Anti Money Laundering and Compliance Program Training Ppt
The PPT Training Module on Anti Money Laundering and Compliance Program offers a comprehensive overview of Customer Due Diligence CDD and related compliance practices in the context of Anti Money Laundering AML. It starts by explaining the concept Know Your Customer and Customer Due Diligence CDD, and then compares Enhanced Due Diligence EDD vs Simplified Due Diligence, highlighting their differences and applications. The PowerPoint Deck then explores What is Ongoing Monitoring. It discusses the basis of CDD, detailing when and how it should be conducted. It also addresses handling Politically Exposed Persons and the procedure for filing a Suspicious Activity Report SAR, including a step by step guide on the process. A Sample Customer Due Diligence Flowchart and CDD Decision Flow are included for visual representation of the CDD process. Best practices, benefits, and challenges of CDD and EDD are thoroughly discussed, offering a balanced perspective. The PowerPoint Presentation also includes CDD Checklists for various account types. Additionally, it covers Designated Non Financial Businesses and Professions DNFBPs, outlining the industries included and their FATF requirements. Finally, it provides practical tools like an AML Policy Template and an AML Questionnaire, making this PowerPoint a vital resource for organizations aiming to enhance their AML and compliance programs. The Presentation also has Key Takeaways and Discussion Questions related to the topic to make the training session more interactive.
The PPT Training Module on Anti Money Laundering and Compliance Program offers a comprehensive overview of Customer Due Dil..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Anti Money Laundering and Compliance Program. This deck comprises of 38 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 3
This slide introduces the concept of Know Your Customer and Customer Due Diligence. CDD is the process of collecting & identifying information to verify or confirm a customer’s identity and accurately determine the level of criminal risk they present.
Slide 4
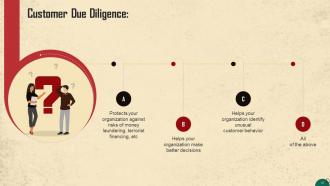
This slide discusses the importance of Know Your Customer and Customer Due Diligence. CDD is vital for organizations for a variety of reasons such as protection against financial crimes, identification of unusual customer behavior, etc.
Slide 5
This slide highlights the difference between Simplified Due Diligence and Enhanced Due Diligence. Simplified Due Diligence is a less rigorous version of standard due diligence whereas Enhanced Due Diligence is implemented for high-risk clients such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs).
Slide 6
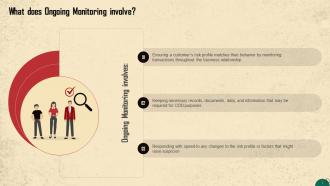
This slide talks about the concept of Ongoing Monitoring. Ongoing monitoring refers to the continuous examination of business relationships. This approach is essential because, while occasional transactions may not seem suspicious at first, they may indicate a pattern of behavior over an extended period.
Slide 7
This slide talks about the concept of Ongoing Monitoring. Ongoing monitoring involves ensuring a customer’s risk profile matches their behavior, keeping relevant records, and responding quickly to any changes in a customer’s risk profile.
Slide 8
This slide discusses what CDD is based on. CDD is based on three basic regulatory obligations: Customer identification, beneficial ownership, and business relationship.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Customer Identification: Companies are required to identify their clients by gathering personal information and data, such as name, government ID, address, and birth certificate, from a reliable and independent source
- Beneficial Ownership: Companies should try to identify Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO) when a business or third party is working on the behalf of someone else. The idea is to have a record of individual(s) who benefit from the actions of a person or a group of people
- Business Relationship: Companies must identify the nature and purpose of the business relationship they are forming with the client in addition to identifying the customer and the beneficial ownership of the entity
Slide 9
This slide depicts when customer due diligence is required. CDD is required under the following circumstances: New business relationships, occasional transactions, money laundering suspicion, ongoing monitoring, and unreliable documentation.
Instructor’s Notes:
- New Business Relationships: Information collected on new customers will help make sure they are not using a false identity to access services
- Occasional Transactions: CDD procedures are necessary if a transaction exceeds regulatory criteria or involves firms in high-risk foreign nations
- Money Laundering Suspicion: Companies should undertake further CDD checks if a customer is suspected of financing terrorism or money laundering
- Ongoing Monitoring: Companies should carry out CDD throughout the entirety of a business relationship to make sure that transactions match the established risk profiles of their clients
- Unreliable Documentation: Organizations should conduct stricter CDD to resolve discrepancies when customers provide insufficient identification documents
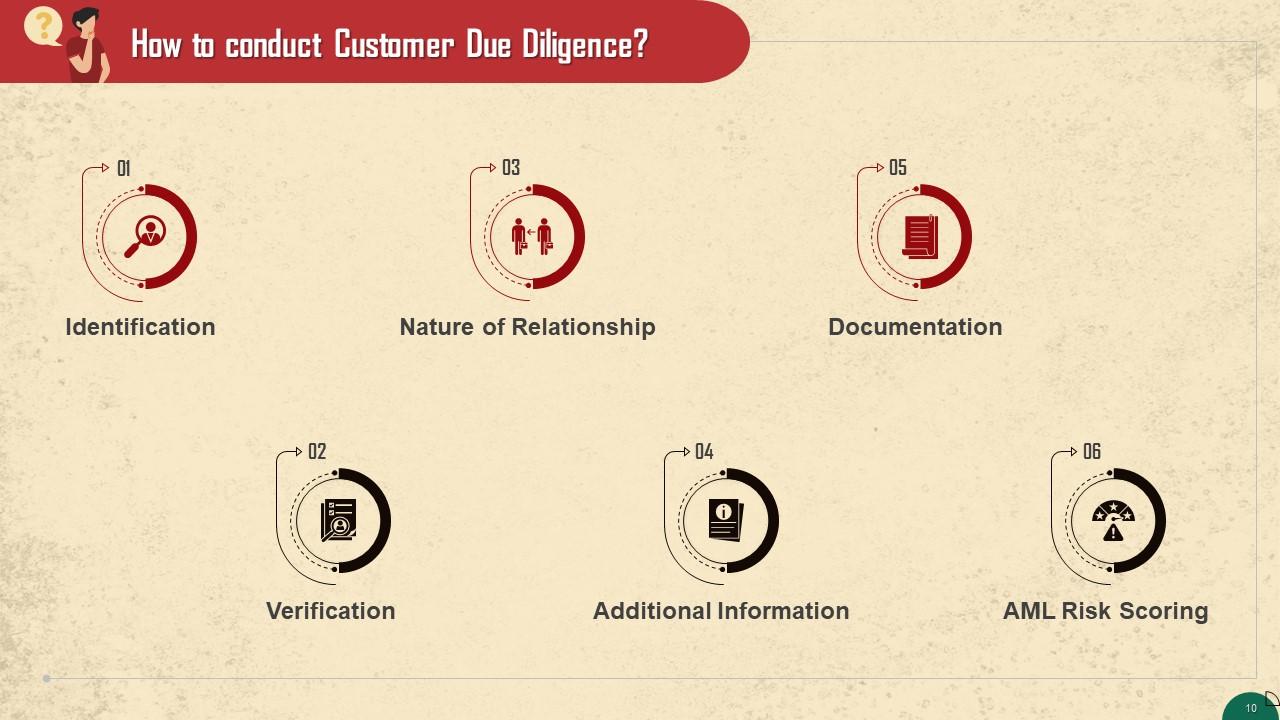
Slide 10
This slide depicts the step-by-step process of conducting customer due diligence. The steps are: Identification, verification, nature of relationship, additional information, documentation, and AML risk scoring.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Identification: The first step is identifying the customer. This can be as basic as identifying their first and last name
- Verification: The next step is verification. This can include verifying your client’s government ID card or passport. The verification of a client’s or beneficial owner’s identity is critically important
- Nature of Relationship: The next thing you should establish as part of your CDD program is the goal and intended nature of the business relation
- Additional Information: The information you gather from the customer may also include their location, their occupation, the types of business transactions they want to do with you, payment methods, their geographical area, and the industry they operate in, etc
- Documentation: It is essential to document all information collected from the customers, preferably on an IT system
- AML Risk Scoring: The last step entails determining the money laundering or terrorist financing risk a customer poses to your organization. You can determine a client’s risk score based on a three-tier scale: low, moderate, high
Slide 11
This slide tells us how to deal with politically exposed persons or PEPs. A PEP is an individual that has been in-charge of a prominent public role or political function.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Identifying PEPs: Numerous databases list people with current or previous political roles or other prominent functions. These databases can be used to identify PEPs. PEPs can also include immediate family members
- Obtaining senior management approval: Since PEPs pose a potentially high risk of money laundering, senior management approval is required to establish or continue a business relationship
- Establishing source of funds: It is essential to determine the source of funds of PEPs to ensure no involvement in money laundering or terrorist financing
- Applying ongoing EDD: Finally, enhanced due diligence and ongoing monitoring are applicable to PEPs
Slide 12
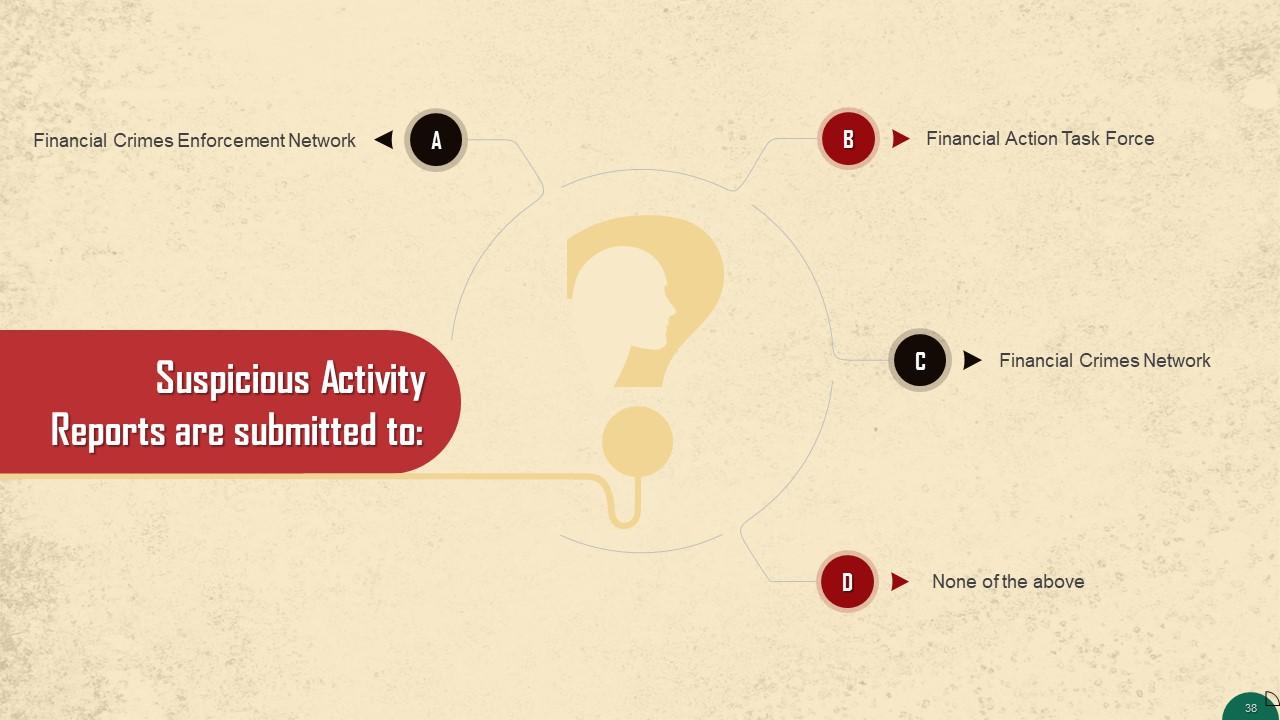
This slide gives information about a suspicious activity report. SARs are documents that financial organizations, and those linked with their organization, must submit to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network when there is an instance of money laundering or fraud.
Slide 13
This slide gives information about filing a SAR. All SAR filings must be submitted using the BSA e-file system that FinCEN operates. This system allows for greater standardization of the information and increased efficiency, which is vital in situations where public safety is a concern.
Slide 14
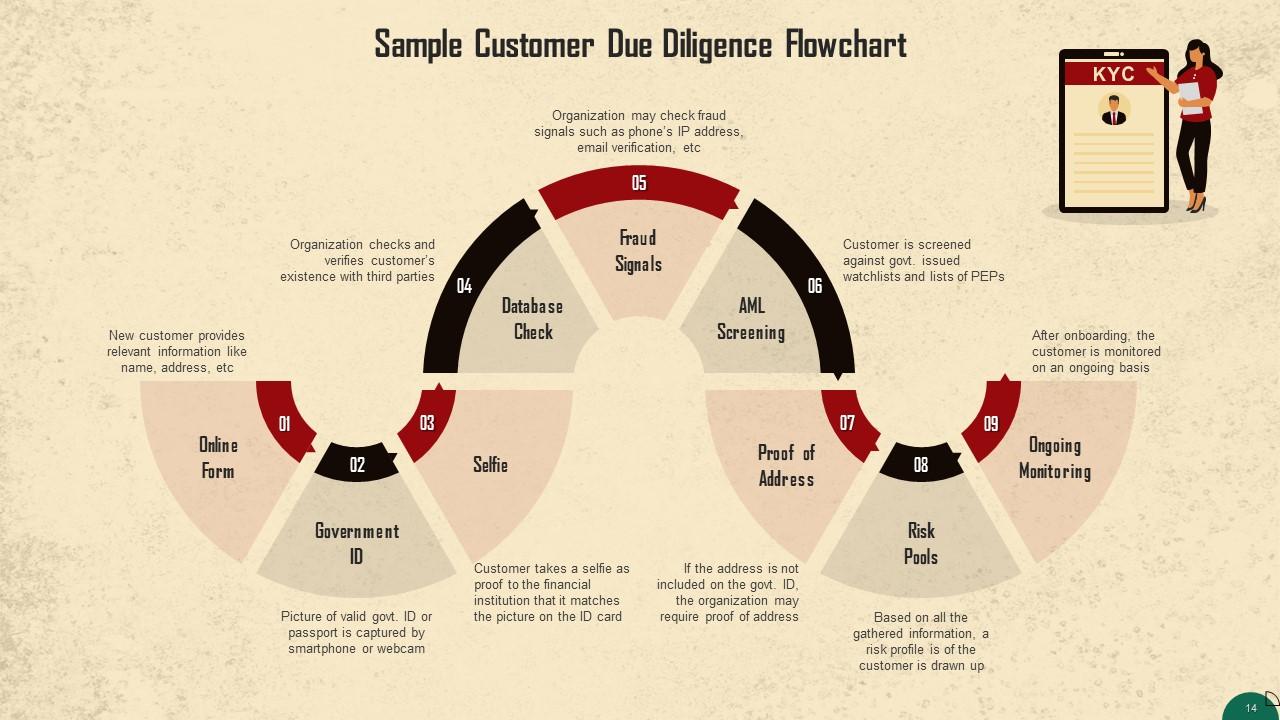
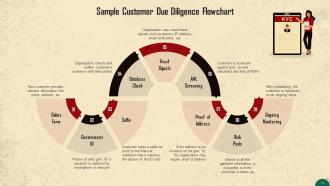
This slide depicts a sample flowchart of the CDD process.
Slide 15
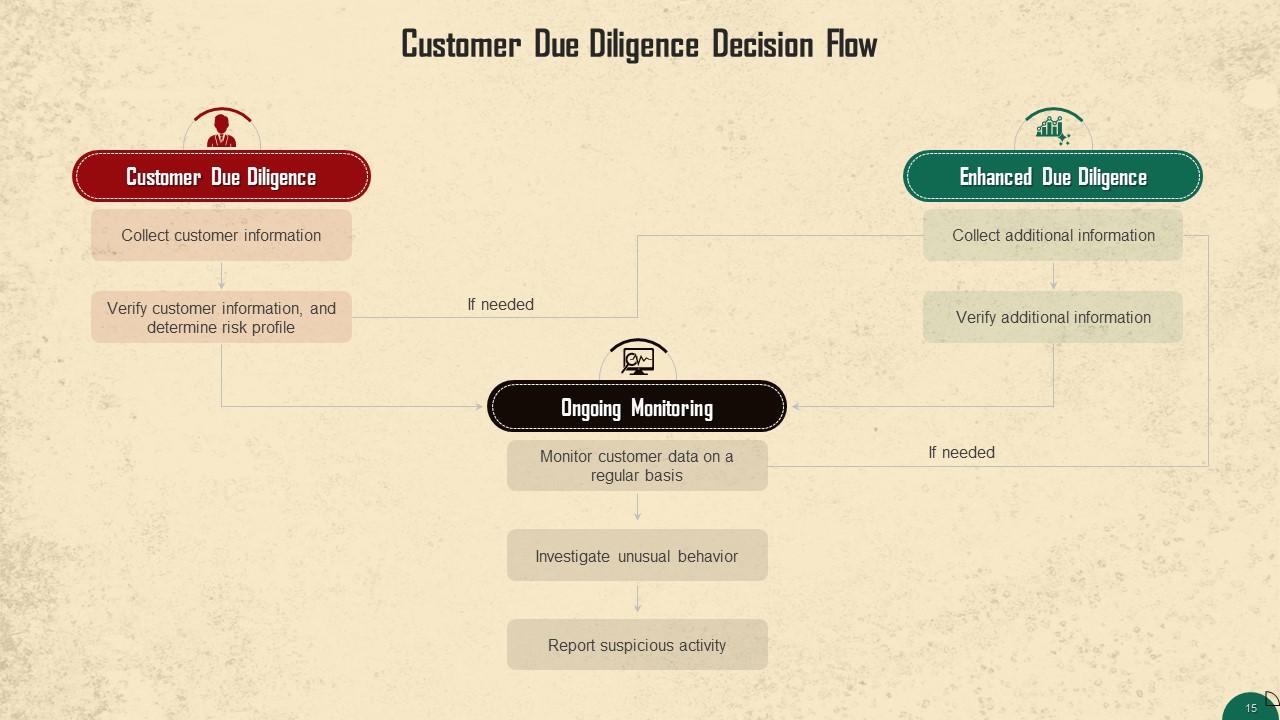
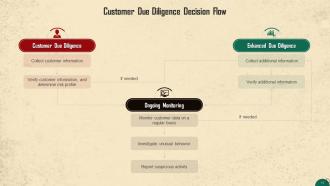
This slide illustrates a decision flow for the CDD process.
Slide 16
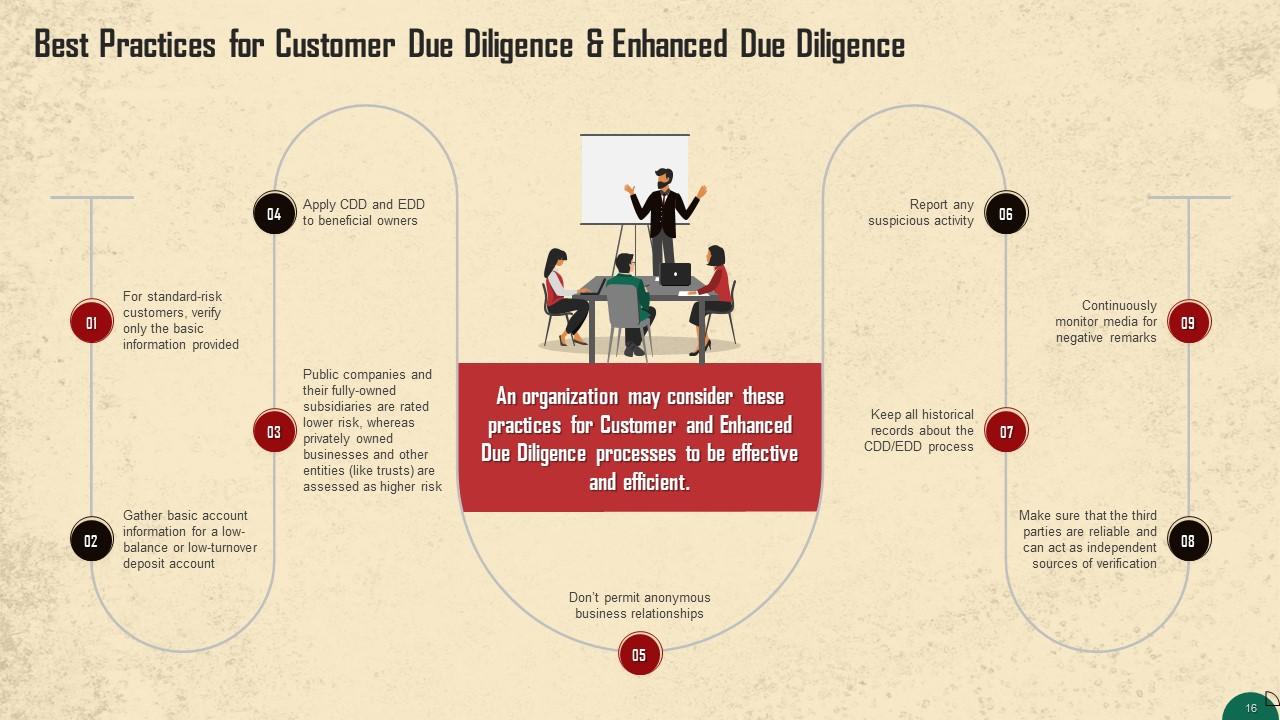
This slide lists the best practices for CDD and EDD. For standard-risk customers, verify only the basic information provided. Public companies and their fully owned subsidiaries are rated lower risk, whereas privately owned businesses and other entities (like trusts) are assessed as higher risk.
Slide 17
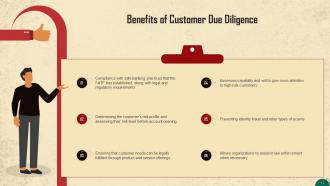
This slide lists the advantages of CDD. Some benefits include: Compliance with safe banking practices established by the FATF, along with legal and regulatory requirements, Allowing organizations to assist in law enforcement when necessary, etc.
Slide 18
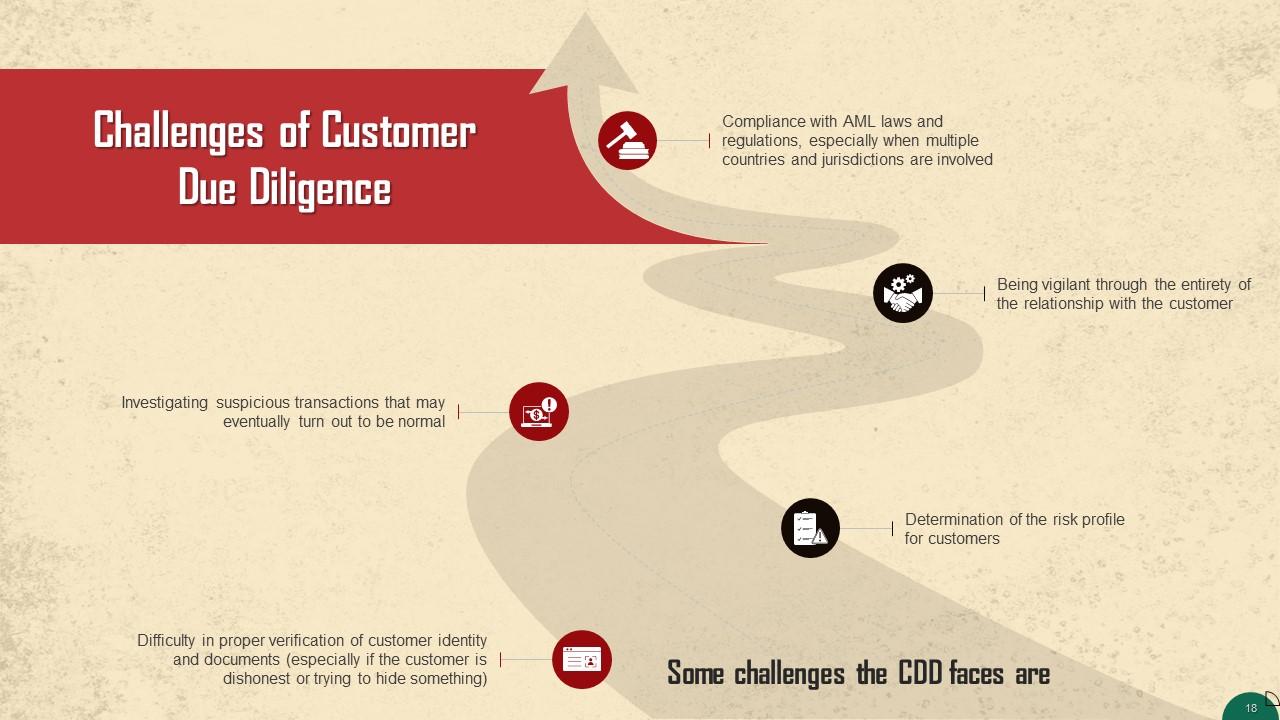
This slide highlights some challenges faced during the process of CDD. Some of these are: Difficulty in proper verification of customer identity and documents (especially if the customer is dishonest or trying to hide something), Determination of the risk profile for customers, etc.
Slide 19 to21
These slides depict CDD checklist for new business accounts, new individual accounts, and new trust accounts.
Slide 22
This slide depicts an EDD checklist for new accounts.
Slide 23
This slide tells us about importance of AML for Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions or DNFBPs. Other than the financial sector, some businesses have ML / TF risks. Adequate caution must be exercised to prevent abuse of their services as it is illegal to attempt to conceal money laundering revenues, regardless of the sector.
Slide 24
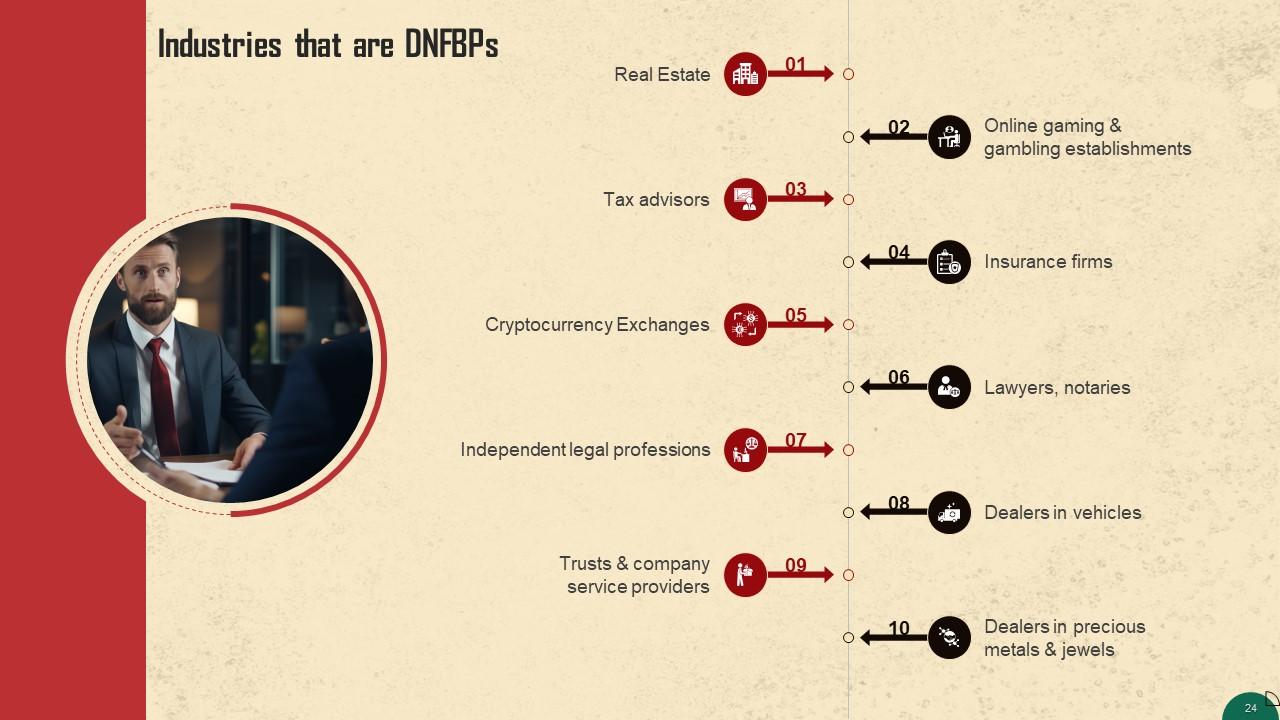
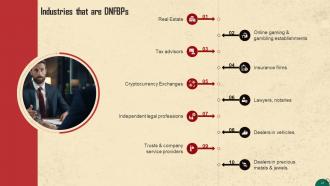
This slide lists industries that are considered to be designated non-financial businesses and professions according to the FATF. Some of these include: Real estate, tax advisors, lawyers, notaries, etc.
Slide 25
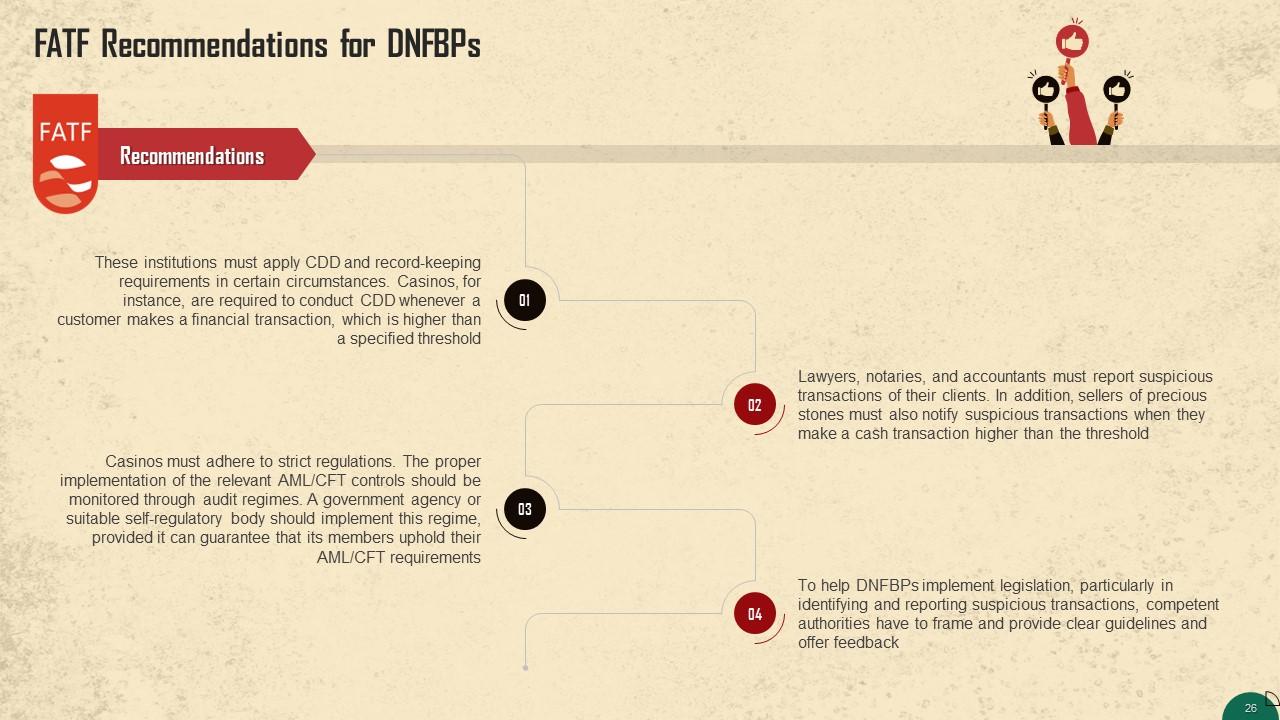
This slide shows that FATF has published four recommendations for DNFBPs to exercise necessary controls on money laundering and terrorist financing.
Slide 26
This slide depicts recommendations published by FATF for DNFBPs. FATF has published four recommendations for DNFBPs to implement necessary controls on money laundering and terrorist financing.
Slide 27 to 29
These slides depict an Anti-Money Laundering Policy Template for organizations.
Slide 30 to 31
These slides contain anti-money laundering questionnaire for organizations.
Slide 51 to 65
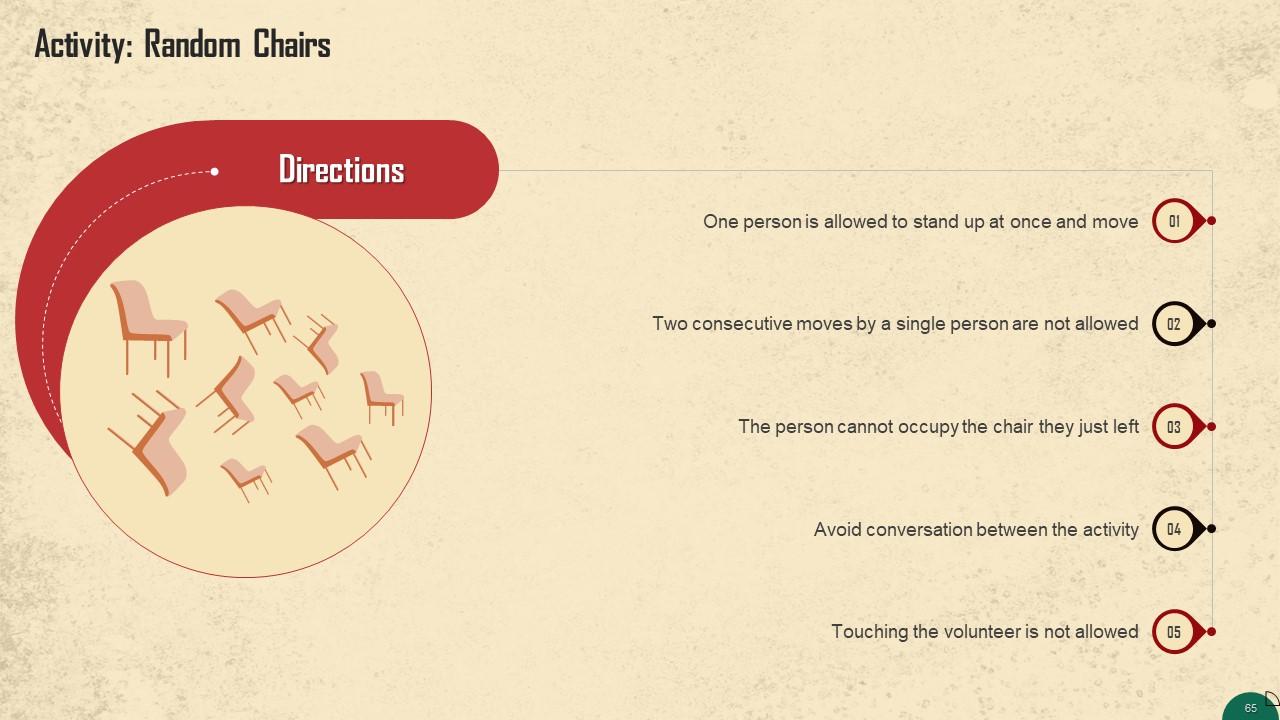
These slides contain energizer activities that a trainer can employ to make the training session interactive and engage the audience.
Slide 66 to 93
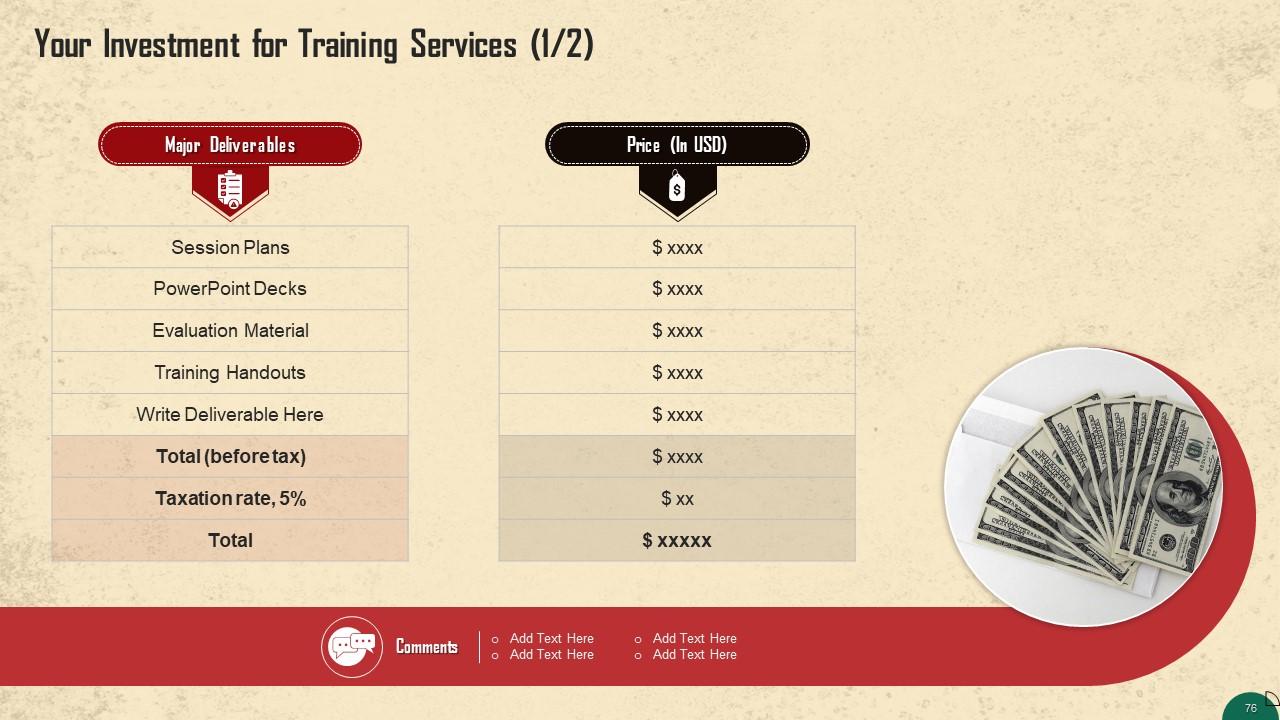
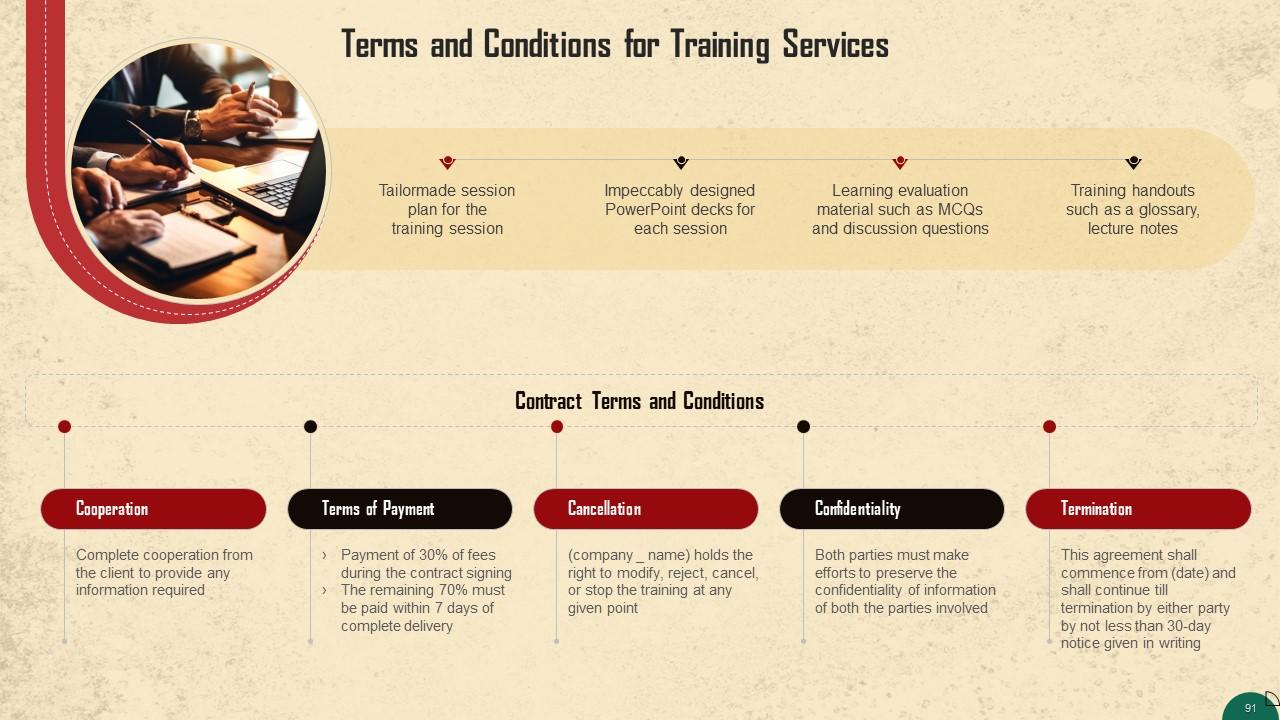
These slides contain a training proposal covering what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for prospective clients.
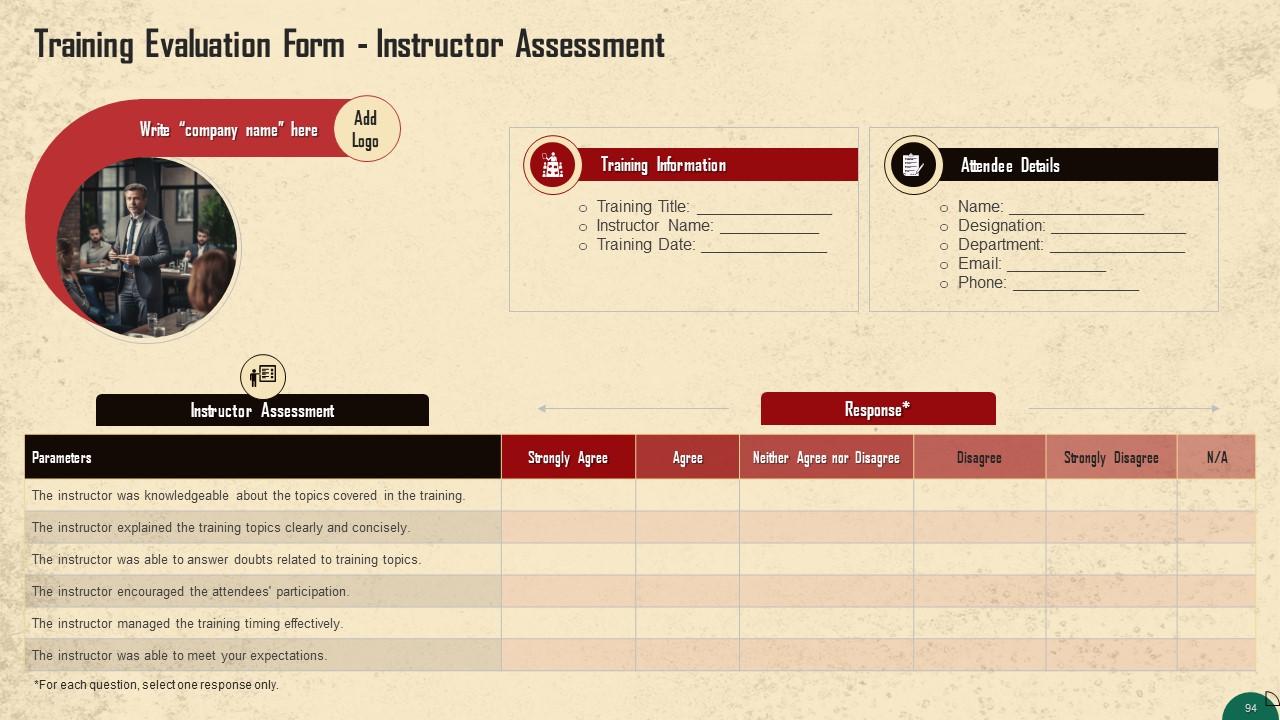
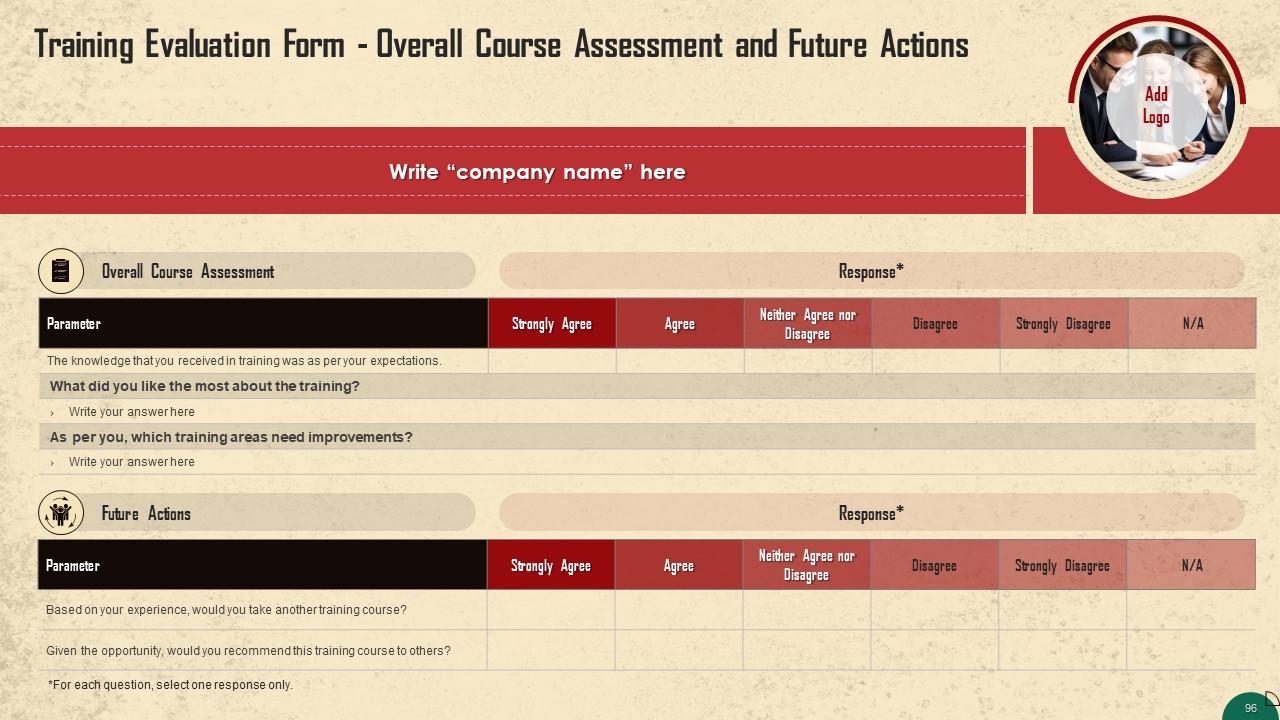
Slide 94 to 96
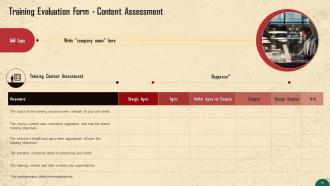
These slides include a training evaluation form for the instructor, content, and course assessment to assess the effectiveness of the coaching program.
Anti Money Laundering and Compliance Program Training Ppt with all 105 slides:
Use our Anti Money Laundering and Compliance Program Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
I came across many PowerPoint presentations with excellent creatives and I believe they would be beneficial to my work.
-
Excellent design and quick turnaround.