Popular Types Alternative Coins In Cryptocurrency Training Ppt
These slides provide in-depth information about the alternative coins in cryptocurrency, which are mining-based coins, stablecoins, meme coins, security tokens, utility tokens, and governance tokens. Further, it also covers the stablecoins types such as fiat-collateralized, commodity-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and non-collateralized.
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Popular Types Alternative Coins in Cryptocurrency. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support is available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon, and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1
This slide introduces the concept of Altcoins. Altcoins refer to cryptocurrencies other than bitcoin. They have some similarities to bitcoin, but differ in other ways.
Slide 2
This slide highlights similarities and differences between Bitcoin and altcoins. Even as both have a similar structure, altcoins build on bitcoin’s perceived drawbacks to gain a competitive advantage.
Slide 3
This slide lists types of altcoins such as coins that are mining based, stablecoins, security tokens, meme coins, utility tokens, and governance tokens
Slide 4
This slide talks about mining-based altcoins. These coins, as the name suggests, are created through mining. Proof of Work (PoW) is a mechanism through which systems generate new coins by solving cryptographic problems to build blocks. Most mining-based Altcoins are using this.
Slide 5
This slide introduces the concept of stablecoins. Stablecoins are digital assets linked to the value of another currency, commodity, or financial instrument.
Slide 6
This slide discusses the main aim of stablecoins, which is to ensure that value of cryptocurrency remains stable.
Slide 7
This slide highlights the four types of stablecoins. These are fiat-collateralized, commodity-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and non-collateralized.
Slide 8
This slide discusses Fiat-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Fiat-collateralized stablecoins are backed by sovereign money such as the Pound Sterling or the US Dollar. To issue a specific number of cryptocurrency tokens, the issuer must provide dollar reserves in the same amount as the collateral
Slide 9
This slide discusses Commodity-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Transferable assets like precious metals, oil, real estate etc can back Stablecoins with collateral. Among these, Gold is the most commonly collateralized asset.
Instructor’s Notes: The value of a real-world asset is also, essentially, exposed to the behaviour of holders of commodity-collateralized stablecoins. These assets can appreciate or depreciate over time, which might impact trade incentives.
Slide 10
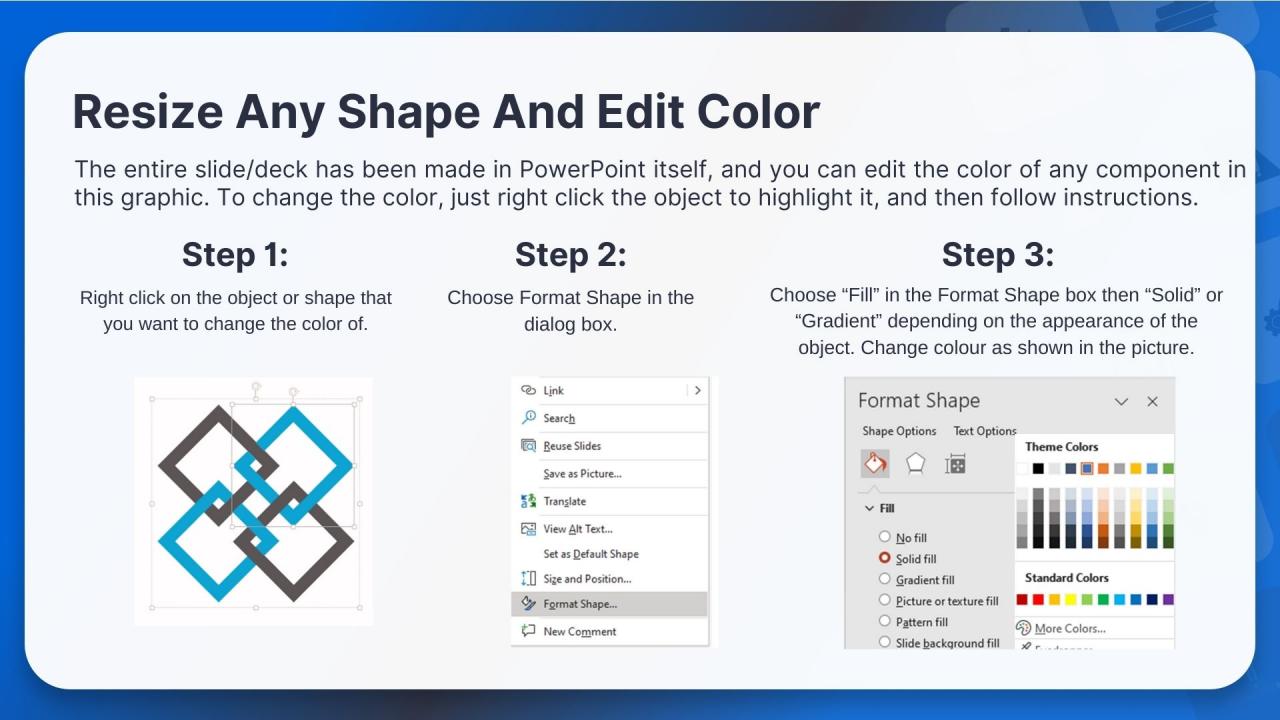
This slide discusses Crypto-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Crypto-collateralized stablecoins are backed by other cryptocurrencies and are over-collateralized.
Instructor’s Notes: For example, to obtain $500 in stablecoins, you must invest $1,000 in Ether (ETH). The stablecoins are now 200 percent collateralized in this situation, and even if the price drops by 25%, the $500 worth of stablecoins is secured by $750 worth of the ETH.
Slide 11
This slide discusses Non-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Non-Collateralized or Algorithmic stablecoins may or may not hold reserve assets. They keep the stablecoin's value stable. This is done through an algorithm, essentially, a computer program that runs a preset formula to control the stablecoin's supply.
Instructor’s Notes: For example, to obtain $500 in stablecoins, you must invest $1,000 in Ether (ETH). The stablecoins are now 200 percent collateralized in this situation, and even if the price drops by 25%, the $500 worth of stablecoins is secured by $750 worth of the ETH.
Slide 12
This slide lists applications of stablecoins. These include the use of stablecoins as a day-to-day currency which is fast & affordable, streamlining recurrent and P2P payments, and providing protection from local currency crashes & market volatility.
Instructor’s Notes:
- A day-to-day currency: Well-designed stablecoins have the potential to be used in commerce just like any other currency. Since no conversion of multiple fiat currencies is required, stablecoins might be used for international money transfers
- Fast & affordable remittances for migrant workers: Many migrant workers currently rely on businesses to transfer money back to their families, which is time-consuming and expensive. Stablecoins can be a better alternative. Workers and their families can use digital wallets to receive stablecoins almost instantaneously from anywhere globally, with low fees and no price volatility
- Streamlining recurrent and P2P payments: Enforcement of smart contracts is also possible with stablecoins. An employer, for example, may set up a smart contract that automatically transfers stablecoins to its employees at the end of each month
- Improve cryptocurrency exchanges: Due to rigorous rules, only a few cryptocurrency exchanges presently offer fiat currencies. However, by simply employing a USD-backed stablecoin instead of actual dollars, exchanges can get past this obstacle and provide crypto-fiat trading pairings. This encourages the general acceptance of cryptocurrency trading since it simplifies the process and allows them to continue thinking in terms of dollars or euros rather than fluctuating bitcoin values
- Protection from local currency crashes & market volatility: Local citizens may instantly trade their crashing currency for comparatively safe USD-backed, EUR-backed, or even gold-backed stablecoins, shielding themselves from further value erosion
Slide 13
This slide highlights the limitations of Stablecoins. The major ones are people’s trust in the solvency of the organisation backing the stablecoin, lower probability of making gains by trading in stablecoins etc
Slide 14
This slide discusses risks and regulations associated with Stablecoins. These are: systematic risk & loss of value, threat to market integrity & investor protection, illicit activity, and tighter regulations.
Instructor’s Notes:
Systematic risk & loss of value: Economic power would be excessively concentrated in a single entity with centralized coins, such as thosethose having fiat backing and that private entities produce. Tether, for example, with its current market share of more than 50%, poses such a threat. Tether's failure could jeopardize an entire ecosystem of apps, businesses, and users who rely on it. Investors may try to cash out their stablecoins if the economy overheats and the value of Tether's non-cash collateral plummets, only to discover that the issuer is unable to return the entire money invested (referred to as 1:1 ratio)
- Threats to market integrity & investor protection: According to the US Treasury Department, the ease and speed of transacting with stablecoins encourage speculative trading of digital assets, endangering market integrity and investor protection
- Illicit activity: Stablecoins could be misused to break laws on Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-terrorist Financing Legislation (CFT). The increased use of stablecoins for cross-border transactions, the lack of international standards for stablecoin providers, the irregular implementation of AML/CFT standards among different countries, and the possibility of anonymity while transacting in stablecoin are all factors that contribute to the risk of the currency being misused for illicit activity
- Tighter regulation: To address the prudential risks of stablecoins, the US Treasury advocated stricter regulation in 2021. These recommendations included that the stablecoin issuers must be insured depository institutions, custodial wallet providers must be subject to "appropriate federal oversight," and interoperability standards must be implemented across stablecoins, among other requirements
Slide 15
This slide discusses security tokens as a type of altcoin. Security tokens are digital assets that are traded on stock exchanges. The transfer of value from an asset to a token made available to investors is known as tokenization.
Slide 16
This slide describes how a security token works. A security token could represent fractional ownership in almost any asset, including business shares, commercial real estate, fine art, and even antique cars. The issuer fractionalizes the asset into a certain number of tokens, which are then sold to investors in a regulated offering.
Instructor’s Notes: The adoption of blockchain technology removes roadblocks to the process of issuing security tokens and allows for a greater variety of securities to be launched into the market.
Slide 17
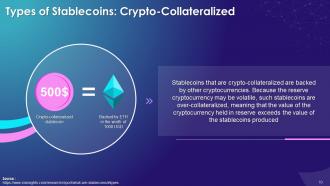
This slide depicts types of Security Tokens. The three main types are equity tokens, debt tokens, and real assets tokens.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Equity Token: Equity tokens represent the value of a company's shares on the blockchain. The technique of registering ownership distinguishes an equity token from a standard stock. A traditional stock is entered into a database and is represented by a paper certificate. On the other hand, an equity token is recorded on an immutable blockchain
- Debt Token: These tokens represent real estate mortgages, corporate bonds, and other debt instruments. These tokens typically pay a regular interest based on the underlying debt instrument's payments. In debt valuation, a debt token is exposed to the risk of debt default. A smart contract can represent the security token, which contains repayment terms and risk indicators related to the underlying debt
- Real Assets Token: They represent ownership of any real-life asset, like commodities, real estate, artwork, etc. Blockchain technology enables transparent records of complex transactions and aids in tracking entities, lowering the risk of fraud
Slide 18
This slide talks about meme coins as a type of altcoin. Meme coins are cryptocurrencies inspired by the Internet and social media memes or jokes. They are highly volatile and are primarily community-driven.
Slide 19
This slide discusses the reason behind meme coins’ popularity. It is difficult to identify particular reasons, some claim that the crypto market grew during the COVID-19 pandemic as retail investors sought to hedge against inflation. Meme coins grew in market valuation due to the hype.
Slide 20
This slide lists popular meme coins. These are: Dogecoin (DOGE), Shiba Inu (SHIB), Dogelon Mars (ELON), and Samoyedcoin (SAMO).
Instructor’s Notes:
- Dogecoin (DOGE): Software programmers Billy Markus and Jackson Palmer founded Dogecoin (DOGE) in 2013. It was designed as a joke cryptocurrency to grab mainstream attention and was inspired by a Shiba Inu dog meme. DOGE uses the same Proof of Work (PoW) process as Litecoin (LTC) and has no limit on supply
- Shiba Inu (SHIB): Shiba Inu (SHIB) is DOGE's main competitor, known as the "Dogecoin killer." A Japanese dog breed inspired SHIB, and in August 2020, an anonymous developer named Ryoshi produced it. The primary distinction between DOGE and SHIB is that the latter has a finite quantity of 1 quadrillion tokens, of which 50% were burned and donated to charity
- Dogelon Mars (ELON): ELON is named after the CEO of Tesla, Elon Musk. It is a fork of Dogecoin with a 557 trillion token circulating supplyLaunched in April 2021, ELON had risen 3780% in value by November 2021, ELON has increased by nearly 3,780% as of November 2021
- Samoyedcoin (SAMO): Samoyedcoin is a Solana blockchain-based dog meme coin project. Over 13% of SAMO supply was airdropped to community members upon launch. SAMO's roadmap includes burning events (sending cryptocurrency to an unusable wallet to remove that amount of it from circulation), airdrop tools, a decentralized exchange, and the construction of NFTs. Within a month, SAMO had grown by nearly 4,300%. In 30 days in October 2021, the price skyrocketed from $0.005 to almost $0.22
Slide 21
This slide discusses utility tokens as a type of altcoin.Utility tokens are used to deliver network services. They could be used to buy services, pay network costs, or redeem rewards.
Slide 22
This slide discusses governance tokens as a type of altcoin. Governance tokens grant holders certain privileges on a blockchain, such as voting on protocol modifications or having a role in Decentralized Autonomous Organization decisions (DAO). Examples are: Uniswap (UNI) and Compound (COMP).
Slide 23
This slide lists advantages and disadvantages of altcoins. The benefits include high potential rewards, certain advantages over Bitcoin, and the presence of multiple coins that bring different competitive advantages. The drawbacks are that they don’t have a first-mover advantage, many of them are scams or fail, and that they are difficult to obtain being available only on a few exchanges.
Slide 24
This slide discusses governance tokens as a type of altcoin. Governance tokens grant holders certain privileges on a blockchain, such as voting on protocol modifications or having a role in Decentralized Autonomous Organization decisions (DAO). Examples are: Uniswap (UNI) and Compound (COMP).
Slide 25
This slide lists popular Altcoins. These include Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, and USD Coin
Instructor’s Notes:
- Ethereum: Ethereum was the first cryptocurrency to introduce a programmable blockchain for developers in July 2015. It rapidly overtook Bitcoin as the most popular cryptocurrency
- Cardano: Cardano is a two-layer solution with a difference. The platform has a control layer and a unit of account that manages the use of smart contracts, recognizes identity, and maintains a degree of separation from the money it supports
- Solana: Solana is an open-source project founded and managed by the Solana Foundation in Geneva in 2017. Solana Labs in San Francisco developed the blockchain. Compared to other blockchains like Ethereum, Solana is substantially faster in transaction processing and has significantly cheaper transaction costs
- USD Coin: USD Coin, a stablecoin launched in September 2018 is linked to the US dollar. Centre, a consortium that includes Coinbase Global, Inc., founded this coin
Slide 26
This slide discusses the future of Altcoins. The current status of the altcoin marketplaces suggests that a single cryptocurrency is unlikely to dominate. However, most of the hundreds of altcoins listed on crypto exchanges are unlikely to survive. The altcoin market will ultimately be reduced to a handful of these that will dominate the markets.
Instructor’s Notes: Altcoins are likely to be less expensive than Bitcoin. Regardless of the coin type, the cryptocurrency market is new and volatile. With cryptocurrencies still figuring out their place in the global economy, it's advisable to proceed with caution while dealing with it.
Popular Types Alternative Coins In Cryptocurrency Training Ppt with all 42 slides:
Use our Popular Types Alternative Coins In Cryptocurrency Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Use of icon with content is very relateable, informative and appealing.
-
The PPT layout is great and it has an effective design that helps in presenting corporate presentations. It's easy to edit and the stunning visuals make it an absolute steal!