Overview Of Money Laundering Techniques Training Ppt
This set of slides in detail covers money laundering techniques such as financial businesses, non-financial businesses, trade-based methods, black market peso exchange, and unconventional methods. It also includes case studies for each of the methods.
This set of slides in detail covers money laundering techniques such as financial businesses, non-financial businesses, tra..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Overview of Money Laundering Techniques. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1
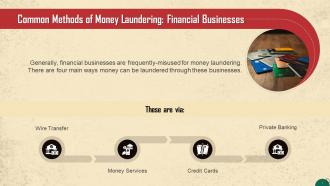
This slide discusses how money can be laundered through financial businesses. These are wire transfers, money services, credit cards, and private banking.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Wire Transfer: Wire transfer is a simple and everyday banking product but is the most common method criminals use to launder money. For instance, by taking cash advances on a stolen credit card, criminals can initiate unauthorized domestic or international wire transfers and deposit the money into an account set up to receive such transfers. It is generally used in the layering stage to move the funds around to make it difficult to track
- Money Services: These businesses generally provide forex exchange services, money transfers, or check-cashing. For instance, money launderers make funds available to the criminal organization in the target country in the local currency with the use of money remitters and currency exchangers. The money-launderer or broker then trades the stolen funds for genuine export-related purchases from overseas businessmen
- Credit Cards: Since the industry typically restricts cash payments, credit card accounts are used in the layering or integration stages, not the initial placement stage. For instance, money launderers use funds they have previously placed in the financial system to prepay credit cards, creating a balance on them. Then, they request a refund of the advance payment, thereby creating a layer. These funds can then be used to purchase goods
- Private Banking: Private banking is subject to money laundering risks since a typical client is fairly affluent and is powerful economically, socially, or politically. Banks profit significantly from private banking clients and may not pay close attention to the source of such funds
Slide 2
This slide discusses how money is laundered through non-financial businesses. The conduits in most such cases are casinos, real estate, car dealerships, and cash-intensive businesses.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Casinos: One way to launder money through casinos is when a criminal walks into a casino and buys chips with illegal cash. The criminal then plays for a brief period, loses some money, wins some money, and finally cashes in the chips. The criminal then receives a check and a receipt so that the proceeds can be claimed as gambling winnings
- Real Estate: Money laundering through real estate allows illegal cash to be incorporated into the legitimate economy. It helps criminals to benefit from assets and derived funds while disguising the source of the funds used for payment. This can be done through cash payments, excessively high or low pricing, or non-transparent businesses, trusts, and other third parties that act as legal owners on behalf of the criminals
- Car Dealerships: In this method, a money launderer would generally visit a car dealership and offer to give cash to buy cars, usually at the asking price. Then, the money launderer can resell the vehicle to imply that the money came from selling the vehicle
- Cash-Intensive Businesses: In this kind of fraud, a company that generally expects to receive a significant amount of its revenue in cash also uses its accounts to deposit money obtained illegally. Such businesses frequently conduct their operations openly, generating legal and illegal cash. Parking structures, arcades, pubs, restaurant are a few examples of these enterprises
Slide 3
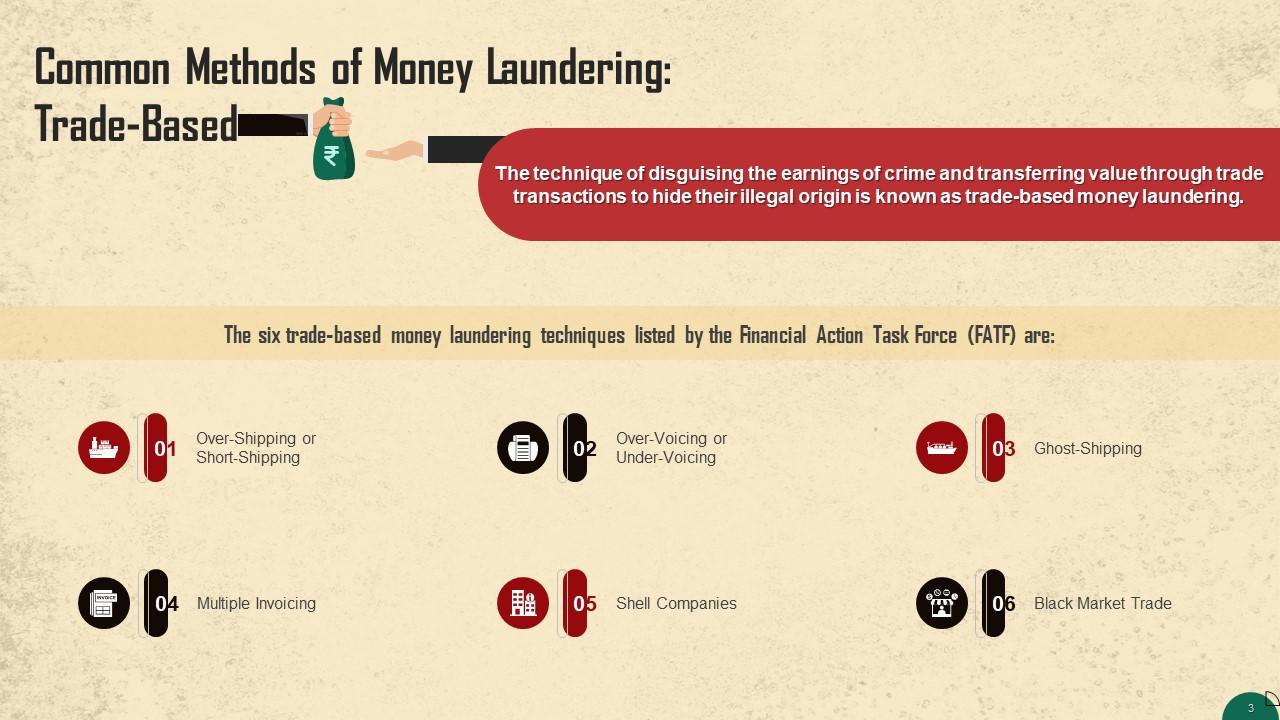
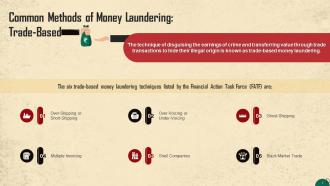
This slide highlights the trade-based methods of money laundering. The technique of disguising the proceeds of crime and transferring value through trade transactions to hide their illegal origin is known as trade-based money laundering.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Over-shipping or short-shipping: This process involves a discrepancy between the number of items billed and shipped, so the customer or seller receives excess value depending on the payment made
- Over-voicing or under-voicing: In the event of over-invoicing, the product or service is priced higher than its actual market cost, allowing the seller to profit from the sale. In contrast, when goods are under-invoiced, the seller can transfer value to the buyer because the goods are priced below the fair market value
- Ghost-shipping: When a buyer and seller work together to produce paperwork stating that products were sold, shipped, and payments were made when no goods were ever shipped, is known as ghost-shipping
- Multiple invoicing: Multiple invoicing refers to the issuance of multiple invoices for the same shipment of goods, giving the potential for money launderers to make multiple payments and use such invoices as documentary evidence to support them
- Shell companies: Shell companies are primarily used to reduce the transparency of ownership in the transaction
- Black market trades: Black market transactions, often known as the Black-Market Peso Exchange, occur when a foreign importer uses a domestic money transfer to pay for goods
Slide 4
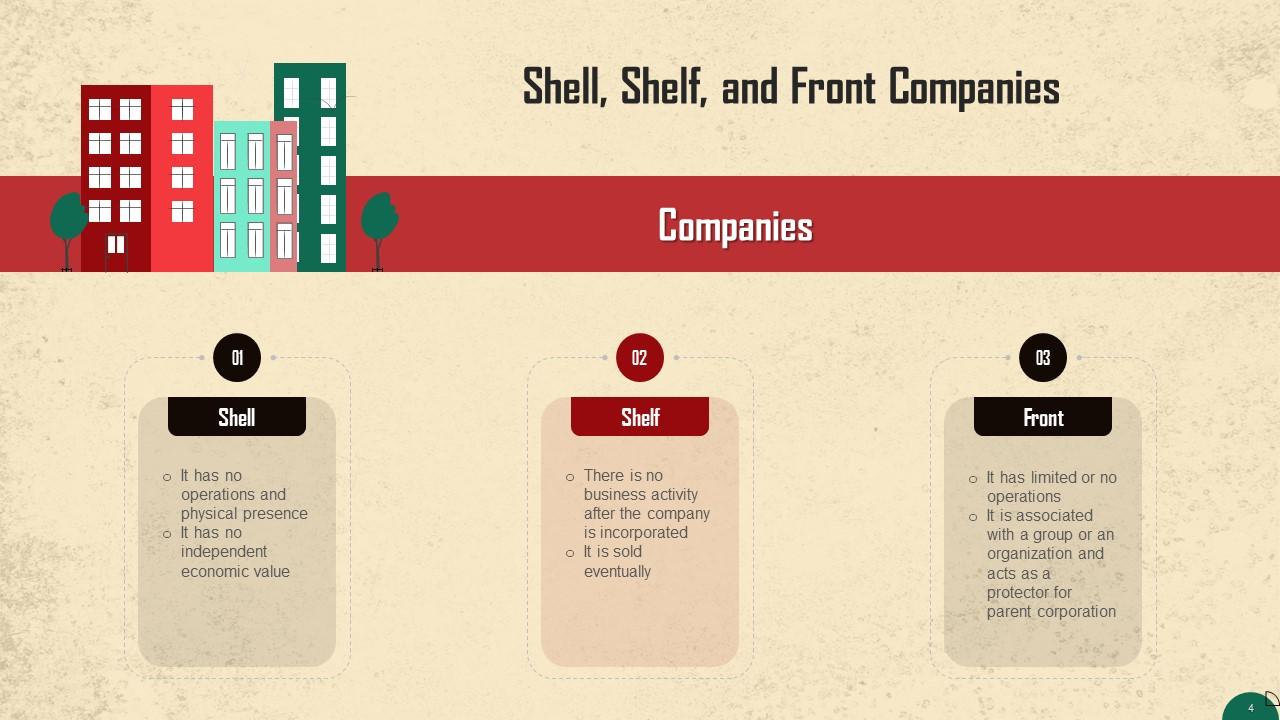
This slide introduces the concept of shell, shelf, and front companies that can be used to launder money. Shell companies are generally non-publicly traded companies, limited liability companies, and trusts. These have emerged as tools for financial crimes such as money laundering since these are easy and inexpensive to form and operate.
Slide 5
This slide lists the red flags for identifying shell companies.
Slide 6
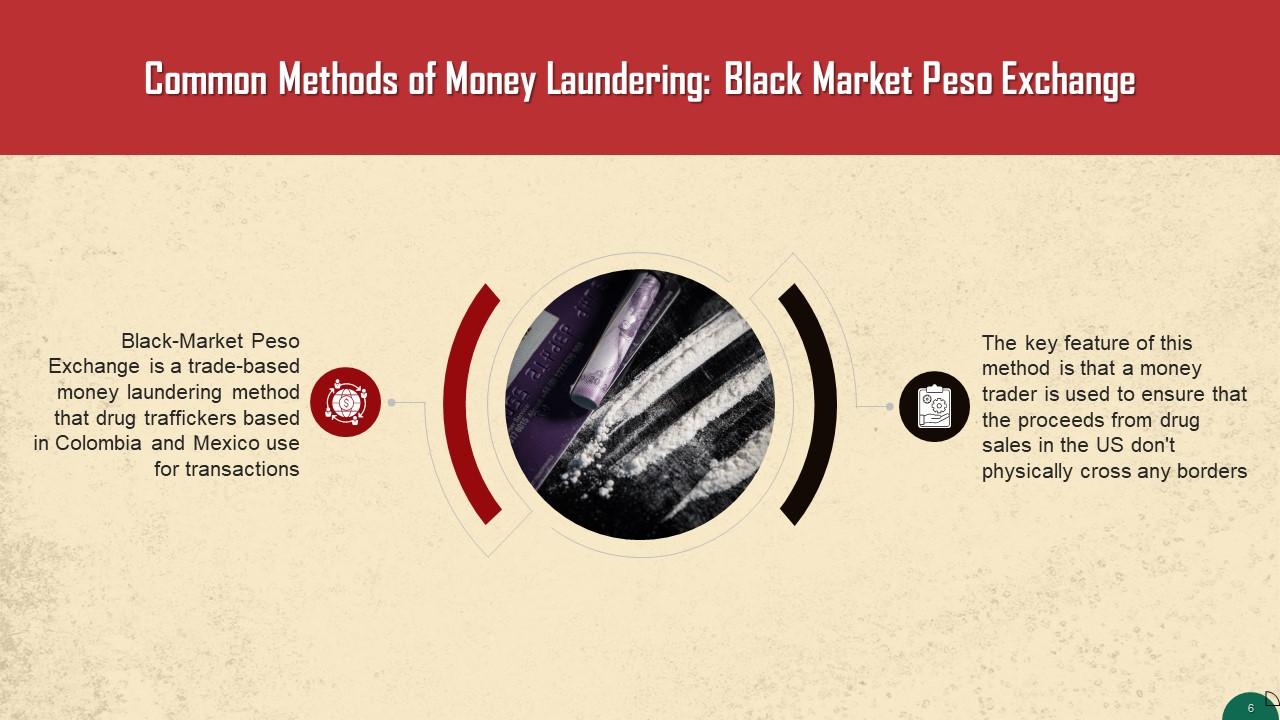
This slide introduces the concept of Black Market Peso Exchange. It is a trade-based money laundering method used by drug traffickers based in Colombia and Mexico.
Slide 7
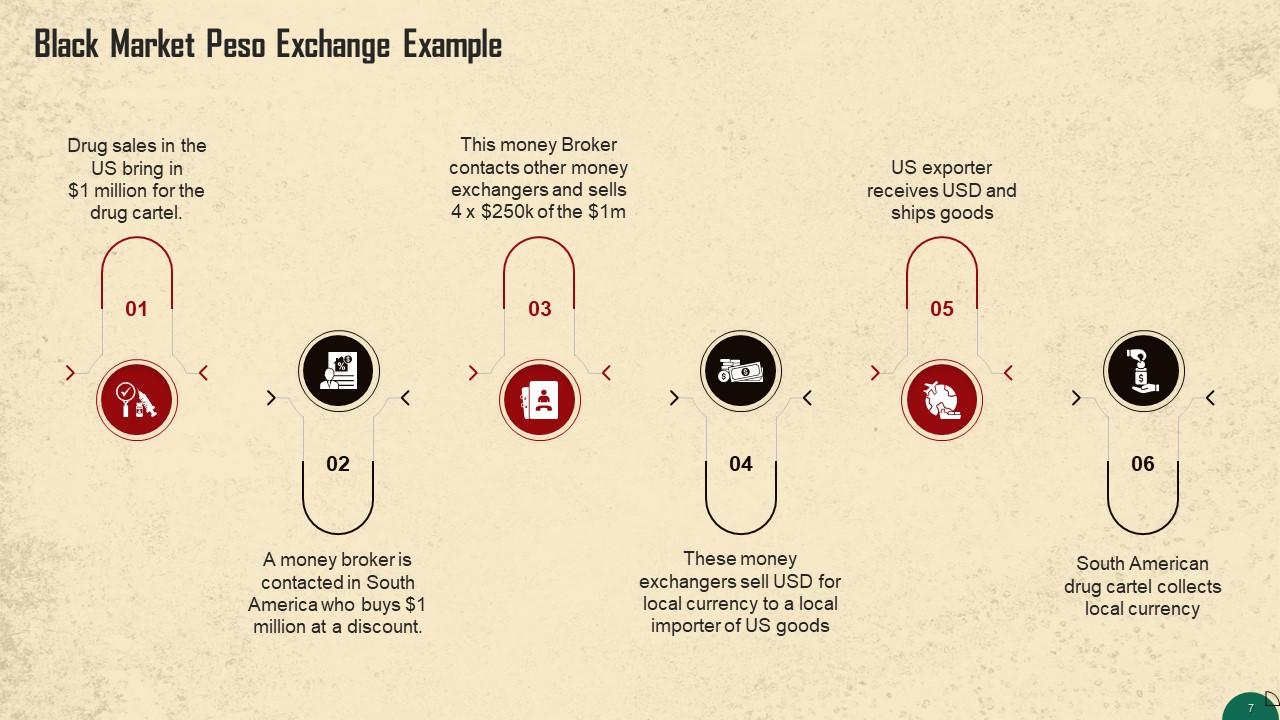
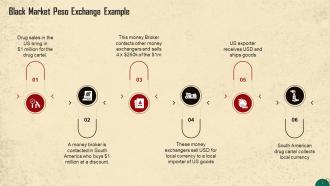
This slide showcases an example of the working of the black market peso exchange. The process is explained by showing the drug cartel making $1 million in drug sales in the US and ends with them being able to convert it to the local currency.
Slide 8
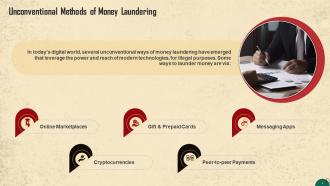
This slide lists some unconventional ways of money laundering. In today’s digital world, several unconventional ways of money laundering have emerged that leverage the opportunities of modern technologies, unfortunately, for illegal purposes.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Online Marketplaces: Numerous online marketplaces have emerged in recent years, enabling people to earn additional income from their resources. Micro merchants or individuals who offer their goods or services through an online marketplace have also increased, which has resulted in a massive economy with vast transaction volume. This is an appealing target for money launderers
- Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrencies, which are digital currencies created to function as a medium of exchange, give criminals another way to legalize their money. The US Drug Enforcement Administration has said that manufacturers with operations in China were using bitcoin, a cryptocurrency as a means of evading capital regulations
- Gift & Prepaid Cards: Another method criminals use to generate untraceable funds is by using gift and prepaid cards. They buy prepaid cards in bulk and can then sell them for hard cash
- Peer-to-Peer Payments & Messaging Apps: Peer-to-peer payments are available in many mobile apps due to the expansion of instant messaging and direct communication. For instance, WeChat, PayPal, MasterCard, American Express, Facebook Messenger. This gives criminals another way to launder money
Slide 9
This slide discusses how money can be laundered in the cryptocurrency industry. Criminals launder money by moving digital assets across blockchains, bypassing a centralized service that can track and freeze transactions.
Overview Of Money Laundering Techniques Training Ppt with all 29 slides:
Use our Overview Of Money Laundering Techniques Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
The templates are handy and I can personalize them as per my needs. Glad to be your subscriber!
-
Great product with highly impressive and engaging designs.