Network Security A Cybersecurity Component Training Ppt
These slides, in detail, cover the importance, working, elements, and types of network security, a component of cybersecurity.
These slides, in detail, cover the importance, working, elements, and types of network security, a component of cybersecuri..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Network Security a Cybersecurity Component. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon, and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 2
This slide talks about network security. Network security protects your physical network and devices connected to it.
Slide 3
This slide discusses the importance of network security. Network security is crucial because it prevents hackers from accessing sensitive and valuable data.
Slide 4
This slide highlights reasons for protecting networks. These are: Financial risks for Personally Identifiable Information (PII), or stolen intellectual property, operational risks, and regulatory issues.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Financial Risks for Personally Identifiable Information: Both individuals and corporations may incur costs as a result of data breaches. Companies that handle PII, such as passwords and Social Security numbers, must keep data secure. The victims of exposure may incur expenses like fines, restitution, and repairs for compromised devices
- Financial Risks for stolen Intellectual Property: It is expensive for businesses to have their intellectual property stolen. Loss of business and competitive advantages can result from losing a company's ideas, inventions, and products
- Operational Risks: Companies use networks for the majority of internal and external communication. Without sufficient network security, a company runs the danger of having its activities interrupted. Businesses and home networks rely on hardware and software that cannot function properly when infected with malware, viruses, or other cyberattacks
- Regulatory Issues: Many governments have laws governing network security and data security that firms must follow. Breaking these rules may result in fines, bans, and even jail time
Slide 5
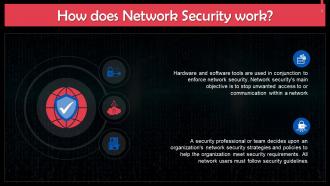
This slide gives information about the working of network security. Hardware and software tools are used in conjunction to enforce network security. Network security's main objective is to stop unwanted access to or communication within a network.
Slide 6
This slide highlights the nine elements of network security. These are: Network firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, unified threat management, advanced network threat prevention, network access control, cloud access security brokers, DDoS mitigation, network behavior anomaly detection, and SD-WAN security.
Slide 7
This slide tells us about network firewalls. Firewalls are used to manage network traffic using pre-established security rules. Firewalls are an essential component of daily computing since they block malicious traffic.
Slide 8
This slide gives information about Intrusion Prevention Systems. Network security attacks like brute force attacks, DoS attacks, and exploits of known vulnerabilities can be found or prevented by technologies based on Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS).
Slide 9
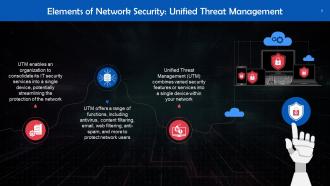
This slide tells us about Unified Threat Management (UTM), which combines several security features or services into a single device within your network.
Slide 10
This slide tells us about Advanced Network Threat Perception (ATP), which combines analysis tools to defend against advanced threats that employ known and unknown attack vectors.
Slide 11
This slide gives information about network access control. Network access control assists in ensuring that unauthorized users and devices are kept out of a private network.
Slide 12
This slide tells us about Cloud Access Security Brokers. Cloud Access Security Broker is an on-premise or cloud-based software between cloud service users and cloud applications that monitors activity and implements security policies.
Slide 13
This slide tells us about Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Mitigation. The process of successfully defending a targeted server or network from a DDoS attack is known as DDoS mitigation.
Slide 14
This slide gives information about Network Behavior Anomaly Detection. It uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to detect hidden threats in parts of network infrastructure that other security tools cannot reach. It also notifies the IT team of those threats.
Slide 15
This slide tells us about SD-WAN Security. As businesses increasingly employ cloud-hosted SaaS apps to support digital transformation initiatives, they are deploying Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions to ensure they have the required high-performance and reliable network connectivity.
Slide 16
This slide lists types of network security. Some of these include email security, network segmentation, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Sandboxing, etc.
Slide 17
This slide discusses the importance of email security. Email is one of the most vulnerable areas in a network. Clicking on email links that covertly download harmful software makes employees targets of phishing and malware attacks.
Slide 18
This slide talks about anti-virus and anti-malware software for network security. Malicious software or malware includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware. Malware can infect a network and remain inactive for days or weeks.
Slide 19
This slide discusses the importance of network segmentation. Network segmentation is a technique that companies with large networks and network traffic use to divide a network into smaller, manageable sections.
Slide 20
This slide talks about Data Loss Prevention (DLP) as a type of network security. These tools help in monitoring data in use, in motion, and at rest to identify and stop data breaches.
Slide 21
This slide discusses the importance of mobile device security. Business applications for smartphones and other mobile devices have made such devices a crucial component of network security.
Slide 22
This slide talks about Virtual Private Network (VPN) for network security. Remote access VPN provides remote and protected access to an organization network's individual hosts or clients, such as mobile users, telecommuters, and extranet consumers.
Slide 23
This slide discusses the importance of Security Information & Event Management (SIEM). This security management strategy records information from network hardware and application logs while being extremely watchful for unusual activity.
Slide 24
This slide talks about Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) for network security. An IDS watches network traffic for suspicious activity and sends an alert when it is found.
Slide 25
This slide discusses sandboxing as a type of network security. Sandboxing is a cybersecurity technique that allows you to run programs or access files on a host computer in a secure, isolated environment that closely resembles end-user operating environments.
Instructor’s Notes: For instance, malware in Microsoft Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and PDF files can be safely detected and prevented before the files are downloaded by an unsuspecting end user.
Slide 26
This slide talks about Software Defined Perimeter (SDP) for network security. SDP is a technique to hide Internet-connected infrastructure (servers, routers, etc.) so that external parties and attackers are unable to see it, whether it is hosted on-premise or in the cloud.
Slide 27
This slide talks about workload security as a type of network security. When organizations balance workloads across multiple devices on the cloud and hybrid environments, they increase the risk of cyber attacks.
Slide 28
This slide discusses the importance of wireless security. Wireless networks are one of the most vulnerable parts of a system and require rigorous security measures and monitoring.
Slide 29
This slide talks about web security as a type of network security. A web security solution controls your staff’s web use, blocks web-based threats, and blocks access to malicious websites.
Slide 30
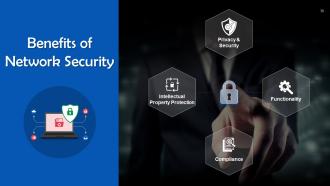
This slide lists benefits of network security. These include: privacy & security, functionality, compliance, and intellectual property protection.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Privacy & Security: Organizations must protect the privacy, integrity, and accessibility of network data since it contains sensitive user data. Network security guards against lapses that could reveal PII and other sensitive data, harm a company's reputation, and cause financial losses
- Functionality: Network security ensures that organizations and individuals continue to operate efficiently
- Compliance: Many nations have laws requiring compliance with data security and privacy, and secure networks are crucial for adhering to these mandates
- Intellectual Property Protection: The capacity of many businesses to compete depends on their intellectual property. Securing access to intellectual property helps organizations retain their competitive edge
Slide 31
This slide lists challenges to network security. These are: Remote & mobile access, user adherence, third-party partners, and evolving network attack actors.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Remote & Mobile Access: As more businesses implement Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, there will be extensive and complicated network of devices for firms to secure. Since users are more likely to access business networks over a personal or public network, wireless security is becoming even more crucial
- User Adherence: Every network user is accountable for maintaining security. It can be challenging for organizations to ensure that everyone follows the best practices while simultaneously evolving those strategies to address the newest threats
- Third-Party Partners: A company's network is frequently accessed by cloud service providers, managed security service providers, and security product suppliers, creating additional potential security flaws
- Evolving Network Attack Actors: As technology advances, threat actors and their techniques also become more sophisticated. For instance, emerging technologies like blockchain have given rise to new malware attacks like cryptojacking. Network security defensive tactics must evolve to counter these new threats
Network Security A Cybersecurity Component Training Ppt with all 51 slides:
Use our Network Security A Cybersecurity Component Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Their products can save your time, effort and money. What else you need. All in one package for presentation needs!
-
Great quality slides in rapid time.