Digital Transformation in Banking Industry Training ppt
The PPT training deck provides a comprehensive overview of digital transformation in the banking industry. It includes the benefits of digital banking for customers, such as personalized service and real-time remote access, as well as advantages of digital transformation to banks, such as staying in sync with ever-evolving consumer needs. The PowerPoint module also covers factors that drive digital transformation in the banking industry along with the implementation challenges, such as the limited acceptability of an entirely digitized bank and internal barriers. It also includes innovations in the digital banking industry, such as advanced self-service capabilities, instant payments, and chatbots. Further, the deck covers the use case of big data and blockchain technology in banks and the advantages of neo-banking. It includes PPT slides on peer-to-peer P2P lending, DeFi Decentralized Finance, and investment banking. It also contains case studies and discussion questions to make the training session interactive. Digital Transformation PPT slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, and energizer activities.
The PPT training deck provides a comprehensive overview of digital transformation in the banking industry. It includes the ..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Digital Transformation in Banking Industry. This deck comprises of 105 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts and every slide consists of an appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
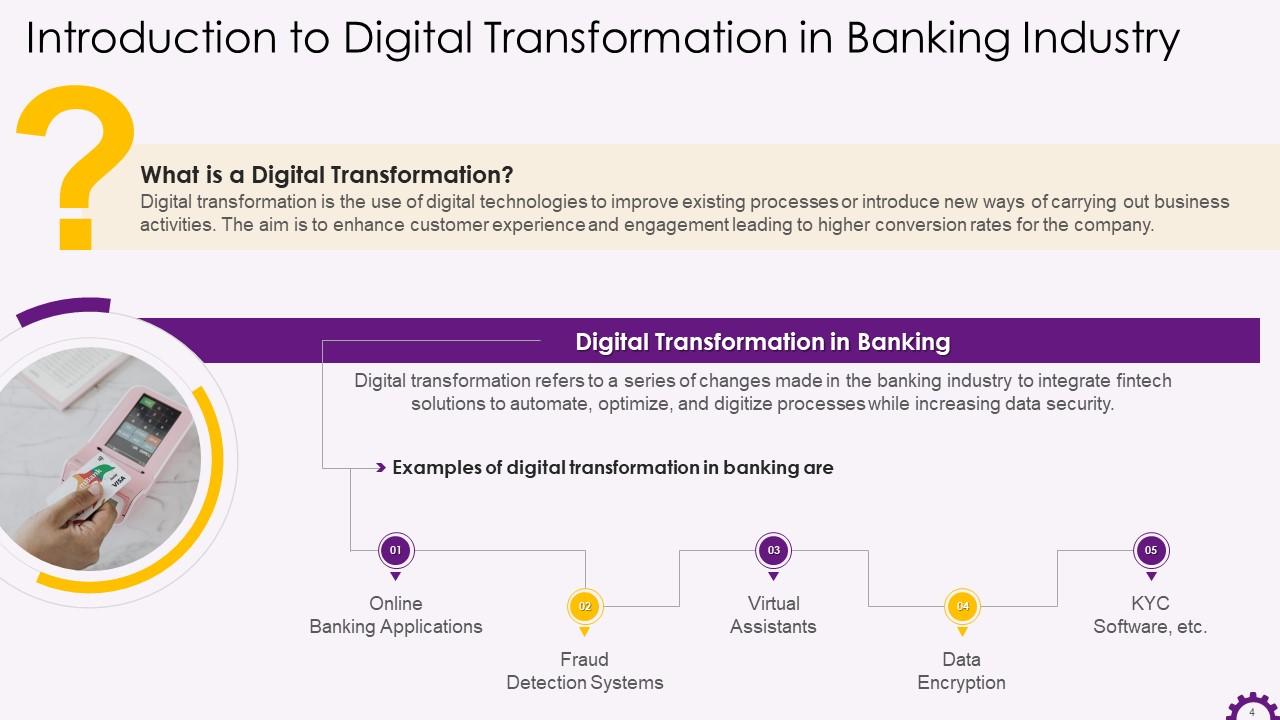
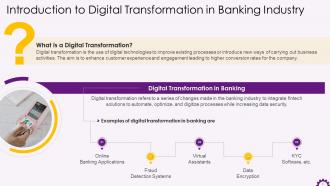
This slide depicts introduction to digital transformation and digital transformation in the banking industry. It illustrates that digital transformation uses digital technologies to improve existing processes or introduce new business ways. In the banking industry, digital transformation refers to integrating fintech solutions to automate, optimize, and digitize processes while increasing data security.
Slide 5
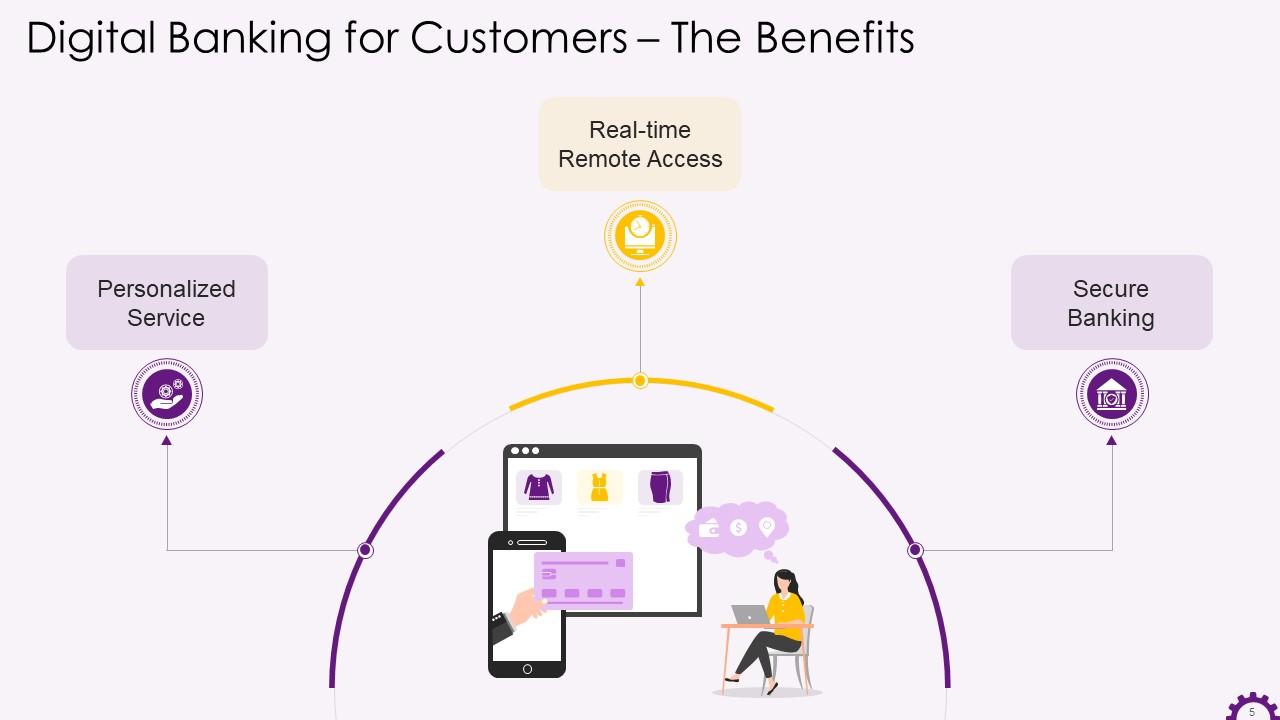
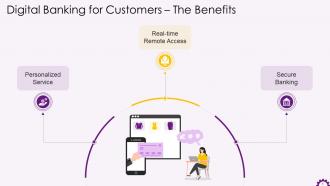
This slide illustrates the benefits the digital banking for customers. The benefits are personalized service, real-time remote access, and secure banking.
Slide 6
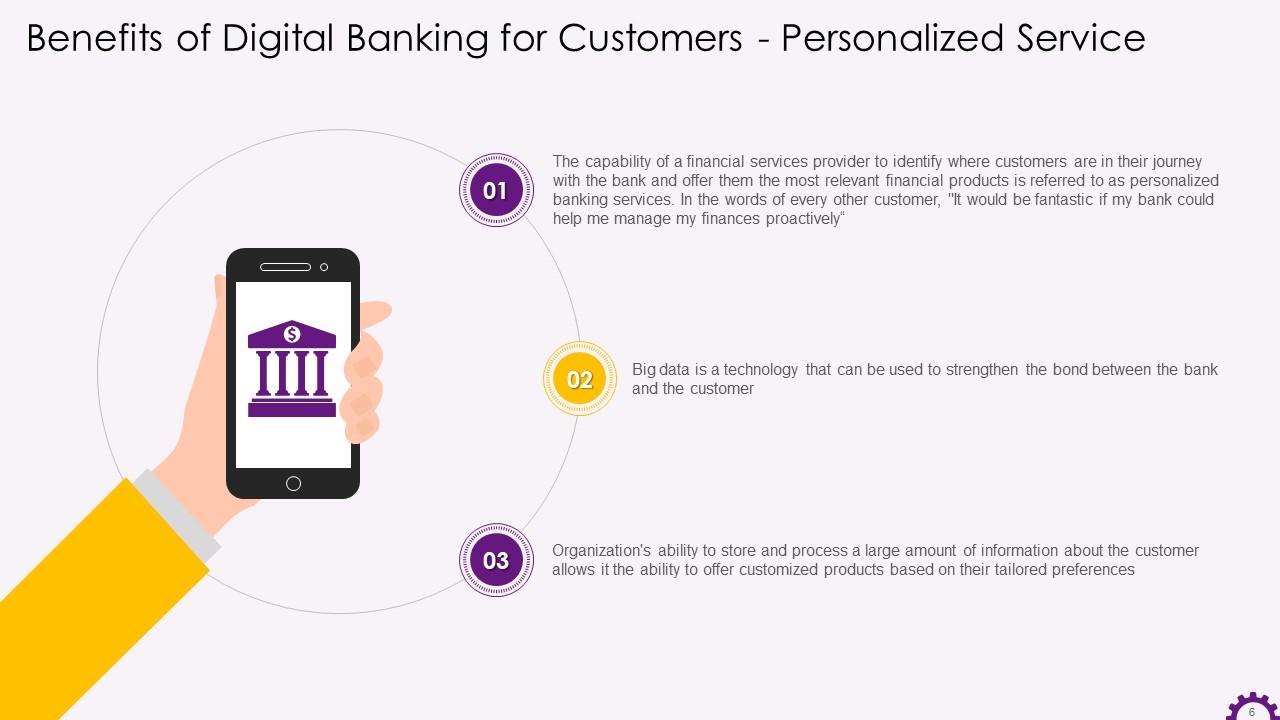
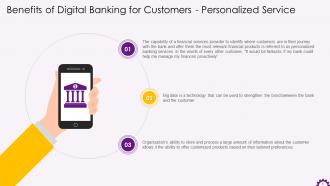
This slide depicts that digital banking allows bank to offer personalized banking as a major benefit. The slide illustrates that personalized banking services refer to capability of a financial services provider to identify where customers are in their journey with the bank, and offer them the most relevant financial products. It also mentions that big data analysis is a technology that can strengthen the bond between the bank and the customer.
Slide 7
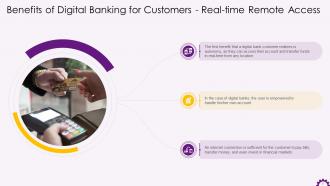
This slide depicts real-time remote access as a benefit of digital banking for customers. It also illustrates that the first benefit a digital bank customer enjoys is autonomy, as they can access their account and transfer funds in real-time from any location. In the case of digital banks, the user is empowered to carry out his own account management.
Slide 8
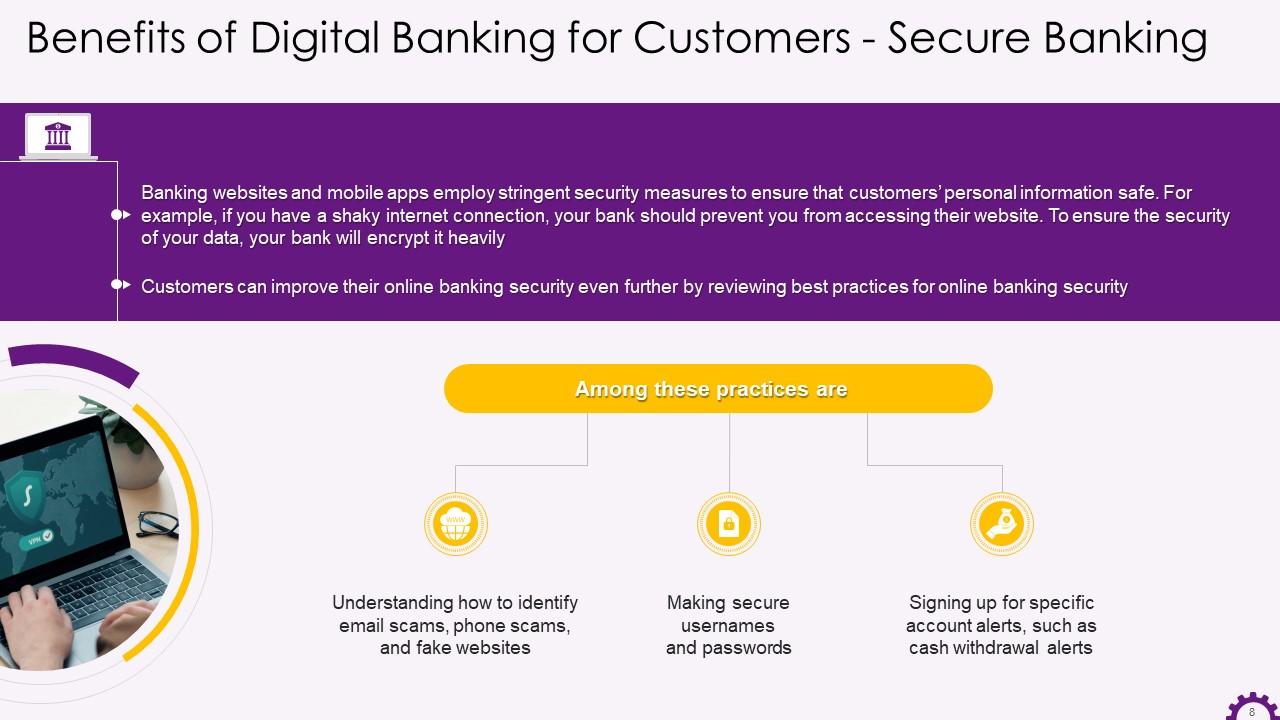
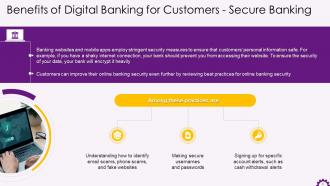
This slide showcases secure banking as a benefit of digital banking for customers. It illustrates that banking websites and mobile apps employ stringent security measures to ensure that customers’ personal information safe. It also mentions that customers can improve their online banking security even further by reviewing best practices for online banking security. The practices include identifying email scams and fake websites, making secure usernames and passwords, and signing up for specific account alerts, such as cash withdrawal alerts.
Slide 9
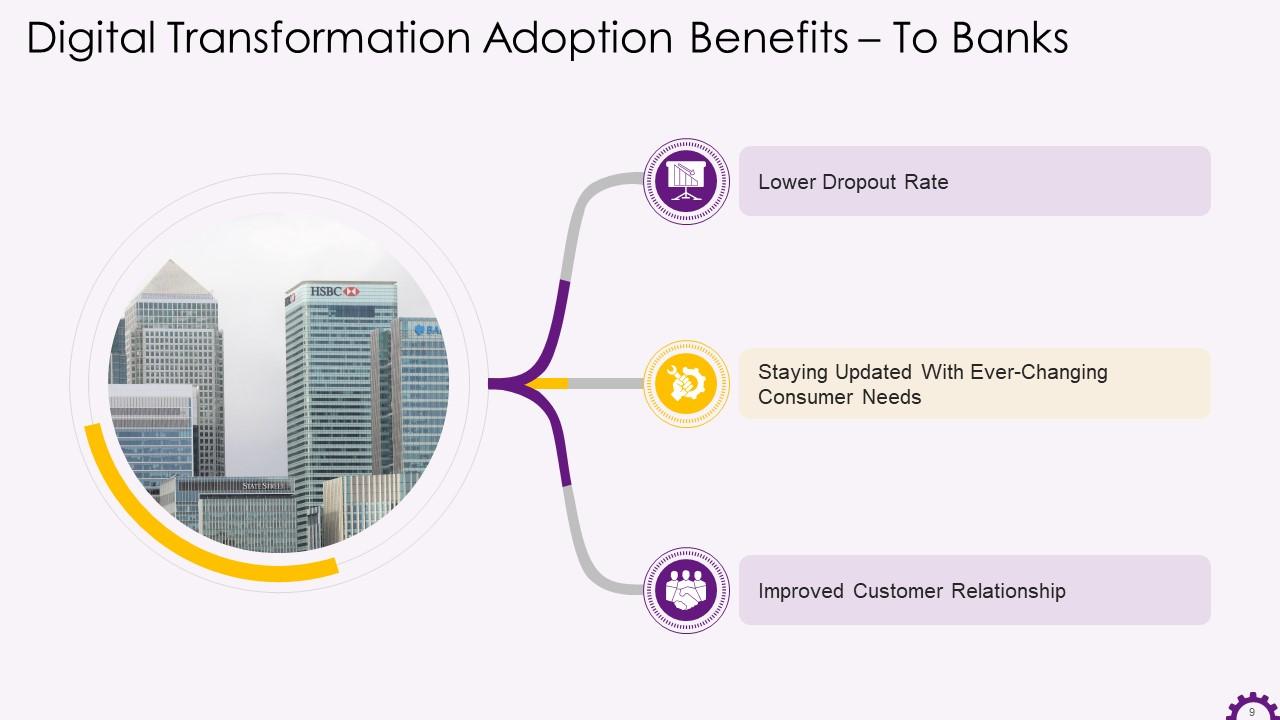
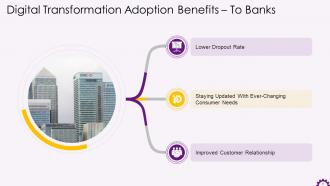
This slide illustrates the benefits of adopting digital transformation to banks. The benefits are a lower dropout rate, staying updated with ever-changing consumer needs, and improved customer relationships.
Slide 10
This slide depicts a lower dropout rate as an advantage for banks that choose to embrace digital transformation. It also demonstrates that modern customers prefer not to be enslaved by traditional banking services. That is why digital products appeal to new generations of customers who value their time and freedom.
Slide 11
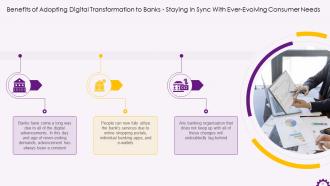
This slide depicts staying in sync with ever-evolving consumer needs as a benefit for banks that choose to embrace digital transformation. It also demonstrates how far banks have come due to digital advancements. People can now fully utilize the bank's services because of online shopping portals, individual banking apps, and e-wallets.
Slide 12
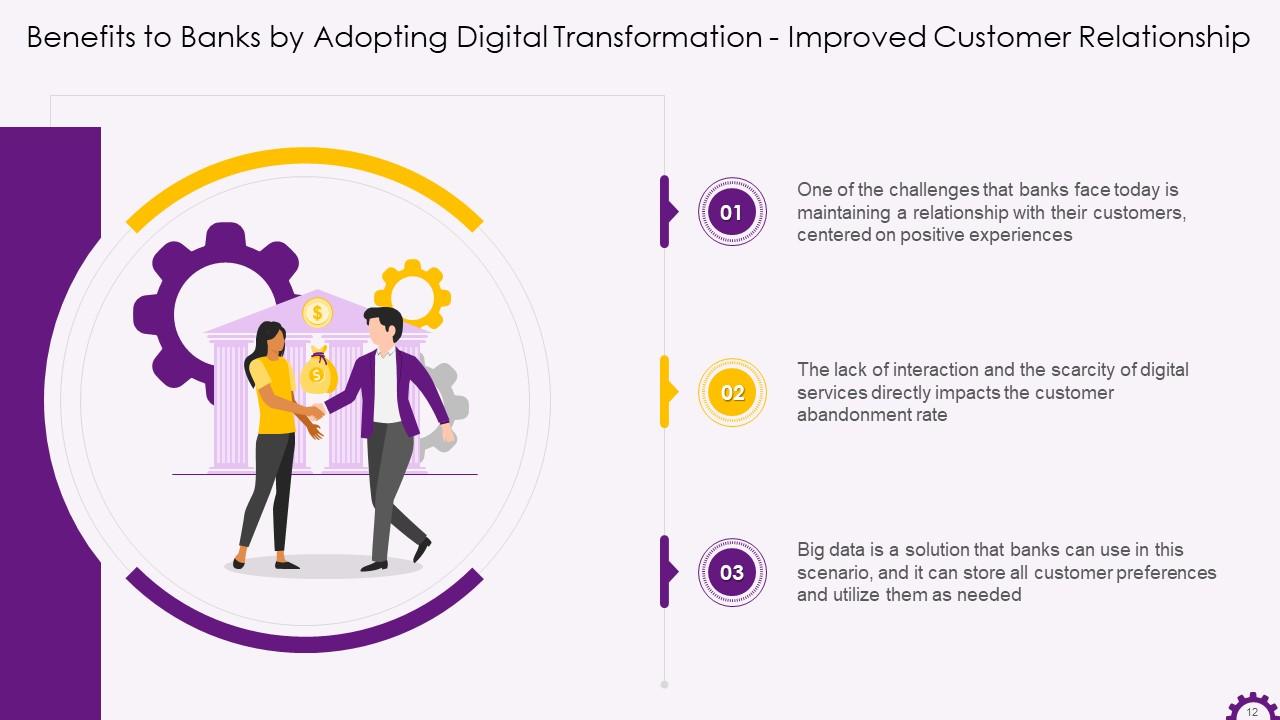
This slide illustrates the benefit of improved customer relationships for banks that choose to implement digital transformation. It also mentions that one of the challenges that banks face today is maintaining a positive relationship with their customers. In this scenario, banks can use big data to store all customer preferences and use them as needed.
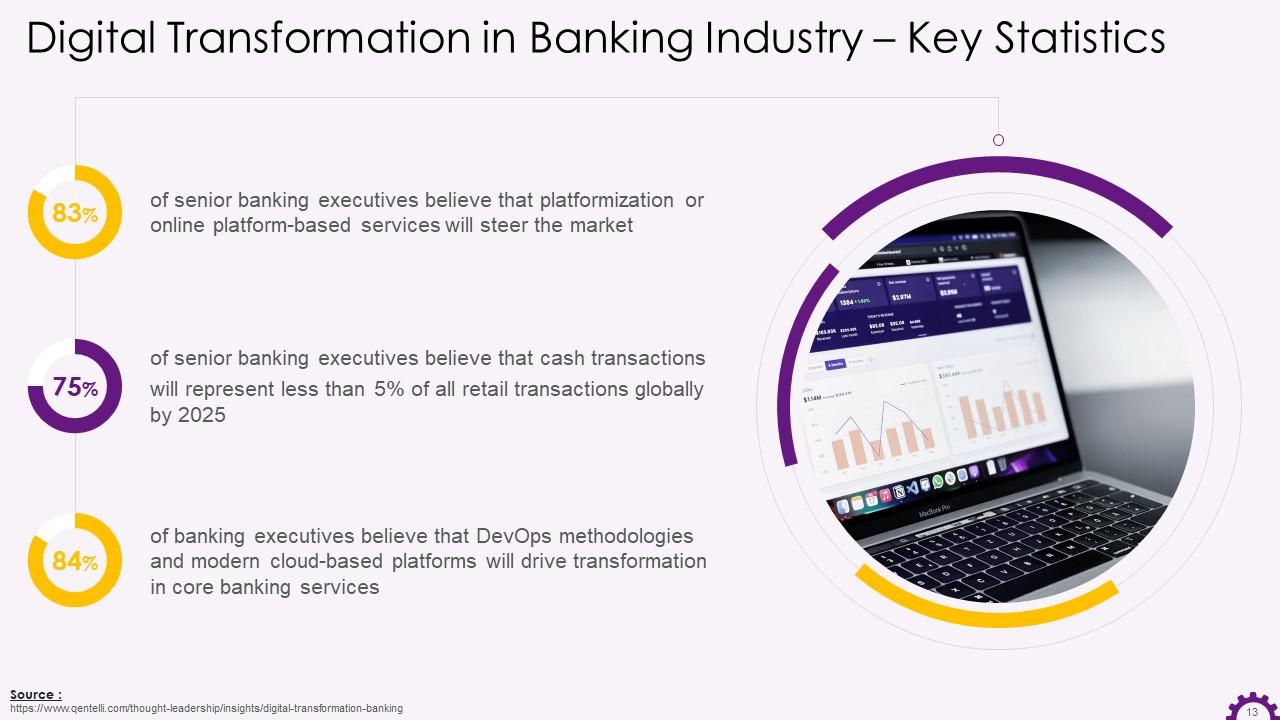
Slide 13
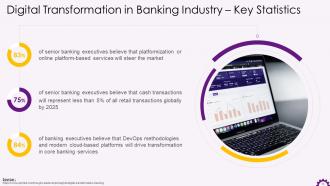
This slide depicts the potential impact of digital transformation will have on the banking sector. It shares the opinion of business leaders on how platformization, DevOps methodology will disrupt banking and lead to more cashless transactions and so on.
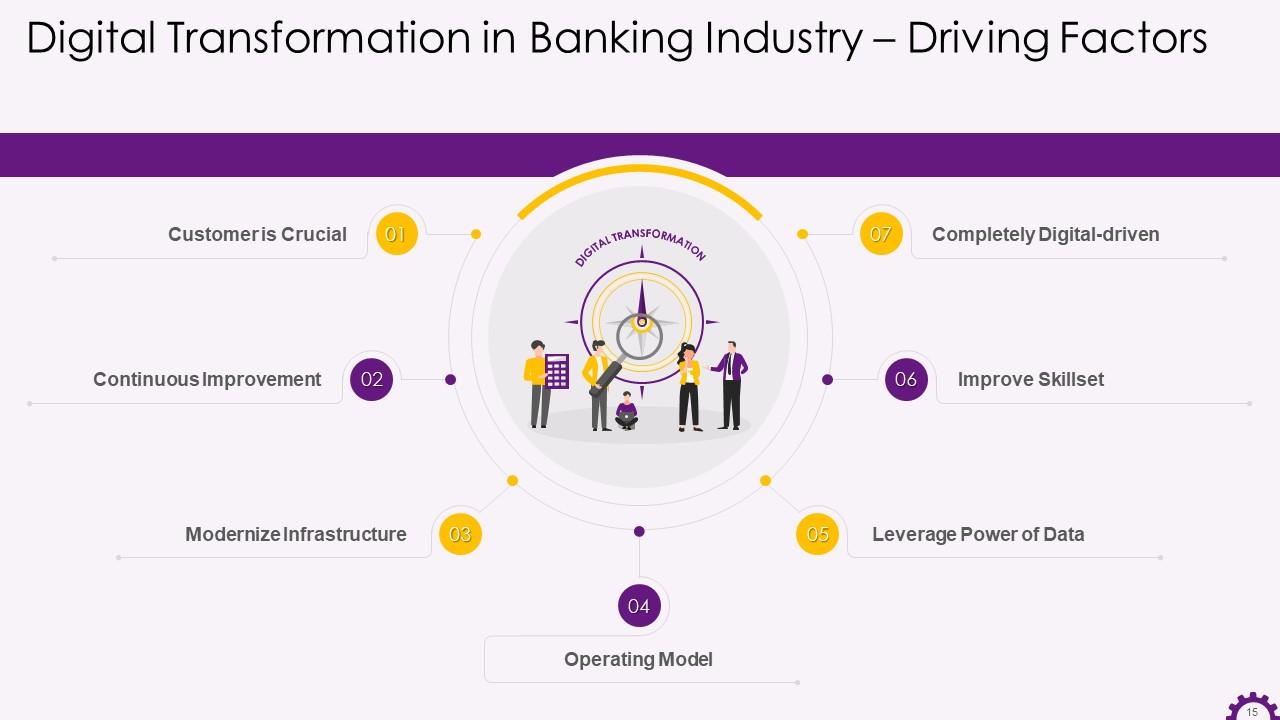
Slide 15
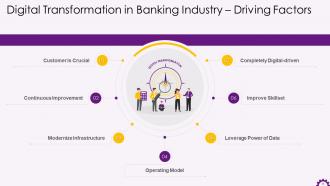
This slide depicts the factors that drive digital transformation in the banking industry. The factors are a customer is crucial, continuous improvement, modernize infrastructure, operating model, leverage power of data, improve skill-set and be completely digital-driven.
Instructor’s Notes:
The factors that drive digital transformation in banking industry are:
- Customer is Crucial: Banks must understand and analyze what the customer is looking for. In today's fast-changing market, seamless service delivery, high end-user experience, personalized product experience, transparency, and security are at the heart of customer satisfaction. To be successful in this competitive environment, organizations must adopt a 'customer-first' approach
- Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement requires a seamless innovation delivery pipeline built on agile principles. The pipeline should be highly effective and easily track changing market trends, test innovative products, and facilitate quick feedback mechanisms to iterate products for enhancements
- Modernize Infrastructure: Achieving digital transformation entails more than just introducing new digital technologies. The underlying infrastructure is critical in facilitating the information flow required for digital front-end operations. As a result, It is critical to modernize legacy infrastructure to support digital platforms. In this regard, micro service architecture, APIs, and DevOps can benefit continuous integration and delivery, resulting in shorter release cycles
- Operating Model: Customers now require a hybrid experience, a mix of never-seen digital experiences in terms of speed and convenience, and the personalized look and feel of the product. This is possible by dividing the company into three distinct operational models:
- Digital as a Business- at the management level
- Digital as a New Line of Business- create a separate digital division to handle digital activities
- Digital Native- a new set-up with its technology stack that focuses solely on customers
- Leverage Power of Data: Banking institutions must recognize the value of data and the tools and resources that go with it to drive business success. They should think about implementing data analytics practices to better understand and monitor customer behavior patterns. This will also assist them in gaining critical market insights that will help in improving product offerings, experience and deepening customer relationships
- Improve Skill-set: Employees in the finance sector will need to upgrade their skill set to meet current and changing operational demands. The drive for improved skill sets will necessitate investment in organizational culture, thinking patterns, learning culture, skill set training, and other areas across teams
- Completely Digitally-driven: To complete a digital transformation journey, the organization should have all digital capabilities such as strategy, culture, relevant technologies, funding, skillset, and more. Banks must learn from past mistakes, implement best practices, and create an ideal digital strategy
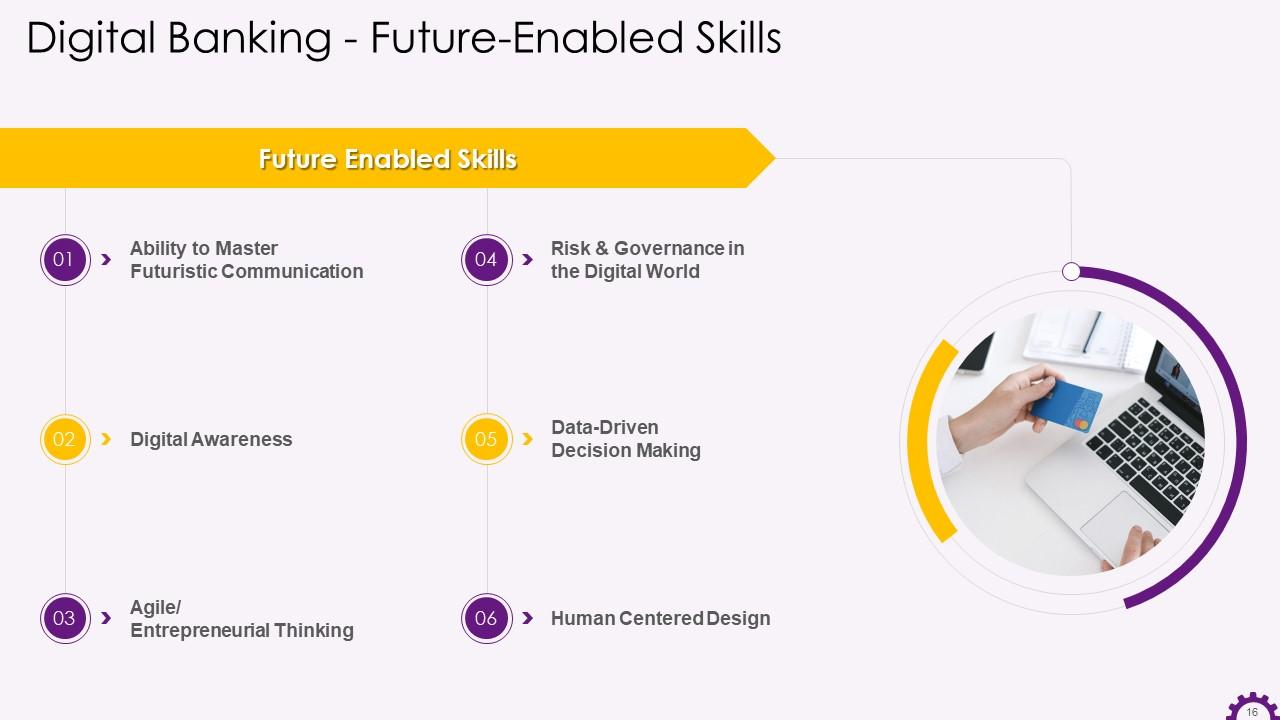
Slide 16
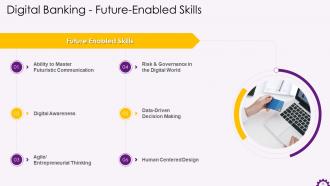
This slide illustrates the future-enabled skills in digital banking. The skills are ability to master futuristic communication, digital awareness, agile/entrepreneurial thinking, risk & governance in the digital world, data-driven decision making, and human-centered design.
Slide 17
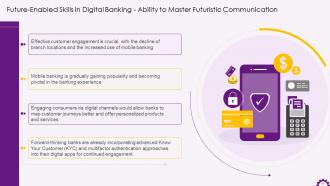
This slide depicts futuristic communication as a future-enabled skill in digital banking. It illustrates that effective customer engagement is critical with the decline of branch locations and growth of mobile banking use. It also includes that mobile banking is gradually gaining popularity and becoming pivotal in the banking experience. Engaging consumers via digital channels would allow banks to map customer journeys better and offer personalized products and services.
Slide 18
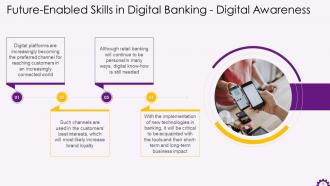
This slide illustrates digital awareness as a future-enabled skill in digital banking. It demonstrates that digital platforms are increasingly becoming the preferred channel for reaching customers in an increasingly connected world. Such channels are used in the customers' best interests, most likely increasing brand loyalty. With the implementation of new technologies in banking, it will be critical to become acquainted with the tools and their short-term and long-term business impact.
Slide 19
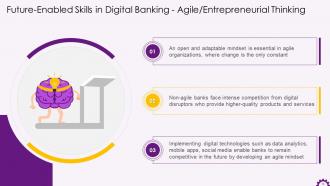
This slide depicts agile and entrepreneurial thinking as a future-enabled skill in digital banking. It also illustrates that an open and adaptable mindset is a prerequisite in agile organizations. Non-agile banks face intense competition from digital disruptors who provide higher-quality products and services. It also mentions that implementing digital technologies such as data analytics, mobile apps, and social media helps banks develop an agile mindset. This will ensure banks remain competitive.
Slide 20
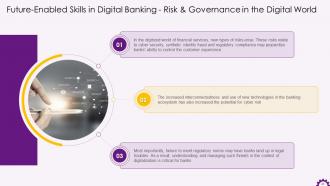
This slide illustrates risk and governance in the digital world as a future-enabled skill in digital banking. It mentions that new types of risks arise in the digitized world of financial services. The risks related to cyber security, synthetic identity fraud and regulatory compliance may risk banks' ability to control the customer experience. It also indicates that failure to meet regulatory expectations may put banks at the risk regarding legal compliance. As a result, understanding and managing such threats in the context of digitalization is critical for banks.
Slide 21
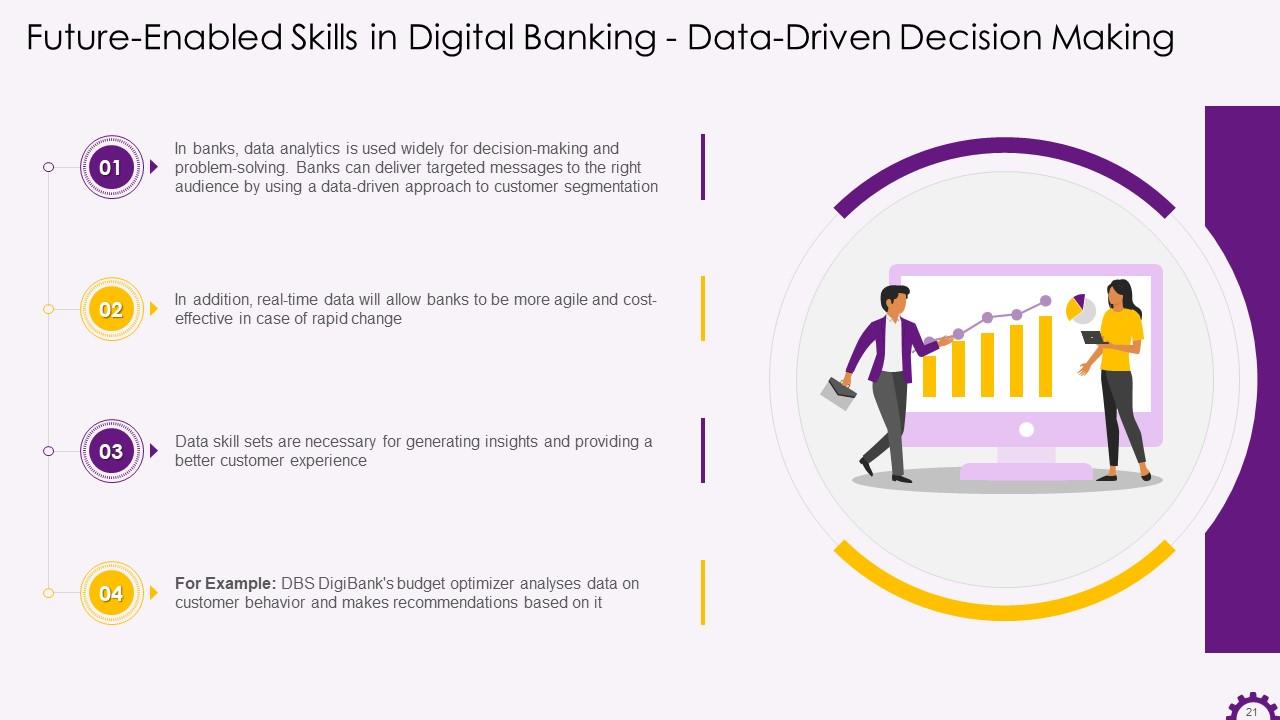
This slide depicts data-driven decision-making as a skill that will be useful in the future of digital banking. It demonstrates how banks widely use data analytics for decision-making and problem-solving. Banks can deliver targeted messages to the right audience by using a data-driven approach to customer segmentation. Furthermore, Real-time data will enable banks to be more agile and cost-effective in the face of unexpected changes.
Slide 22
This slide illustrates human-centered design as a skill that will be useful in the future of digital banking. It mentions that customer centricity and providing a consistent customer experience across multiple channels are essential in digital banking. When banks involve customers in the design process to ensure that products and services meet their needs, they become more valuable to the customer.
Slide 23
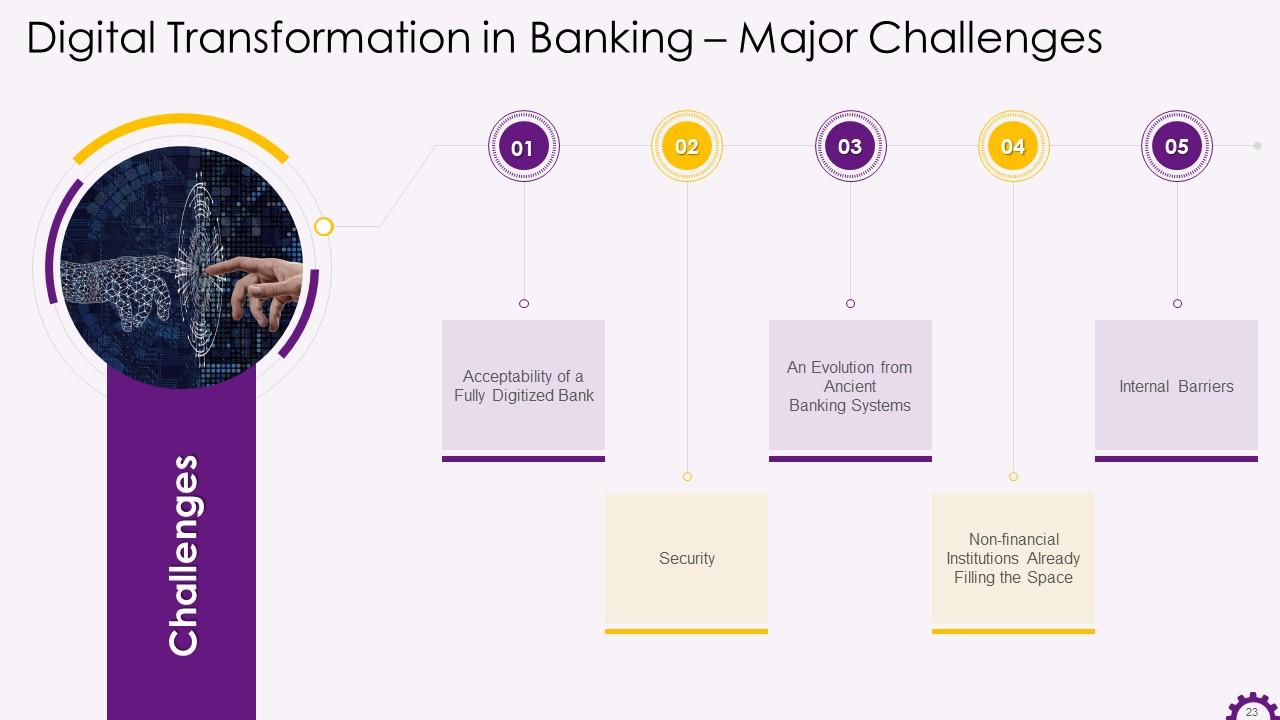
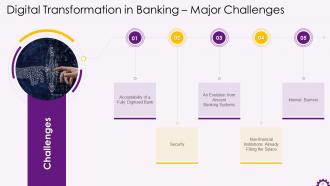
This slide illustrates the challenges of digital transformation in banking. The challenges are an entirely digitized bank, brick, and mortar or both, security, non-financial institutions already filling the space, and internal barriers.
Instructor’s Notes:
The challenges of digital transformation in banking industry are:
- Acceptability of a Fully Digitized Bank- Even though the adoption of digital banking is on the rise, there is considerable skepticism as well. Furthermore, some people are skeptical of going completely digital then will face this acceptability change for sure.
- Security- One of the most significant digital transformation challenges that banks face in undergoing digital transformation is the security of their IT infrastructure and data.
- Legacy of Ancient Banking Systems- Most legacy banking systems use the COBOL programming language. This has been around for a long time and is not compatible with today’s technology. While the demand for seamless digital banking increases, upgrading and these banking systems usually takes a long time
- Non-financial Institutions Already Filling the Space- Several non-financial institutions provide services similar to what is expected of a digital bank today. Users of social media platforms, such as Facebook, can now send money directly to another person's bank account. It is difficult for financial institutions to cope because the unregulated tech platforms are not bound by any rules
- Internal Barriers- To fully digitize banking, both the banking system and its employees must undergo a cultural shift. Banks, however, have a distinct way of departmentalizing, which has a significant impact on the level of technology to be used. While a digital banking system will benefit some departments, it will force others to lay off workers. Employee education and training may also be required
Slide 25
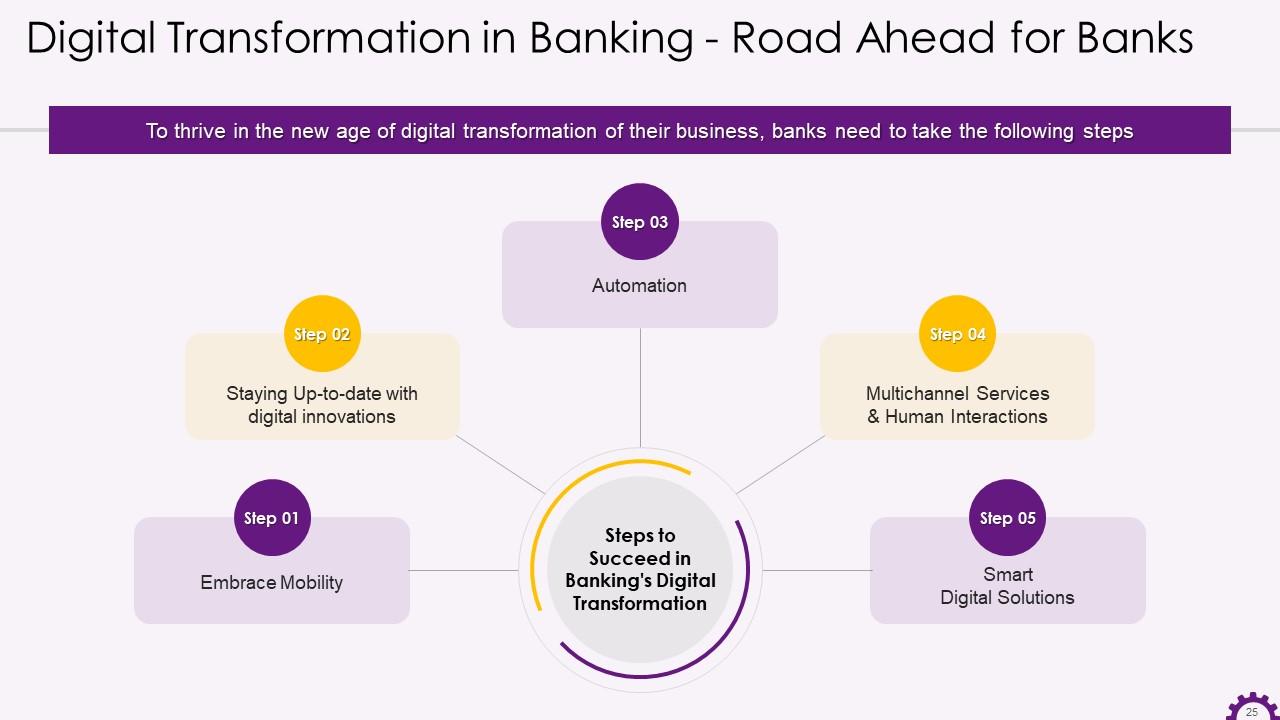
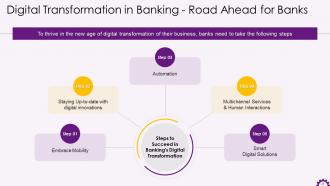
This slide depicts the steps that can be followed for a successful banking digital transformation journey. The steps are embracing mobility, staying updated with digital innovations, automation, multichannel services & human interactions, and smart digital solutions.
Instructor’s Note:
The steps to succeed in banking’s digital transformation are:
- Embrace Mobility: Banks can embrace mobility by developing mobile applications that provide account information and engage customers and allow them to share their financial goals
- Staying Up-to-date with digital innovations: Banks can stay relevant by embracing new technologies and trends
- Automation: Banks can use automation to boost productivity and customer satisfaction wherever possible
- Multichannel Services & Human Interactions: Even in the midst of banking's digital transformation, human interaction can be critical because it actively builds customer trust and opens the door to new banking experiences. Banks should prioritize multichannel services embracing both automation and human interactions
- Smart Digital Solutions: Banks can implement intelligent digital solutions, such as installing self-service stations in branches that allow customers to perform transactions independently
Slide 26
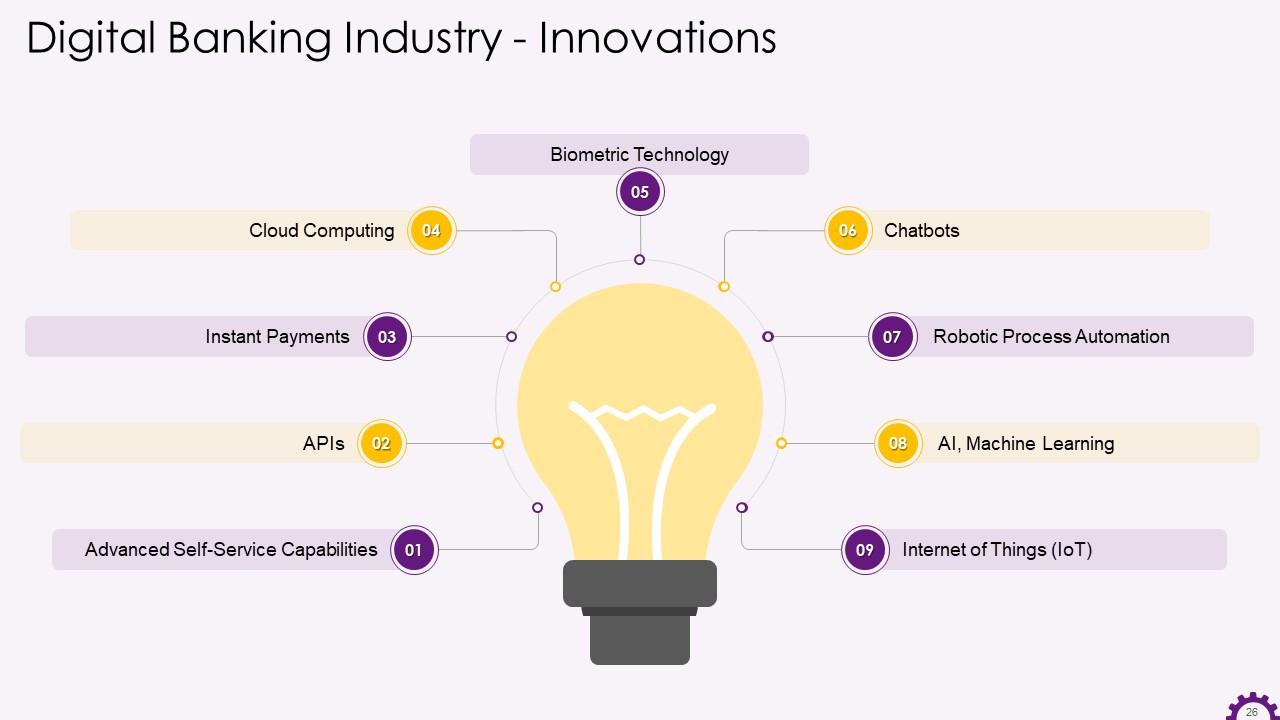
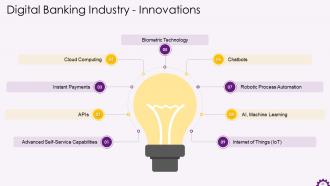
This slide illustrates the innovations, technologies, and trends that help banks provide future-oriented digital banking services. The technologies are advanced self-service capabilities, APIs, instant payments, cloud computing, biometric technology, chatbots, process automation (RPA, AI, Machine Learning), micro-services, and the internet of things.
Slide 27
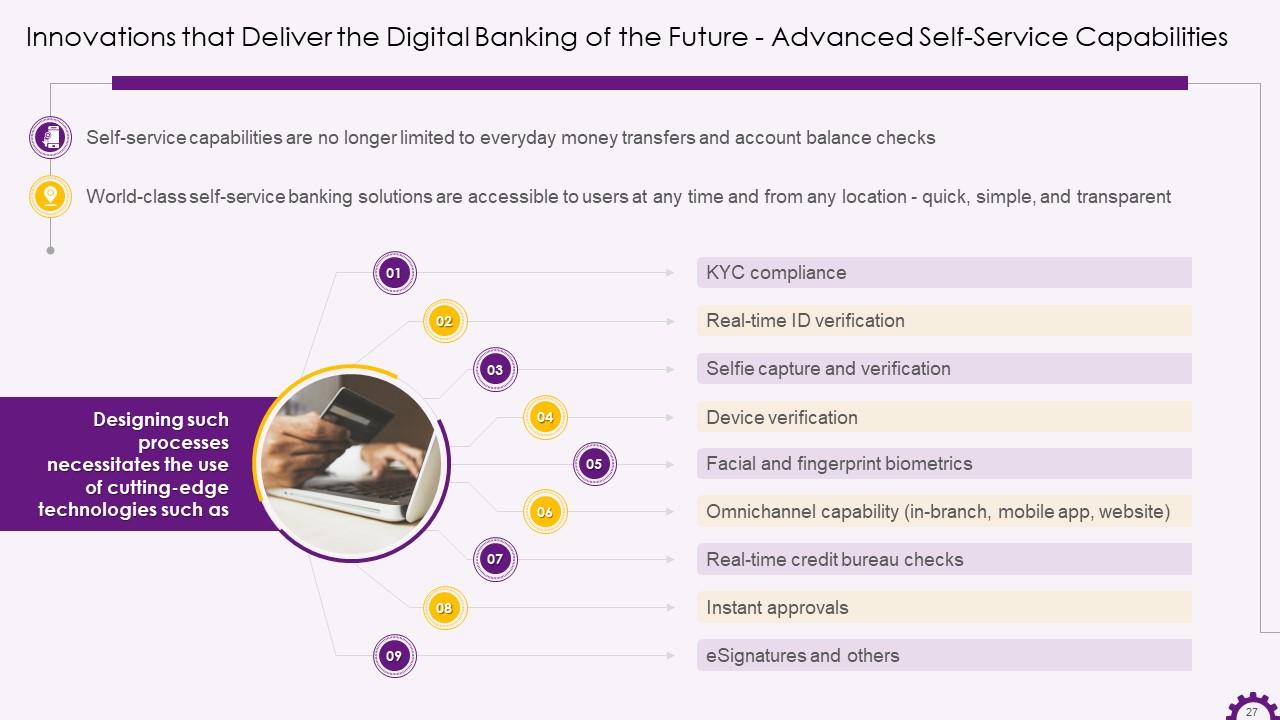
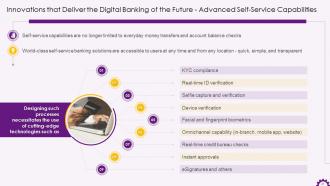
This slide depicts advanced self-service capabilities as a digital banking innovation. It demonstrates that self-service capabilities are no longer restricted to simple money transfers and account balance checks. It also states that developing advanced self-service capabilities necessitates the use of cutting-edge technologies such as KYC compliance, real-time ID verification, selfie capture and verification, facial and fingerprint biometrics, real-time credit bureau checks, and so on.
Slide 28
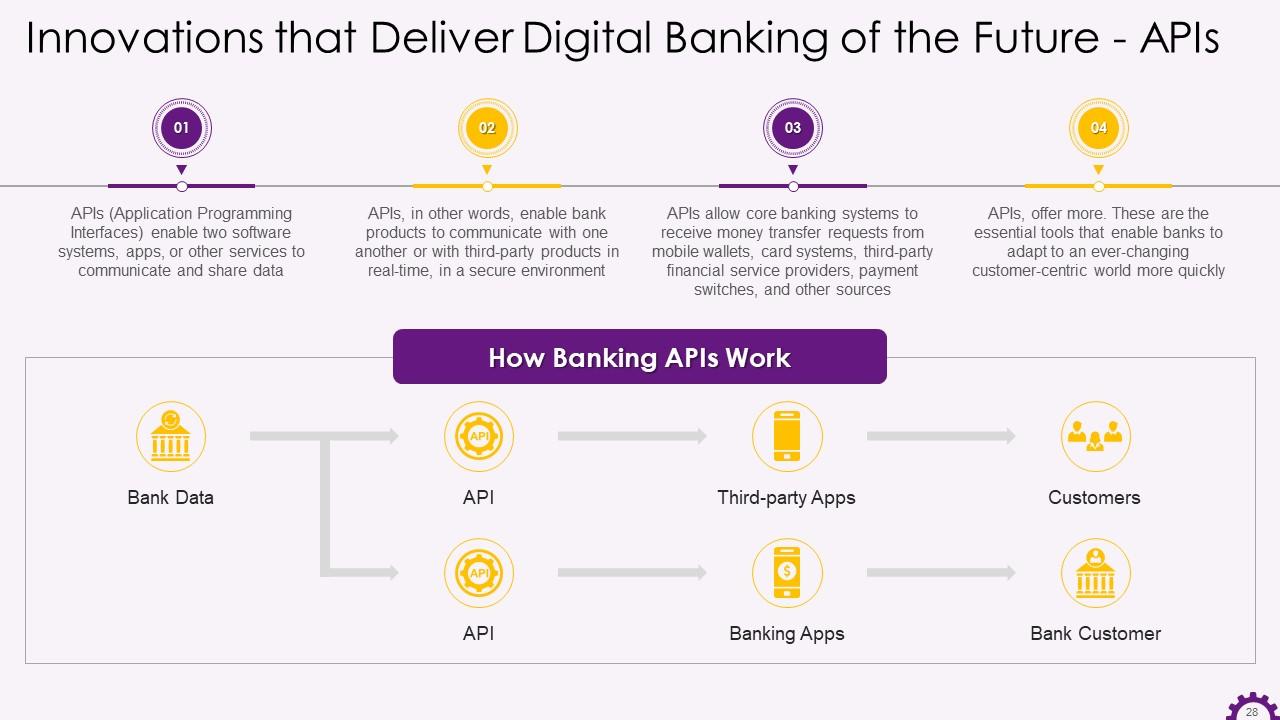
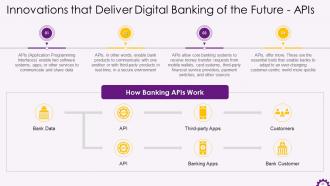
This slide depicts information about Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) in digital banking. APIs allow banks' products to communicate with one another or with third-party products in real-time, in a secure environment. It also demonstrates the working of banking APIs.
Slide 29
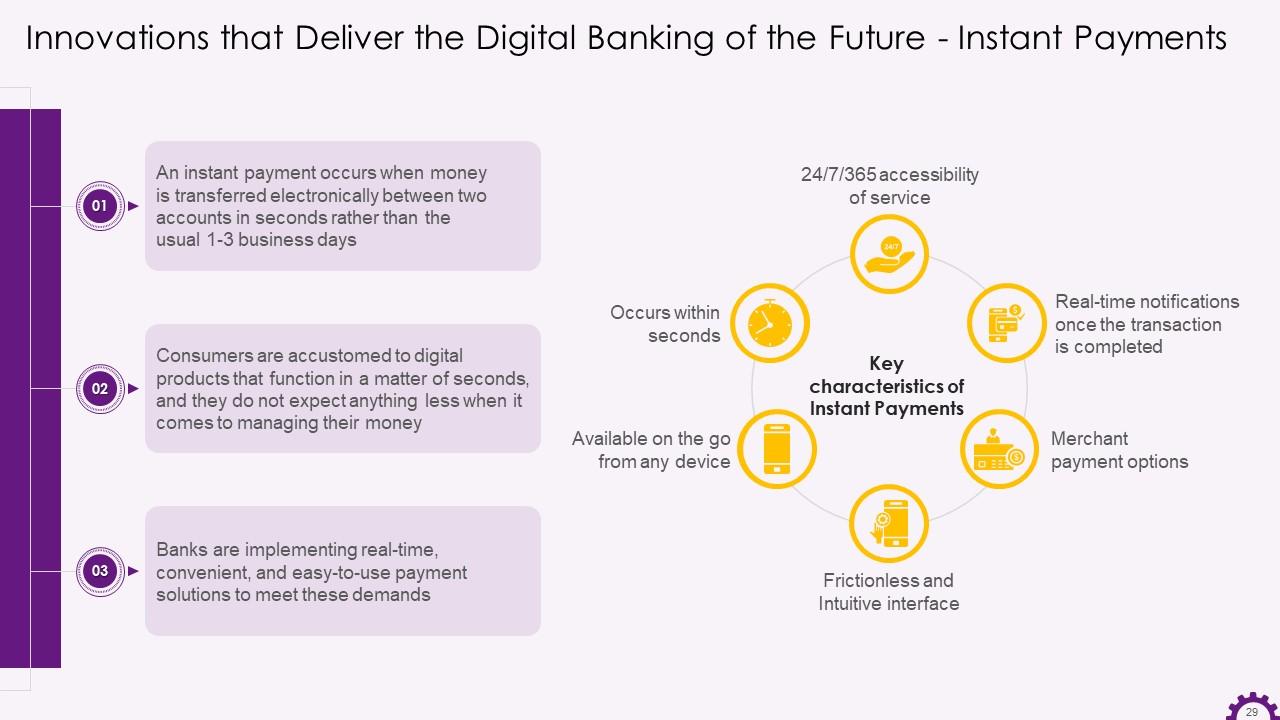
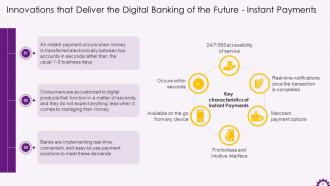
This slide showcases information regarding instant payments in banking industry. It illustrates that consumers are familiarized with digital products that function in seconds. Therefore, banks are implementing real-time, convenient, and easy-to-use payment solutions to meet these demands. It also mentions the key characteristics of instant payments.
Slide 30
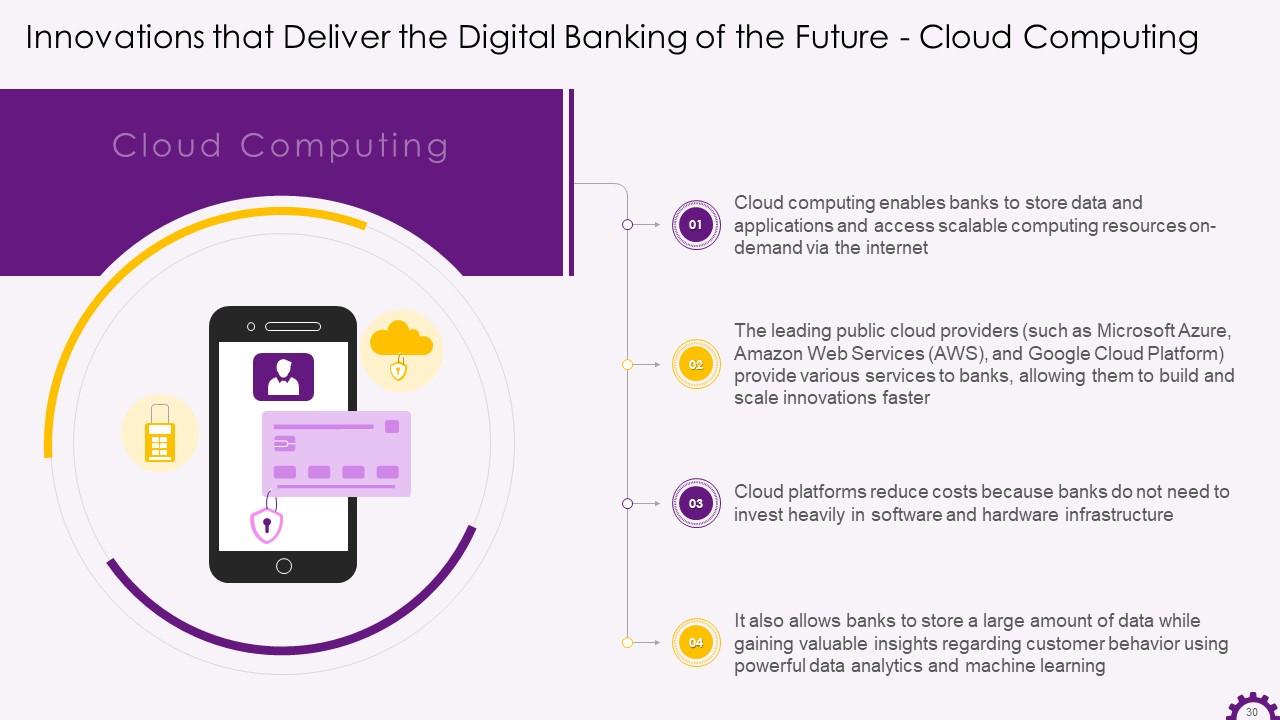
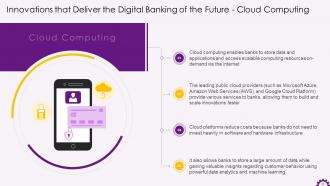
This slide depicts information regarding cloud computing in banking industry. It mentions how cloud computing enables banks to store massive amounts of data while gaining valuable insights about customer behavior with data analytics and machine learning. It also shows how public cloud providers such as Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform offer a variety of services to banks.
Slide 31
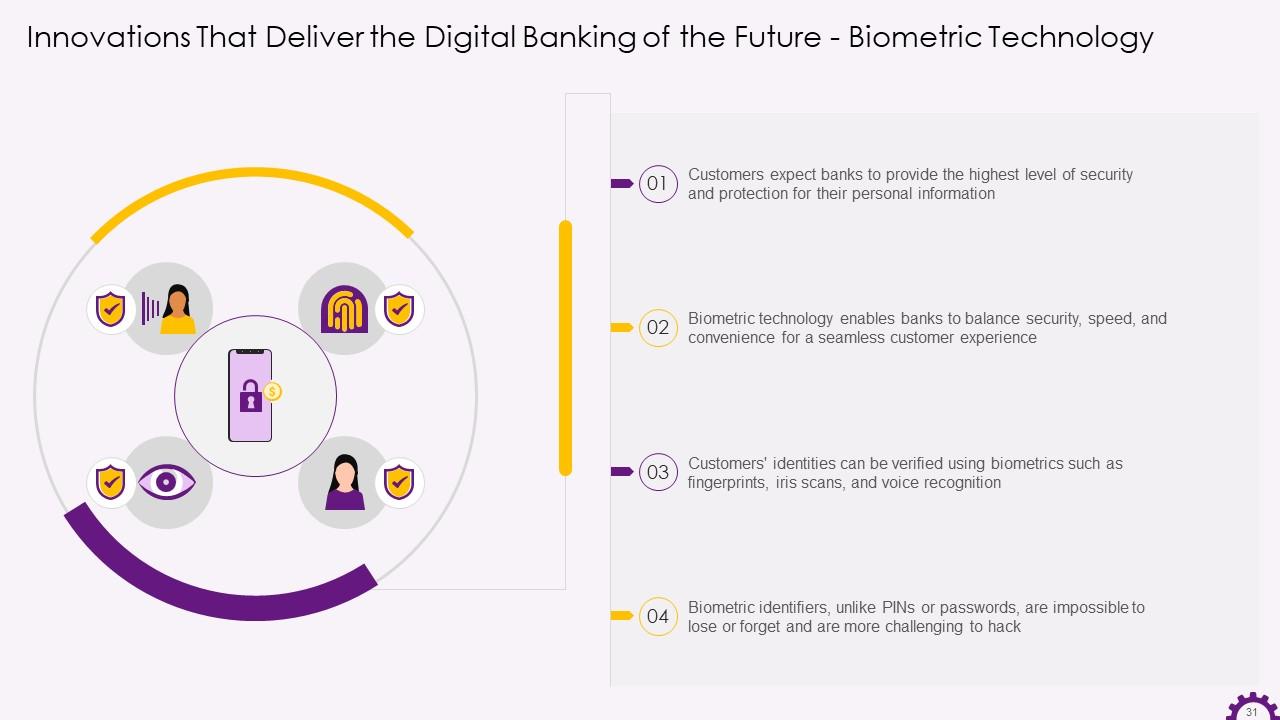
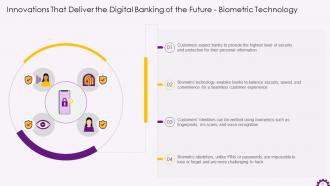
This slide illustrates information about biometric technology in the banking industry. It demonstrates how biometric technology enables banks to balance security, speed, and convenience to provide a seamless customer experience. It also mentions that customers' identities can be verified using biometrics such as fingerprints, iris scans, and voice recognition.
Slide 32
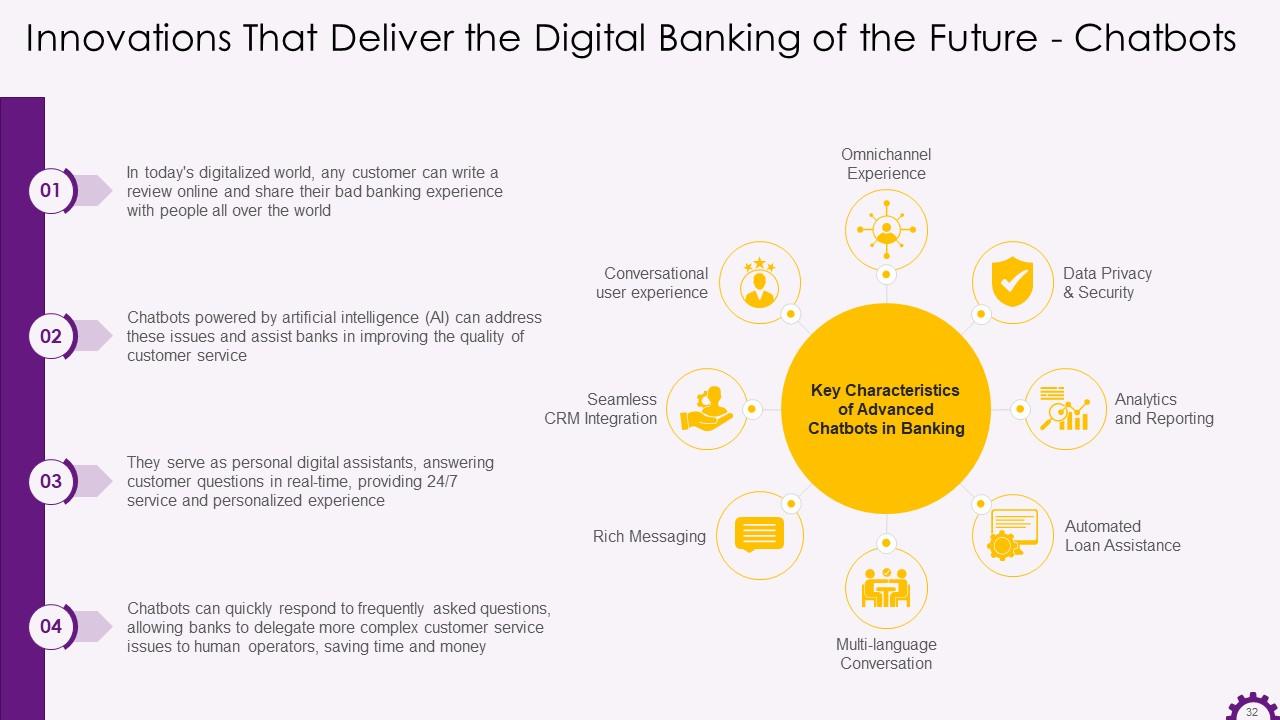
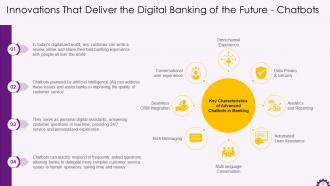
This slide depicts information regarding chatbots in the banking industry. It illustrates that chatbots powered by artificial intelligence (AI) addresses issues and assist banks in improving the customer service quality. It also mentions the key characteristics of advanced chatbots in the banking industry.
Slide 33
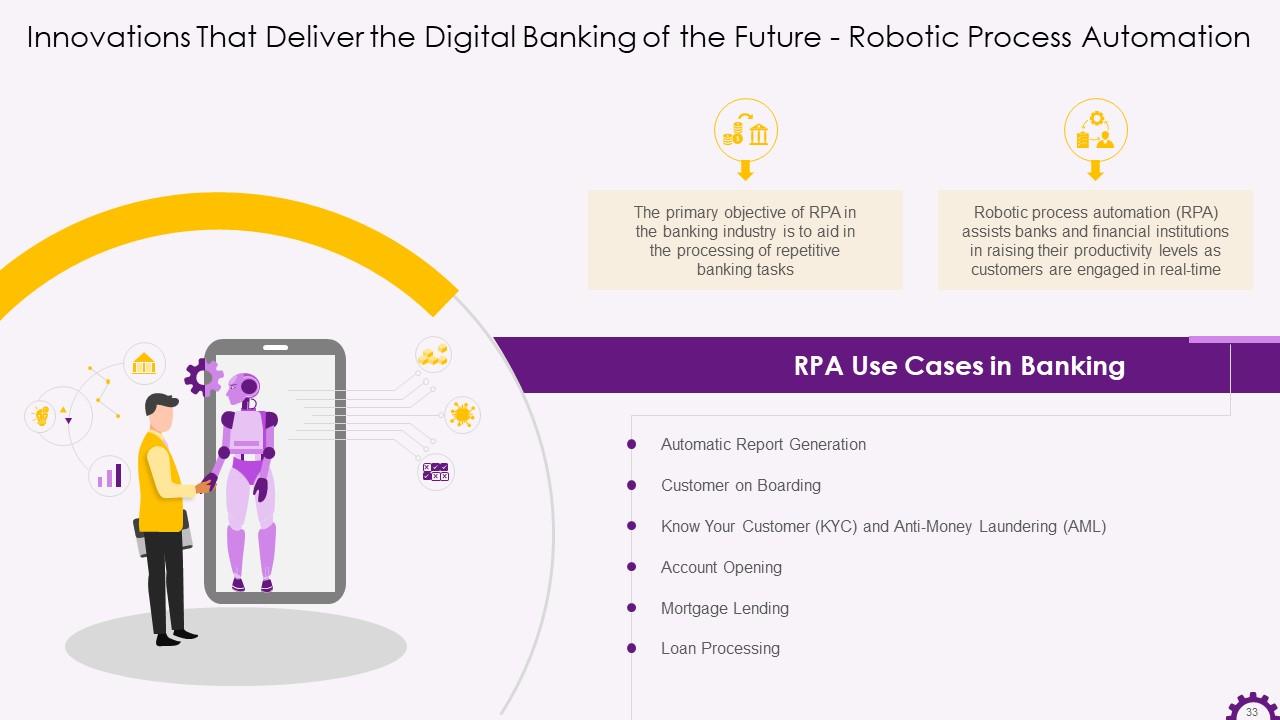
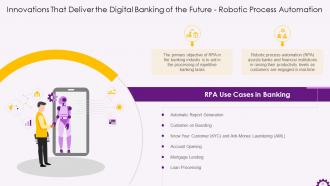
This slide illustrates information regarding Robotic Process Automation in the banking industry. It demonstrates that robotic process automation aids in processing repetitive banking tasks, and it assists banks increase productivity by leveraging robots’ immense benefits. It also mentions the use cases in the banking industry such as automatic report generation, customer onboarding, KYC, anti-money laundering, mortgage lending, loan processing, etc.
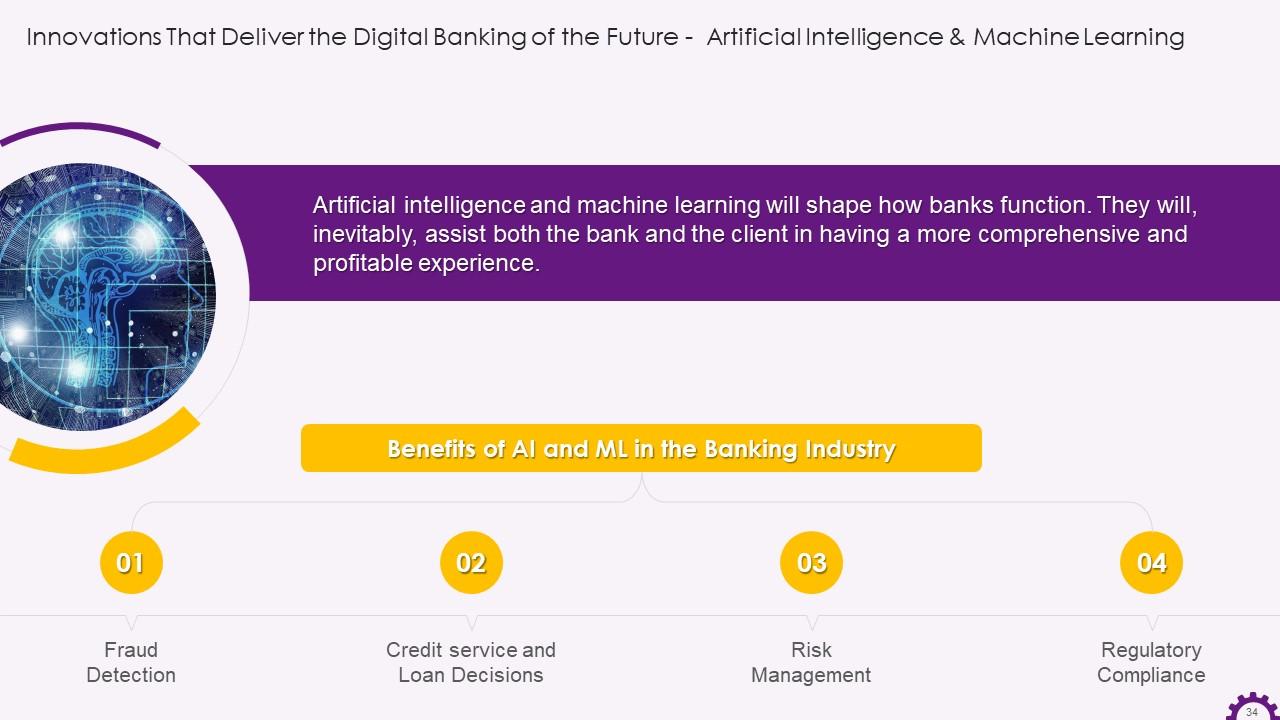
Slide 34
This slide illustrates information regarding the adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the banking industry. It demonstrates that AI and ML assist banks and the customers in having a comprehensive and profitable experience. It also highlights the benefits of AI and ML in the banking industry, such as fraud detection, risk management, etc.
Slide 35
This slide depicts information regarding the IoT in the banking industry. It mentions that the IoT is a network of inter-connected devices that collect and transmit data. It also illustrates the use cases of the technology in banks, for purposes such as payments and notifications.
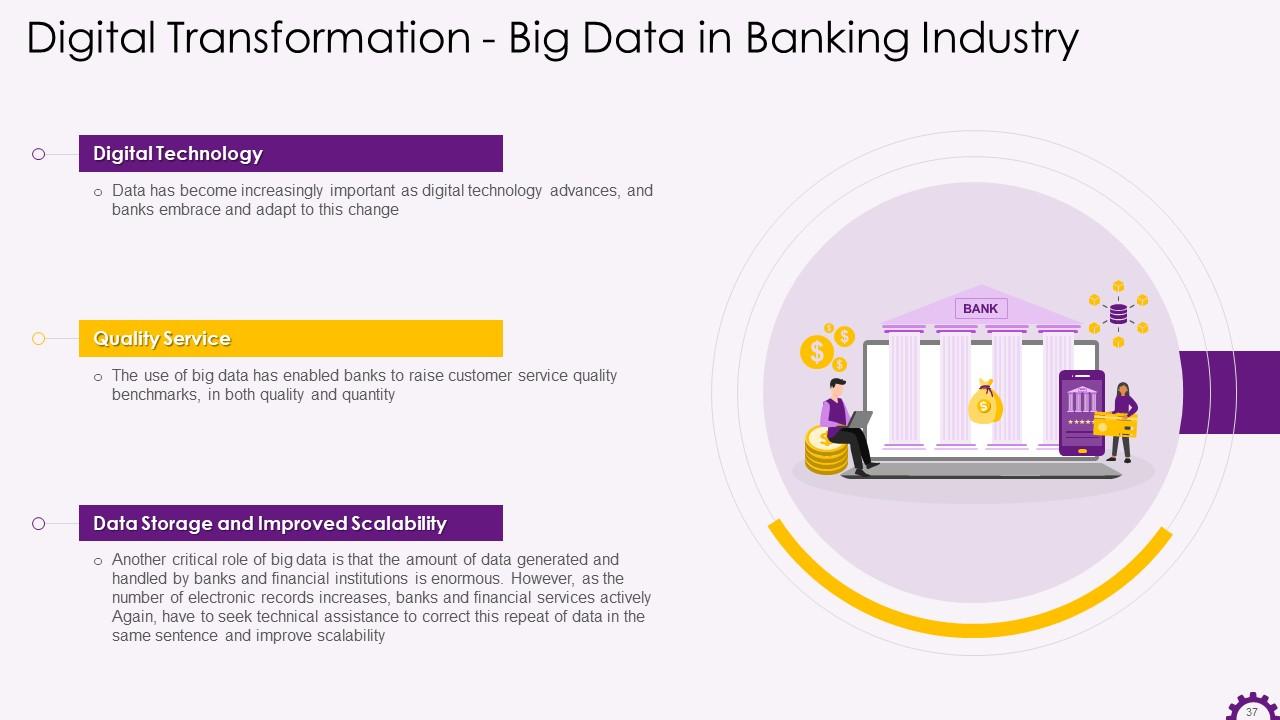
Slide 37
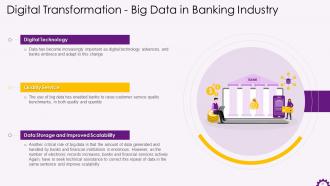
This slide illustrates information about big data in the banking industry. It mentions that as digital technology advances, data has become increasingly important, and banks are embracing and adapting to this change. It also shows that banks and financial institutions generate and manage massive amounts of data. Banks and financial institutions are actively using big data to store data and improve scalability as the number of electronic records grows.
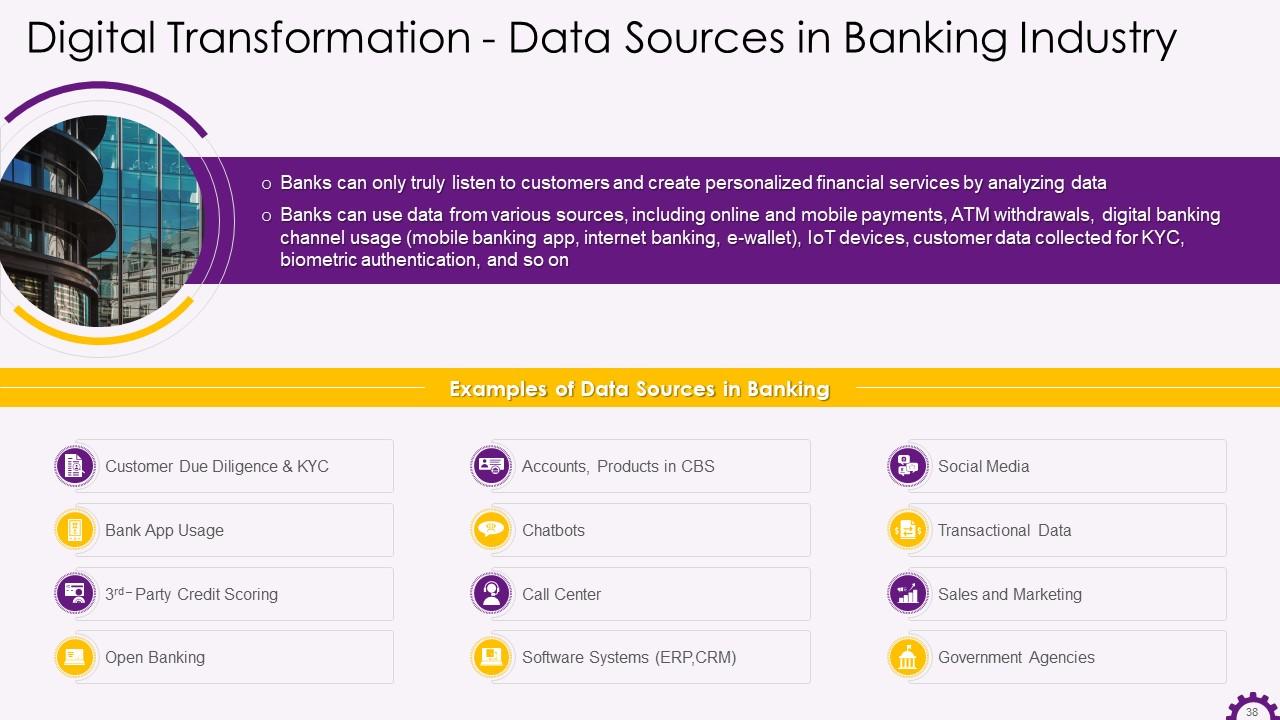
Slide 38
This slide depicts that by analyzing data, banks can listen to its customers and create personalized financial services. It highlights that bank can use data from various sources, including online and mobile payments. It also mentions the sources from which data is taken. These are bank application, third-party credit scoring, chatbots, call center, social media etc.
Slide 39
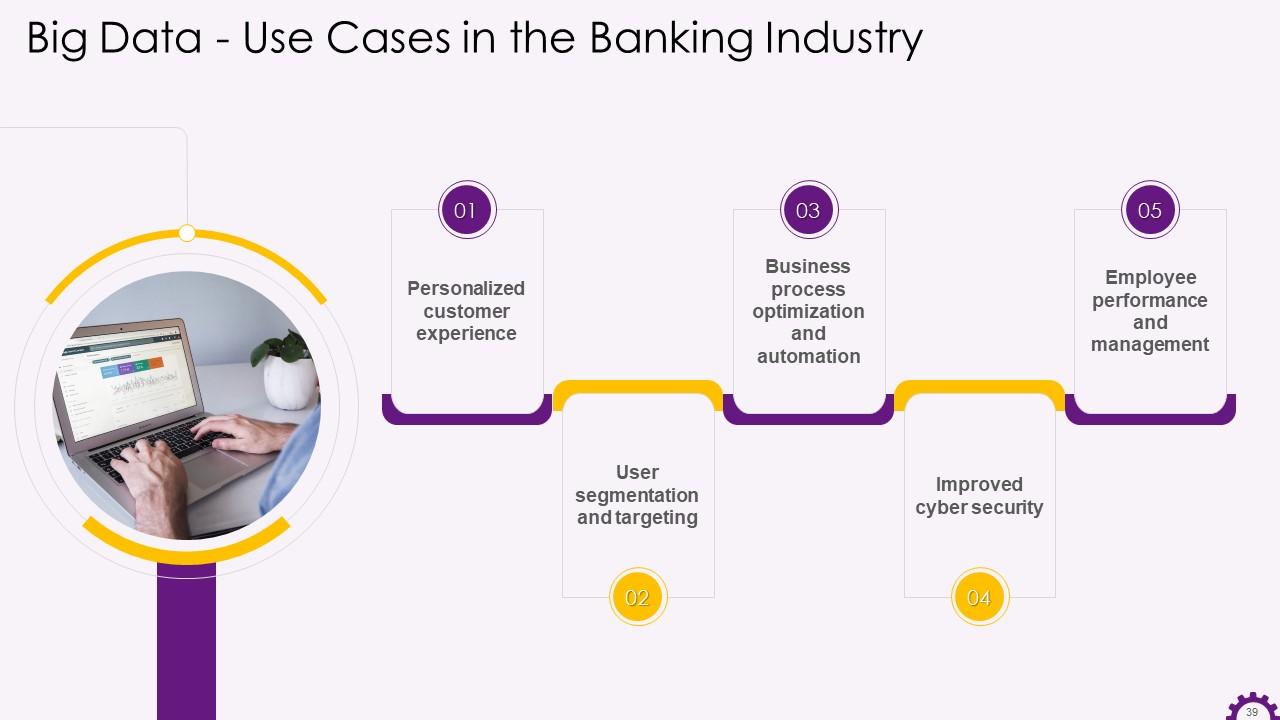
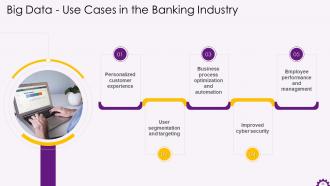
This slide illustrates the use cases of big data in the banking industry. The use cases are personalized customer experience, user segmentation and targeting, business process optimization automation, improved cyber security, and employee performance and management.
Slide 40
This slide depicts the implementation of personalized customer experiences in the banking industry using big data. It states that banks use big data to learn more about their customers. This knowledge is used to find new ways to cater to their needs, connect with them more meaningfully, and provide more value.
Slide 41
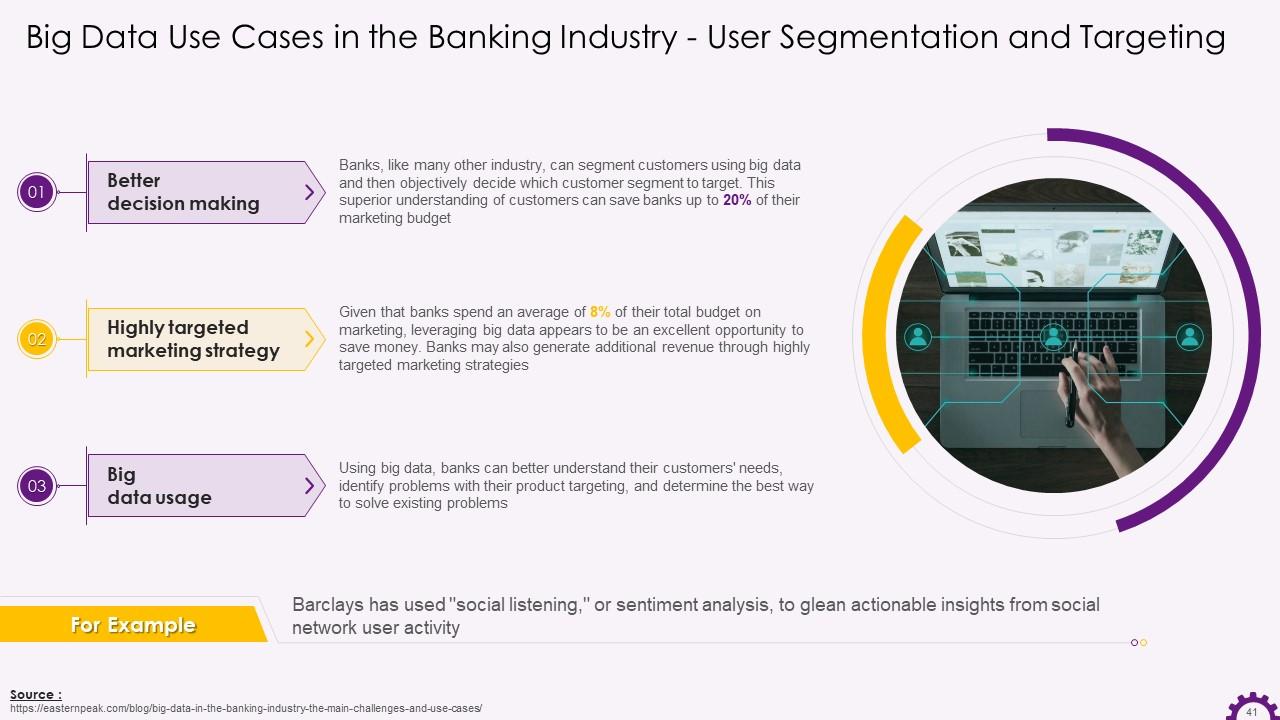
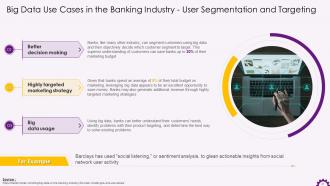
This slide illustrates the adoption of big data for user segmentation and targeting in the banking industry. It highlights that big data can save the banks' marketing budget and mentions how using big data, banks can better understand their customers' needs, identify issues with their product targeting, and determine the best way to solve existing problems.
Slide 42
This slide depicts the use of big data to optimize and automate business processes in the banking industry. It emphasizes that all banking work can be automated using technology, and big data holds the key to this. By removing the human element from certain critical processes, banks can save money. Advanced automation reduces the risk of failure due to advanced automation.
Slide 43
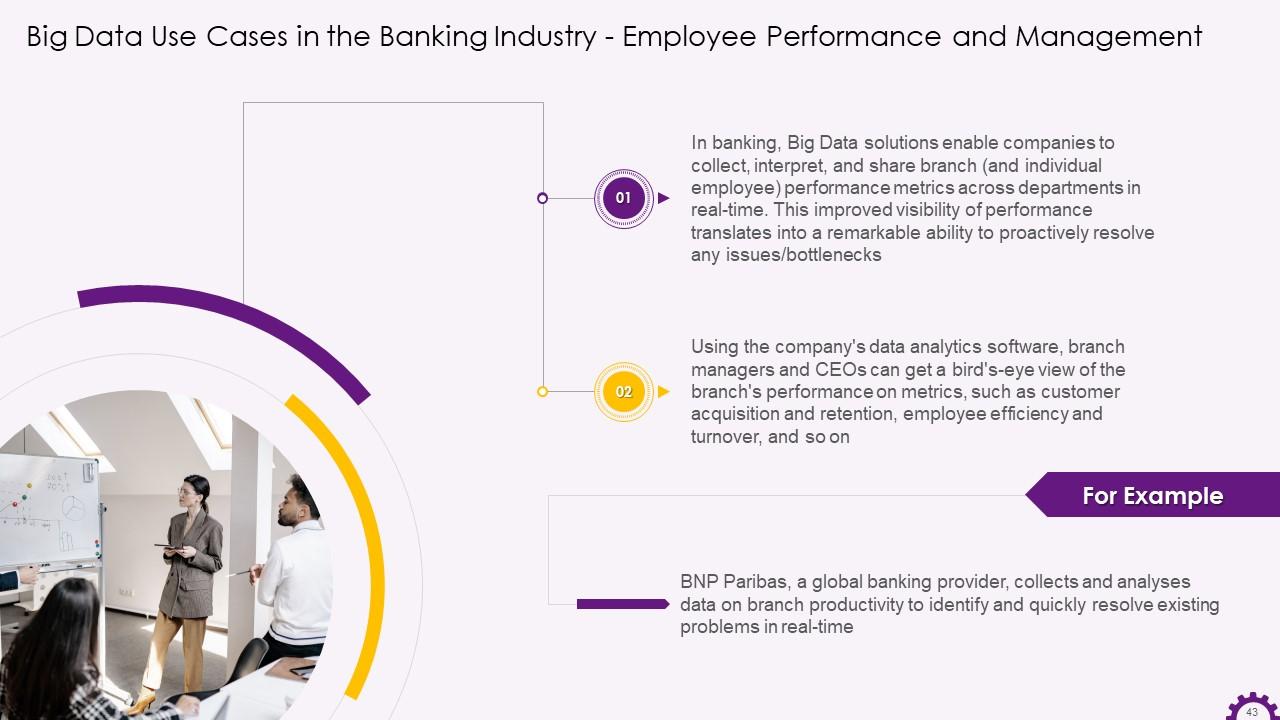
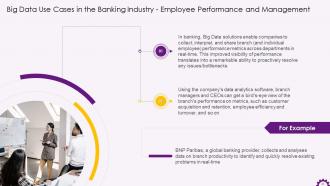
This slide illustrates the application of big data in employee performance and management in the banking industry. It demonstrates how companies can use Big Data to collect, interpret, and share branch and employee performance metrics across departments in real-time. Branch managers and CEOs can view the branch's performance on metrics, such as customer acquisition and retention, employee efficiency and turnover, and so on, using data analytics software.
Slide 44
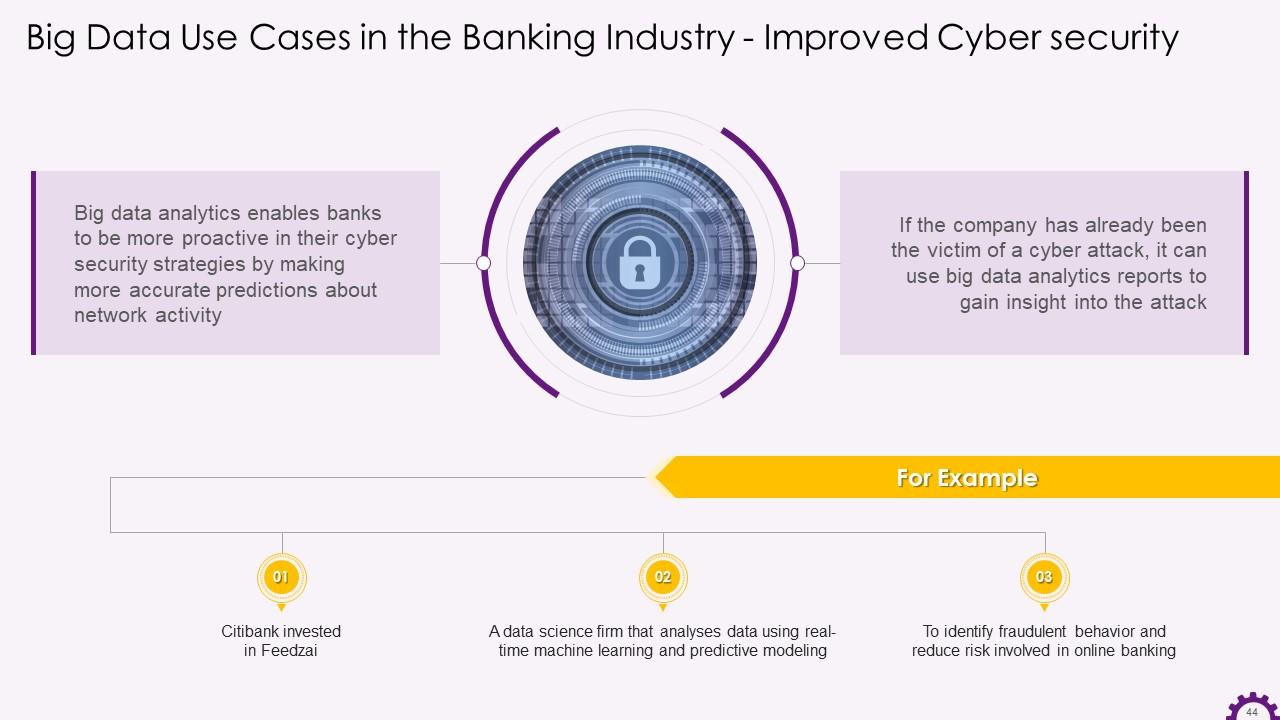
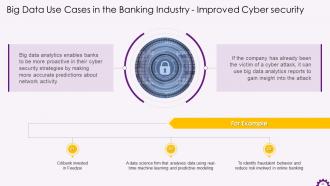
This slide provides information about big data analytics in the banking industry. It emphasizes how big data analytics allows banks to be more proactive in their cyber security strategies by making more accurate predictions about network activity. It also states that big data analytics reports help gain insight into cyber security and even prevent an attack.
Slide 46
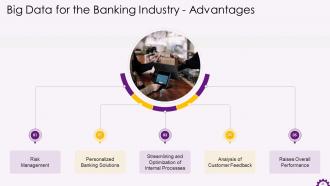
This slide illustrates the advantages of big data for the banking industry. The advantages are risk management, personalized banking solutions, streamlining and optimization of internal processes, analysis of customer feedback, and raising overall performance.
Instructor’s Notes:
The advantages of big data for the banking industry are:
- Risk Management - Big data can be used by banks to analyze market trends and determine whether to lower or raise interest rates. Banks can quickly identify customers with poor credit scores and refuse loans. Using fraud detection algorithms banks can detect fraud and prevent potentially malicious activities
- Personalized Banking Solutions- Big data analytics can help banks understand customer behavior based on inputs from their investments, shopping trends, or financial background. It aids banks in customer retention. Personalized banking solutions can help you gain customer loyalty
- Streamlining and Optimization of Internal Processes- Banks can use big data to optimize and streamline their internal processes, improving performance and lowering operating costs
- Analysis of Customer Feedback- Customer service phone lines at bank remain overburdened. Big data tools can assist in sorting through large amounts of data and responding to each of them in a timely and adequate manner. Customers will feel valued because their complaints are being addressed with speed
- Raises Overall Performance- Employee performance can also be assessed using performance analytics to determine whether or not they have met the targets. Big data can assist in determining how it can help them scale more effectively
Slide 47
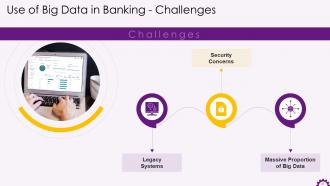
This slide illustrates the challenges with the use of big data in the banking industry. The challenges are legacy systems, security concerns, and massive proportion of big data.
Instructor’s Notes:
The challenges with the use of big data in banking are:
- Legacy Systems- The banking industry has been a little slow to innovate. The majority of legacy systems are incapable of handling the increasing workload. Its process of collecting, storing, and analyzing data with outdated infrastructure may put additional strain on the system and jeopardize its stability
- Security Concerns- If we consider using legacy systems, there may be a risk of dealing with vast amounts of data. Banking providers must make sure that use data and the processes of handling it remains secure at all times. Only a small percentage of banks worldwide can handle the threat
- Massive Proportion of Big Data- Banks may struggle to coherently deal with a large volume of different types of data
Slide 48
This slide showcases the factors that need to be ensured while implementing big data in banking industry. The elements are data quality management and consolidation after acquisition.
Slide 49
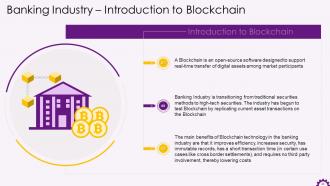
This slide depicts Blockchain's introduction to the banking industry. It emphasizes how the banking industry is transitioning from traditional securities to high-tech securities. The industry has begun to put Blockchain to the test by simulating current asset transactions. It also mentions the advantages of Blockchain technology to banking, such as increased efficiency, security, immutable records, and quick transaction times.
Slide 50
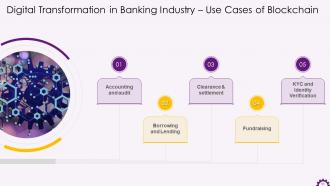
This slide depicts the usage of Blockchain in banking industry. The use cases are accounting and audit, borrowing and lending, clearance & settlement, fundraising, and KYC and identity verification.
Slide 51
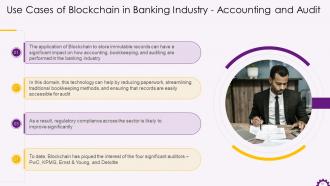
This slide illustrates how Blockchain can be used in accounting and auditing in the banking industry. It emphasizes the application of Blockchain to store immutable records, which can have a significant impact on how accounting, bookkeeping, and auditing are performed in the banking sector. It also mentions how Blockchain has piqued the interest of four significant auditors: PwC, KPMG, Ernst & Young, and Deloitte.
Slide 52
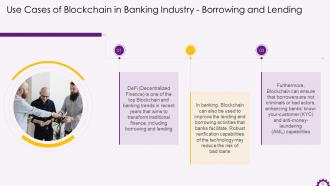
This slide illustrates how Blockchain can be used in the banking sector for borrowing and lending. Blockchain can help banks strengthen their know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money-laundering (AML) capabilities by ensuring that borrowers are not criminals or bad actors.
Slide 53
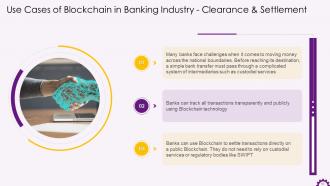
This slide depicts Blockchain's use case in clearance and settlement in the banking industry. It mentions that banks could keep track of transactions and settle them more efficiently with decentralized Blockchain technology than with existing protocols such as SWIFT. Banks can track all transactions transparently and publicly using Blockchain technology.
Slide 54
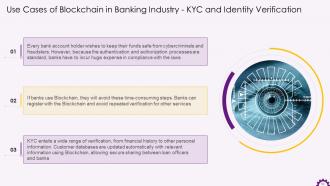
This slide depicts how Blockchain is used for KYC and identity verification in the banking industry. It demonstrates that every bank account holder wants to protect their funds from cybercriminals and fraudsters. On the other hand, banks suffer significantly in terms of efficiency because the authentication and authorization processes are to be complied with. Blockchain can help banks avoid repeated verification for some services, creating more efficiencies.
Slide 55
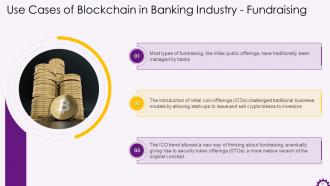
This slide illustrates Blockchain's use case in the banking industry. It emphasizes that traditionally, banks have merged most types of fundraising like Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). Now, Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) have challenged traditional businesses, as it allows start-ups to issue and sell crypto tokens to investors.
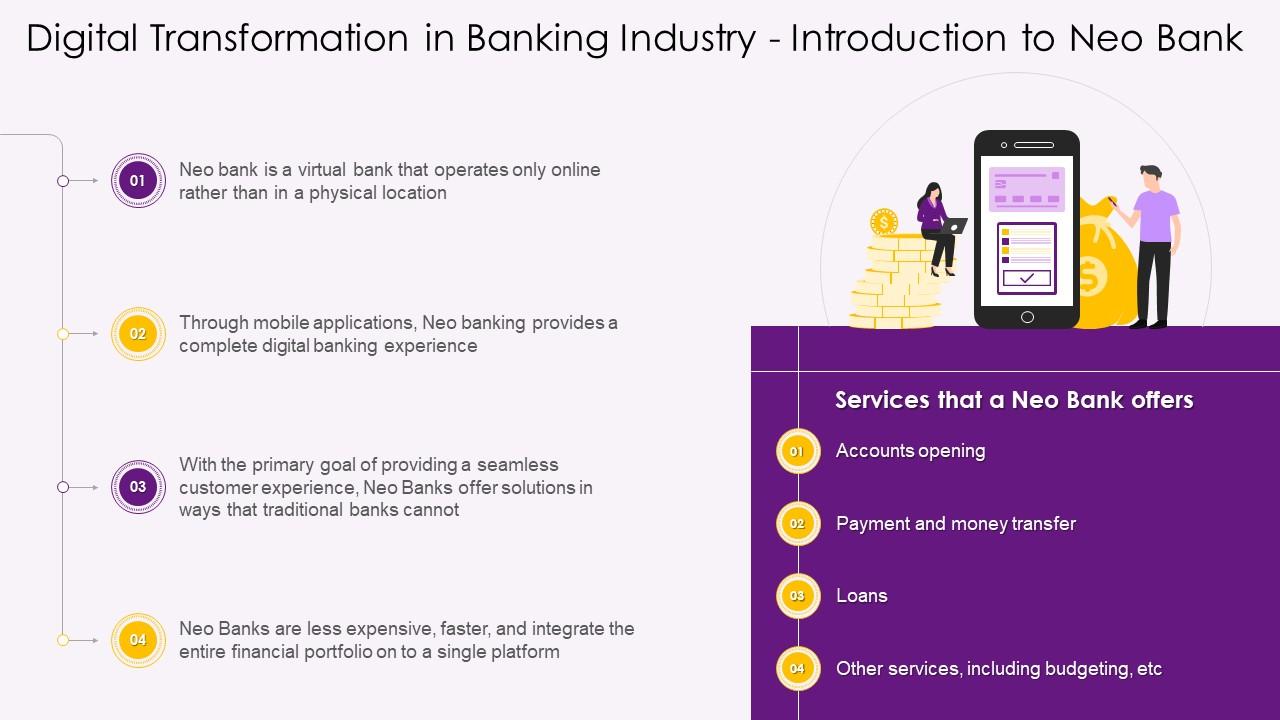
Slide 57
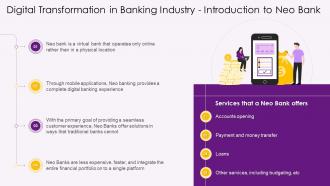
This slide depicts information regarding Neo Banks. It highlights that Neo Banks are virtual banks with no physical branches providing a complete digital banking experience through mobile applications. It also mentions services that a Neo Bank offers such as account opening, payment, and money transfer, etc.
Slide 58
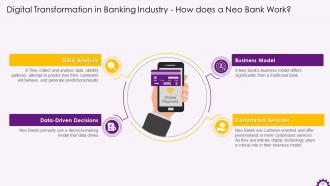
This slide showcases information regarding how neo bank works. It mentions that Neo Banks are customer-oriented and offer personalized services, it is data that drives their decision-making process and implementation.
Slide 59
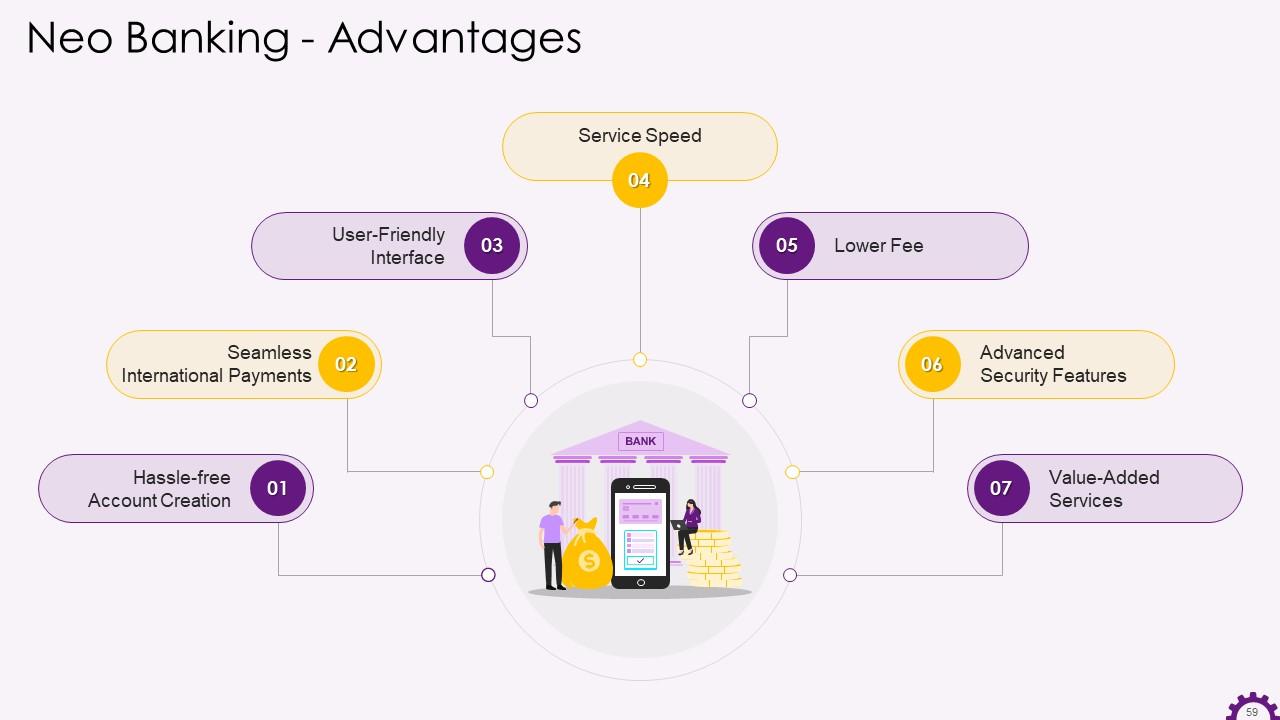
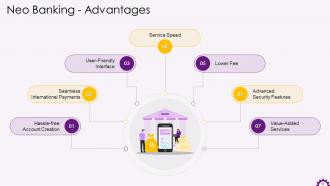
This slide illustrates the advantages of Neo Banking. The advantages are hassle-free account creation, seamless international payments, user-friendly interface, service speed, lower fee, advanced security features, and value-added services.
Instructor’s Notes:
The advantages of neo banking are:
- Hassle-free account creation- Account creation in traditional banks is frequently perceived as time-consuming due to the required physical presence and lengthy process. Though there has been significant progress, the inconvenience remains. There are no such issues with Neo Banks. Because it only exists online and has no physical branches, anyone with a smartphone, tablet, or PC can create an account in a few simple steps
- Seamless international payments- International transactions are not available on cards that bank issue. Unlike traditional banks, Neo Banks allow you to conduct international transactions. Depending on the current exchange rate, one can use Neo bank cards to make purchases or transact while on an international trip
- User-friendly interface- Unlike traditional banks, Neo Banks provide a better user experience by using cutting-edge technologies. Customers do not have to deal with slow-loading net banking websites. Neo banking is available through user-friendly mobile applications and responsive websites tailored to the specific needs of consumers
- Service Speed- Transactions in a neo bank are real-time and immediate. It provides customers with a dashboard that displays an overview of all transactions and the current balance. It also assists customers in managing their finances, expenses, and savings and can be customized
- Lower Fee- One disadvantage of traditional banks is their high operating costs, which are frequently reflected in fee for services such as account statements, transaction alerts, etc. This is eliminated by neo banking, and it works digitally and provides customers with a wide range of services in a few clicks. In the case of Neo bank, there is no physical infrastructure, maintenance for physical branches, or ATMs, which saves money. Neo Banks provide their essential services for free
- Advanced Security Features- Security becomes a major concerning factor when it comes to digital transactions. The Neo bank application employs 2FA (2-factor authorization), biometric verification, RBAC (Role-Based Access Control), encryption technology, and other security measures to protect customer data. The applications are designed to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering laws, complete customer privacy, and prevent malware attacks
- Value-added Services- Banking is no longer just about money transfers. Neo Banks use AI to recommend other financial services to customers based on their account information, customer data, patterns, etc. Customers' profiles are leveraged by Neo Banks, which recommend services based on demographics. This makes it simple for customers to make their own investment decisions
Slide 61
This slide depicts information about peer-to-peer lending. It emphasizes that peer-to-peer (P2P) lending networks consist of two or more users who communicate, share data, and provide lending services without using a central server. It also mentions that peer-to-peer lending networks are integrating with Blockchain-based smart contracts. This is leading now to the evolution of Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
Slide 62
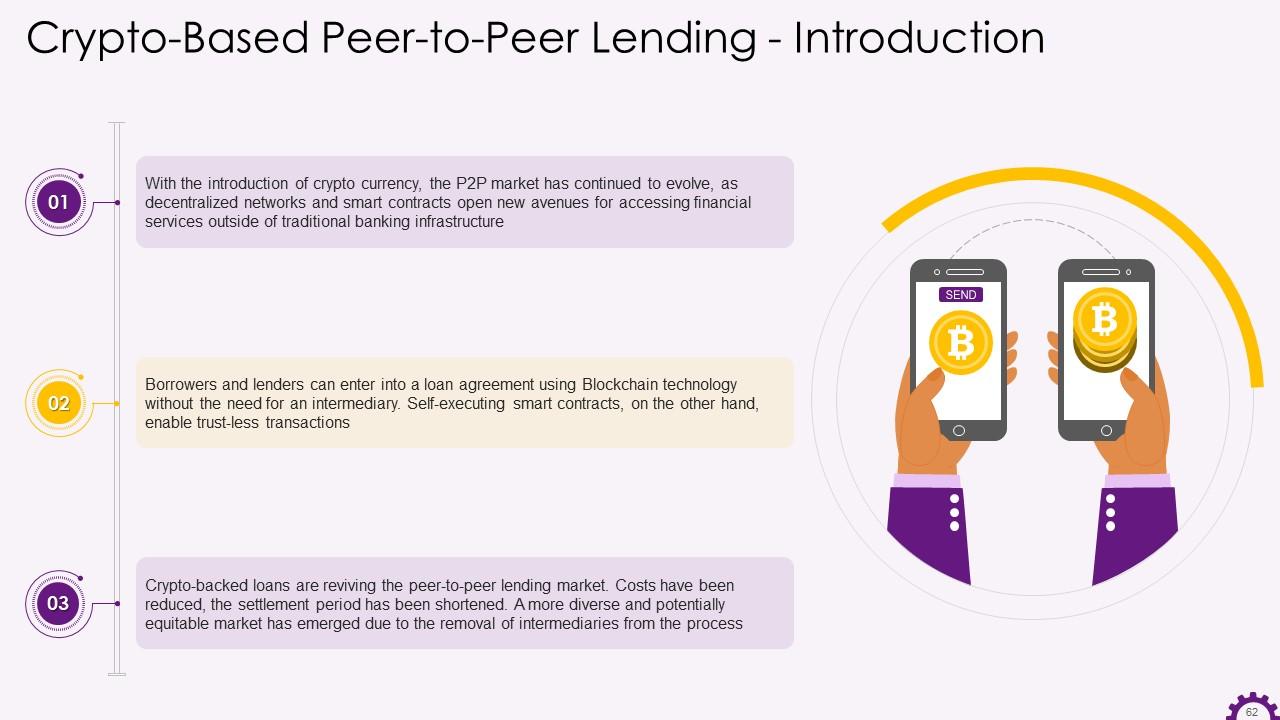
This slide illustrates information regarding Crypto-Based Peer-to-Peer Lending. It highlights that the P2P market has continued to evolve with the introduction of cryptocurrency, as decentralized networks and smart contracts open new avenues for accessing financial services outside of traditional banking infrastructure. Borrowers and lenders can enter into a loan agreement using Blockchain technology without the need for an intermediary.
Slide 63
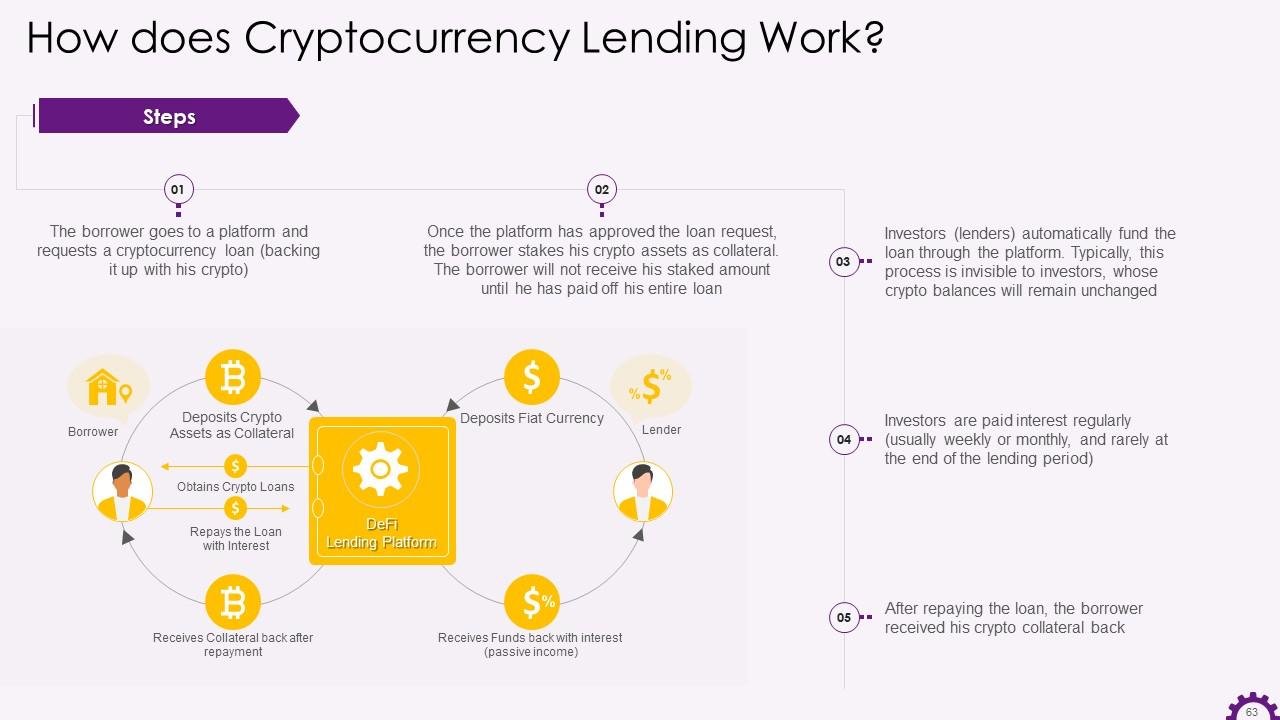
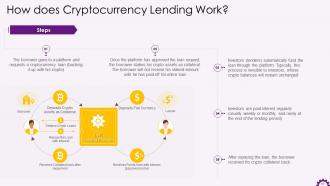
This slide showcases the information regarding Cryptocurrency Lending. It highlights detailed steps in the cryptocurrency lending process.
Slide 64
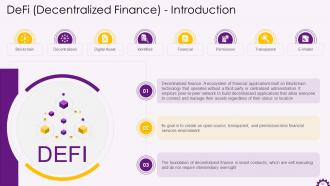
This slide depicts information about decentralized finance. It emphasizes that decentralized finance is an ecosystem of financial applications based on Blockchain technology. It operates without a third party or centralized administration. It also mentions smart contracts as the foundation of DeFi (decentralized finance). The smart contracts are self-executing and not require intermediary oversight.
Slide 65
This slide illustrates information regarding DeFi lending. It highlights that a borrower can obtain a loan directly from a decentralized platform known as P2P lending. It mentions that Defi lending platforms aim to provide crypto loans in a trust-less manner, that is, without intermediaries, and to allow users to stake their crypto coins on the platform for lending purposes.
Slide 66
This slide illustrates the difference between DeFi and Traditional lending. It also highlights that Blockchain is the underlying technology for DeFi lending. Defi takes advantage of its unique features and outperforms traditional lending.
Slide 67
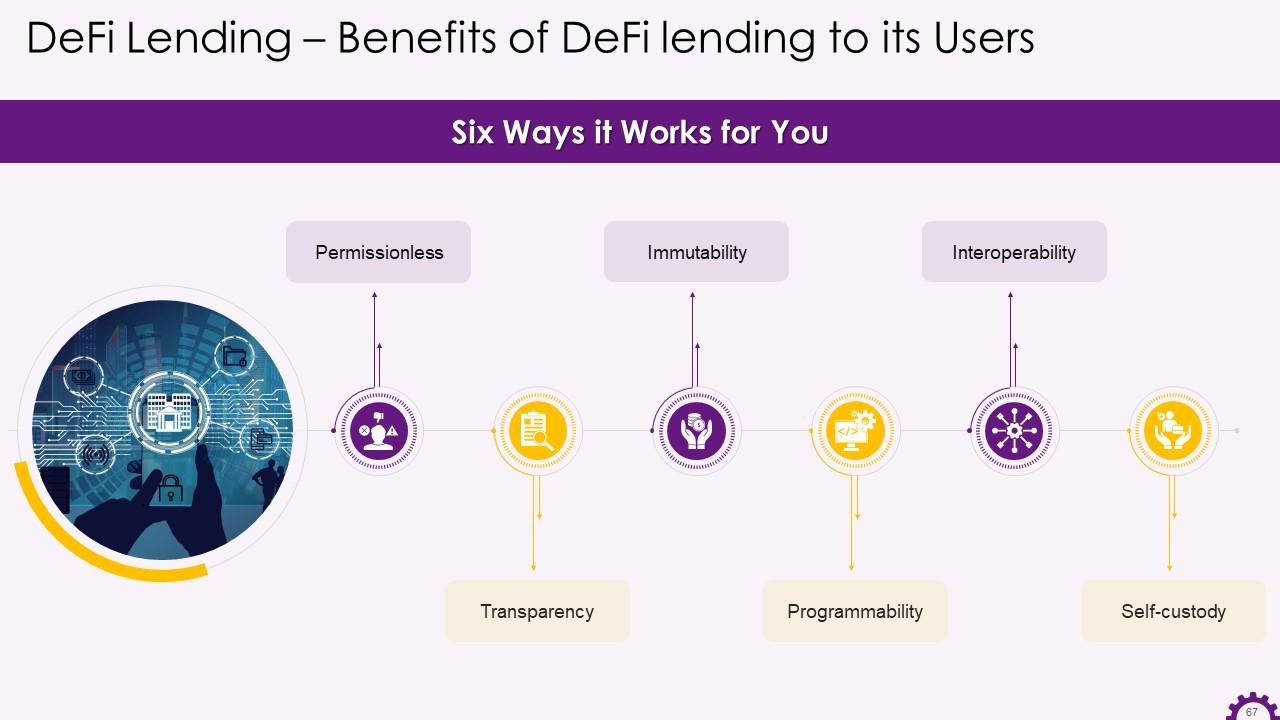
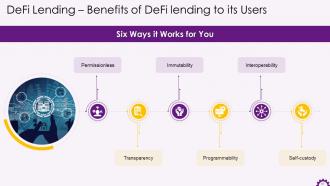
This slide depicts the benefits that DeFi lending provides to its users. The benefits are permissionless, transparency, immutability, programmability, interoperability, and self-custody.
Instructor’s Notes:
The benefits that DeFi lending provides to its users are:
- Permissionless: Defi lending allows for open, permissionless access, which means that anyone with a crypto wallet can access Defi applications built on Blockchain, regardless of location or minimum amount of funds required
- Transparency: The public blockchain broadcasts every transaction on the network and every user identifies it. This level of transparency around transactions enables rich data analysis and ensures that every user on the network has verified access
- Immutability: The decentralized architecture of Blockchain ensures tamper-proof data coordination while also increasing security and ease of audit
- Programmability: Smart contracts are highly programmable, allow for automated execution, and create new digital assets and financial instruments
- Interoperability: The use of a software stack that is interconnected ensures that Defi protocols and applications integrate and complement one another
- Self-custody: The usage of Web3 wallets like Metamask assures that Defi market users retain substantial custody of their assets and control over their data
Slide 69
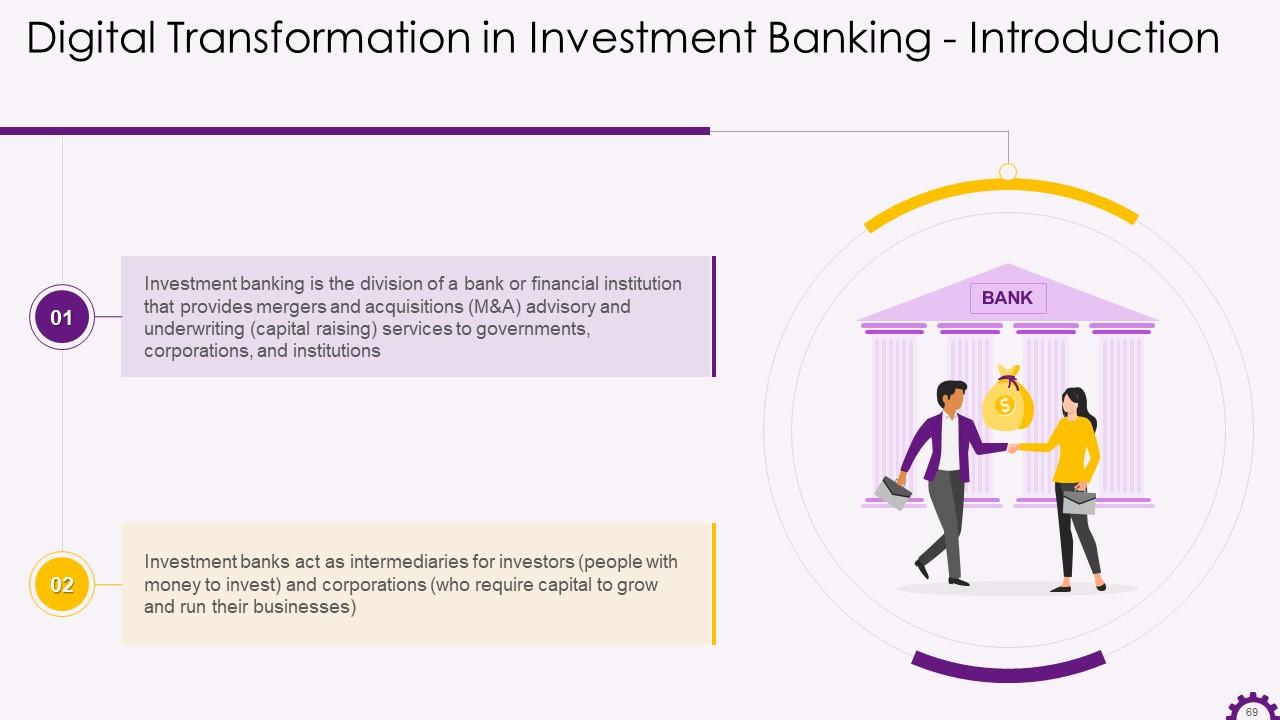
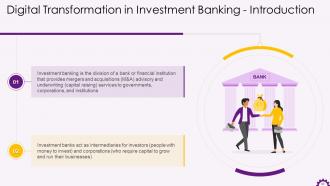
This slide illustrates the introduction to investment banking. It highlights that investment banking is the division of a bank or financial institution that provides mergers and acquisitions (M&A) advisory and underwriting (capital raising) services to governments, corporations, and institutions.
Slide 70
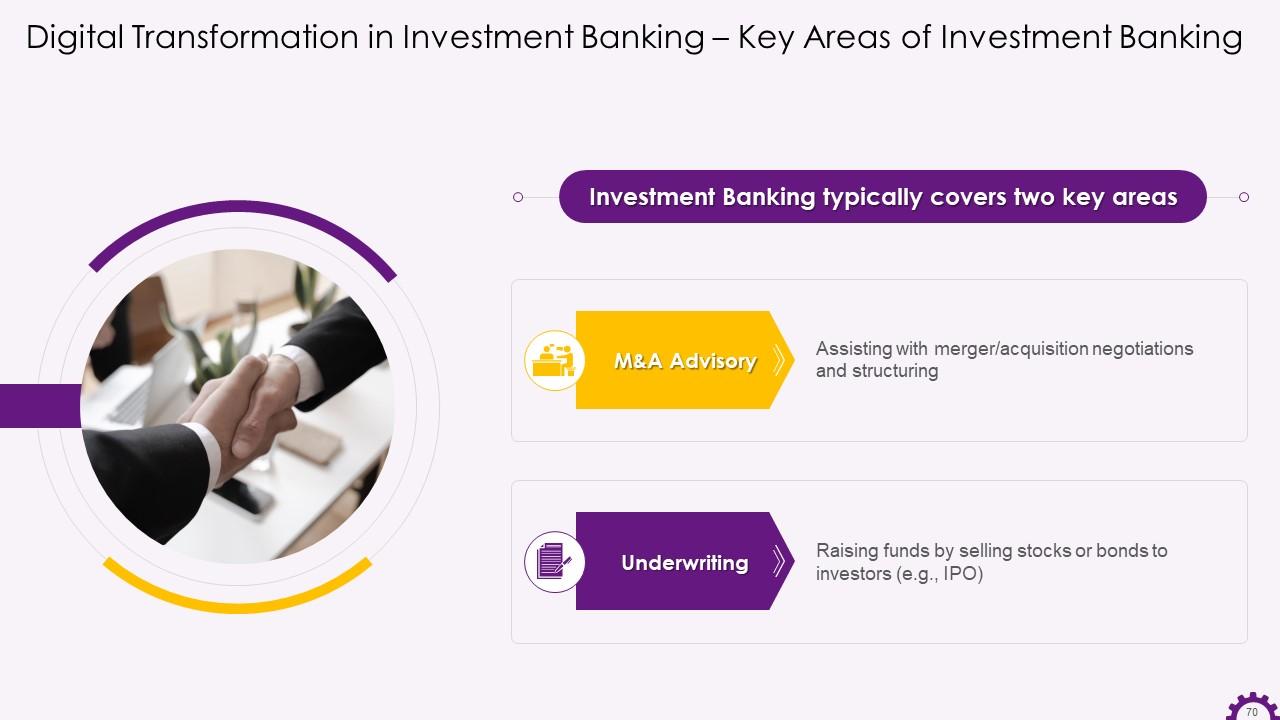
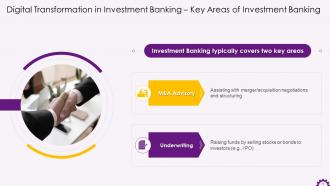
This slide depicts significant areas of investment banking. It offers merger and acquisition advisory as well as underwriting services.
Instructor’s Notes:
The following services are provided by full-service banks:
- Sales and Trading- Entails bringing together securities buyers and sellers in the secondary market. Investment banking sales and trading teams act as agents for clients or trade the firm's own capital assets
- Equity Research- The equity research group's research, or "coverage," of securities assists investors in making investment decisions and facilitates stock trading
- Asset Management- Entails managing investments for diverse investors, including institutions and individuals, across various investment styles
- Underwriting- Capital raising and underwriting teams connect investors and companies to raise capital or go public through IPO. This function serves the primary market, known as "new capital. “
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)- Advisory roles for business buyers and sellers, managing the M&A process from start to finish
Slide 71
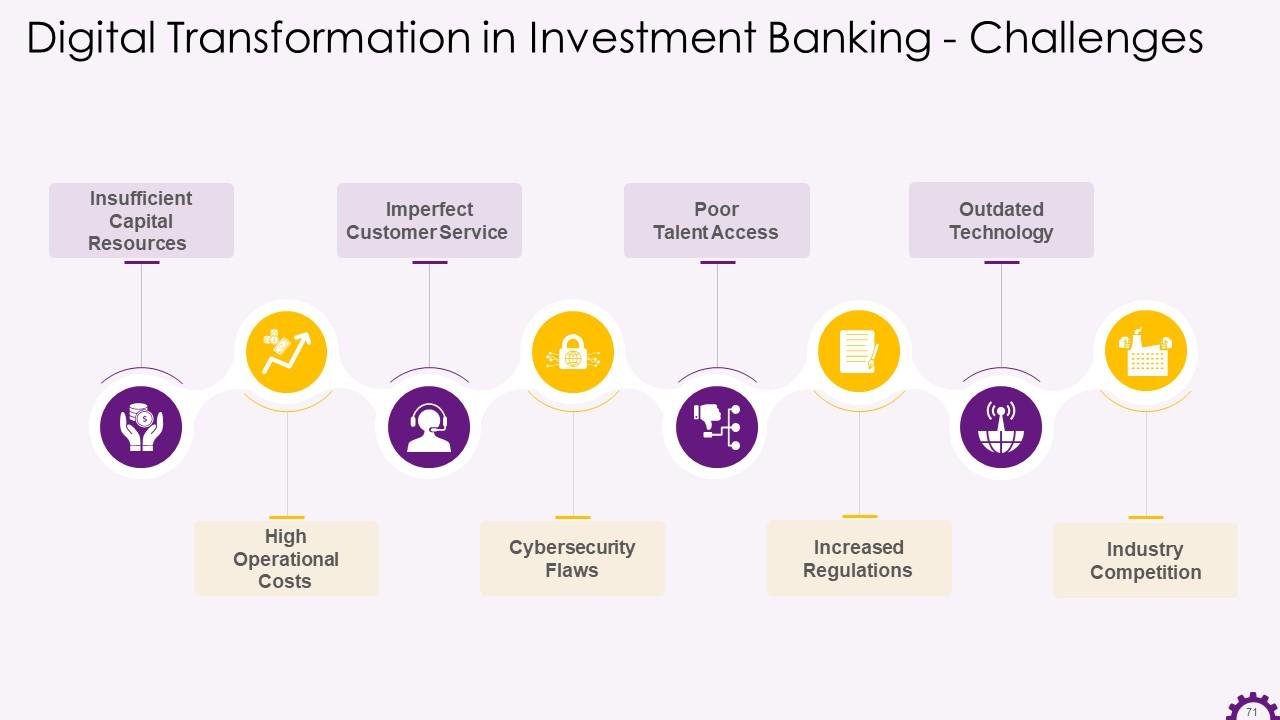
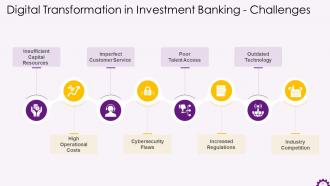
This slide depicts challenges faced by investment banking. The challenges are Insufficient capital resources high operational costs, imperfect customer service, cybersecurity flaws, poor talent access, increased regulations, outdated technology, and industry competition.
Slide 72
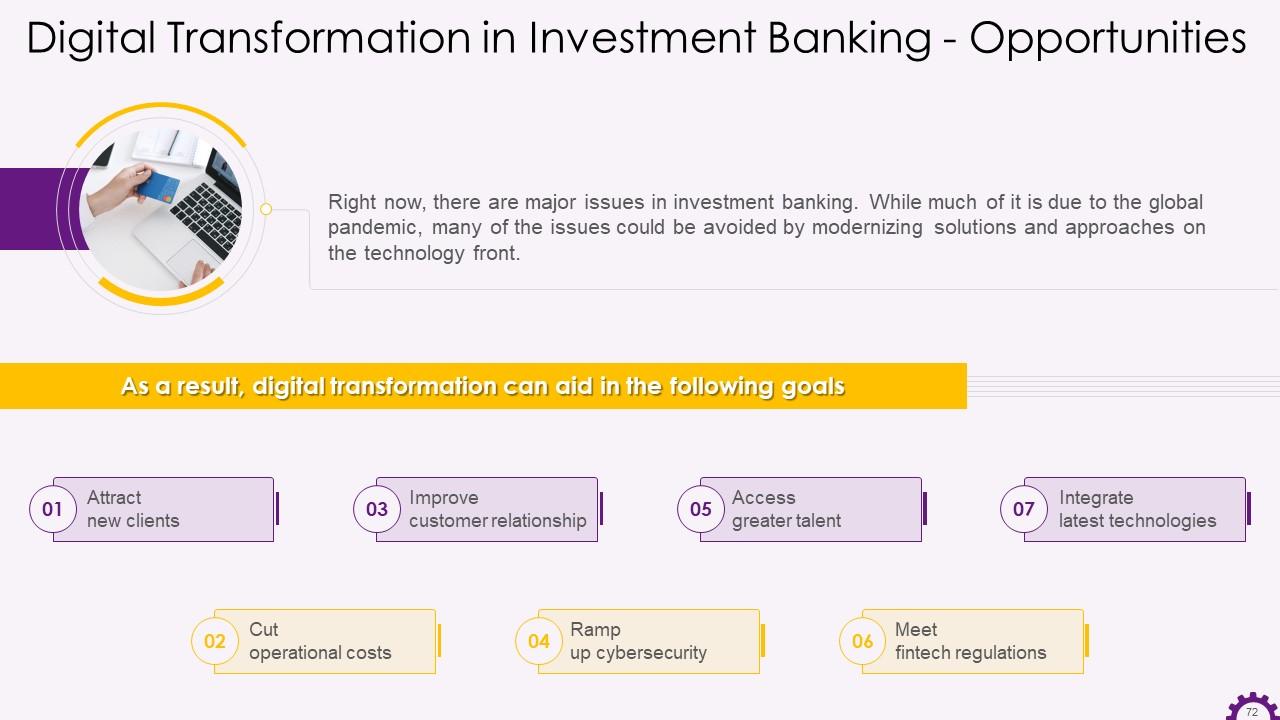
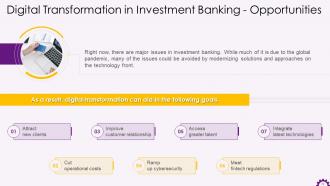
This slide depicts investment banking opportunities. The opportunities are attracting new clients, cutting operational costs, improving customer relationships, ramping up cybersecurity, accessing great talent, meeting fintech regulations, and integrating latest technologies.
Slide 74
This slide depicts the information regarding the DBS mission to make banking enjoyable. It highlights that DBS recognized the need to compete in the same space as the tech upstarts, leveraging new technologies to eliminate needless hassle in traditional banking
Slide 75
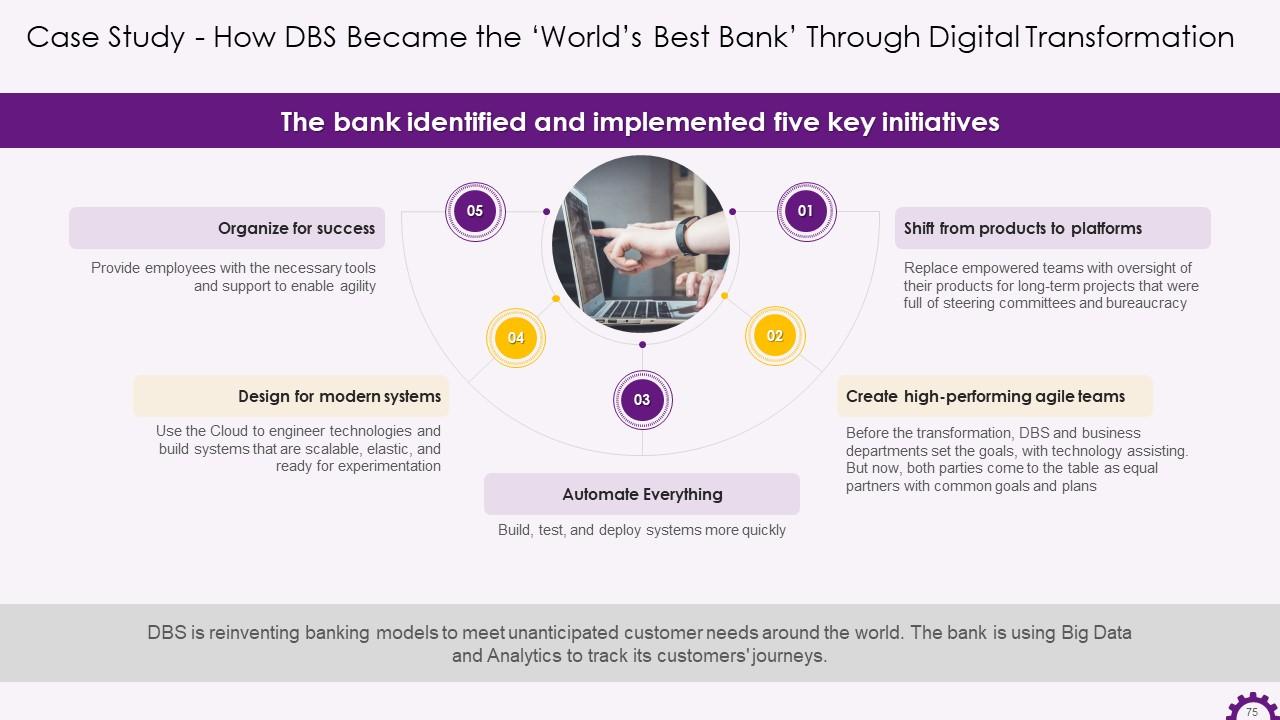
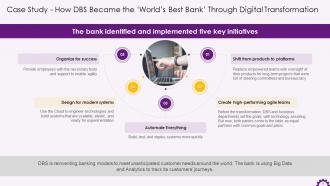
This slide illustrates the key initiatives that the bank implemented. The initiatives are: a shift from products to platforms, creating high-performing agile teams, automating everything, designing for modern systems, and organizing for success.
Slide 76 to 77
These slides illustrate the key takeaways for the section digital transformation in banking industry.
Slide 78
This slide mentions various questions for discussion on the topic digital transformation in banking industry.
Slide 90 to 105
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Digital Transformation in Banking Industry Training ppt with all 110 slides:
Use our Digital Transformation in Banking Industry Training ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Out of the box and creative design.
-
Great experience, I would definitely use your services further.