Unlocking The Fundamentals Of NLP NLU And NLG Training Ppt
This training module on Unlocking the Fundamentals of NLP, NLU, and NLG presents a comprehensive overview of Natural Language Processing, Natural Language Understanding, and Natural Language Generation. It explains the working of NLP, NLU, and NLG along with their importance, applications, and advantages. It also compares NLP, NLG, and NLU, AI Artificial Intelligence and ML Machine Learning, ML and DL Deep Learning, and AI, ML, and DL. It also includes Activities, Key Takeaways, and Discussion Questions related to the topic to make the training session more interactive. The deck has PPT slides on About Us, Vision, Mission, Goal, 30-60-90 Days Plan, Timeline, Roadmap, Training Completion Certificate, and Energizer Activities. It also includes a Client Proposal and Assessment Form for training evaluation.
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Unlocking the Fundamentals of NLP, NLU, and NLG. This deck comprises of 99 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
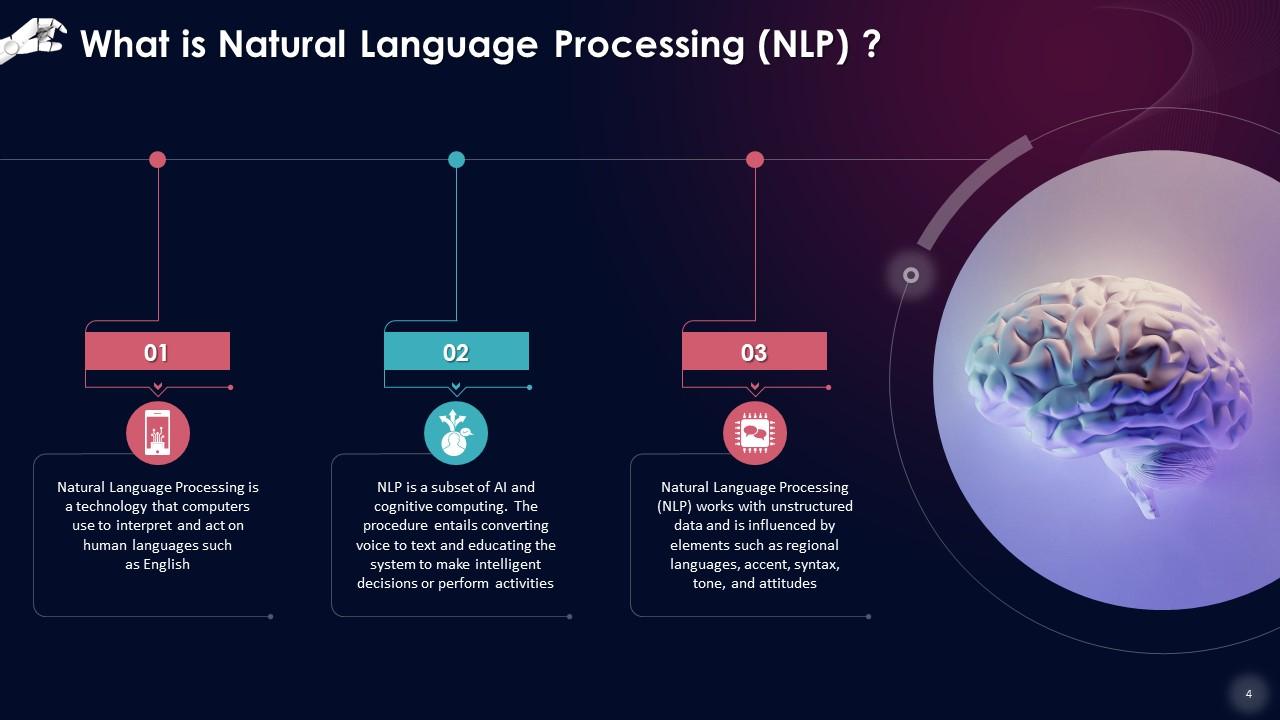
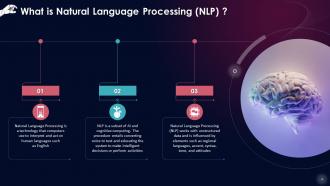
This slide describes that Natural Language Processing is a technology that computers use to interpret and act on human languages such as English. NLP is a subset of AI and cognitive computing. The procedure entails converting voice to text and educating the system to make intelligent decisions or perform activities.
Slide 5
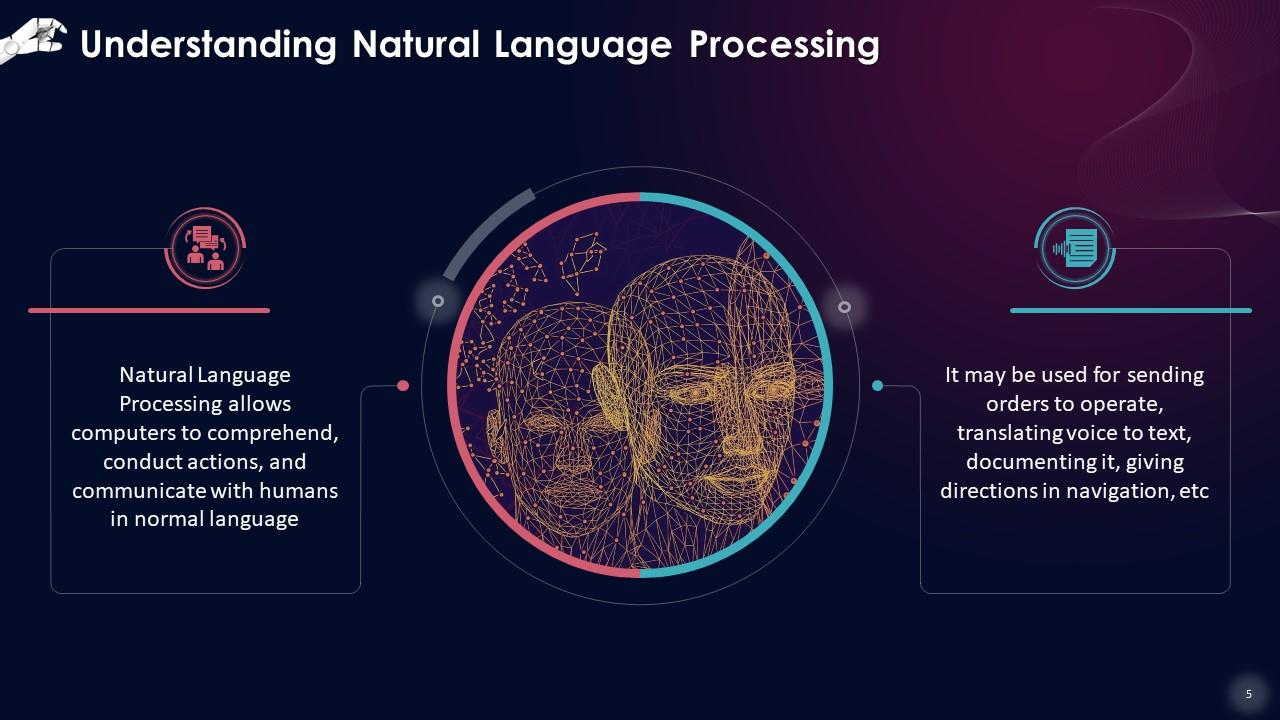
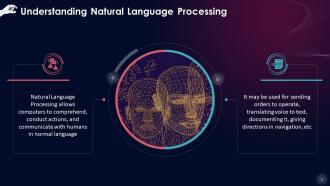
This slide gives an overview of Natural Language Processing, allowing computers to comprehend, conduct actions, and communicate with humans in normal language. It may be used for sending orders to operate, translating voice to text, documenting it, giving directions in navigation, etc.
Slide 6
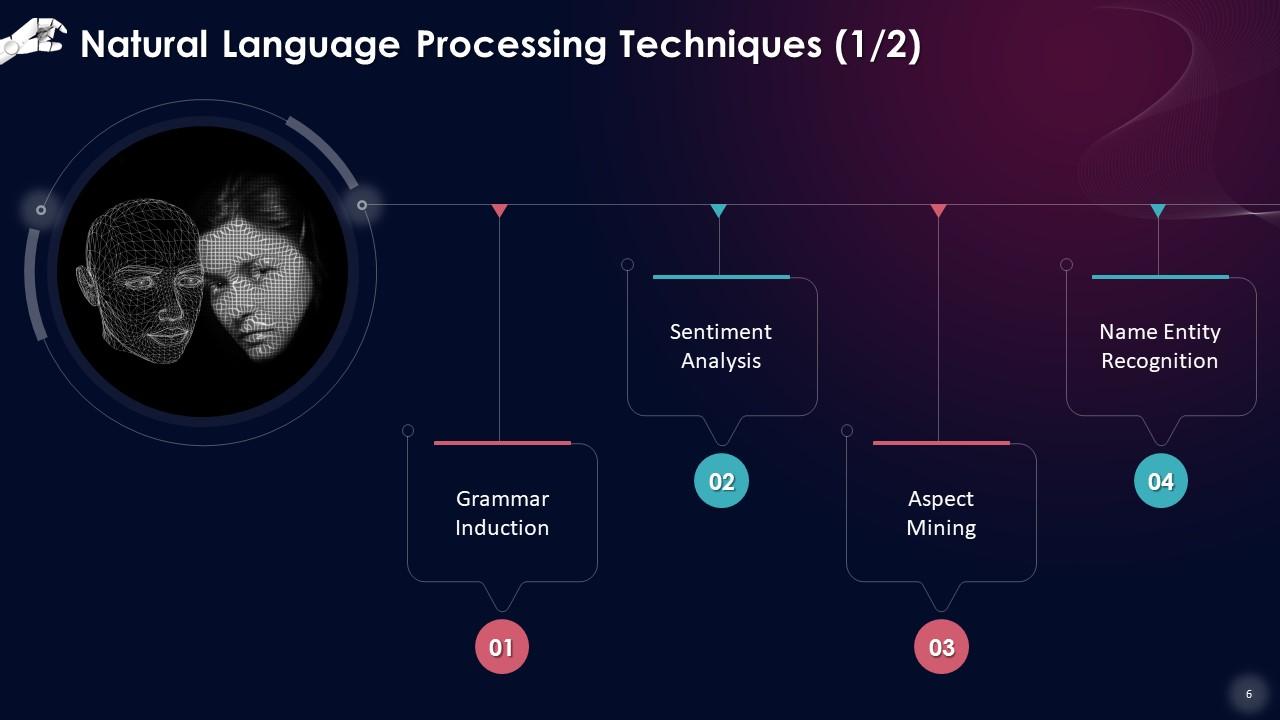
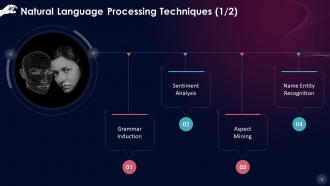
This slide lists Natural Language Processing techniques such as: grammar induction, sentiment analysis, aspect mining and name entity recognition.
Instructor Notes:
- Grammar Induction: It aids in the use of proper grammar when writing
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP is used to examine the sentence's positive and negative aspects
- Aspect Mining: Aspect mining is used in NLP to discover which aspects are favorable and which are bad
- Name Entity Recognition: It is used to recognize notable people's names, organizations, locations, and dates
Slide 7
This slide states a few of the Natural Language Processing techniques such as: Summarization, Topic Recognition and Speech to Text Conversion
Instructor Notes:
- Summarization: NLP may also summarize the content and offer the text's essence. It scores sentences based on their resemblance to other sentences
- Topic Recognition: NLP examines the text to determine the principal topic to which it is connected. It will extract certain keywords and organize them into categories
- Speech to Text Conversion: Speech to text enables machines to comprehend human language and interpret it with the intent of acting and responding in the same way that people do. The primary idea behind NLP is to feed human language as data to intelligent text-to-speech systems, which may subsequently be used in many fields
Slide 8
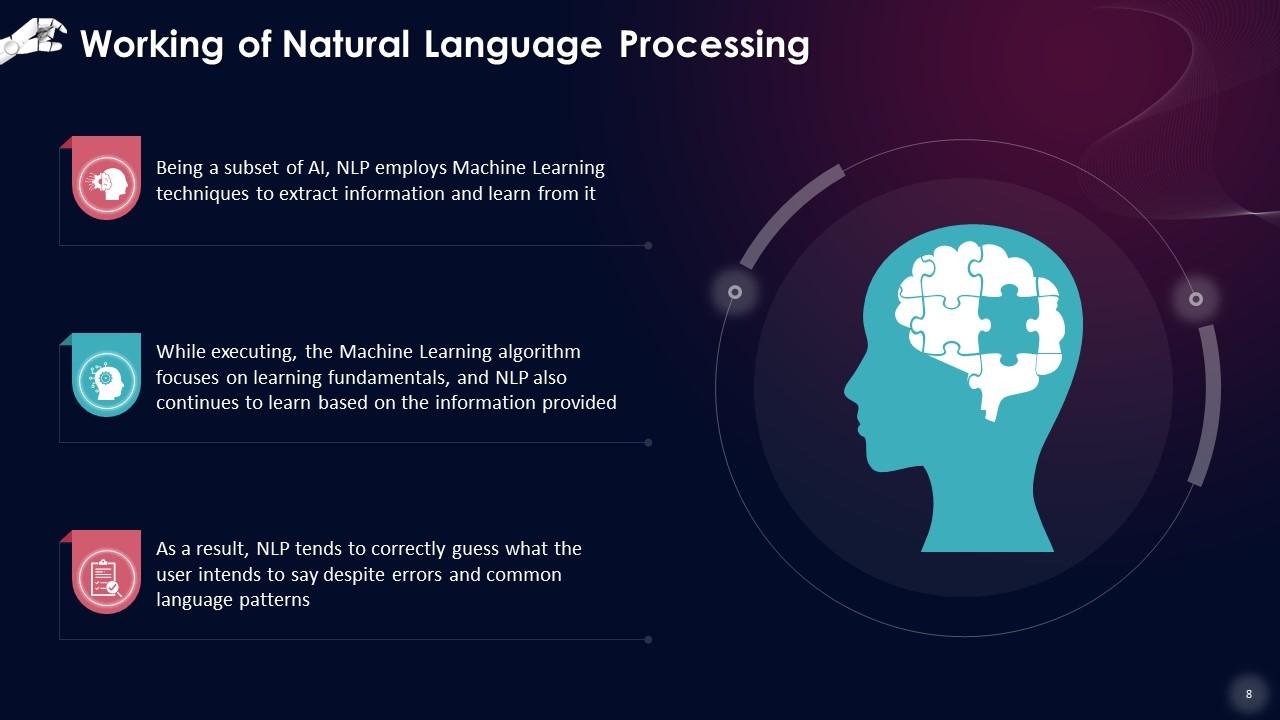
This slide showcases the operation of Natural Language Processing. Being a subset of AI, NLP employs machine learning techniques to extract information and learn from it. While executing, the machine learning algorithm focuses on learning fundamentals, and NLP also continues to learn based on the information provided. Due to this, NLP tends to correctly guess what the user intends to say despite errors and common language patterns.
Slide 9
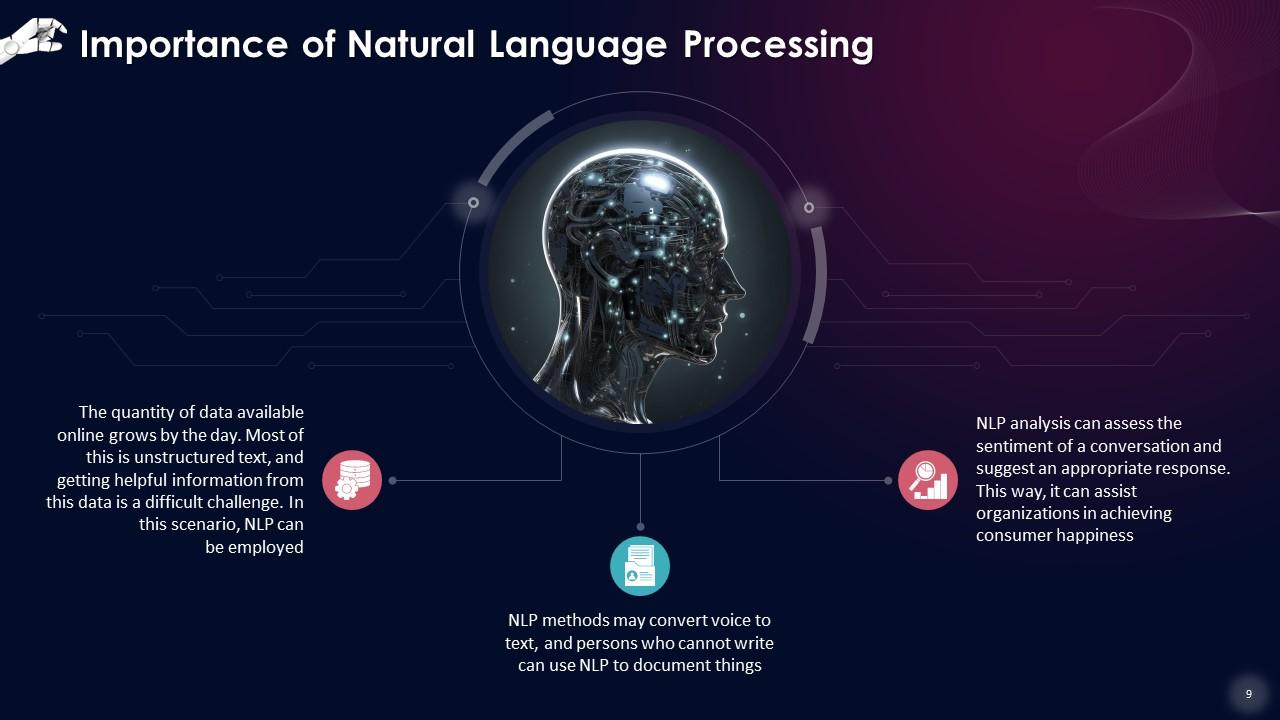
This slide states that the quantity of data available online grows by the day. Most of this is unstructured text, and getting helpful information from this data is a difficult challenge. In this scenario, NLP can be employed. NLP methods may convert voice to text, and persons who cannot write can use NLP to document things. NLP analysis can assess the sentiment of a conversation and suggest an appropriate response. This way, it can assist organizations in achieving consumer happiness.
Slide 10
This slide lists steps involved in Natural Language Processing, starting from the initial phase of Lexical Analysis to the last stage of Pragmatic Analysis.
Slide 11
This slide states that the Lexical Analysis phase is the initial stage of NLP. This stage analyses the source code as a stream of characters and turns it into meaningful lexemes. It is, here, too that it breaks down the entire text into paragraphs, phrases, and words.
Instructor Notes:
A lexeme is a series of characters that are included in the source programme based on a token's matching pattern. It is nothing more than a token instance.
Slide 12
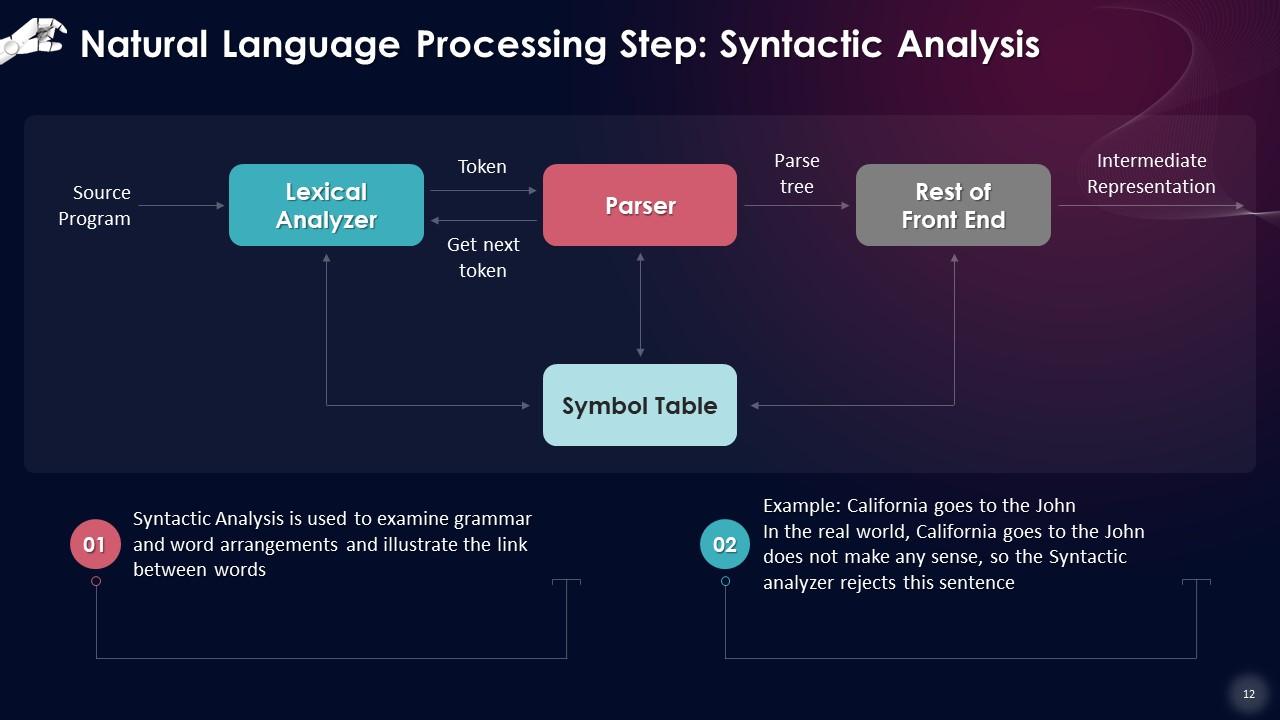
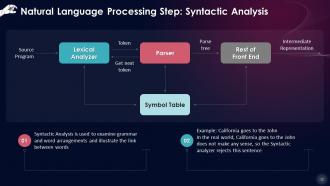
This slide showcases that Syntactic Analysis is used to examine grammar and word arrangements and illustrate the link between words. This approach entails associating words with other words, arranging them in a phrase, and determining their relative significance.
Slide 13
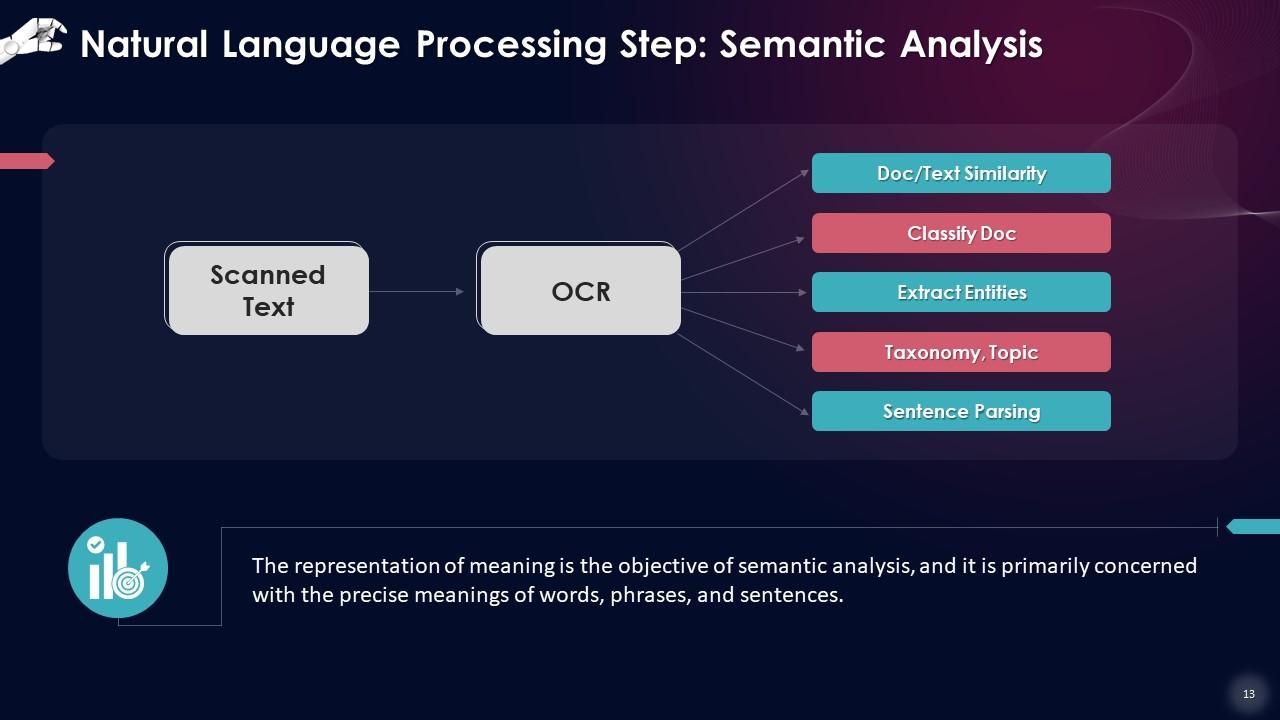
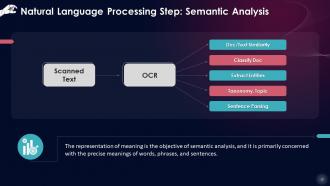
This slide describes that the representation of meaning is the objective of semantic analysis, and it is primarily concerned with the precise meanings of words, phrases, and sentences.
Instructor Notes:
OCR: Optical Character Recognition
Slide 14
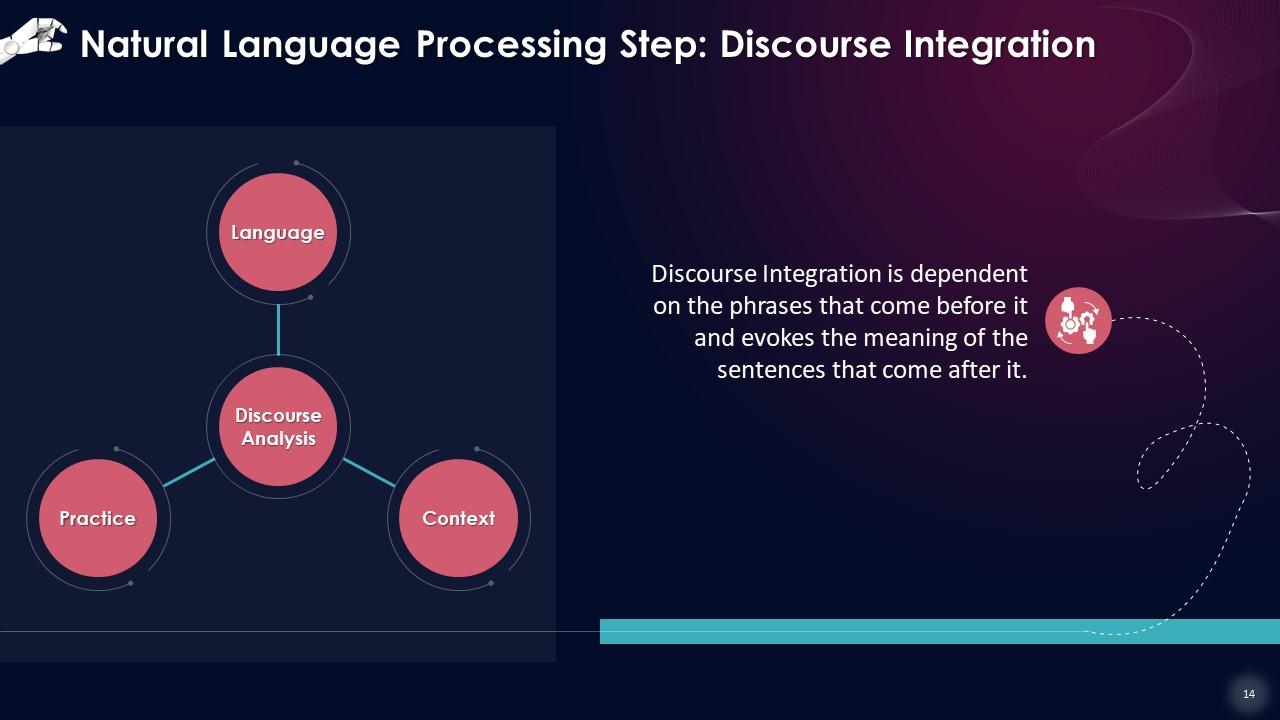
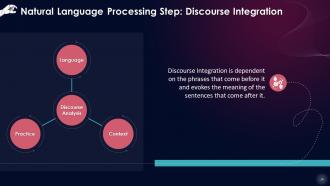
This slide states that Discourse Integration is dependent on the phrases that come before it and evokes the meaning of the sentences that come after it. This strategy examines the relative meaning of sentences and the relationships these form with other sentences.
Slide 15
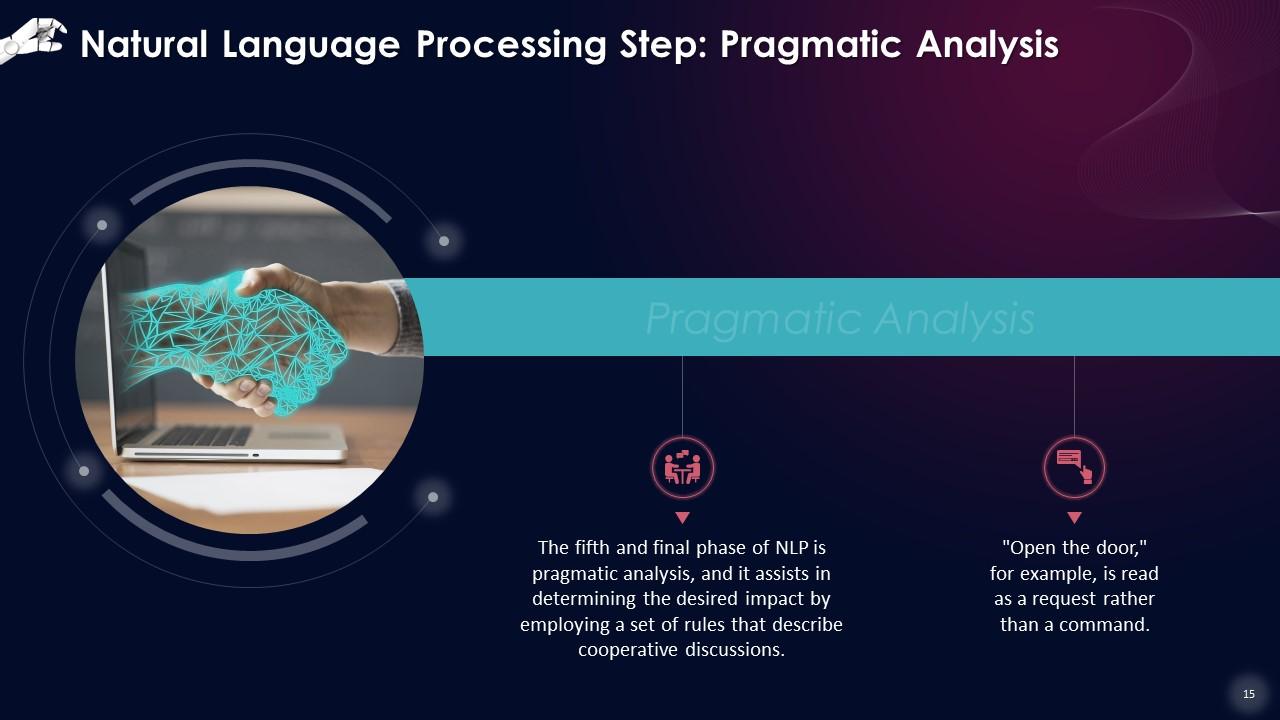
This slide describes that the fifth and final phase of NLP is pragmatic analysis, and it assists in determining the desired impact by employing a set of rules that describe cooperative discussions. This strategy addresses a sentence's real-world meaning.
Slide 16
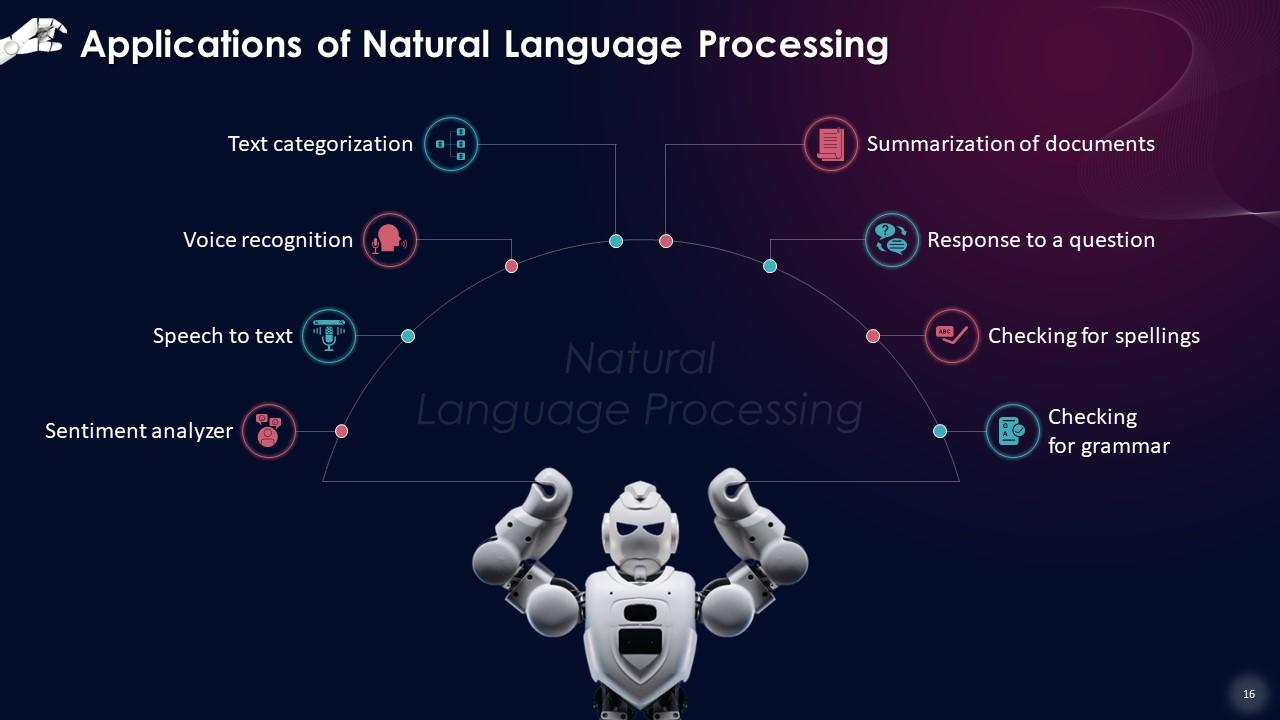
This slide lists types of Natural language Processing applications like sentiment analyzer, summarization of documents, checking for grammar, and more.
Slide 17
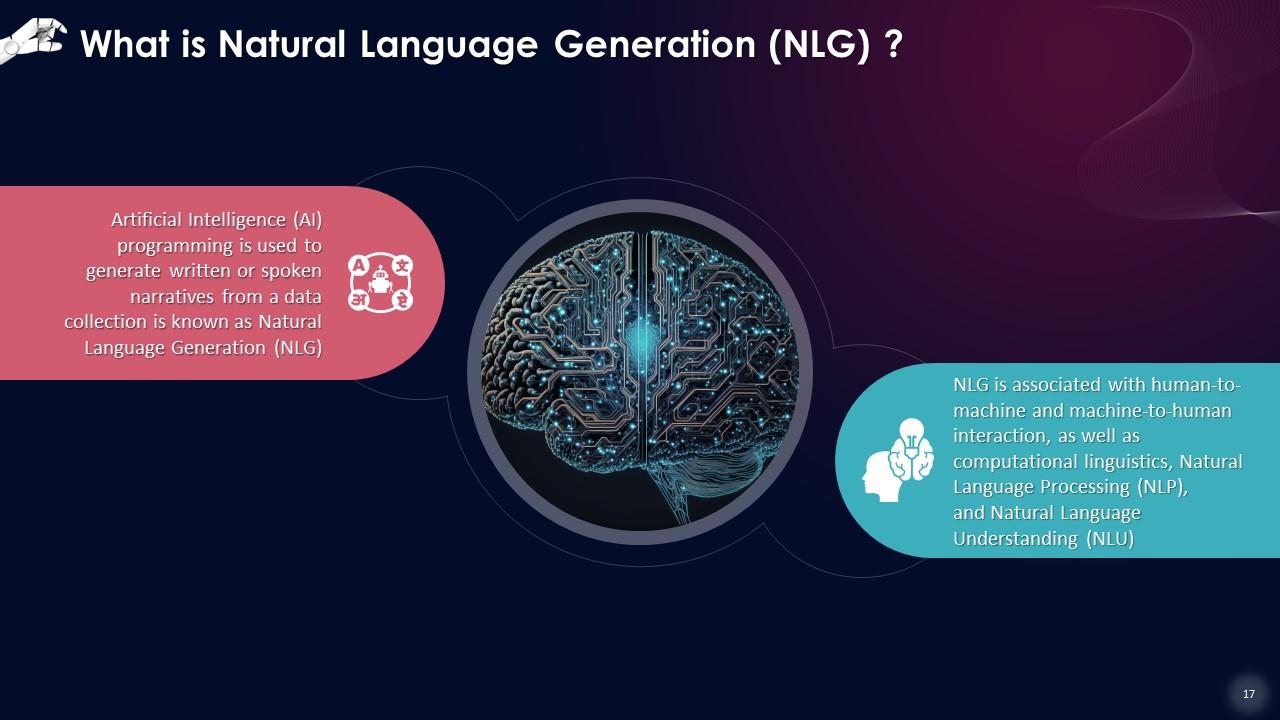
This slide gives an overview of Natural Language Generation (NLG). Artificial Intelligence (AI) programming is used to generate written or spoken narratives from a data collection. NLG is associated with human-to-machine and machine-to-human interaction, as well as computational linguistics, natural language processing (NLP), and natural language understanding (NLU).
Slide 18
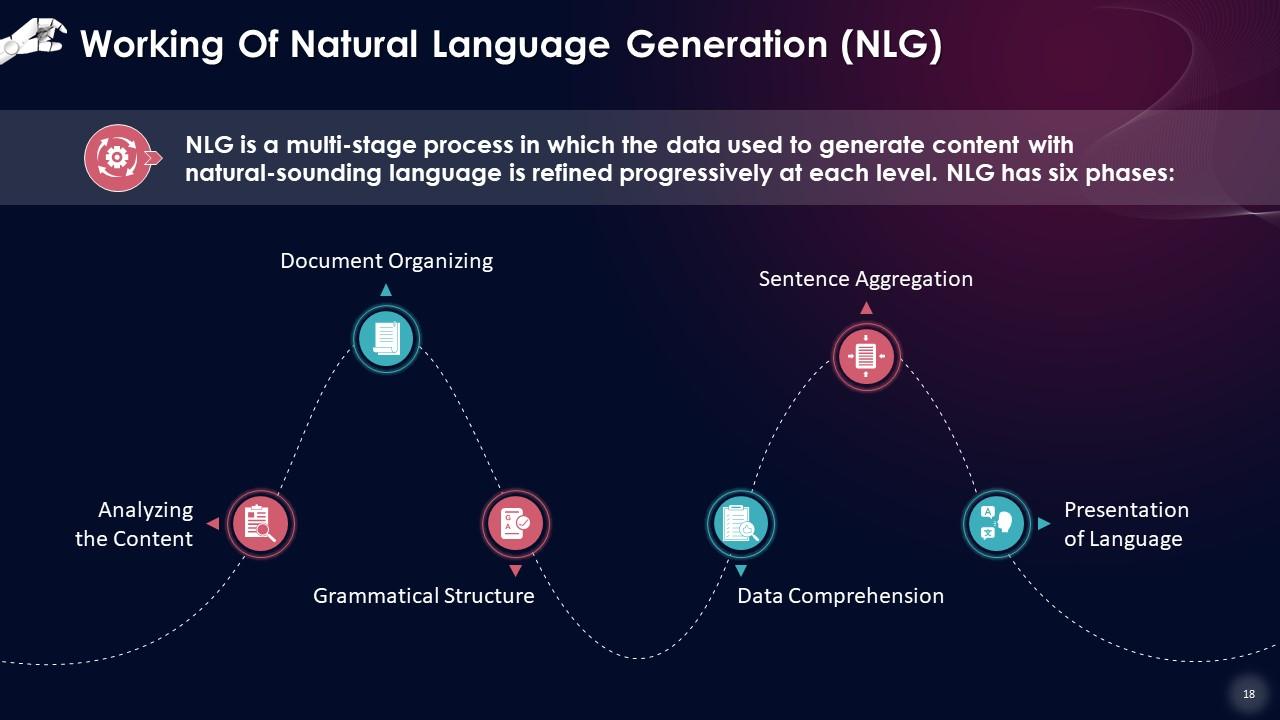
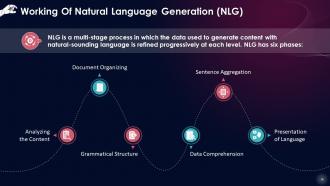
This slide states that NLG is a multi-stage process in which the data used to generate content with natural-sounding language is refined progressively at each level.
Instructor Notes:
- Analyzing the content: Data is screened to determine what should be incorporated into the final output of the process. This stage entails determining the primary themes and linkages in the original document
- Data comprehension: The data is evaluated, patterns are discovered, and placed in context. At this point, Machine Learning is frequently applied
- Document organizing: Based on the data being analyzed, a documented plan is constructed, and a narrative framework is established
- Sentence aggregation: Relevant sentences or sections of sentences are blended to provide an accurate summary of the issue
- Grammatical structure: To create natural-sounding writing, grammatical rules are employed. The software determines the sentence's syntactical structure, and this information is then used to rephrase the statement in a grammatically accurate manner
- Presentation of language: The final output is created depending on the template or the chosen by the user or programmer
Slide 19
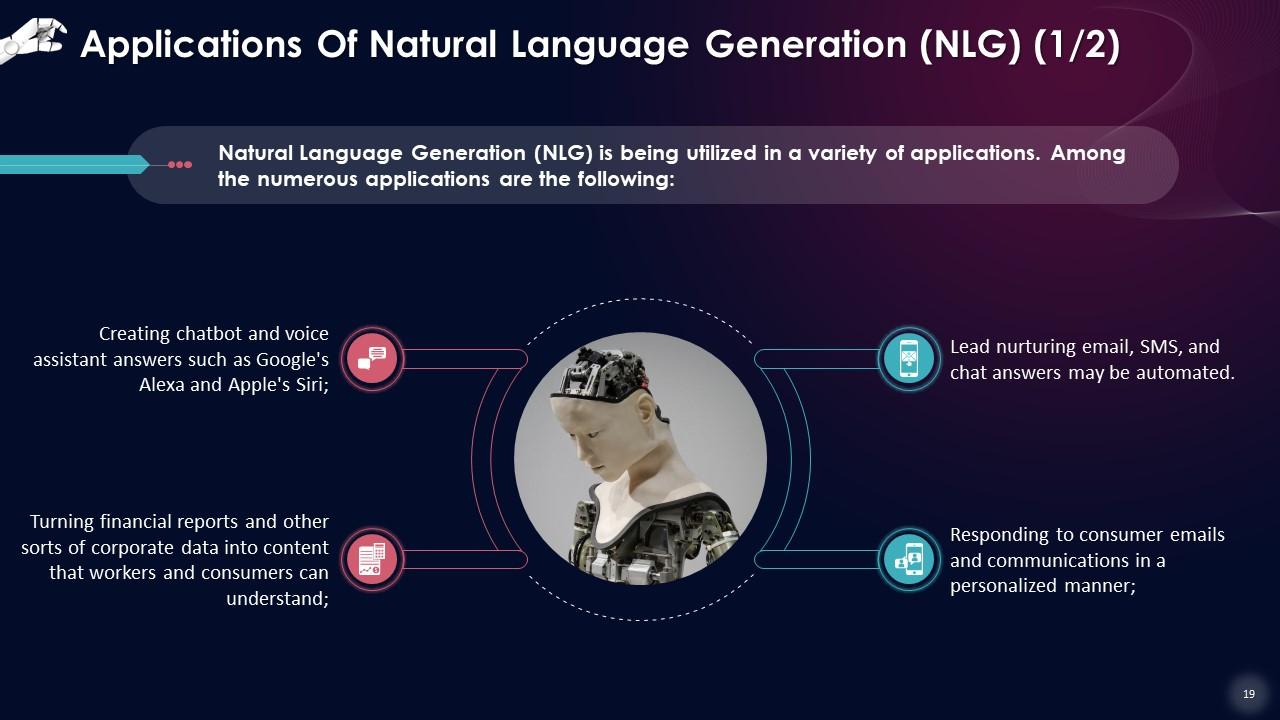
This slide describes that Natural Language Generation (NLG) is being used in various applications such as creating chatbots and voice assistant answers like Google's Alexa and Apple's Siri. Turning financial reports and other corporate data into content that workers and consumers can understand. Lead nurturing email, SMS, and chat answers may be automated.
Slide 20
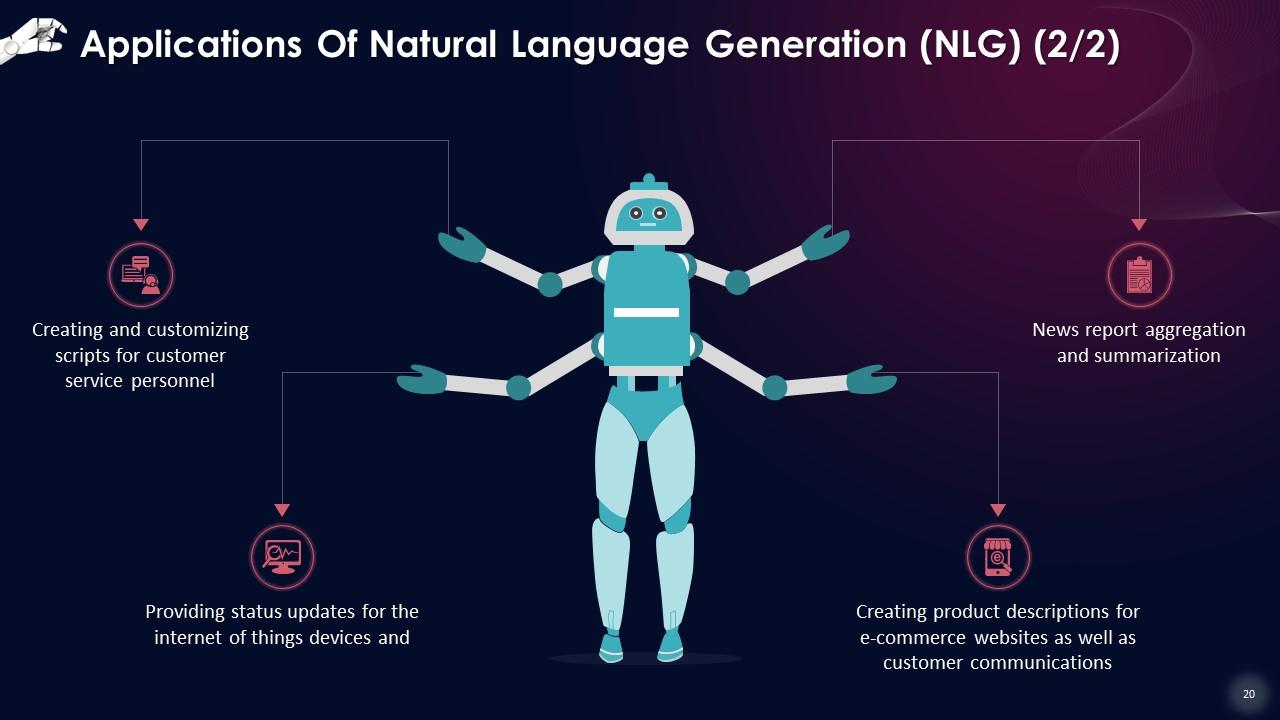
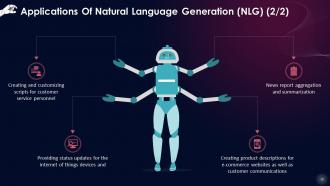
This slide lists applications of Natural Language Generation (NLG), such as creating and customizing scripts for customer service personnel, news report aggregation and summarization. Providing status updates for the internet of things devices; and creating product descriptions for e-commerce websites as well as customer communications.
Slide 21
This slide states advantages of Natural Language Generation (NLG), such as consistently high-quality content, enhanced content creation, topical coverage that would be unprofitable otherwise, allows human energy to focus high-value tasks, and scalable personalization.
Slide 23
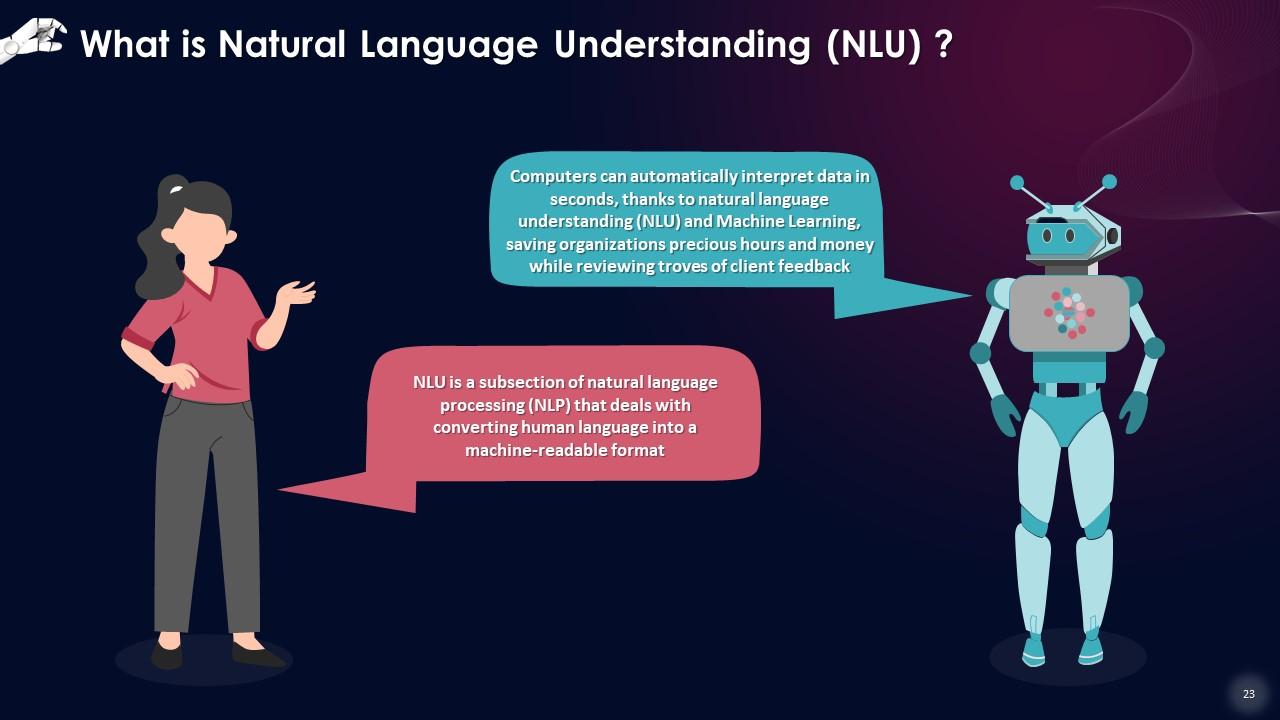
This slide gives an overview of NLU, a subsection of Natural Language Processing (NLP) that deals with converting human language into a machine-readable format. Computers can automatically interpret data in seconds thanks to Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Machine Learning, saving organizations precious hours and money while reviewing troves of client feedback.
Slide 24
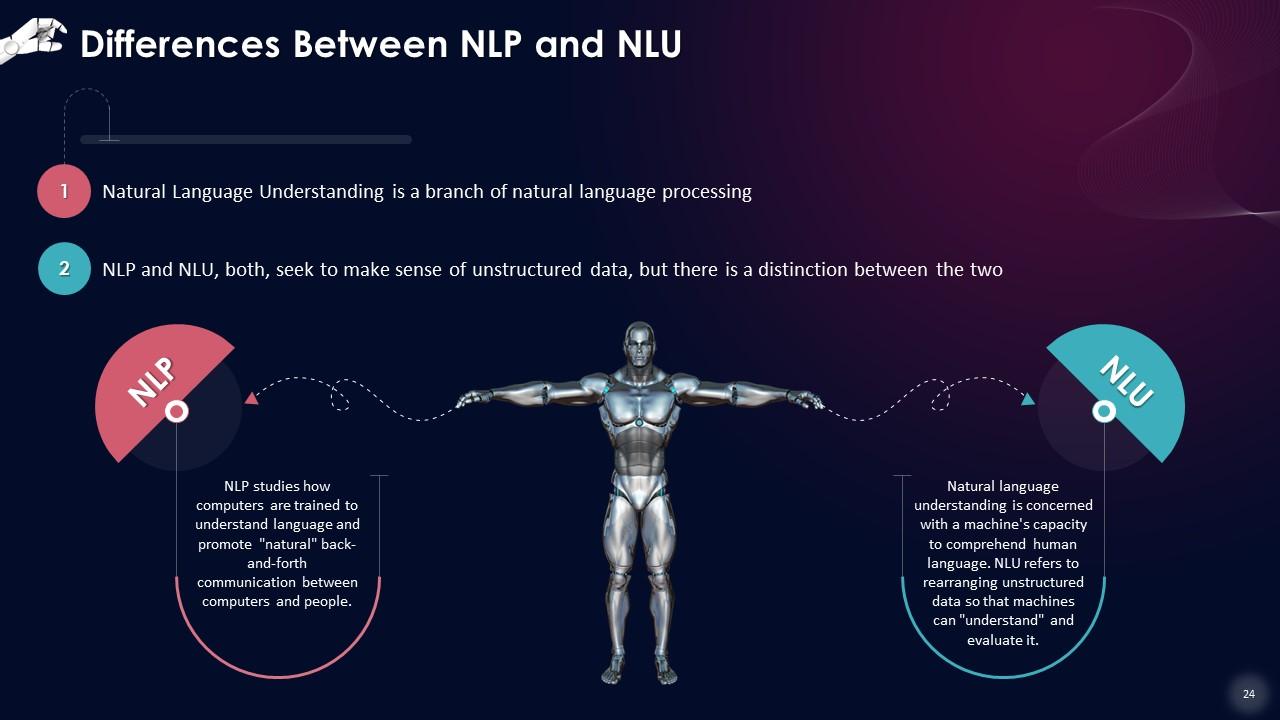
This slide states that Natural language Understanding is a branch of natural language processing. NLP and NLU, both, seek to make sense of unstructured data, but there is a distinction between the two.
Instructor Notes:
- NLP studies how computers are trained to understand language and promote "natural" back-and-forth communication between computers and people
- Natural language understanding is concerned with a machine's capacity to comprehend human language. NLU refers to rearranging unstructured data so that machines can "understand" and evaluate it
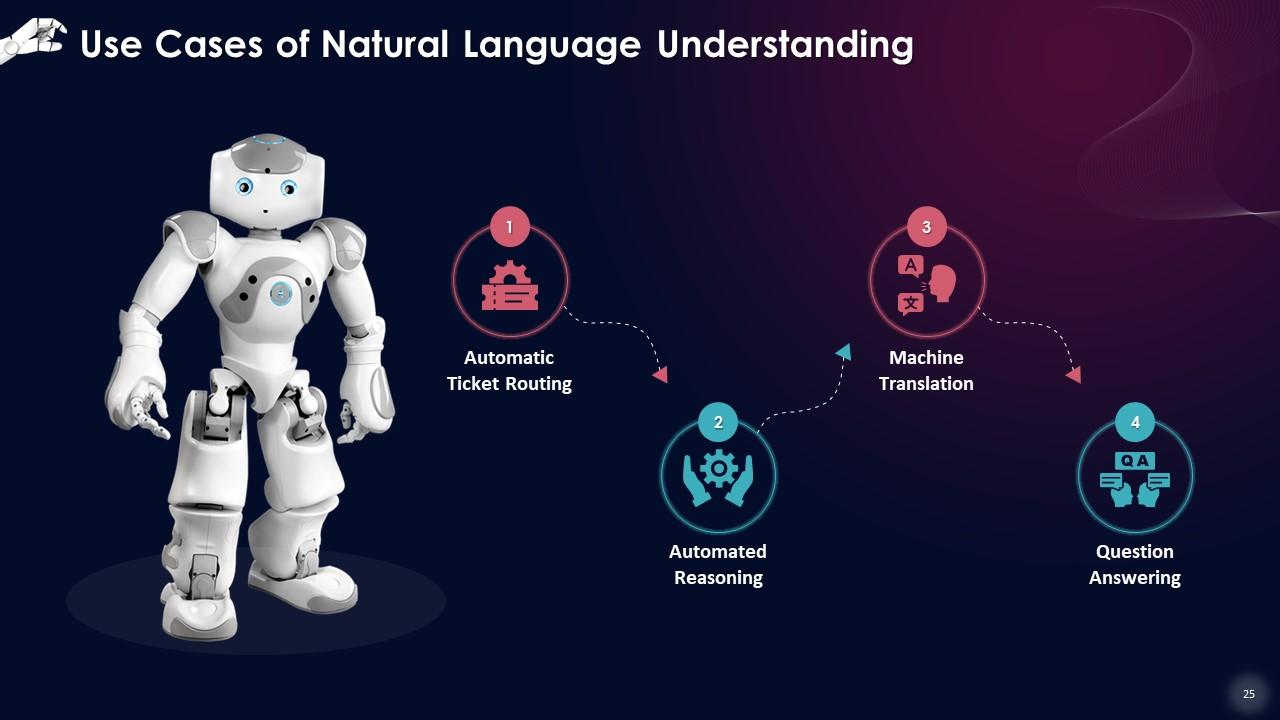
Slide 25
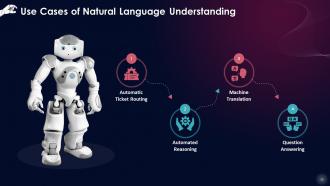
This slide lists the use cases for natural language understanding, such as automatic ticket routing, automated reasoning, machine translation and question answering.
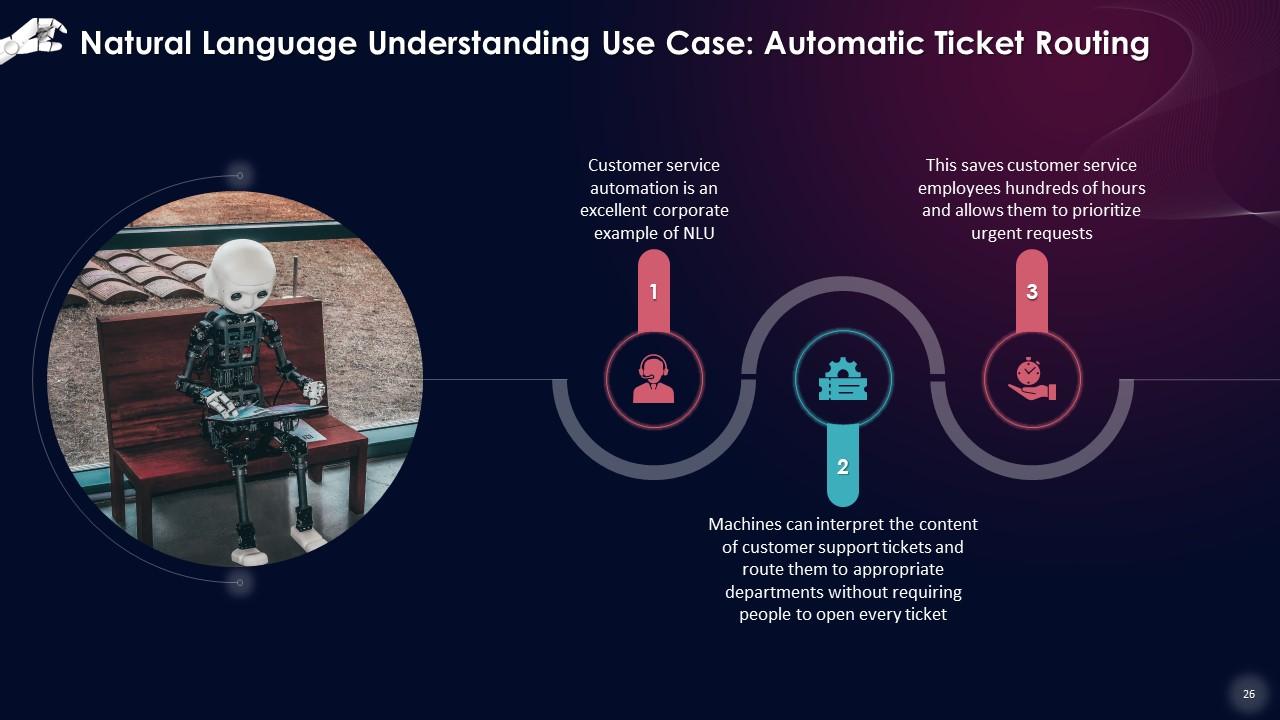
Slide 26
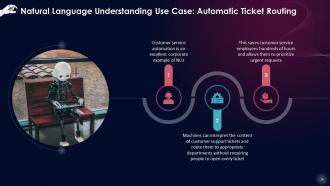
This slide states that customer service automation is an excellent corporate example of NLU. Machines can interpret the content of customer support tickets and route them to the appropriate departments without requiring people to open every ticket. This saves customer service employees hundreds of hours and allows them to prioritize urgent requests.
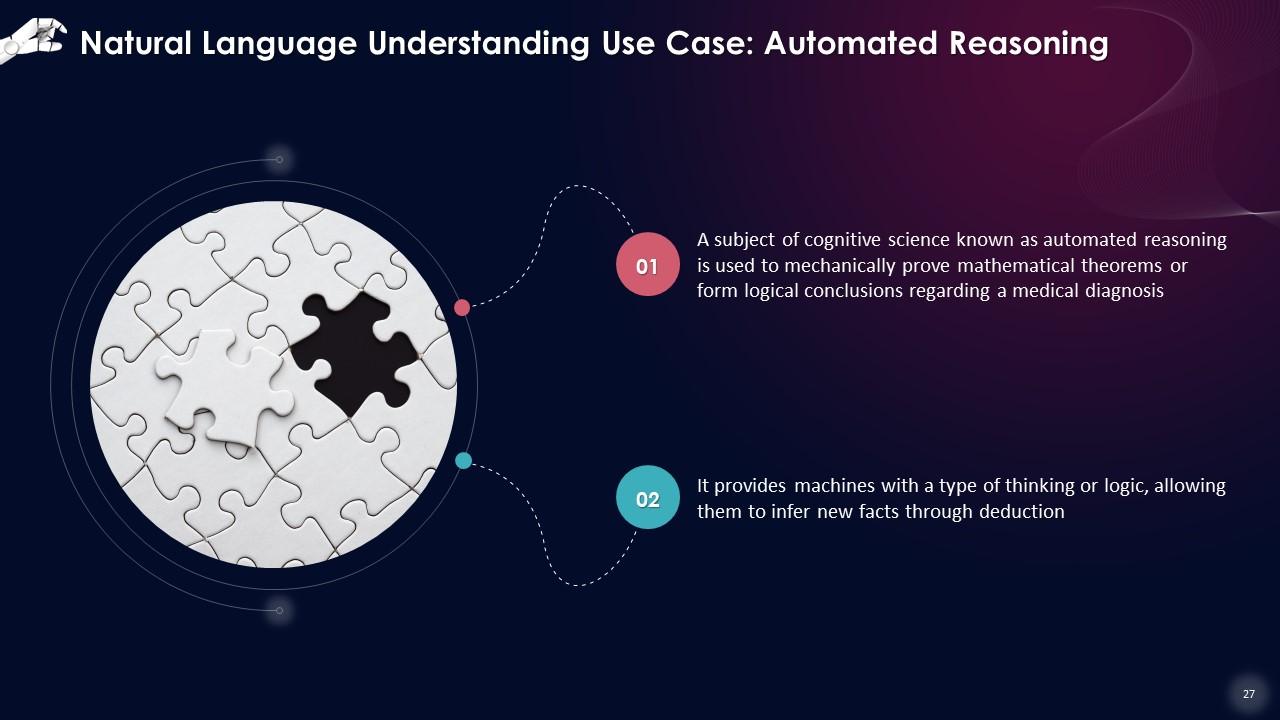
Slide 27
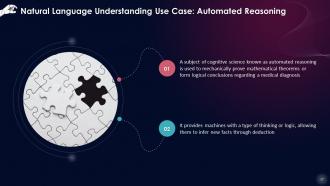
This slide describes that a subject of cognitive science known as automated reasoning is used to mechanically prove mathematical theorems or form logical conclusions regarding a medical diagnosis. It provides machines with a type of thinking or logic, allowing them to infer new facts through deduction.
Instructor Notes:
Computer algorithms may create conclusions based on previously obtained and processed data. In medicine, for example, using IF-THEN deduction rules, robots may deduce a diagnosis based on past diagnoses.
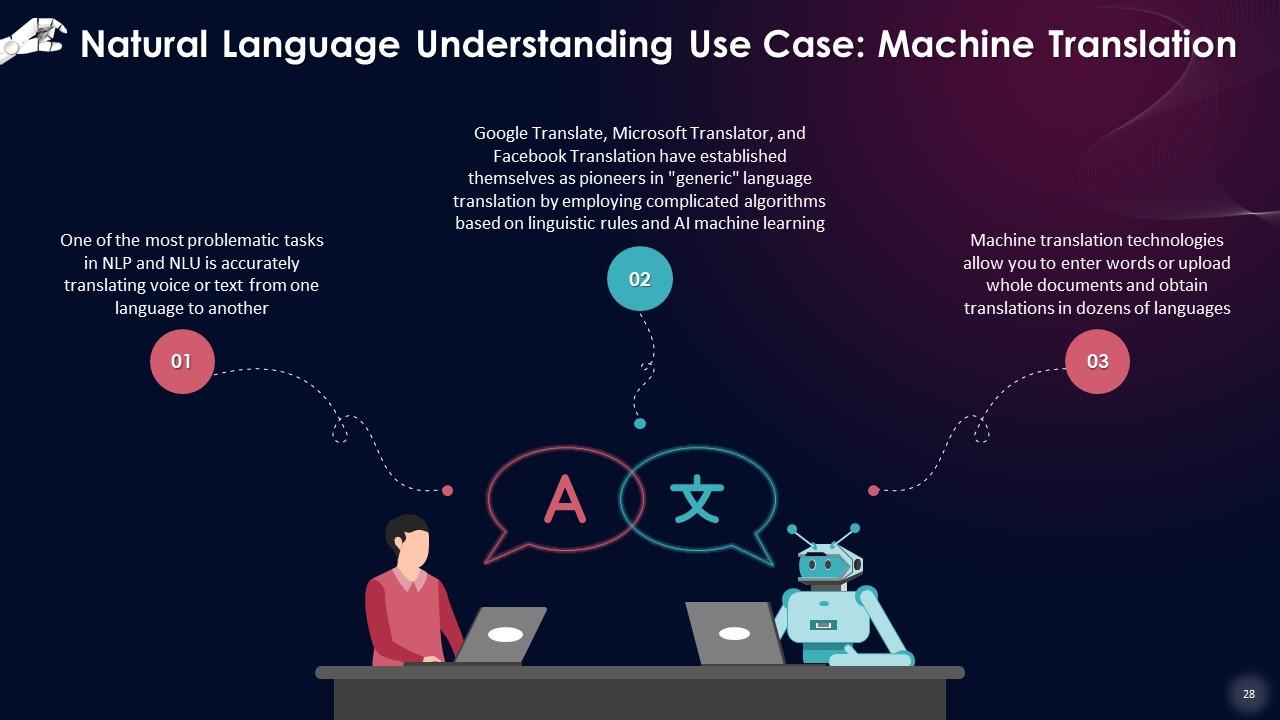
Slide 28
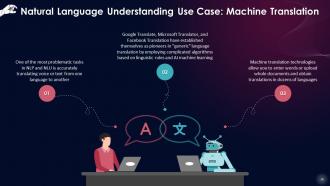
This slide states that one of the most problematic tasks in NLP and NLU is accurately translating voice or text from one language to another. Machine translation technologies allow you to enter words or upload whole documents and obtain translations in dozens of languages.
Instructor Notes:
Google Translate incorporates optical character recognition (OCR) software, enabling machines to extract text from photos, interpret it, and translate it.
Slide 29
This slide describes that answering questions is a branch of NLP and voice recognition that use NLU to assist computers in understanding natural language inquiries.
Instructor Notes:
Unless you designate a specific city, virtual assistants will tell you the weather for your present location by default. The purpose of question answering is to respond in the user's native language rather than a list of written replies.
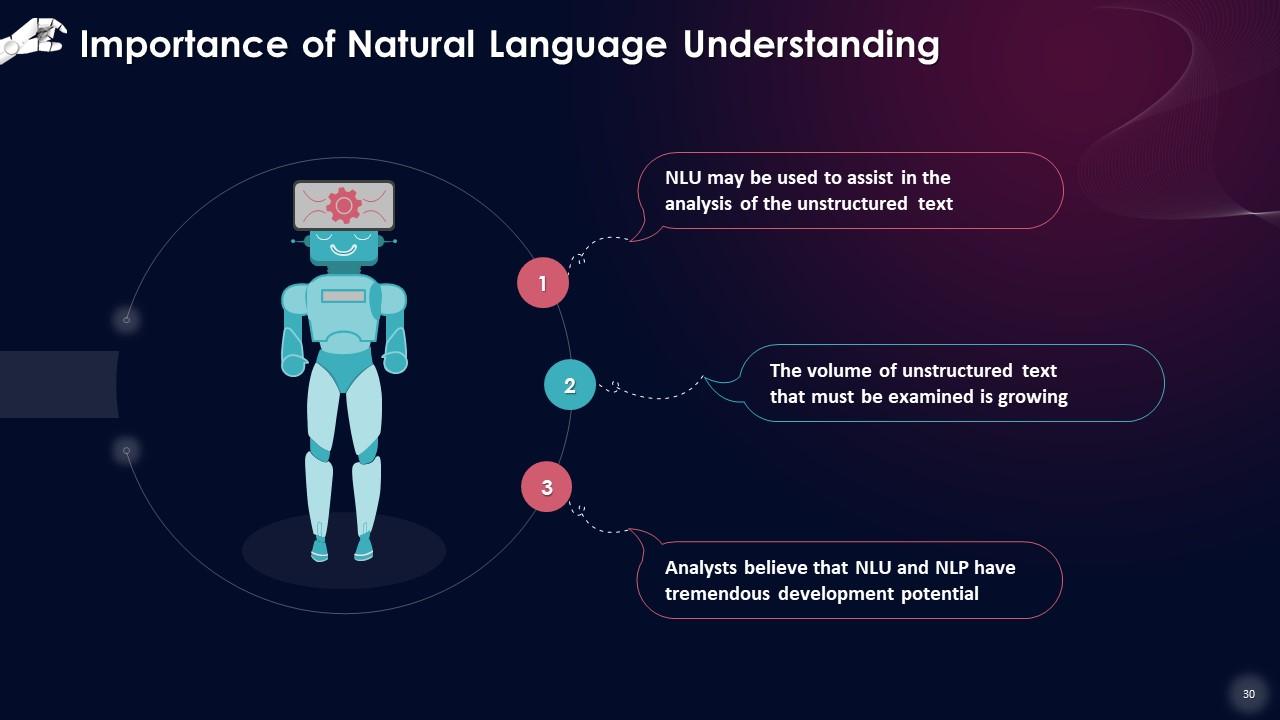
Slide 30
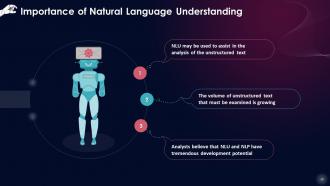
This slide lists the importance of natural language understanding. This is that NLU may be used to assist in the analysis of the unstructured text, analysts believe that NLU and NLP have tremendous development potential as the volume of unstructured text that must be examined is growing.
Instructor Notes:
- NLU may be used to assist in the analysis of the unstructured text: People can express themselves in a variety of ways, and this can differ from person to person. The accurate knowledge of the user is essential for personal assistants to be successful. NLU converts the language's complicated structure into a machine-readable format, allowing for text analysis and for robots to respond to human questions
- Analysts believe that NLU and NLP have tremendous development potential: Computers can undertake language-based analysis in a consistent and unbiased manner 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Given the volume of raw data created every day, NLU and NLP are crucial for effective data analysis. This data can be read, listened to, and analyzed by a well-developed and designed NLU-based application
- The volume of unstructured text that must be examined is growing: Analysts predict a CAGR of more than 20% between 2020 and 2025. According to Markets Insider's 2019 study, the worldwide natural language processing (NLP) industry is anticipated to be valued at $35 billion by 2025. The primary underlying cause for the growth is a shift away from product-centric experiences towards customer-oriented experiences. The growing popularity of smart devices and IoT is also contributing to the general use of NLU
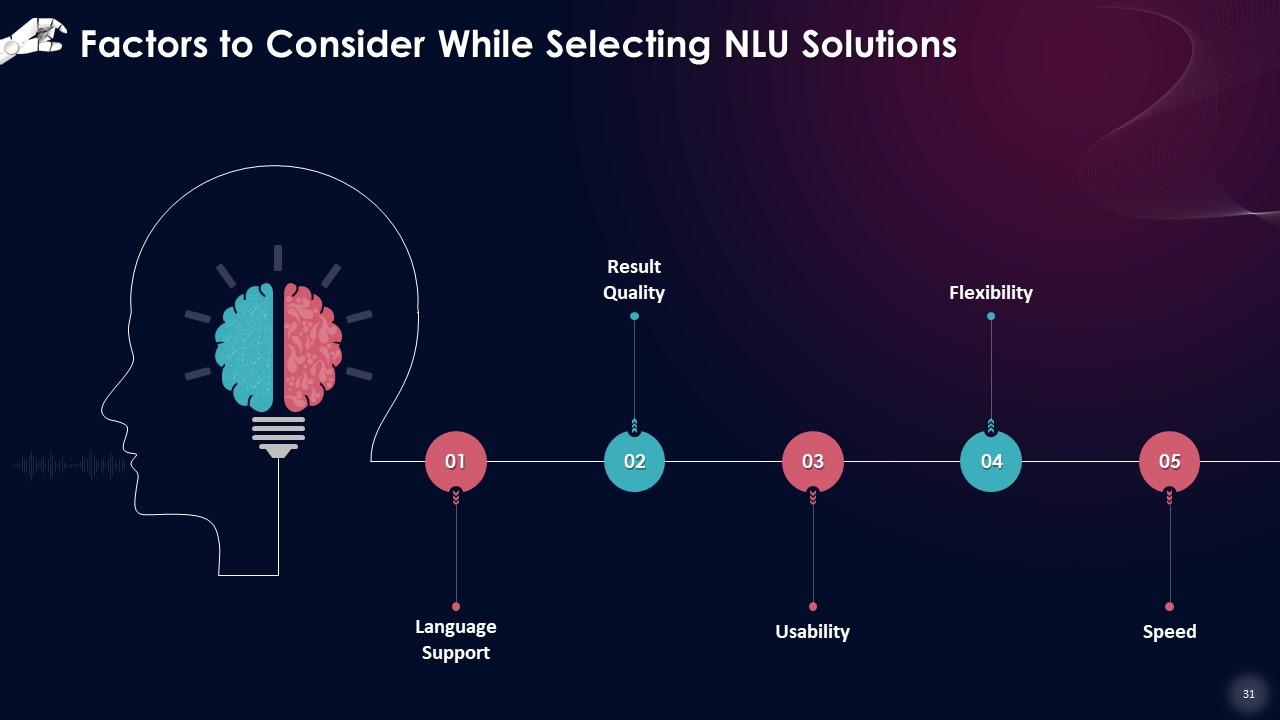
Slide 31
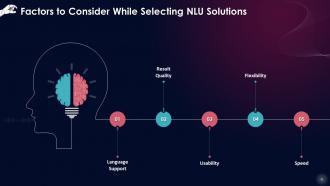
This slide showcases factors that should be considered while selecting natural language understanding solutions, such as language support, result quality, usability, flexibility, and speed.
Instructor Notes:
- Language Support: The language of the input data should be supported by the NLU platform. Currently, the quality of NLU in non-English languages is poorer due to the languages' commercial potential. This is changing, though, as research interest grows
- Result Quality: A successful NLU solution should be able to detect linguistic elements, extract their connections, and apply semantic software to understand the information, regardless of how it is written. Continuous learning, aided by Machine Learning, has the potential to increase the quality of results over time
- Usability: The solution should be simple to use for both technical and non-technical staff. A solution with many interfaces can be explored, allowing a non-tech person (such as a customer care representative) to build this system with input. With the distinct possibility that non-techies may use chatbots, the usability of the program and the convenience of use of the user interface are critical
- Flexibility: It is critical to be adaptable to solution areas. This is accomplished through the NLU solution's training and continuous learning capabilities
- Speed: In conversational AI applications, understanding the language is part of the process, and other components include creating a response or acting in response to the enquiry. As a result, seeing and comprehending the language must be completed fast. However, there may be an exchange between the quality of the findings and the speed at which they are computed. This decision needs to be based upon the application
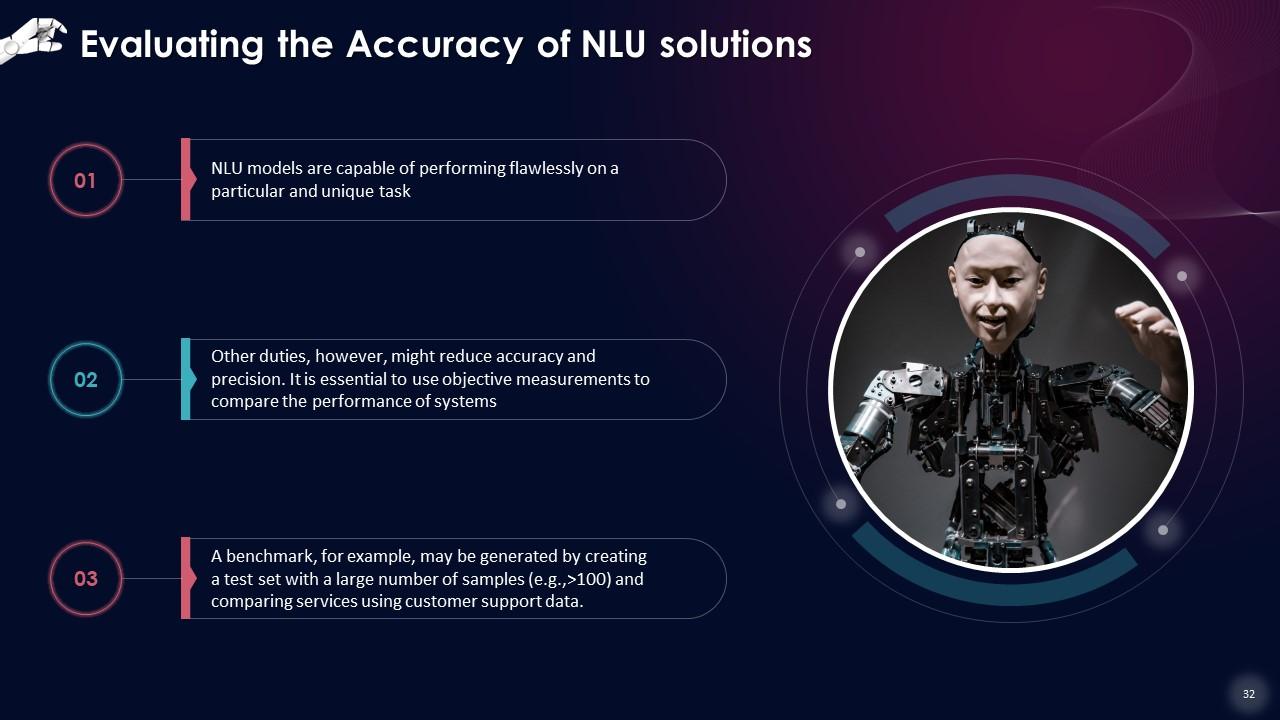
Slide 32
This slide states that NLU models are capable of performing flawlessly on a particular and unique task. Other duties, however, might reduce accuracy and precision. It is essential to use objective measurements to compare the performance of systems.
Slide 33
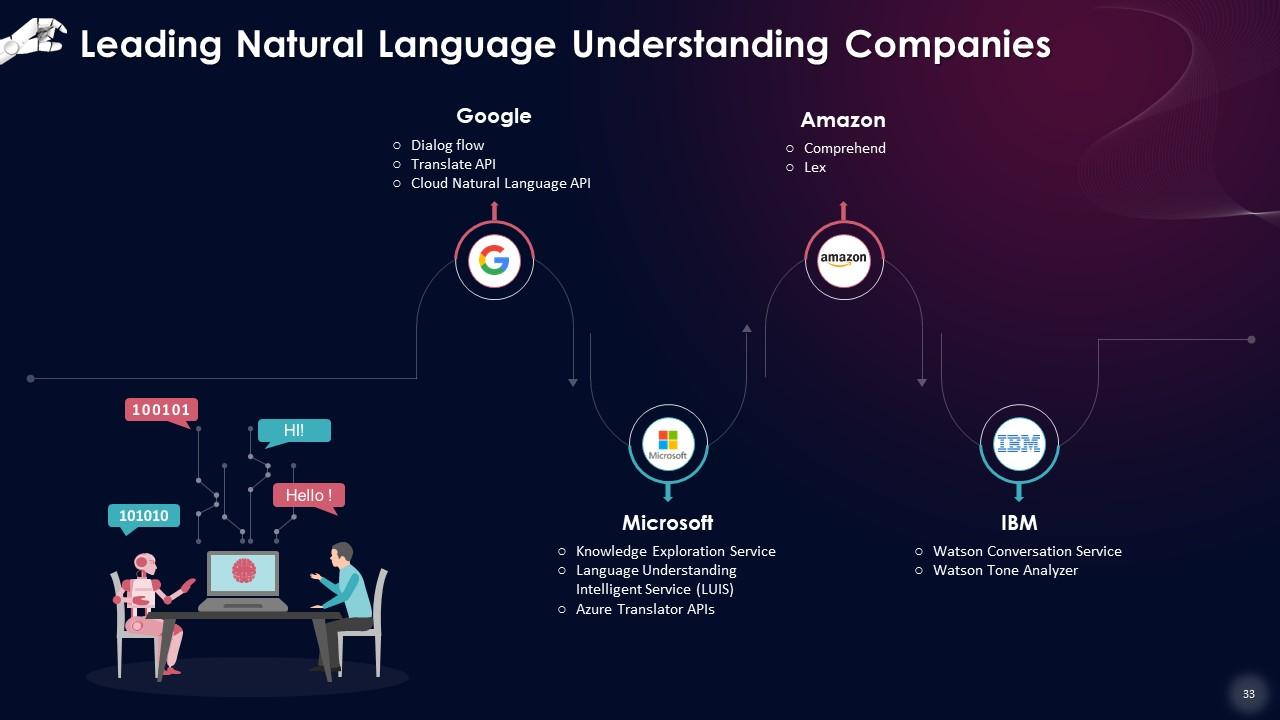
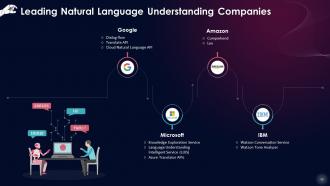
This slide lists technology giants leading in the natural language understanding ecosystem, such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and IBM.
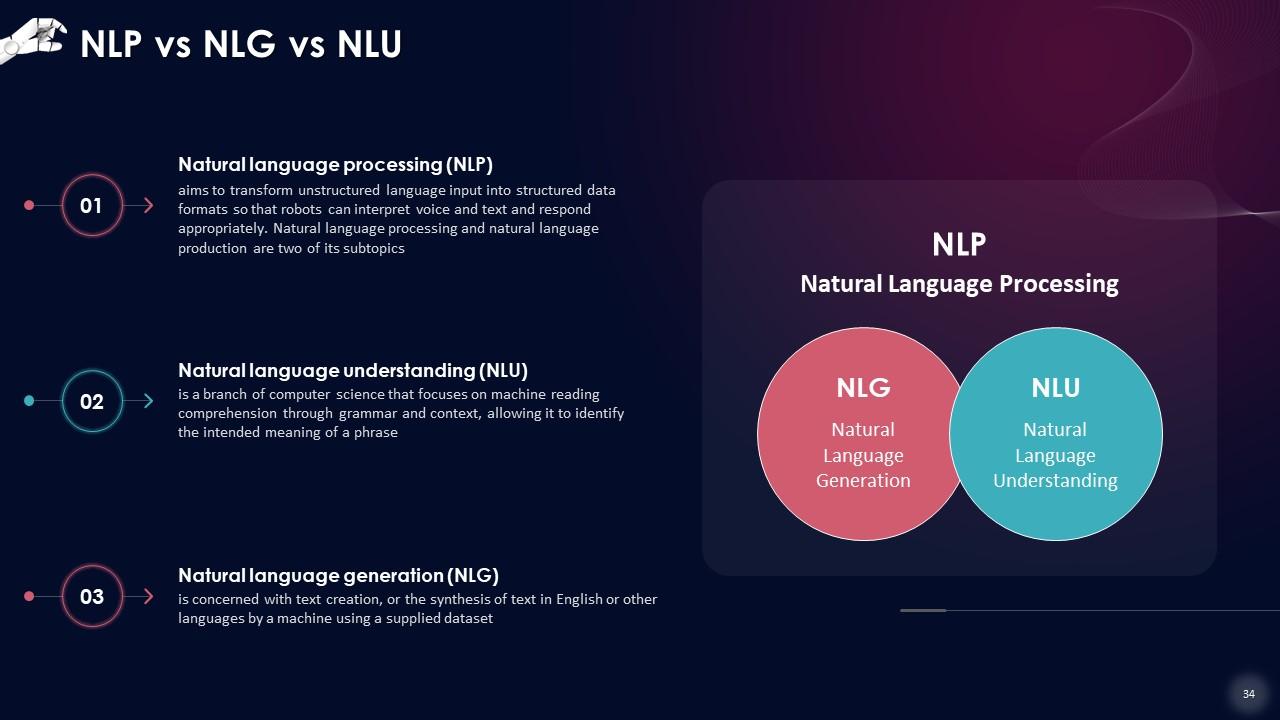
Slide 34
This slide draws a comparison between Natural Language Processing (NLP), Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG)
Instructor Notes:
- NLP (Natural Language Processing): It comprehends the meaning of the text
- NLU (Natural Language Understanding): NLU handles whole processes such as choices and actions
- NLG (Natural Language Generation): This method creates human language text from structured data provided by the system to reply
Slide 35
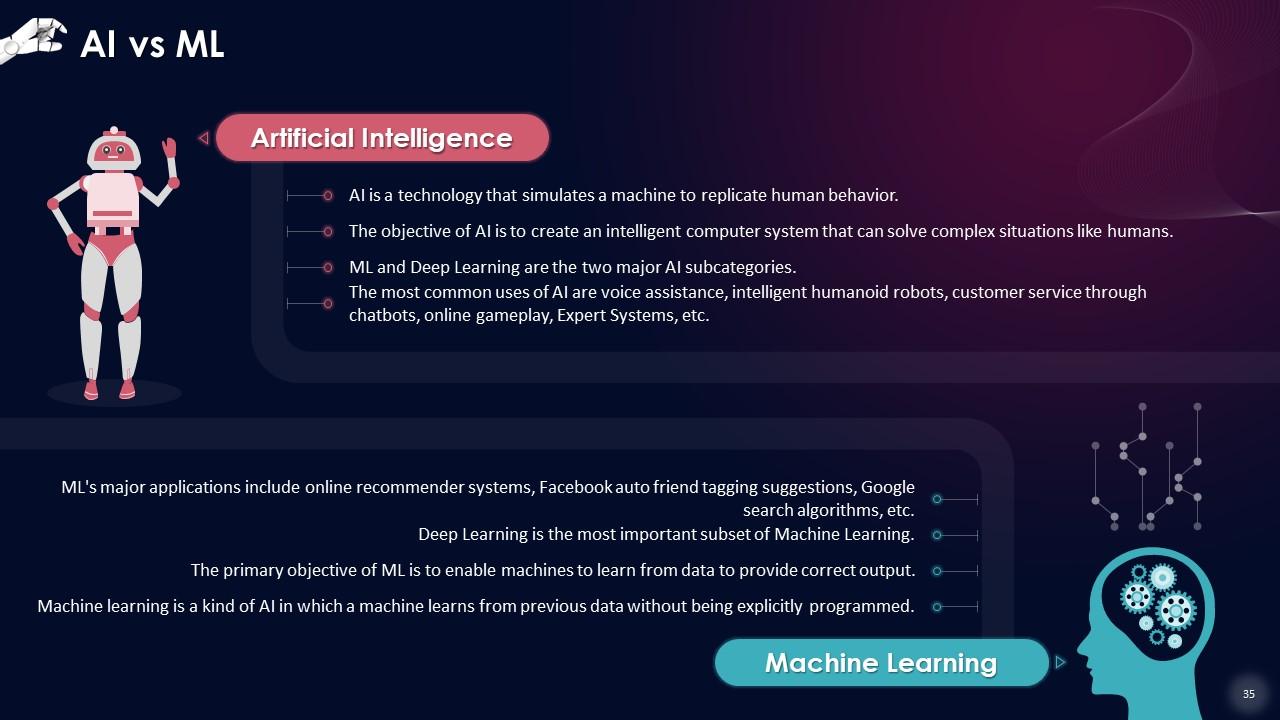
This slide lists the difference between Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). AI is a technology that simulates a machine to replicate human behavior. Machine Learning is a kind of AI in which a machine learns from previous data without being explicitly programmed.
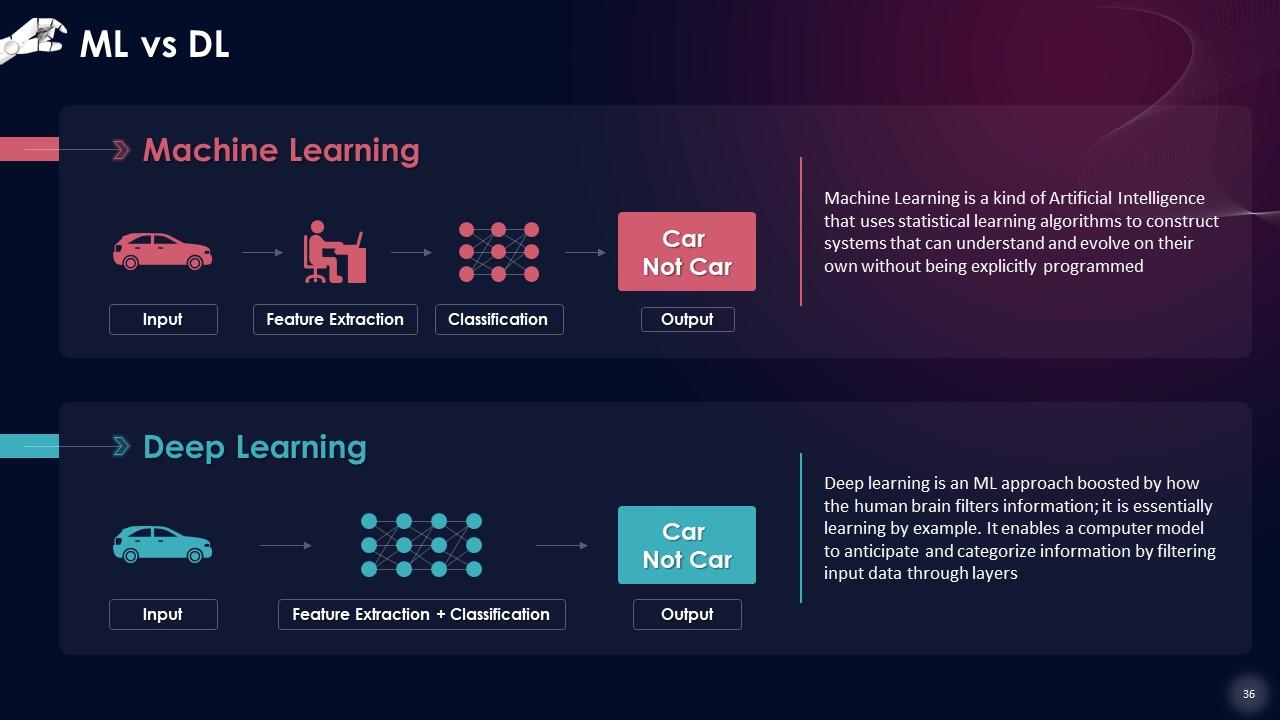
Slide 36
This slide states that Machine Learning is a kind of Artificial Intelligence that uses statistical learning algorithms to construct systems that can understand and evolve on their own without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is an ML approach boosted by how the human brain filters information; it is essentially learning by example. It enables a computer model to anticipate and categorize information by filtering input data through layers.
Slide 37
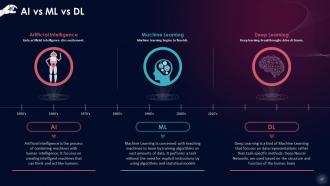
This slide states a comparison between Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL). Artificial Intelligence is the process of combining machines with human intelligence. Machine Learning is concerned with teaching machines to learn by training algorithms on reams and reams of data. Deep Learning is a kind of Machine Learning that focuses on data representations rather than task-specific methods.
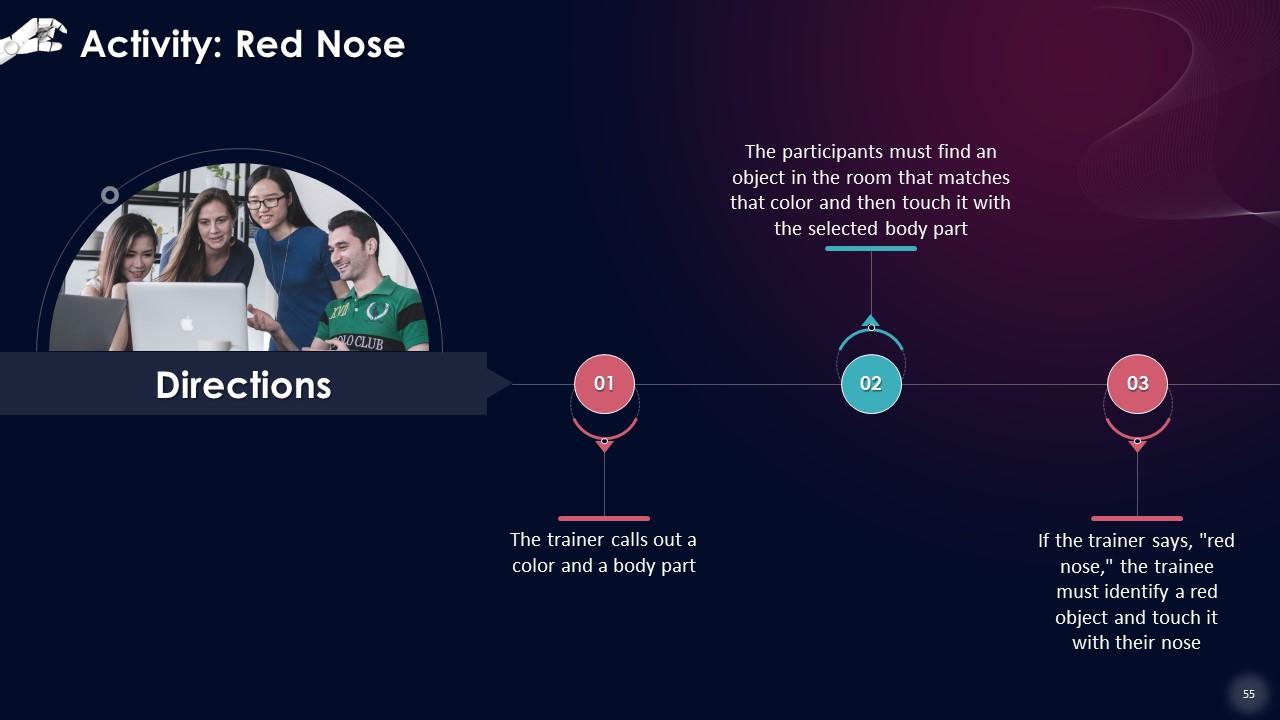
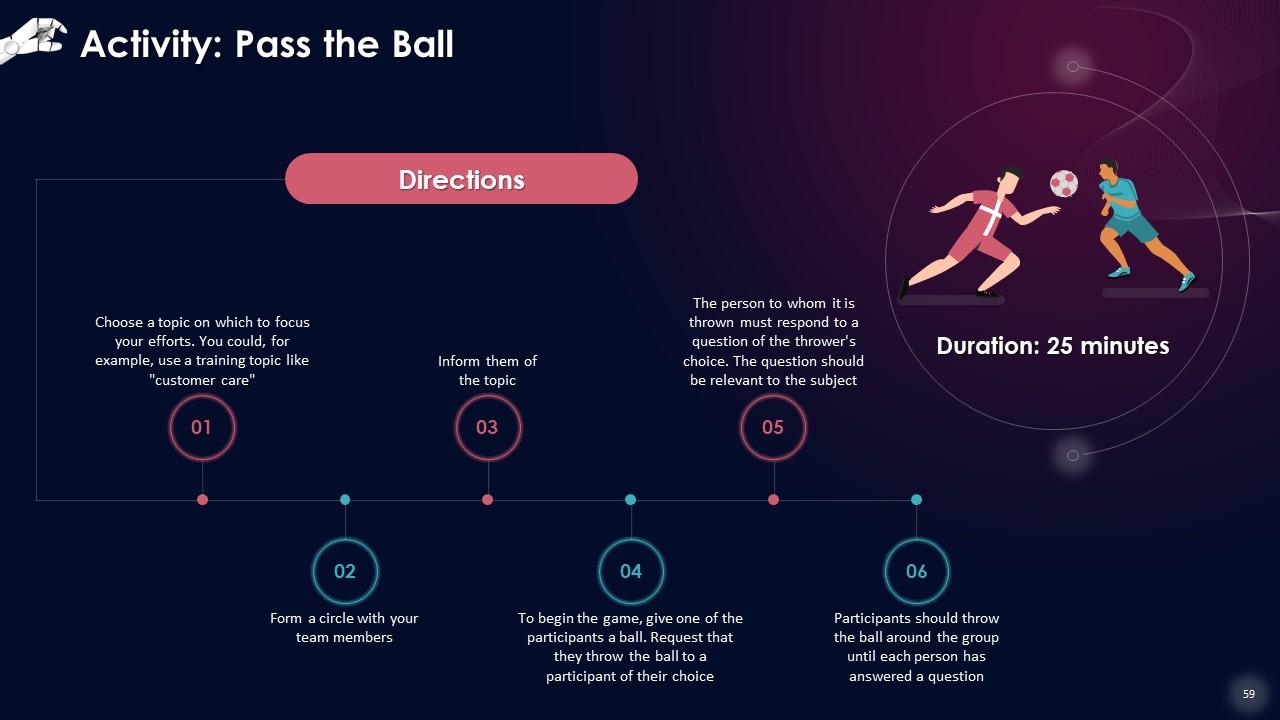
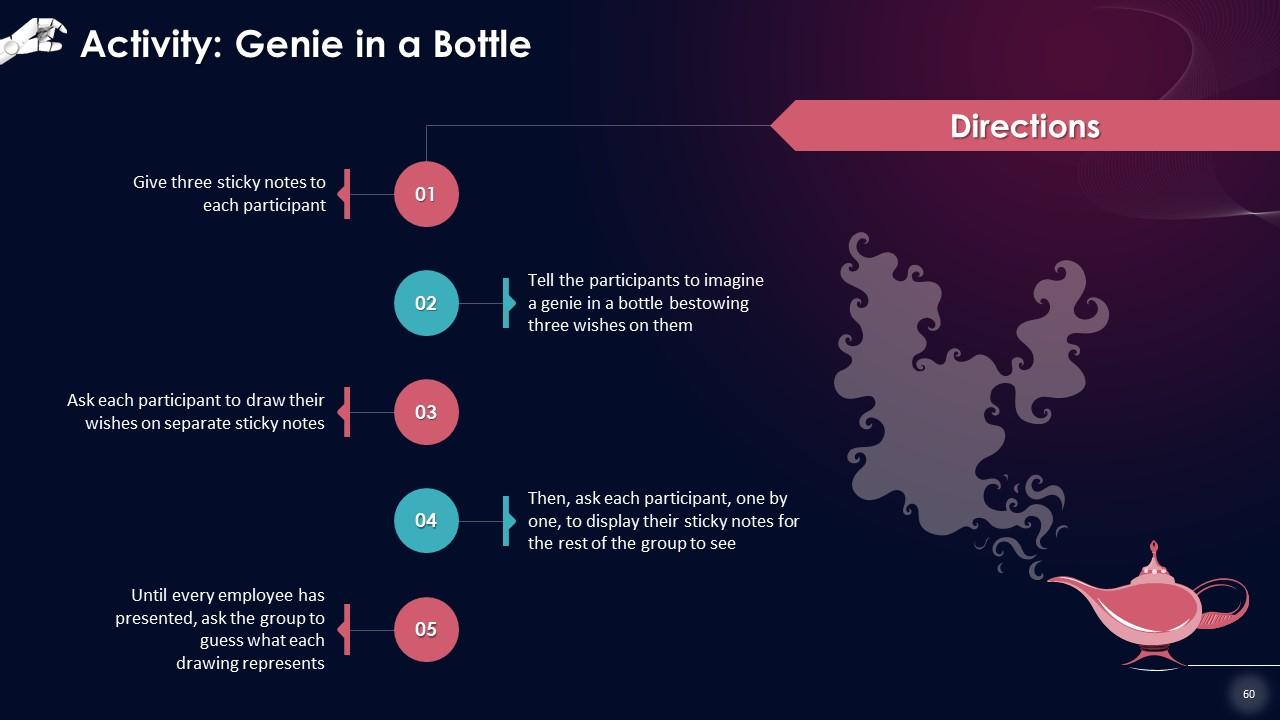
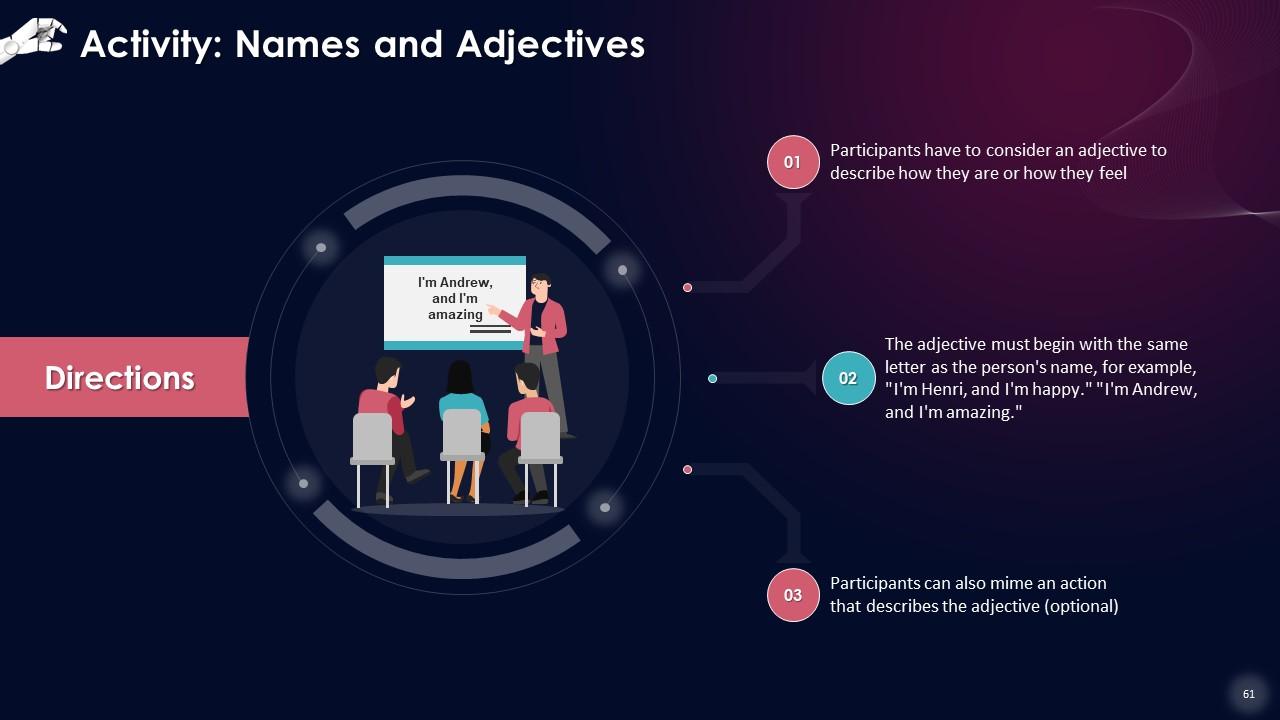
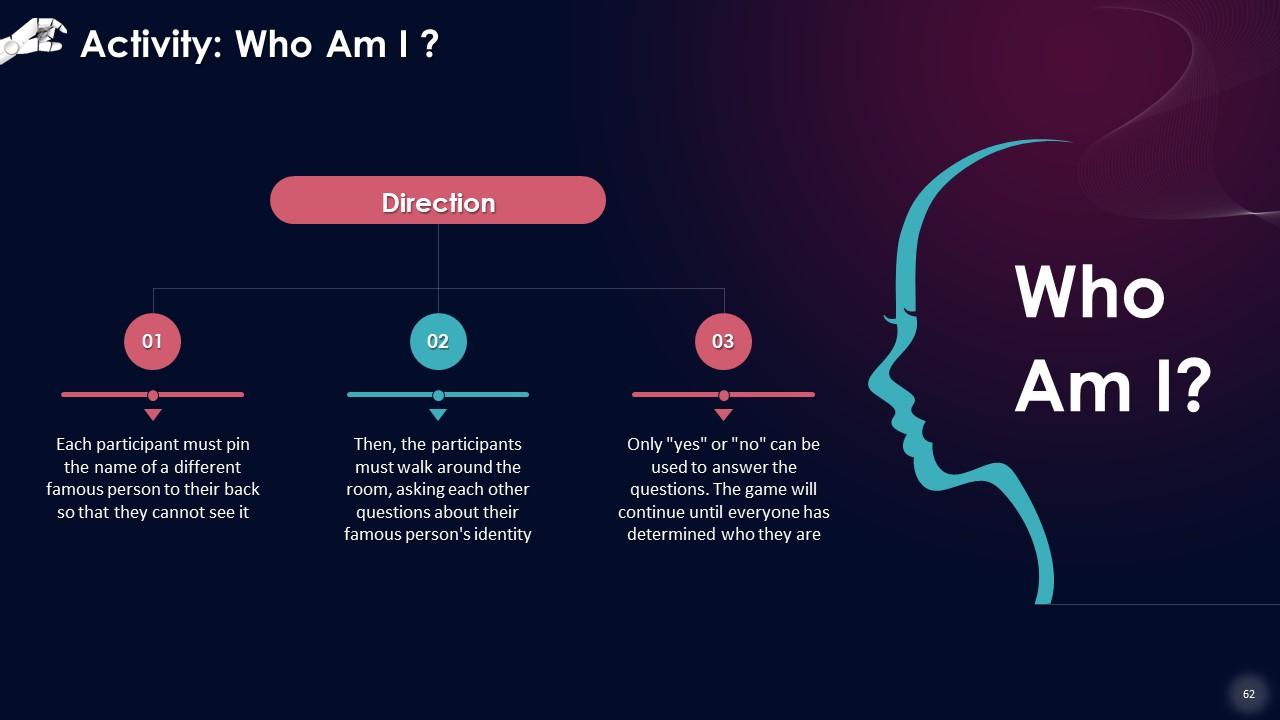
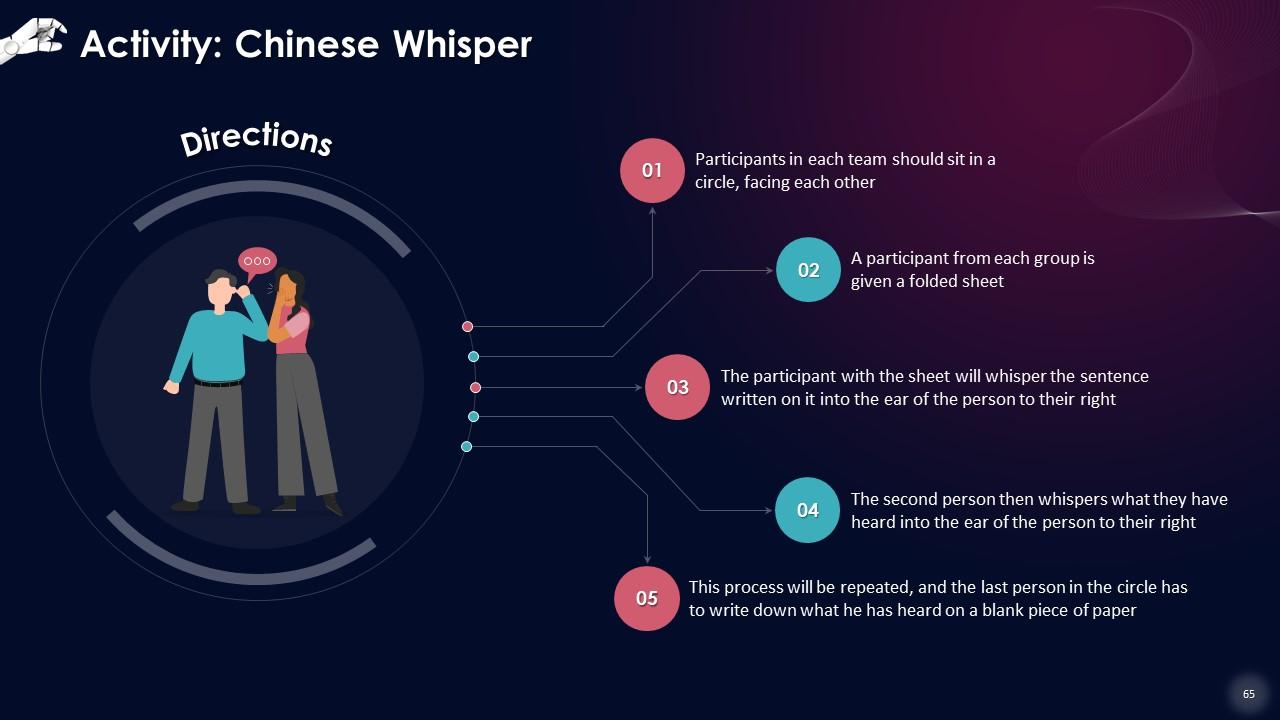
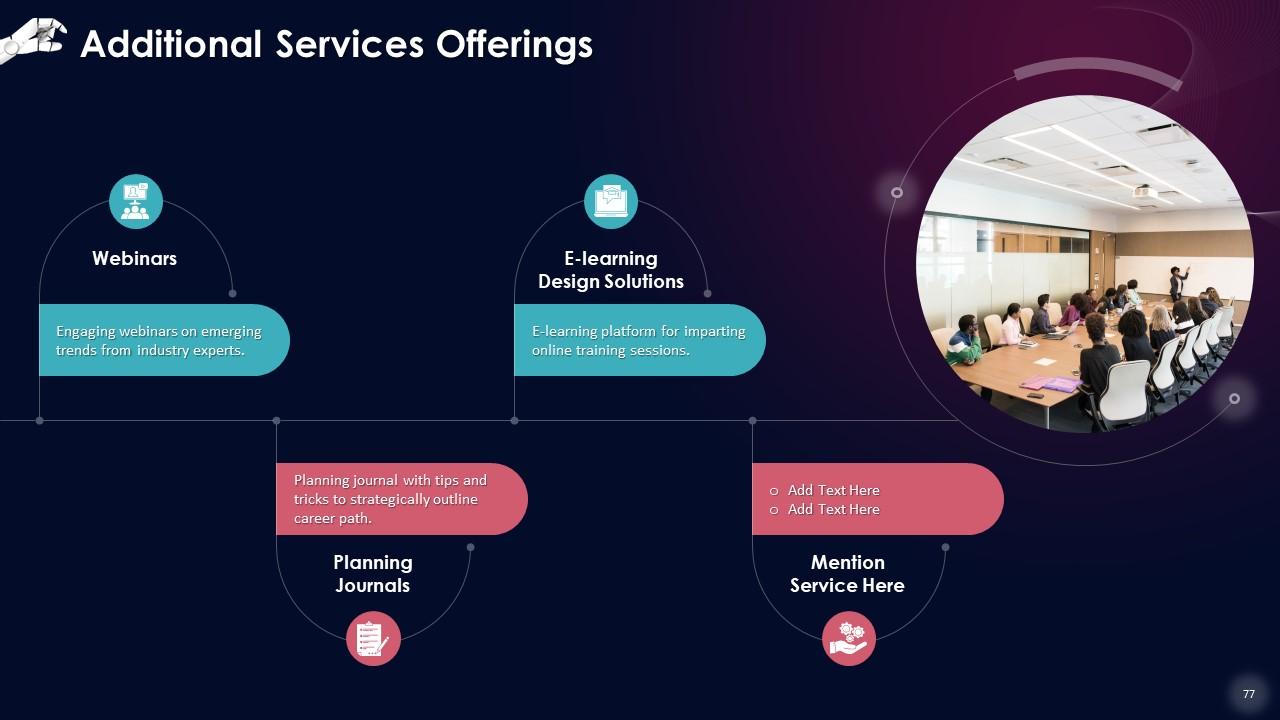
Slide 53 to 68
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 69 to 96
These slides contain a training proposal covering what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
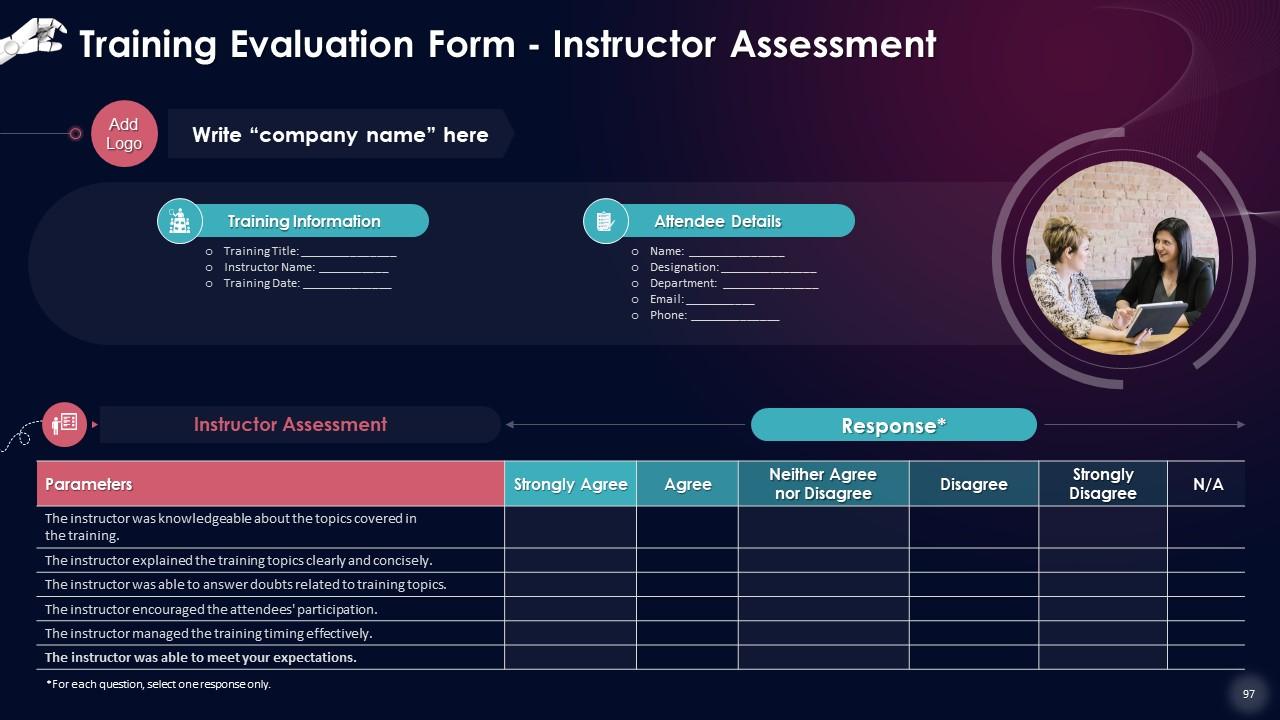
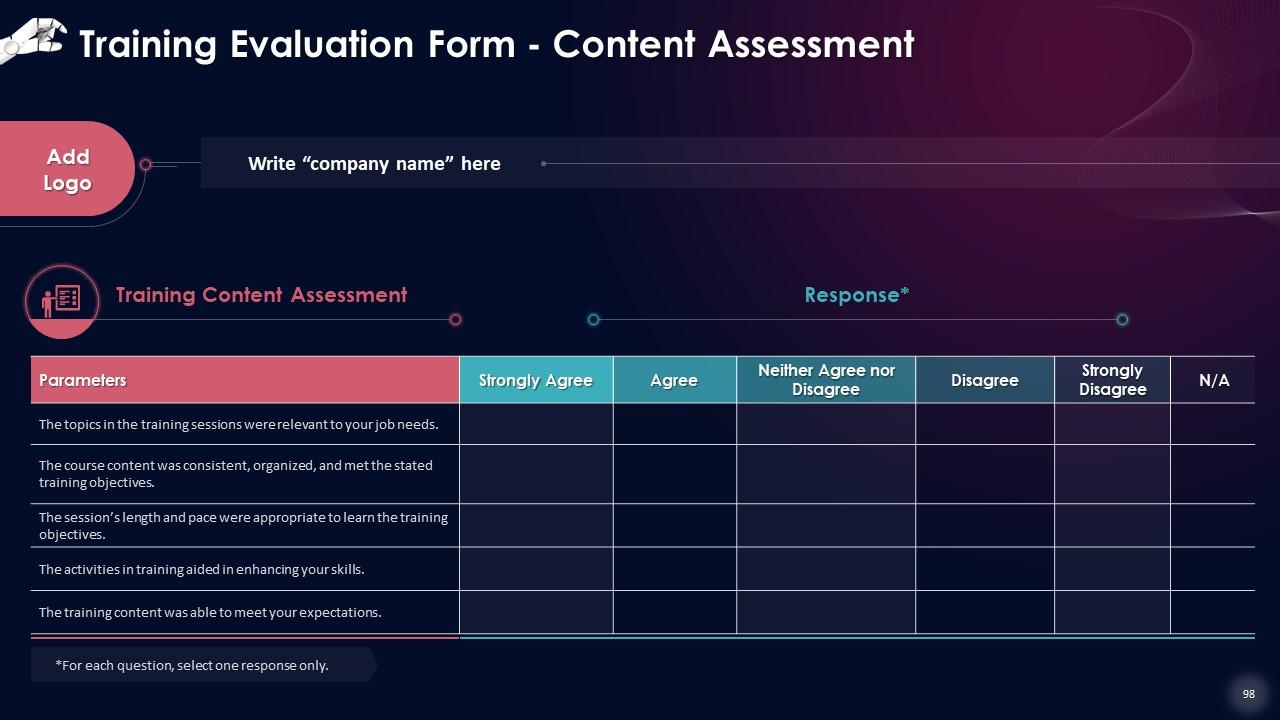
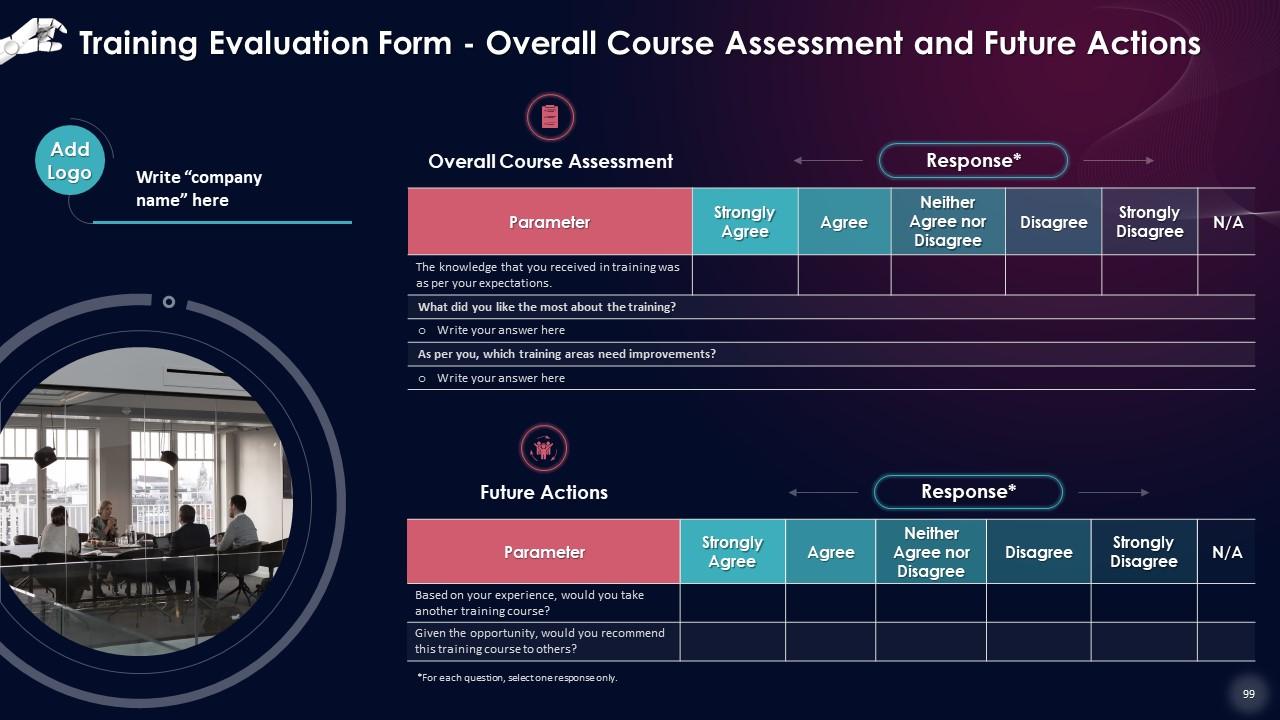
Slide 97 to 99
These slides include a training evaluation form for instructor, content and course assessment.
Unlocking The Fundamentals Of NLP NLU And NLG Training Ppt with all 104 slides:
Use our Unlocking The Fundamentals Of NLP NLU And NLG Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Impressive templates. Designing a presentation is fun now!
-
“There is so much choice. At first, it seems like there isn't but you have to just keep looking, there are endless amounts to explore.”