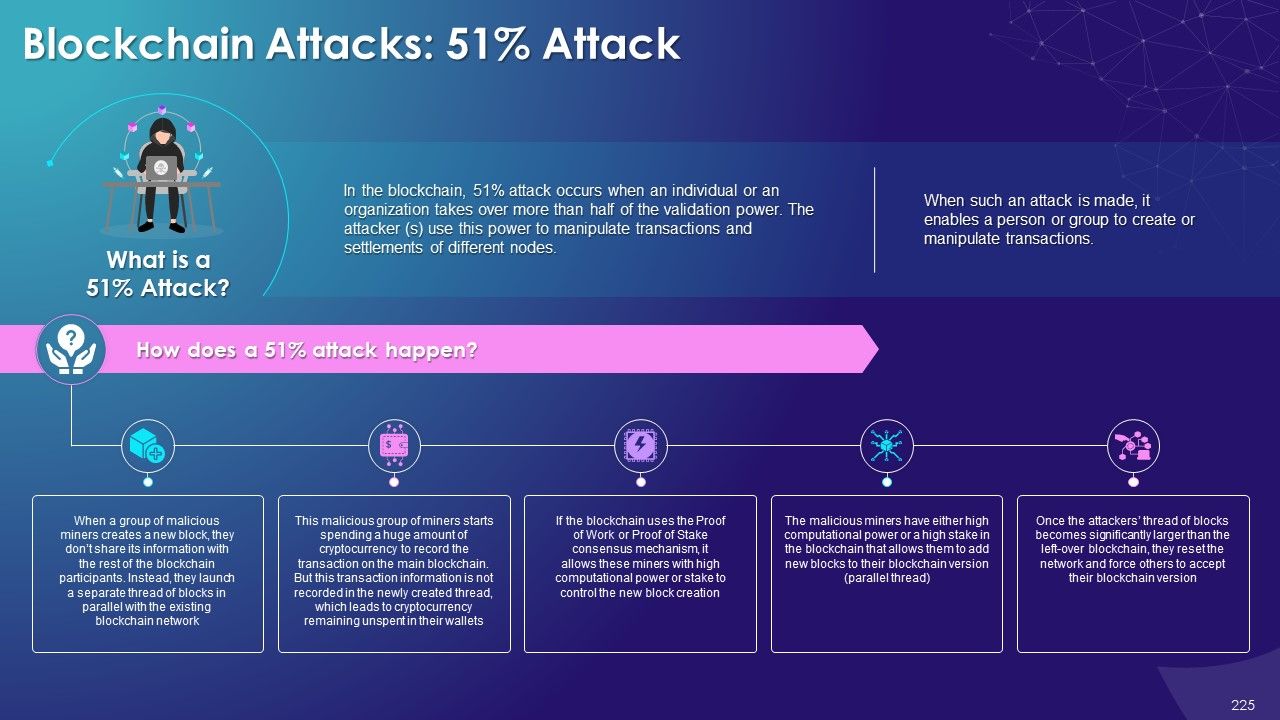
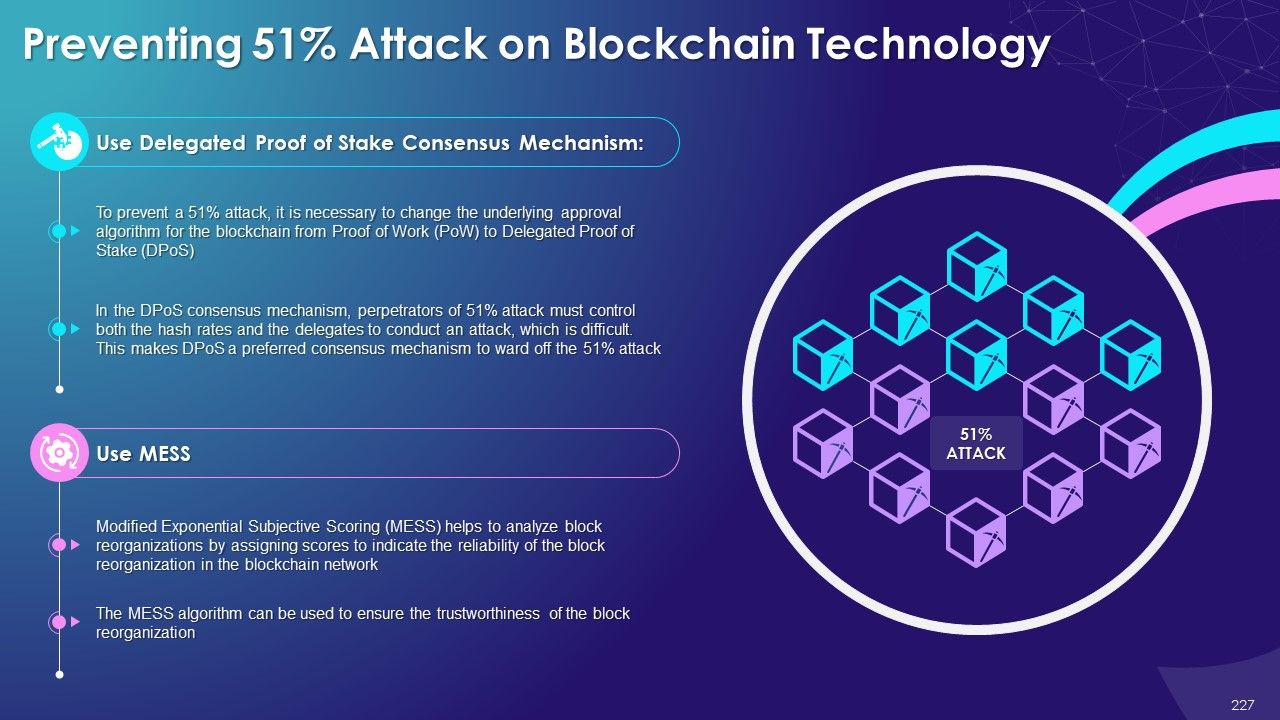
- 51% Attack
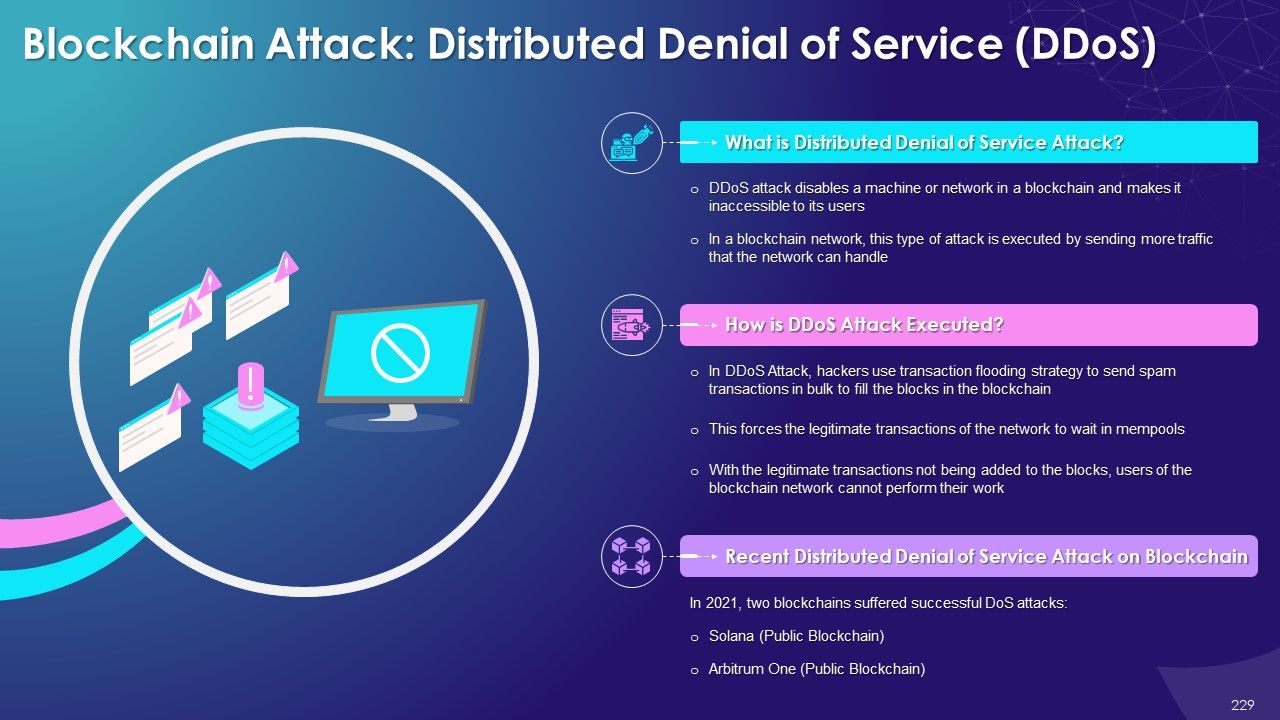
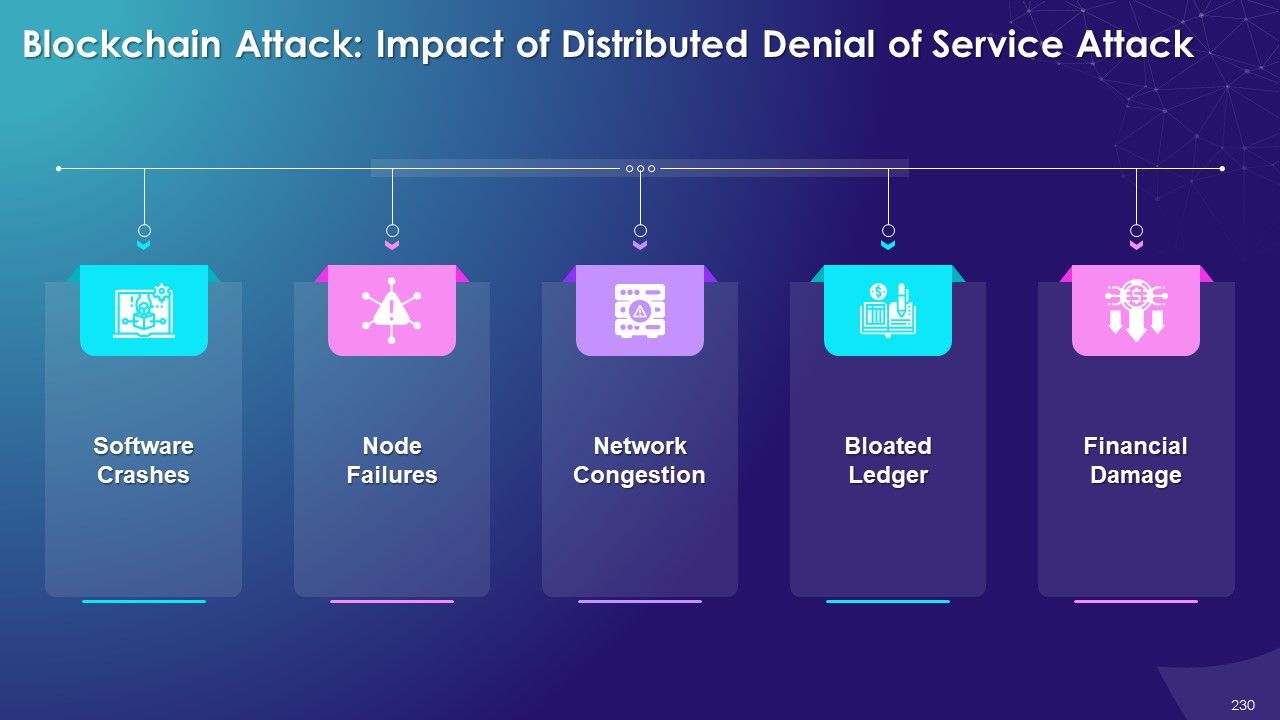
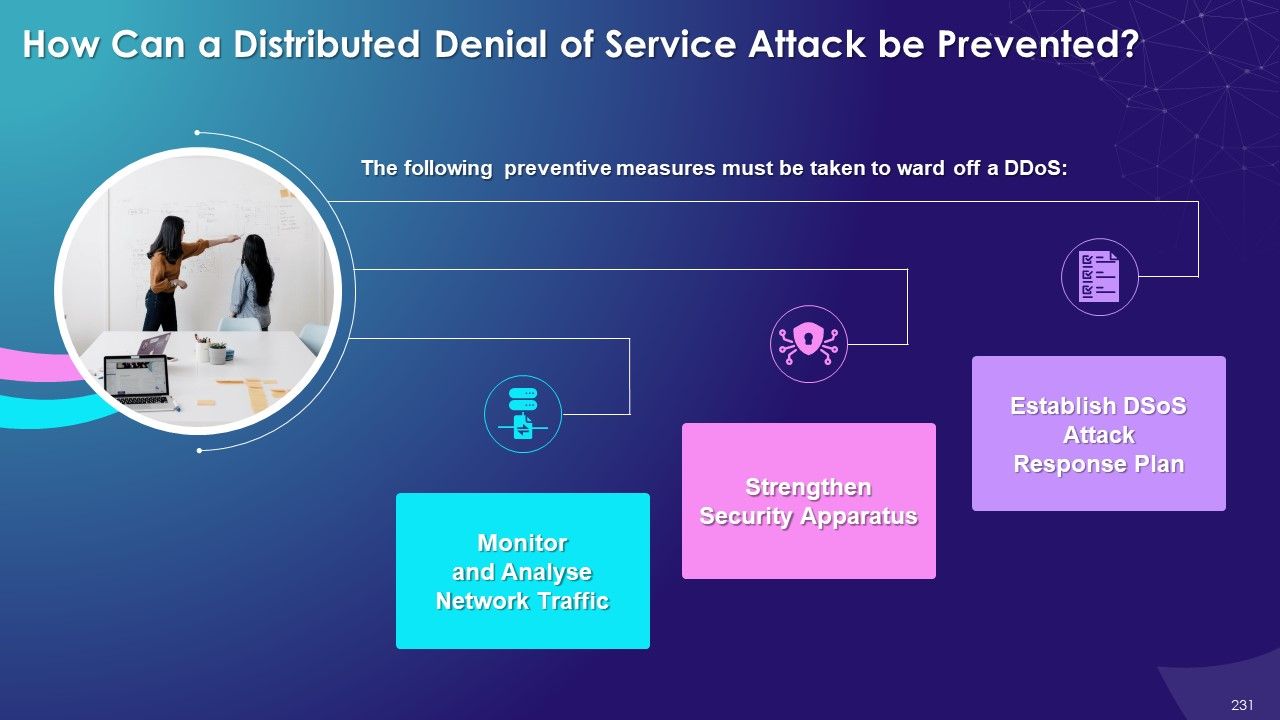
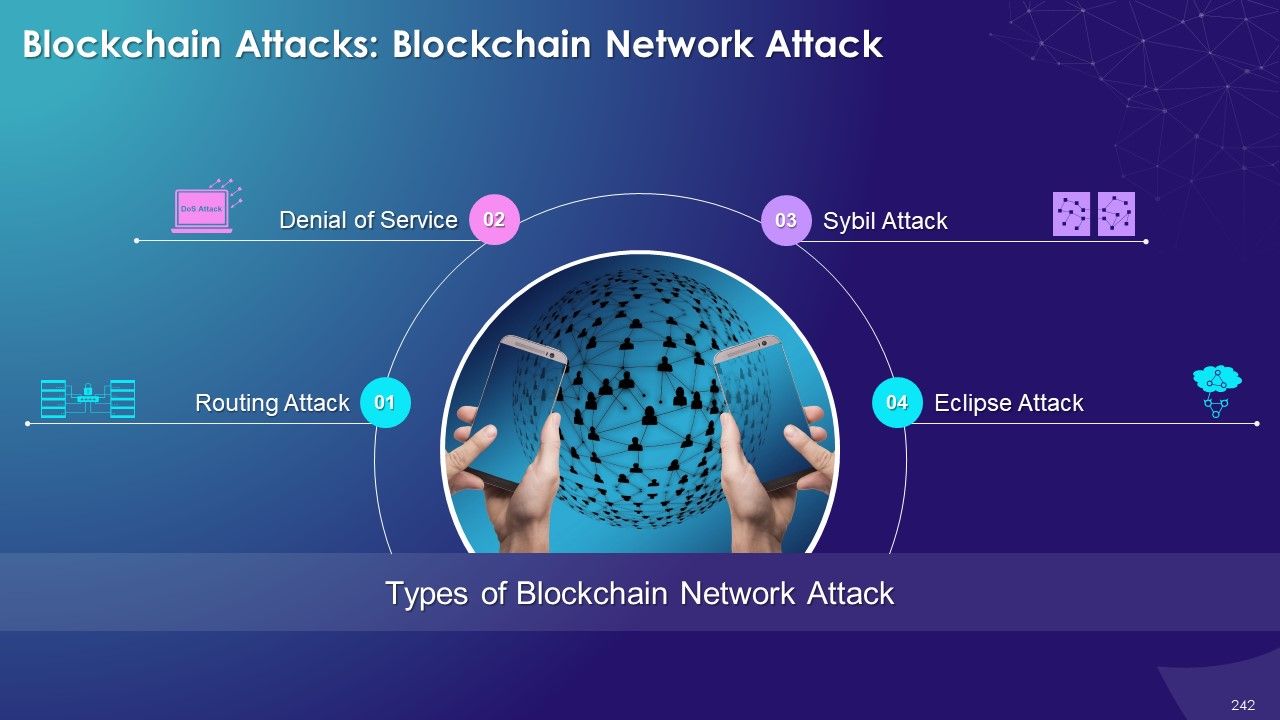
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
- Routing Attacks
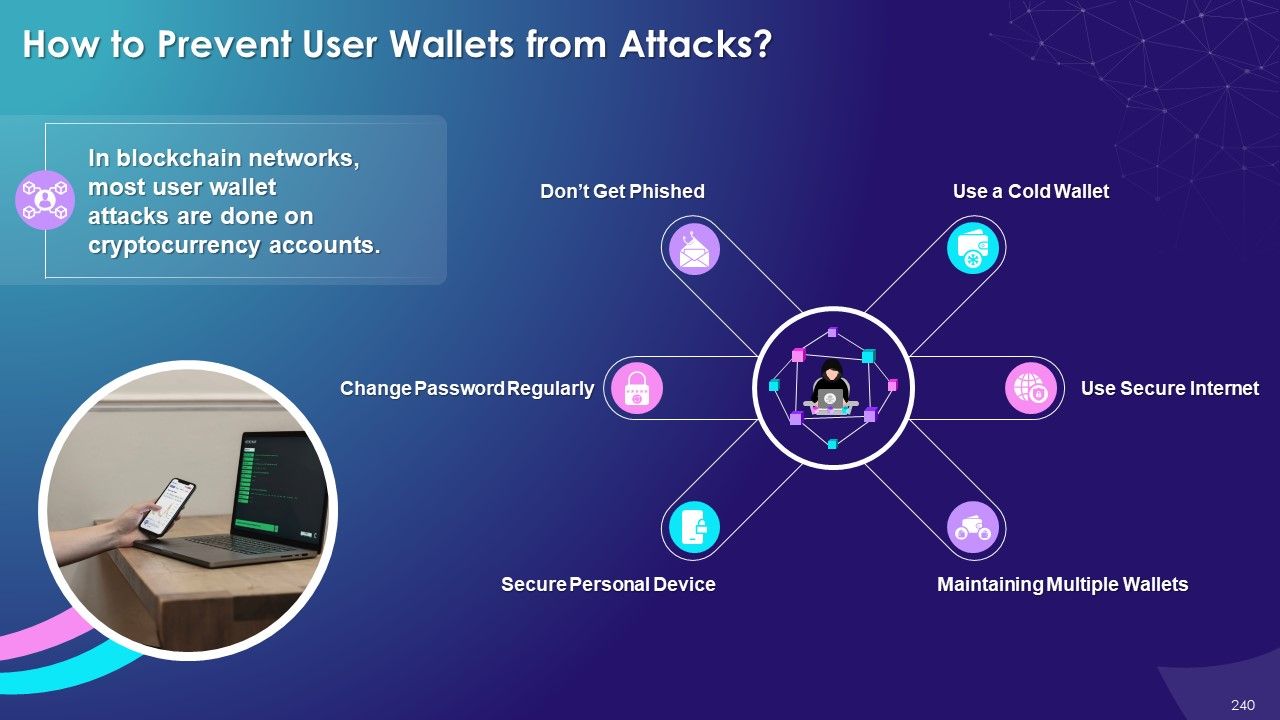
- User Wallet Attack
- Blockchain Network Attack
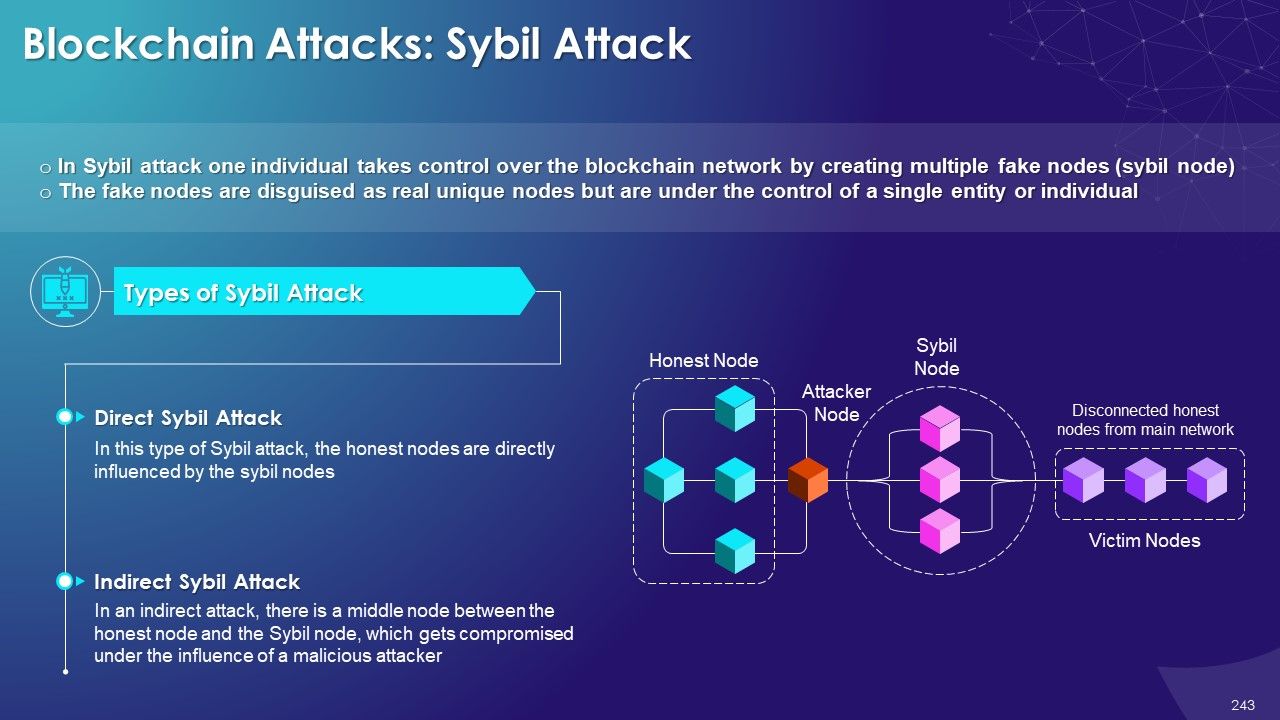
- Sybil Attack
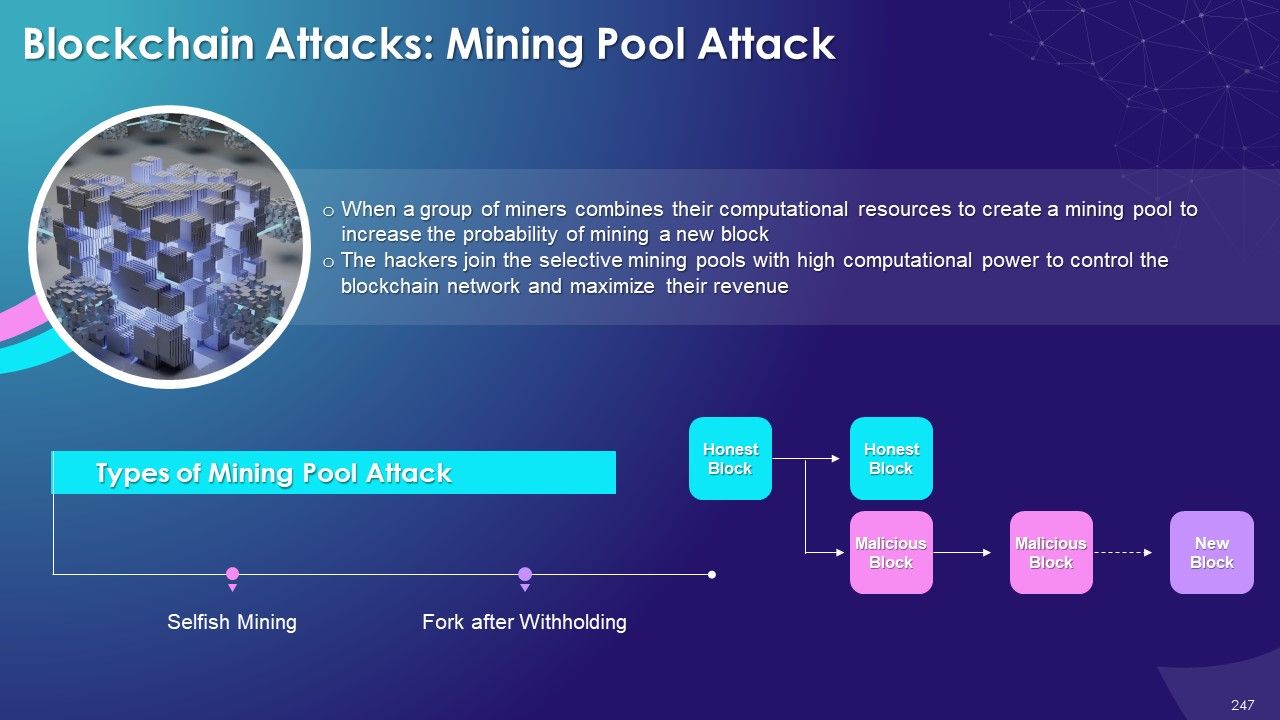
- Mining Pool Attack
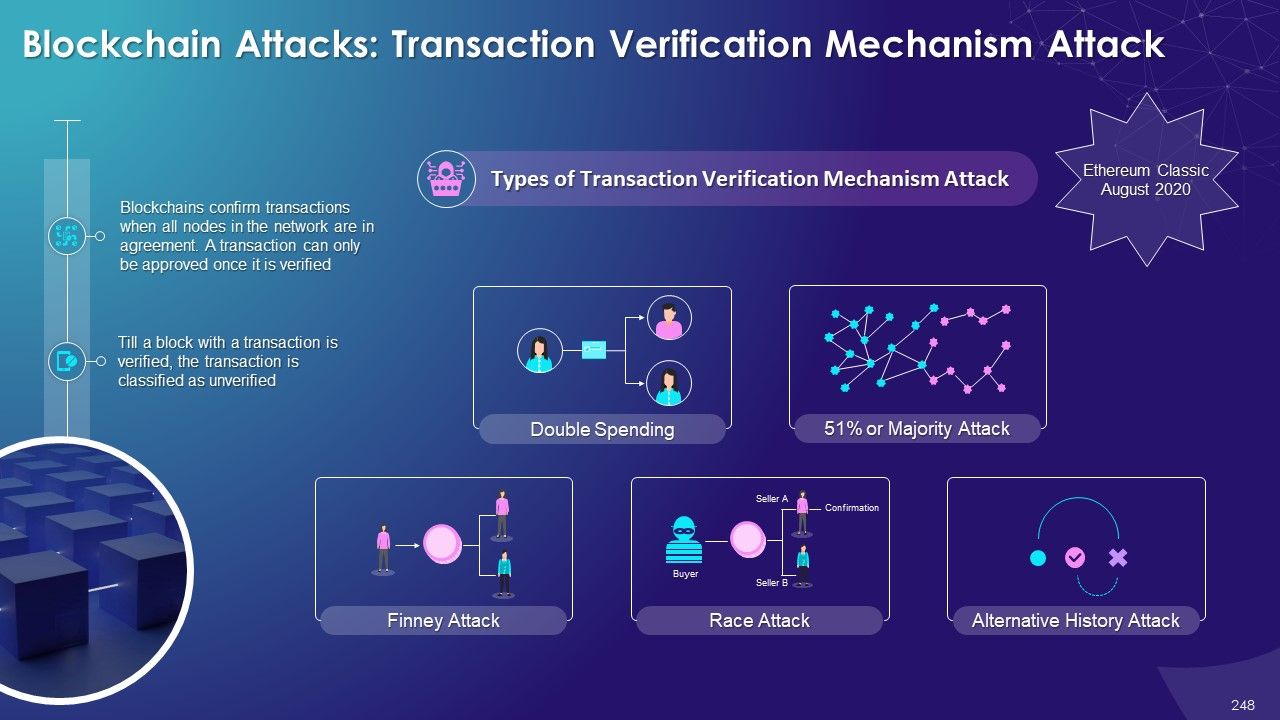
- Transaction Verification Mechanism Attack
- Key Takeaway
- Let’s Discuss
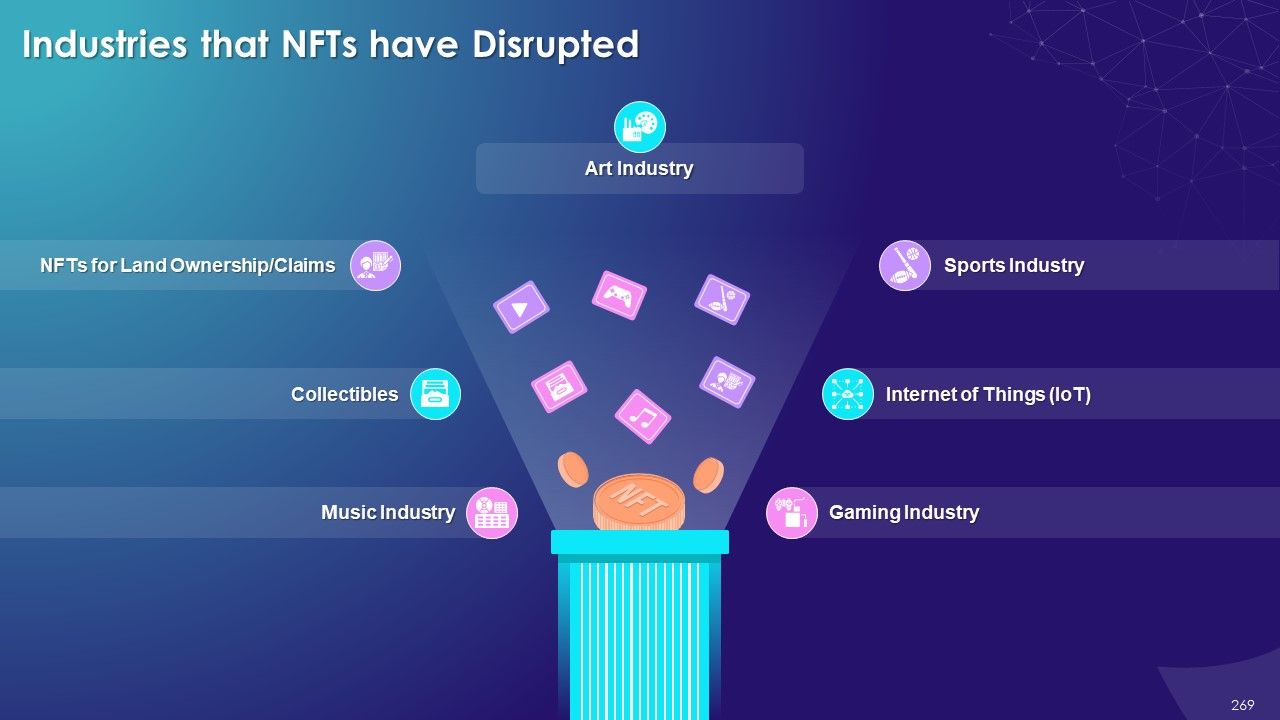
- Emerging Trends around Blockchain
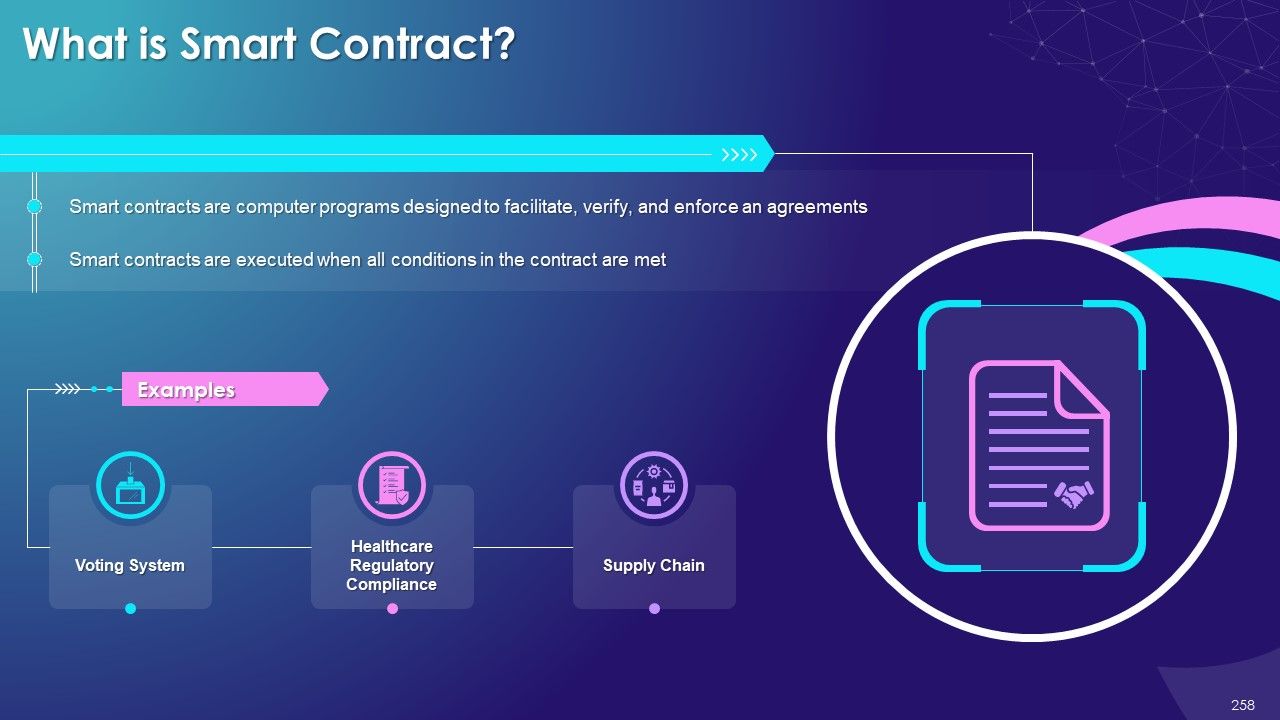
- Smart Contract
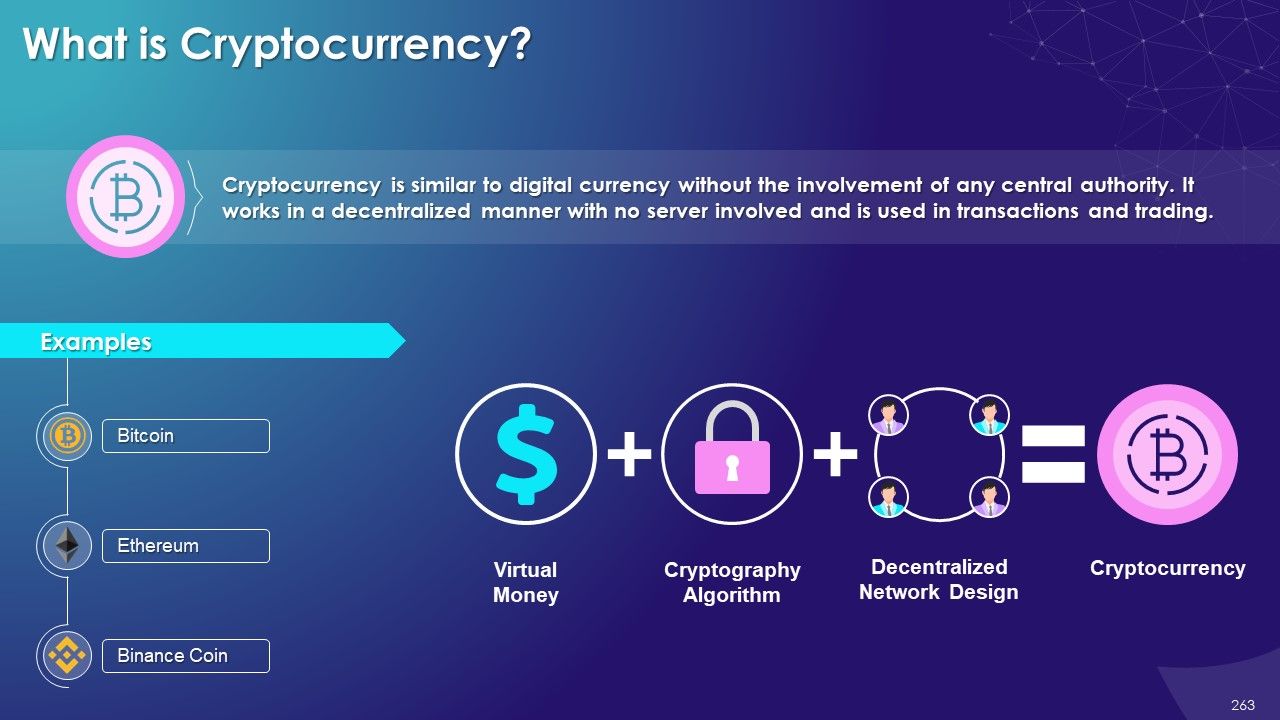
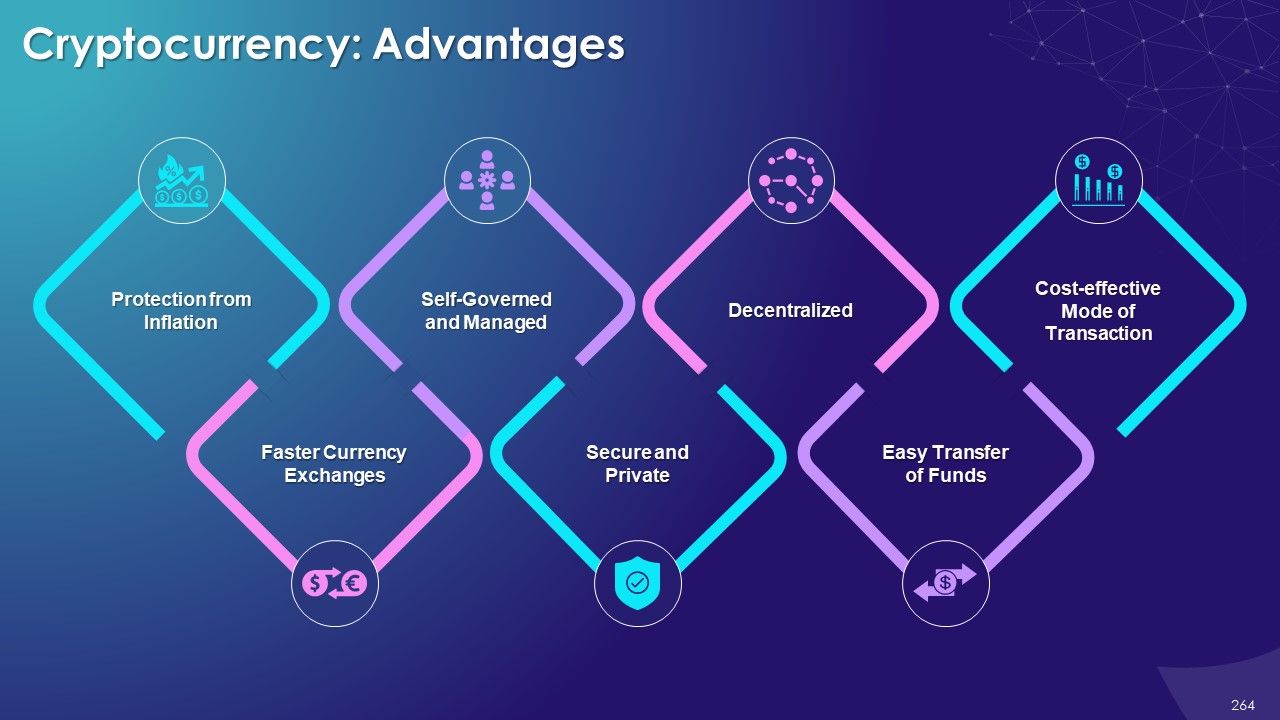
- Cryptocurrency
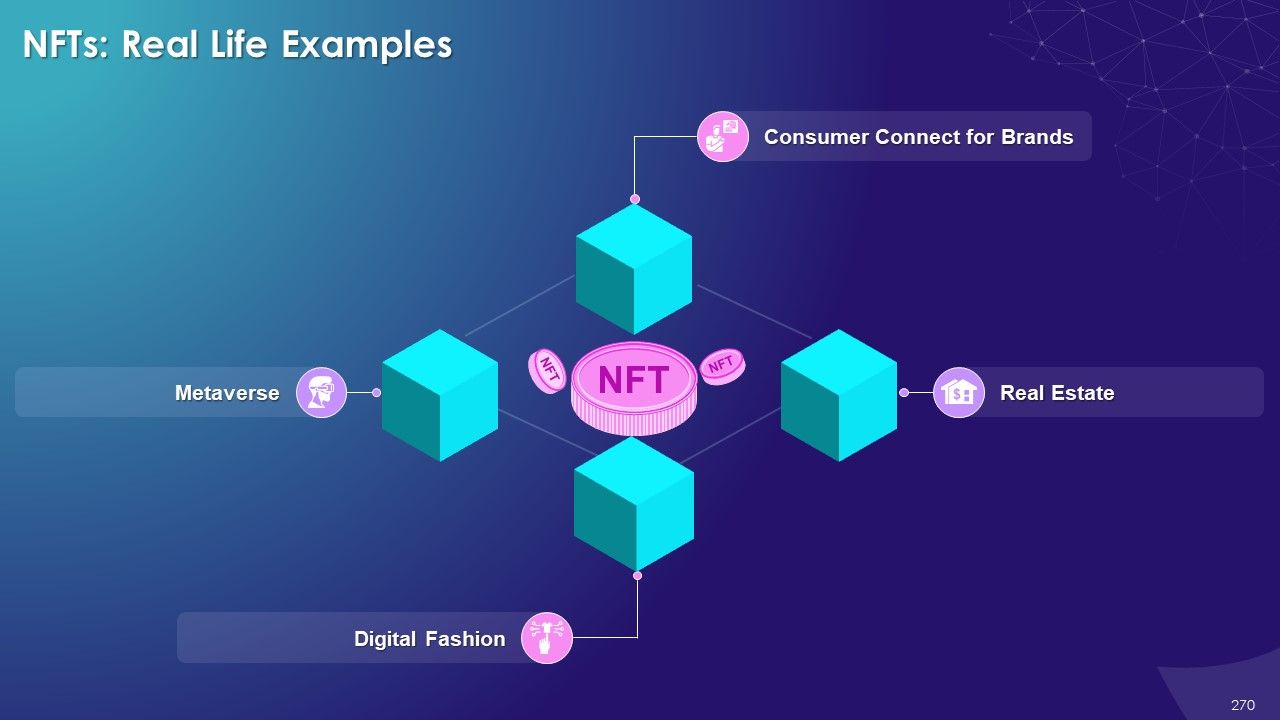
- NFTs (Non-fungible Tokens)
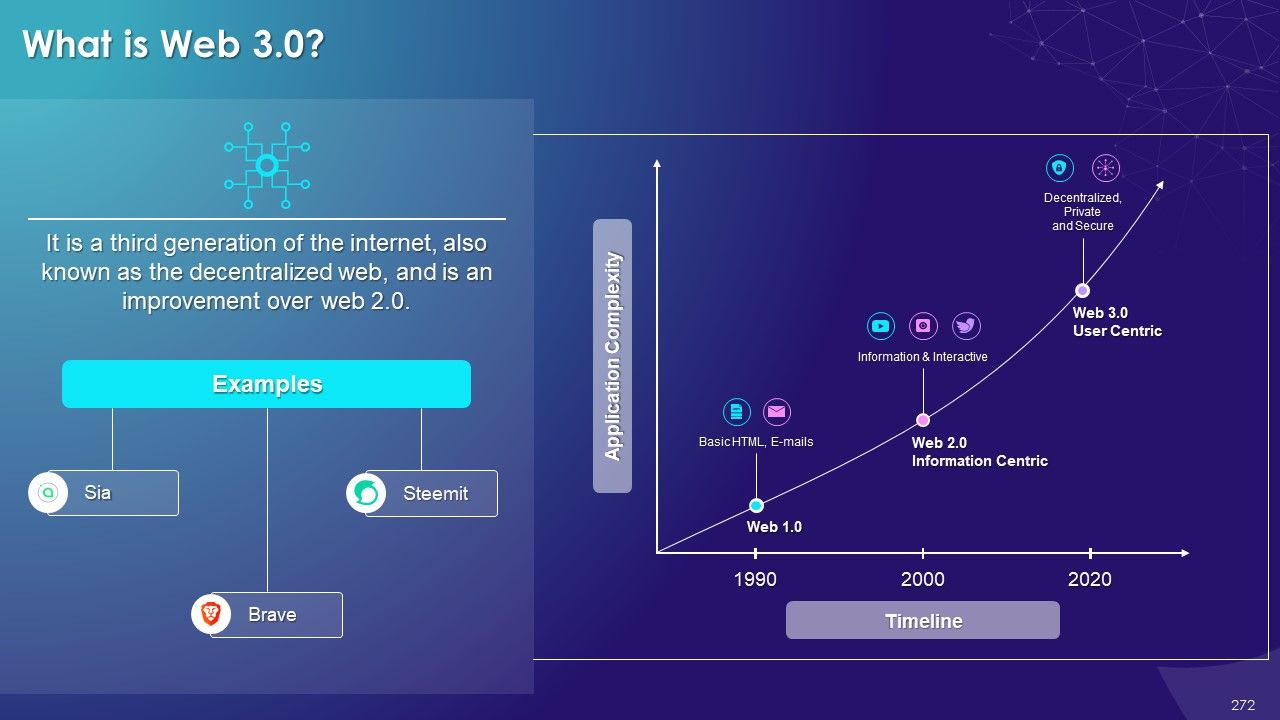
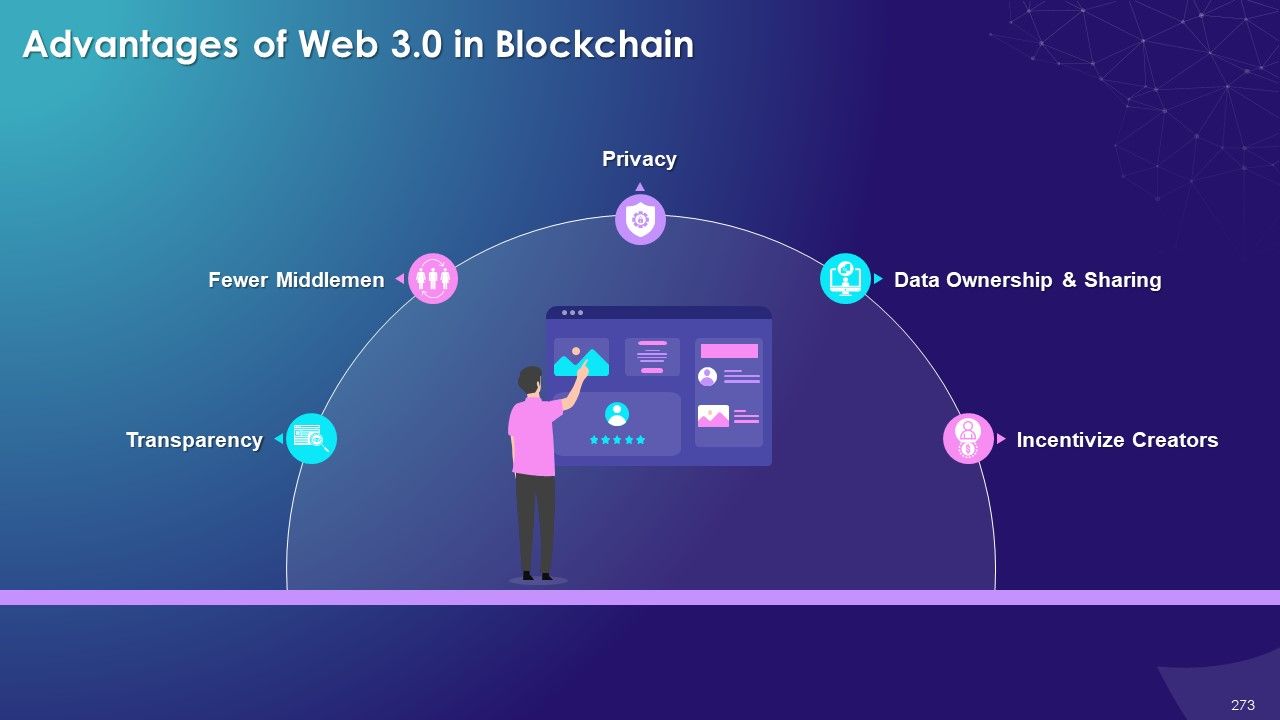
- Web 3.0
- Metaverse
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
Sample Instructor Notes
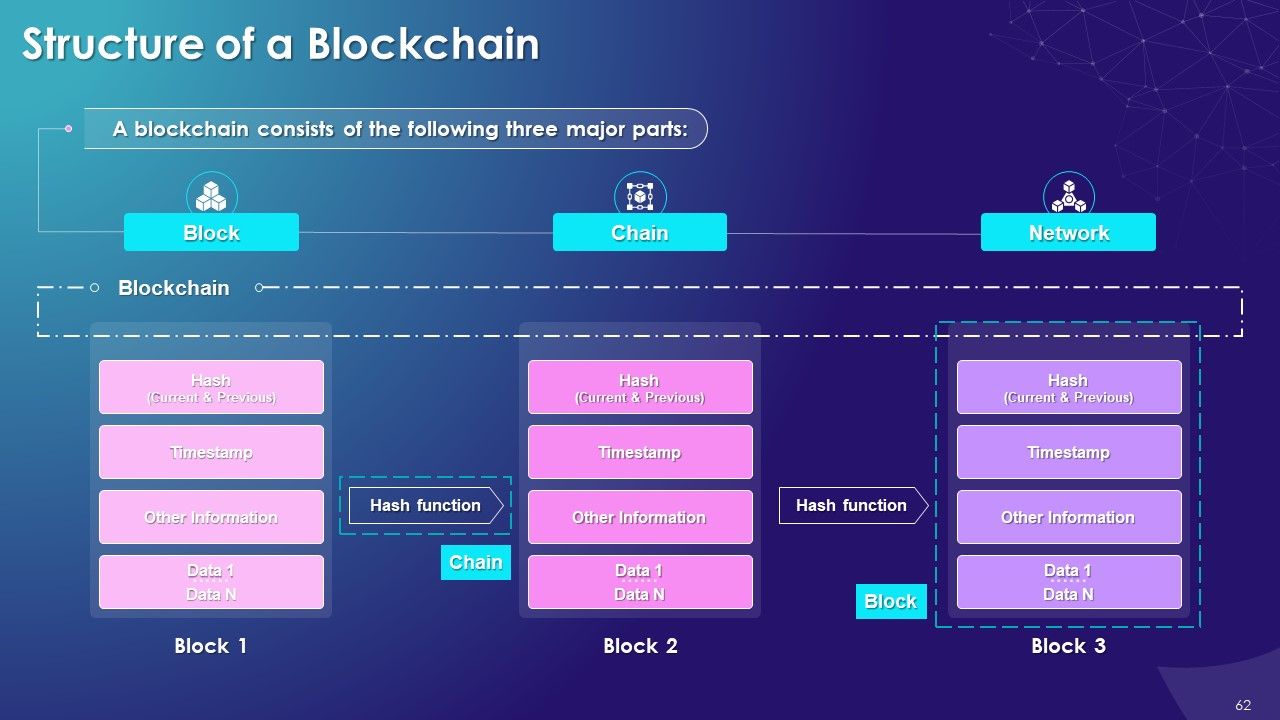
What is this slide for: Simplified Structure of a Blockchain
This slide covers: This slide provides an overview of the structure of blockchain, covering the key components such as block, chain, and network.
Instructor’s Notes:
The structure of blockchain is similar to that of linked lists or binary trees in which the linking is done using pointers that point to the previous or next list element on the nodes in the linked list.
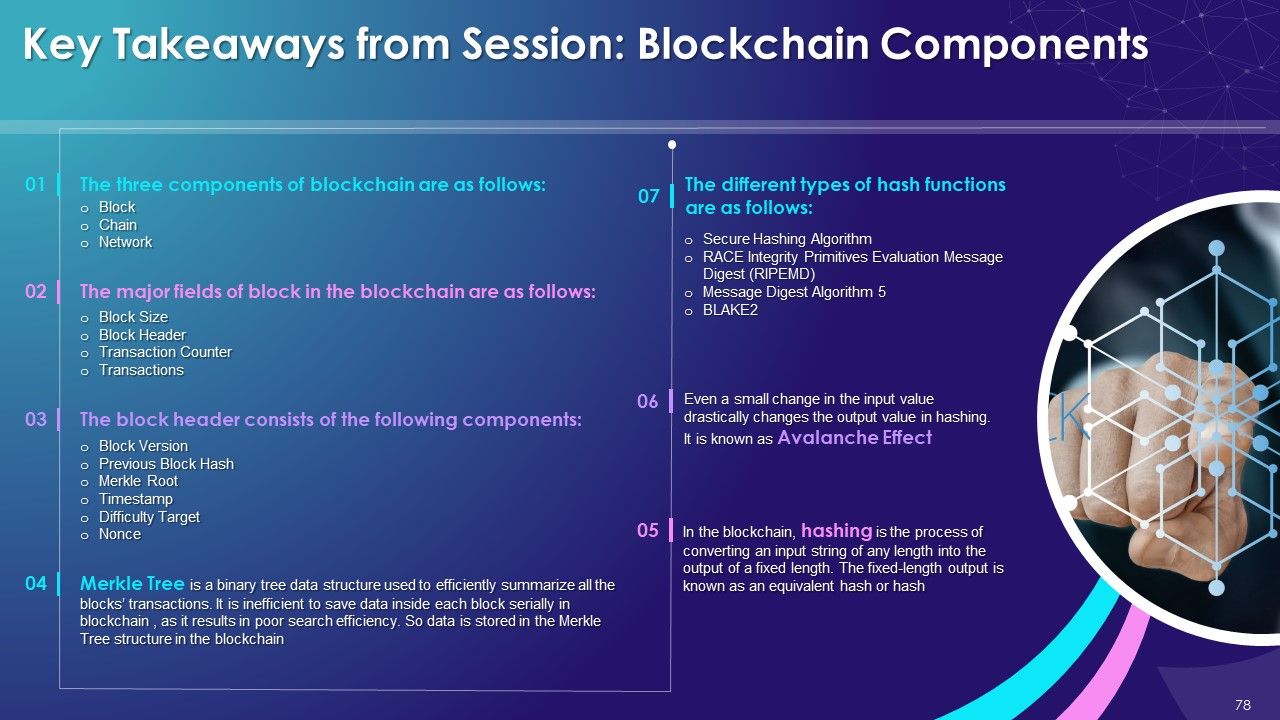
The three major parts of blockchain are:
- Block: It contains the list of transactions recorded into a ledger over a time period. For every blockchain, the size, period, and triggering event varies
- Chain: Chain is a hash that glues multiple blocks together in the blockchain and enables trust creation. In the blockchain, the SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm) hashing algorithm is primarily used
- Distributed Network: The network consists of multiple nodes across the globe to achieve the decentralized structure of the blockchain. Each node will contain the complete record of all transactions which have been carried out in the blockchain
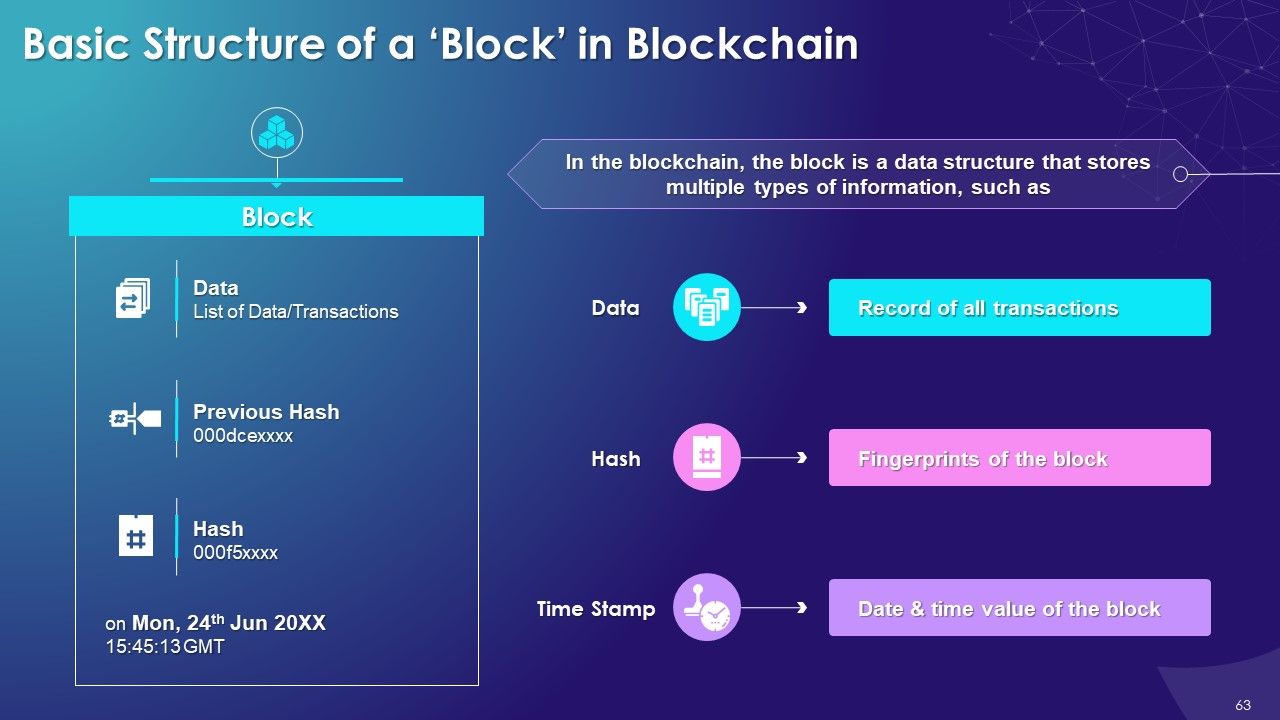
What is this slide for: Basic Structure of a Block in Blockchain
This slide covers: The purpose of this slide is to highlight the key components of a block in the blockchain, which are data, hash, and previous hash. The slide also includes details of timestamp and genesis block.
Instructor’s Notes:
The key components of a block in blockchain are as follows:
- Data: The record of all the transactions. Each block of a blockchain can contain thousands of transaction data. The type of data stored depends upon the use case of blockchain
- Hash: The hash is like a block fingerprint as it helps identify the block and its content. A hash is always unique for each block
- Previous Hash: As the name suggests, it contains the hash information of the preceding block. Its primary function is to create the chain of blocks and make blockchain secure
- Genesis Block: The first block created for any blockchain with the previous hash as “0” is the genesis block
- Timestamp: A timestamp is a date-time value that is stored in a block. It provides information about the time when the block was created. In the blockchain, this value is in the form of a Unix timestamp format
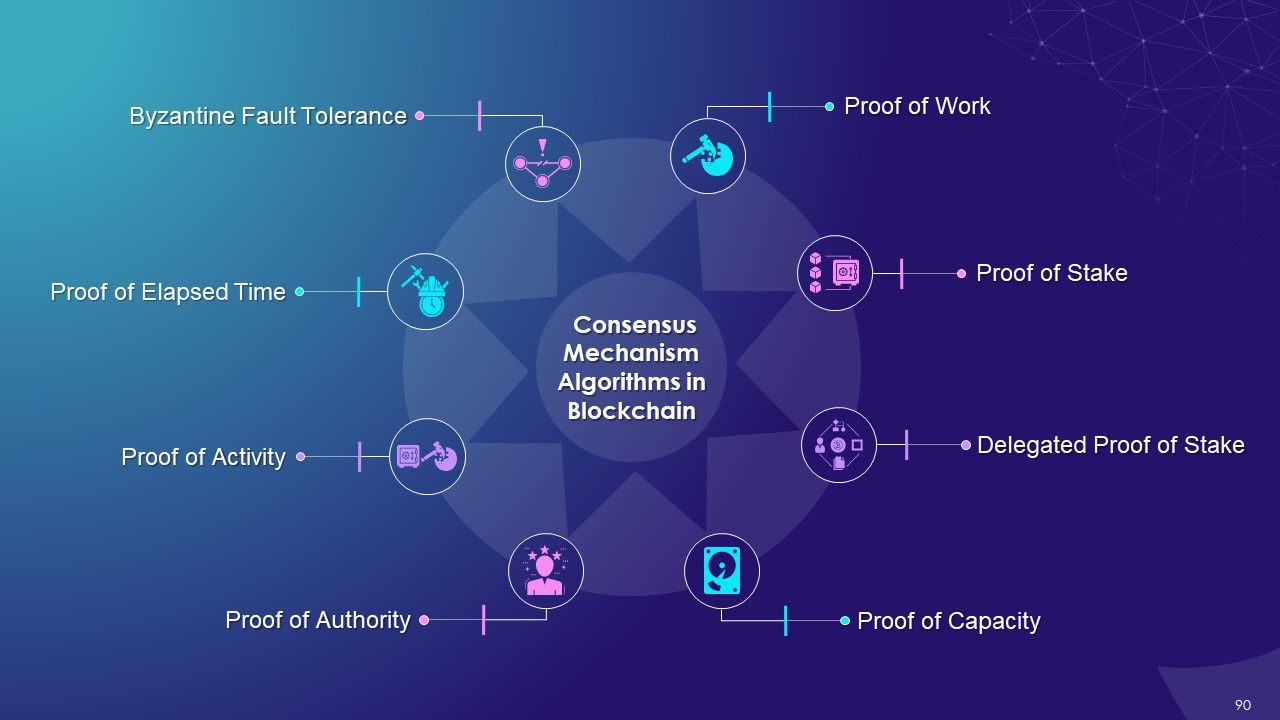
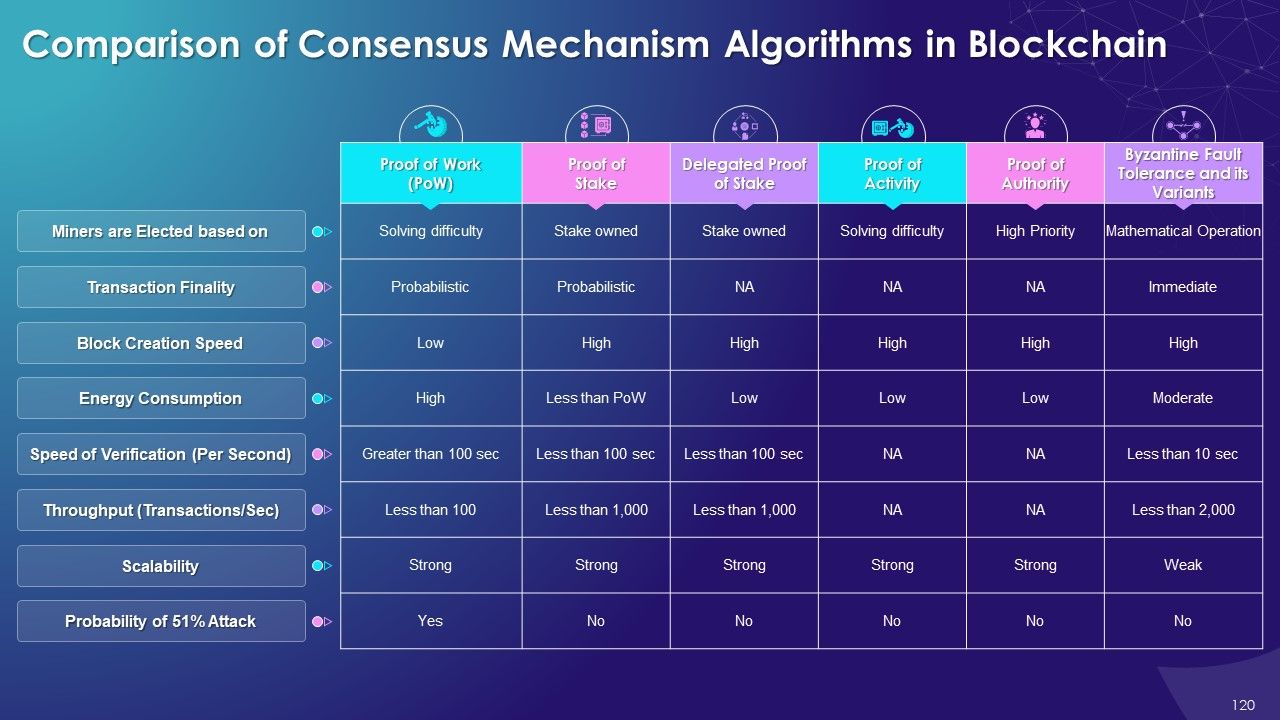
What is this slide for: Multiple Types of Consensus Mechanism Algorithms in Blockchain
This slide covers: this slide indicates multiple types of consensus mechanism algorithms in blockchain that are Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, Delegated Proof of Stake, Proof of Capacity, Proof of Authority, Proof of Activity, Proof of Elapsed Time and Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple types of consensus mechanism algorithms in blockchain are as follows:
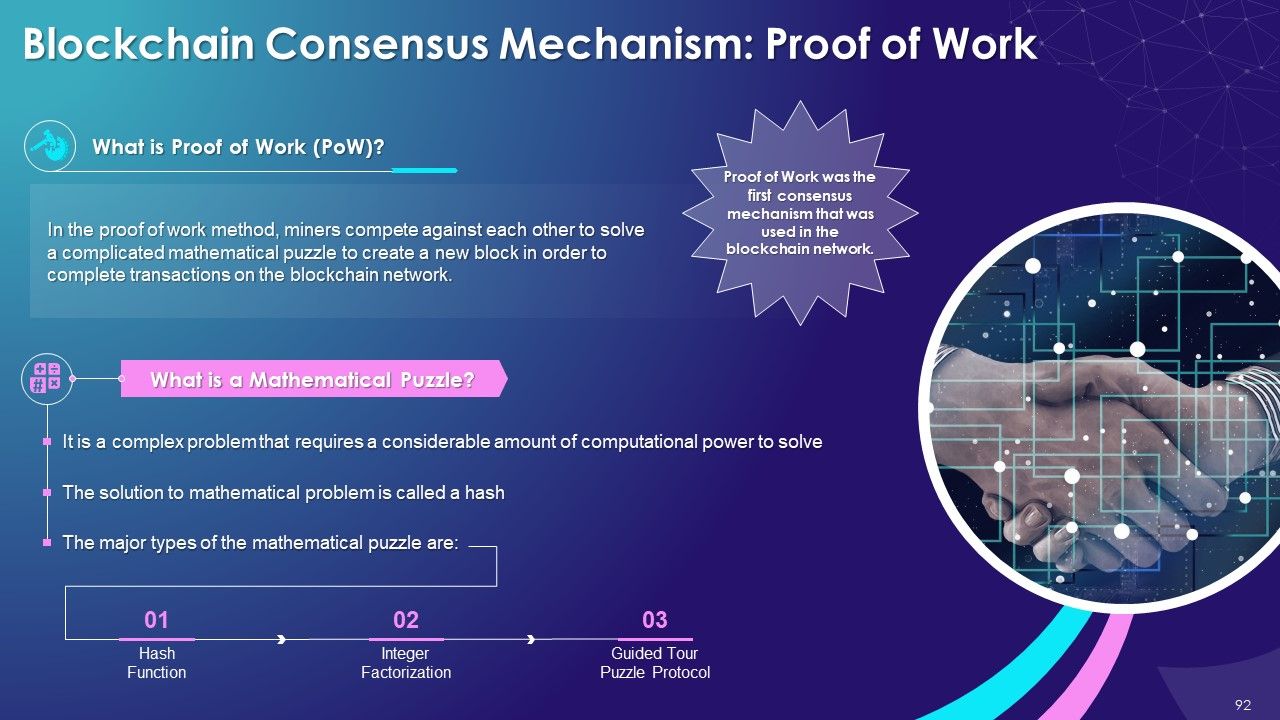
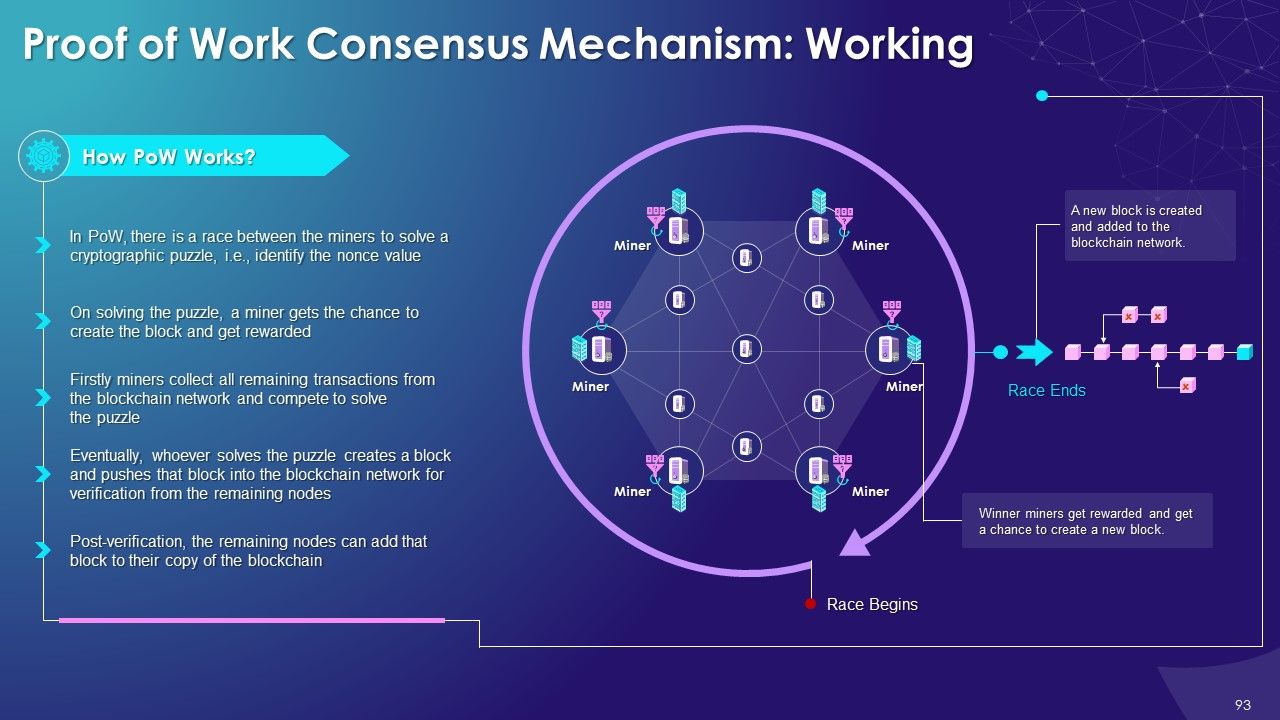
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners compete against each other to solve a complicated mathematical puzzle to create a new block in order to complete transactions on the blockchain network
- Proof of Stake (PoS): The Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism in which validator are selected in a deterministic manner to create blocks based on their stake or equity ownership in the blockchain
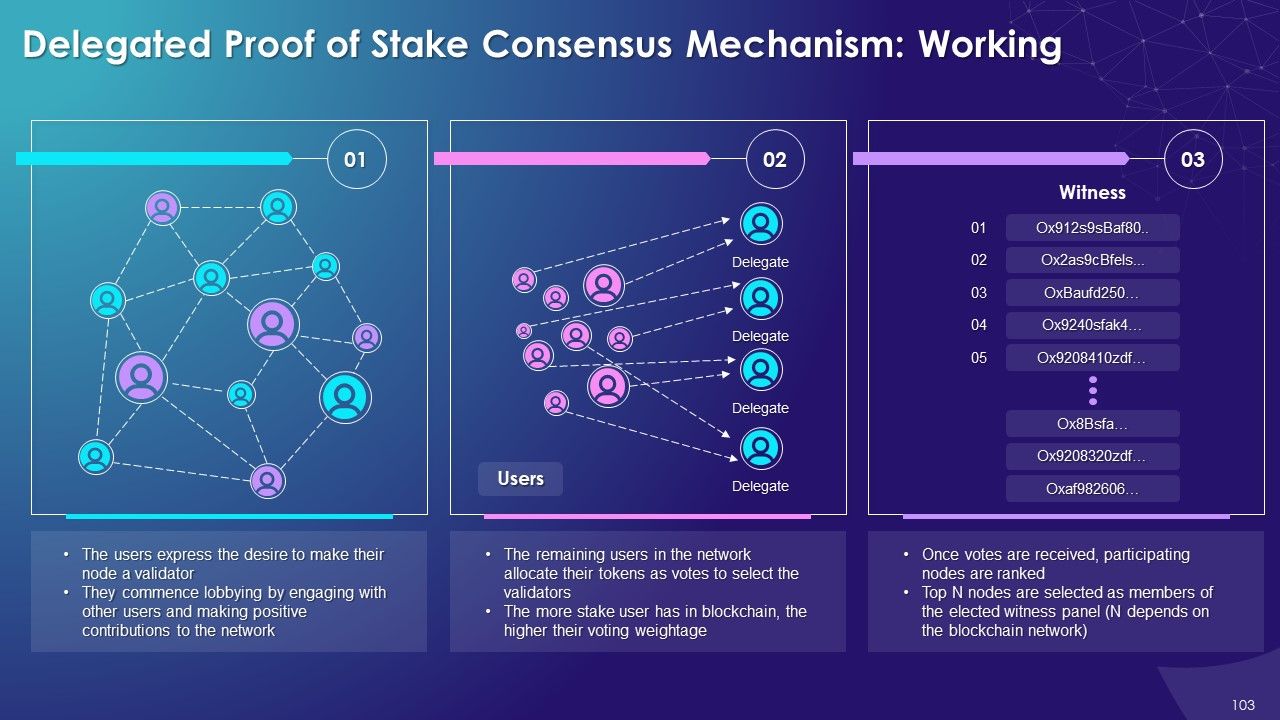
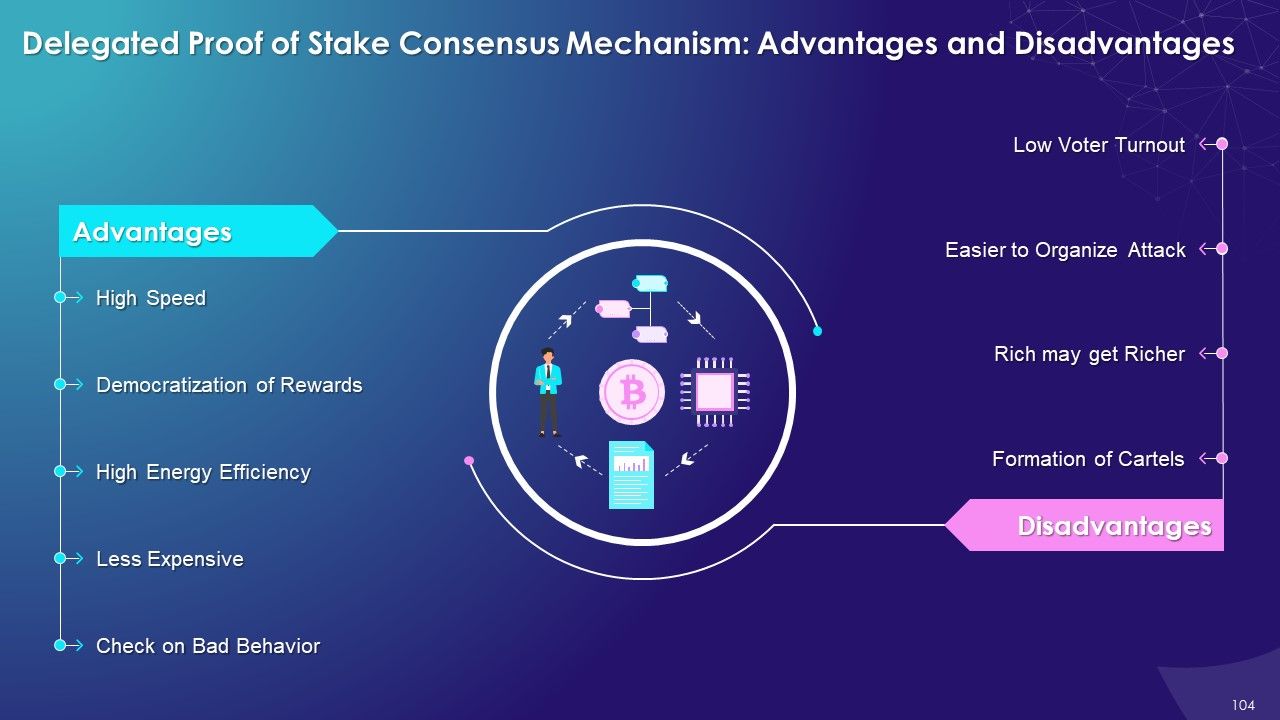
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): In the DPoS consensus mechanism, blockchain users vote and select delegates/witnesses to validate transactions in the blockchain
- Proof of Capacity (PoC): In the Proof of capacity (PoC) consensus mechanism, the mining equipment uses their available hard drive device space to decide the mining rights
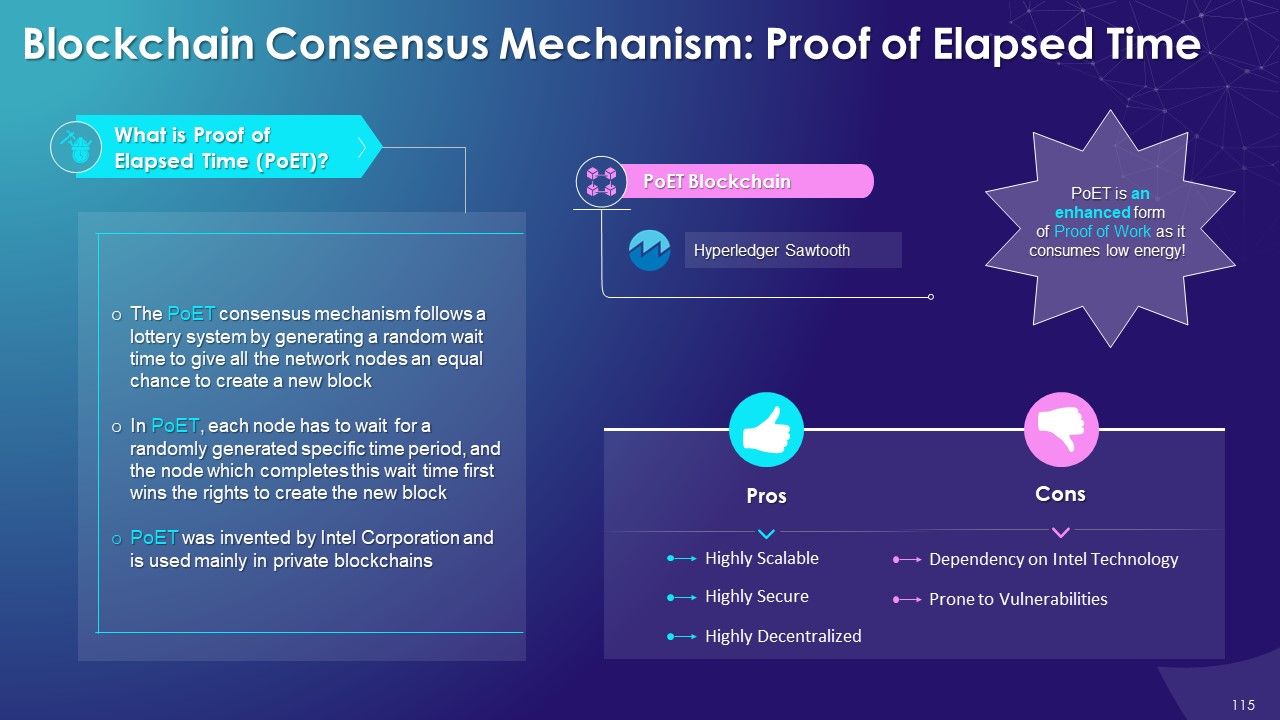
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET): In PoET, the user who generates a new block is decided randomly and fairly using the waiting time
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Proof of Authority is a reputation-based consensus mechanism in which the right to generate new blocks are awarded to nodes that have proven their authority to do so
- Proof of Activity: In the blockchain, Proof of Activity is a hybrid consensus mechanism that combines features of both Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithms
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET): In PoET, each node has to wait for a randomly generated specific time period, and the node which completes this wait time first wins the rights to create the new block
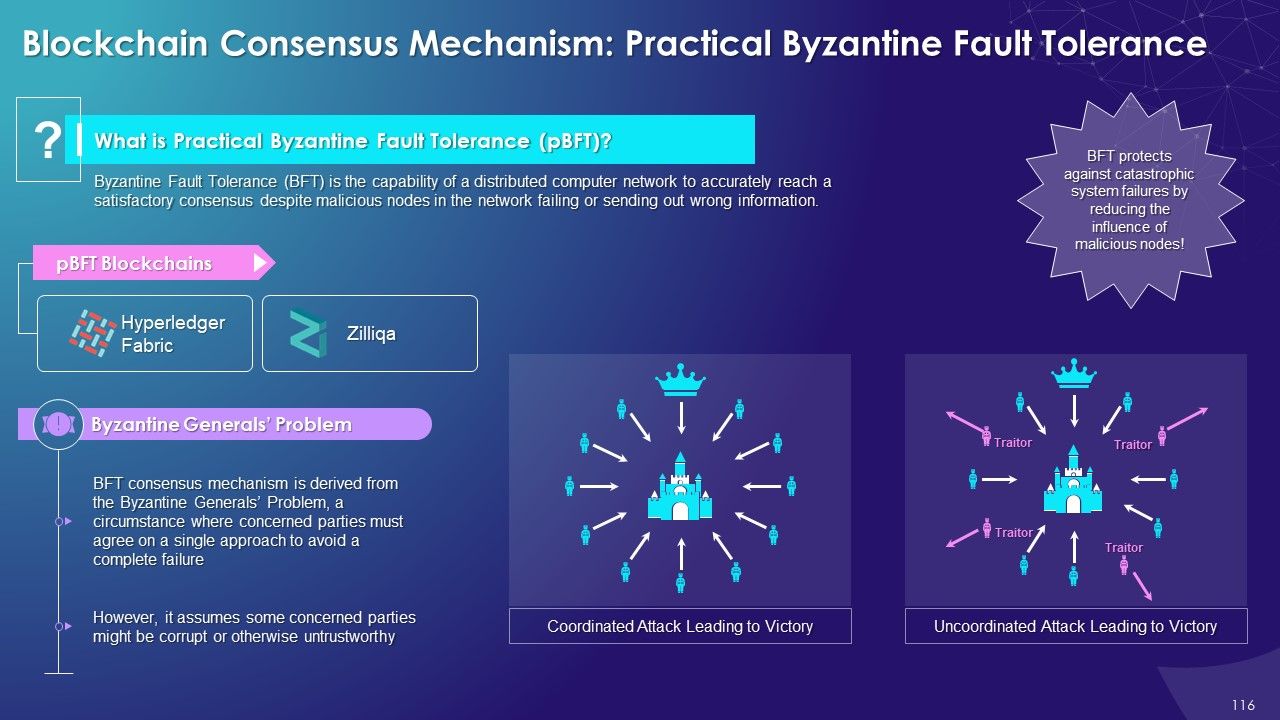
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT): BFT helps create a new block in blockchain by reaching the consensus even if some nodes in the network fail to respond or respond with incorrect information. There are many variations of BFT that are deployed based on use cases
What is this slide for: Consequences of 51% Attack on Blockchain Technology
This slide covers: This slide illustrates the impact on the blockchain after the 51% attack is done. The major negative consequences of 51% attack are preventing initiation of transactions, activating double spendings, preventing transaction validation, controlling the network, and threat to business.
The major consequences of 51% attack on blockchain networks are as follows:
- Prevent Transactions Initiation: After the 51% attack, the miners can prevent the other members from sending or receiving any transaction by either rejecting or halting the payment between some or all users
- Activate Double Spendings: The miners can also activate double spending of coins by reversing completed transactions while controlling the network
- Prevent Transaction Validation: The miners can also stop other miners from performing blockchain transaction, validation, and finalization
- Controlling Networks: 51% attacks can also affect other miners by controlling the network’s computing power
- Threat to Business: 51% attack also presents a significant threat to businesses who have use blockchain for financial transactions and keeping transaction records
FAQs
We provide training decks on a wide variety of business and technical topics such as Diversity & Inclusion, Customer Service, Search Engine Optimization, Blockchain Technology, and many more. These are ready-to-present decks that can be downloaded and presented in their current form. These decks are carefully created by industry experts, designed by professionals to deliver a power packed training session.
We want our training decks to evoke curiosity and inspire passion for learning. Each training deck consists of multiple sessions with impeccably designed slides to explain concepts in-depth, key takeaways to summarize sessions, discussions, and multiple-choice questions to assess trainees’ learning. The deck also contains activities and memes to break the monotony and make the training more interactive. Each training deck comes with an assessment form and editable proposal to help pitch your training to clients with success.
It depends on the trainer's content delivery pace, but each deck is created to ensure that training content is for a minimum of 16 hours.
Yes. A significant segment of our customers are professional mentors, coaches and teachers. You can create presentations with our content and distribute these to your trainees. The only caveat is that you cannot share your subscription to our content with others; the license is not transferable. Also, you cannot resell SlideTeam content to others.
Each slide is 100% editable in PowerPoint. Every element of the slide – text, icons, images, vectors, color scheme, etc. can be modified to build an effective PowerPoint presentation. Simply DOWNLOAD, EDIT, and PRESENT!
All PPT slides are compatible with PowerPoint 2007 and above. Some diagrams will not show up correctly with older versions of PowerPoint, like PowerPoint 2003 or lower, because of rendering issues. Yes, they work with PowerPoint for MAC, and decks are compatible with Google Slides too.
Absolutely yes! Our decks are yours to keep and build upon even after your subscription expires. You will not be able to download any additional decks once your subscription expires, but the ones you've downloaded are yours to keep forever.
Our entire website is HTTPS secure, and our payment system is managed by PayPal and Stripe, two of the world's leaders in credit card payment systems and very respected companies in online payments. This makes our systems 100% secure. We do not store or have access to any credit card information ourselves. We direct you to these third-party secure sites with 100% secure SSL connections where you can safely purchase a subscription and then direct you back to our site to download products.
You are allowed to log in and download content from 3 computers. Our website keeps track of login IP addresses, MAC Address Usage, and Browser and Computer Operating System fingerprinting, and you will not be able to log in from more than three computers.