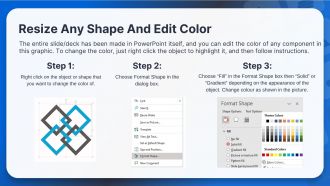
Types Of Load Balancer Powerpoint Presentation Slides
A load balancer increases concurrent user capacity and overall application dependability. A load balancer can arm by spreading the workload over several servers and reducing the total strain on each server. Check out our competently designed Types of Load Balancer template that gives a brief idea about a load balancer company, services, techniques provided for load balancing, and business needs. In this Load Balancer PowerPoint Presentation, we have covered the introduction of load balancing and load balancer, its benefits to the business, and its various types based on functions and configurations. In addition, this Load Balancing PPT contains cloud load balancing and its types and working of load balancers. Also, the PPT presentation covers methods and techniques used for load balancings, such as round-robin, source IP hash, least connections, least response time, and least bandwidth. Furthermore, this template shows a slide conducting a comparative analysis of load balancer with other technologies. Some of those are weighted round-robin vs. round-robin, hardware load balancer vs. software load balancer, etc. Download this template now.
A load balancer increases concurrent user capacity and overall application dependability. A load balancer can arm by spread..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
This complete presentation has PPT slides on wide range of topics highlighting the core areas of your business needs. It has professionally designed templates with relevant visuals and subject driven content. This presentation deck has total of fifty eight slides. Get access to the customizable templates. Our designers have created editable templates for your convenience. You can edit the color, text and font size as per your need. You can add or delete the content if required. You are just a click to away to have this ready-made presentation. Click the download button now.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1: This slide introduces Types of Load Balancer. State Your Company Name and begin.
Slide 2: This is an Agenda slide. State your agendas here.
Slide 3: This slide presents Table of Content for the presentation.
Slide 4: This is another slide continuing Table of Content for the presentation.
Slide 5: This slide highlights title for topics that are to be covered next in the template.
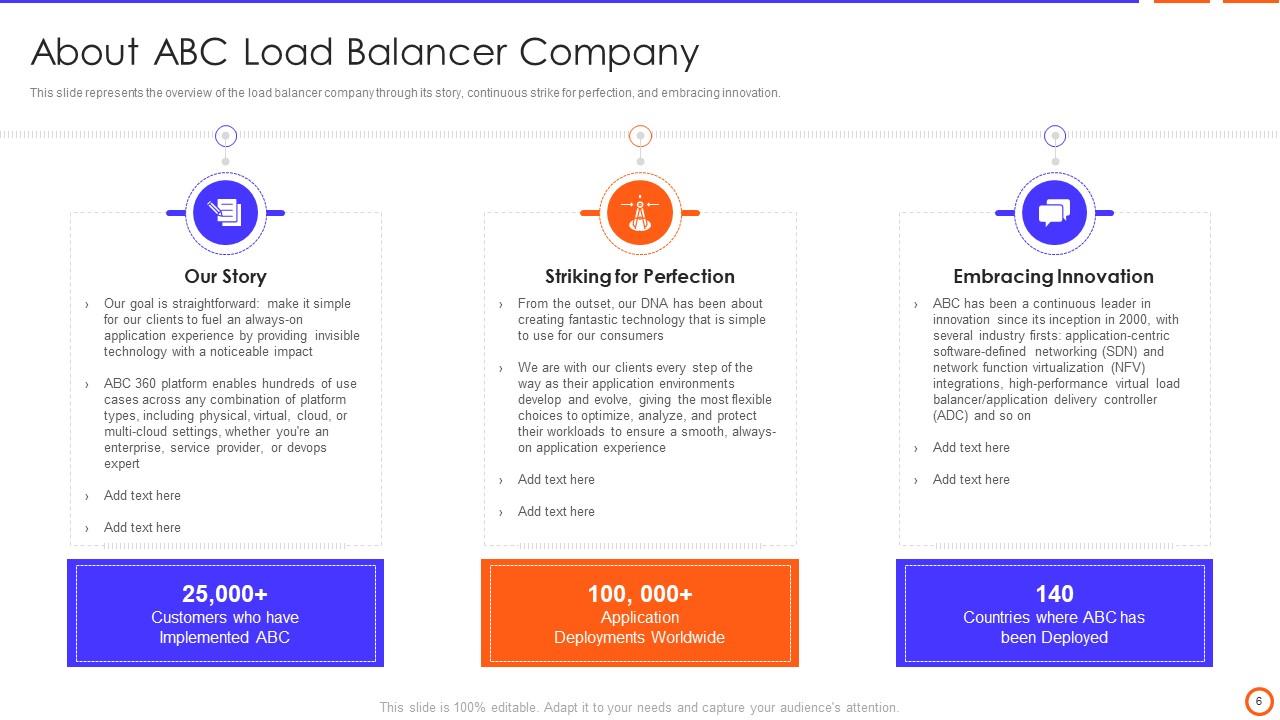
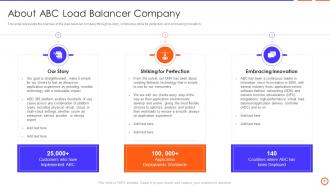
Slide 6: This slide represents the overview of the load balancer company through its story, continuous strike for perfection, and embracing innovation.
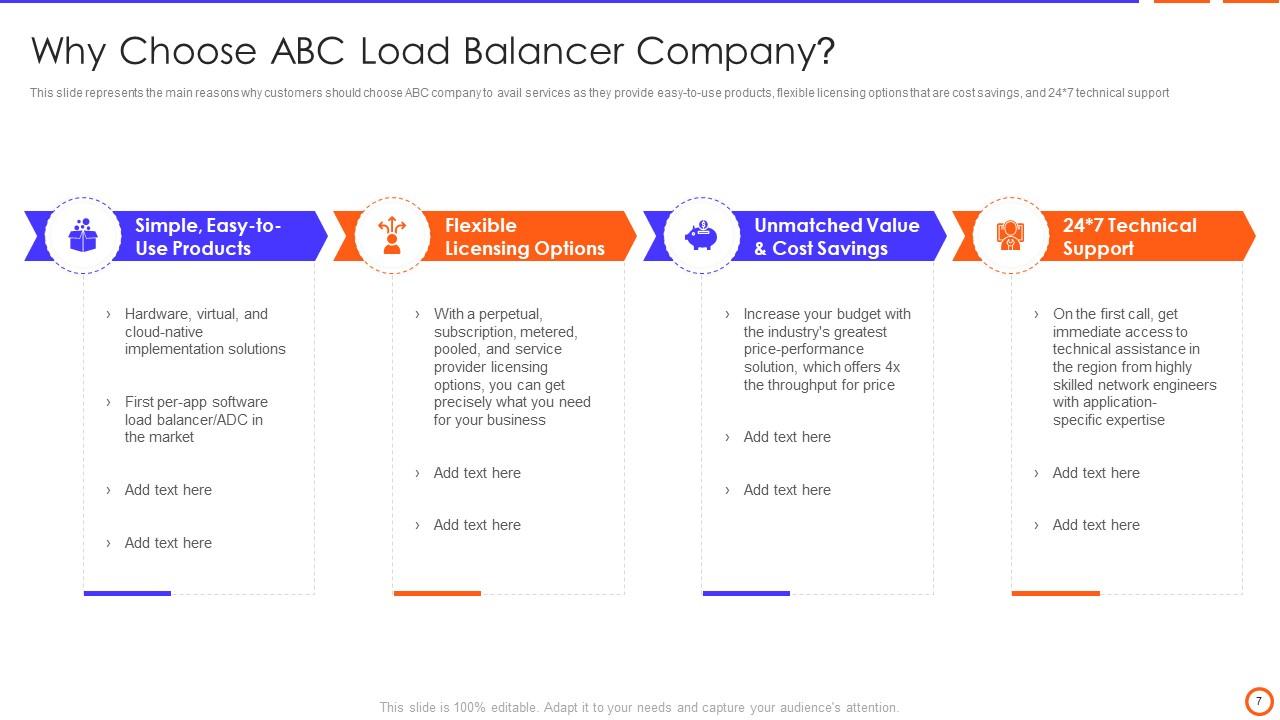
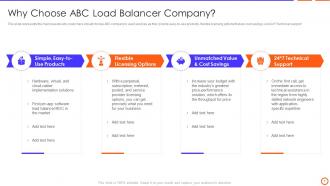
Slide 7: This slide represents the main reasons why customers should choose ABC company to avail services as they provide easy-to-use products, etc.
Slide 8: This slide displays the title for introduction of load balancing.
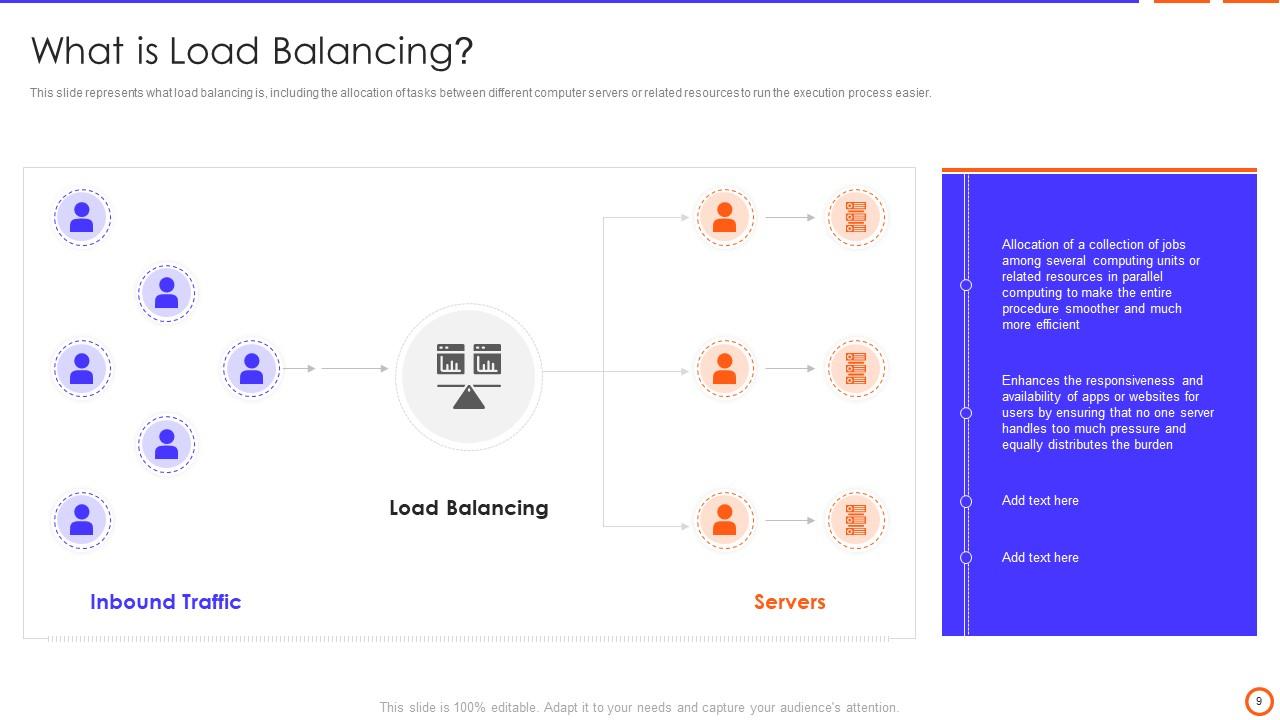
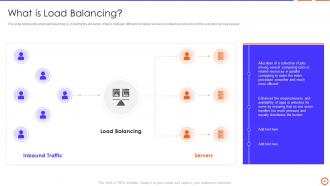
Slide 9: This slide represents what load balancing is, including the allocation of tasks between different computer servers or related resources.
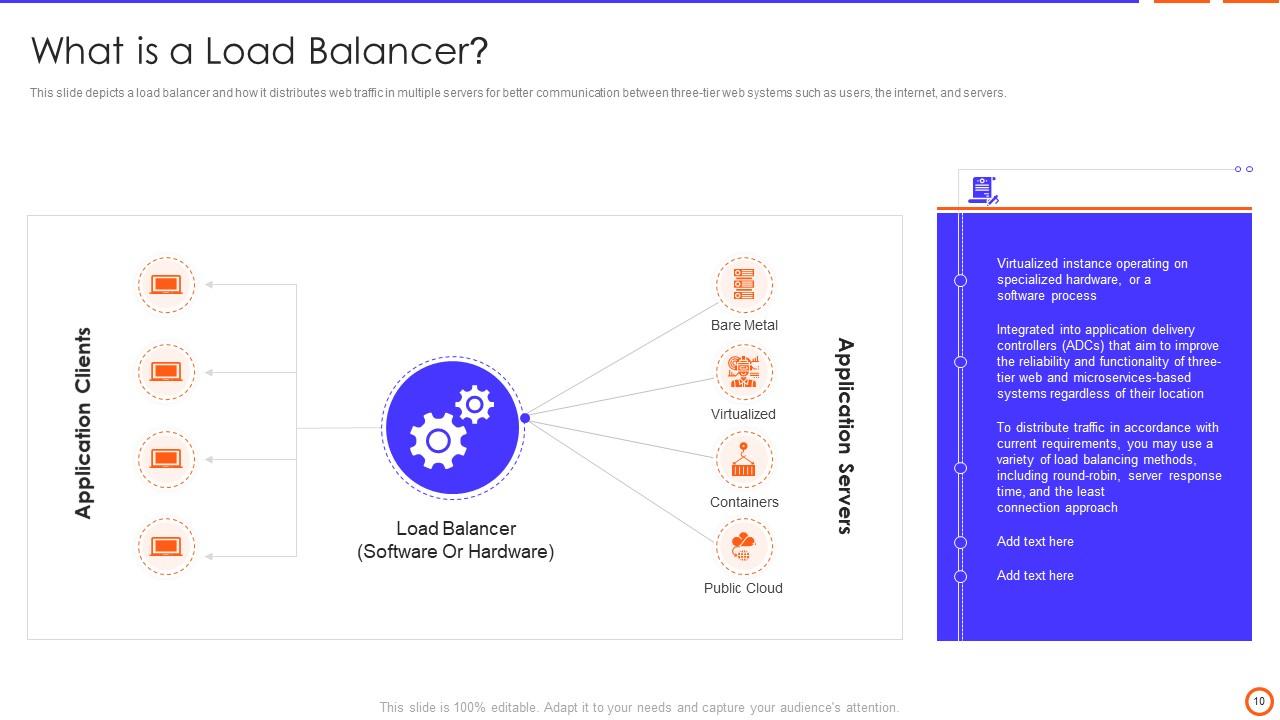
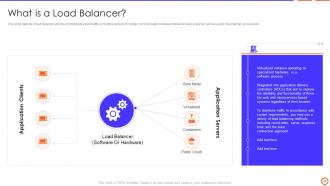
Slide 10: This slide depicts a load balancer and how it distributes web traffic in multiple servers.
Slide 11: This slide displays the title for need of load balancing in businesses.
Slide 12: This slide depicts two main reasons why load balancing is essential to achieve high availability and placing a command center in front of services.
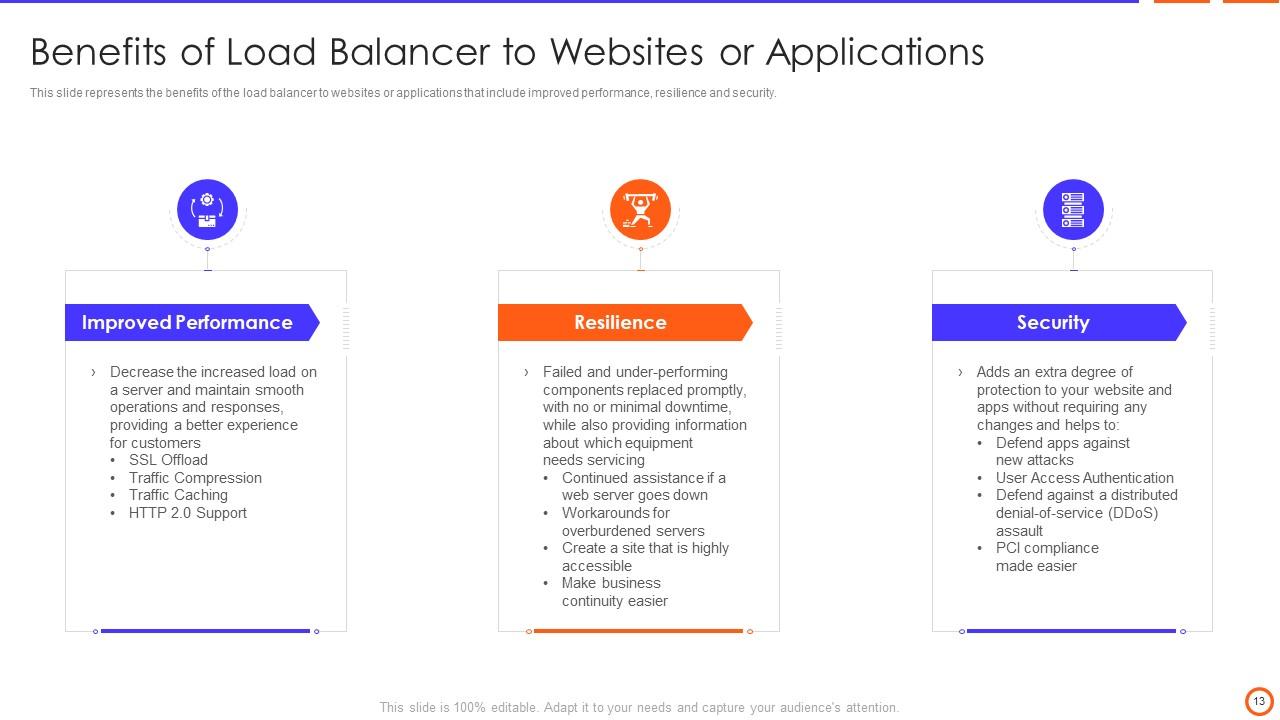
Slide 13: This slide represents the benefits of the load balancer to websites or applications that include improved performance, resilience and security.
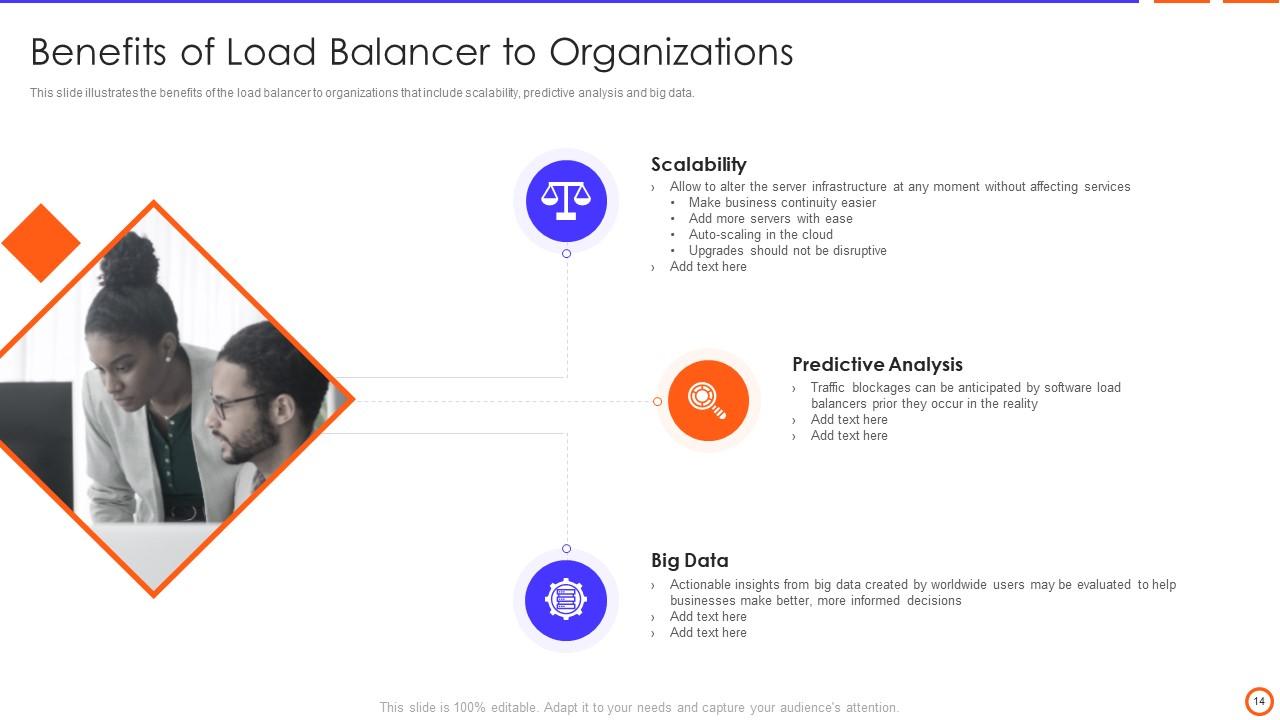
Slide 14: This slide illustrates the benefits of the load balancer to organizations that include scalability, predictive analysis and big data.
Slide 15: This slide presents the title for types of load balancers.
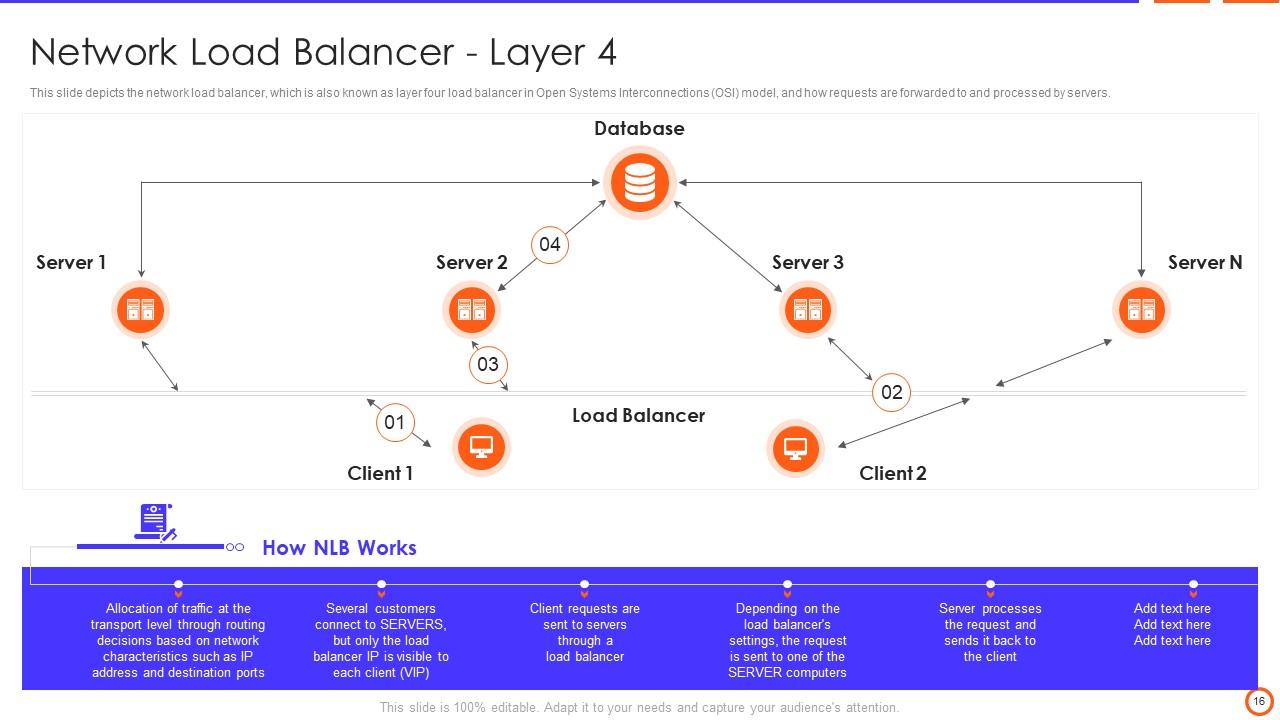
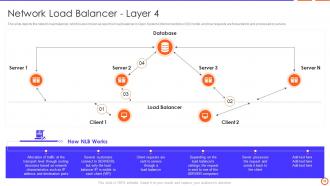
Slide 16: This slide depicts the network load balancer, which is also known as layer four load balancer in Open Systems Interconnections (OSI) model.
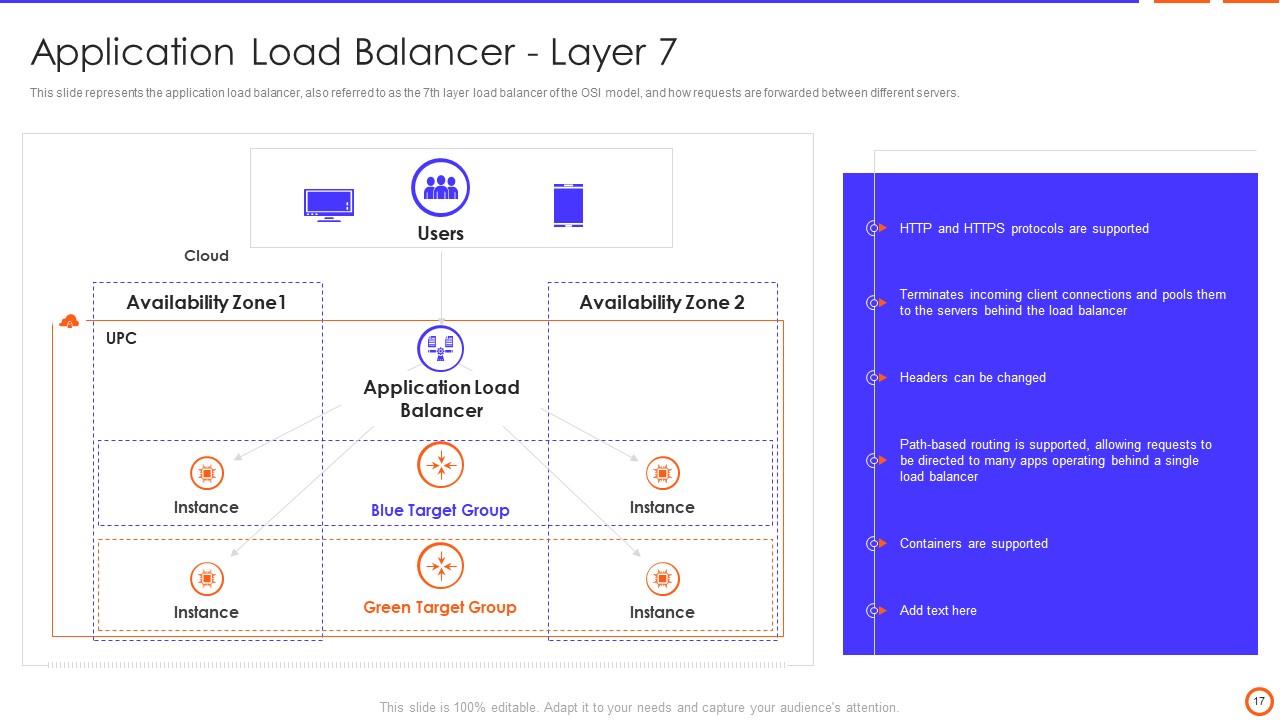
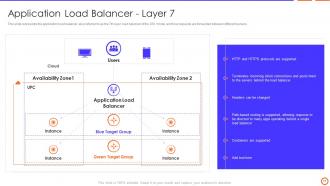
Slide 17: This slide represents the application load balancer, also referred to as the 7th layer load balancer of the OSI model.
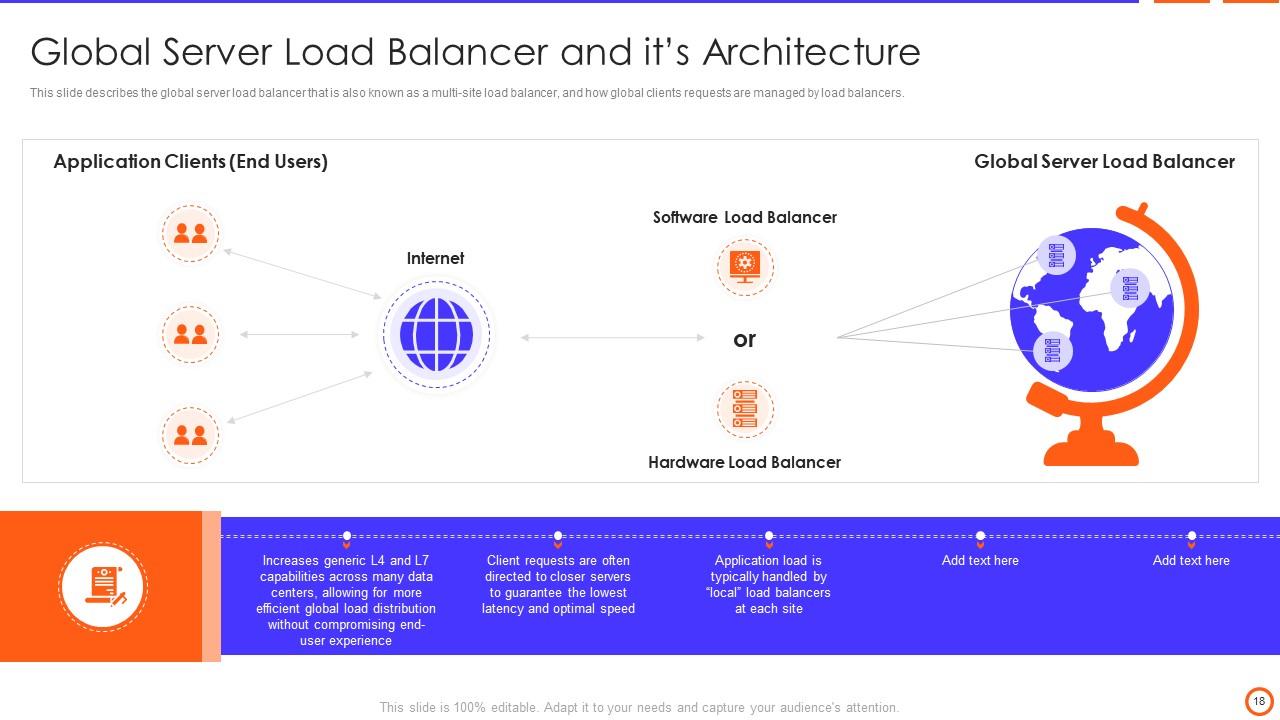
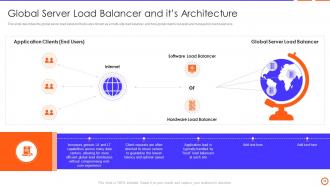
Slide 18: This slide describes the global server load balancer that is also known as a multi-site load balancer.
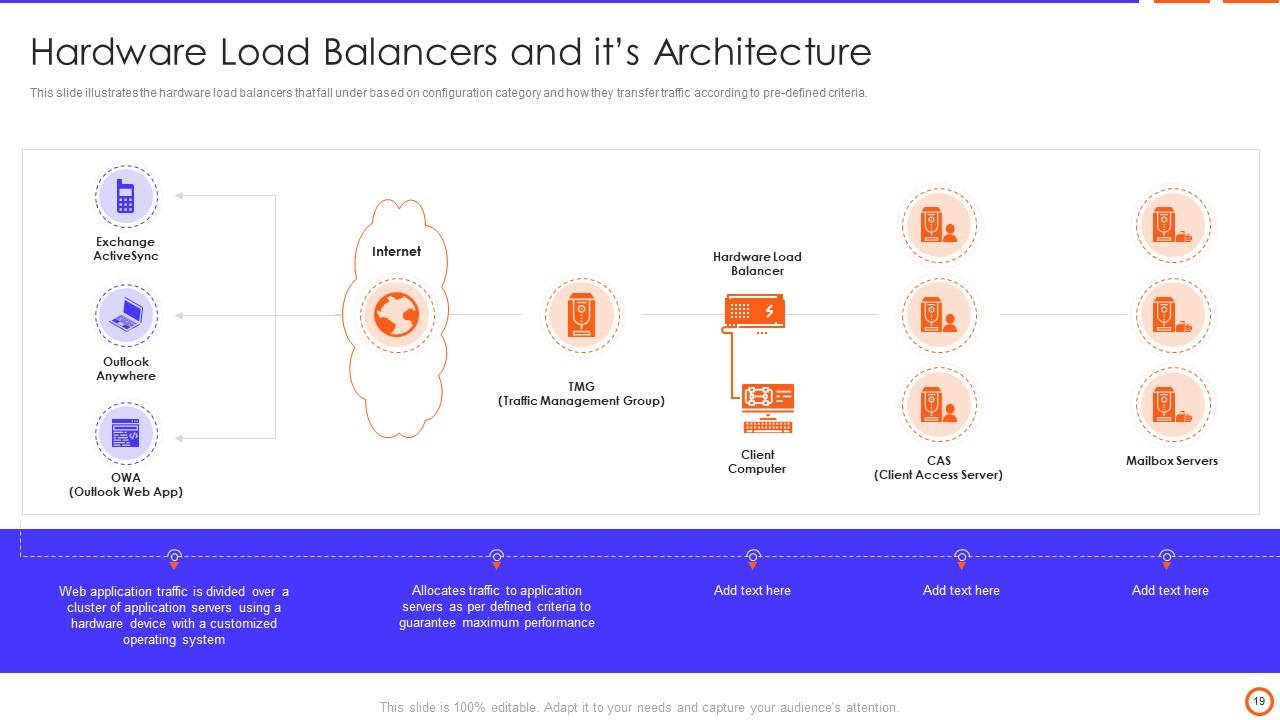
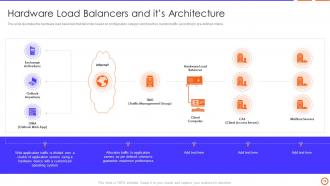
Slide 19: This slide illustrates the hardware load balancers based on configuration category and how they transfer traffic according to pre-defined criteria.
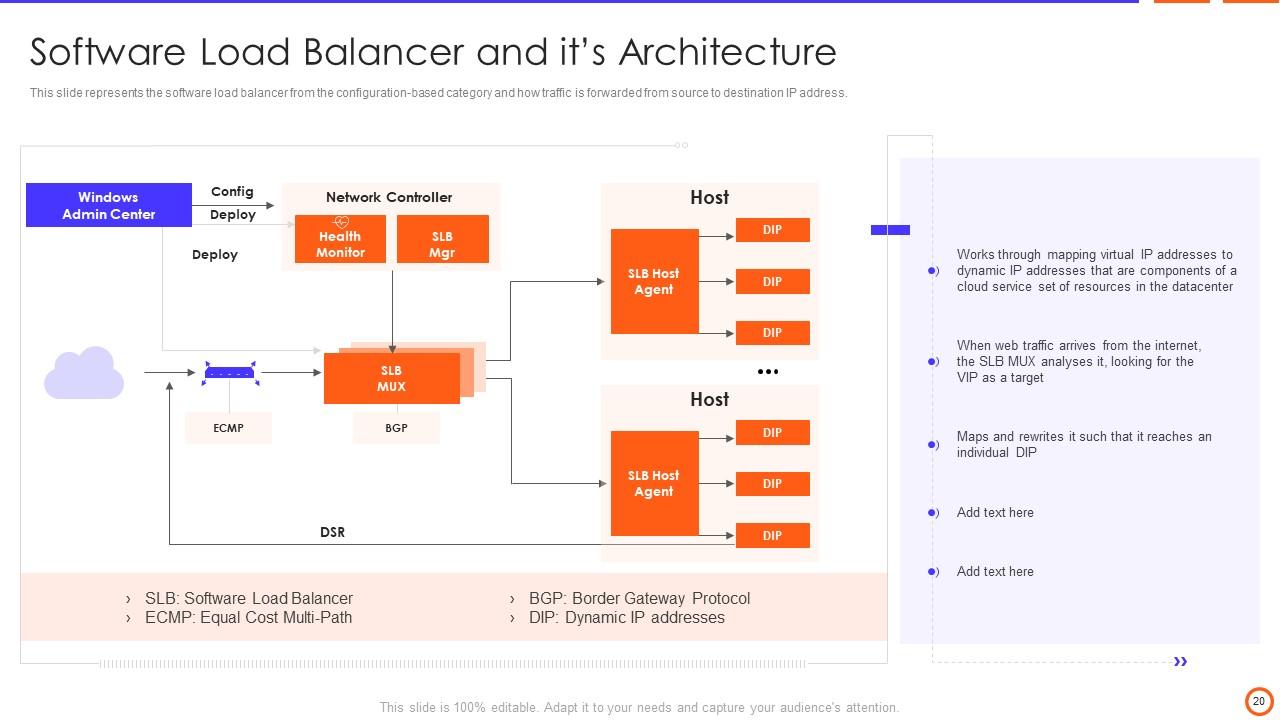
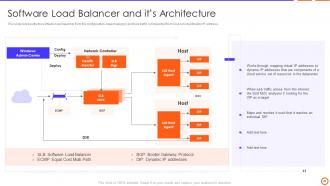
Slide 20: This slide represents the software load balancer from the configuration-based category and how traffic is forwarded from source to destination IP address.
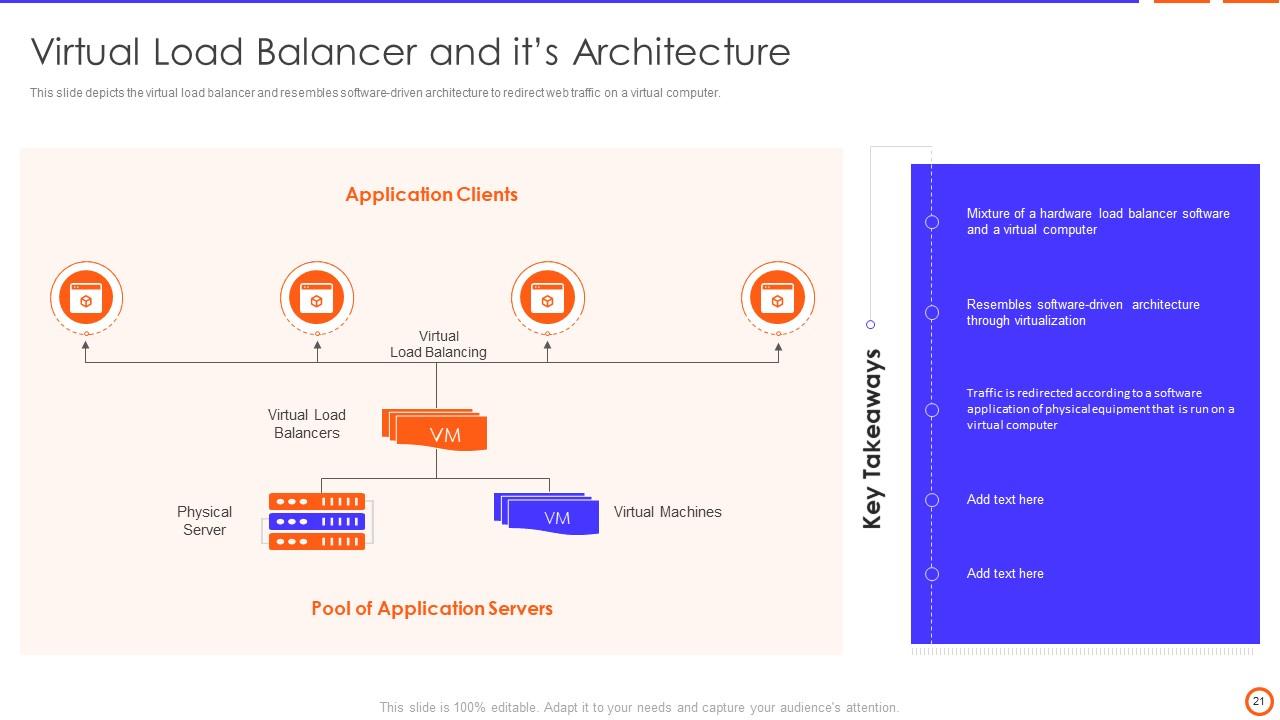
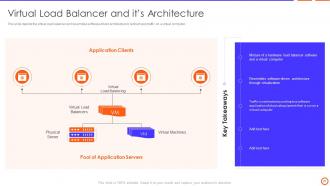
Slide 21: This slide depicts the virtual load balancer and resembles software-driven architecture to redirect web traffic on a virtual computer.
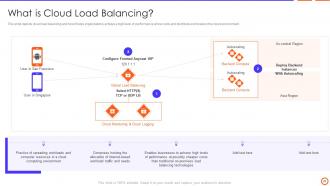
Slide 22: This slide depicts cloud load balancing and how it helps organizations achieve a high level of performance at low costs.
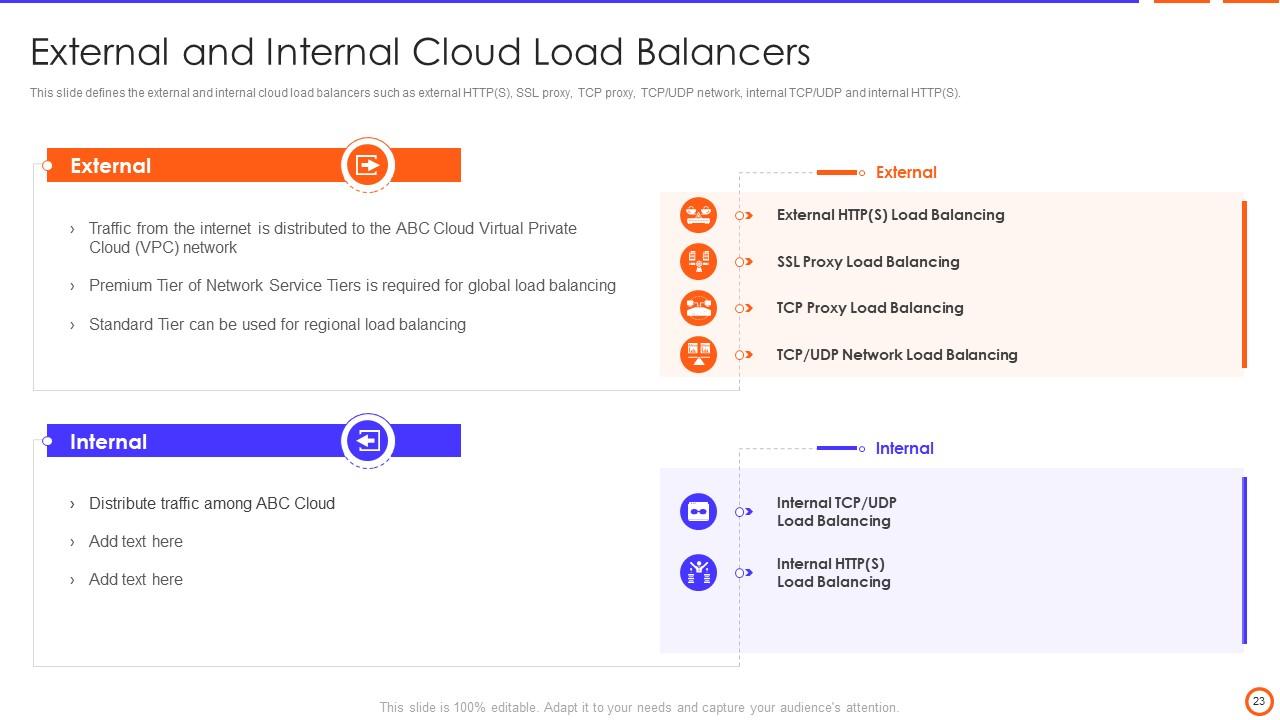
Slide 23: This slide defines the external and internal cloud load balancers such as external HTTP(S), TCP/UDP network, internal TCP/UDP and internal HTTP(S), etc.
Slide 24: This slide exhibits the title for working of a load balancer.
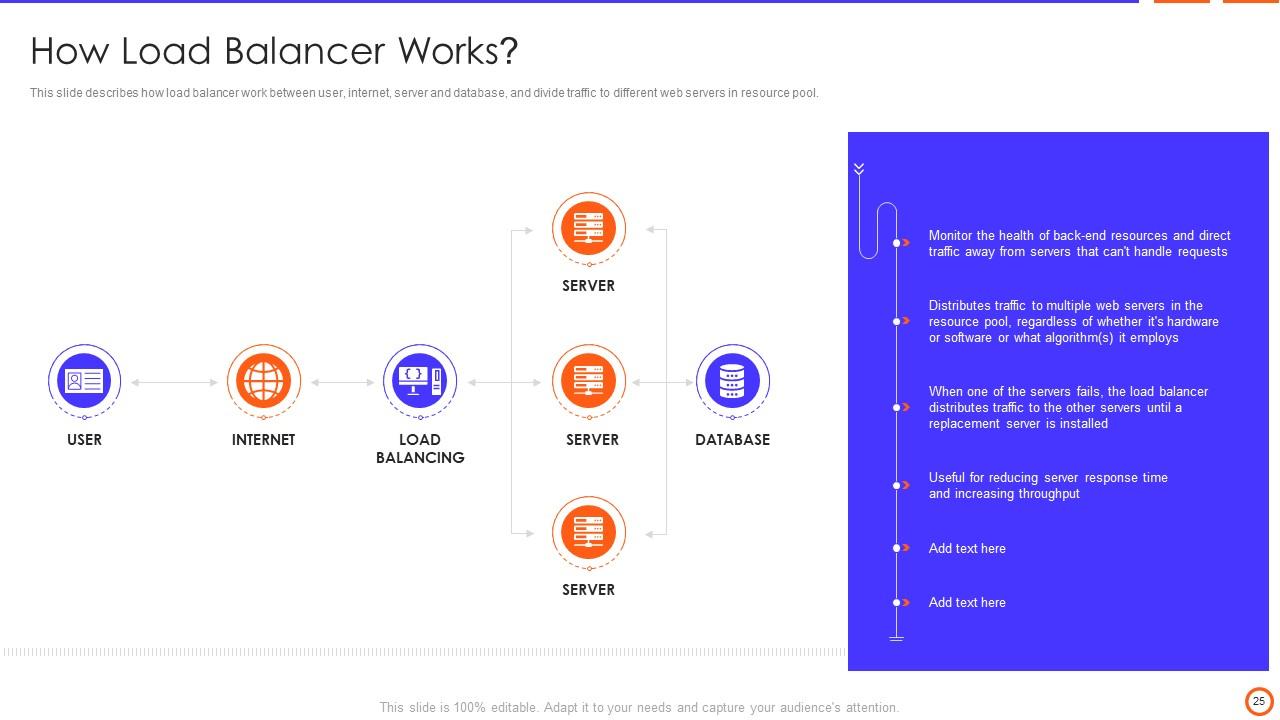
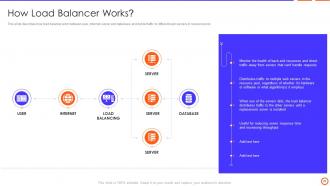
Slide 25: This slide describes how load balancer work between user, internet, server and database, and divide traffic to different web servers in resource pool.
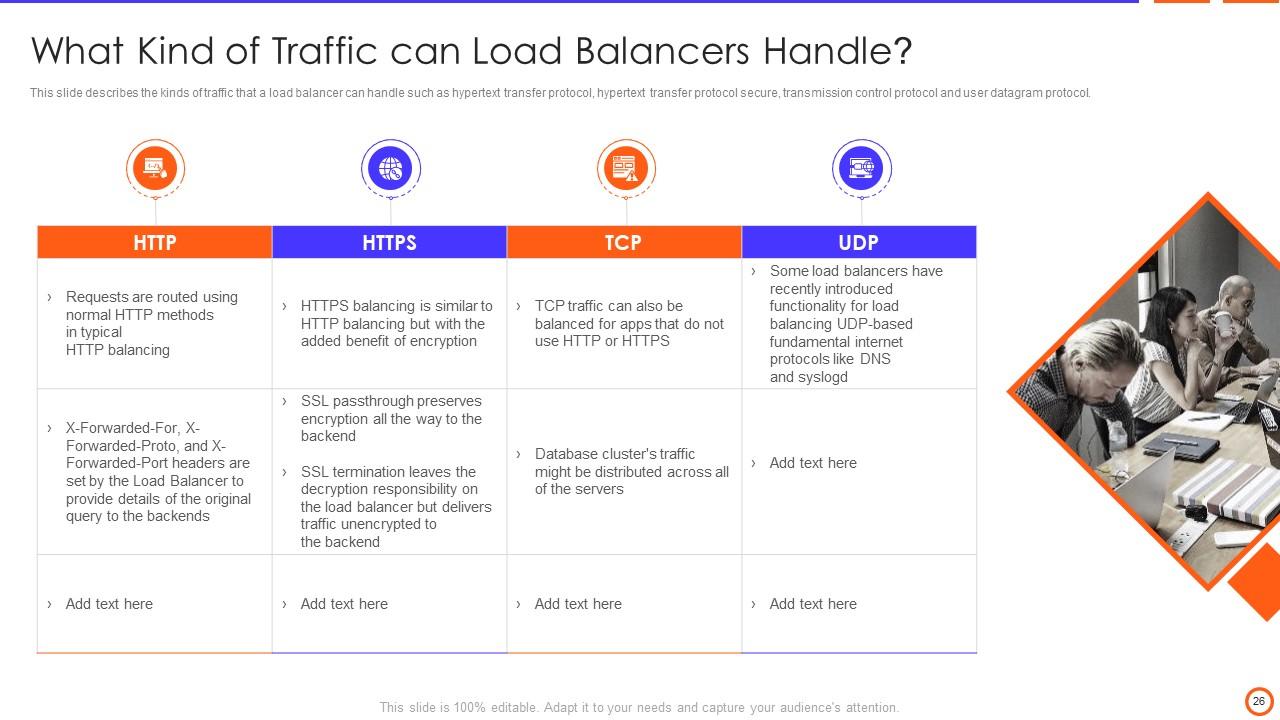
Slide 26: This slide describes the kinds of traffic that a load balancer can handle such as hypertext transfer protocol, hypertext transfer protocol secure, etc.
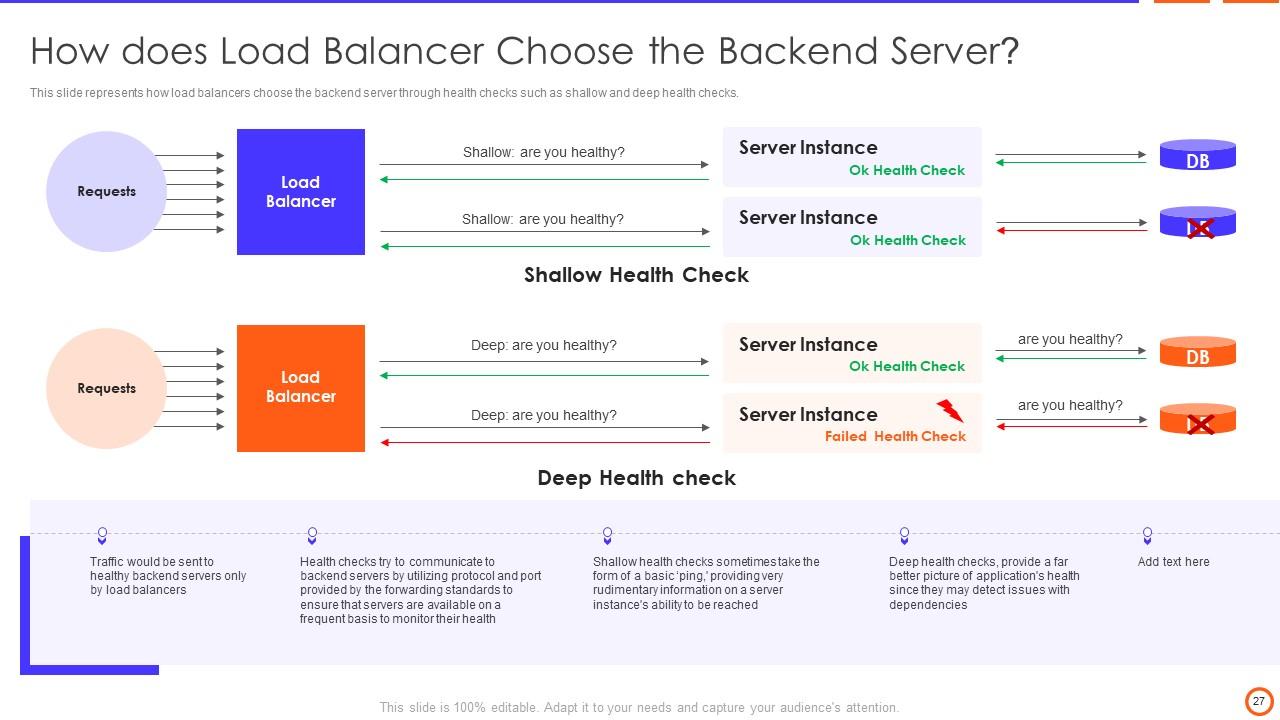
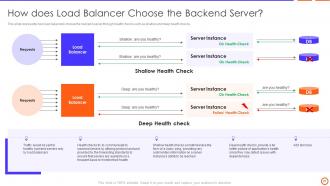
Slide 27: This slide represents how load balancers choose the backend server through health checks such as shallow and deep health checks.
Slide 28: This slide presents the title for methods & techniques used for load balancing.
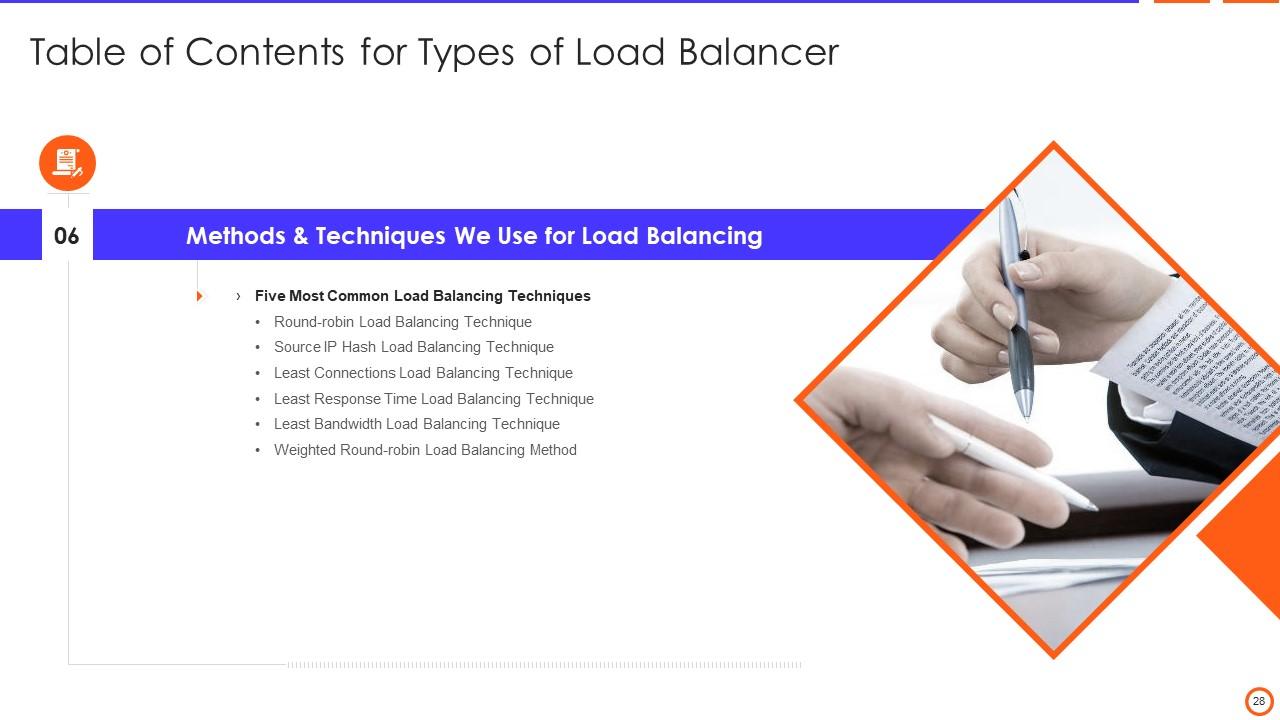
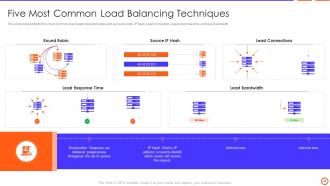
Slide 29: This slide represents the five most common load balancing techniques such as round-robin, least response time, and least bandwidth, etc.
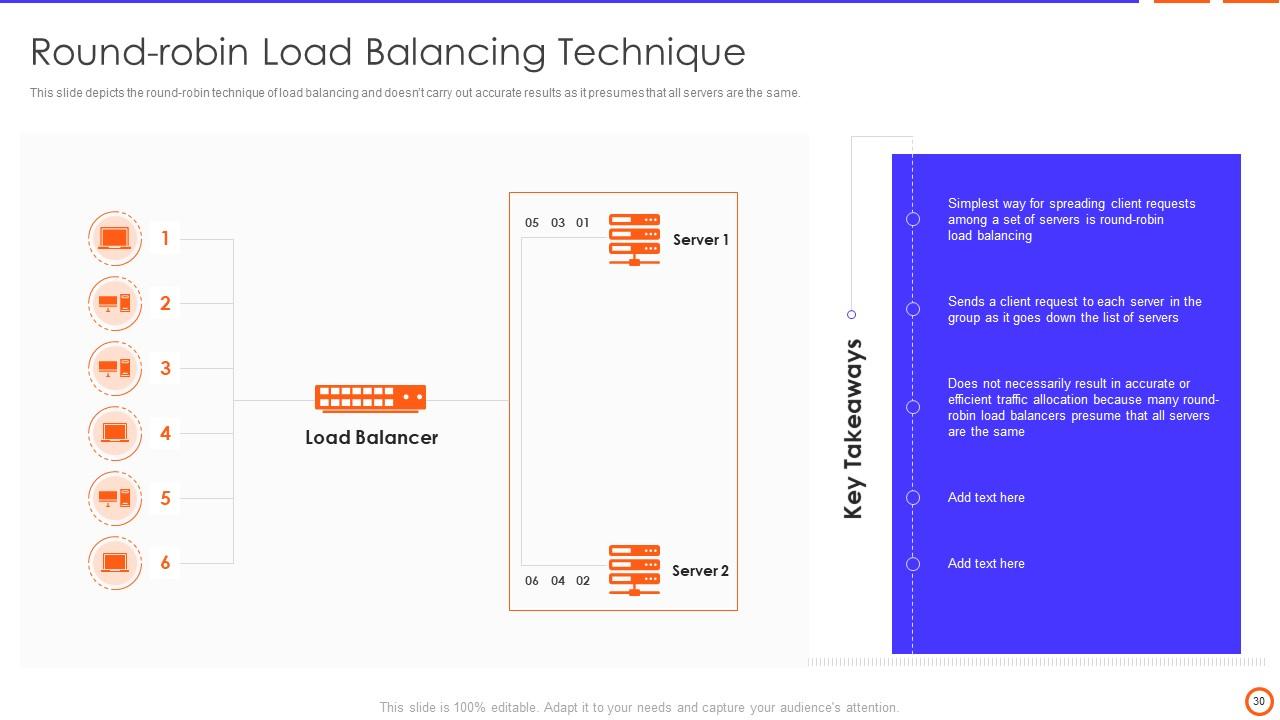
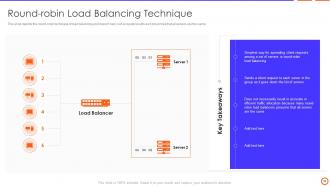
Slide 30: This slide depicts the round-robin technique of load balancing and doesn’t carry out accurate results as it presumes that all servers are the same.
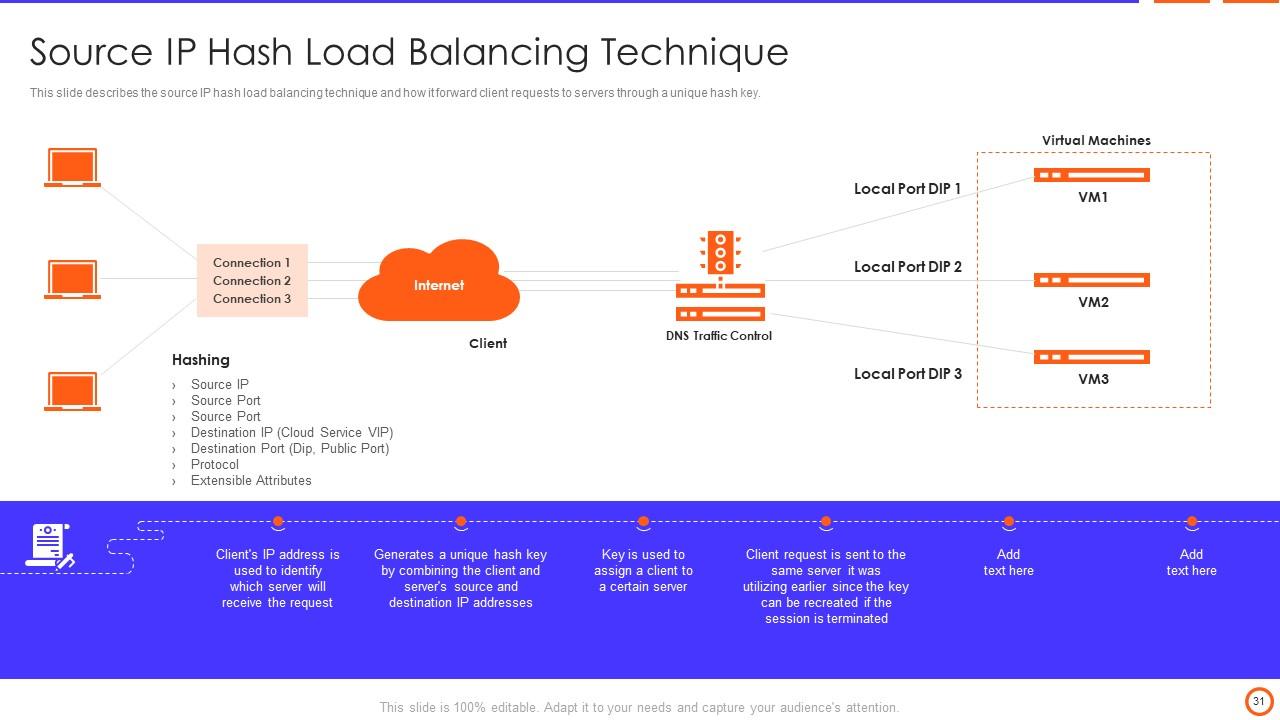
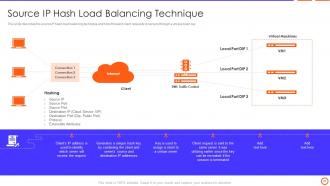
Slide 31: This slide describes the source IP hash load balancing technique and how it forward client requests to servers through a unique hash key.
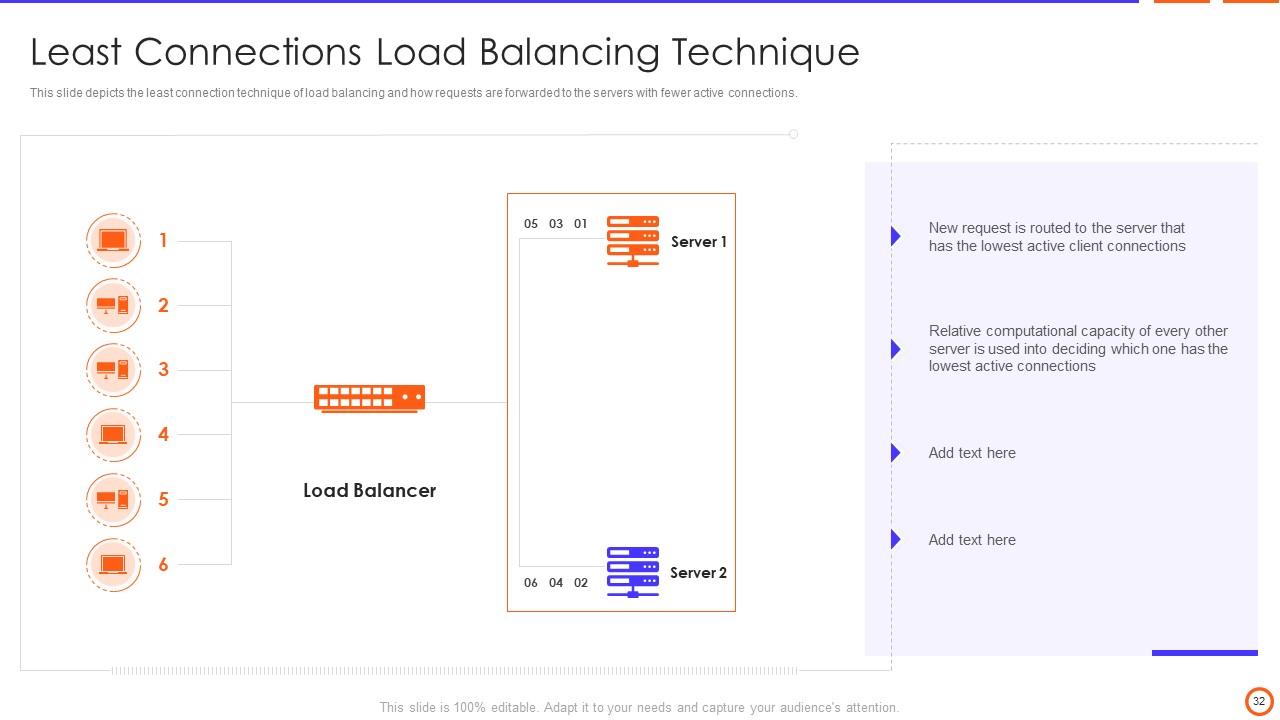
Slide 32: This slide depicts the least connection technique of load balancing and how requests are forwarded to the servers with fewer active connections.
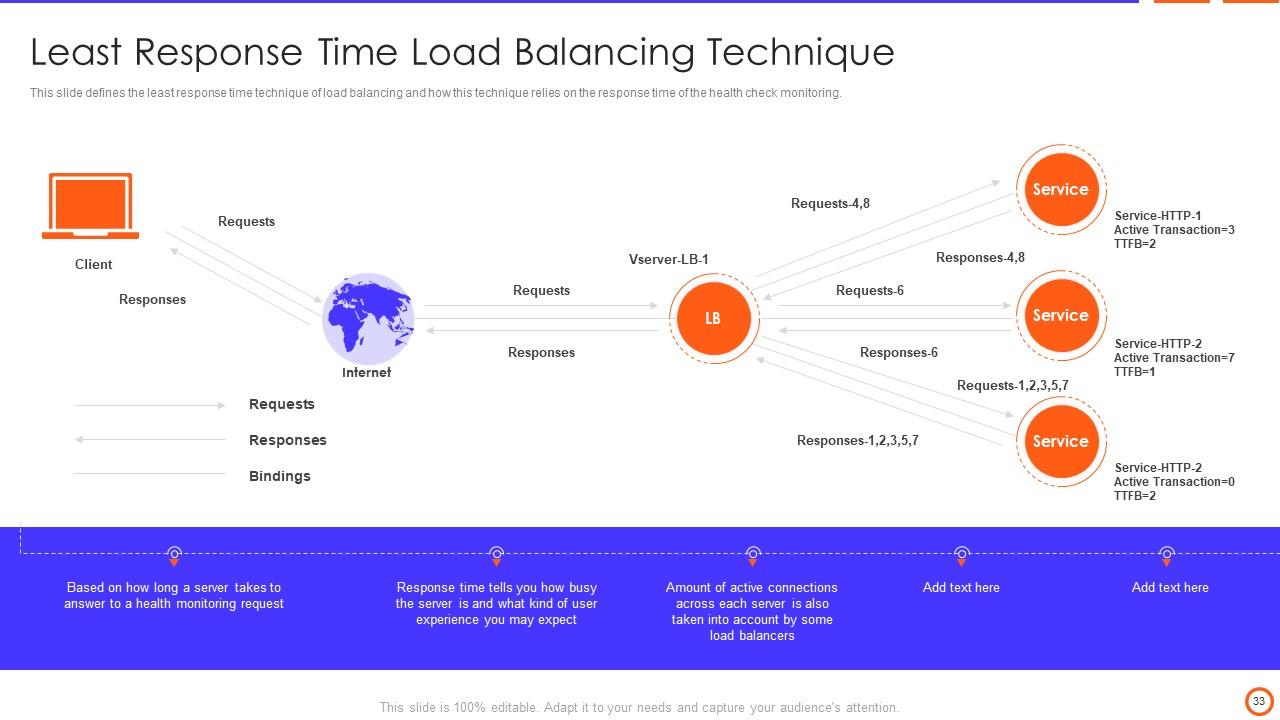
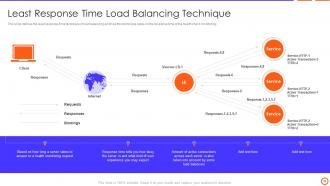
Slide 33: This slide defines the least response time technique of load balancing and how this technique relies on the response time of the health check monitoring.
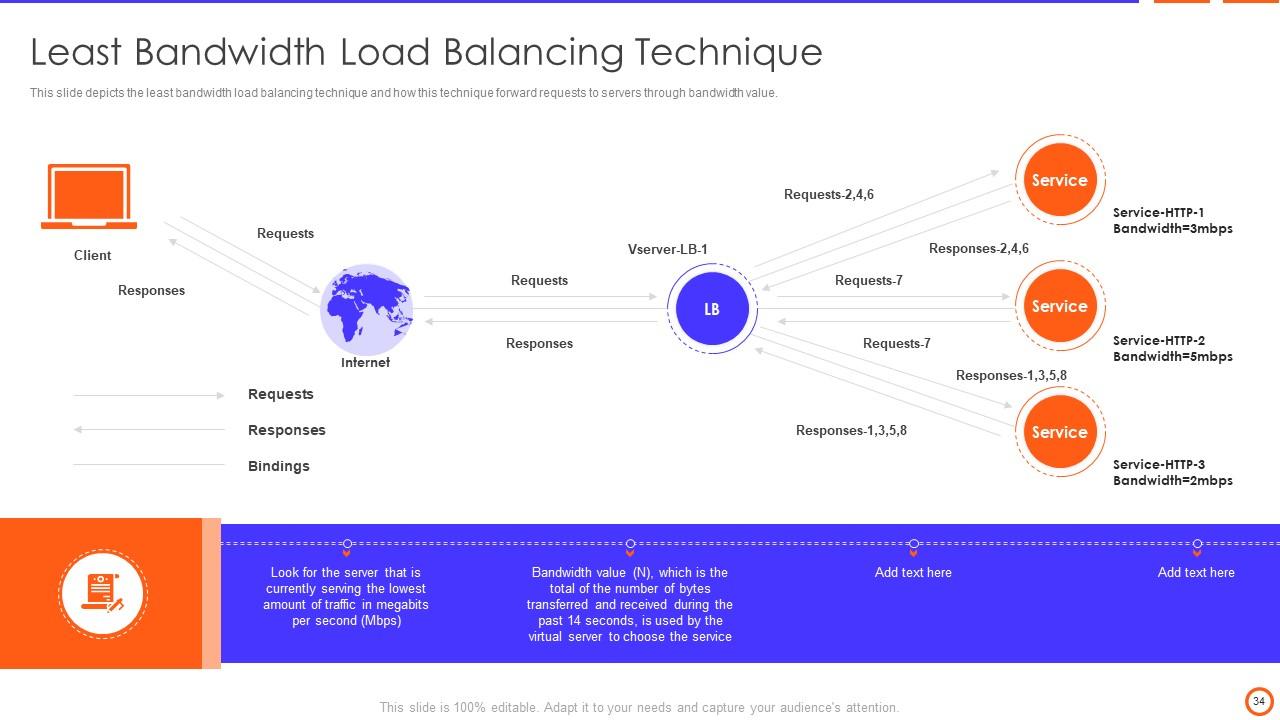
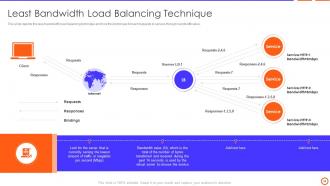
Slide 34: This slide depicts the least bandwidth load balancing technique and how this technique forward requests to servers through bandwidth value.
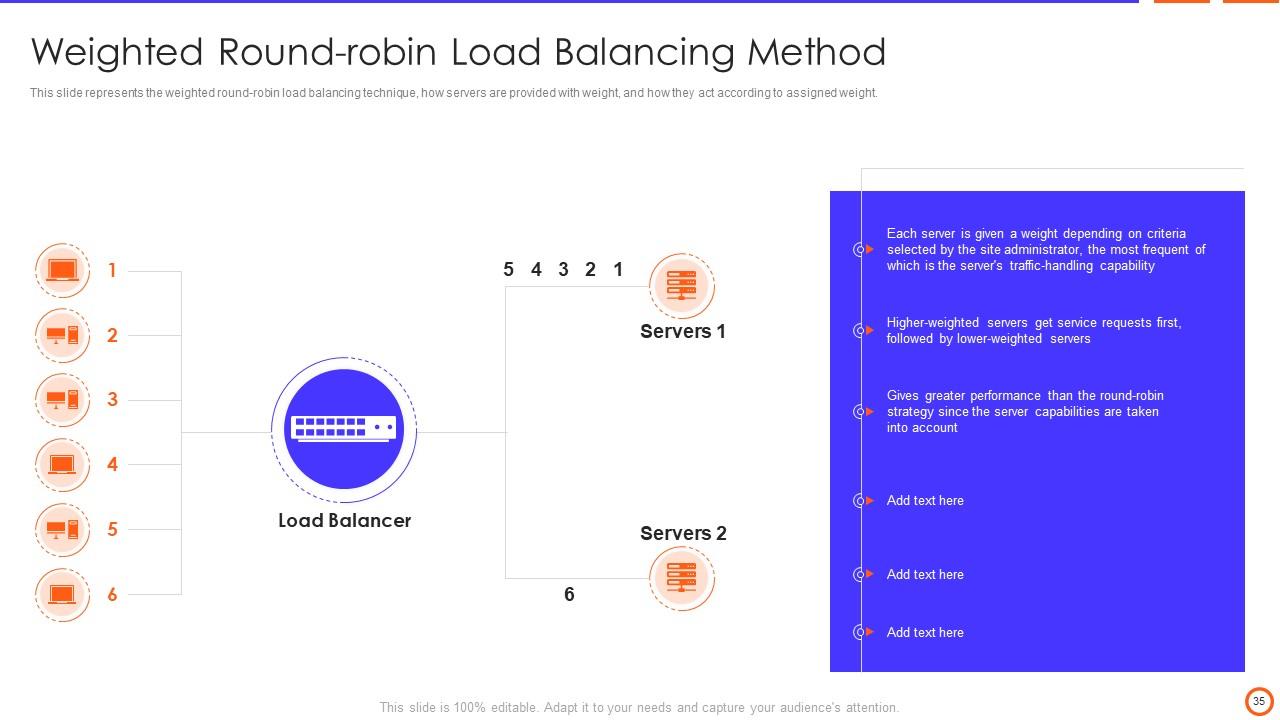
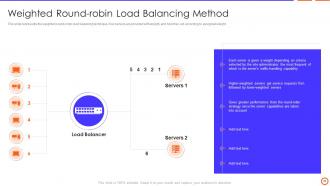
Slide 35: This slide represents the weighted round-robin load balancing technique, how servers are provided with weight, and how they act according to assigned weight.
Slide 36: This slide displays the title for comparison of load balancers with other technologies.
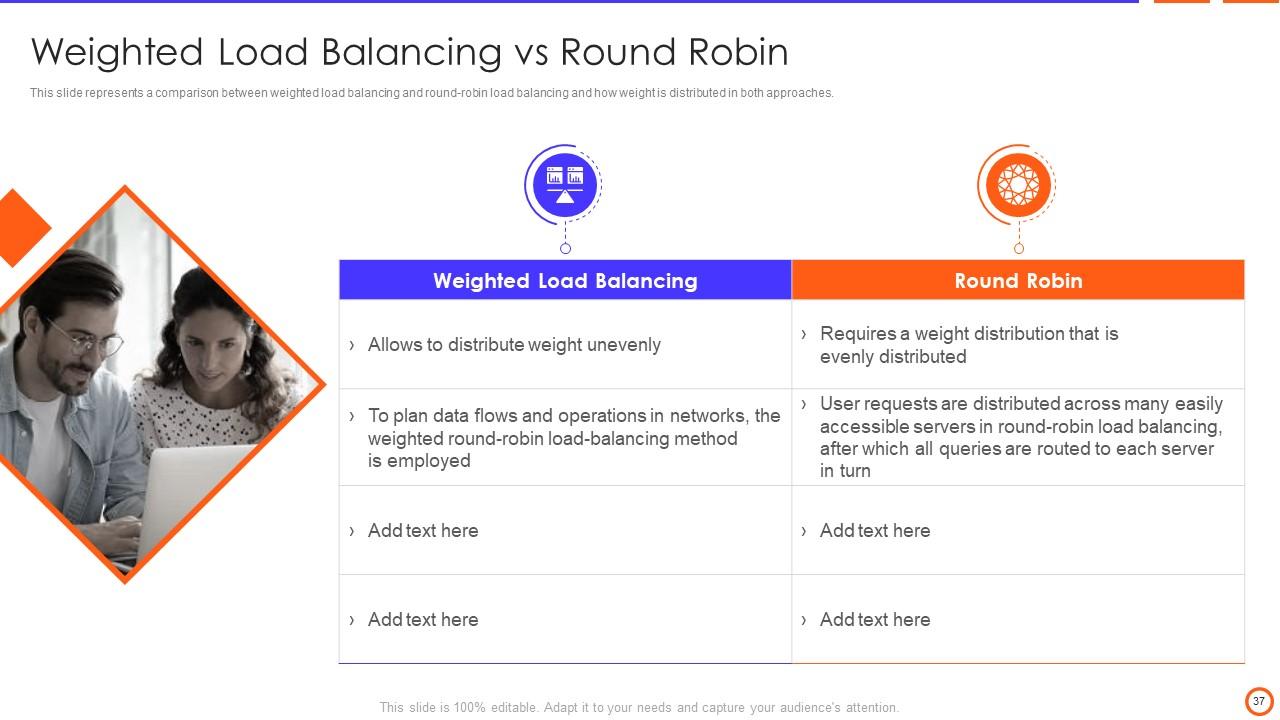
Slide 37: This slide represents a comparison between weighted load balancing and round-robin load balancing and how weight is distributed in both approaches.
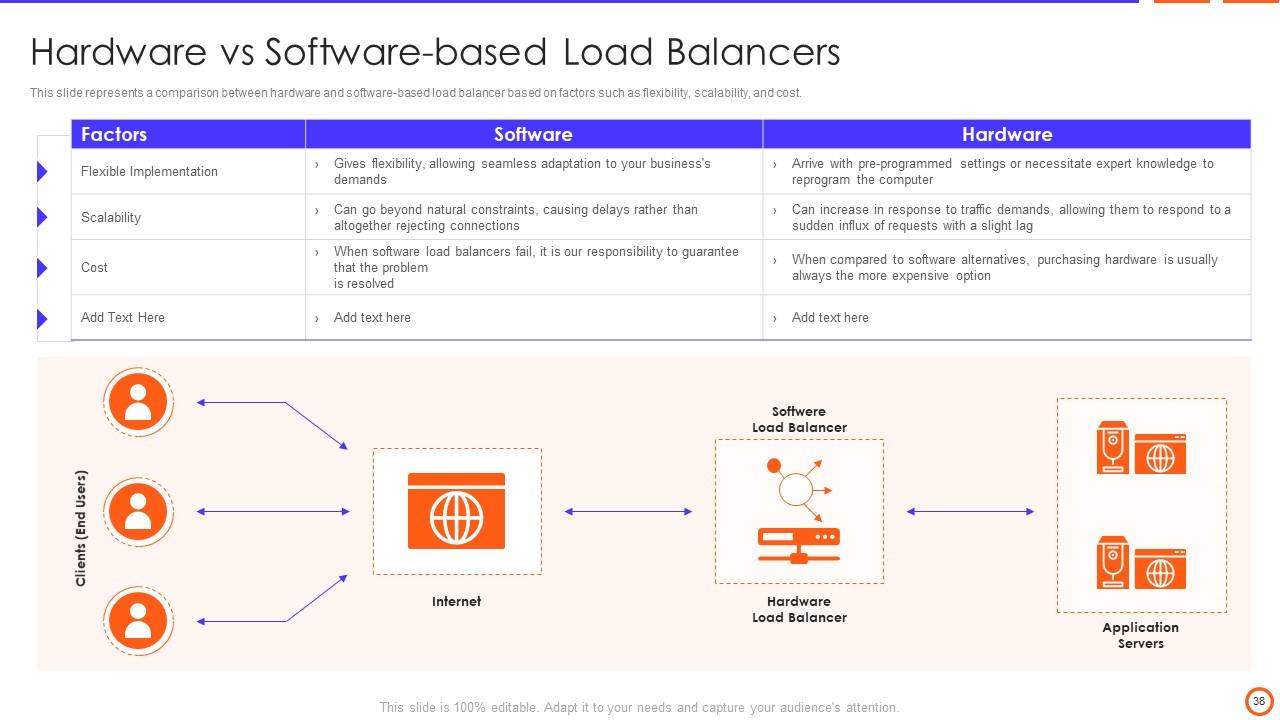
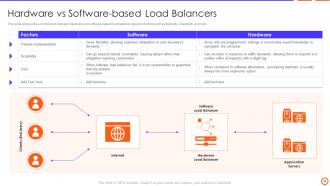
Slide 38: This slide represents a comparison between hardware and software-based load balancer based on factors such as flexibility, scalability, and cost.
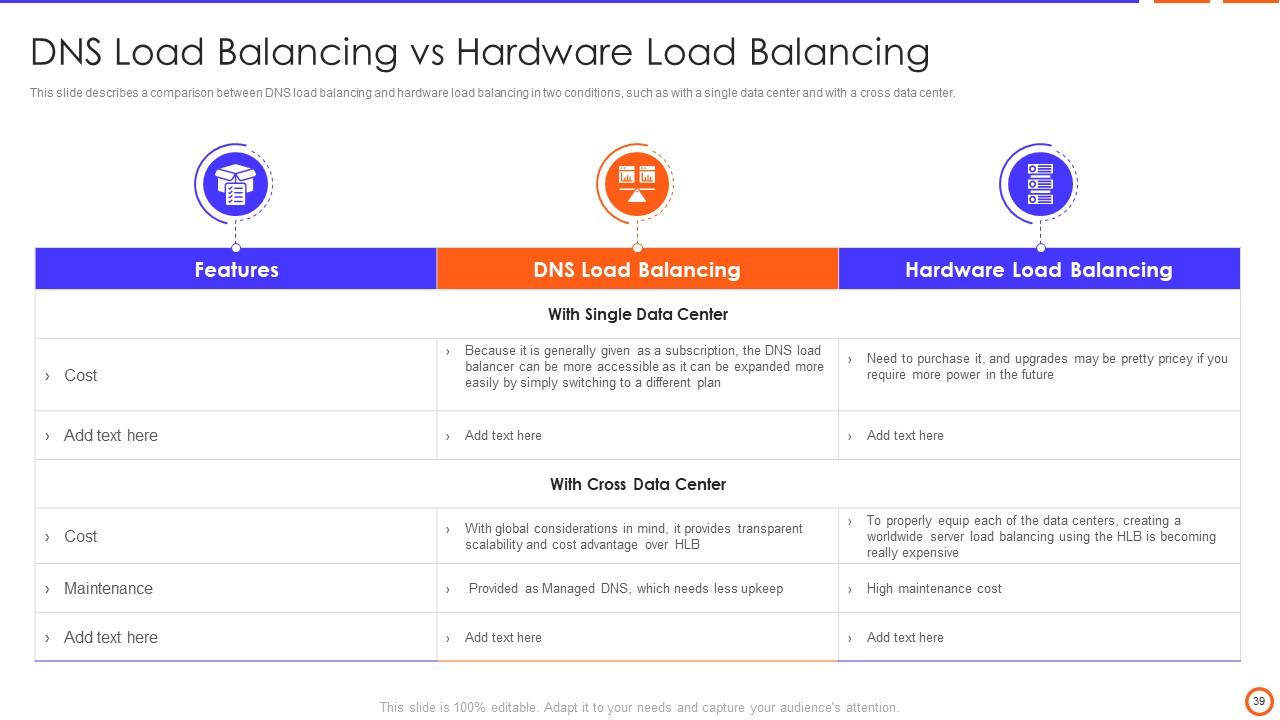
Slide 39: This slide describes a comparison between DNS load balancing and hardware load balancing in two conditions, like with a single data center and cross data center.
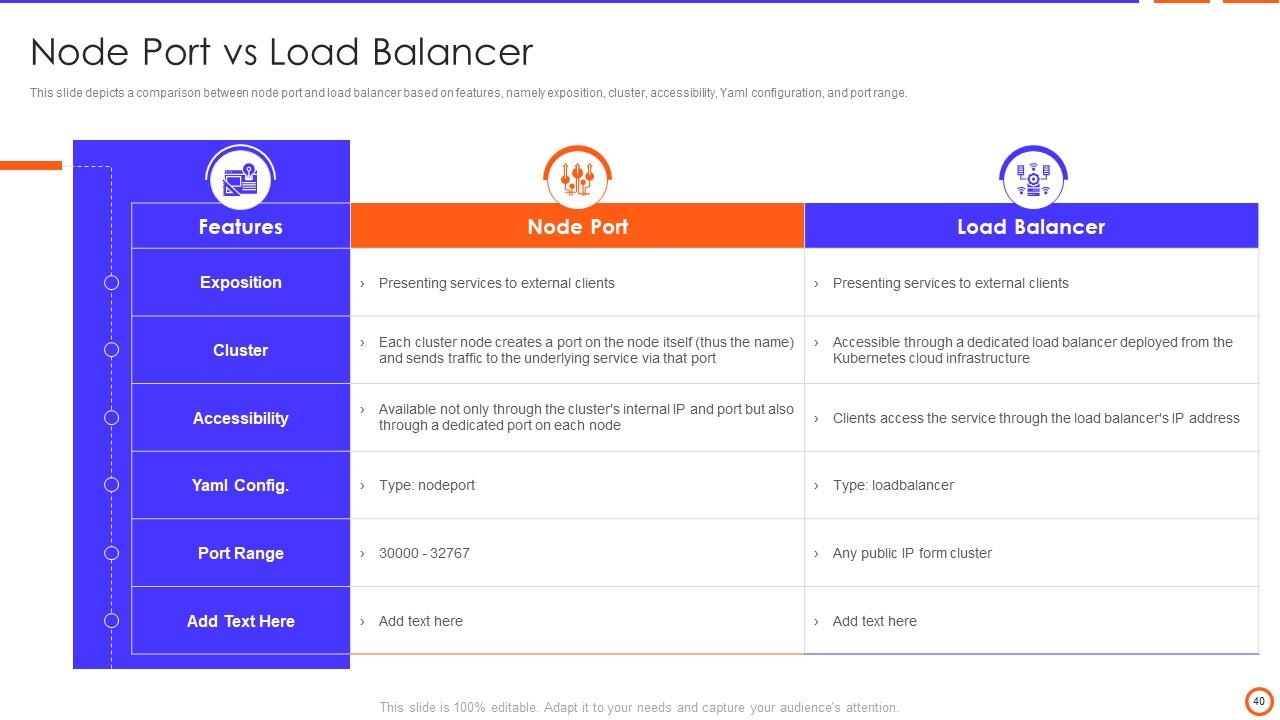
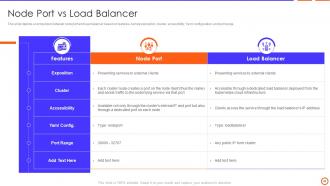
Slide 40: This slide depicts a comparison between node port and load balancer based on features, cluster, accessibility, port range, etc.
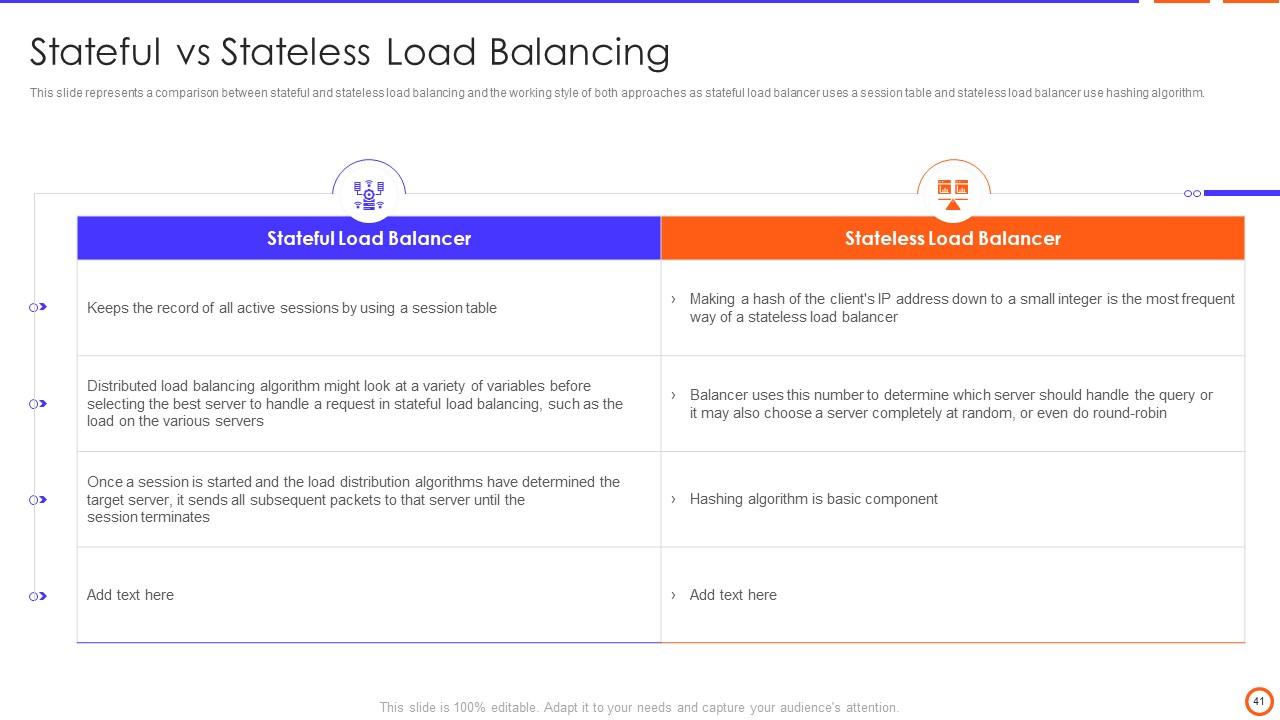
Slide 41: This slide represents a comparison between stateful and stateless load balancing and the working style of both approaches.
Slide 42: This slide presents the title for implementation of load balancer.
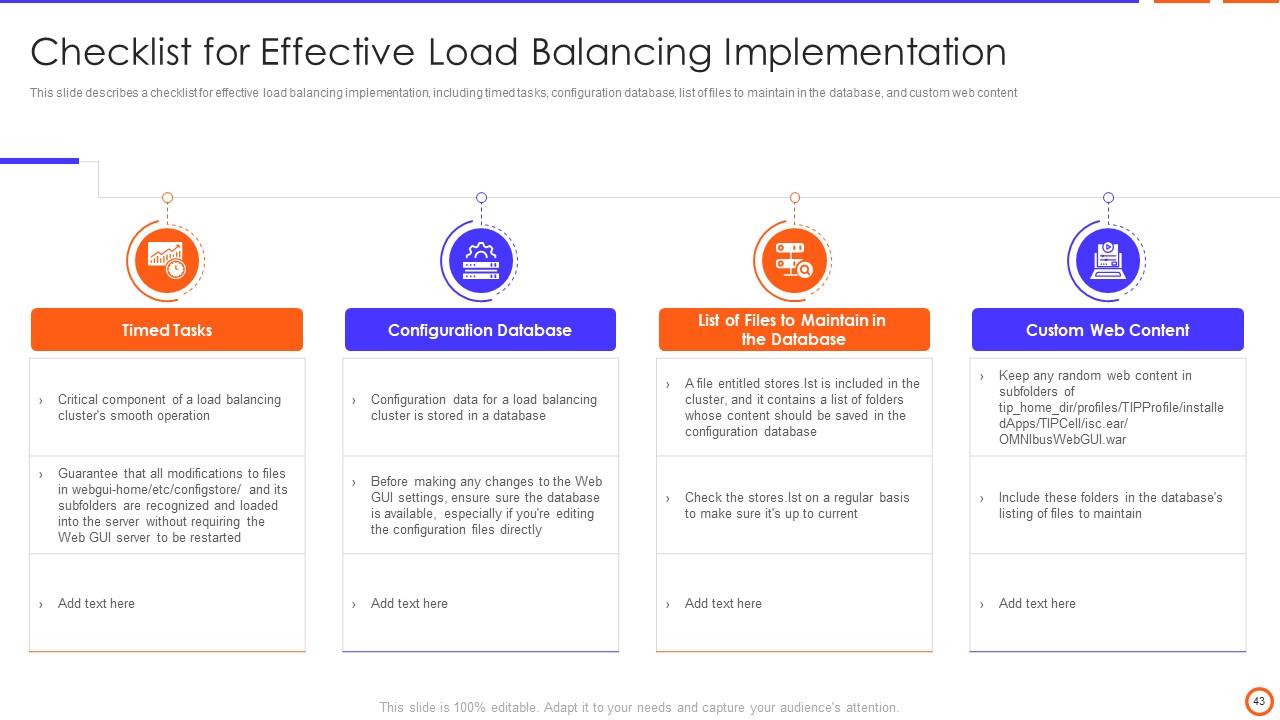
Slide 43: This slide describes a checklist for effective load balancing implementation, including timed tasks, list of files to maintain in the database, etc.
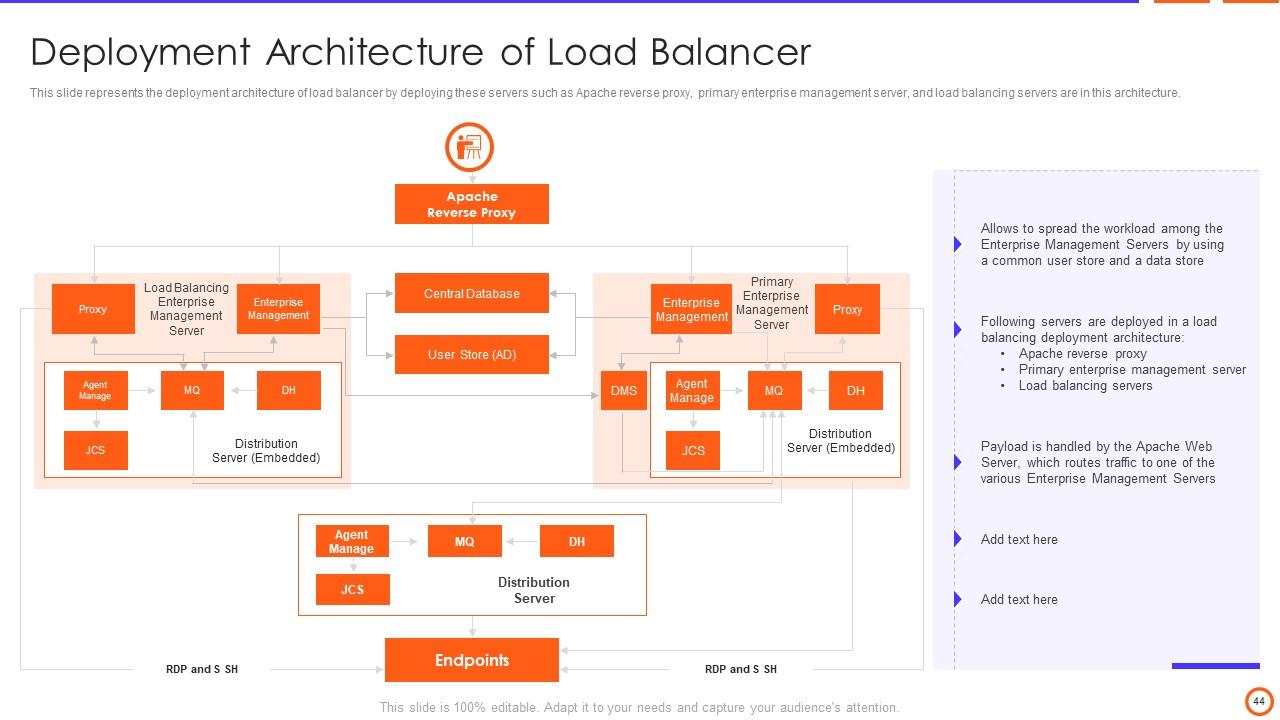
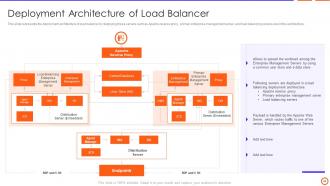
Slide 44: This slide represents the deployment architecture of load balancer by deploying servers such as Apache reverse proxy, load balancing servers, etc.
Slide 45: This slide represents the training program for the IT team members of an organization, including modules, trainer name, schedule and mode of training.
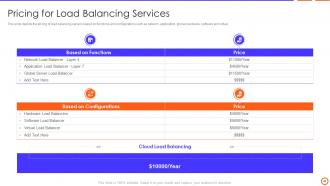
Slide 46: This slide depicts the pricing of load balancing servers based on functions and configurations such as global, hardware, software and virtual, etc.
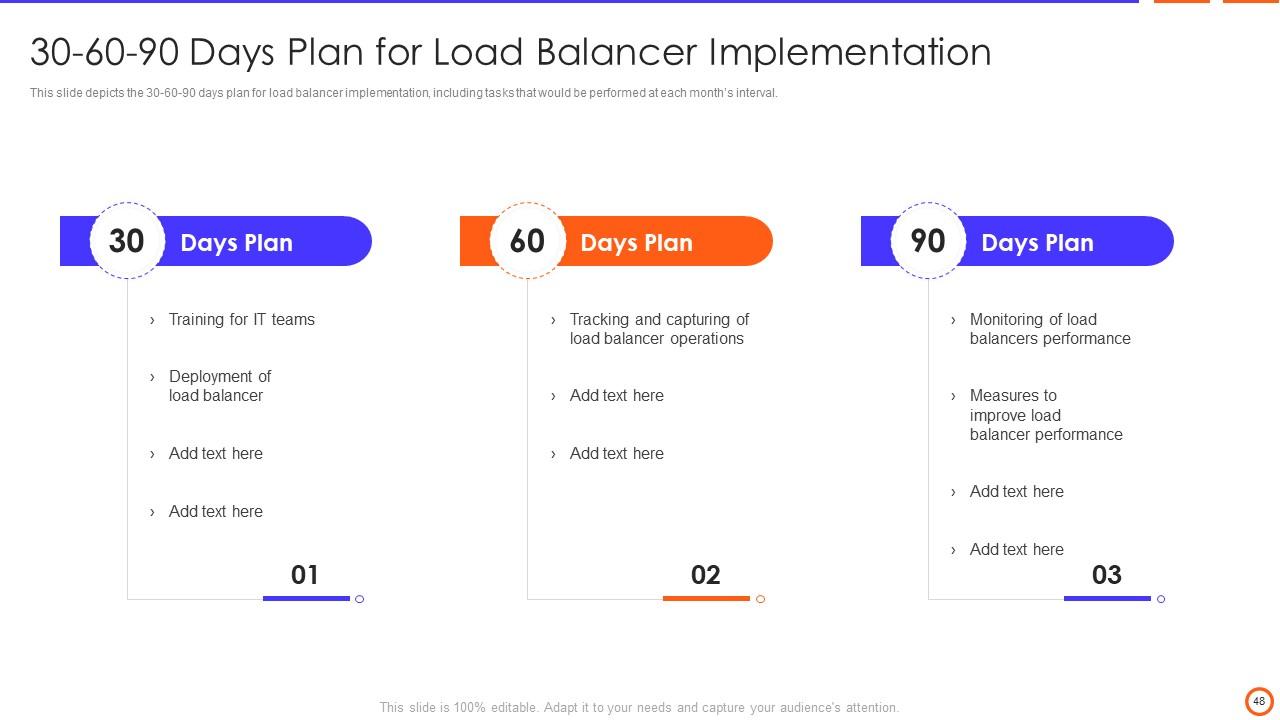
Slide 47: This slide displays the title for 30-60-90 days plan for load balancer implementation.
Slide 48: This slide shows content for the above title.
Slide 49: This slide depicts the title for roadmap for load balancer implementation.
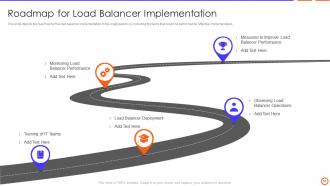
Slide 50: This slide represents Roadmap for Load Balancer Implementation.
Slide 51: This slide displays Icons for Types of Load Balancer.
Slide 52: This slide is titled as Additional Slides for moving forward.
Slide 53: This is a Timeline slide. Show data related to time intervals here.
Slide 54: This is a Comparison slide to state comparison between commodities, entities etc.
Slide 55: This slide shows Post It Notes. Post your important notes here.
Slide 56: This is About Us slide to show company specifications etc.
Slide 57: This slide contains Puzzle with related icons and text.
Slide 58: This is a Thank You slide with address, contact numbers and email address.
Types Of Load Balancer Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 63 slides:
Use our Types Of Load Balancer Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
FAQs
A load balancer is a device or software that distributes network traffic across multiple servers to prevent any one server from becoming overwhelmed with traffic.
There are two main types of load balancers: hardware load balancers and software load balancers.
A load balancer works by distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers, using algorithms to determine which server should receive each request.
Load balancers can improve the performance and reliability of a web application by distributing traffic evenly across multiple servers and providing failover support.
Load balancers are commonly used in web applications to improve performance and reliability, and in data centers to distribute traffic across multiple servers. They can also be used to improve security by providing a single entry point for traffic.
-
Informative presentations that are easily editable.
-
Good research work and creative work done on every template.