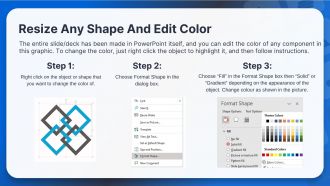
Closing Stage In Sales Process Training Ppt
This training module on Closing Stage in Sales Process in depth covers the concept of Closing and its Importance and why Salespeople Fail while Closing Salespeople Fail to Address the Needs of the Buyer, Salespeople Dont Establish Personal Relationships, Salespeople Dont Know How to Close, Salespeople Cant Converse Effectively with the Senior, The Salesperson is Not a Respected or Trusted Executive, Salespeople Fail to Express Knowledge About their Industry. Then, it comprehensively covers the popular Closing Techniques in Sales 1-2-3 Close, Adjournment Close, Affordable Close, Artisan Close, Assumptive Close, Empathy Close, Now-or-Never Close, Puppy Close, Quality Close, Rational Close, Summary Close, Opportunity-Cost Close, Ownership Close, Best-Time Close, Calendar Close, Testimonial Close, Concession Close, Conditional Close, Exclusivity Close, Yes-Set Close. Further, it includes the Top Customer Buying Signals and Complex Sales Closing Techniques SPIN, Challenger, NEAT, MEDDPICC. It also includes Activities, Key Takeaways, and Discussion Questions related to the topic to make the coaching session more interactive. The deck has PPT slides on About Us, Vision, Mission, Goal, 30-60-90 Days Plan, Timeline, Roadmap, Training Completion Certificate, and Energizer Activities.
This training module on Closing Stage in Sales Process in depth covers the concept of Closing and its Importance and why Sa..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Closing Stage in Sales Process. This deck comprises of 92 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content and present it confidently.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
This slide defines the closing stage in sales and its importance. The activities done by a salesperson to secure an agreement to the sale are known as "closing the deal," and they constitute one of the most crucial selling stages.
Slide 5
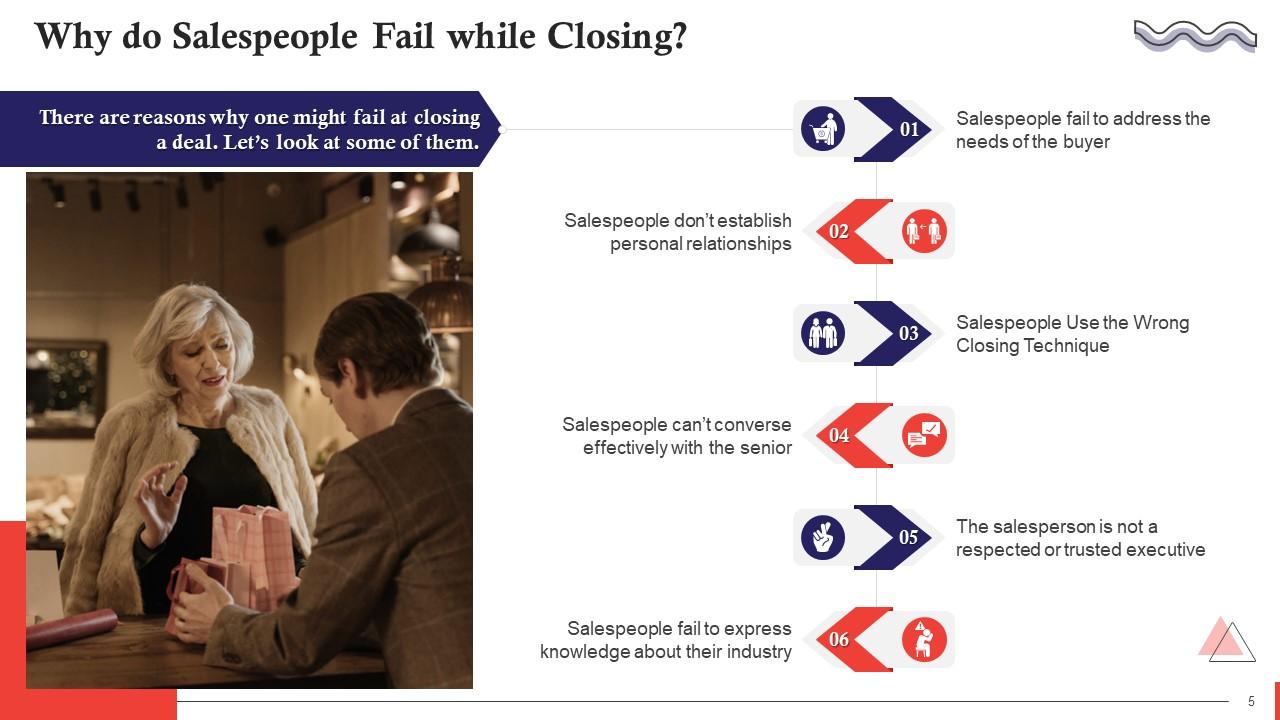
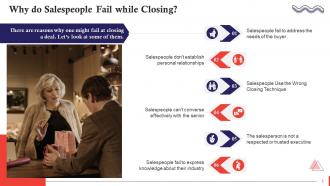
This slide highlights the reasons lead to failure, while closing in sales. The deal fails when a salesperson fails to address the needs of the buyer, doesn’t establish a personal relationship, uses the wrong closing technique, is unable to converse effectively, is not a respected or trusted executive, and fails to express knowledge about their industry.
Slide 6
This slide discusses the salesperson’s failure to address the needs of the buyer as a reason of a failed deal. Clients always look for ways to decrease expenses, increase revenues, gain competitive advantages, and anything that provides strategic value. As a salesperson, it becomes your responsibility to address those needs, and the client won't be able to justify the purchase if you fail to do so.
Slide 7
This slide discusses the salesperson’s failure to establish personal relationships as a reason for a failed deal. Sales revolve around building relationships and require you to be persistent. There is a point in the sales process where the client respects the salesperson's conviction and does not take offense at their persistence, which gives the desired room to establish a relationship.
Slide 8
This slide highlights the salesperson’s wrong choice of closing technique as a reason for the deal’s failure. All organizations need to realize how this inability to identify the appropriate closing technique hinders achievement of their goals. Companies must train their salespeople on how to close a deal successfully.
Slide 9
This slide discusses how a deal fails when salespeople are not able to converse with the seniors effectively. While salespeople primarily engage with lower-level or middle-level personnel, the occasional conversations with senior executives can determine the deal's outcome.
Slide 10
This slide talks about how a deal becomes difficult to close when the salesperson is not a trusted or respected executive. It is essential to train salespeople on how to build trust with their prospects. They should have genuine conversations with their clients to identify their needs and how the product/service they are offering meets a pressing and important need of their business.
Slide 11
This slide talks about how a deal fails when the salesperson is unable to express knowledge about his/her industry. The salesperson needs to display themselves as someone who knows the ins and outs of their industry. Moreover, they also need to showcase that they have done their research on the client and understands their needs
Slide 13
This slide introduces the concept of closing techniques in sales. There are many methods that salespeople use to persuade the customer into buying their product or service.
Slide 14
This slide discusses the 1-2-3 Closing Technique in Sales. This technique summarizes the points in groups of three, which could be the product’s attributes, advantages, or additional components. This slide also shows examples of this technique.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
The 1-2-3 Close technique works through the principle of triples, a pattern in which three elements are presented together, which serve as a coherent set of three hammer-blows to convey a compelling message.
Slide 15
This slide describes the Adjournment closing technique in sales. It also demonstrates an example that can be implemented during a sales presentation.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
- The relationship is crucial in many sales scenarios since the salesperson might return to the customer with new sales to make in the future. Therefore, it is better not to pressure them into making a decision when they are not ready
- Offering an adjournment is a pleasant surprise for the consumer who might be anticipating a pushier sales approach. This creates an exchange tension, which encourages them to accept your offer of more time in exchange for later accepting the agreement
Slide 16
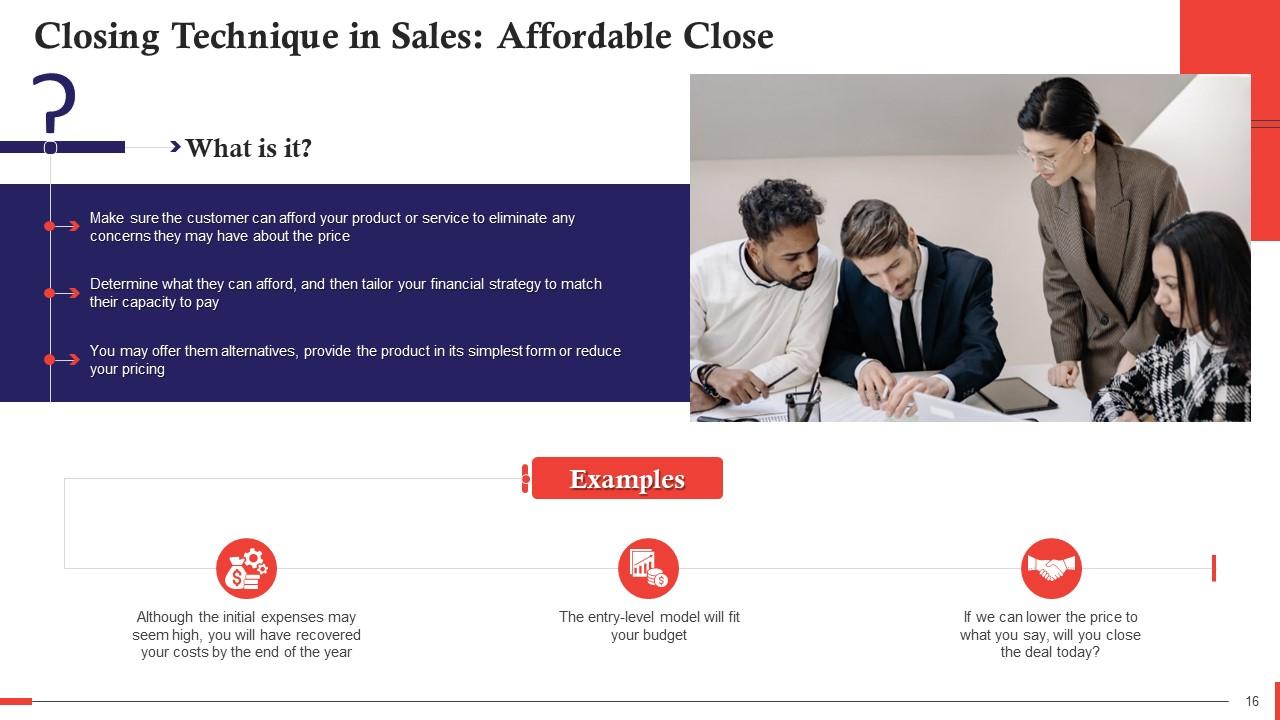
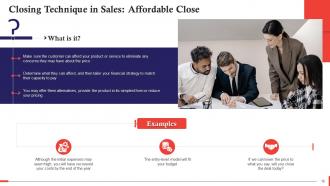
This slide describes the Affordable Closing technique in Sales. The affordable close makes sure that customer is able to afford your product or service to eliminate any concerns they may have about the price. This slide also shows examples of how to implement it.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
- The working principle behind affordable close is to design the deal's financial aspect that fits the customers' paying capabilities
- "I can't afford it," is typically used as an excuse rather than a genuine concern. An excellent way to distinguish the former from the latter is that the party will usually move on to another reason to reject the deal when the affordability concern is addressed and resolved
Slide 17
This slide talks about the artisan close. In this technique, the salesperson highlights the art, talent, and aptitude that went into creating the product or service being sold. This slide also shows examples of how to implement it.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
- While evaluating a product's cost, we consider the amount of time and labor that went into it. We frequently undervalue things because we are unaware of the time and work it took to create them
- Selling a product with artisan close increases the perceived value of the product by simply mentioning the skill of the manufacturers and the amount of time they spent creating it
Slide 18
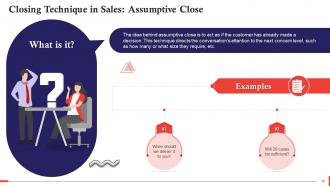
This slide describes the technique of assumptive close in sales. The idea behind assumptive close is to act as if the customer has already made a decision. This technique directs the conversation's attention to the next level of concern, such as how many or what size they require, etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
The Assumptive Close relies on the Assumption Principle, which states that when someone acts as though something is real & accurate, it is difficult for the other person to contradict/oppose it meaningfully.
Slide 19
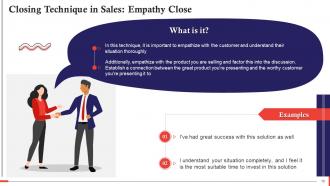
This slide discusses the technique of empathy close. In this technique, it is important to empathize with the customer and understand their situation thoroughly. This slide also shows examples of how to implement it.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
Empathy close entails harmonizing with the customer. When done right, you'll be able to close at the right time and for the correct reasons for the customer.
Slide 20
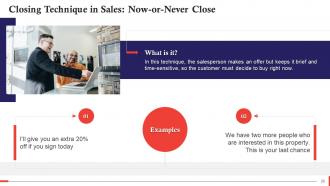
This slide talks about the Now-or-Never close. In this technique, the salesperson makes an offer but keeps it brief and time-sensitive, so the customer must decide to buy right now. This slide also shows examples of how to implement it.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
- The principle behind the Now-or-Never close is to give the customers a one-time deal
- Since there is less time to reflect and seek advice from others, the customer will be pushed to decide to buy now, fearing the loss of the deal
Slide 21
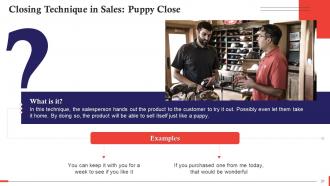
This slide discusses the puppy close technique in sales. In this technique, the salesperson hands out the product to the customer to try it out. Possibly even let them take it home. By doing so, the product will be able to sell itself just like a puppy.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
The puppy close works on the investment principle. When customers are given to try out the products, they associate with the products better and develop a natural fondness for them, which will make it difficult for him/her not to close the deal.
Slide 22
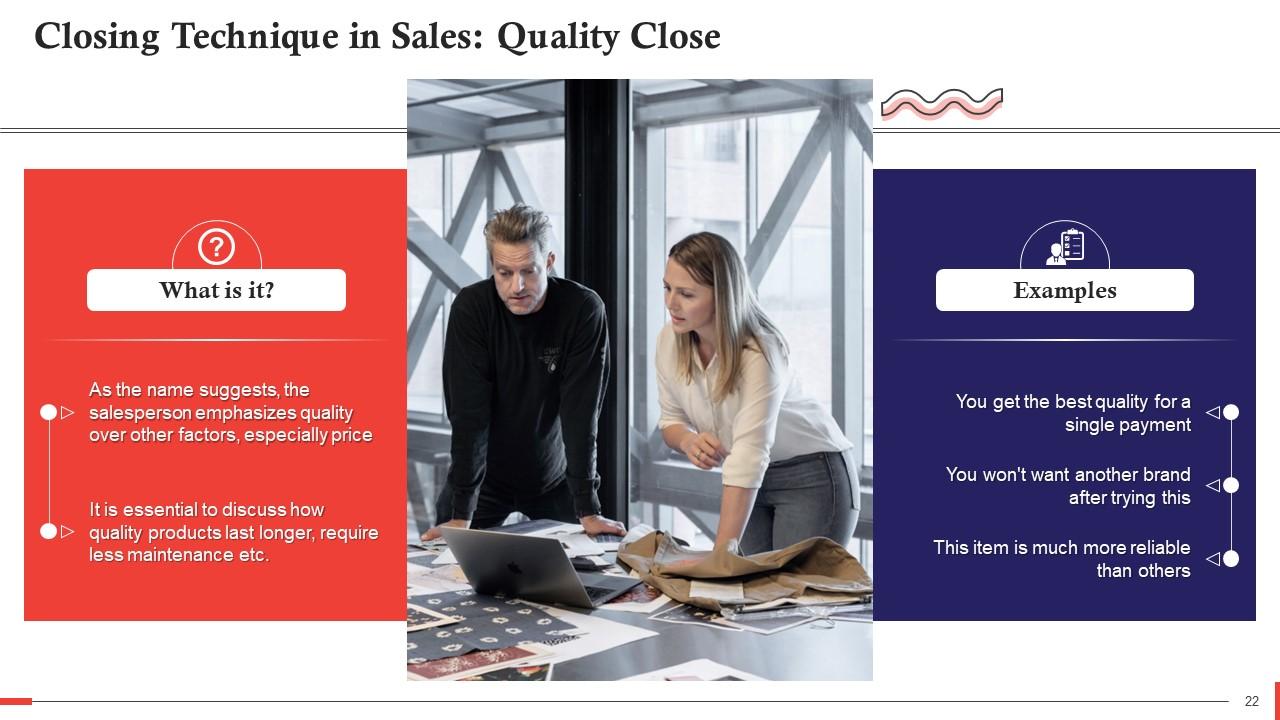
This slide talks about quality close technique in sales. As the name suggests, the salesperson emphasizes quality over other factors, especially price. This slide also shows examples of how to implement it.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
In this technique, the salesperson appeals either to the customer's vanity or their sense of long-term value. You associate them with higher and better quality for the former, and for the latter, you are reframing price across a long-time span.
Slide 23
This slide talks about rational close as a closing technique in sales. In this, the salesperson uses logic and reason to persuade the customer to buy the product. This is the most commonly used sales closing technique in B2B sales.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This strategy is effective simply by applying logic and scientific rational reasoning.
Slide 25
This slide discusses the summary closing technique in sales. In this technique, the salesperson summarizes all the benefits the customer will receive along with the full scope of what they are getting for their money.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
The summary close works by reaffirming the previously established understanding. When everything is put together in the end, it appears to be an even bigger package.
Slide 26
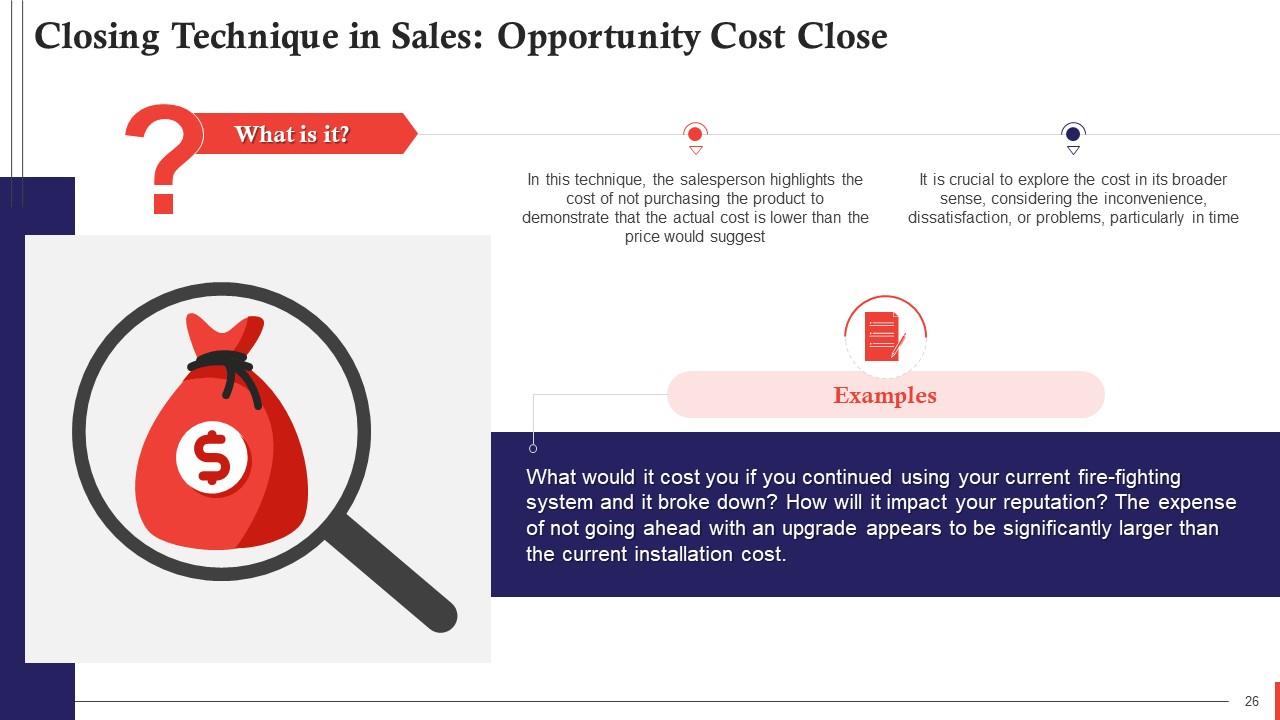
This slide talks about Opportunity cost closing technique in sales. In this technique, the salesperson highlights the cost of not purchasing the product to demonstrate that the actual cost is lower than the price would suggest.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
- The working of this technique lies in the difference between cost and price. In financial terms, "the opportunity cost" is the cost of not doing something. Cost refers to a range of issues which may or may not be measurable in money
- However, the price of a product is what the customer pays in cash, making the cost a salesperson's friend
Slide 27
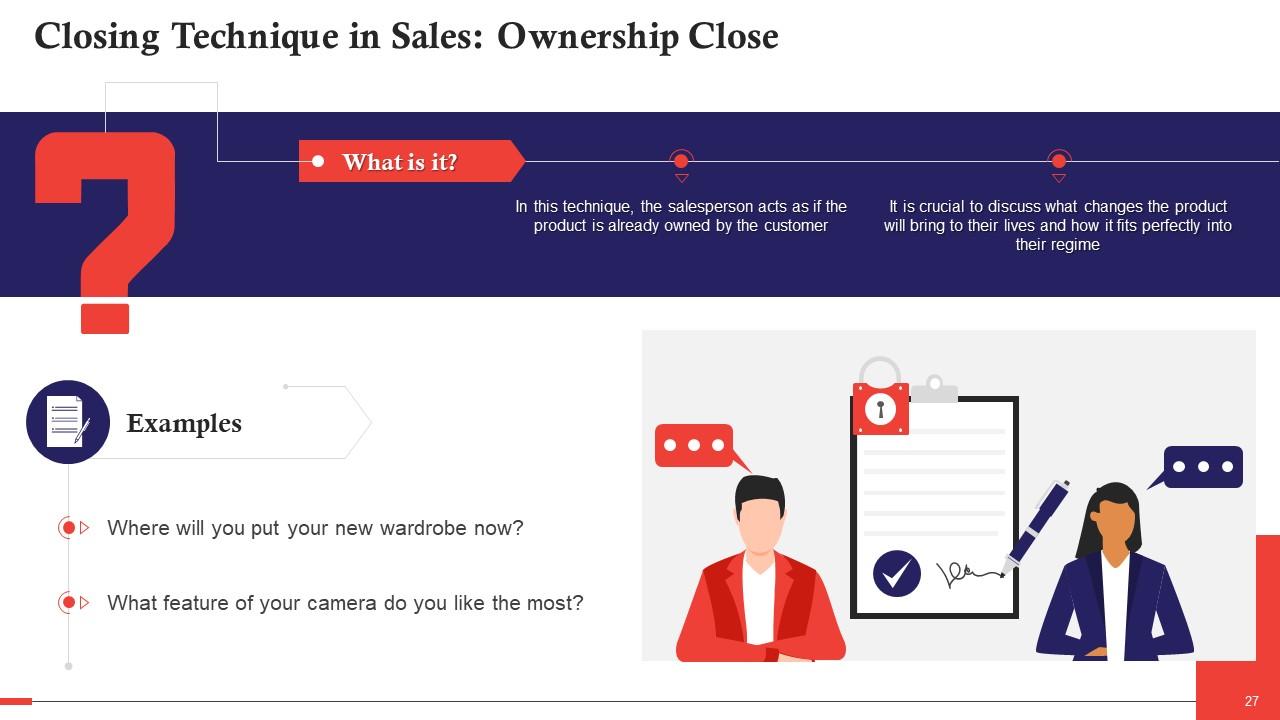
This slide discusses ownership close as a type of closing technique in sales. In this, the salesperson acts as if the product is already owned by the customer. It is crucial to discuss what changes the product will bring to their lives and how it fits perfectly in their regime.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This technique works on the principle of assumption, which implies that the customer already owns the product, and this assumption leaves no room for the thought of not owning the product.
Slide 28
This slide talks about the best-time closing technique in sales. This technique is generally used when customers procrastinate or are hesitant to go through with the deal. The salesperson must remind them of the short-term reasons that may affect the sale and other personal reasons which may prompt them to buy now.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This technique emphasizes that now is the best time to buy, and delaying would not be a wise decision.
Slide 29
This slide discusses the calendar closing technique in sales. In this technique, the salesperson fixes a future date for a meeting if the customer is not ready to go through with the sale now.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This technique makes the customer more comfortable as a future date may be agreed upon in exchange for you not pushing for the sale now. This time can be beneficial, as the customer can remain engaged with the product and consider the possibility of buying it.
Slide 30
This slide talks about the testimonial closing technique is sales. In this, the salesperson presents testimonials of happy customers to convince the prospect of the sale.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
By presenting a testimonial from an existing client, a salesperson can establish a strong connection of trust and prove credibility
Slide 31
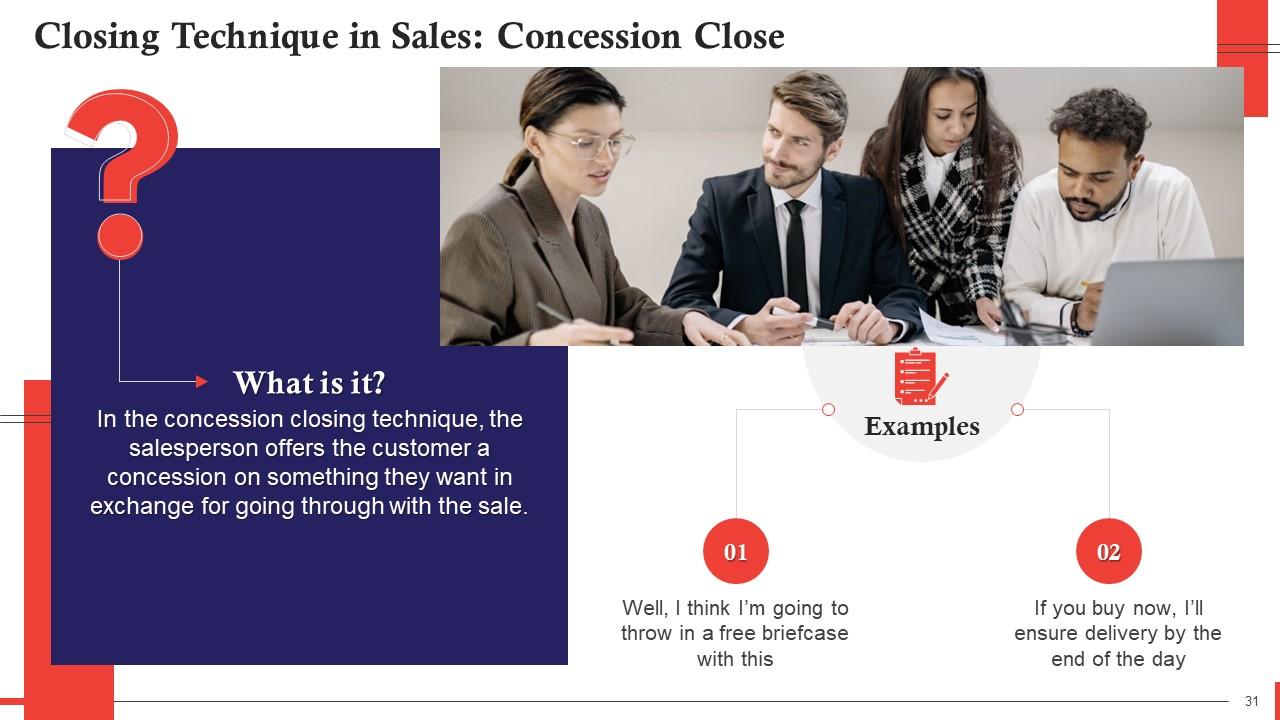
This slide talks about the concession closing technique in sales. In this, the salesperson offers the customer a concession on something they want in exchange for going through with the sale.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This technique works on the principle of incentivizing the customer by offering them a concession on something which will prompt them to go through with the sale.
Slide 32
This slide discusses the conditional closing technique in sales. In this, the salesperson offers to resolve the customer's objection in return for a sale.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This technique works on the exchange principle, which helps build a social agreement between the salesperson and the customer. The customer agrees to buy the product when the salesperson resolves their objection.
Slide 33
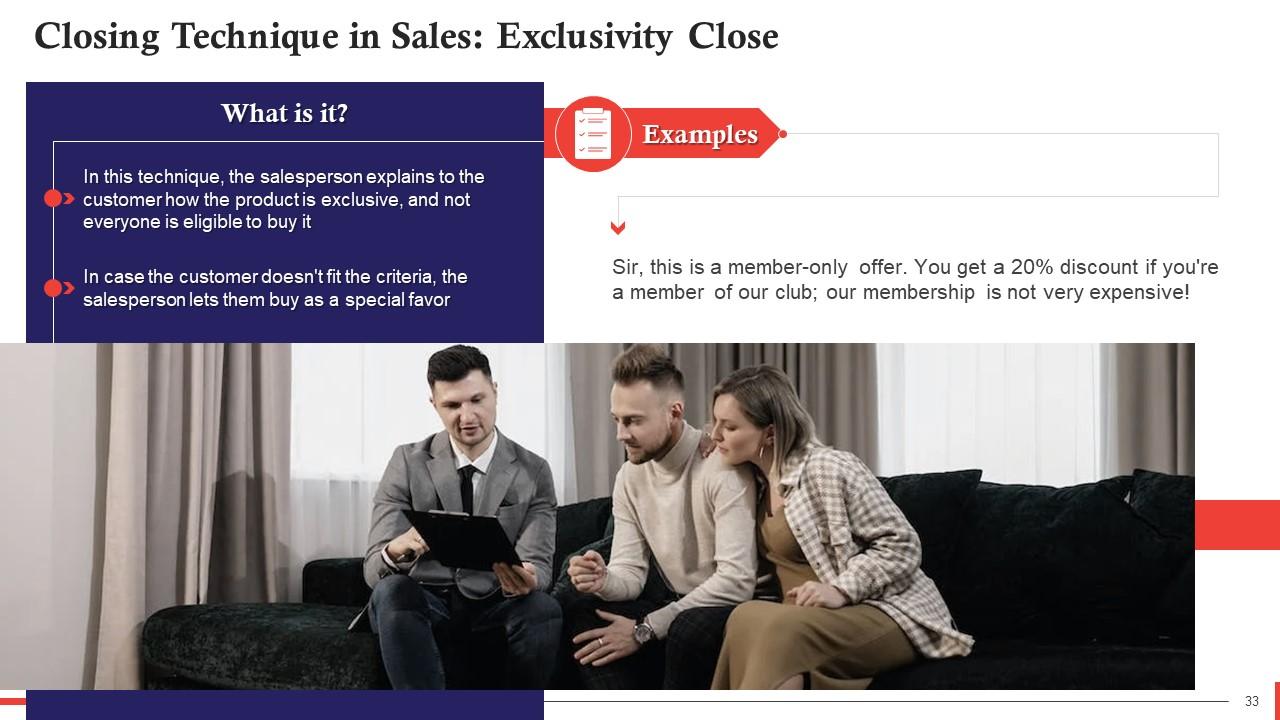
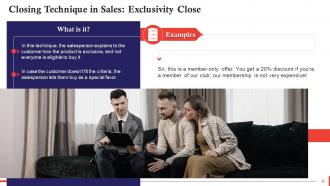
This slide talks about the exclusivity closing technique in sales. In this, the salesperson explains to the customer how the product is exclusive, and not everyone is eligible to buy it.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
- This technique establishes a sense of identity in customers when they're told that they qualify for something and belong in a "special group"
- When we are told that we can't have something, we are motivated to be a part of the special community and take control
Slide 34
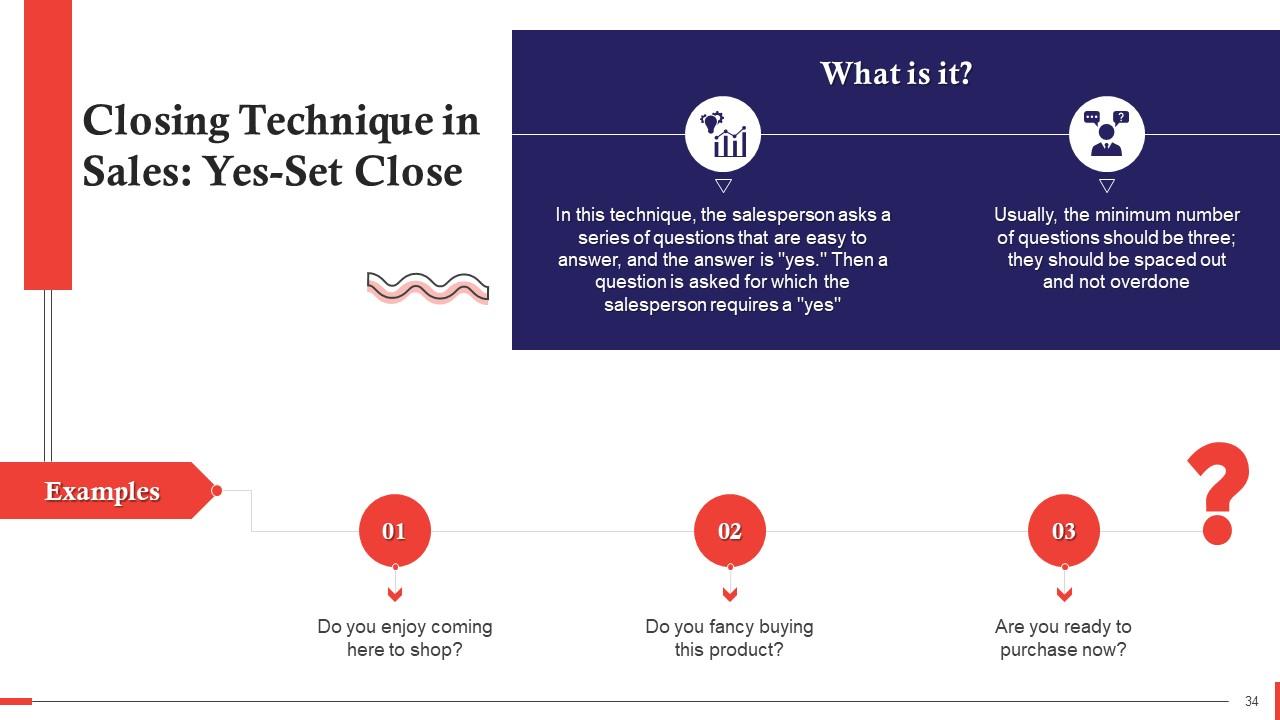
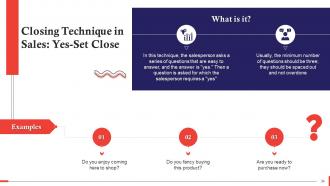
This slide discusses the yes-set closing technique in sales. In this, the salesperson asks a series of questions that are easy to answer, and the answer is "yes." Then a question is asked for which the salesperson requires a "yes"
Instructor’s Notes:
How does it work?
This technique works by getting the customer to answer “yes” repeatedly to make it the customer’s habitual response. After the pattern is established, the salesperson slips in the question he needs a “yes” to. Some people, in particular, don’t like answering “no” as they consider it impolite.
Slide 36
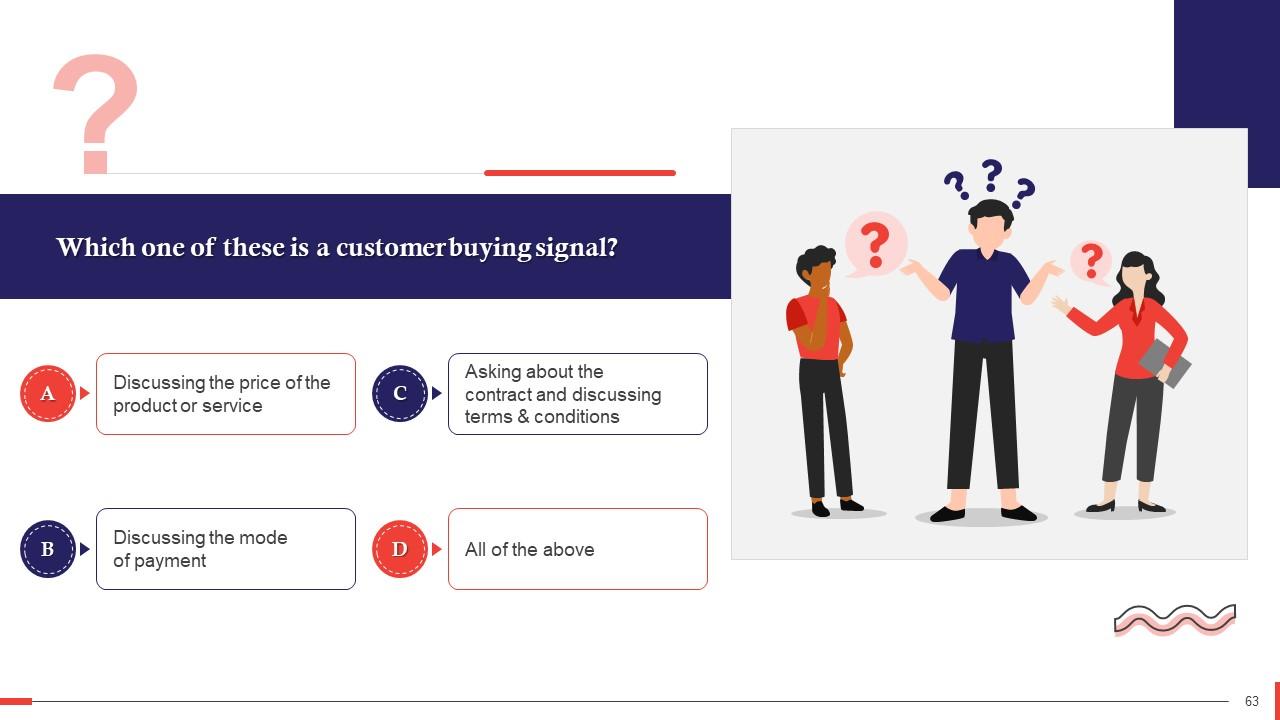
This slide introduces the concept of customer buying signals and their importance. A buying signal is an involuntary action by a customer to show their interest in your product, indicating that they're close to making a purchase.
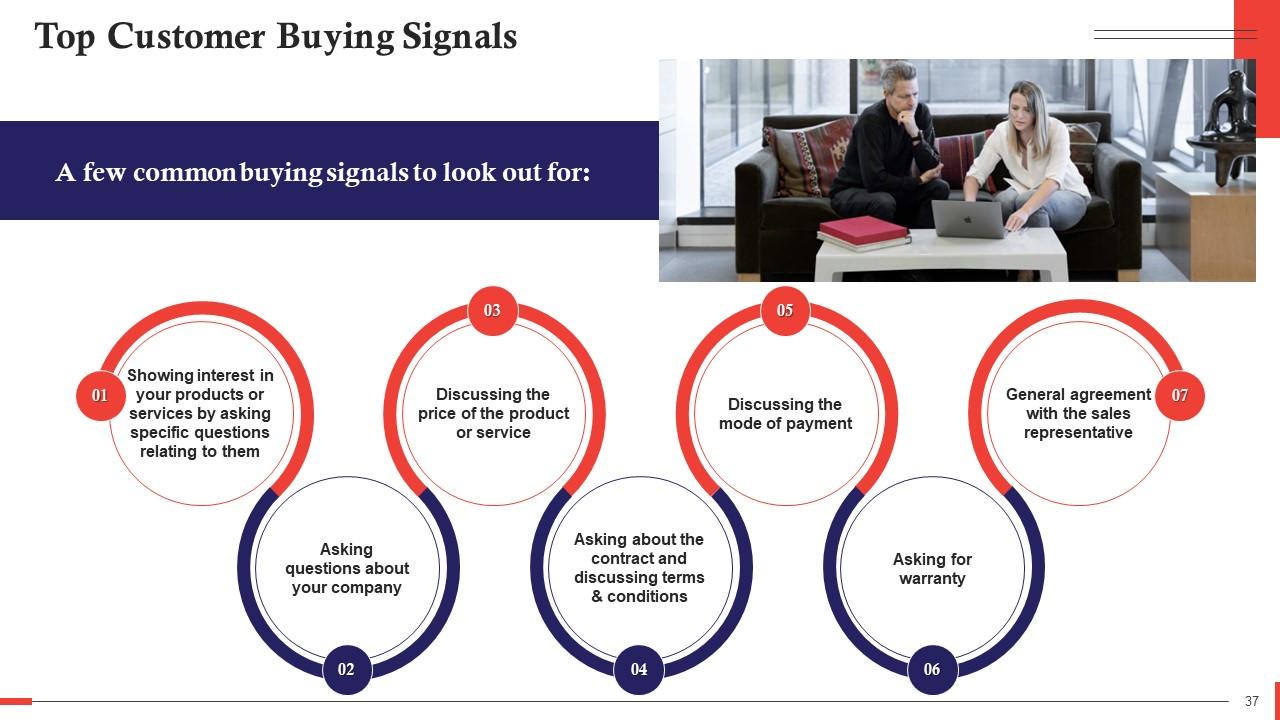
Slide 37
This slide lists some common buying signals. These are the customer showing interest in your products or services by asking specific questions relating to them, asking questions about your company, discussing the price of the product or service, etc.
Slide 38
This slide showcases how to respond to customer buying signals. While responding to the buying signals, the salesperson should move forward swiftly. There's a high chance that the customer is also looking at your competitors' products and not recognizing or responding to the buying signals promptly can cost you the sale.
Slide 39
This slide gives an introduction to a complex sale and how to close it. A complex sale generally involves a lengthier sales cycle which may require a lot of deliberation, multiple stakeholders and decision-makers, and frequently a high purchase price. Closing a complex sales process requires a more strategic approach to keep track of all variables. A salesperson may use many types of sales methodologies to close a sale.
Slide 40
This slide lists types of techniques to close sales with complex customers. These are SPIN selling, challenger sale, NEAT selling, and MEDDPICC.
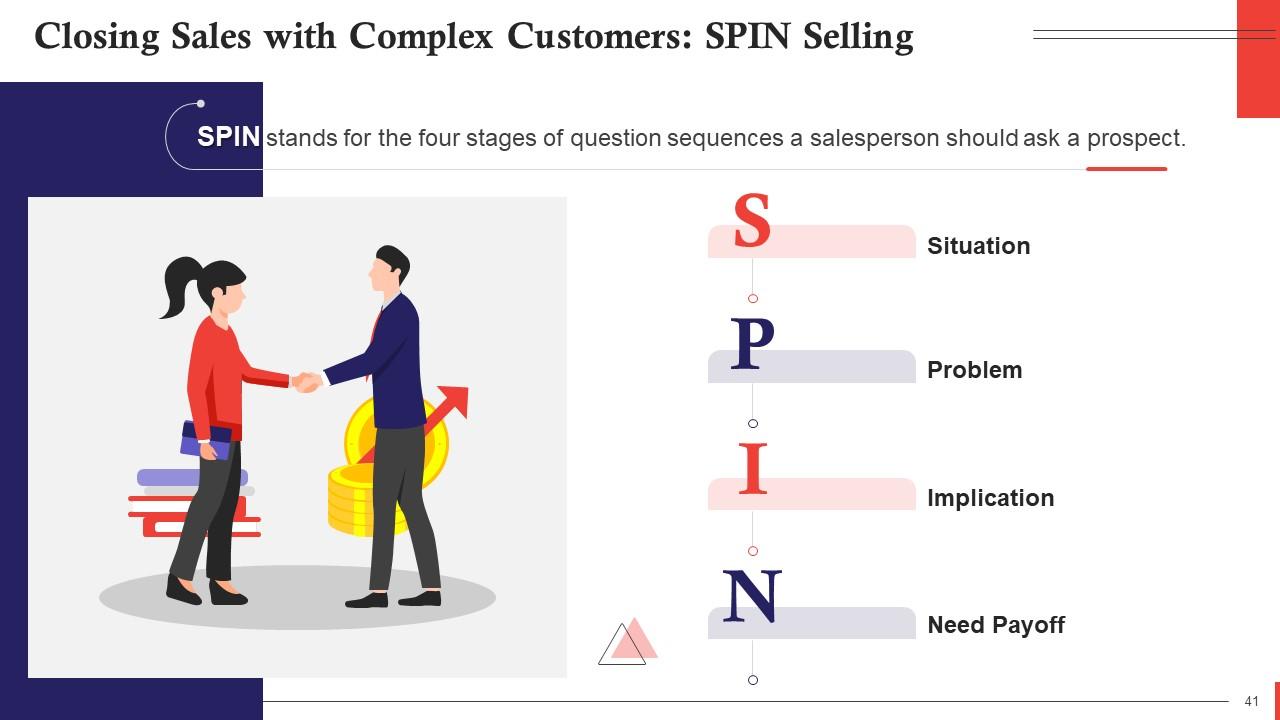
Slide 41
This slide gives an introduction to SPIN selling methodology to close complex sales. SPIN stands for the four stages of question sequences a salesperson should ask a prospect. These are situation, problem, implication, and need payoff.
Slide 42
This slide highlights the importance of Situation stage in SPIN selling. The aim behind the questioning sequence in this stage is to learn about and understand your prospect’s perspective.
Slide 43
This slide highlights the importance of Problem Stage in SPIN selling. In this stage, the aim is to get to the core of the prospect's issue. Sales representatives try to identify areas of potential opportunity and issues that the prospects may be unaware of or dissatisfied with.
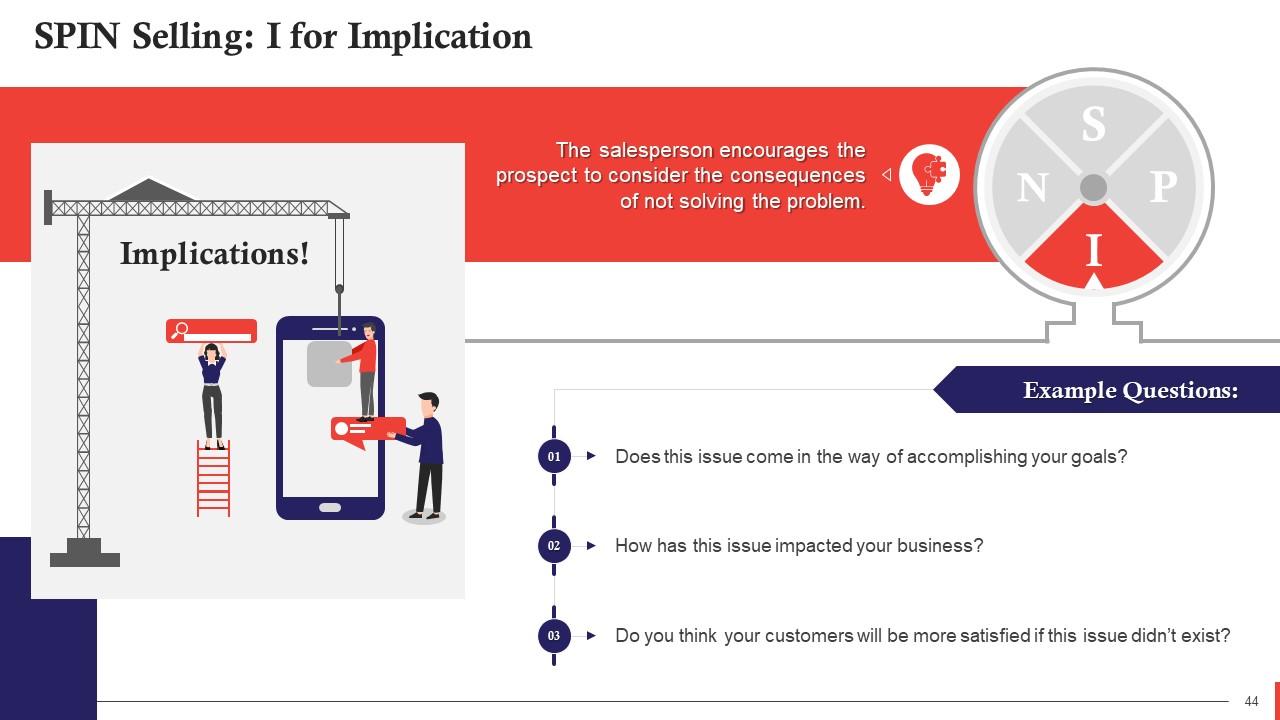
Slide 44
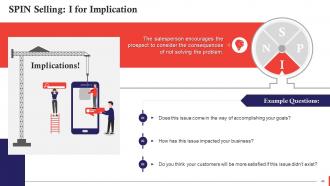
This slide highlights the importance of Implication Stage in SPIN selling. In this stage, the salesperson encourages the prospect to consider the consequences of not solving the problem.
Slide 45
This slide highlights the importance of Need Payoff Stage in SPIN selling. In this final questioning stage, the salesperson encourages the prospect to consider how their situation can improve if the problem is solved.
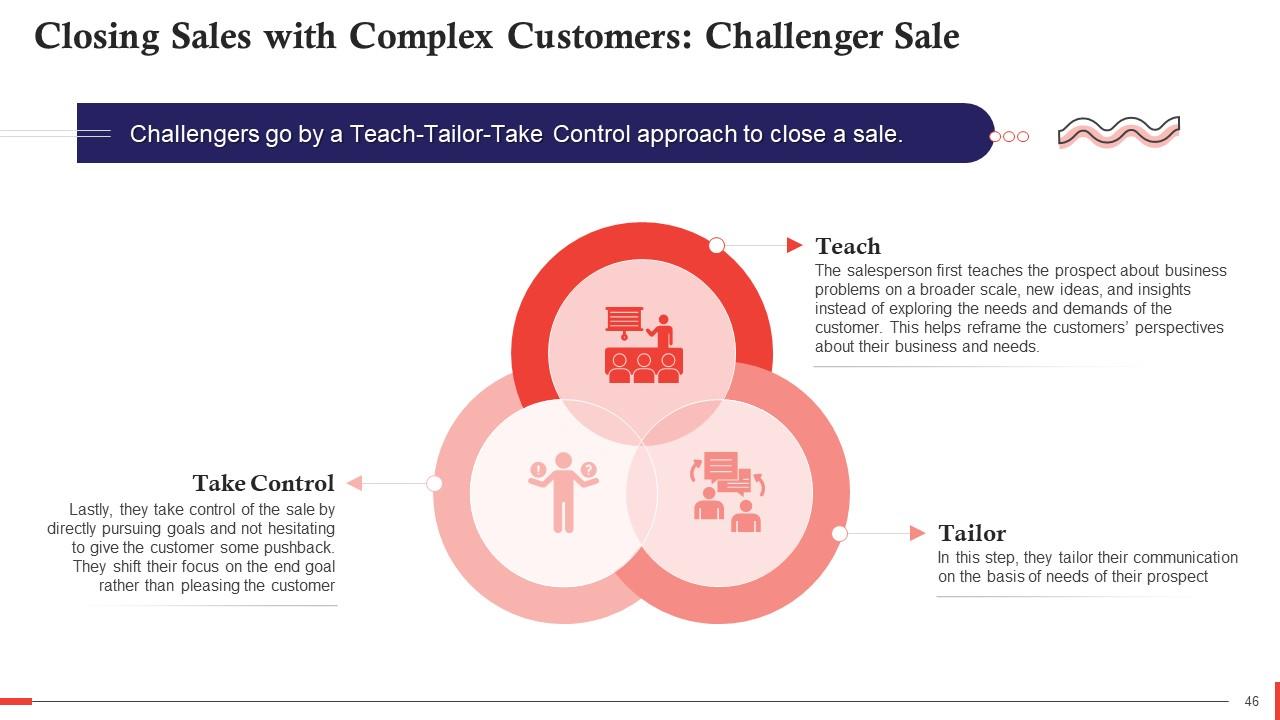
Slide 46
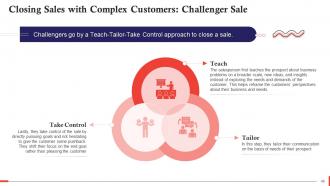
This slide gives an introduction to a Challenger Sale for closing sales with complex customers. In this methodology, challengers go by a Teach-Tailor-Take Control approach to close a sale.
Slide 47
This slide shows an example of how to close a complex deal using the challenger sale methodology. The situation entails a problem of acquiring customers. The sales rep disagrees with the solution the client thinks would be best for them. The sales rep then goes on to explain how their solution will be a better suit for their business supporting it through facts and data. The sales rep will be able to close the deal based on his domain knowledge and confidence rather than by pleasing the customer
Slide 48
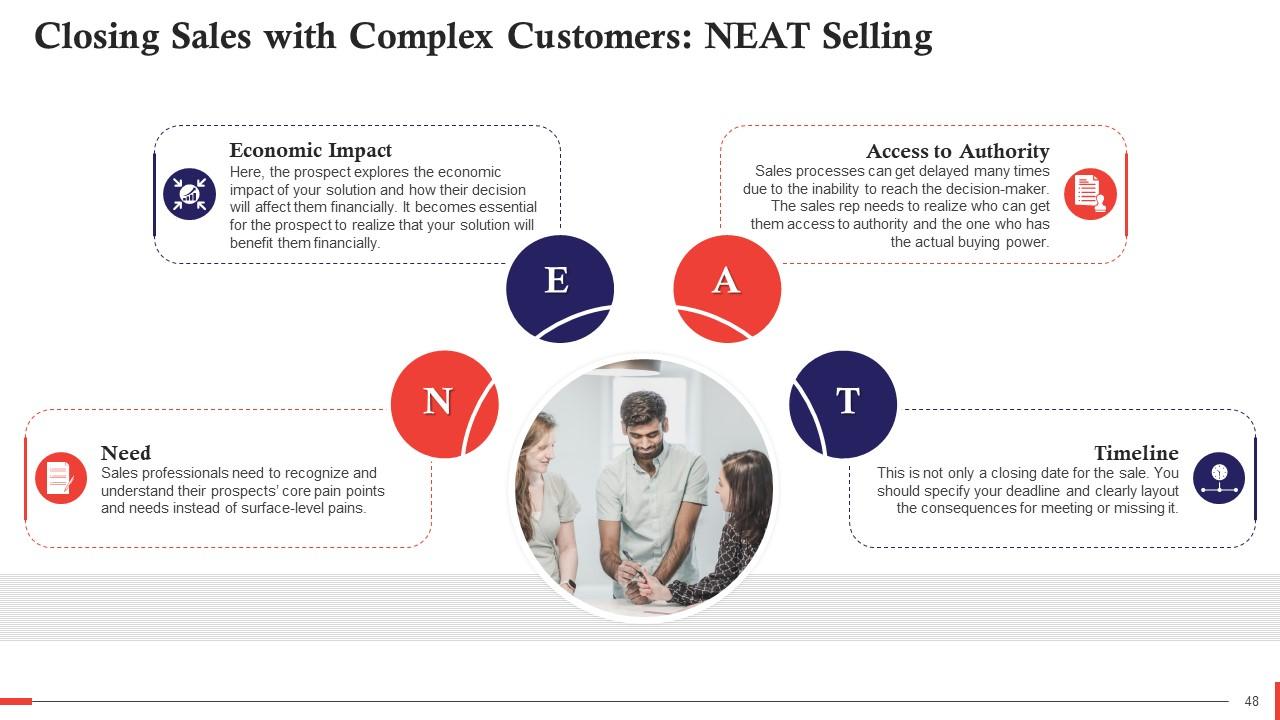
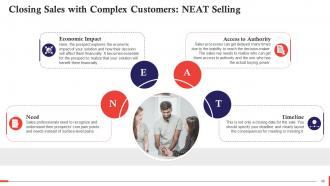
This slide depicts the NEAT selling methodology for closing sales with complex customers. NEAT is an abbreviation for Needs, Economic Impact, Access to Authority, and Timeline. It discusses the importance of understanding the customers’ core pain points, and making them understand how your solution will benefit them financially. NEAT also allows the sales rep to identify the person with actual buying power and help set a timeline for the sale.
Slide 49
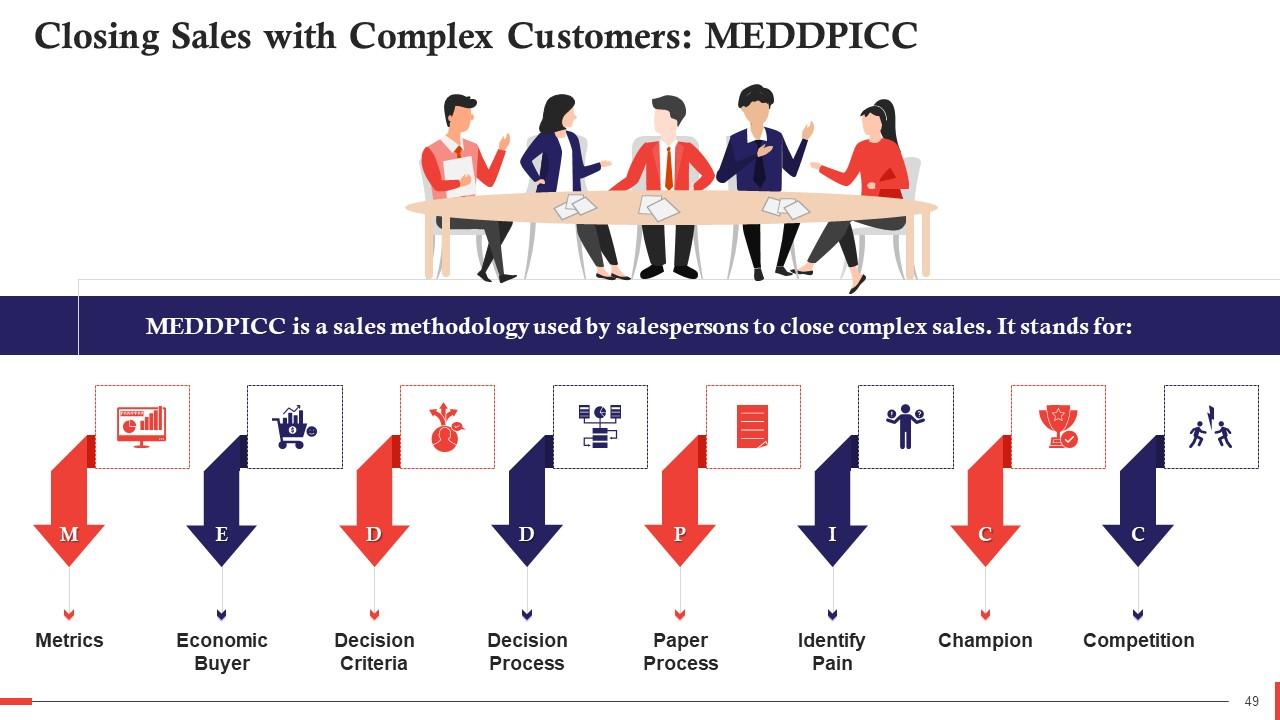
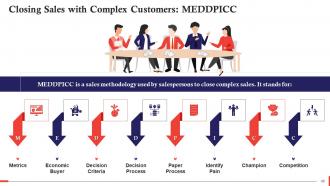
This slide showcases the MEDDPICC sales methodology to close sales with complex customers. It stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Paper Process, Identify Pain, Champion, and Competition.
Slide 50
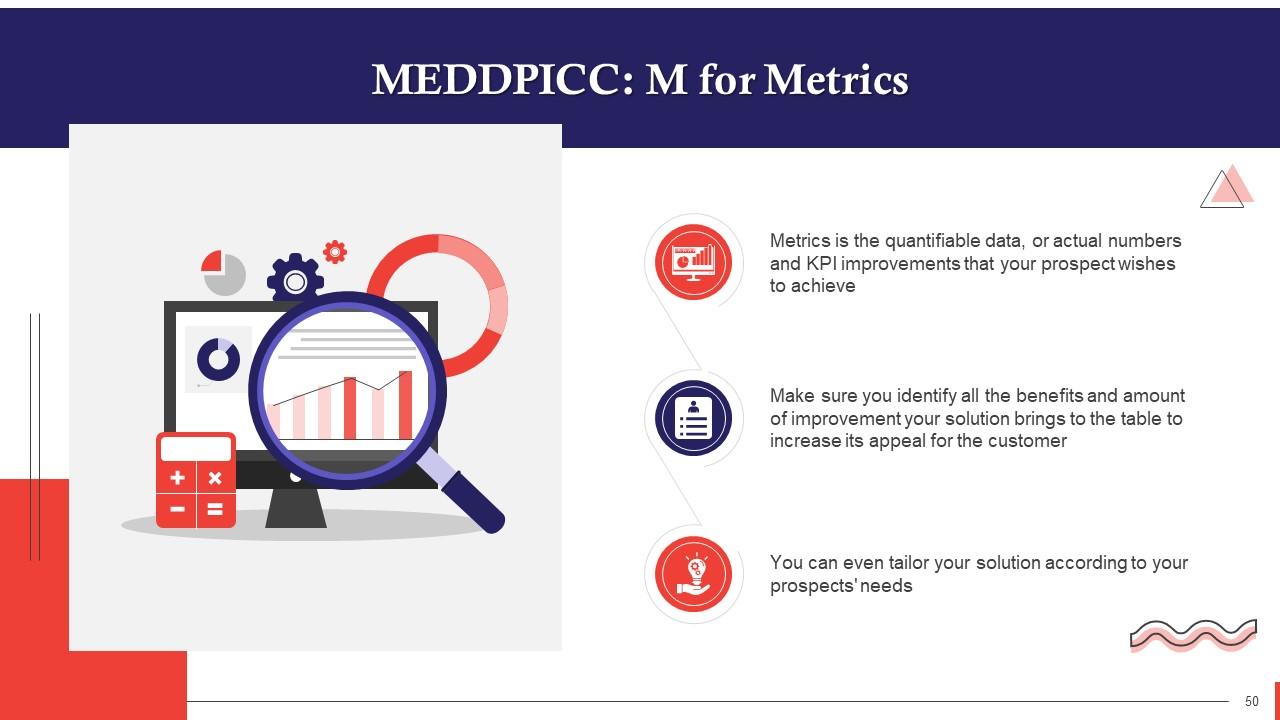
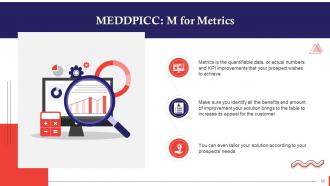
This slide highlights the importance of M or Metrics in MEDDPICC selling. Metrics is the quantifiable data, or actual numbers and KPI improvements that your prospect wishes to achieve. Make sure you identify all benefits and amount of improvement your solution brings to the table to increase its appeal for the customer.
Slide 51
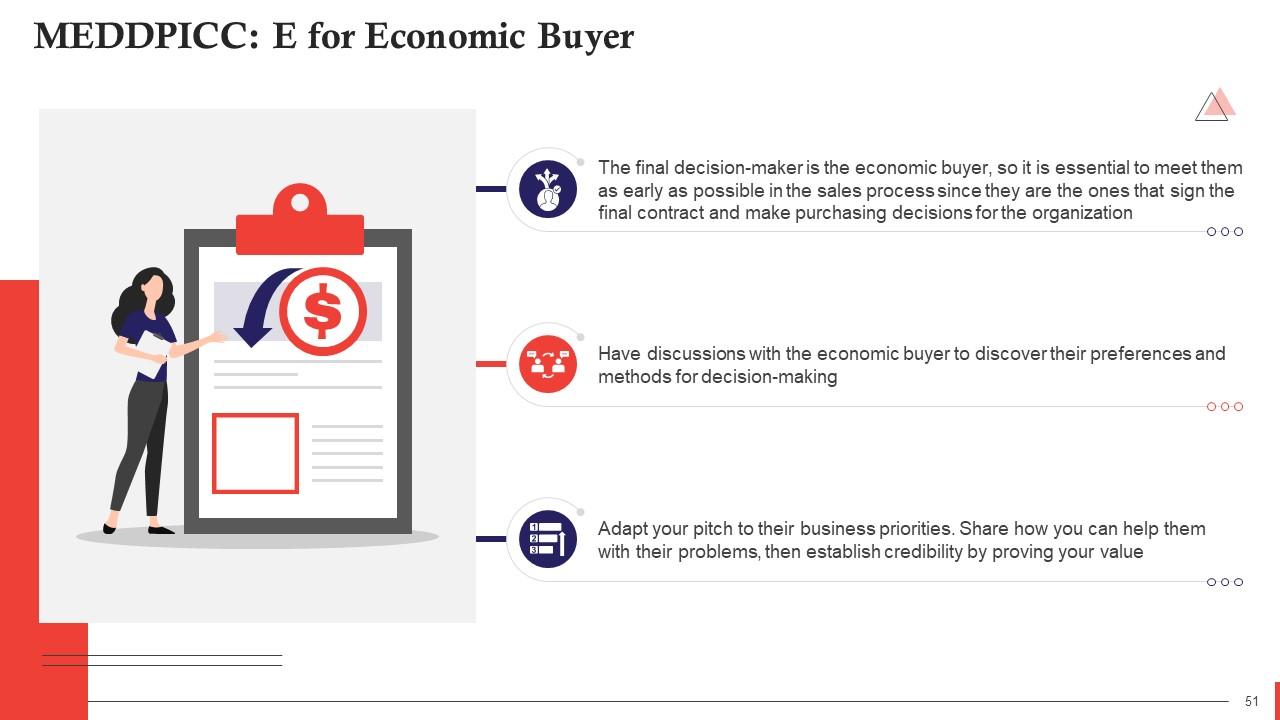
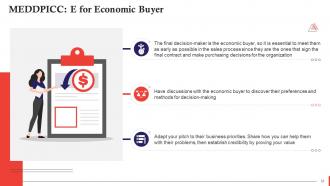
This slide talks about the importance of E or Economic Buyer in MEDDPICC selling. The final decision-maker is the economic buyer, so it is essential to meet them as early as possible in the sales process since they are the ones that sign the final contract and make purchasing decisions for the organization.
Slide 52
This slide highlights the importance of D or Decision Criteria in MEDDPICC selling. You need to understand how the prospect makes decisions. The objectives of buyers vary, and it is your responsibility to present your solution in such a way that the prospect believes it perfectly matches their unique wants and needs.
Slide 53
This slide talks about the importance of D or Decision Process in MEDDPICC selling. The Decision Process gives you information about your prospect company's decision-making process. You should gather all sorts of information like who is to be present in the meeting, what paperwork is required, insights about the approval process, etc.
Slide 54
This slide highlights the importance of P or Paper Process in MEDDPICC selling. A clear understanding of the paper process can help the sales rep make better decisions during the sales process and make more accurate predictions, increasing the chance of closing the deal.
Slide 55
This slide talks about the importance of I or Identify Pain in MEDDPICC selling. Customers will only buy your solution if they consider it valuable, meaning that your product or service can help them solve an issue they are facing. By recognizing their pain points accurately, sales reps can tailor their pitch accordingly to help the prospect understand how their solution will eliminate the pain.
Slide 56
This slide highlights the importance of C or Champion in MEDDPICC selling. This step entails engaging with your champion. Your internal representative, or an end-user who stands to gain the most from your solution, is your champion—an advocate who defends you in front of decision-makers and the economic buyer.
Slide 57
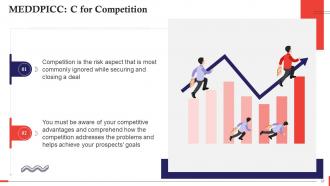
This slide talks about the importance of C or Competition in MEDDPICC selling. Competition is the risk aspect that is most commonly ignored when securing and closing a deal. You must be aware of your competitive advantages and comprehend how the competition addresses the problems and helps achieve your prospects' goals.
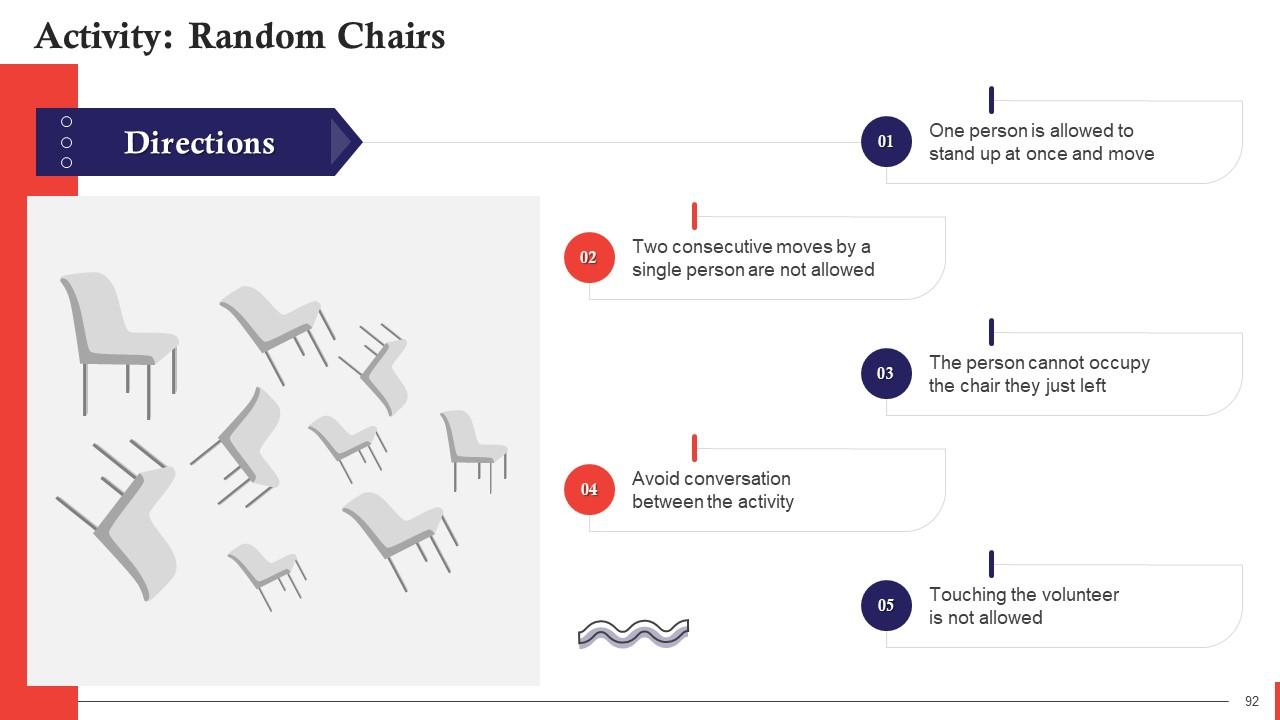
Slide 77 to 92
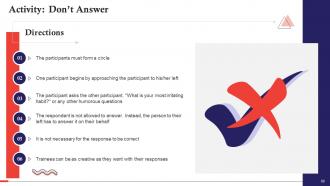
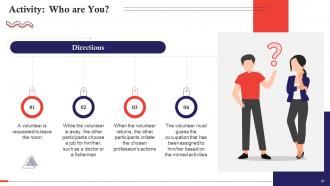
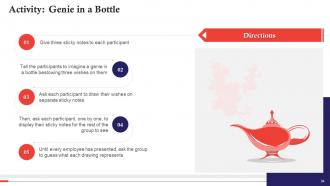
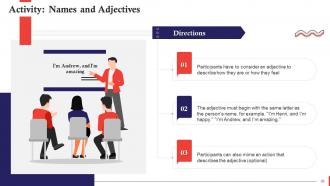
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Closing Stage In Sales Process Training Ppt with all 97 slides:
Use our Closing Stage In Sales Process Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Superb! The innovative and inspiring template designs provide an edge to the presentation.
-
Best Representation of topics, really appreciable.