Overview Of Negotiation Fundamentals Training Ppt
This training module on Overview of Negotiation Fundamentals covers the topics What is Negotiation, Why Negotiation Skills Matter, Statistics on Negotiation, Why we Avoid Negotiation, Winners Curse in Negotiation, Top Negotiation Myths. Further, it contains the Approaches to Negotiation Distributive and Integrative, Types of Negotiation Principled Negotiation, Team Negotiation, Multiparty Negotiation, and Adversarial Negotiation, Special Types of Negotiators Assertive, Analyst, and Accommodator, Effective vs. Ineffective Negotiators, Negotiation Strategies Win-Lose, Win-Win, Lose-Lose, and Lose-Win, Negotiation Styles Competitive, Compromising, Accommodating, Avoiding, and Collaborating, and Harvard Negotiation Model. It includes Key Takeaways and Discussion Questions related to the topic to make the coaching session more interactive. The deck has PPT slides on About Us, Vision, Mission, Goal, 30-60-90 Days Plan, Timeline, Roadmap, Training Completion Certificate, and Energizer Activities. It also includes a Client Proposal and Assessment Form for training evaluation.
This training module on Overview of Negotiation Fundamentals covers the topics What is Negotiation, Why Negotiation Skills ..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Overview of Negotiation Fundamentals. This deck comprises of 91 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
This slide explains the concept of Negotiation. It highlights that Negotiation is a strategic conversation that resolves an issue in a way that is acceptable to both parties. By negotiating, parties involved make an attempt to agree on some form of compromise. It also mentions that negotiation can happen between buyers and sellers, an employer and a prospective employee, or governments of two or more countries.
Slide 5
This slide depicts the importance of Negotiation in businesses and in everyday life. It highlights that in businesses, negotiations can assist in developing stronger relationships, avoiding future problems and conflicts. It also mentions that Negotiations in everyday life, negotiation can assist in building confidence, developing interpersonal skills, improving strategizing and planning.
Slide 6
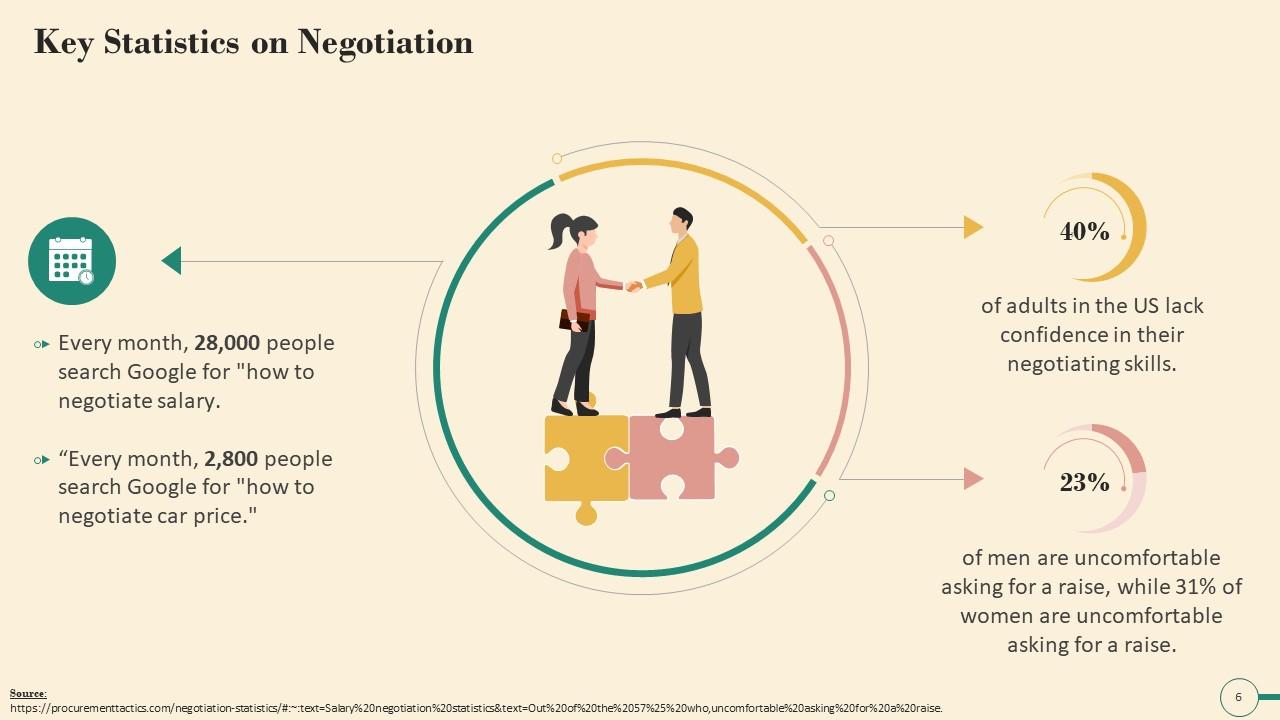
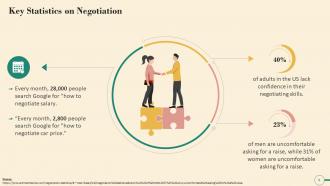
This slide illustrates key statistics on negotiation. It highlights the percentage of people in the U.S. who lacks negotiation skills, and also mentions that women are more uncomfortable than men in asking for a raise.
Slide 7
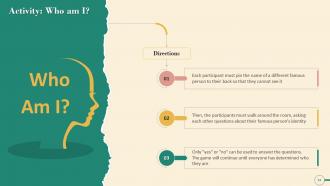
This slide depicts an activity named “Compete and Collaborate Simultaneously” on Negotiation that can be performed during the training session.
Slide 9
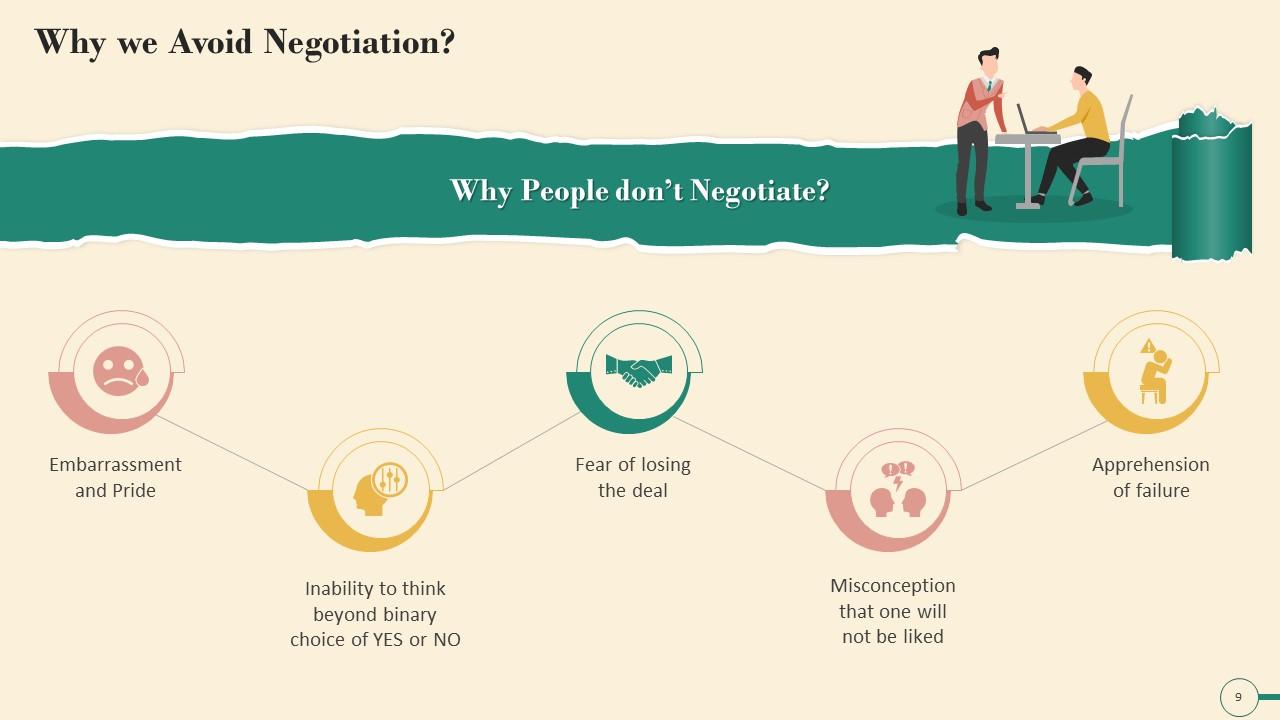
This slide illustrates common reasons people avoid Negotiation. The reasons are embarrassment and pride, inability to think beyond binary choice of YES or NO, fear of losing the deal, being liked, and fear of negotiating badly.
Instructor’s Notes:
Common Reasons Why People Avoid Negotiation are
- Embarrassment and Pride: People are easily embarrassed when they consider negotiating, but they should not be
- Inability to think beyond binary choice of Yes or No: People must realize that there is always a choice beyond reluctantly saying YES or unhelpfully saying NO. People should never forget that there is always the option of Negotiating and creating a win-win deal for all parties involved
- Fear of losing the deal: People believe that attempting to negotiate will result in a complete loss of the deal. Hence, they abstain from Negotiating
- Being disliked: Many people are afraid that if they negotiate, others will dislike them. But whether they like you or not, you're not going to see them again. Even if you pay the full amount, there is no guarantee that they will like you
- Fear of doing a bad job at negotiating: This is the fear that engulfs all of us. Many people believe that their negotiating skills are inadequate, so why even try? However, the ability to negotiate never arises because they never ask. If you never ask, you will never be able to negotiate
Slide 10
This slide depicts an example of Winner’s Curse in Negotiation. In the example, an employee believes he could have negotiated with his boss for a better raise.
Slide 11
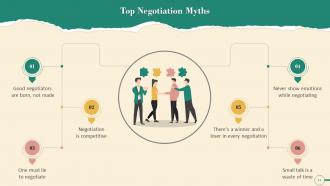
This slide illustrates common Negotiation myths. The common myths are: Good negotiators are born and not made, negotiation is competitive, you must lie to negotiate, never show emotions while negotiating, there's a winner and a loser in every negotiation, and small talk is a waste of time.
Instructor’s Notes:
Common Negotiation Myths are:
- Good negotiators are born and not made: This myth holds that certain people are born with an innate ability to persuade others. Some people appear to be born with a natural ability to negotiate. On the other hand, their talent is frequently the result of a lot of hard work and hours of practice. Negotiation is a learned skill
- Negotiation is competitive: Negotiation skills can be used to form collaborative partnerships and resolve potential conflicts. An expert negotiator is the one who achieves mutually beneficial outcomes
- One must lie to negotiate: It is critical to negotiate with integrity, which precludes outright lying. Your opponent will eventually lose trust if you lie. On the other hand, being truthful does not imply showing the other party all your cards. One must be selective about which information to share for a favorable negotiation
- Never show emotions while negotiating: Negotiation experts have advised negotiators to be rational in their feelings. Furthermore, there is no room for emotional outbursts at the negotiating table. Recent research, however, indicates that if you appear favorable, your opponents will take positive cues from you. Because emotions are contagious, it is best to cultivate a positive mindset. When people are in a good mood, they are more likely to think creatively and, as a result, to expand the pie
- There's a winner and a loser in every negotiation: If one enters a negotiation with a transactional, "win-lose" mindset, that is precisely what will happen. And, by definition, transactional/distributive negotiations are a win-lose situation. Any transactional negotiation, however, has the potential for integration. Bringing other issues to the table allows both parties to end up with more than they started, resulting in a win-win negotiation
- Small Talk Is a Waste of Time: Many experienced professionals avoid small talk. According to them, the "getting-to-know-you" game is a waste of time and has little place in business. However, many negotiators' perceptions have shifted. Small talk aids in developing rapport, trust, and willingness to cooperate, and it improves people's perceptions of cooperation and likeability. Most importantly, engaging in small talk frequently allows you to learn about the other party's needs and values
Slide 12
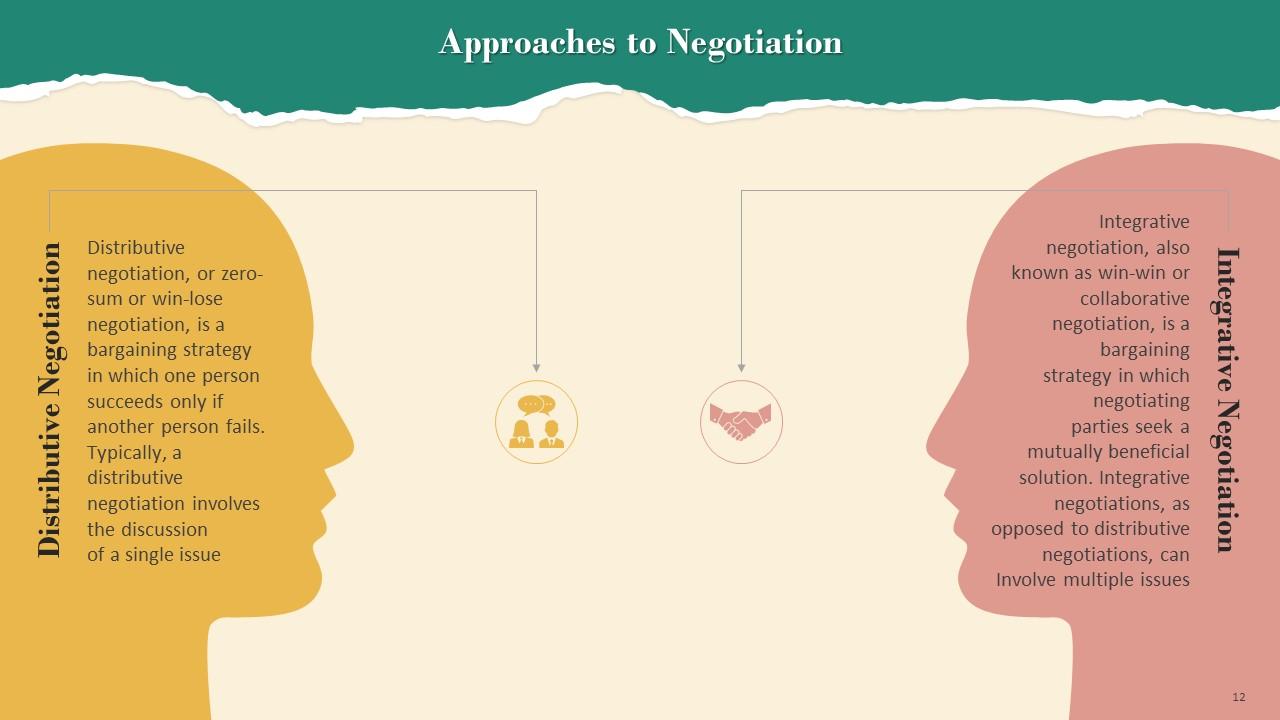
This slide depicts approaches to negotiation, which are Distributive and Integrative negotiation. A bargaining strategy in which one person succeeds only if another person fails is distributive negotiation, also known as zero-sum or win-lose negotiation. Integrative negotiation, also known as win-win or collaborative negotiation, is a bargaining strategy in which negotiating parties seek a mutually beneficial solution for both parties.
Instructor’s Notes:
Examples of Approaches to Negotiation are:
- Distributive negotiation: For example, a sales company may wish to with engage with a vendor for IT services. The business wants most IT services at the lowest possible cost, while the IT vendor intends to provide the fewest resources at the highest possible price. The desire of each party to get a better deal represents a distributive negotiation strategy
- Integrative negotiation: For example, a well-established fashion company and a cosmetics startup agree to collaborate on a product aimed at their common target market. They reach an agreement that will allow the cosmetics startup to acquire more exposure while also permitting the fashion company to meet its financial and marketing goals
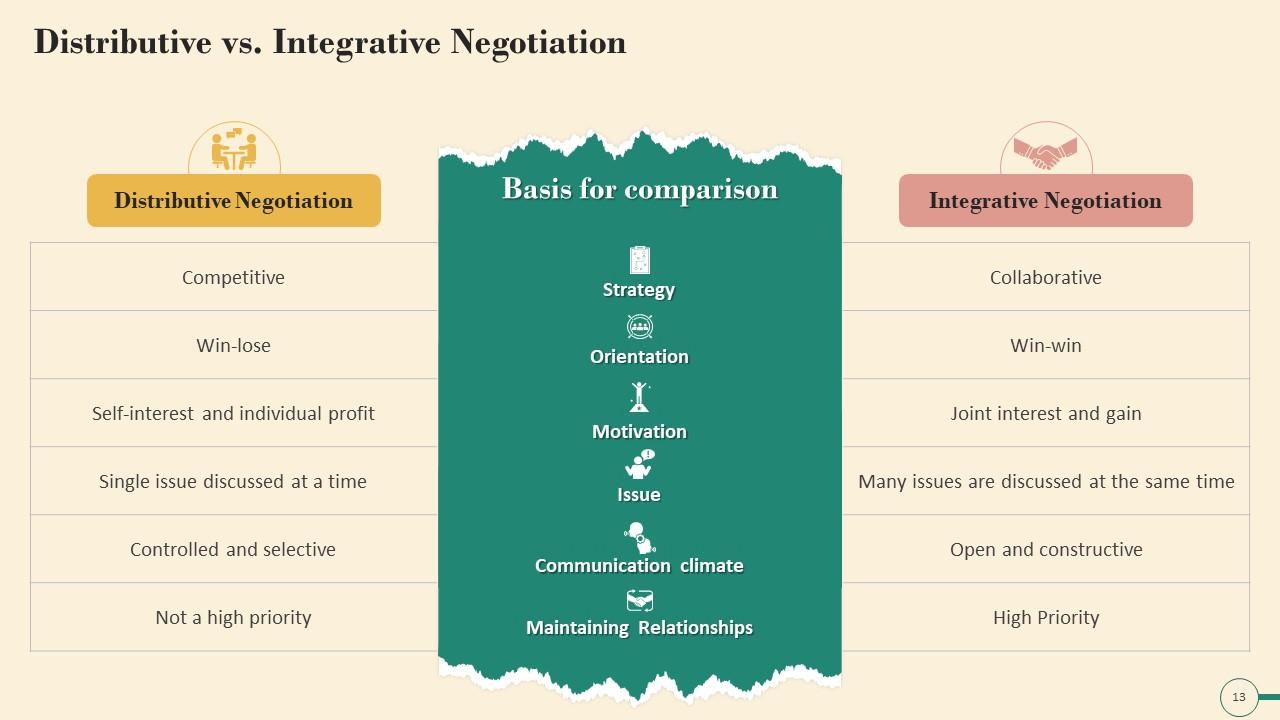
Slide 13
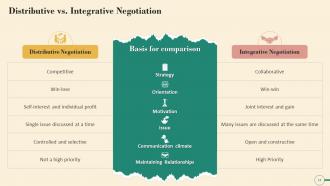
This slide illustrates the major difference in distributive and integrative negotiation. It mentions that distributive approach is competitive, discusses one issue at a time and integrative approach is collaborative, discusses several issues at the same time etc.
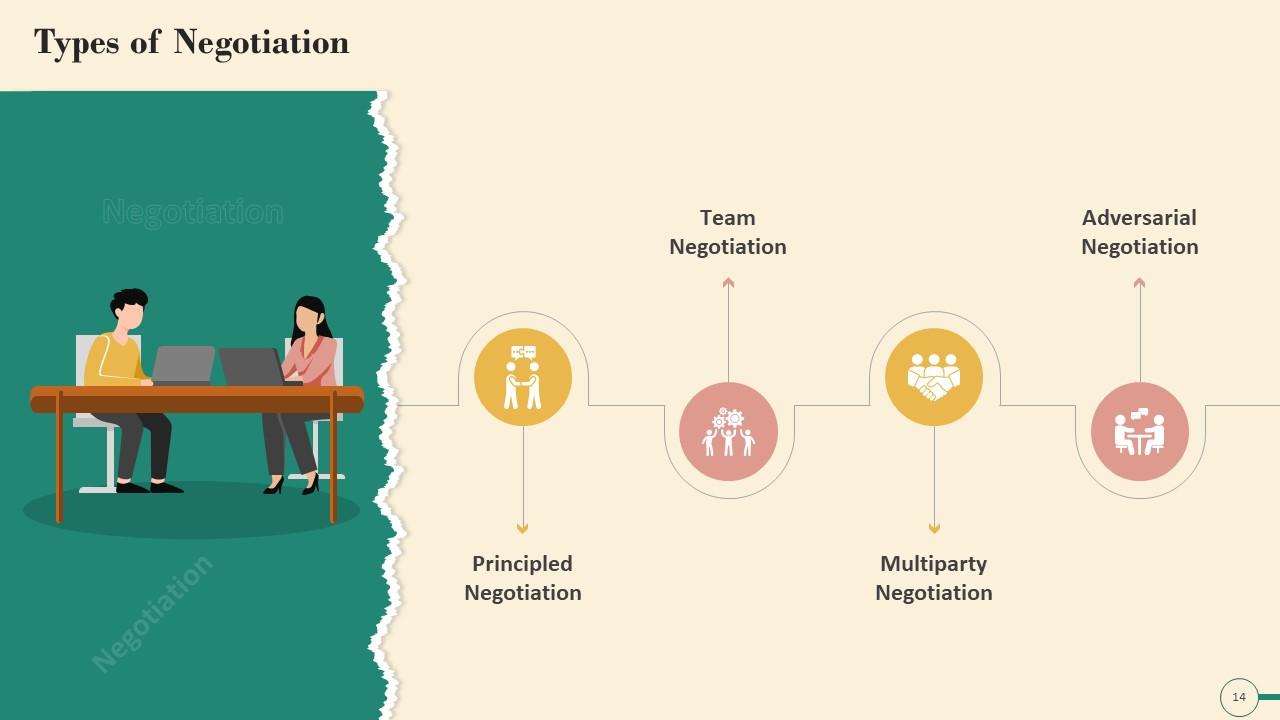
Slide 14
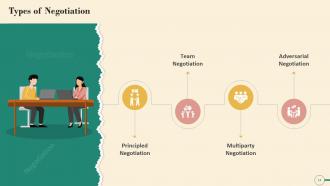
This slide illustrates the most common Negotiation types. The types are: Principled negotiation, team negotiation, multiparty negotiation, and adversarial negotiation.
Instructor’s Notes:
Common Negotiation Types are:
- Principled negotiation: A type of bargaining in which the principles and interests of the parties are used to reach an agreement. Conflict resolution is frequently the focus of this type of negotiation. To serve the interests of both parties, this type of bargaining employs an integrative negotiation strategy.
- Team negotiation: In a team negotiation, multiple people bargain on each side of the negotiation to reach an agreement. Team negotiations are common in significant business transactions. On a negotiation team, personalities play different roles. In some cases, an individual may play multiple positions
- Multiparty negotiation: A multiparty negotiation is a form of bargaining where more than two parties work together to reach an agreement. Bargaining between multiple department heads in a large company is an example of a multiparty negotiation
- Adversarial negotiation: It is a distributive strategy in which the most aggressive party in a negotiation obtains an agreement that serves their interests
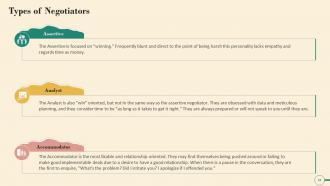
Slide 16
This slide depicts the most common types of Negotiators. Assertive, Analyst and Accommodator are the three types. The Assertive Negotiators are concerned with "winning." Frequently direct and blunt, almost to the point of being harsh. The Analyst is also "win" oriented but in a different way. They are obsessed with data and meticulous planning, and the accommodators are the most likable and relationship-oriented.
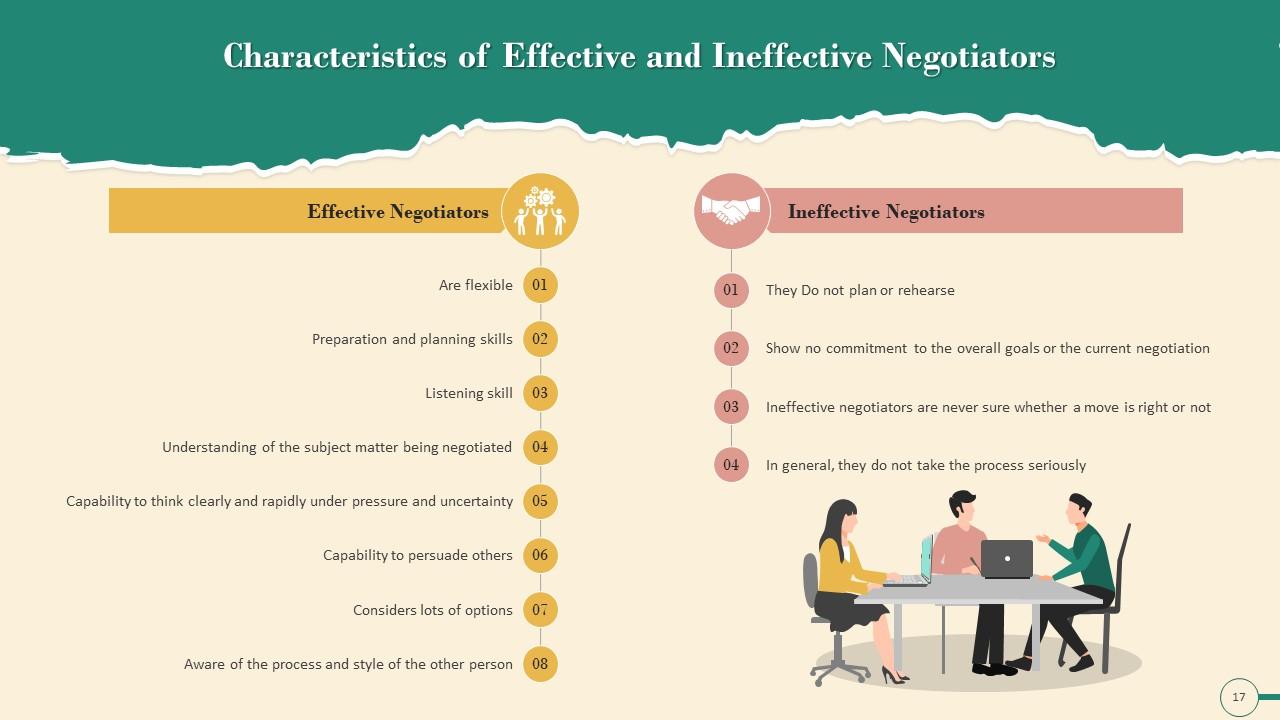
Slide 17
This slide illustrates the characteristics of Effective and Ineffective Negotiators. Effective Negotiators are flexible, have preparation and planning skills, listening skills, understanding of the subject matter being negotiated, ability to persuade others, etc. The characteristics of Ineffective Negotiators are: They do not plan or rehearse, don’t commit to the overall goals or the current negotiation.
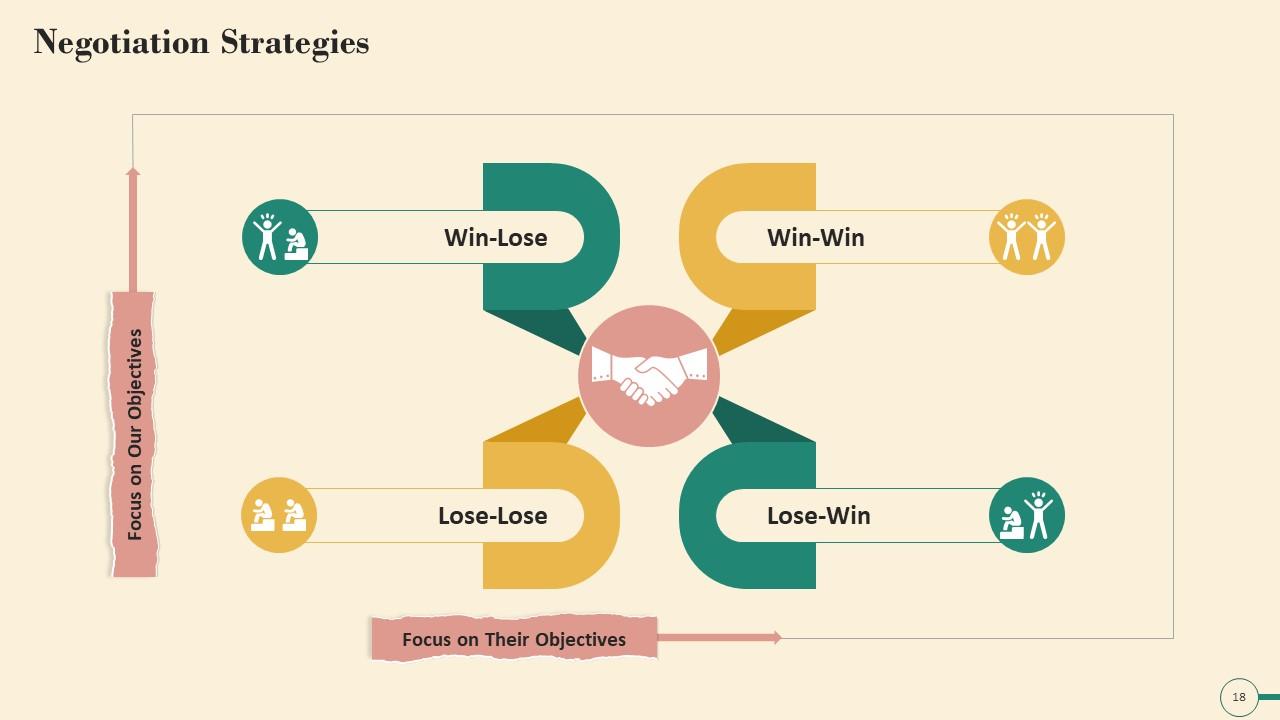
Slide 18
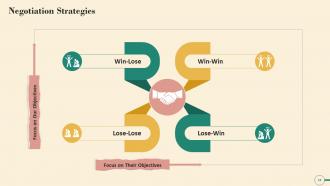
This slide illustrates the Negotiation Strategy Matrix. The parameters of the matrix are Win-Lose, Win-Win, Lose-Lose, and Lose-Win.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Lose-Win: Lose-Win situations are frequently the result of a lack of courage to pursue one's own goals while caving to the other party's desires. Playing for a short-term loss can be used as part of a long-term strategy on occasionally
- Lose-Lose: Typically, Lose-Lose scenarios result from focusing on the wrong goals or broken relationships
- Win-Lose: The strategy in Win-Lose is to meet your objectives, even at the expense of the other party's objectives. As a result, we compete with our "opponent" for the most significant value share
- Win-Win: With Win-Win, we achieve our goals by assisting the other party in achieving their goals or collaborating with our "partner" to maximize value creation
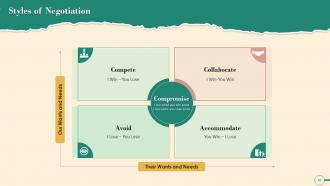
Slide 19
This slide illustrates the five styles of negotiation. These negotiation styles are: Competitive, Compromising, Accommodating, Avoiding, And Collaborating.
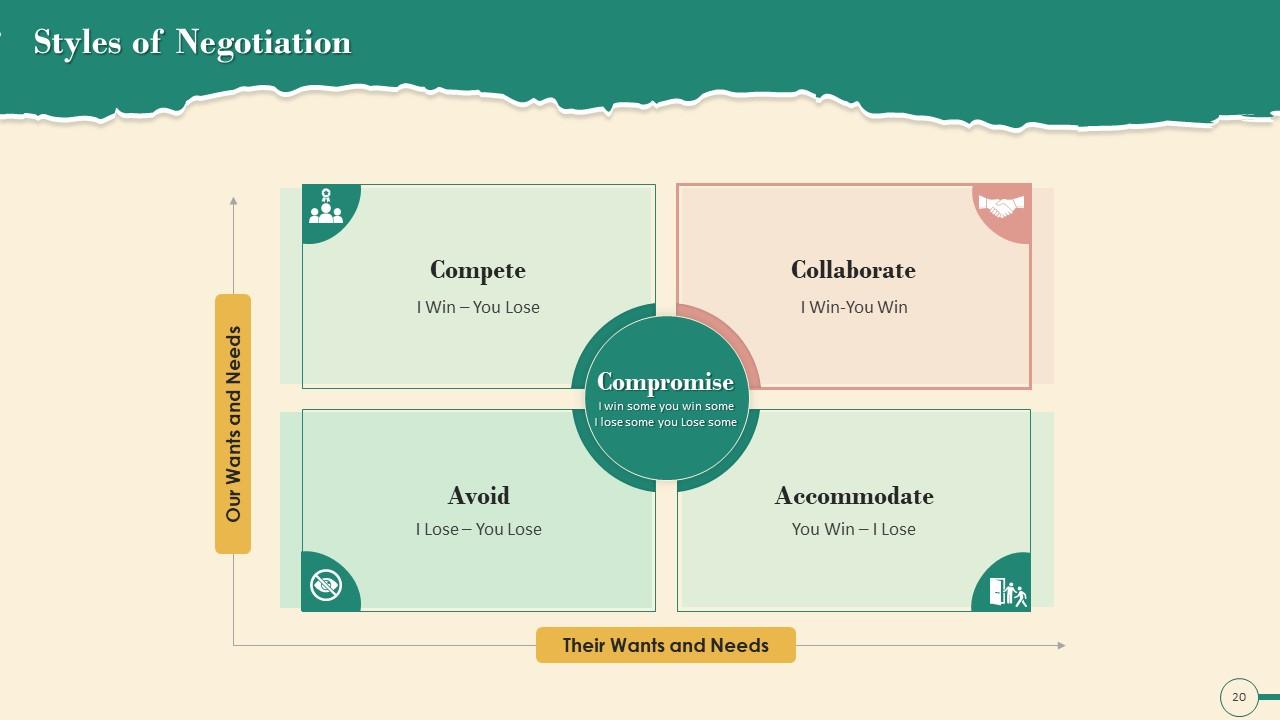
Slide 20
This slide showcases five negotiation styles that are: Compete, Compromise, Accommodate, Avoid, And Collaborate.
Slide 21
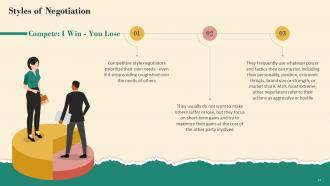
This slide explains the competitive negotiation style. It emphasizes that competitive style negotiators prioritize their own needs, even if it means sacrificing the needs of others. It also mentions that they do not want to make others suffer or lose, but they are more concerned with short-term gains at the cost of the other party involved.
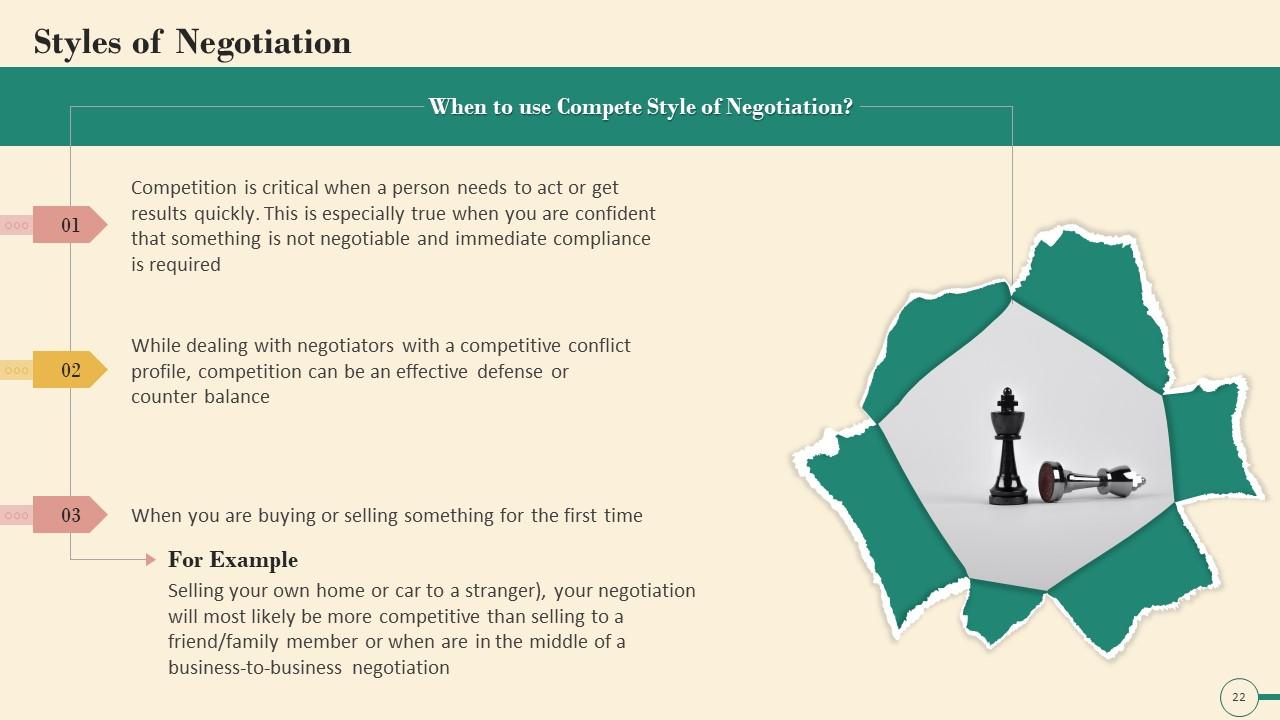
Slide 22
This slide illustrates information about when to use competitive style of negotiation. It emphasizes the importance of competition when a person needs to act or obtain results quickly. This is especially true when you are confident that something is not negotiable and immediate compliance is required.
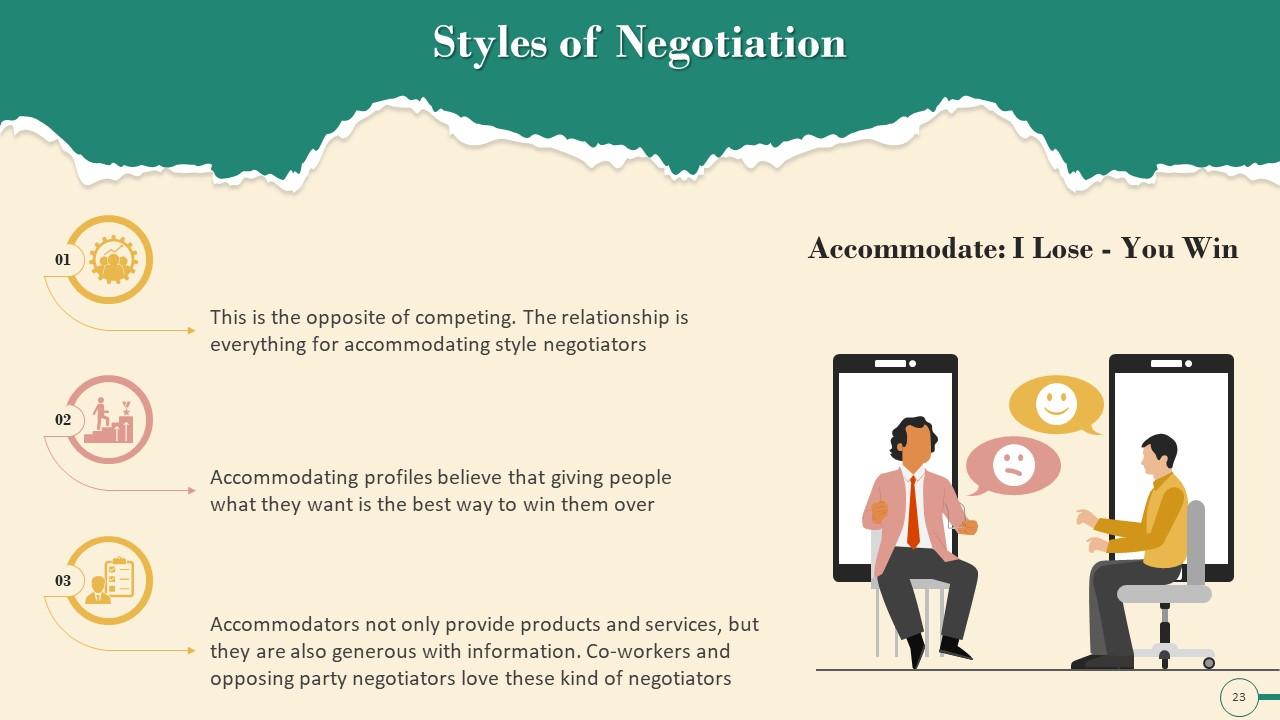
Slide 23
This slide depicts information on accommodating negotiation styles. It emphasizes the opposite of competing. For accommodating style negotiators, the relationship is everything. It also mentions that accommodating negotiators believe that giving people what they want is the most effective way to win them over.
Slide 24
This slide depicts information on when to use accommodating style of negotiation. It emphasizes that the accommodating style is used when a person or the company is at fault, and repairing the relationship is critical, especially if there is nothing else a person can do to help the other side. It also mentions that when a person is in bad situation, the best thing he/she can do is to give up gracefully.
Slide 25
This slide depicts information on avoid negotiation style. It mentions that avoiding negotiation style is known as "passive-aggressiveness." People who use this style avoid conflict. It also emphasizes people adopting this style may seek revenge without your knowledge instead of confronting you directly about the issue.
Slide 26
This slide depicts information about when to use avoiding style of negotiation. It mentions that the avoiding negotiation style can be used when the cost of devoting time to resolve the conflict outweighs the benefit, or when the issue is minor (for both parties).
Slide 27
This slide depicts information about the compromise negotiation style. It emphasizes that a compromising negotiator's primary concern is to find a middle ground and do what is fair for both parties. It also states that main drawback of a compromising negotiator can be that sometimes they rush into negotiations and make too many concessions, leading to a loss.
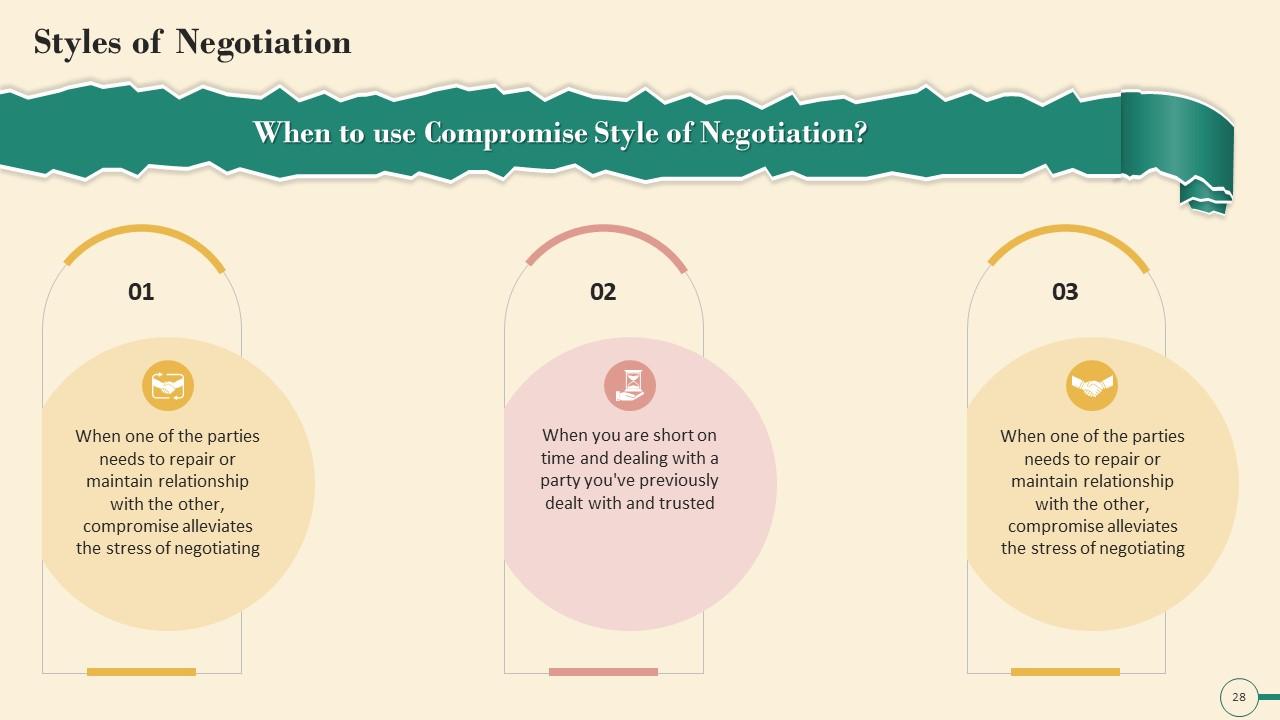
Slide 28
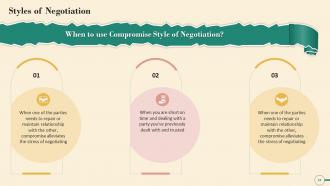
This slide depicts information about when to use the compromise style of negotiation. It mentions that when one of the parties need to repair or maintain relationship with the other, compromise reduces the stress of negotiating. It also highlights that compromise negotiation style can be used when you are short on time and dealing with a party you've previously dealt with and trusted.
Slide 29
This slide showcases information about the collaborative negotiation style. Collaborative negotiation is a strategy in which both parties have a common goal. They attempt to achieve their objective by extracting more value from the transaction to benefit both parties. It is also known as integrative, interest-based, or problem-solving negotiation.
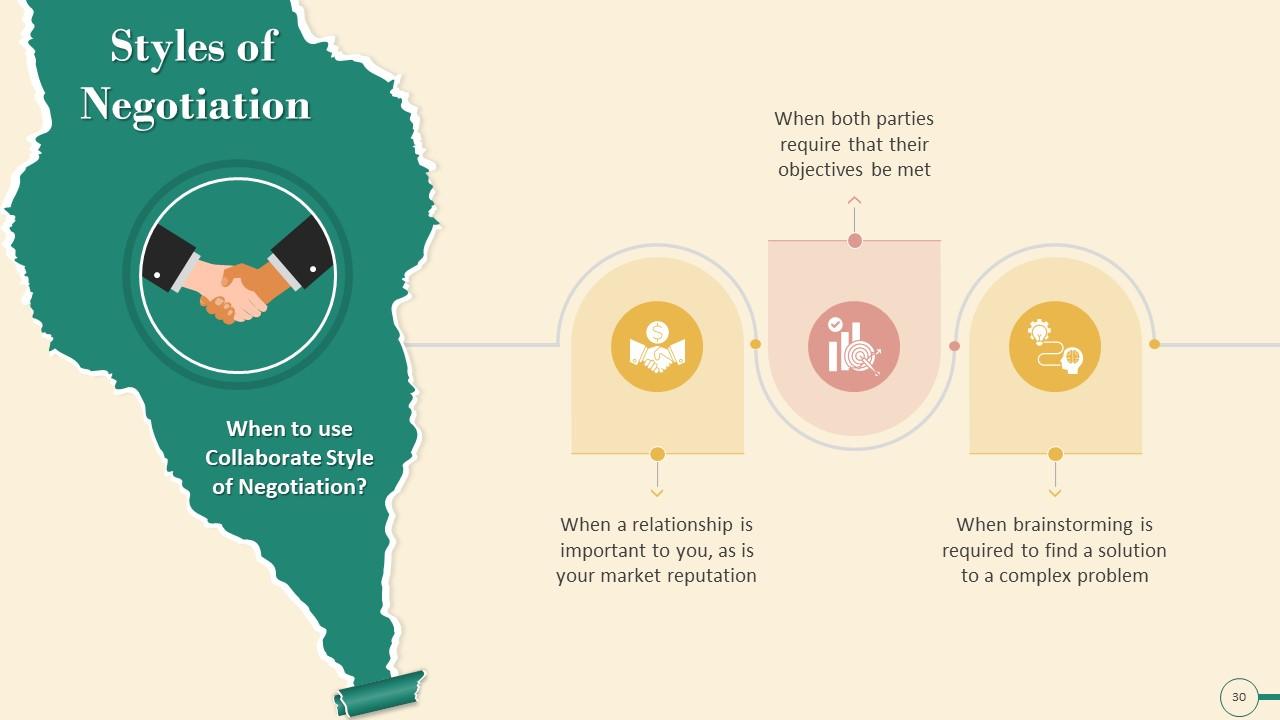
Slide 30
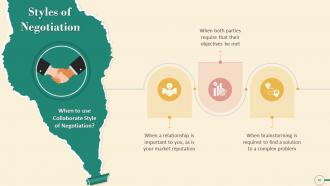
This slide explains when to use a collaborative negotiation style. It emphasizes using collaborative style when a relationship is important to you, as is your market reputation, and when both parties require their objectives to be met.
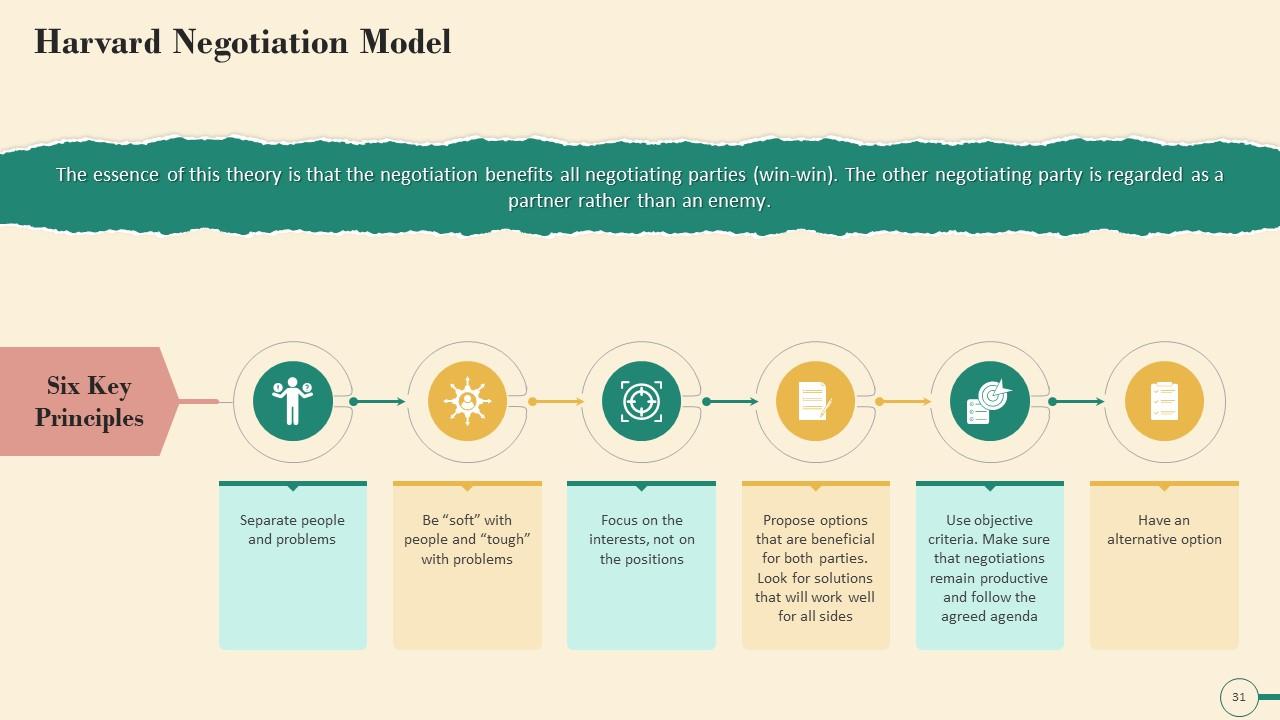
Slide 31
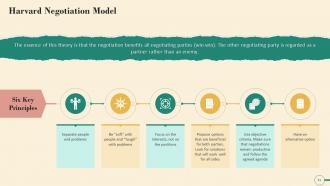
This slide contains information about the Harvard Negotiation Model. The essence of this theory is that all negotiating parties benefit from the negotiation (win-win), and the other negotiating party is viewed as a collaborator rather than an opponent. The Harvard Negotiation Model's Six Key Principles are as follows:
- Separate people and problems
- Be “soft” with people and “tough” with problems
- Focus on the interests, not on the positions
- Propose various mutually beneficial options. Look for solutions that will work well for all negotiating parties
- Use objective criteria. Make sure that negotiations remain productive and follow the agreed agenda
- Have an alternative option
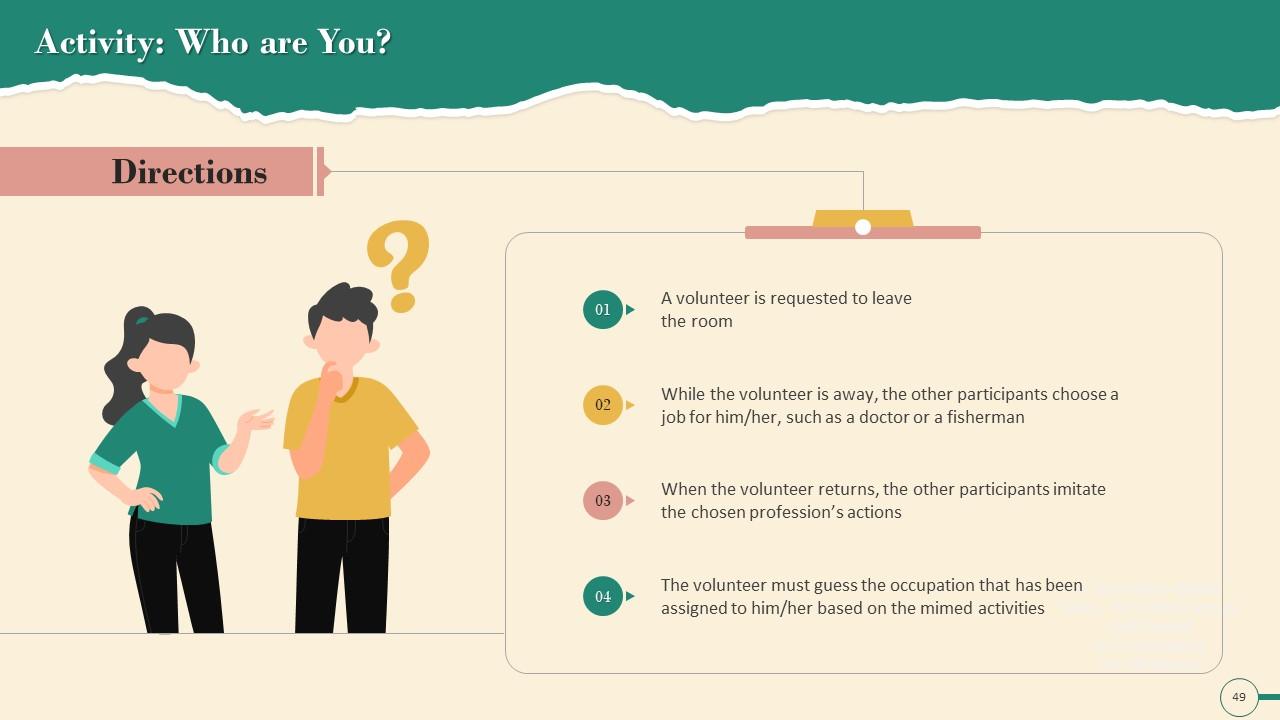
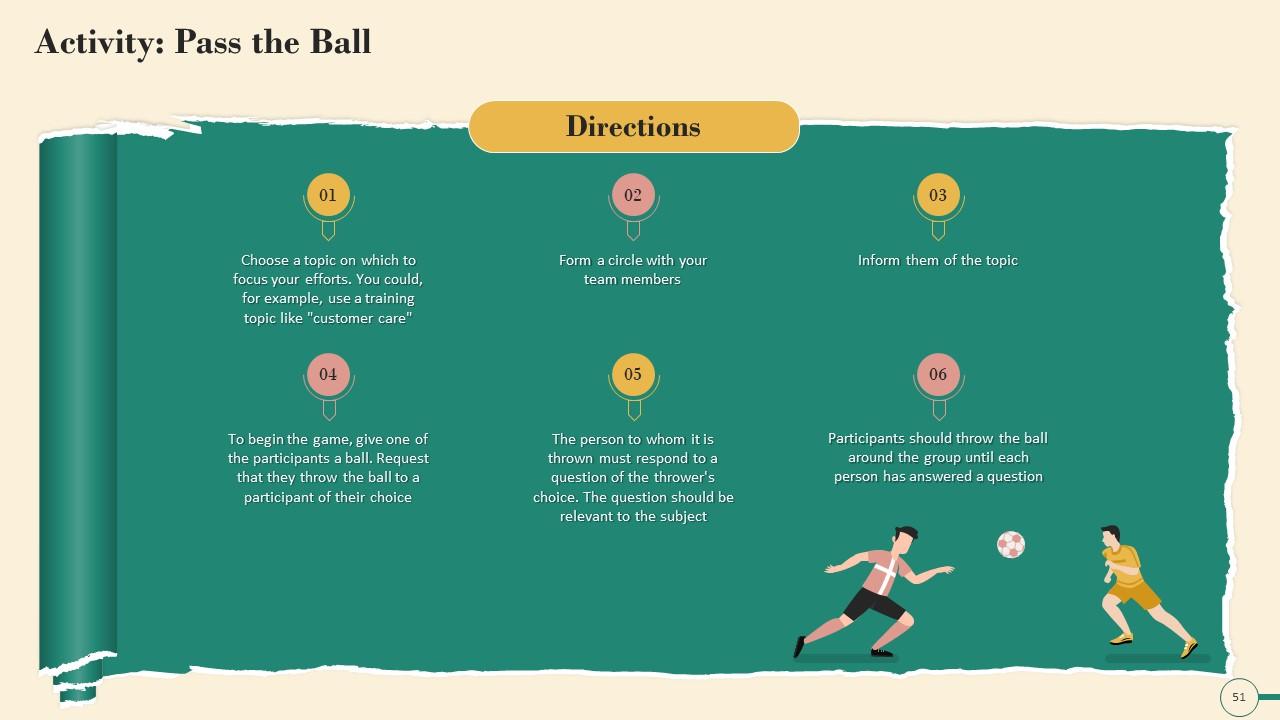
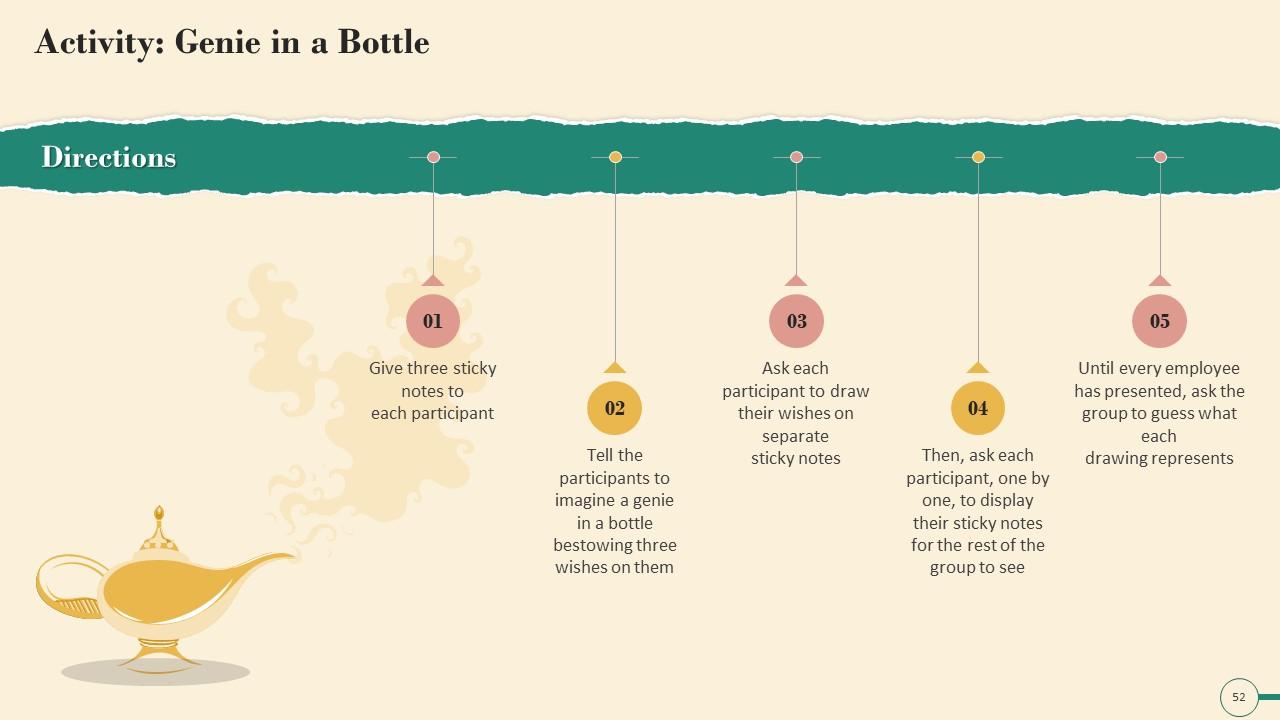
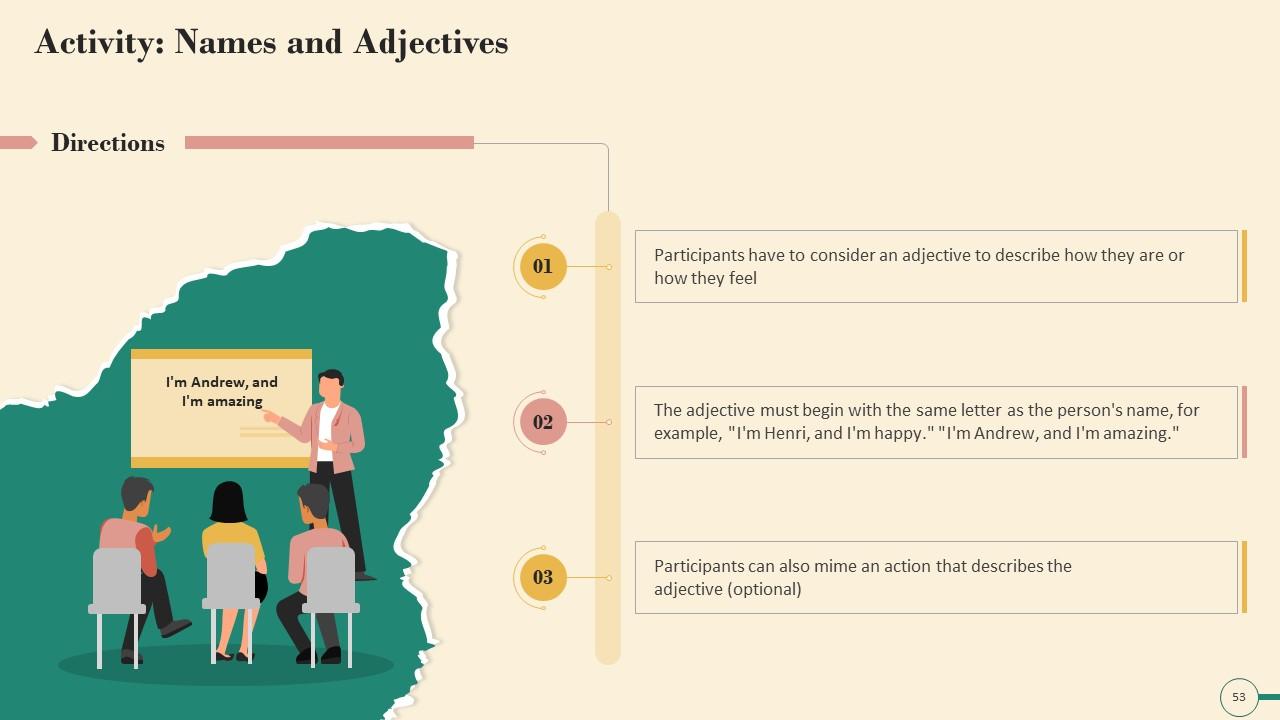
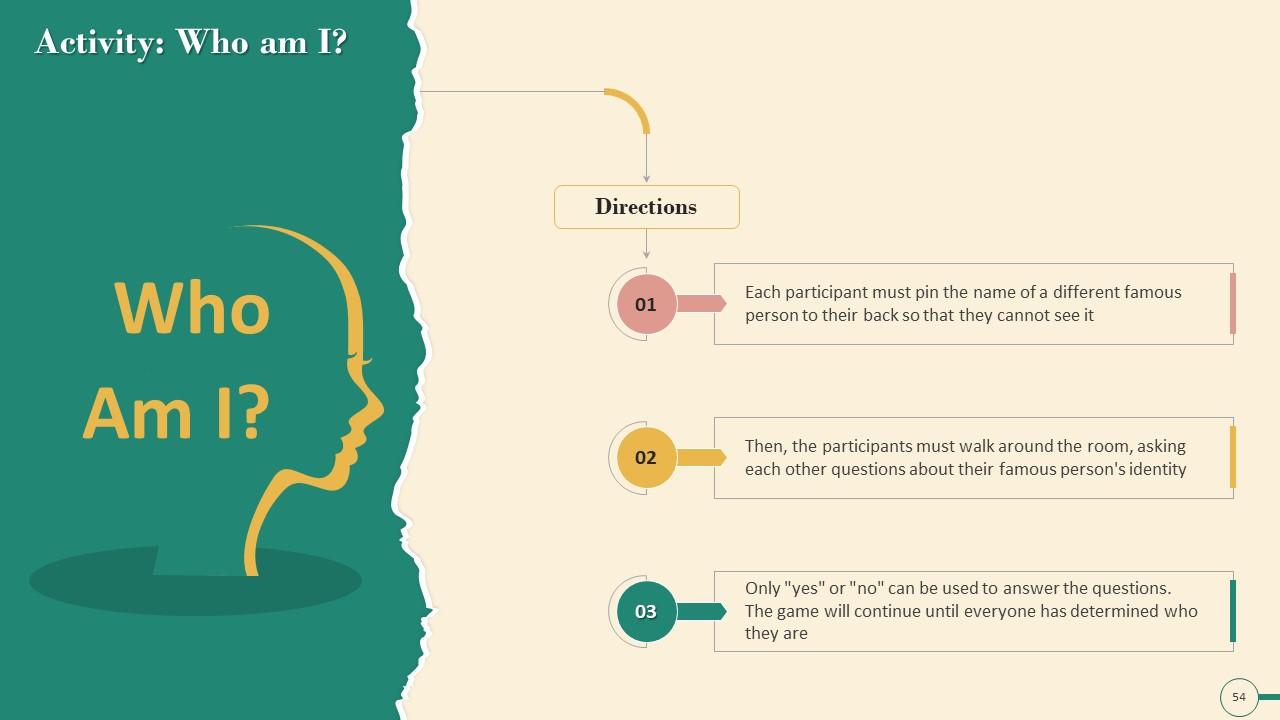
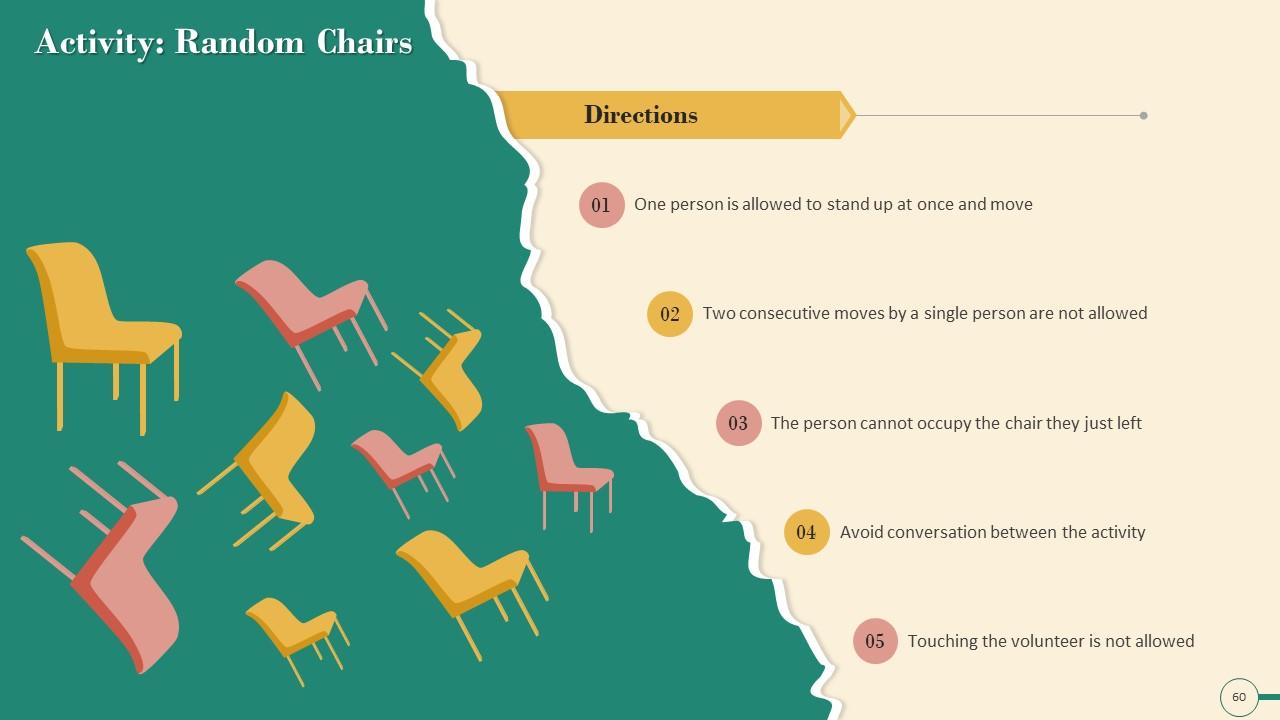
Slide 45 to 60
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 61 to 88
These slides contain a training proposal covering what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
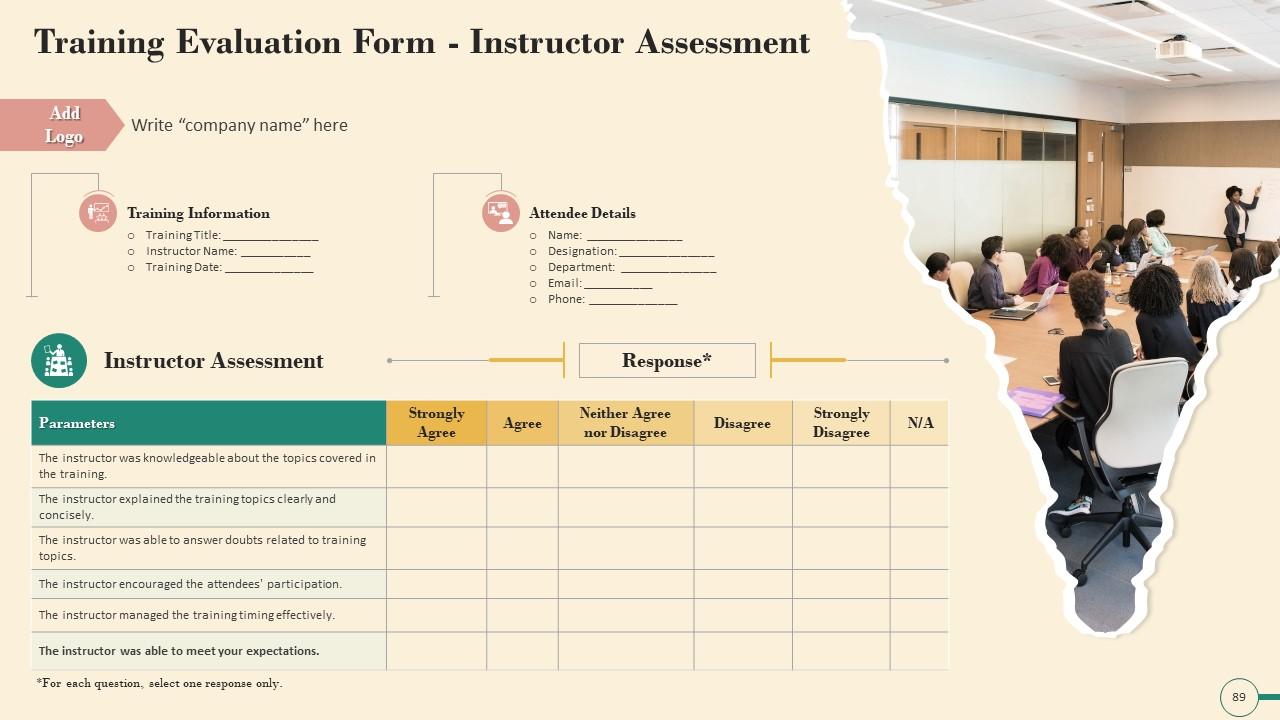
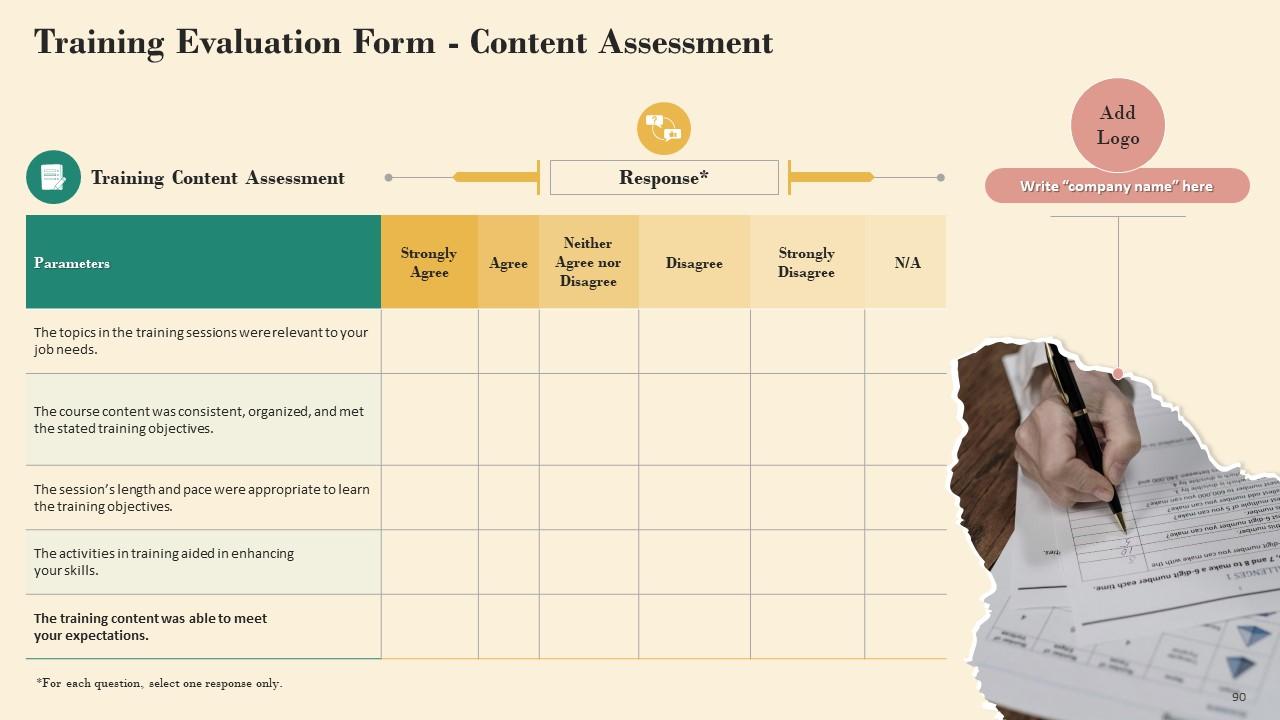
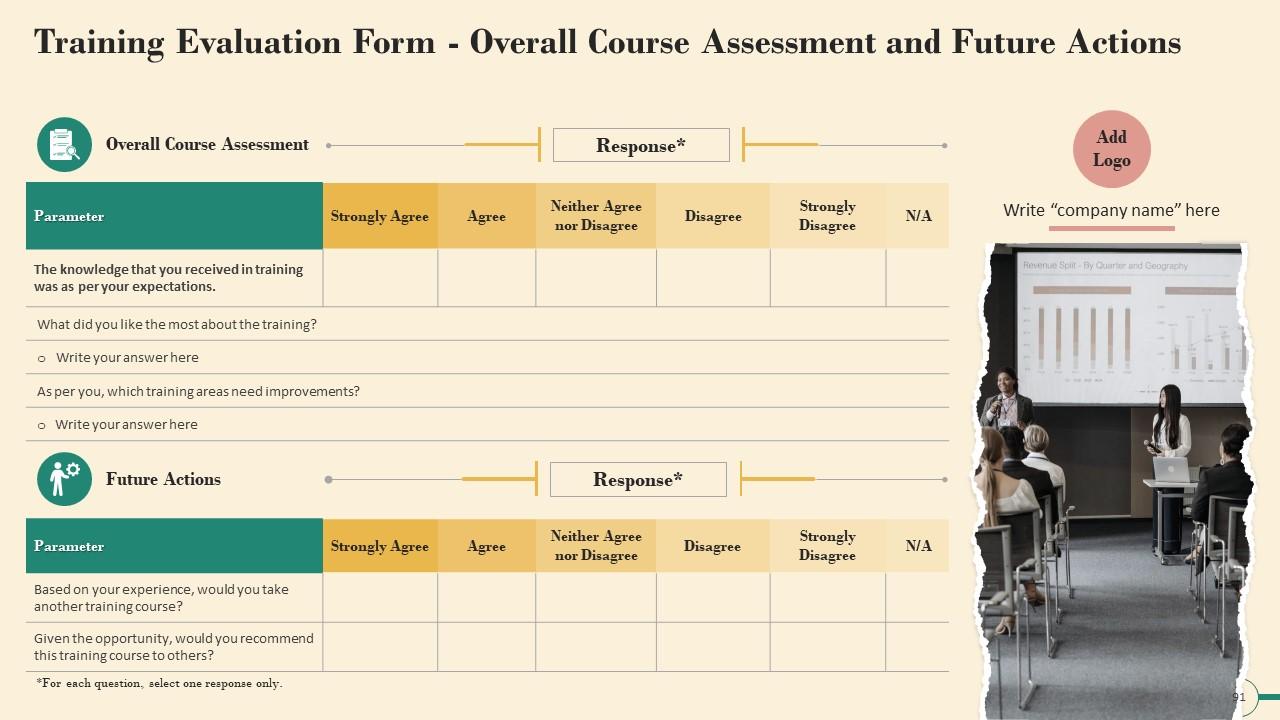
Slide 89 to 91
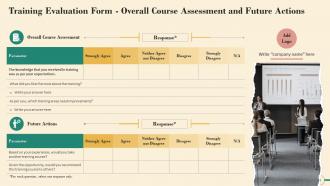
These slides include a training evaluation form for instructor, content and course assessment.
Overview Of Negotiation Fundamentals Training Ppt with all 96 slides:
Use our Overview Of Negotiation Fundamentals Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Exclusive and extensive collection of templates. Really helped me create a professional presentation in just no time.
-
Amazing slides! Unique, attractive, and easy to understand.