Decentralization And Distributed Systems In Blockchain Training Module Training Ppt
This PPT training deck covers the types, characteristics, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of decentralization and distributed systems in the blockchain. It also contains slides on misconceptions regarding blockchain technology. The PowerPoint module also contains key takeaways, discussion, and multiple-choice questions related to the topic to make the training session interactive. Further, it contains additional slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, energizer activities, detailed client proposal, and training assessment form.
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Session on Decentralization and Distributed Systems in Blockchain. This presentation deck contains 78 well-researched and uniquely designed slides. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon, and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
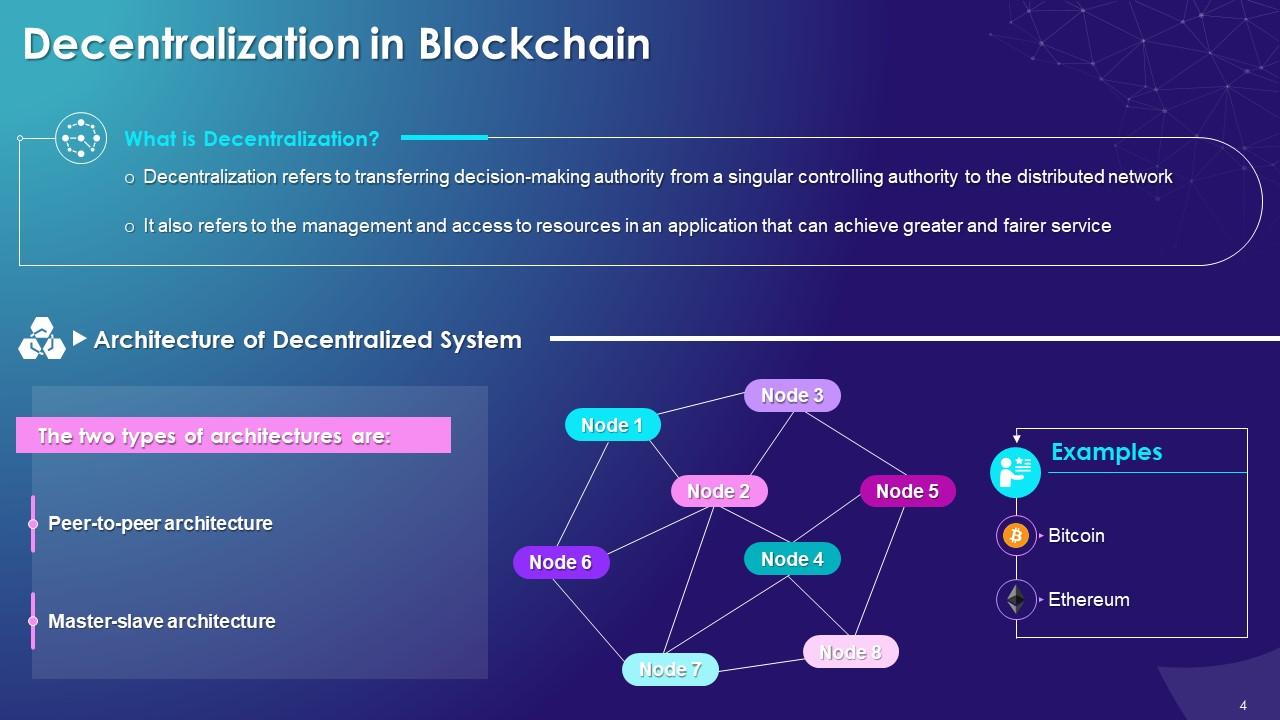
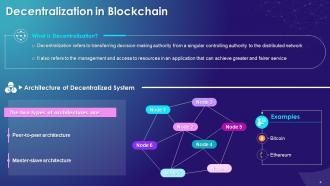
This slide showcases the concept of decentralization in the blockchain. It also provides information regarding the definition, architecture types, and examples of the decentralization of blockchain.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple architectures of decentralization are as follows:
Peer-to-peer (P2P) Architecture:
- Peer-to-peer architecture refers to the distributed application architecture that separates tasks or workloads between peers and forms a P2P network of nodes
- In a P2P network, each peer use network resources for the completion of allocated tasks
Master-slave Architecture:
- The master is the actual data keeper in decentralization, while a slave is a copy of the master
- Any node can become a master by voting out the other nodes
- The master node helps coordinate a part of the system, but this does not mean that one node has supremacy over the other nodes
- It is used to help stabilize a system
Slide 5
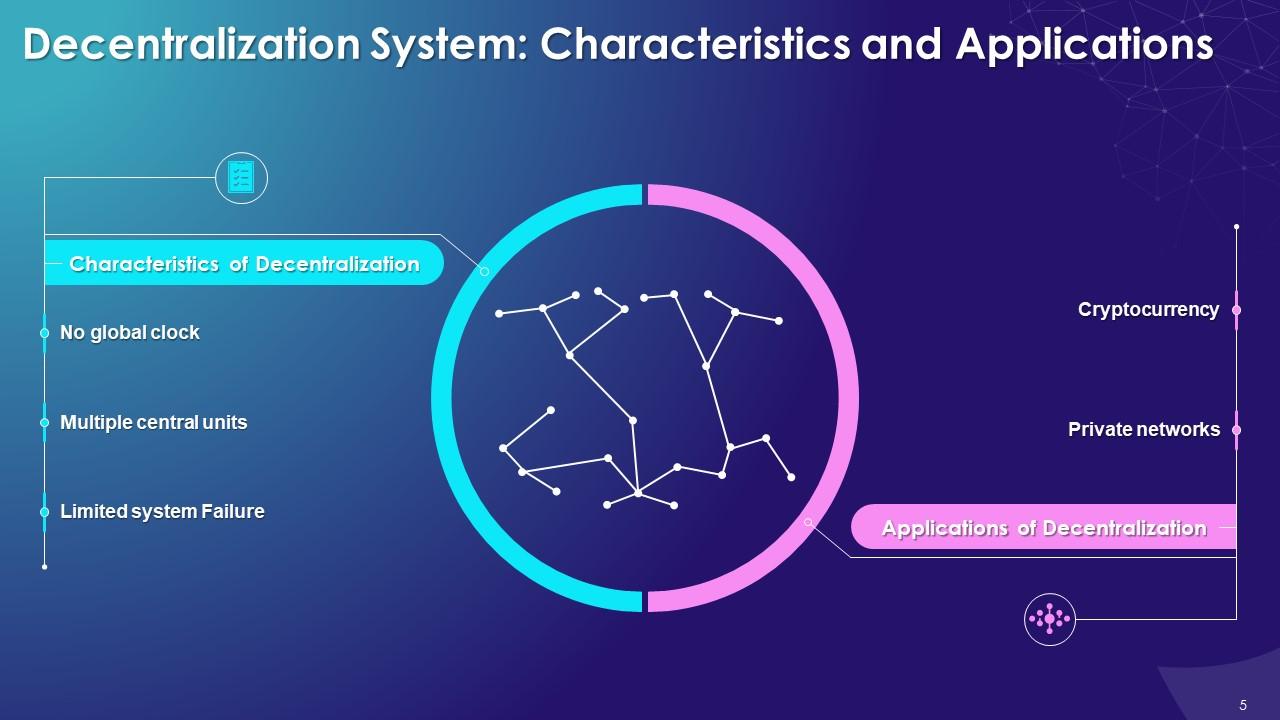
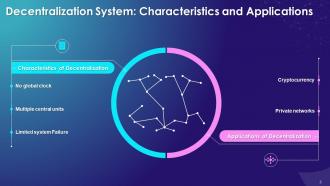
The purpose of this slide is to showcase the features of the decentralized system. It also contains details of applications of decentralization such as private networks and cryptocurrency.
Instructor’s Notes:
Characteristics of Decentralization System:
- No global clock: In decentralization, each node is independent. It runs on and follows its own different clock
- Communication among nodes: Multiple units such as computers, nodes, and servers can communicate with other nodes in the network
- Limited System Failure: If one node fails, only that section of the system fails, not the entire system
Applications of Decentralized System:
Private Network:
- A private network refers to any connection within a specified network that is configured so that devices outside the network cannot access it
- It is used to establish limitations to promote a secured network environment
- Peer nodes communicate with each other to form a private network
Cryptocurrency:
- In cryptocurrency, each node is merged to become a part of a system that helps in exchanging digital currency without any trace
- No central monetary authority is required in cryptocurrency, and each transaction can be done without the need of government or bank
Slide 6
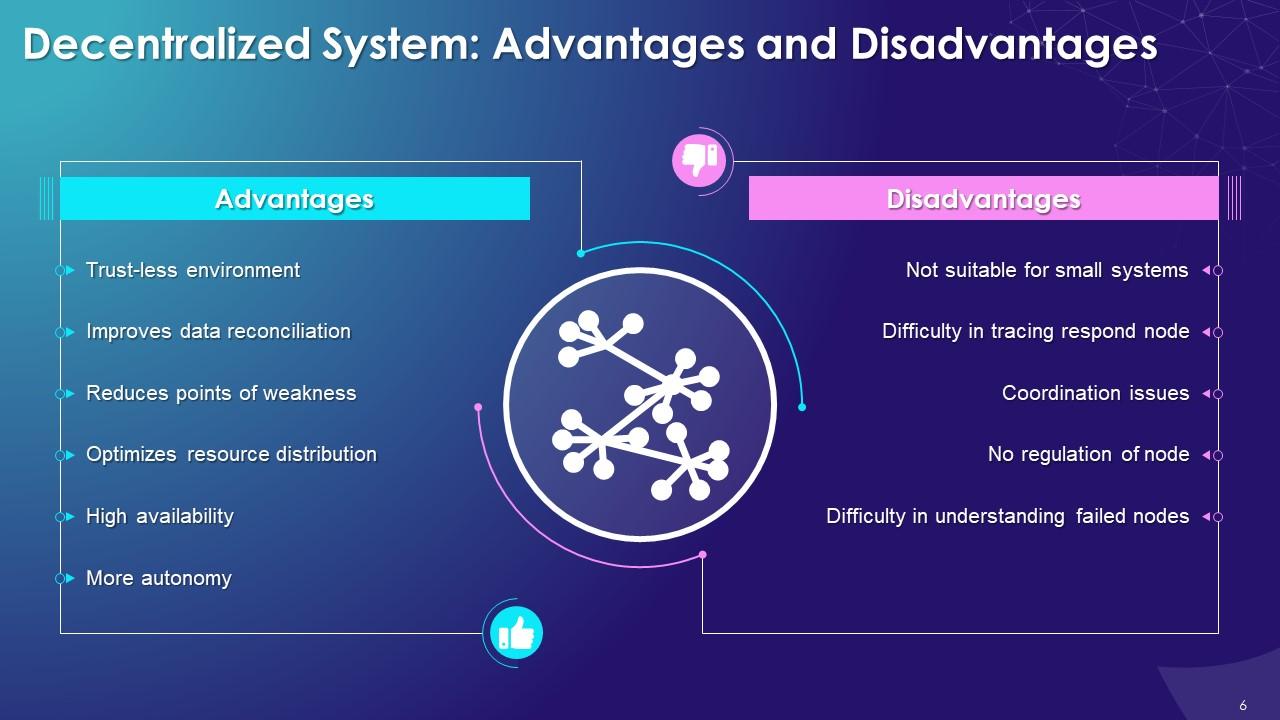
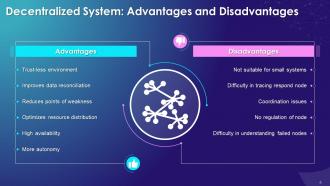
This slide illustrates the benefits of the decentralization system such as trust-less environment, improved data reconciliation, reduced points of weakness, optimized resource distribution, high availability, and more autonomy. It also includes the limitations of decentralization systems which are not suitable for small systems, difficulty interacting respond nodes, coordination issues, no regulation of nodes, and difficulty understanding failed nodes.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple advantages and disadvantages of decentralization are as follows:
Advantages of Decentralization:
Trust-less environment:
- In a decentralized blockchain network, no individual needs to trust anyone. Trust is established through technology
- Since each member in the blockchain network has a copy of the exact data in the form of a distributed ledger, the network is very difficult to hack and manipulate
Improves data reconciliation:
- Different companies usually exchange data with their associates, which leads to data loss or incorrect data updating
- Decentralization helps in creating multiple copies of the same data on different nodes that keep data secure and available for upgrade and improvement
Reduces points of weakness:
- Decentralization can reduce points of imperfection in systems where there may be too much reliance on specific members, and these weak points could cause systemic failures
Optimizes resource distribution:
- Decentralization helps optimize resource allocation, so that services promised are provided with better performance and consistency
High availability:
- Some nodes are always available/online for work, which leads to high availability
More autonomy:
- In decentralization, each node controls its behavior, and it has a degree of autonomy leading to more control over resources
Disadvantages of Decentralization:
Not suitable for small systems:
- It is not suitable for building and managing small decentralized systems because of the high fixed cost involved
Difficulty in tracing respond node:
- When a decentralized system makes a request, one of the nodes in the system processes and serves it. It is not easy to establish which node made the request
Coordination issues:
- In decentralization, each node is the owner of its behavior, and it's challenging to get collaborative tasks done
No regulation of nodes:
- In decentralization, no particular node controls the behavior of other nodes
Difficulty in tracing failed nodes:
- Each node must be individually pinged in a decentralized blockchain network to check for proper working
- In case of any node failure, tracing a not-working node is time-consuming
Slide 8
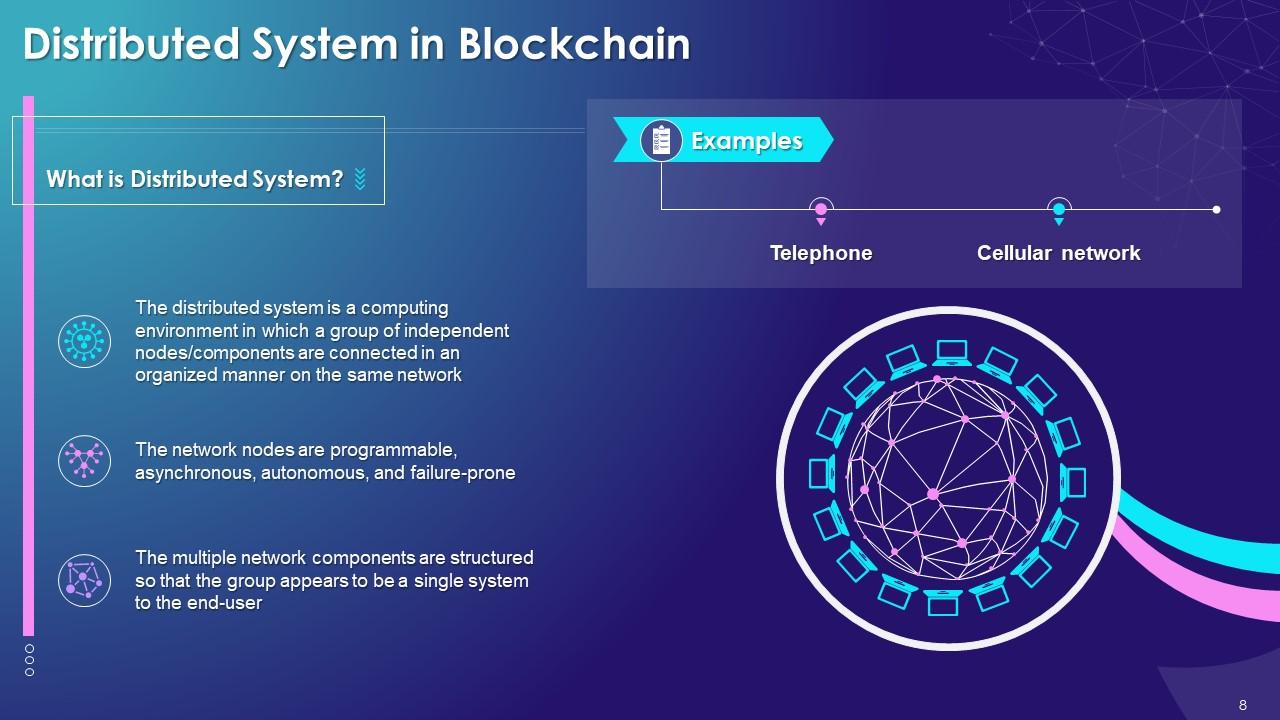
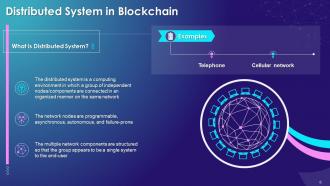
This slide showcases the concept of a distributed system in the blockchain. It also provides information regarding the definition and examples of the distributed system of blockchain.
Slide 9
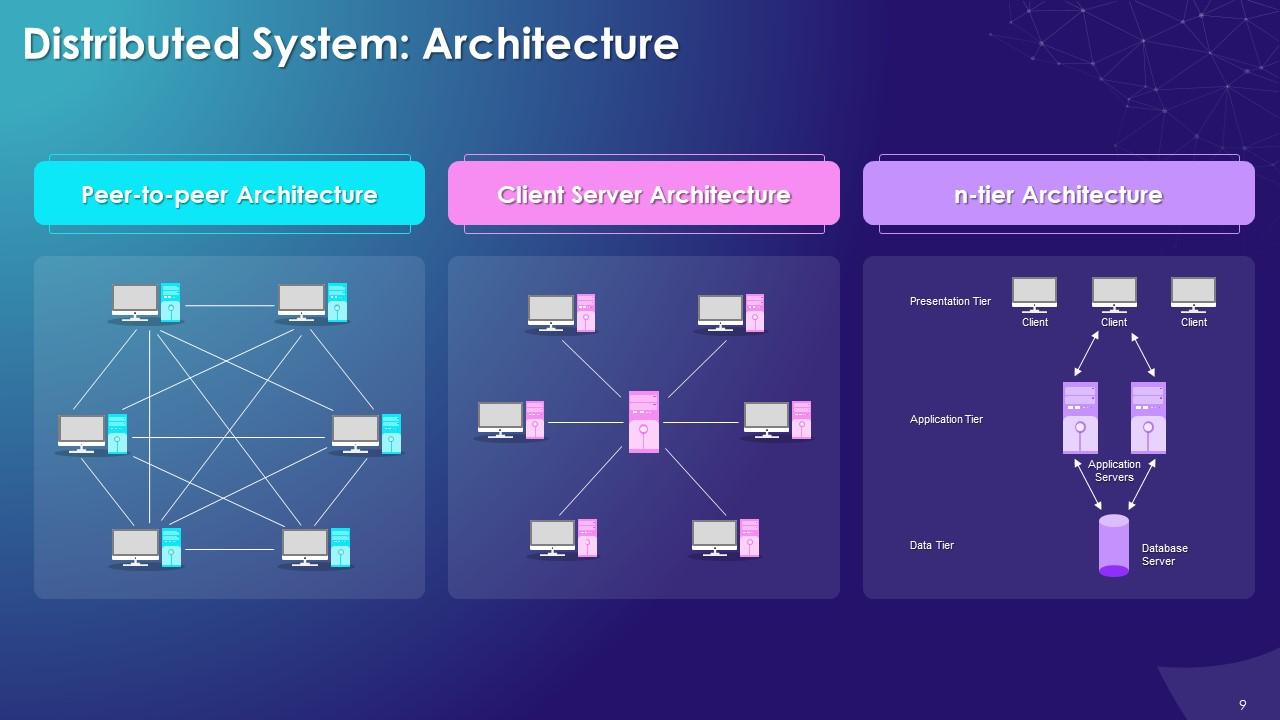
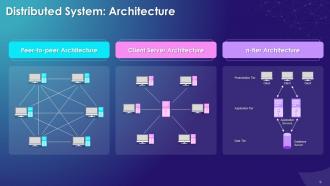
This slide showcases the concept of the architecture of the distributed system in the blockchain. It also provides information regarding the different types of architecture systems in blockchain
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple architectures of a distributed system are as follows:
Peer-to-peer Architecture:
- In a distributed system, nodes are peers and work towards a common goal
- This type of system has nodes with equal participation and authority
Client-Server Architecture:
- In this architecture, a few nodes become ‘server nodes’ for the purpose of coordination
n-tier Architecture:
- Different systems nodes contain multiple parts of an application and work together to meet needs of users
Slide 10
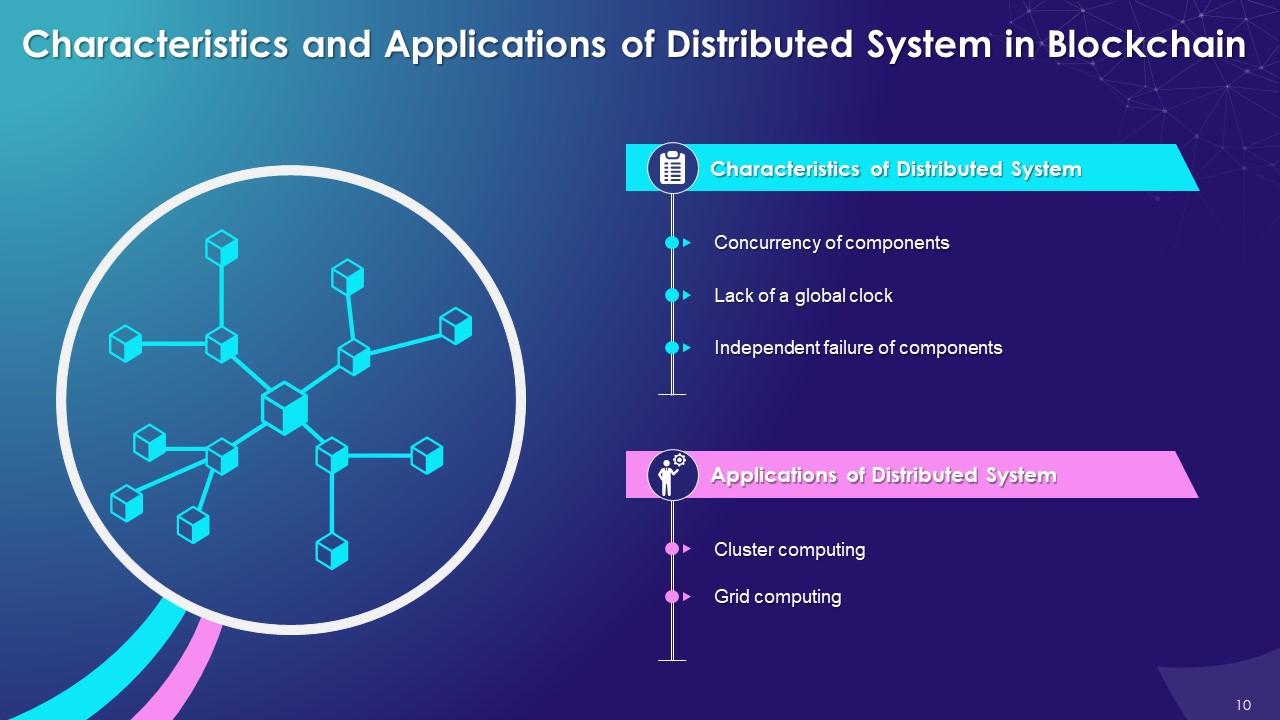
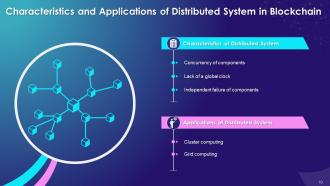
The purpose of this slide is to showcase the features of the distributed system. It also contains details of applications of a distributed system such as cluster computing, and grid computing.
Instructor’s Notes:
Characteristics of Distributed System:
The multiple characteristics of a distributed system are as follows:
- Concurrency of components: In a distributed system, each node applies consensus protocols to agree on the same transactions
- Lack of global clock: In a distributed system, all nodes maintain their own logical clock for capturing chronological and causal relationships
- Independent failure of components: When a node fails, only that part of the system fails, and it has no significant effect on the complete system
Applications of Distributed System:
- Cluster Computing: Cluster computing refers to the collection of tightly-connected computers that work together as a single entity
- Many web applications such as security, search engine, database servers, web servers, etc., use cluster computing as a functioning tool
- Grid Computing: Grid computing refers to networked computers working together as a virtual supercomputer to perform large tasks
- Government agencies use grid computing for coordinating all the data
Slide 11
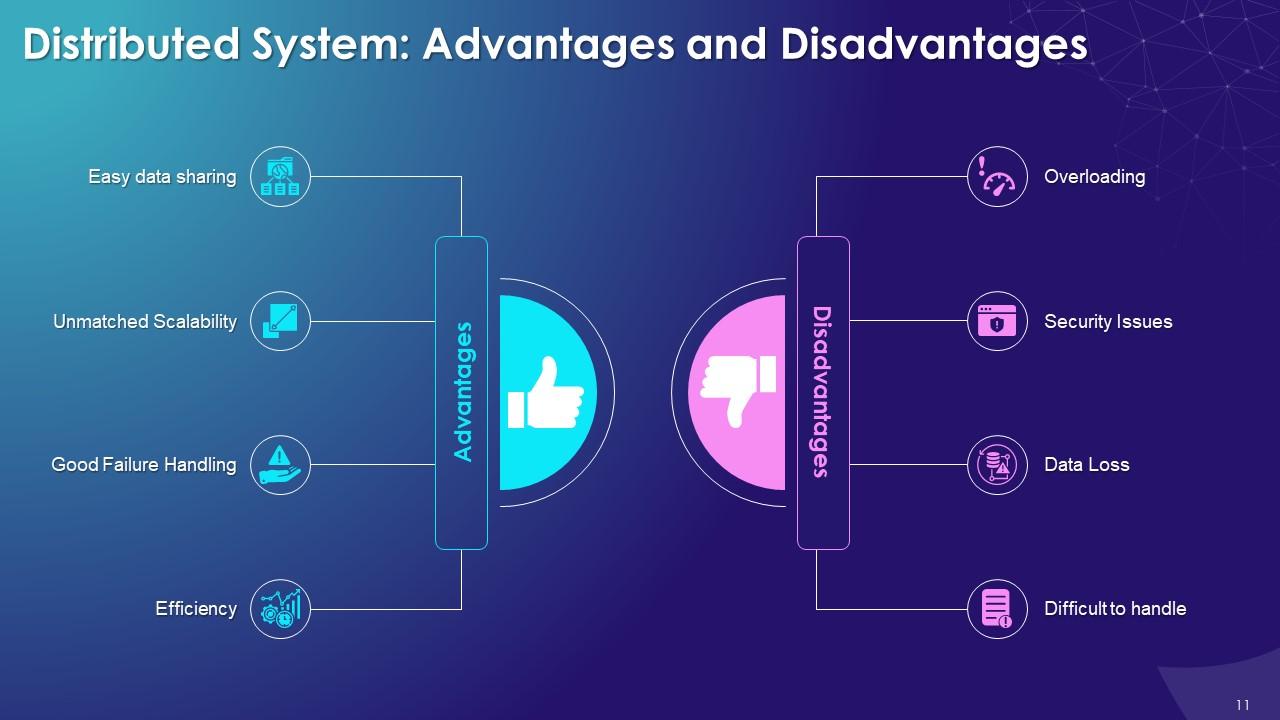
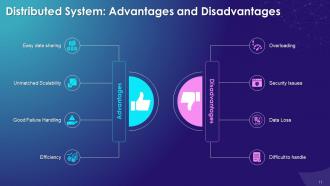
This slide illustrates the benefits of a distributed system such as easy data sharing, unmatched scalability, good failure handling, and efficiency. It also includes the cons of a distributed system such as overloading, security issue, data loss, and difficult handling.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple advantages and disadvantages of a distributed system are as follows:
- Easy Data Sharing: In a distributed network, each node is connected, and nodes can easily share data
- Unmatched Scalability: The addition of new nodes can be easily done in a distributed system
- Good Failure Handling: One node failing, does not mean that the entire distributed network will fail because the other nodes can keep communicating
- Efficiency: Highly efficient distributed systems involve multiple computers that help save time for users and provide higher performance compared to a centralized system
Disadvantages of Distributed System:
- Overloading: The distributed system gets overloaded when all the nodes in the networks try to send data jointly
- Security Issues: In distributed systems, it is difficult to provide sufficient security
- Data Loss: While moving from one node to another, some messages and data gets lost in the network
- Difficult to Handle: It is challenging to handle the complicated database of a distributed system, when compared to a single-user system
Slide 13
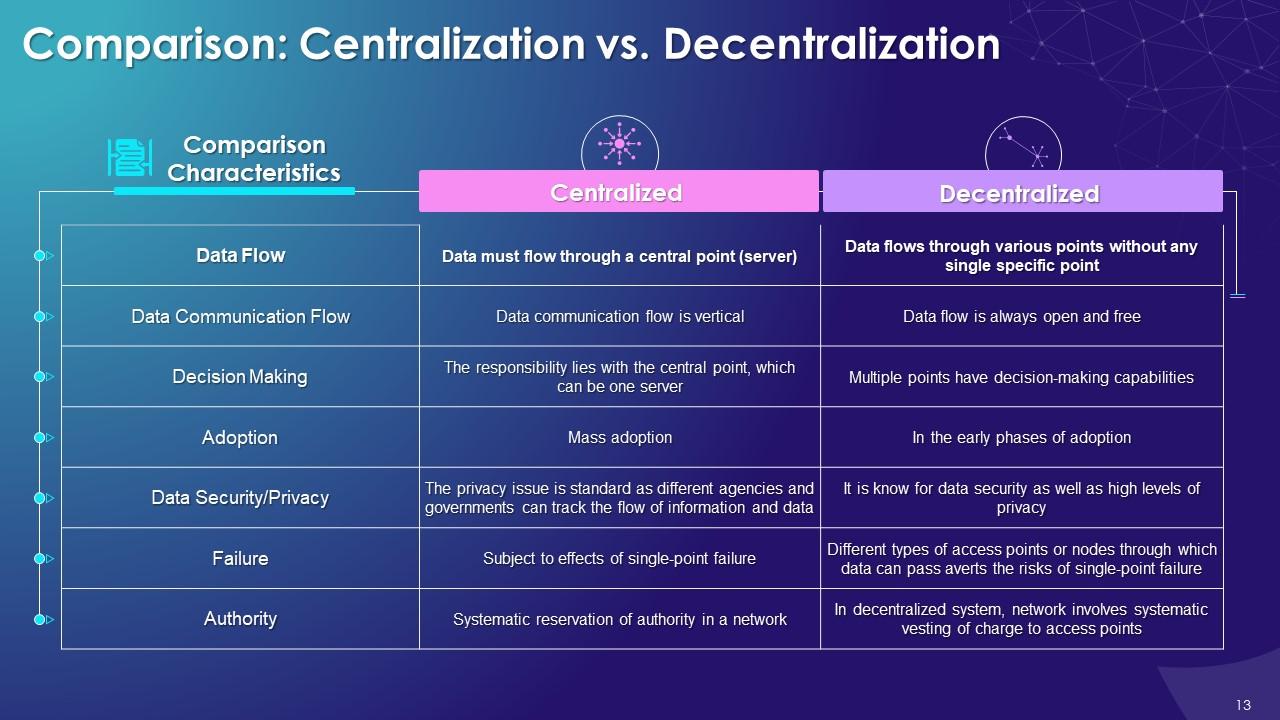
This slide illustrates the comparison between centralized vs. decentralized system. These are compared on characteristics such as data flow, data communication flow, decision making, adoption, data security, authority and failure.
Slide 14
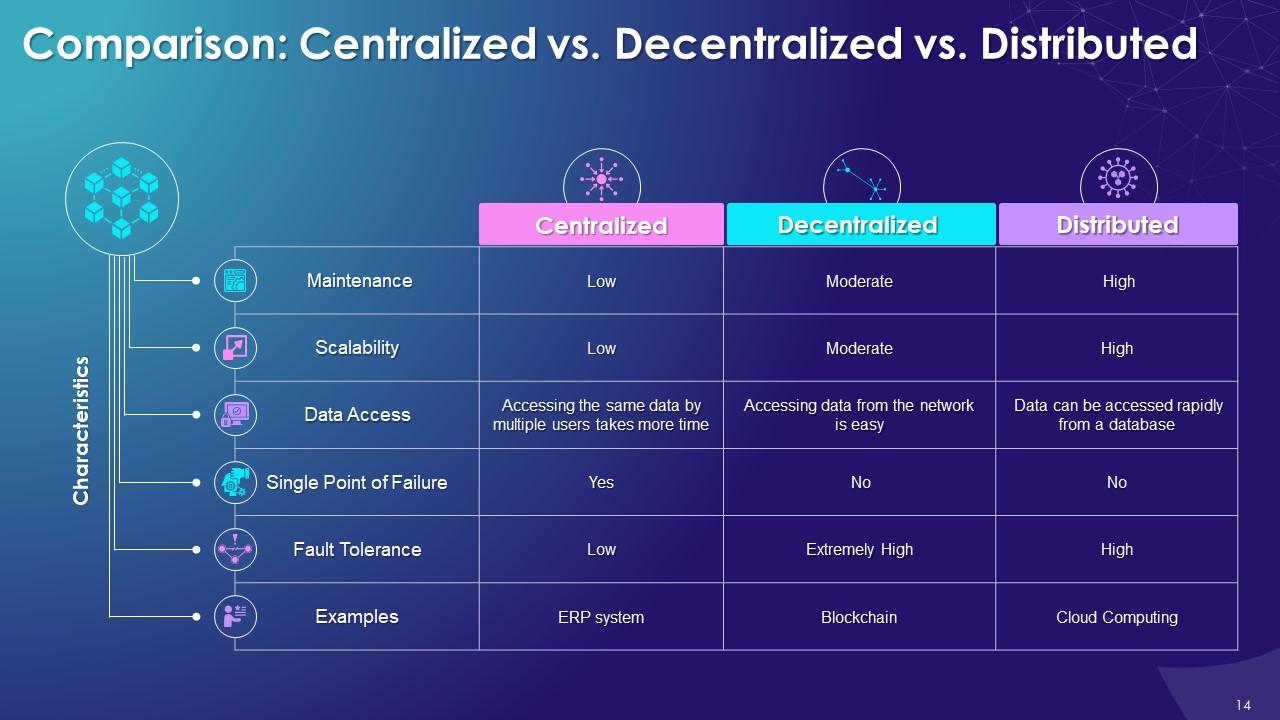
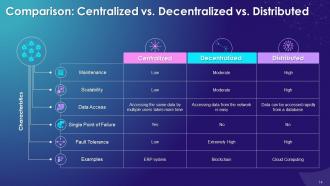
This slide illustrates the comparison between centralized vs. decentralized vs. distributed systems. These are compared on parameters like maintenance, scalability, data access, single point of failure, fault tolerance, etc.
Slide 15
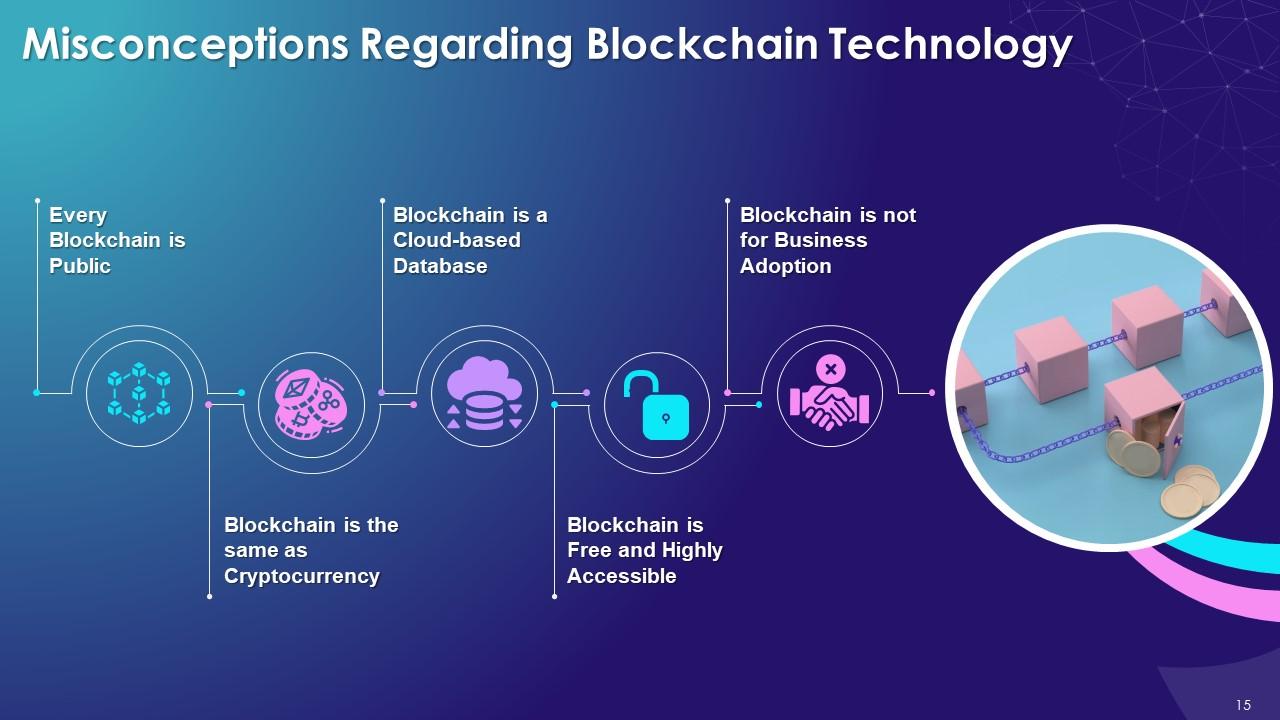
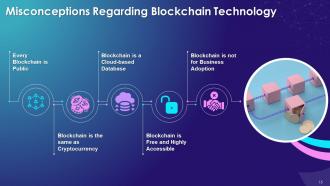
This slide illustrates myths about blockchain technology such as every blockchain is public, is the same as cryptocurrency, is a cloud-based database, is free and highly accessible, and is not prepared for business adoption.
Instructor’s Notes:
Misconceptions about blockchain technology are as follows:
Every Blockchain is Public:
- People misunderstand that all blockchains are public which is not true. Private and Hybrid blockchains don’t share data publicly
Blockchain is the same as Cryptocurrency:
- Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies and, blockchain technology serves as the foundation for building cryptocurrencies. Apart from currencies, there are multiple other use cases of blockchain
Blockchain is a Cloud-based Database:
- Blockchain is referred to as cloud-based databases, which is not true
- In reality, blockchain needs to be downloaded and run-on internet-enabled computers
Blockchain is Free and Highly Accessible:
- It is not possible for a technology like blockchain to do mathematical calculations/functions and implement algorithms without any cost
- While performing transactions, blockchain charges a fee, and thus nothing comes without a cost
Blockchain is not for Business Adoption:
- There is a common myth that different businesses are not adopting blockchain due to the high cost
- It has already transformed banking, financial, art, and gaming sectors
Slide 17
This slide depicts the summary of the decentralization and distributed systems in blockchain training session. The trainer can use it to highlight the essential concepts of the session to trainees.
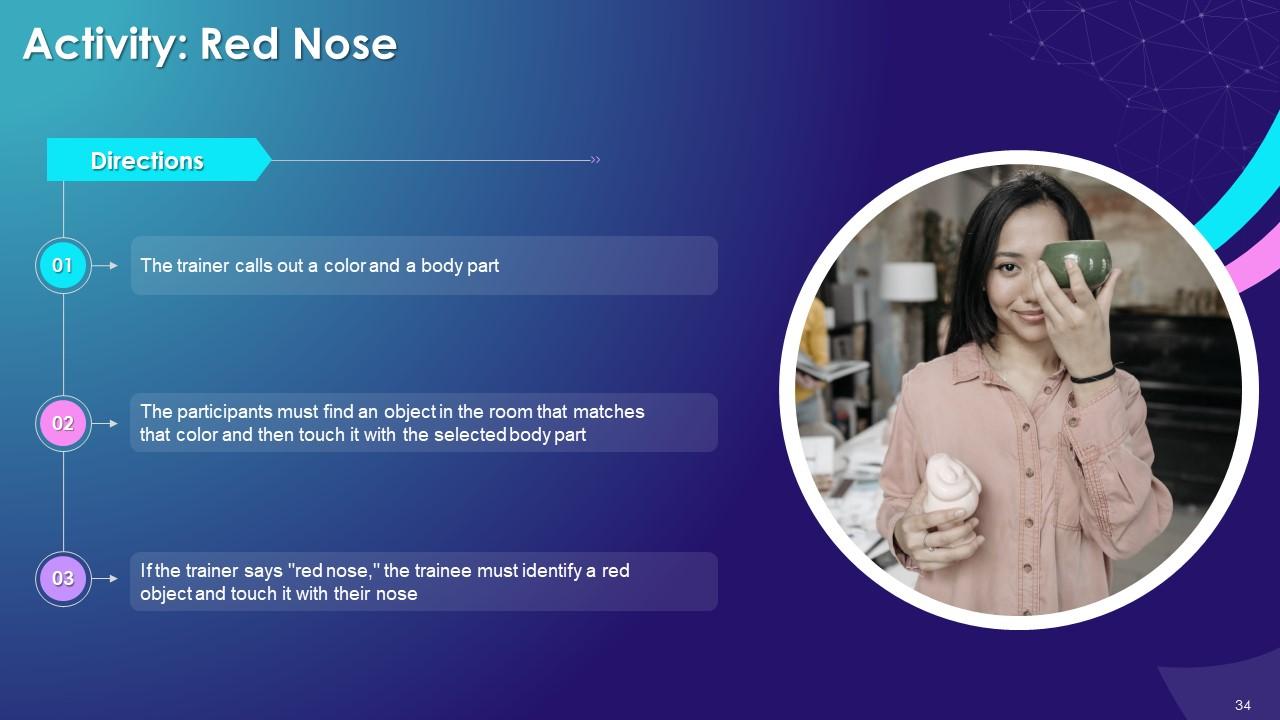
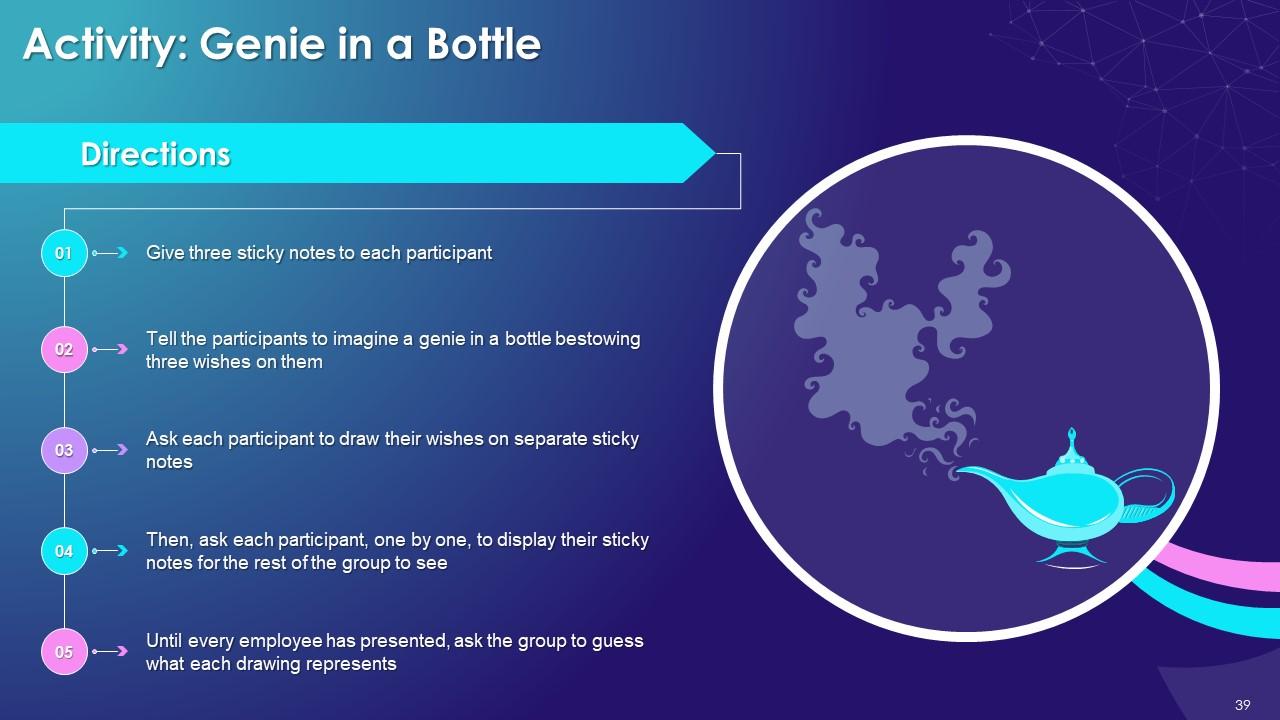
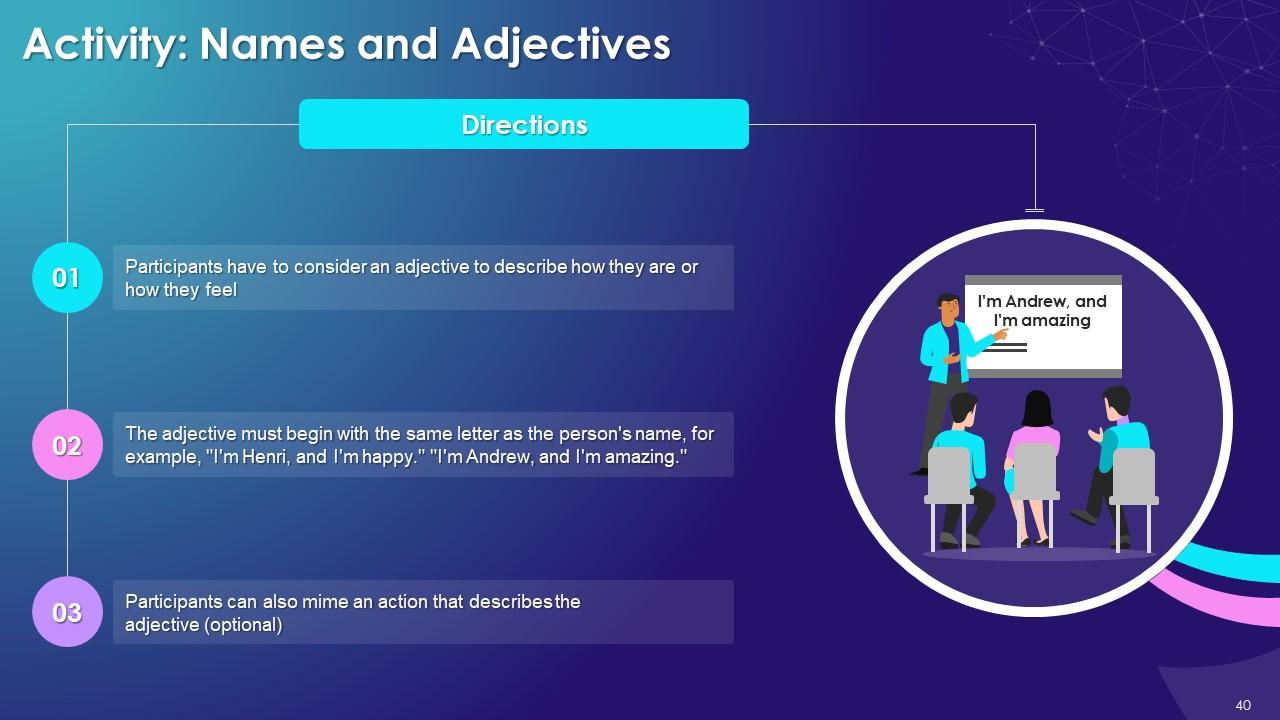
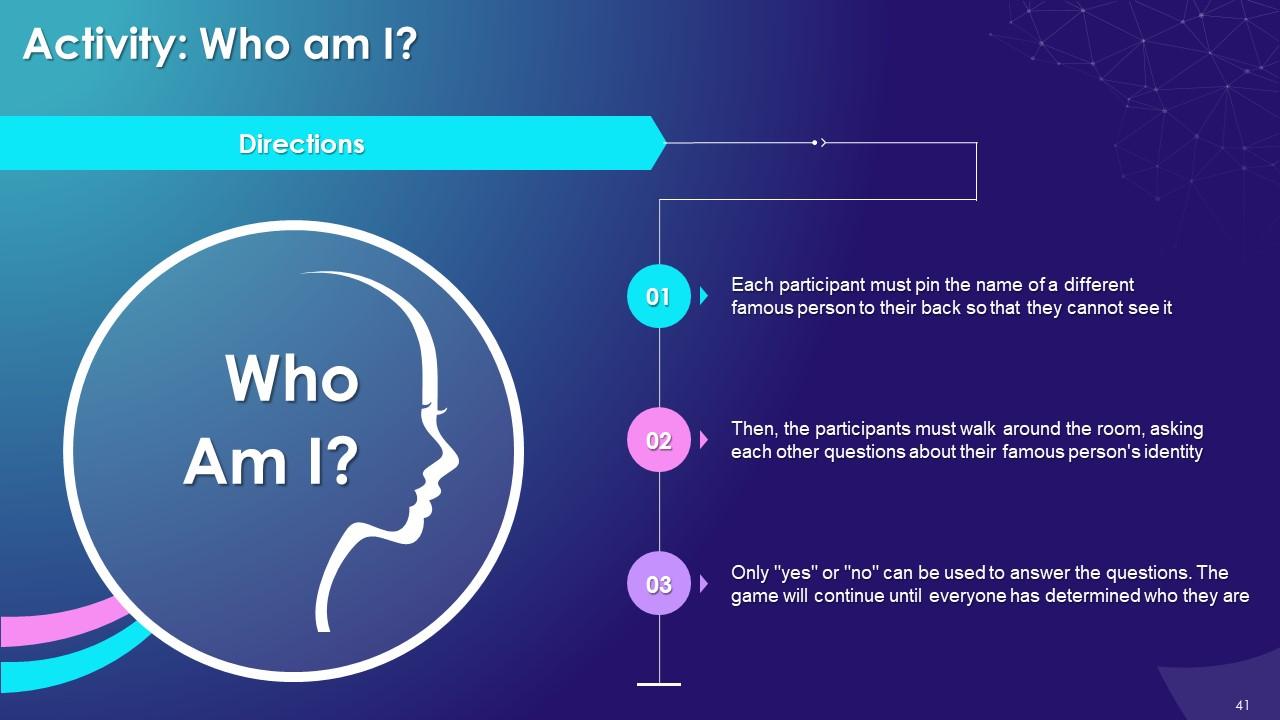
Slide 33 to 47
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 49 to 75
These slides contain a training proposal covering what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
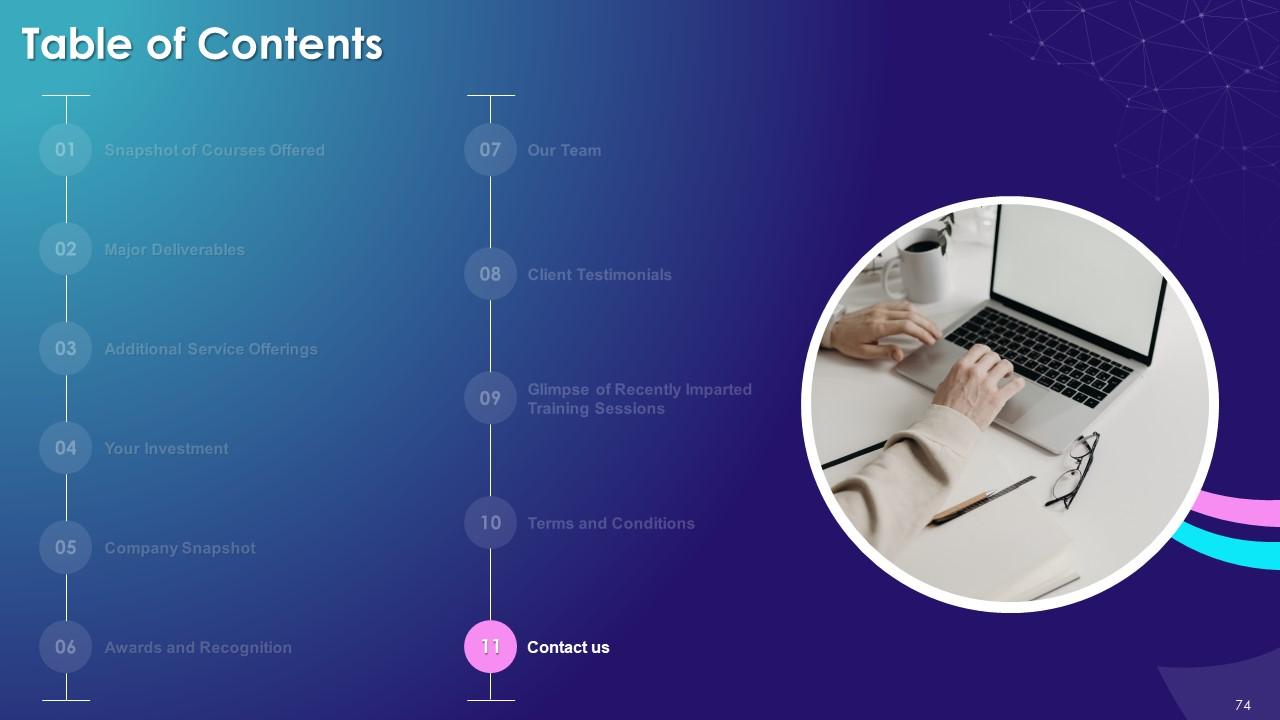
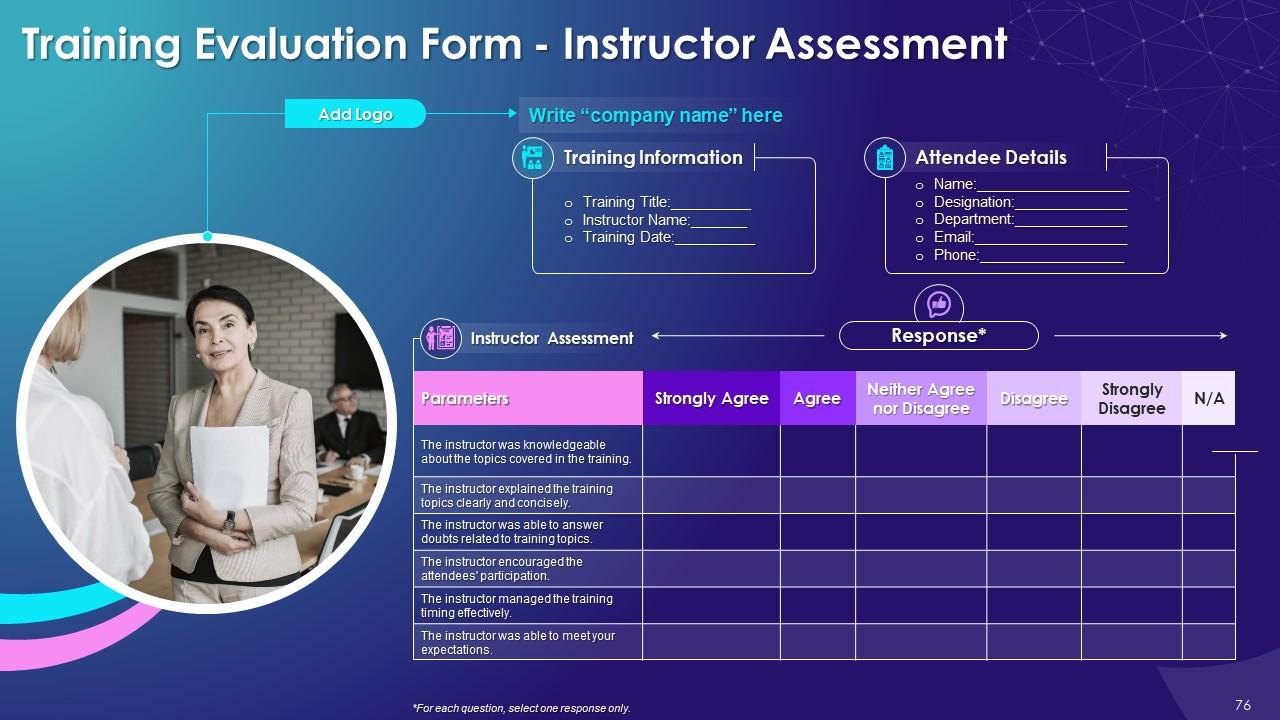
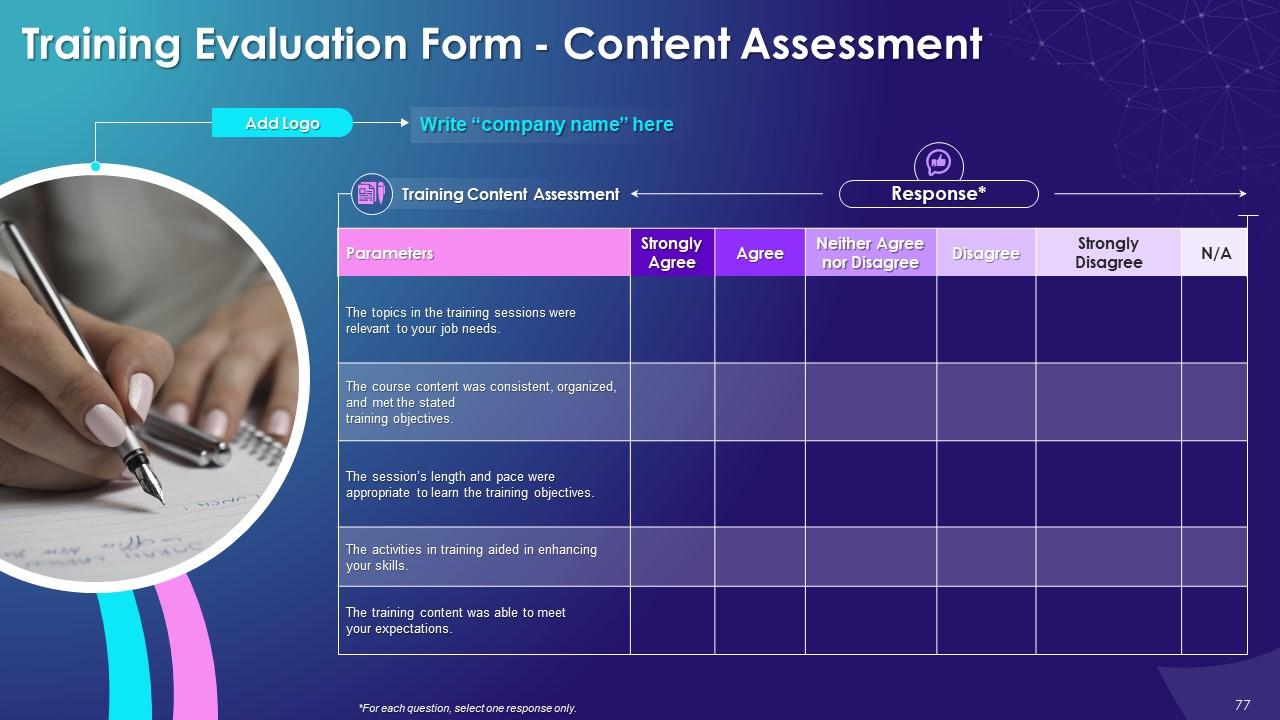
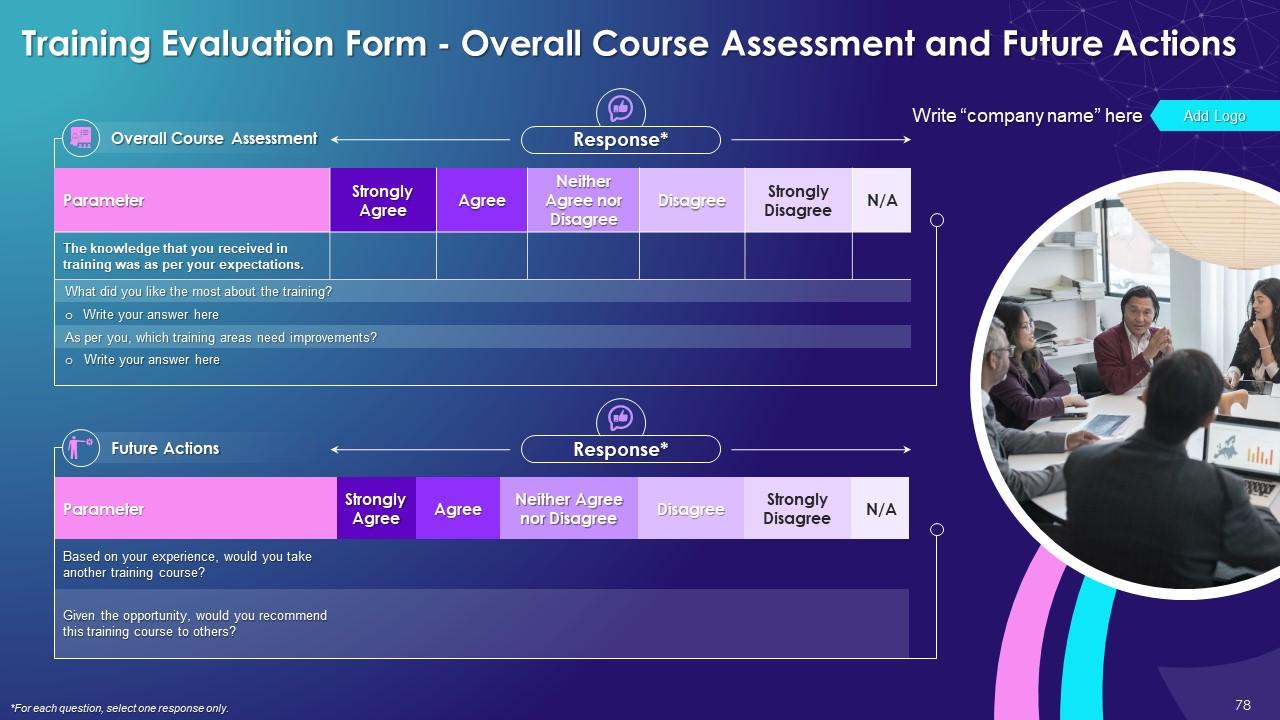
Slide 76 to 78
These slides include a training evaluation form for instructor, content and course assessment.
Decentralization And Distributed Systems In Blockchain Training Module Training Ppt with all 83 slides:
Use our Decentralization And Distributed Systems In Blockchain Training Module Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Colors used are bright and distinctive.
-
SlideTeam is very efficient when it comes to saving time. I am happy that I chose them for my presentation.