Prevention of Cyber Attacks Training Ppt
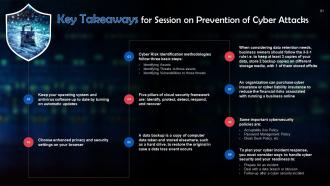
The PowerPoint Training Module on Prevention of Cyber Attacks provides a thorough guide on safeguarding against cyber threats, targeting both individual and organizational levels. It begins by exploring How Can Employees Help in Improving Cyber Security, emphasizing the critical role of workforce awareness and participation. The focus then shifts to Remote Work Security Awareness and Secure Mobile Devices, offering strategies for maintaining security in increasingly mobile and remote work environments. Safe Web Browsing techniques are also discussed as a fundamental aspect of personal cyber hygiene. The PPT Deck then addresses organizational measures, starting with Identifying Risks and Protecting against Risks, which lay the groundwork for robust cybersecurity practices. Sections on Physical Security and Environmental Controls, Data Privacy Management, Cloud Security, and Backup and Recovery provide a comprehensive view of the various layers of security necessary. The importance of Cyber Insurance and the implementation of Cybersecurity Policies, including a Sample Cybersecurity Policy, are also covered. Additionally, the presentation includes a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan, practical Cybersecurity Dos and Does not and helpful Cybersecurity Checklists and Posters, making it a vital resource for anyone looking to bolster their cyber defenses. It also has Key Takeaways and Discussion Questions related to the topic to make the training session more interactive. The deck contains PPT slides on About Us, Vision, Mission, Goal, 30-60-90 Days Plan, Timeline, Roadmap, Training Completion Certificate, and Energizer Activities.
The PowerPoint Training Module on Prevention of Cyber Attacks provides a thorough guide on safeguarding against cyber threa..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Prevention of Cyber Attacks. This deck comprises of 88 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 3
This slide discusses the cyber risks associated with remote working. A remote work environment can increase the risk of a cyber attack or data breach for several reasons. Remote work significantly expands the potential attack surface that must be protected.
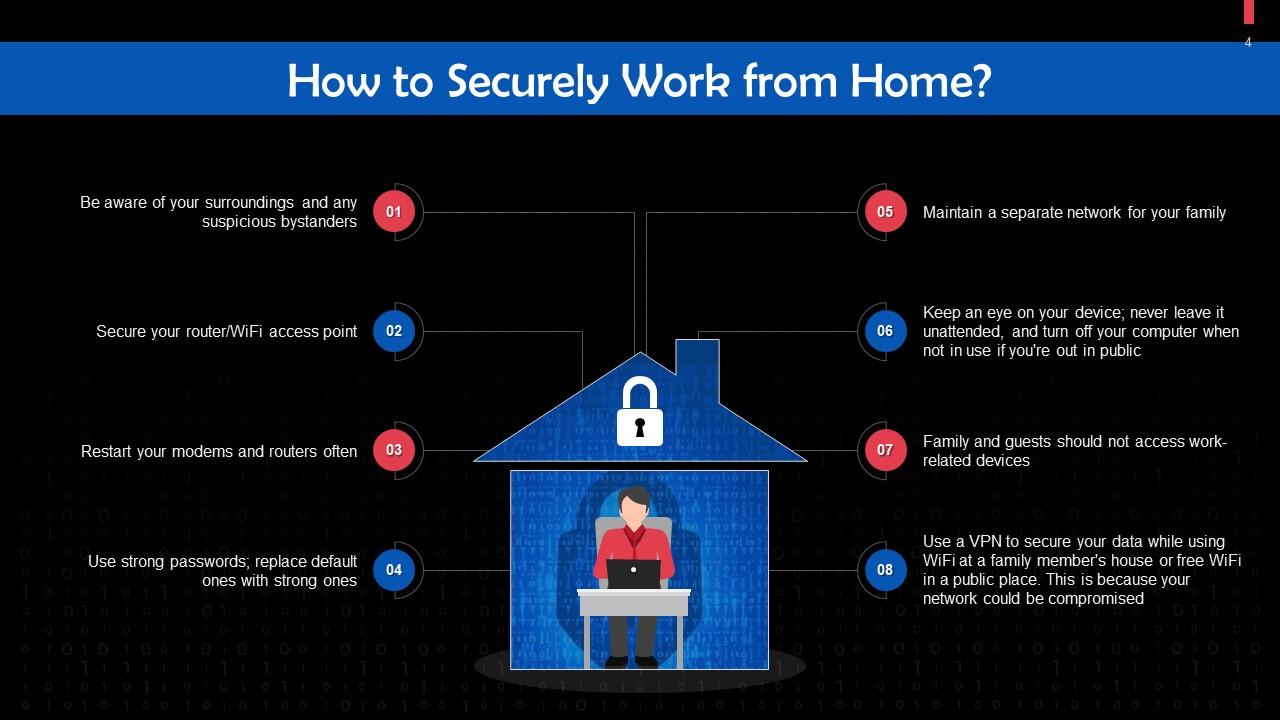
Slide 4
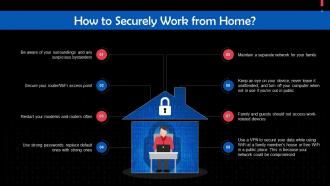
This slide gives tips to work from home securely. Be aware of your surroundings and any suspicious bystanders, secure your router/WiFi access point.
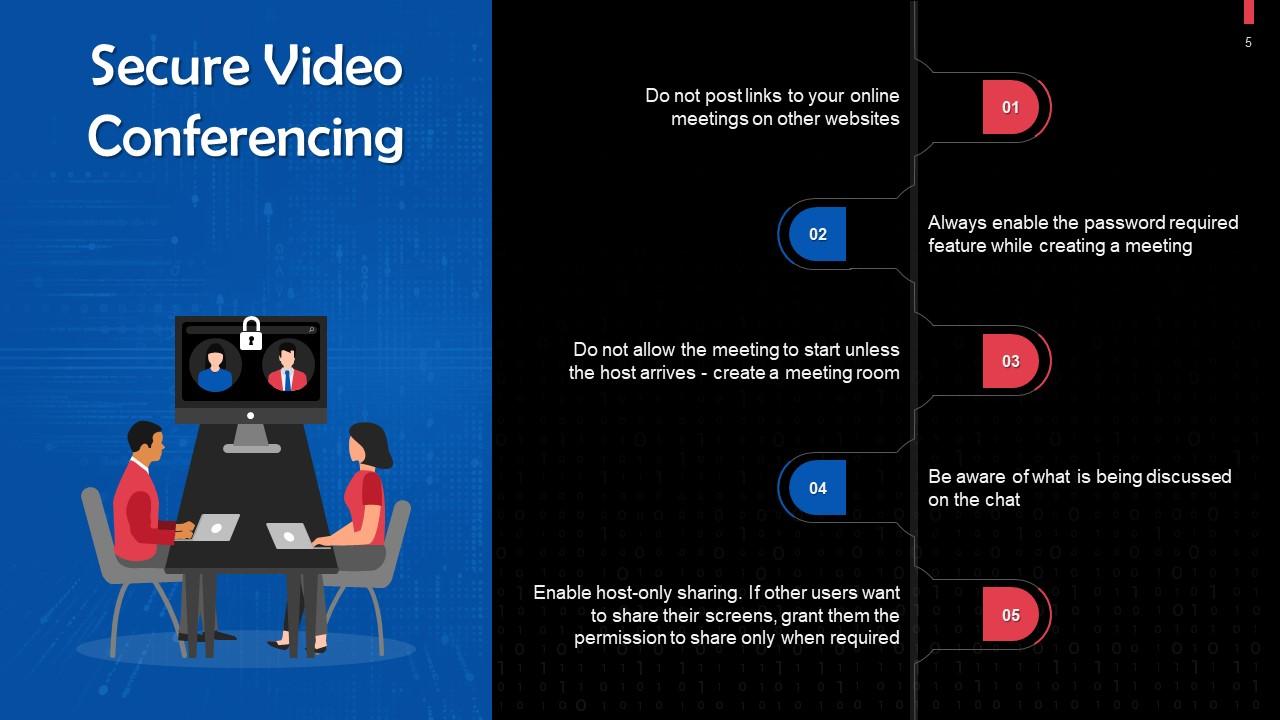
Slide 5
This slide discusses tips for secure video conferencing. Do not post links to your online meetings on other websites.
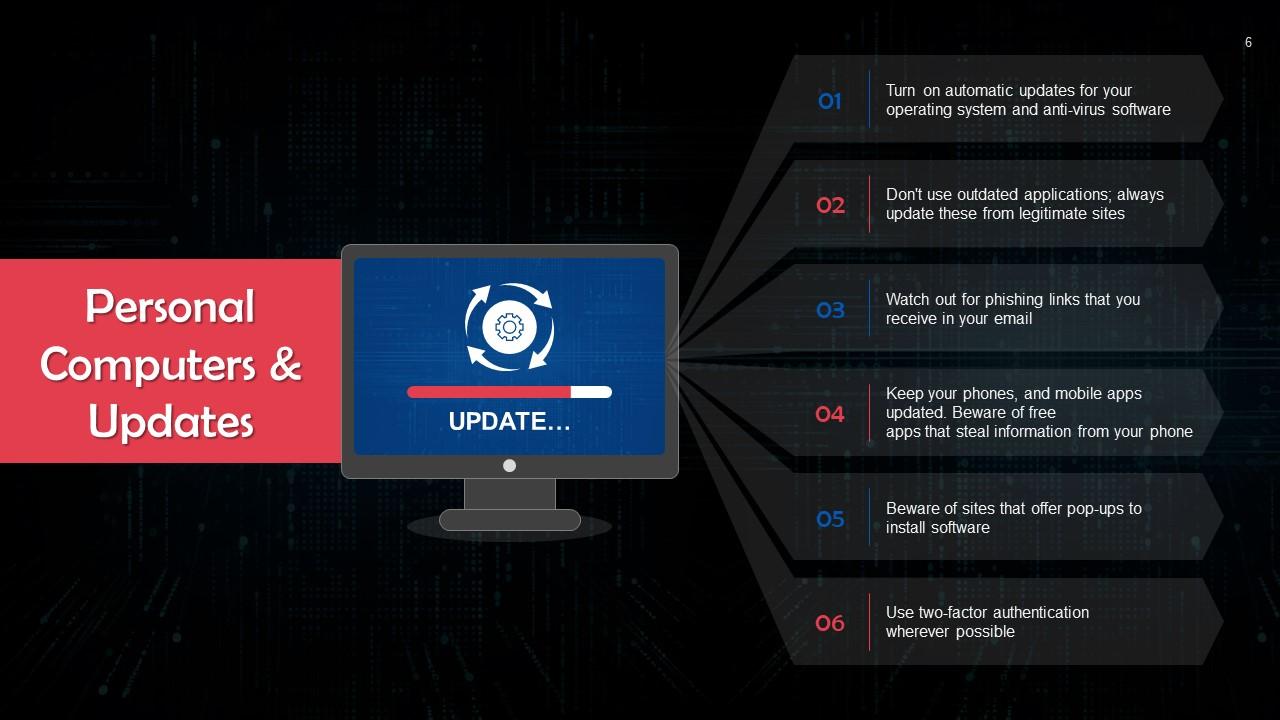
Slide 6
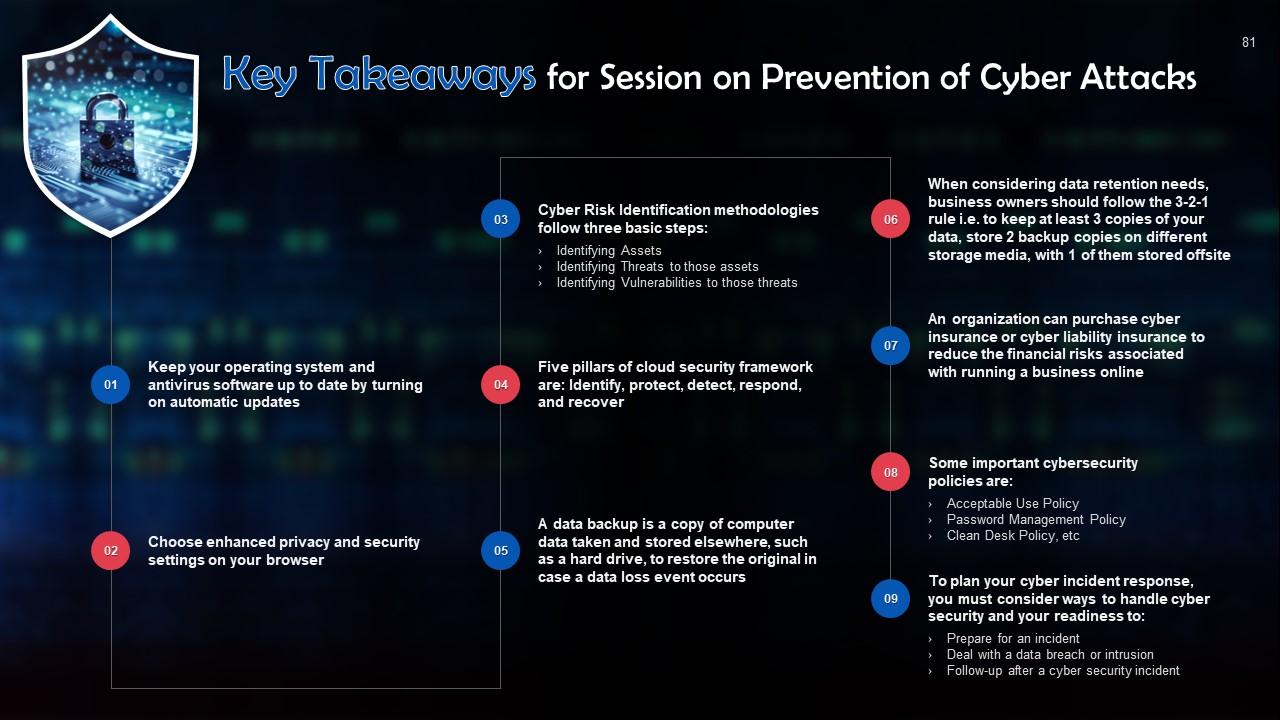
This slide talks about the use of personal computers and importance of updates. Turn on automatic updates for your operating system and anti-virus software.
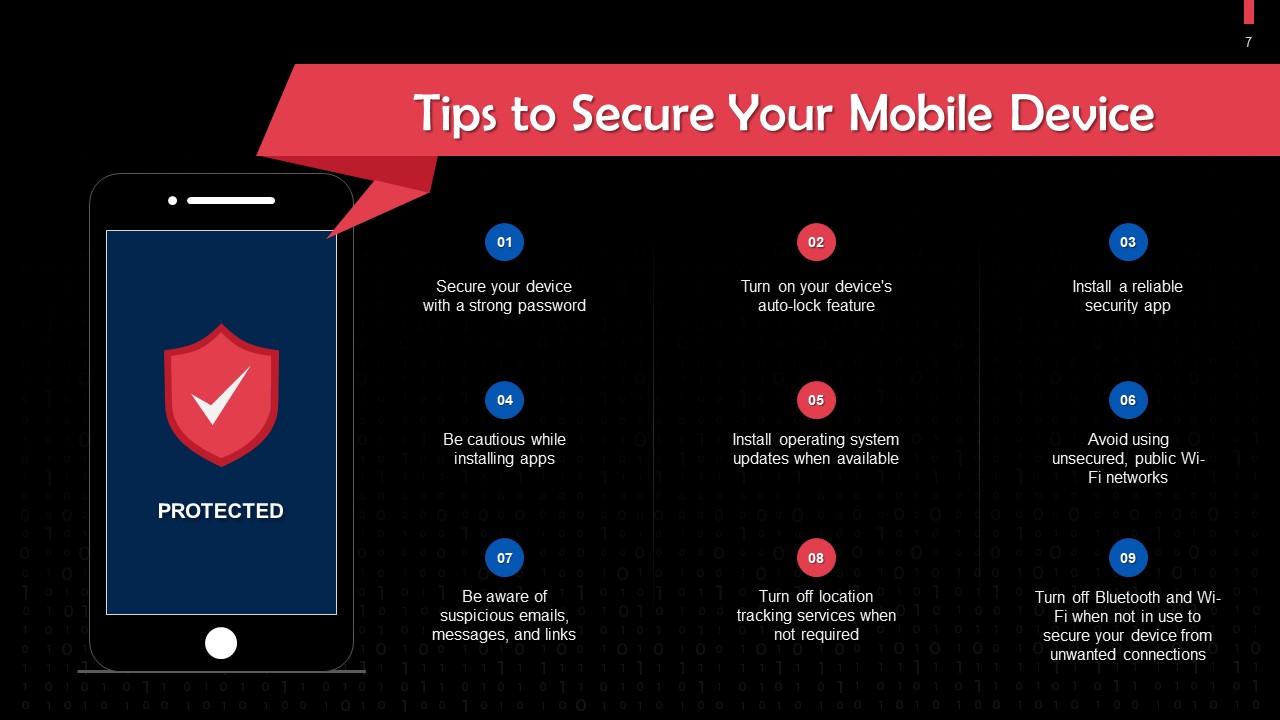
Slide 7
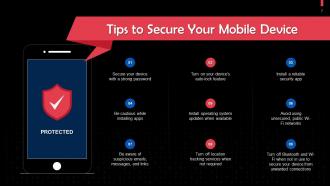
This slide highlights tips to secure your mobile device. Keep a strong password, turn on your device's auto-lock feature.
Slide 8
This slide lists tips for safe web browsing. Regularly update your web browser, choose enhanced privacy and security settings on your browser.
Slide 9
This slide talks about protecting your organizations from cyber risks. A single data breach or attack can lead to the exposure of the personal information of millions of people, eventually causing substantial financial implications and reputational damage to businesses.
Slide 10
This slide introduces the concept of how to identify a cybersecurity risk. The basic approach is to identify assets, threats, and vulnerabilities.
Slide 11
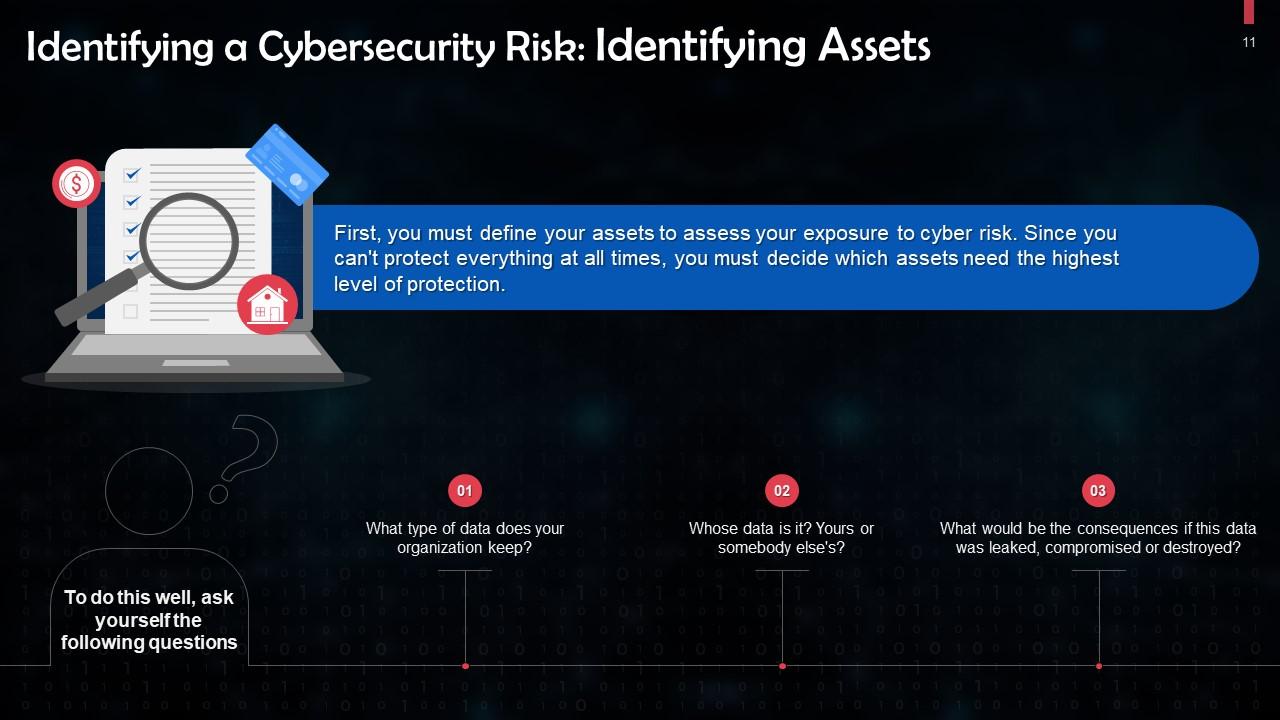
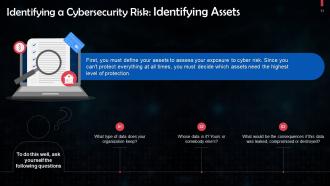
This slide discusses how to identify assets as a part of minimizing cybersecurity risks. First, you must define your assets to assess your exposure to cyber risk. Since you can't protect everything at all times, you must decide which assets need the highest level of protection.
Slide 12
This slide talks about how to identify threats as part of the integrated effort to minimize cybersecurity risks. Threat analysis entails the identification of potential sources of harm to assets (data or information) you need to protect. You will need to refine your identification of the threats.
Slide 13
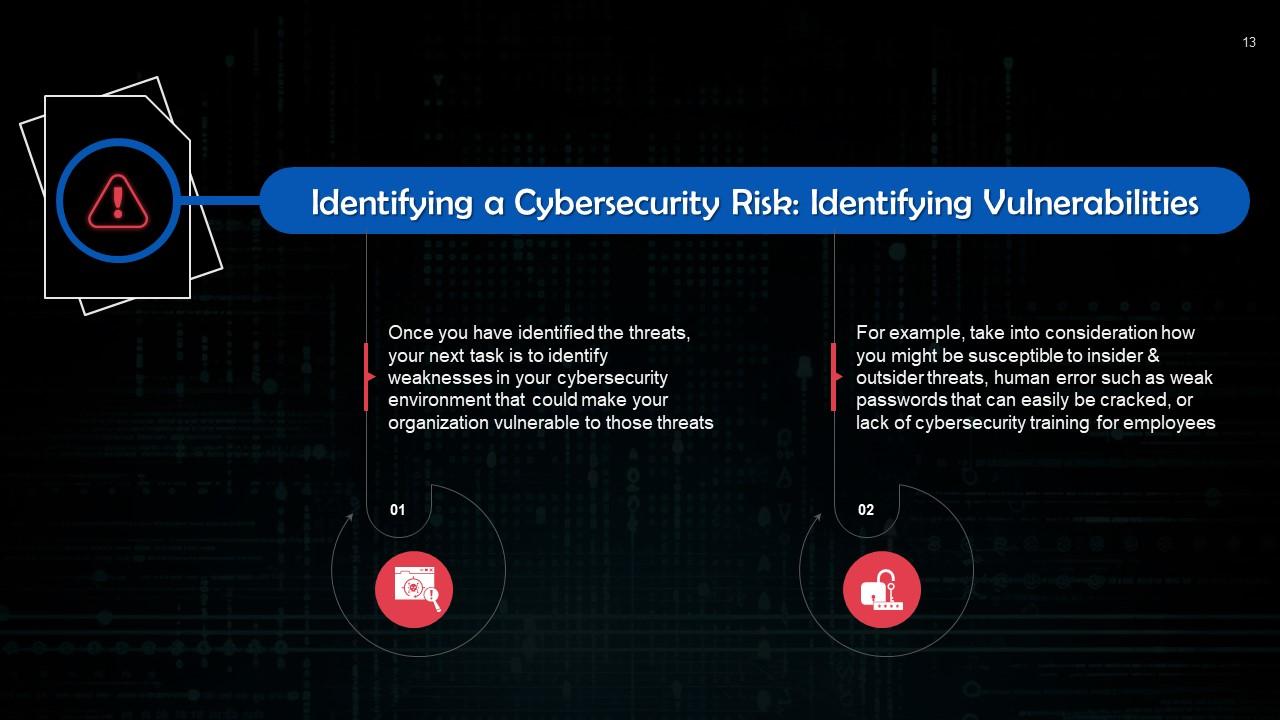
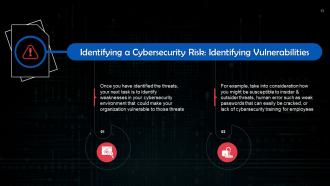
This slide discusses how to identify vulnerabilities to minimize cybersecurity risks. Once you have identified the threats, your next task is to identify weaknesses in your overall cybersecurity environment that could make your organization vulnerable to those threats.
Slide 14
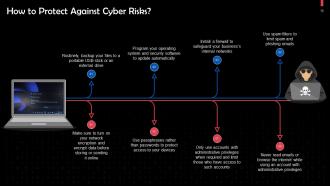
This slide lists signs that may indicate that your business is vulnerable to cyber threats or attacks. These are: Using an outdated operating system, not backing up data properly.
Slide 15
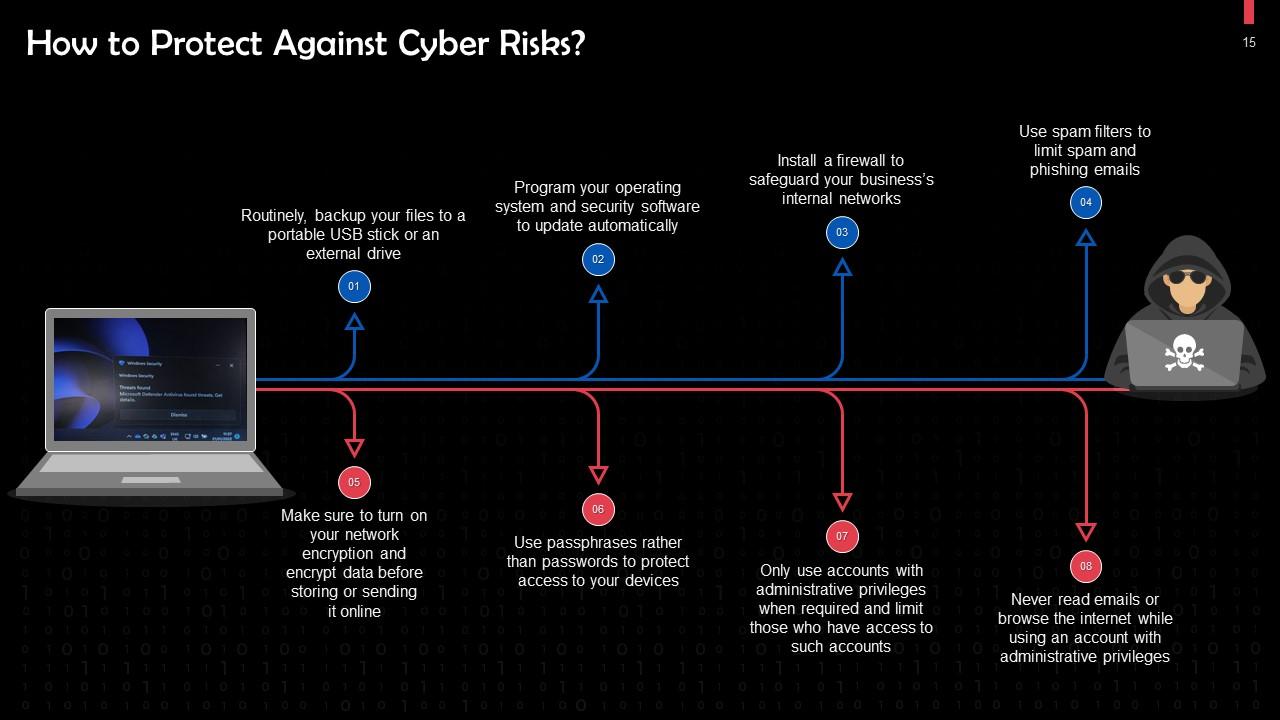
This slide highlights ways to protect yourself against cyber attacks. Routinely, backup your files to a portable USB stick or external drive. Use passphrases rather than passwords to protect access to your devices.
Slide 16
This slide gives information about physical security and environmental controls. Physical and environmental security is often neglected but is crucial in protecting data. Areas that store information and information technology systems must be protected to avoid damage or unauthorized access to data and systems.
Slide 17
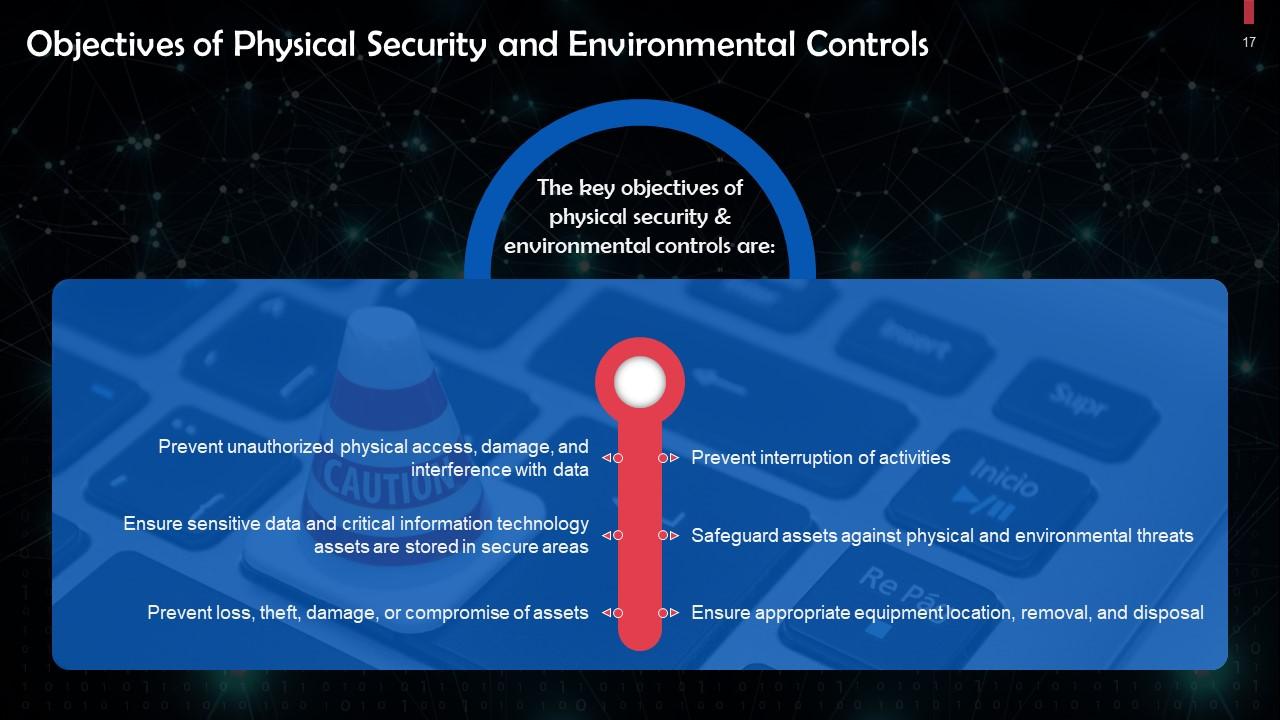
This slide discusses objectives of physical security and environmental controls. Some of these include: Preventing unauthorized physical access, damage, and interference with data, safeguarding assets from physical and environmental threats.
Slide 18
This slide introduces the concept of data privacy management. Data privacy management helps organizations secure sensitive information and address privacy breaches
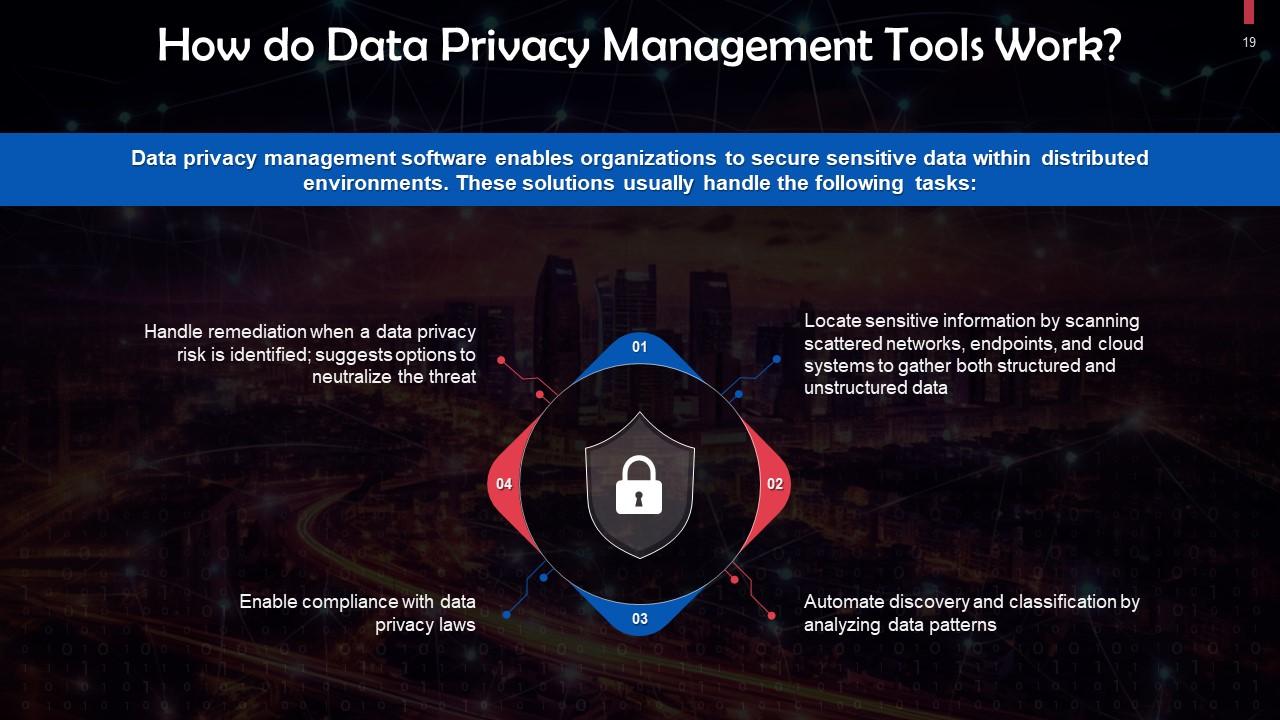
Slide 19
This slide discusses the working of a data privacy management tool. These tools help in locating sensitive information, automating discovery and classification, enabling compliance with data privacy laws, and handling remediation.
Slide 20
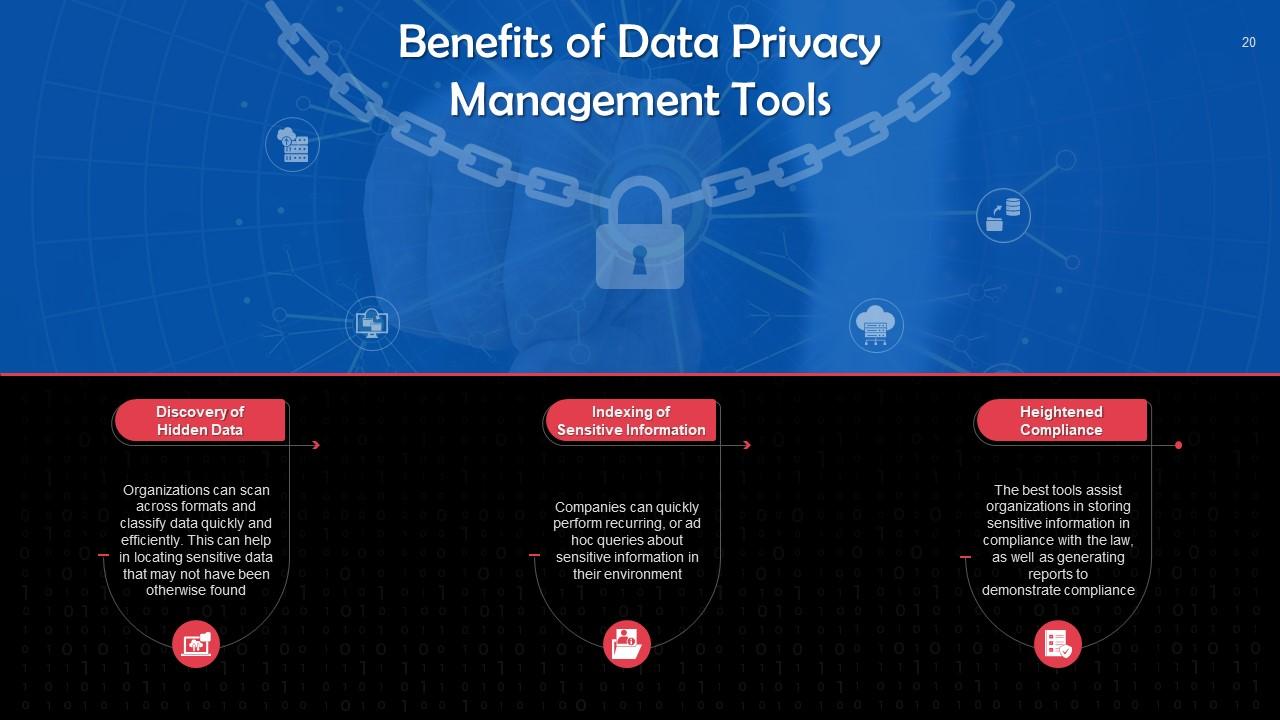
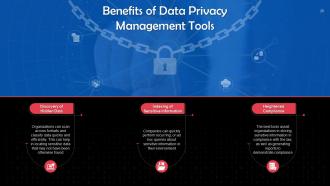
This slide discusses the benefits of data privacy management tools. These are: Discovery of hidden data, indexing of sensitive information, and enhanced compliance.
Slide 21
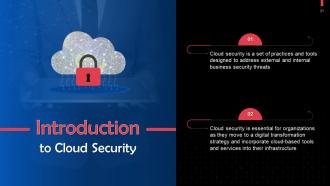
This slide gives information about cloud security. Cloud security is a set of practices and tools designed to address external and internal business security threats.
Slide 22
This slide talks about the importance of cloud security. As organizations shift to the cloud, understanding security requirements for keeping data safe has become essential.
Slide 23
This slide talks about the importance of cloud security. These are: Multitenancy, compliance, access management, misconfigurations, and lack of visibility.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Multitenancy: Public cloud environments store multiple client infrastructures under one roof, a cyber attack on other businesses can compromise your hosted services, referred to as collateral damage
- Compliance: Regulatory compliance management can sometimes become a source of confusion for companies using public or hybrid cloud deployments. General data privacy and security accountability still rest with the organization, and major dependence on third-party solutions to supervise this component can lead to costly compliance issues
- Access Management: While businesses may be able to control and limit access points across on-premises systems, enforcing the same level of restrictions in cloud settings can be difficult
- Misconfigurations: Misconfigurations can include leaving default administrative passwords in place or not setting appropriate privacy settings
- Lack of Visibility: As many cloud services are accessed outside of organization networks and via third parties, it is easy to lose track of who is accessing your data and how
Slide 24
This slide highlights types of cloud security solutions. These are: Data loss prevention, identity and access management, security information and event management, and business continuity and disaster recovery.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Data Loss Prevention: DLP solutions use a combination of data encryption, remediation alerts, and other preventative measures to safeguard all stored information
- Identity and Access Management: Identity and access management tools and services enable organizations to deploy policy-driven enforcement protocols for all users, whether accessing on-premises or through cloud-based services
- Security Information and Event Management: Security information and event management offers a comprehensive security solution that automates threat monitoring, detection, and response in cloud-based environments
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Disaster recovery solutions provide organizations with tools, services, and protocols necessary to expedite the recovery process of lost data and resume normal business operations
Slide 25
This slide tells you how to approach cloud security. The NIST has developed necessary steps that every organization can follow to self-assess security preparedness and apply adequate preventative and recovery security measures to their systems
Slide 26
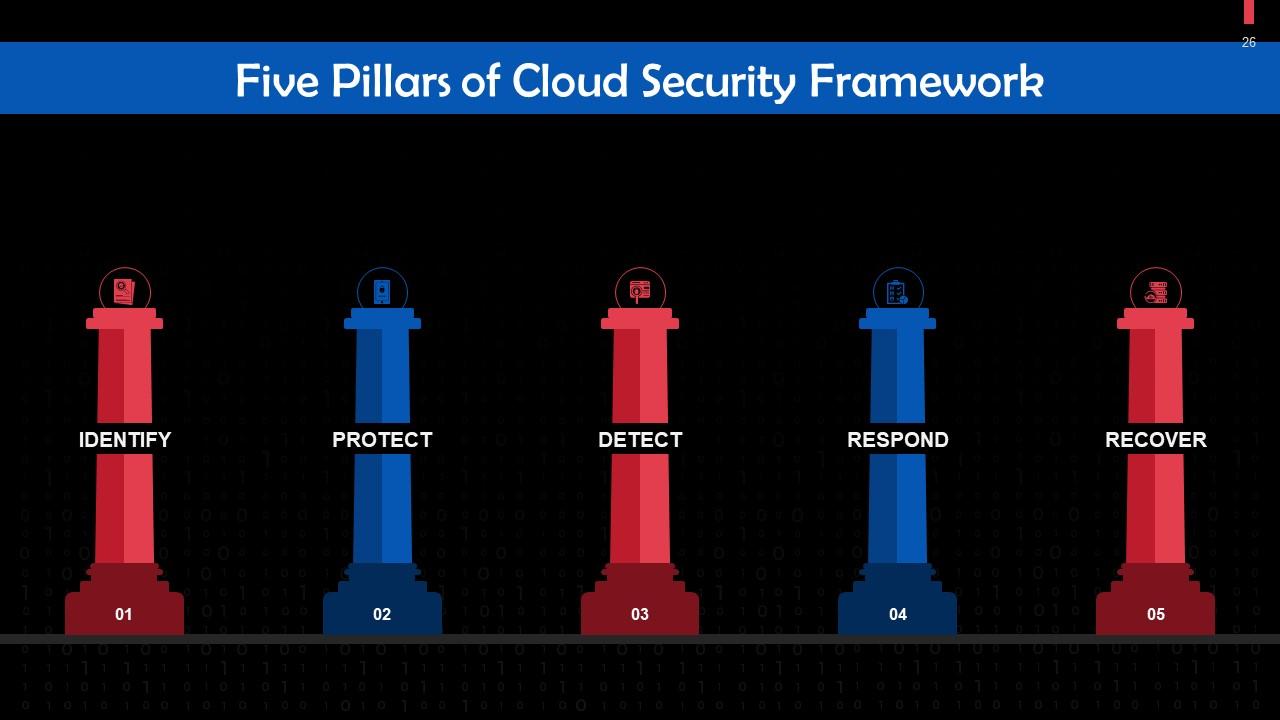
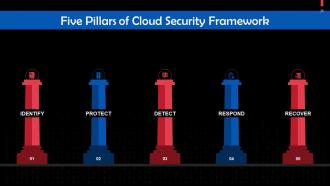
This slide discusses the five pillars of cloud security framework. These are: Identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Identify: This pillar entails identifying an organization's critical functions and cloud security risks could hamper those functions. For instance, if a company accepts payments from customers online, secure collection of this data is an essential or critical function; without it, the company cannot continue to sell its products
- Protect: This task focuses on limiting the impact of a security breach. The protect function outlines safeguards a business must have to ensure that critical functions and their relevant components, such as systems and employees, are safe
- Detect: This function aims to assess whether an organization's systems are compromised. This role analyzes how the organization's cybersecurity team determines a breach has occurred
- Respond: This function aims to minimize damage through rapid response. It defines the actions that the IT team can and should perform based on the type and severity of breach
- Recover: This function aims to recover any data that might have been lost due to a cloud security attack. It also deals with restoring services to critical systems that may have been damaged because of the breach
Slide 27
This slide introduces the concept of data backup and recovery. A data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere, such as a hard drive, to restore the original in case a data loss event occurs.
Slide 28
This slide lists types of backups. These are: Standard, system, and incremental & differential backups.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Standard Backups: Standard backups create copies of files from one or more systems across a network
- System Backups: System backups are complete copies of a system, including the settings and preferences of the operating system
- Incremental & Differential Backups: Incremental and differential backups emphasize changes between files on a system. A differential backup just backs up files that have changed since the last backup. Incremental backups only back up the changed data found in files. Incremental backups are considerably faster than differential backups
Slide 29
This slide tells us about backup strategy. A backup strategy defines data protection goals that direct data backup and recovery policy actions.
Slide 30
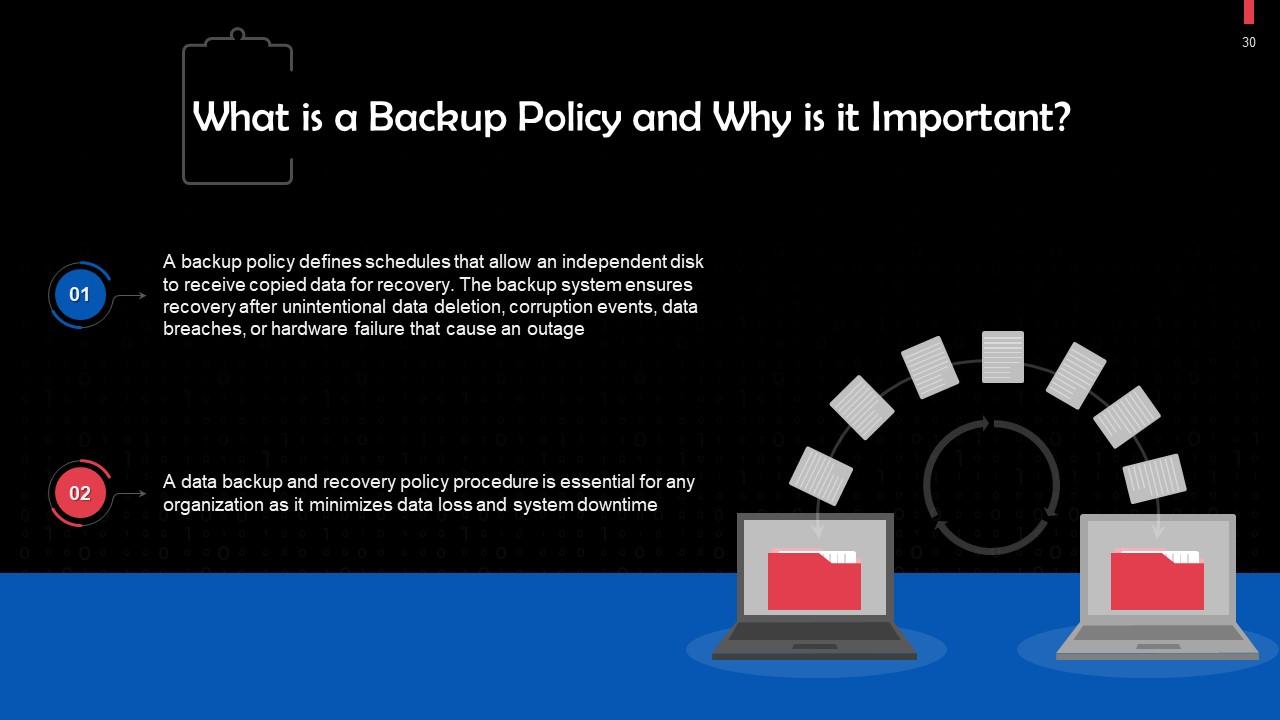
This slide discusses backup policies and their importance. A backup policy defines schedules that allow an independent disk to receive copied data for recovery. The backup system ensures recovery from unintentional data deletion, corruption events, data breaches, or hardware failure that cause an outage.
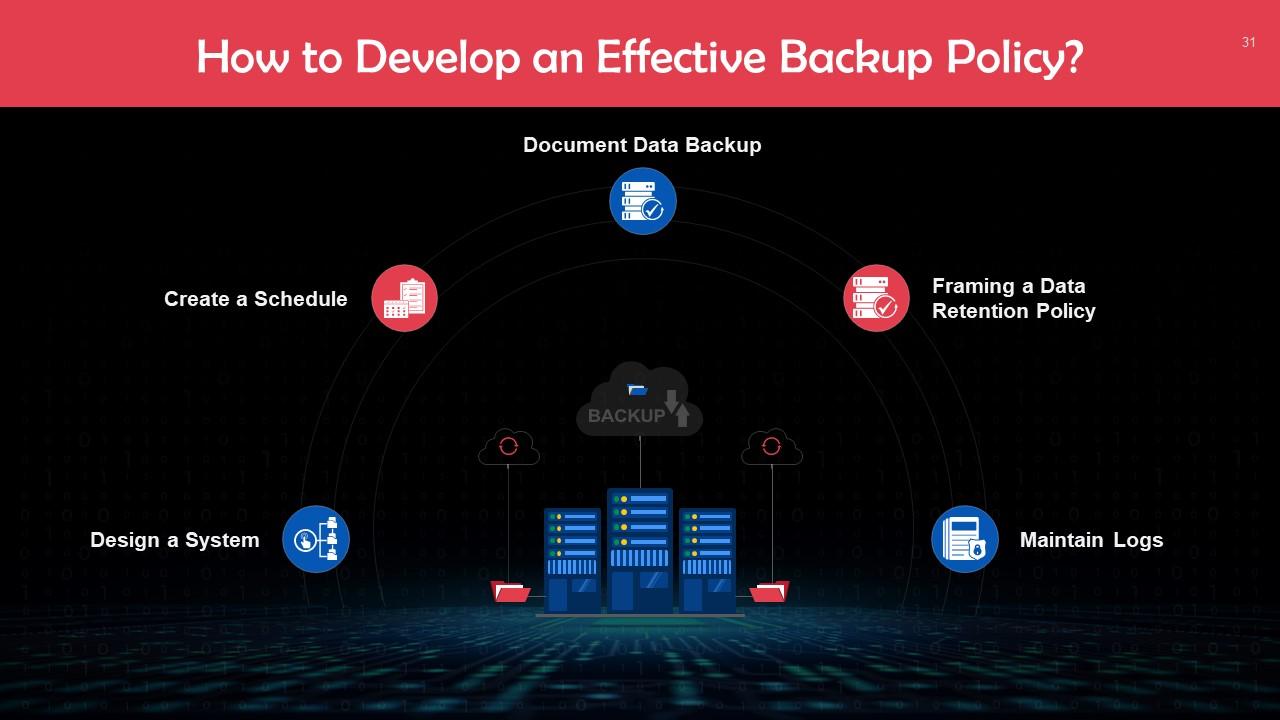
Slide 31
This slide provides guidance on how to make an effective data backup policy. This entails designing a system, creating a schedule, documentation of data backup, data retention policy, and maintaining logs.
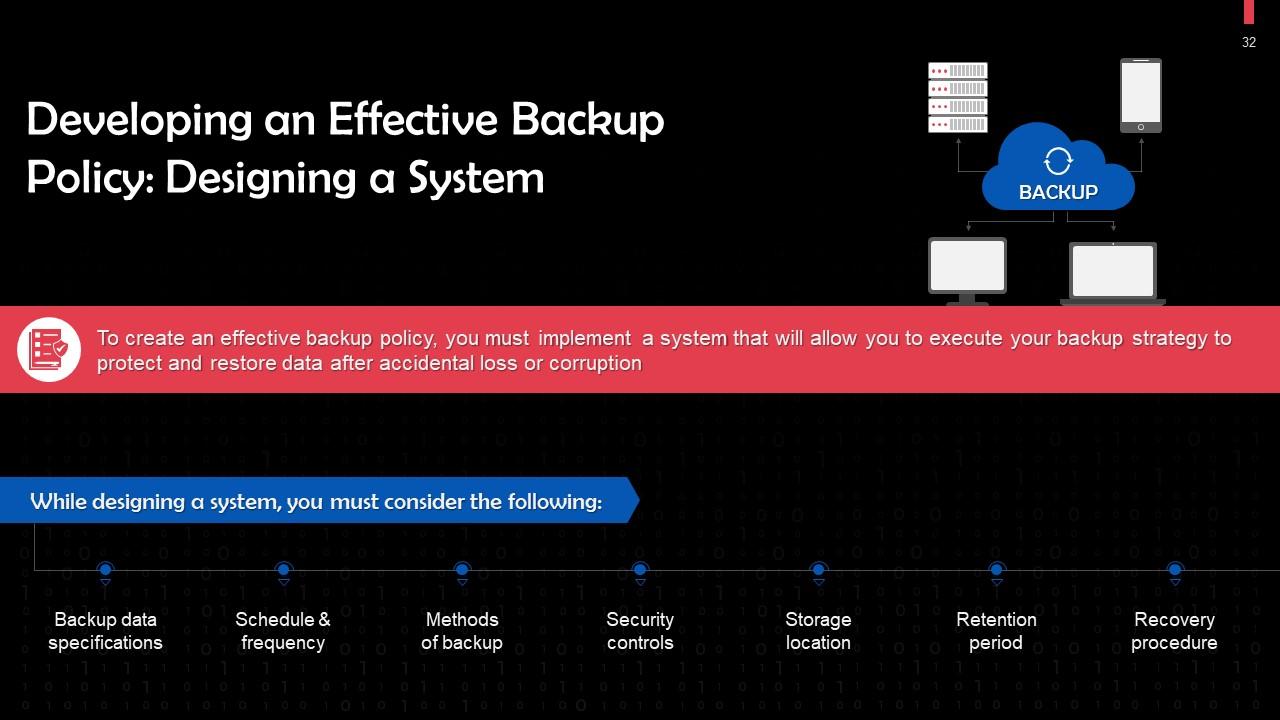
Slide 32
This slide talks about designing a system as the first step in developing an effective backup policy. To create an effective backup policy, you must implement a system that will allow you to execute your backup strategy to protect and restore data after accidental loss or corruption.
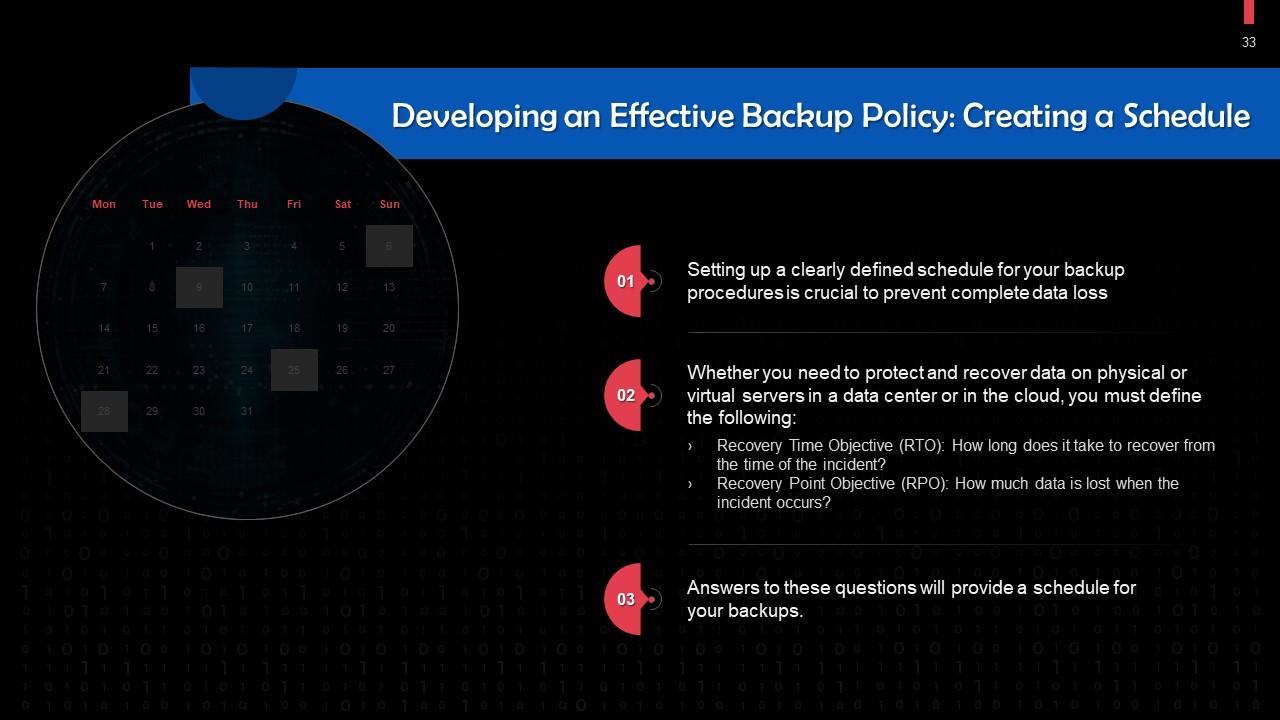
Slide 33
This slide points out the importance of creating a schedule to develop an effective backup policy. Setting up a clearly defined schedule for your backup procedures is crucial to prevent complete data loss.
Slide 34
This slide discusses the documentation of secure data backups and restoration as a part of developing an effective backup policy. This documentation should outline installation procedures for backing up new systems.
Instructor’s Notes: This information reduces the risk of prolonged downtime for organizations when incidents occur. The documentation should be regularly reviewed and updated to match any new backup platform or software changes.
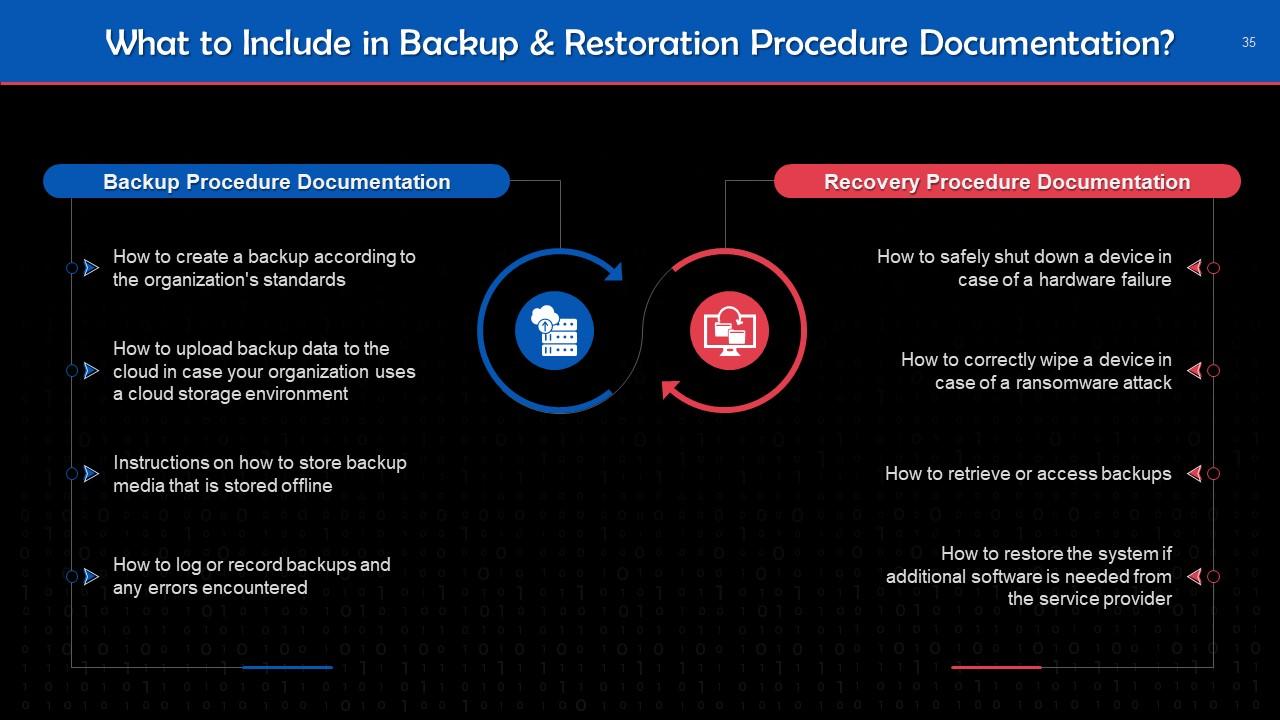
Slide 35
This slide tells us what to include in backup and restoration procedure documentation.
Slide 36
This slide gives information about data retention policy. The next area of focus is to develop a data retention policy. This policy defines how long backups are kept for each sub-system within the backup system.
Slide 37
This slide gives an overview of the 3-2-1 rule for backups. When considering retention needs, business owners should also consider the 3-2-1 rule. The rule is to keep at least 3 copies of your data, store 2 backup copies on inddividual storage media, with one of these stored offsite.
Slide 38
This slide talks about the last step of developing an effective backup policy, which is logging restoration test results. An effective backup policy should comprise periodic tests to measure the backups’ effectiveness and identify and address any issues.
Slide 39
This slide gives information about cyber insurance. An organization can purchase cyber insurance or cyber liability insurance to reduce financial risks associated with an online business.
Slide 40
This slide discusses the working of cyber insurance. Cyber insurance helps cover financial losses that cyber incidents cause for businesses.
Slide 41
This slide discusses some businesses that require cyber insurance. Businesses that create, store, and manage data online, such as customer contacts, customer sales, personally identifiable information, and credit card information, can benefit from cyber insurance.
Slide 42
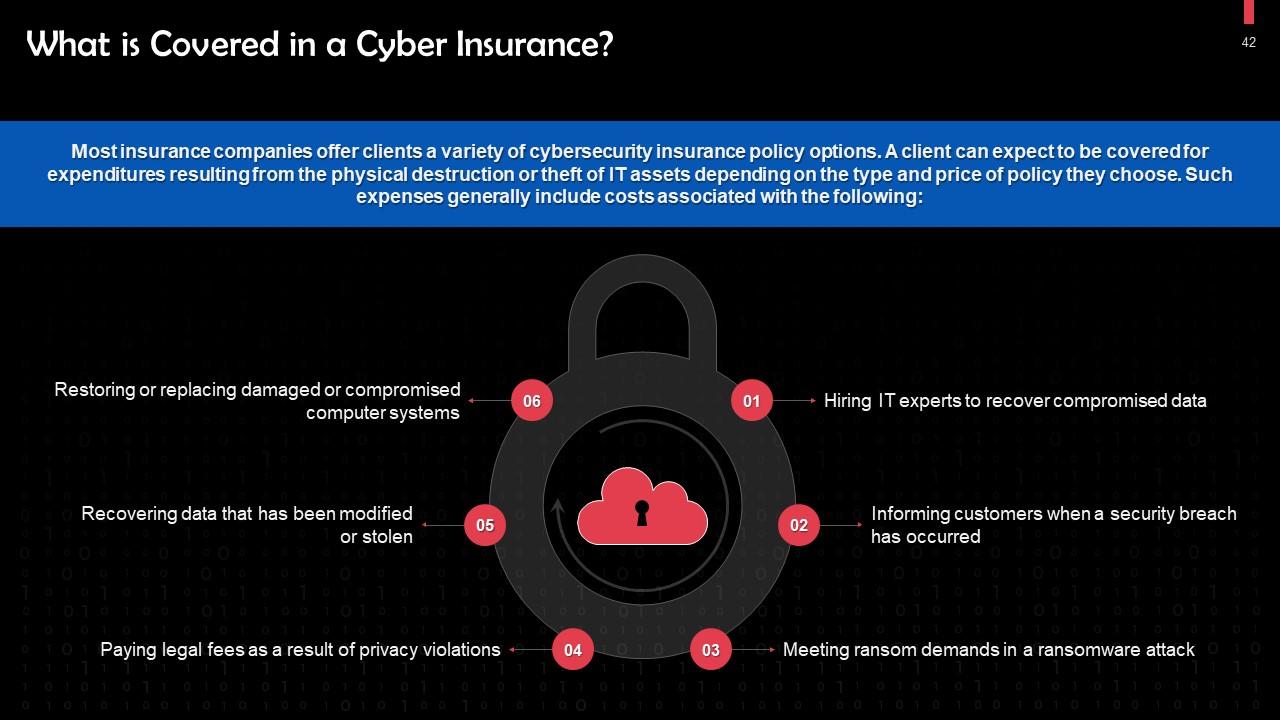
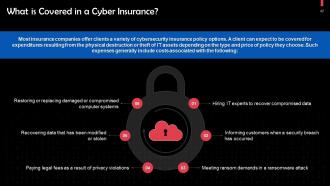
This slide discusses what cyber insurance covers. Most major insurance companies offer clients a variety of cybersecurity insurance policy options. A client can expect to be covered for expenditures resulting from the physical destruction or theft of IT assets depending on the type and price of policy they choose.
Slide 43
This slide lists cyber security policies that every organization must have. These are: Acceptable Use Policy; Change Management Policy; Remote Access Policy; Password Management Policy; Vendor Management Policy; Network Security Policy; Data Retention Policy; Identity Access Management Policy; Security Awareness & Training Policy, and Clean Desk Policy.
Slide 44
This slide tells us what is included in an Acceptable Use Policy (AUP). The AUP defines the inappropriate use of information systems and the risk it may cause. Improper behavior may compromise the network system and result in legal consequences
Instructor’s Notes: The AUP also covers acceptable behavior while handling confidential or private information, general use, and inappropriate use.
Slide 45
This slide talks about change management policy. A company's change management policy ensures the management and approval of changes made to an information system
Instructor’s Notes: The change management policy covers hardware, software, database, and application changes to system configurations.
Slide 46
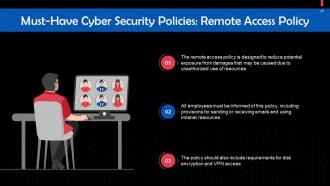
This slide tells us what is included in a Remote Access Policy. The remote access policy is designed to reduce potential exposure from damages that may be caused due to unauthorized use of resources.
Slide 47
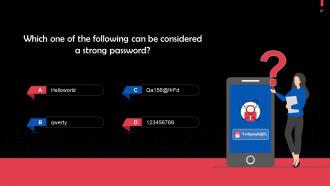
This slide gives information about password management policy. This policy offers guidance on developing, implementing, and reviewing a documented process for appropriately creating, changing, and safeguarding strong and secure passwords. This critical action is used to verify user identities and obtain access to company systems or information.
Slide 48
This slide tells us what is included in a Vendor Management Policy. This policy validates a vendor’s compliance and addresses the procedure for hiring them. The organization should assess the vendor’s ability to create, receive, maintain, or transfer confidential data on the behalf of the company.
Slide 49
This slide discusses network security policy. A network security policy ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information on an organization's systems. The policy follows aa specific process for conducting information system and network activity reviews periodically.
Slide 50
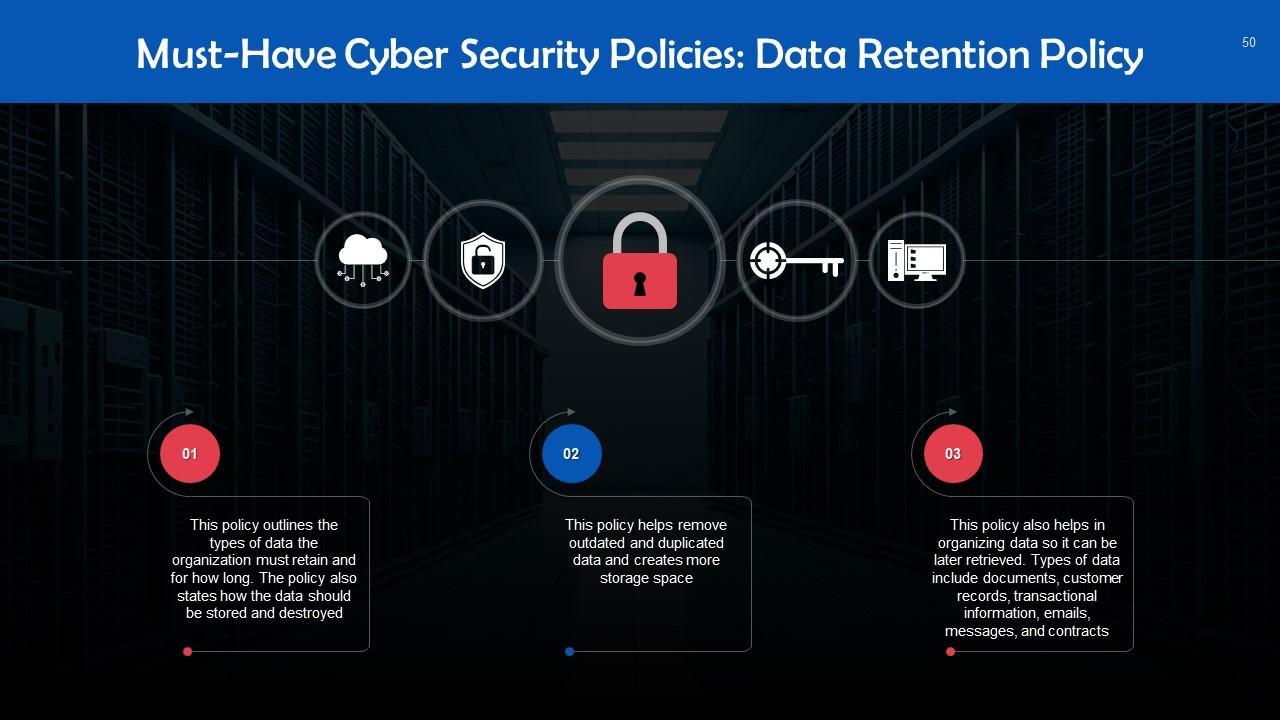
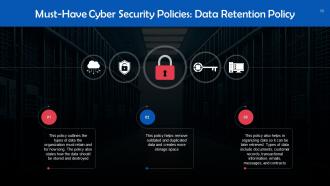
This slide introduces the concept of Data Retention Policy. This policy outlines the types of data the organization must retain and for how long. The policy also states how the data should be stored and destroyed.
Slide 51
This slide tells us what is included in an Identity Access Management Policy. The organization must create and document a process for establishing, documenting, reviewing, and modifying access to systems and sensitive data.
Slide 52
This slide gives information about Security Awareness and Training Policy. All employees of the organization should receive security awareness training to carry out their duties effectively and protect business information
Instructor’s Notes: The policy must also highlight the personnel responsible for creating and conducting the training.
Slide 53
This slide gives information about clean desk policy. A clean desk policy is a company directive that outlines how employees should leave their workspaces when they leave office.
Slide 54
This slide discusses the importance of a clean desk policy. Clean Desk Policies help limit the exposure of sensitive data to unauthorized users, such as outside vendors or cleaning staff, and avoid security breaches.
Slide 55
This slide gives information about the implementation of a clean desk policy. An effective clean desk policy must include the following features: Clarity, availability, electronic documentation, tools, reminders, and enforcement.
Slide 56
This slide depicts a sample cyber security policy template.
Slide 57
This slide discusses the purpose and scope of a sample cybersecurity policy template.
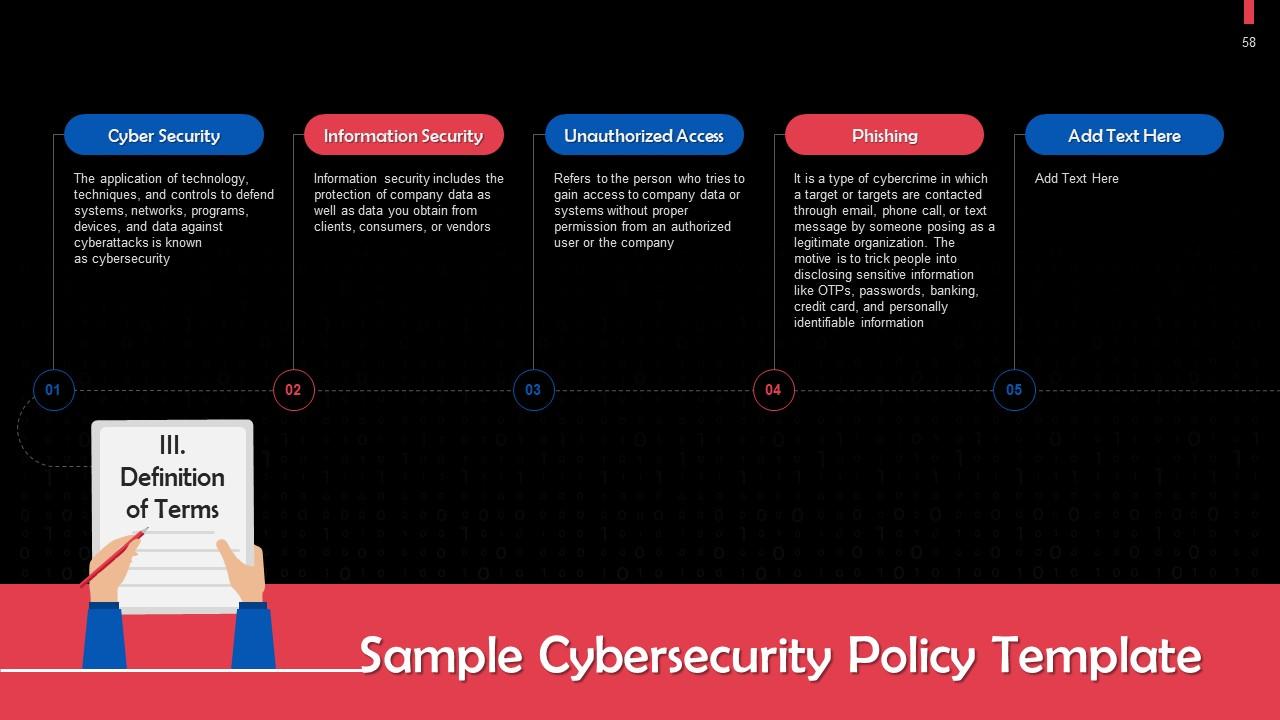
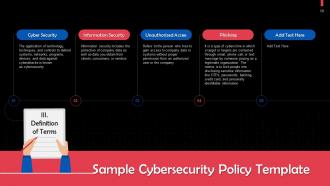
Slide 58
This slide gives definitions of important terms in a sample cybersecurity policy template.
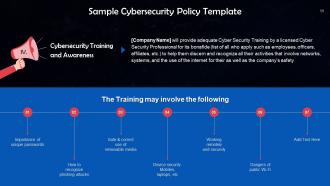
Slide 59
This slide highlights the cybersecurity training and awareness section of the sample cybersecurity policy.
Slide 60
This slide outlines the responsibilities of company personnel. It says that all devices provided by the company are strictly for business use; everyone must properly sign out of the systems and devices after office hours.
Slide 61
This slide discusses the password management policy. Some guidelines are that passwords must be changed every 90 days, and must adhere to a minimum length of 10 characters.
Slide 62
This slide discusses the data transference policy. It states that employees must encrypt sensitive data before transferring it, report suspicious mails or phishing attempts.
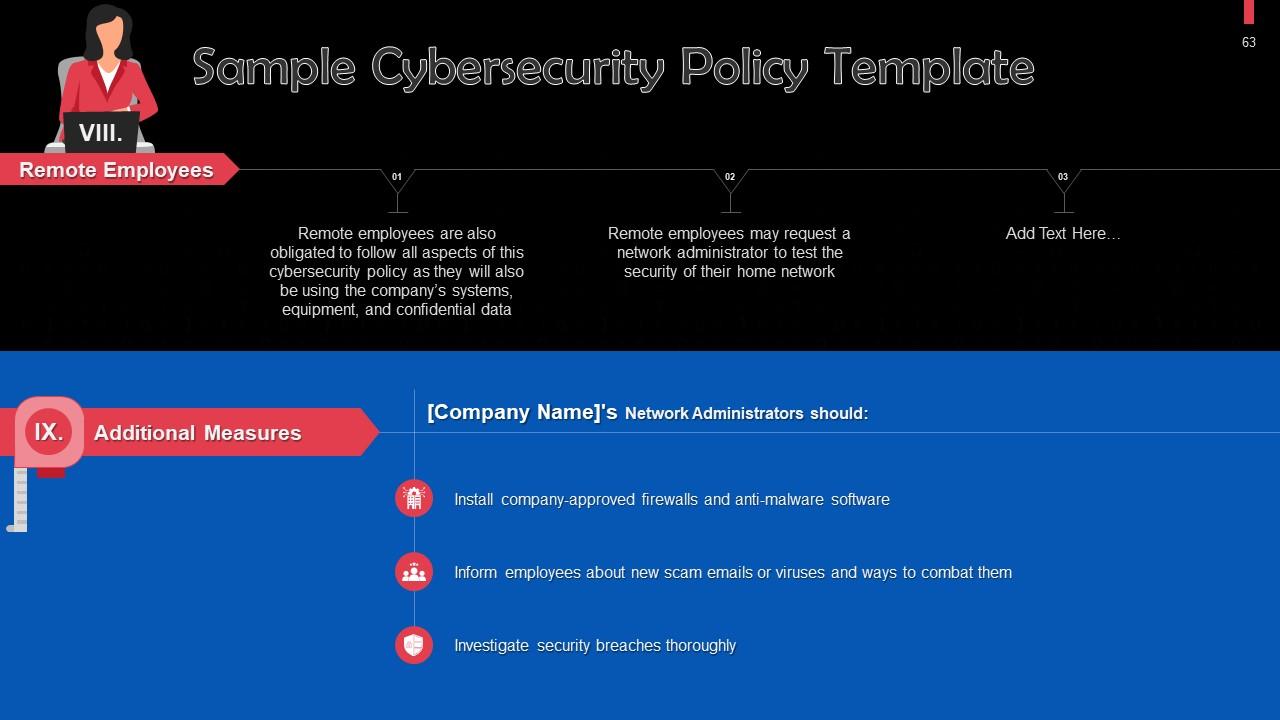
Slide 63
This slide defines the role of remote employees in cybersecurity and presents some additional measures. Remote employees are also obligated to follow all aspects of a cybersecurity policy as they will also be using the company’s systems, equipment, and confidential data
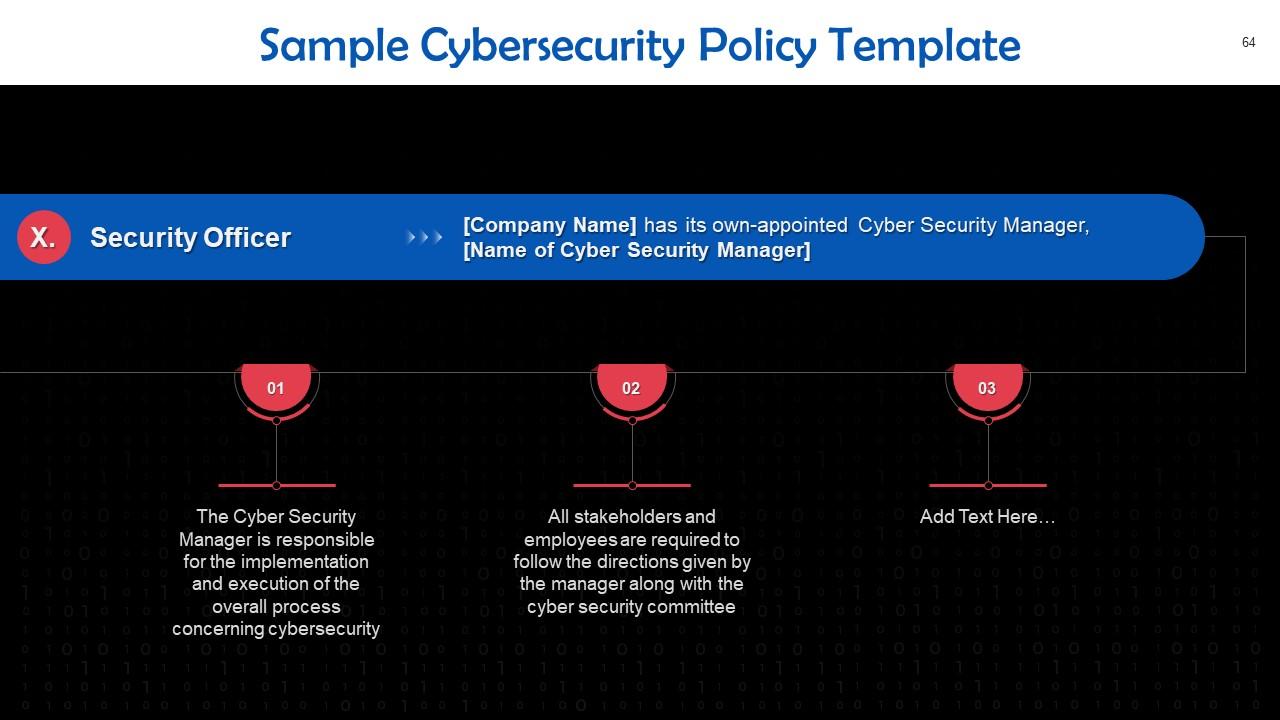
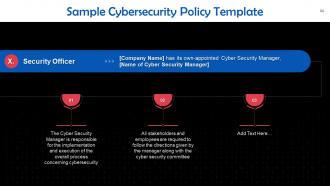
Slide 64
This slide gives information about the profile of the organization’s security officer. The Cyber Security Manager is responsible for the implementation and execution of the overall process concerning cybersecurity.
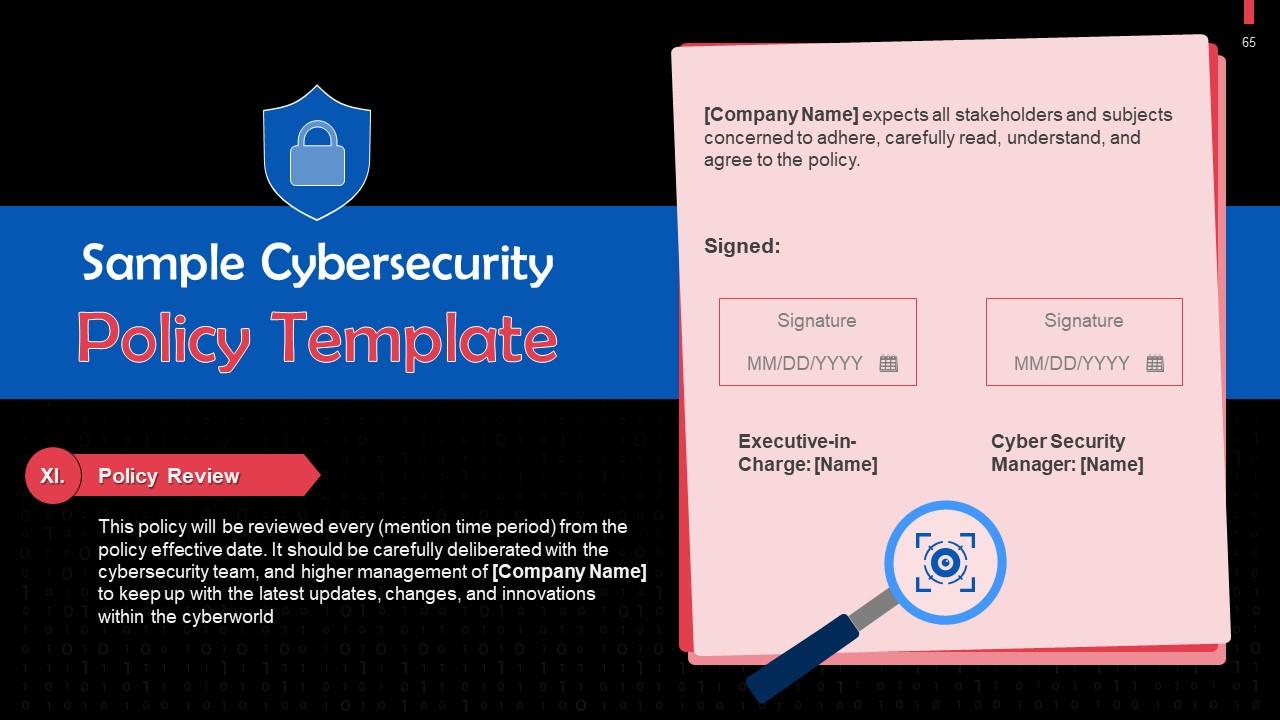
Slide 65
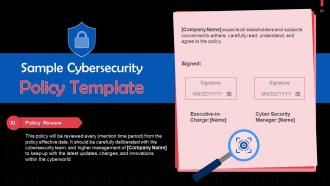
This slide gives information about the policy review section in a cybersecurity policy.
Slide 66
This slide gives an overview of cyber security incident response plan. To plan your cyber incident response, you must consider ways to handle cyber security and your readiness to handle an incident, deal with a data breach or intrusion.
Slide 67
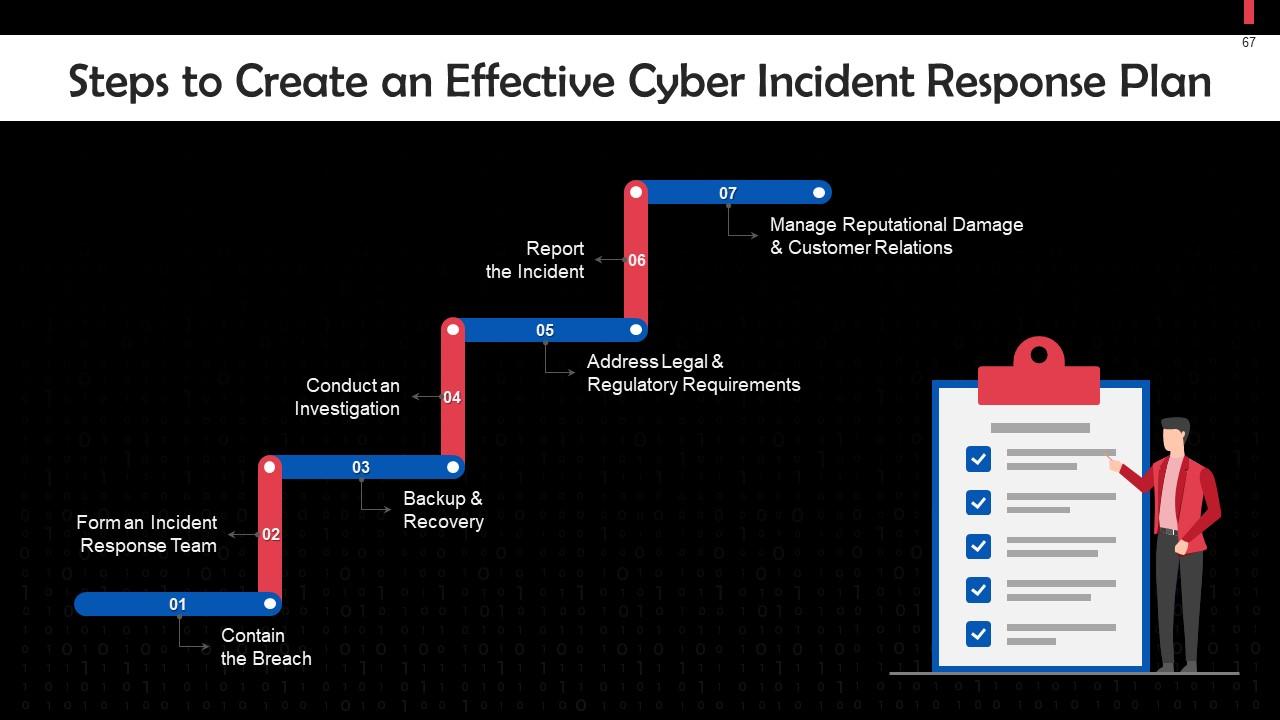
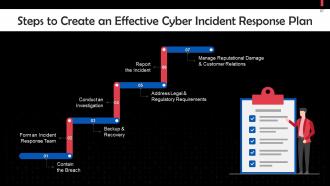
This slide highlights steps to create an effective cyber incident response plan. These steps are: Containing the breach, , forming an incident response team, recovering lost data from backup, conducting an investigation, addressing legal & regulatory requirements, reporting the incident, and managing reputational damage & customer relations.
Slide 68
This slide discusses how to contain a data breach, which is the first step in creating an effective cyber incident response plan. After you detect a breach, the priority is to contain it and mitigate the risk of further damage to your organization or loss of data.
Instructor’s Notes: Sometimes, you may need to suspend your entire organization's network or website. If the breach is limited to certain aspects of your business, then determine which services, processes, and operations can continue without any risk, while you deal with the incident.
Slide 69
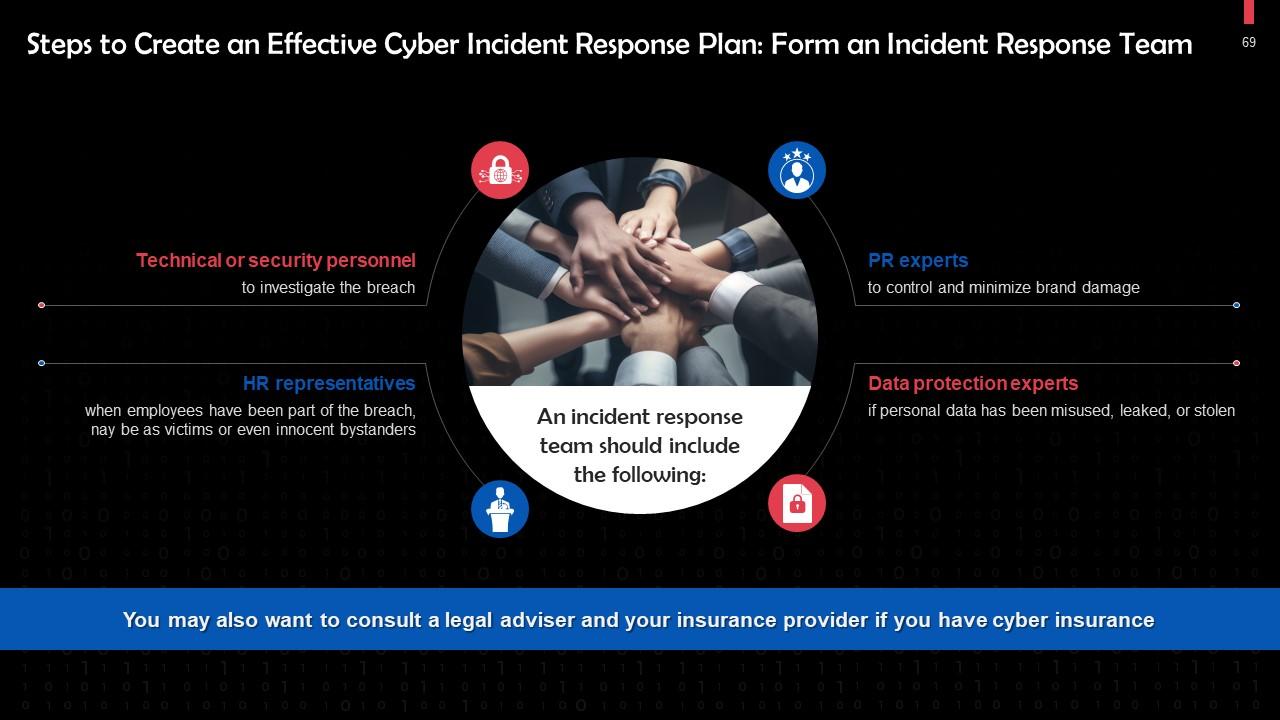
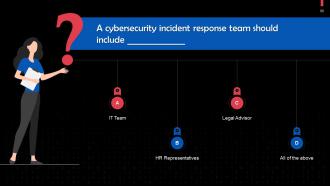
This slide gives information about the formation of a cyber incident response team. The team should comprise the following: Technical personnel, HR representatives, PR experts, data protection experts.
Slide 70
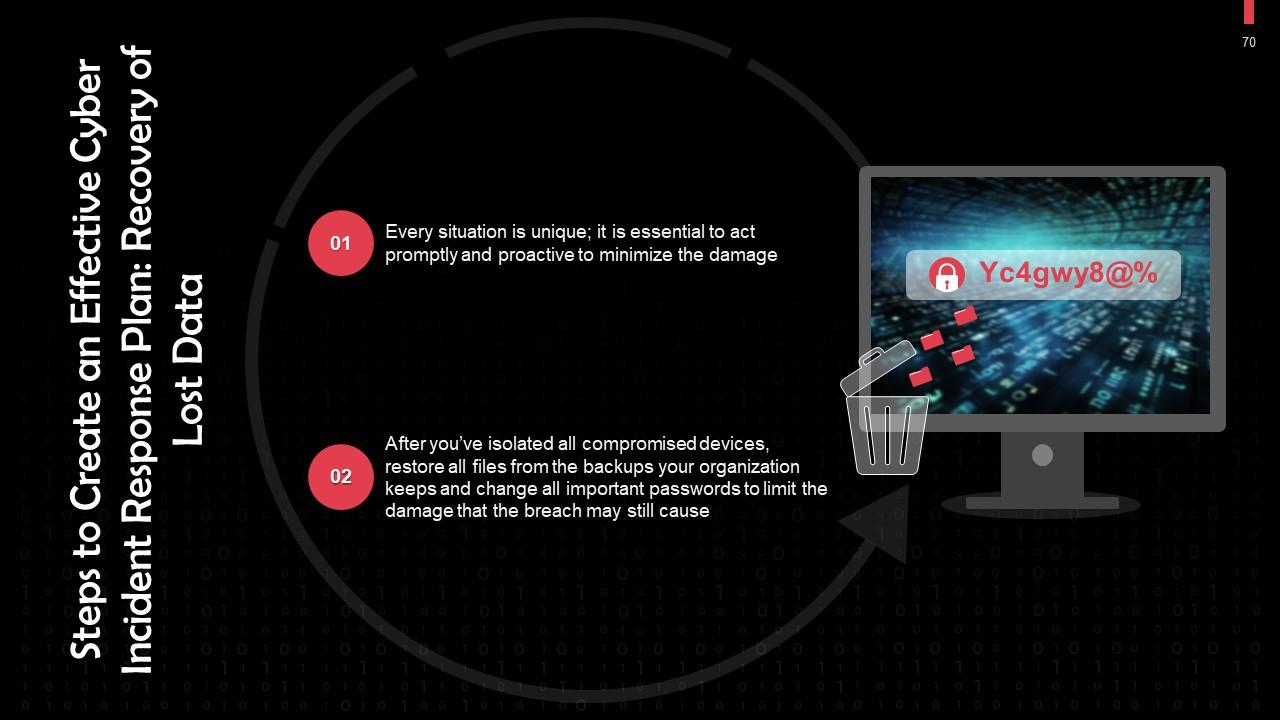
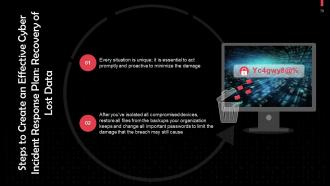
This slide discusses the importance of recovering lost data after a data breach. After you’ve isolated all compromised devices, you should restore all the files from the backups your organization keeps.
Slide 71
This slide discusses how to conduct an investigation, which is a crucial step to create an effective cyber incident response plan. Investigate to analyze which security controls failed and maintain a record of this information.
Slide 72
This slide talks about addressing legal and regulatory requirements when a cyber incident occurs. You may need to inform specific organizations or individuals about the cyber incident to manage the incident. Be clear about who you need to notify and why.
Slide 73
This slide discusses reporting an incident as a part of an effective cyber incident response plan. You should report cybercrime incidents to the law enforcement agency assigned to investigate these.
Slide 74
This slide talks about managing reputational damage and customer relations. If the harm to your reputation and business is severe, you might want to work with a crisis manager or a public relations professional to develop feasible solutions.
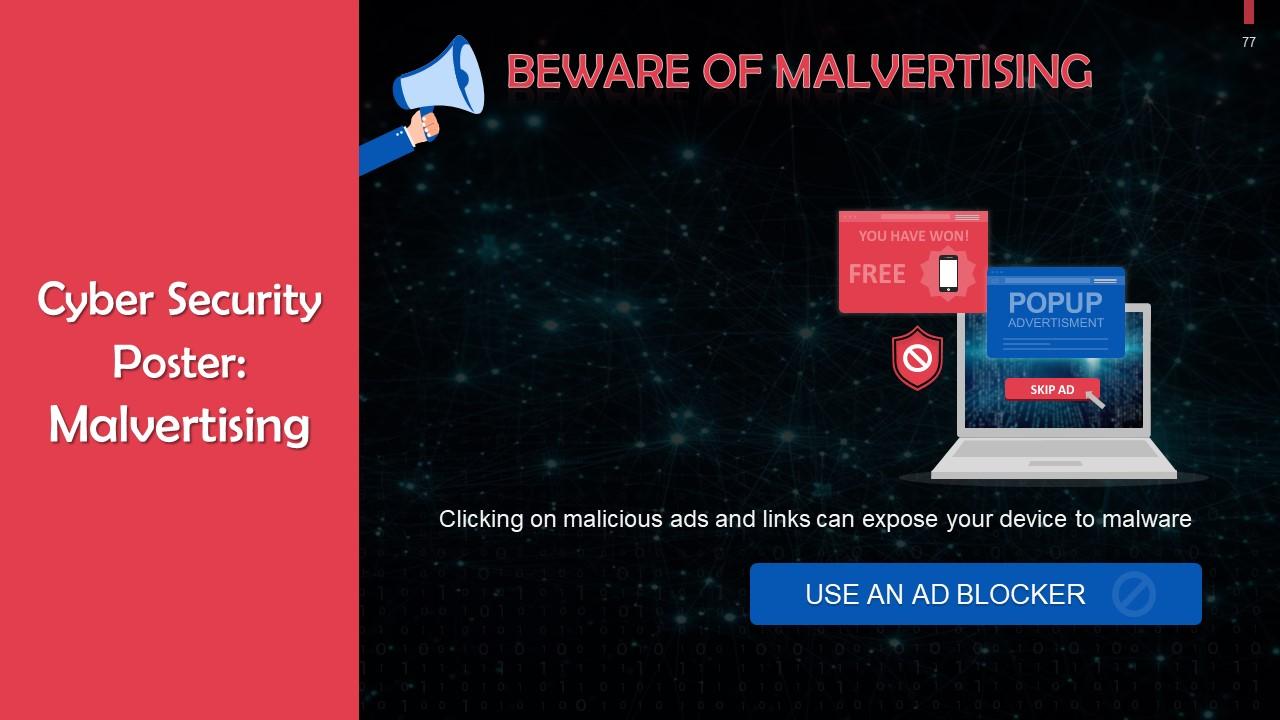
Slide 75 to 77
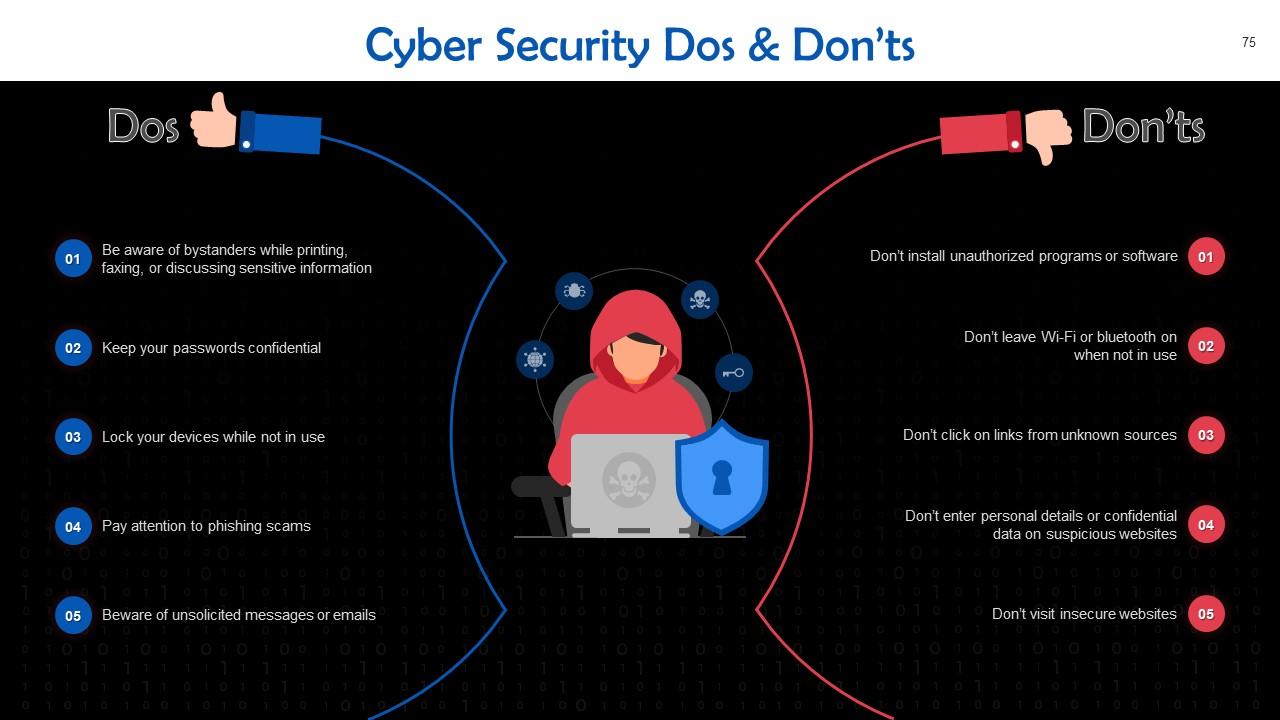
This slide includes cybersecurity posters with tips to protect data.
Slide 78 to 80
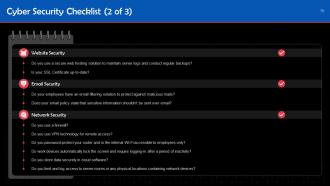
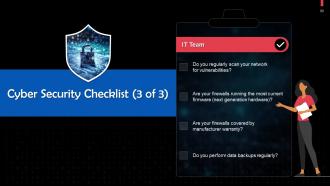
These slides contain a comprehensive checklist to ensure cyber security in the organization.
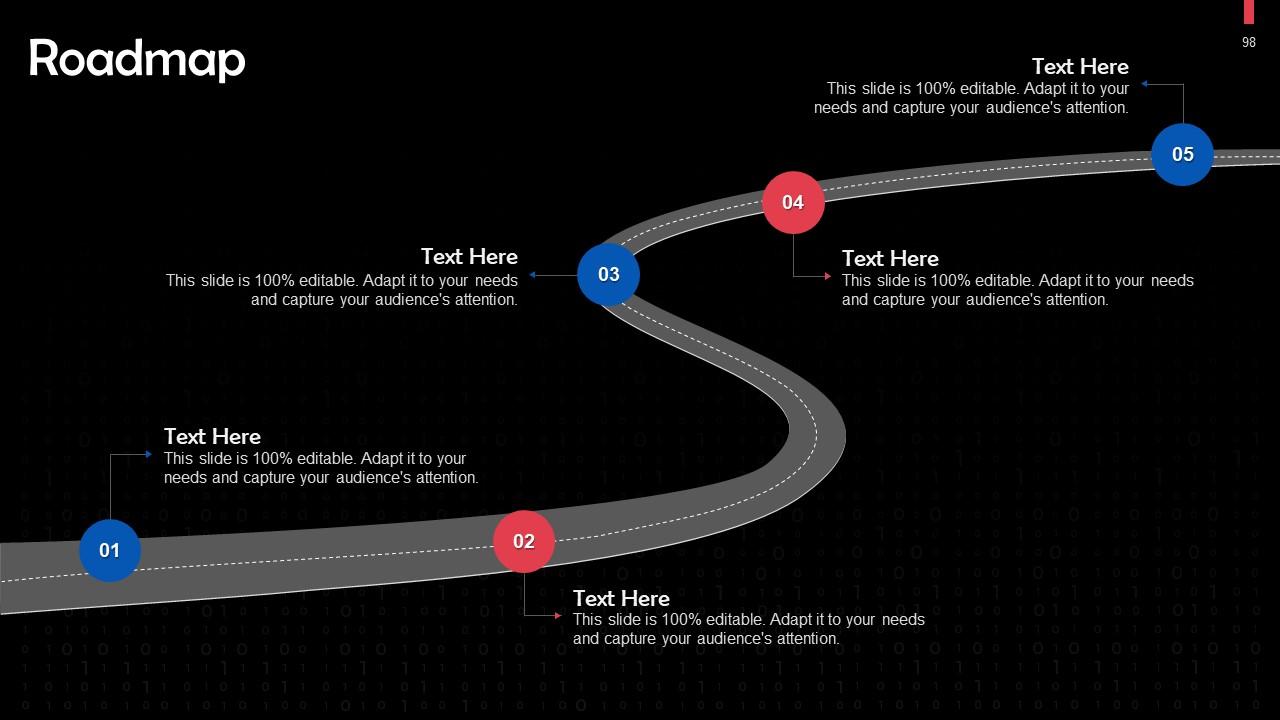
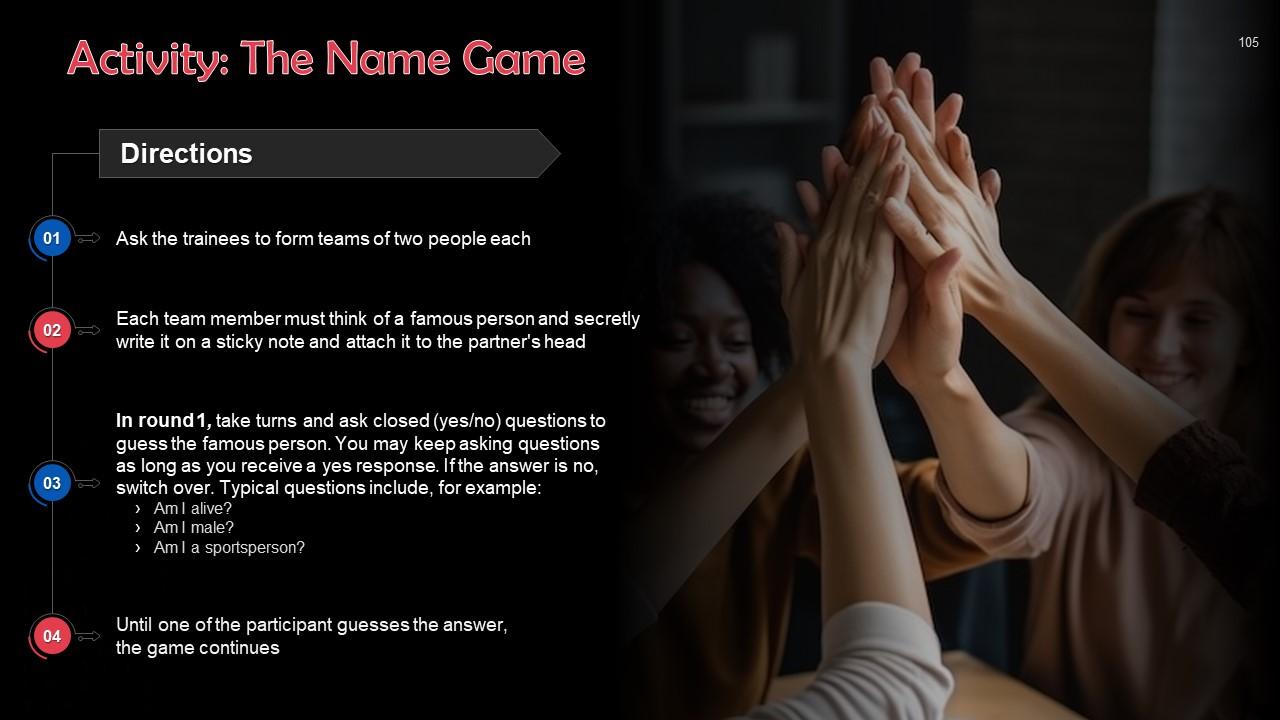
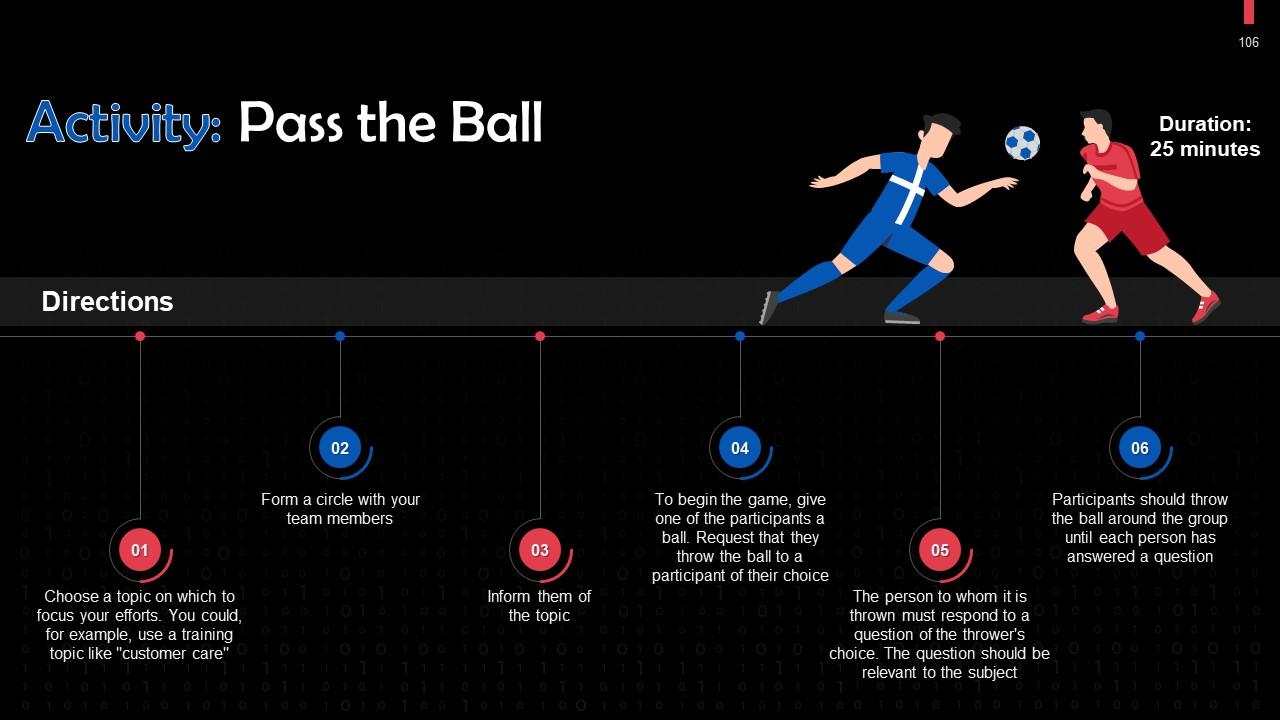
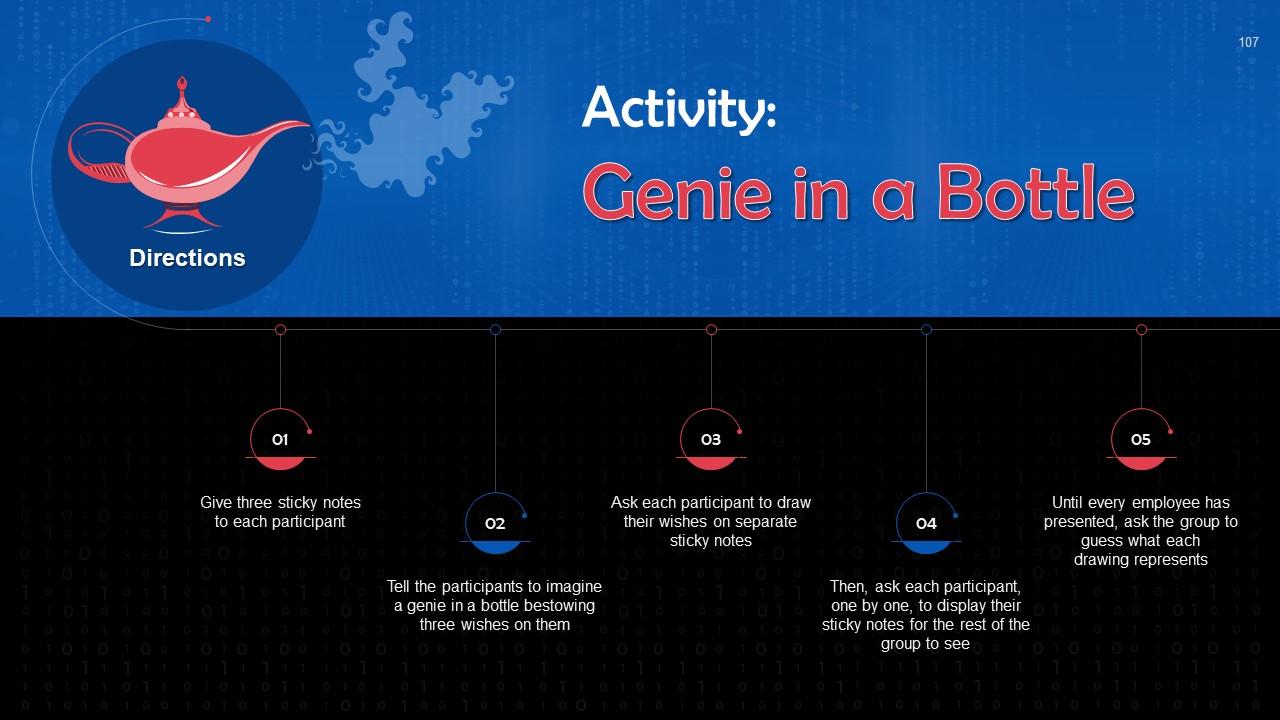
Slide 100 to 115
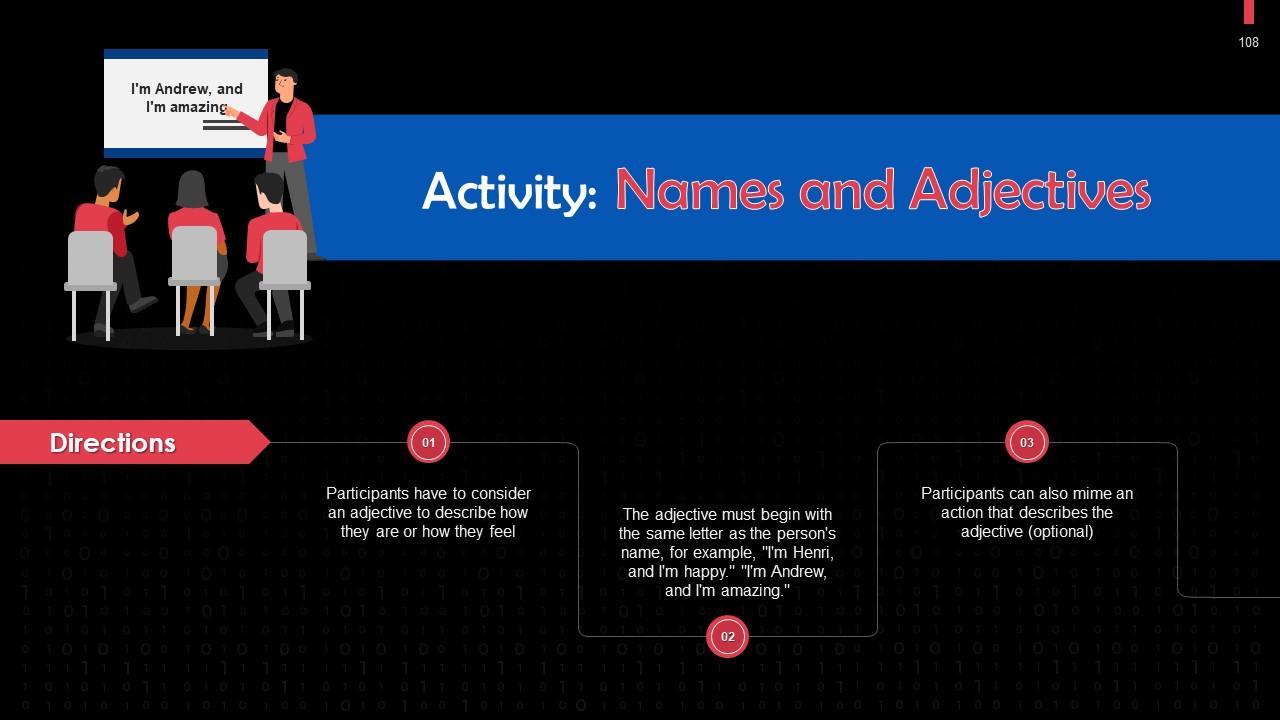
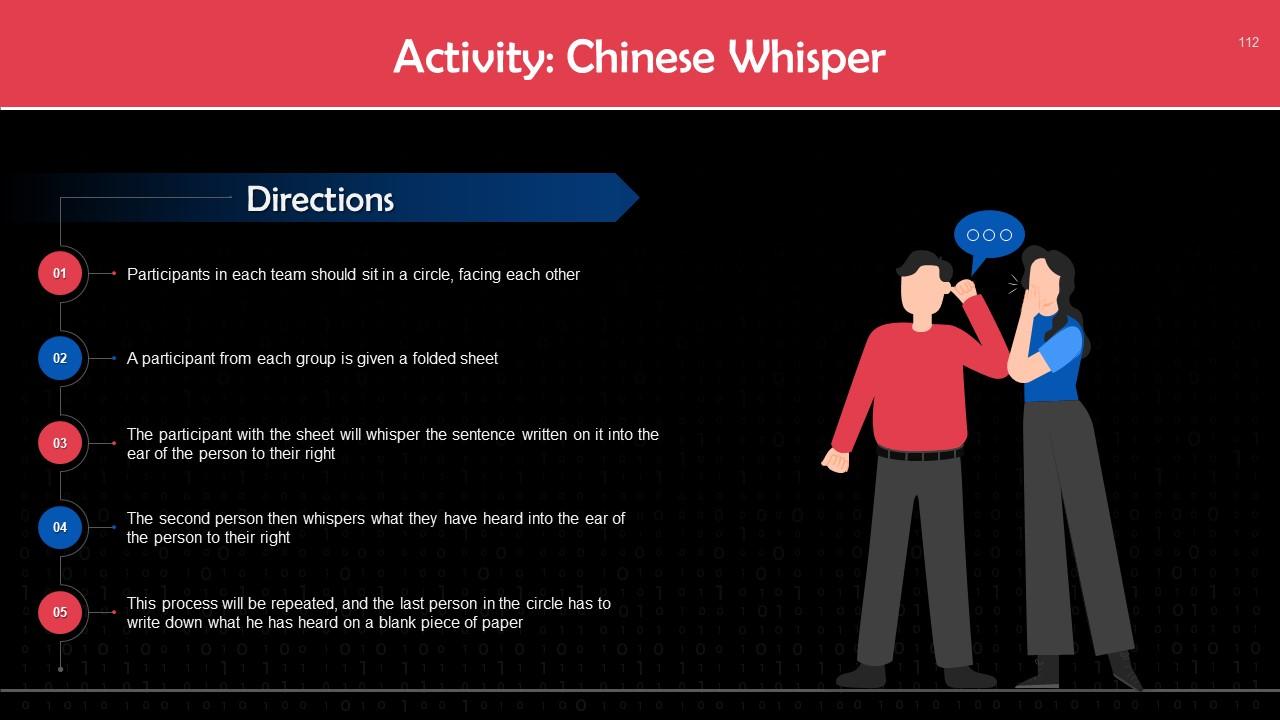
This slide depicts an energizer activity to engage the audience of the training session.
Prevention of Cyber Attacks Training Ppt with all 124 slides:
Use our Prevention of Cyber Attacks Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Good research work and creative work done on every template.
-
Every time I ask for something out-of-the-box from them and they never fail in delivering that. No words for their excellence!