Power Of Feedback Training Ppt
The PPT Training Module on Power of Feedback explores the essence of feedback in the workplace and highlights its pivotal role in enhancing individual and organizational growth. It begins with How Well do I Give Feedback and How Well do I Receive Feedback and progresses to Defining Feedback and its Purpose, laying a solid foundation on the subject and its objectives. The PowerPoint Deck then explores Attributes for Giving and Receiving Feedback Effectively, Benefits of Feedback and eye-opening Statistics Related to Workplace Feedback, and navigates through Common Pitfalls in Feedback Delivery. It categorically addresses Types of Feedback with emphasis on Conduct-based Formal and Informal, Source-based Managers Feedback, Peer-to-Peer Feedback, Self-Feedback, and Tone-based feedback Positive, Negative, Constructive, Destructive Feedback, dissecting each for a comprehensive understanding. The PowerPoint Deck concludes with Key Takeaways and Discussion Questions, designed to engage participants in thoughtful reflection and discussion.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Power of Feedback. This deck comprises of 74 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 3
This slide lists questions that can be used to evaluate one's feedback giving skills. The requirements for giving effective feedback to the employees are: picking a suitable time and place to share feedback, paying heed to the responses of those receiving the feedback, etc.
Instructor's Notes:
How to evaluate?
- If most of the questions are answered with response “often,” person has well developed feedback giving skills
- If response to several questions is done with “rarely” or “sometimes,” the person’s feedback skills probably require further development
Slide 4
This slide lists questions that can be used to evaluate one's feedback receiving skills. The requirements for receiving feedback effectively are: Genuinely listening to what feedback givers are saying, being keen to learn from feedback about my behavior or performance at work, accepting reinforcement and redirection, etc.
Instructor's Notes:
How to evaluate?
- If most of the questions are answered with response “often,” person has well developed feedback giving skills
- If response to several questions is done with “rarely” or “sometimes,” the person’s feedback skills probably require further development
Slide 5
This slide includes an activity that highlights the need of feedback across various levels at the workplaces.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Here, the Area Director did not provide the Division Manager with any feedback, which made her ambiguous about the quality of her work
- The Area Director should have provided the feedback in a timely manner
Slide 6
This slide lists an activity involving an employee and their supervisor. It highlights the need of providing specific feedback across levels at the workplaces.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Although the employee is happy to learn that the boss liked her work, but is unclear what actions she should continue to get the same recognition in the future
- In the feedback, the supervisor should have specified the details of the good work that the employee had done
Slide 7
This slide highlights the meaning and purpose of feedback. It is any response to a business practice, whether it is provided by the clients or customers, or by the employees or leadership team and is directed towards future betterment.
Slide 8
This slide contains information about the characteristics of giving feedback in an organization which are: on a timely basis, specific, recurring, collaborative, non- judgmental, lacking comparison, specific to the employee’s performance, sensitivity towards the feedback receiver, and tied to an action plan.
Instructor's Notes:
Following are the attributes for giving effective feedback:
- On a Timely Basis: There is no use in offering feedback after the person concerned has put the work aside and moved to other things. Feedback must be well-timed to facilitate greater learning and better employee performance
- Specific: Feedback comments should be based on the concrete, observable behavior of employees. This is only possible when an employee is clear about what is expected from them and how they are supposed to act. The concerned employee must be provided with a clear-cut idea of what is being said
- Recurring: Performance reviews should be scheduled monthly or quarterly so as to facilitate a better learning and understanding of things than waiting for the annual reviews. Also, it gives the employees an opportunity to voice their concerns and thoughts at regular intervals
- Collaborative: Being collaborative provides a room for the employee to contribute to the feedback process by offering solutions and doing self-assessment. One-sided talks may make the employees feel as if they are being scolded. So, encouraging them to talk about ways to improve, and recognizing their own performance shortcomings aids in effective feedback
- Non-Judgmental: Avoiding a judgmental attitude will decrease the possibility of employee becoming negative and defensive upon receiving feedback. While sharing feedback, specific inputs rather than value-laden statements will make the employee want to improve. Words like, 'I feel....when you..' could be used
- Avoid Comparison: The context of feedback must be chosen cautiously. Each person's work must be treated as their own, as any sort of comparison will only sabotage intrinsic motivation
- Sensitivity Towards the Feedback Receiver: Sometimes, common goals are not accomplished due to lack of some other individual’s contribution. So, it is necessary that the feedback giver should listen to the feedback receiver’s side of story
- Tied to an Action Plan: While equipping the employee with feedback, managers should also provide measures or actions to be taken to achieve desired results. Employees should know exactly how to work on things and the steps involved in doing so to improve their performance/behavior
Slide 9
This slide lists the characteristics for effectively receiving feedback at the workplace. These are: Be explicit, be attentive, be aware, understand the message, reflect and decide what to do, and be open.
Instructor's Notes:
Following are the attributes for receiving feedback effectively:
- Be Explicit: Being explicit relates to clarifying what kind of feedback one seeks. Feedback from others is entirely for the benefit of the person asking for it, so if one doesn't define what they want, they're unlikely to get it
- Be Attentive: Being attentive requires concentrating fully on what is being said without interrupting the other person. One can absorb more information, if the focus is on listening and understanding instead of being defensive and focusing on their own response
- Be Aware: The body language and tone of the voice of the person receiving feedback reflects a lot about their behavior. A distracted and bored look sends a negative message. At the same time, attentiveness indicates a keen interest in what the individual has to offer
- Understand the Message: The person receiving the message must try to comprehend what is being said by actively listening to the critical points before responding to feedback. In a group environment, others' feedback must be considered before responding
- Reflect and Decide what to Do: Assessing the value of the feedback and the consequences of using it or ignoring must be determined before deciding what to do with it. A person's response to feedback is their own choice. A second opinion could be sought if one disagrees with the feedback
- Be Open: Being open requires being receptive to new ideas and opinions. There could be more than one way of doing something, and others might have a completely different viewpoint on a topic which can lead to learning something new and worthwhile
Slide 10
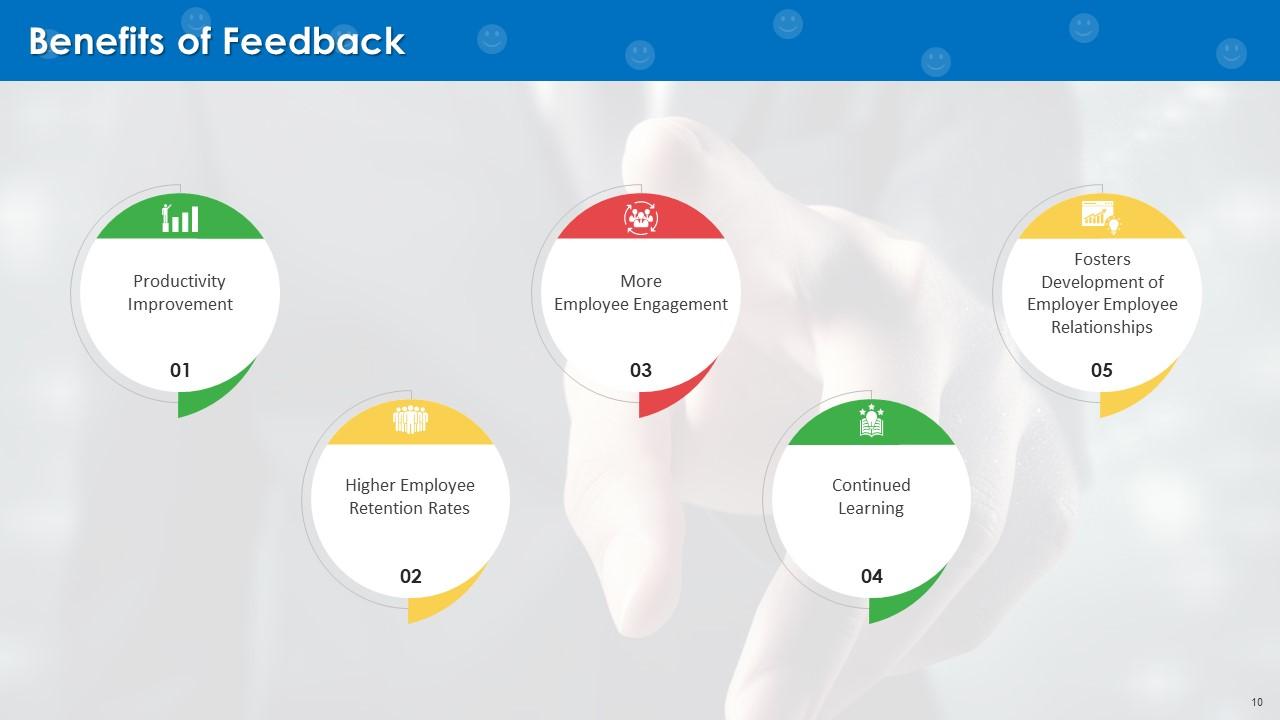
This slide represents the advantages of feedback which are: Productivity improvement, higher employee retention rates, more employee engagement, continued learning, and fosters development of employer employee relationships
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are the benefits of feedback:
- Productivity Improvement: Any new task can seem difficult for an employee who has never done it before, but things start to fall into place after being given the proper guidance. Continuous feedback allows an experienced employee to share knowledge with a novice, thus increasing productivity. Also, not only will it improve the turnaround time on that particular task, but for future projects as well
- Higher Employee Retention Rates: Regular feedback improves staff retention in the workplace by making them feel that their opinions are respected and valued. Moreover, if the manager is invested in assisting the employee through challenging tasks, they will be able to recognize and make adjustments at work when required. So that employees also don't feel dejected. Thus improving employee retention rates
- More Employee Engagement: Workplace feedback is not just about development but also an opportunity to encourage employees' achievements. There is a strong connection between feedback exchange and employee engagement rates. It makes the employee and team efforts to be recognized on a more regular basis
- Continued Learning: To continuously improve its offerings, an organization needs to stay well connected from within, aligned with its objectives. So, it is essential to gain an insight into how employees feel about being linked with the organization goals for which feedback is the key
- Fosters Development of Employer Employee Relationships: Practicing consistent feedback at the workplace allows management and employees to interact more often, so that they know each other better on a professional level which foster effective employee relationships
Slide 11
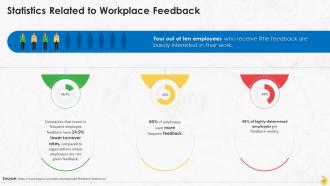
This slide highlights interesting statistics and figures related to feedback in organizations across hierarchical levels.
Slide 12
This slide lists types of ineffective feedback at the workplace which are: Making feedback too personal, making feedback too impersonal, ,“sandwich-ing” negative feedback, self-assumptions by the manager, postponing feedback, and setting vague expectations.
Slide 13
This slide highlights how making feedback too personal leads to ineffective feedback. Often managers address issues related to an employee's performance as being problems with employees themselves, rather than taking it as an issue related to skill or approach.
Slide 14
This slide highlights how making feedback too impersonal leads to it becoming ineffective. Sometimes, managers tend to overcorrect issues to avoid personal accusations. This leads to insufficient feedback and the employees won’t feel the need to improve their performance at all.
Slide 15
This slide highlights how “sandwich-ing” negative feedback makes it ineffective. The manager tries to sugar coat the negative feedback, so that he doesn't seem unkind. It usually leads to the employee only focusing on the positive feedback and ignoring the negative one.
Slide 16
This slide highlights how manager’s presumptions render the feedback ineffective. Providing feedback to employees on guesswork and insight could, at times prove uncomfortable and insulting to the employee.
Slide 17
This slide highlights how postponing feedback makes it ineffective. Receiving feedback long after the occurrence of the event makes it near impossible to improve the situation.
Slide 18
This slide highlights how setting vague expectations makes feedback ineffective. Ensuring that both the manager and employee are on the same wavelength is another one of the main challenges of giving effective feedback in an organization.
Slide 19
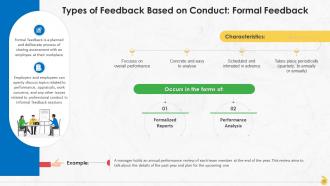
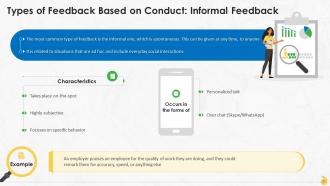
This slide showcases two types of feedback based on conduct, which are formal and informal feedback.
Slide 20
This slide contains information on formal feedback. It is a planned and deliberate process of giving feedback to an employee at their workplace. It takes place annually or bi-annually, is scheduled in advance, is provided through formalized reports, and is concrete and easy to analyze.
Slide 21
This slide contains information on informal feedback. It is the most common type of feedback. It is spontaneous and can happen at any time, between anyone. It takes place on-the-spot, is highly subjective, and focuses on specific behavior.
Slide 22
This slide tabulates differences between formal and informal feedback at workplaces, on parameters such as mode of conduct, sources, and timing.
Slide 23
This slide showcases three types of feedback based on the source. These are manager’s feedback, peer-to-peer and self-feedback.
Slide 24
This slide contains information about manager’s feedback. It happens when the manager gives feedback to employees in the form of annual or quarterly reviews, 360-degree feedback, etc.
Slide 25
This slide contains information about peer-to-peer feedback. It happens when co-workers give each other informal feedback and share their understanding of getting the job done.
Slide 26
This slide contains information about self-feedback wherein the person evaluates his performance and self-reflects on his work.
Slide 27
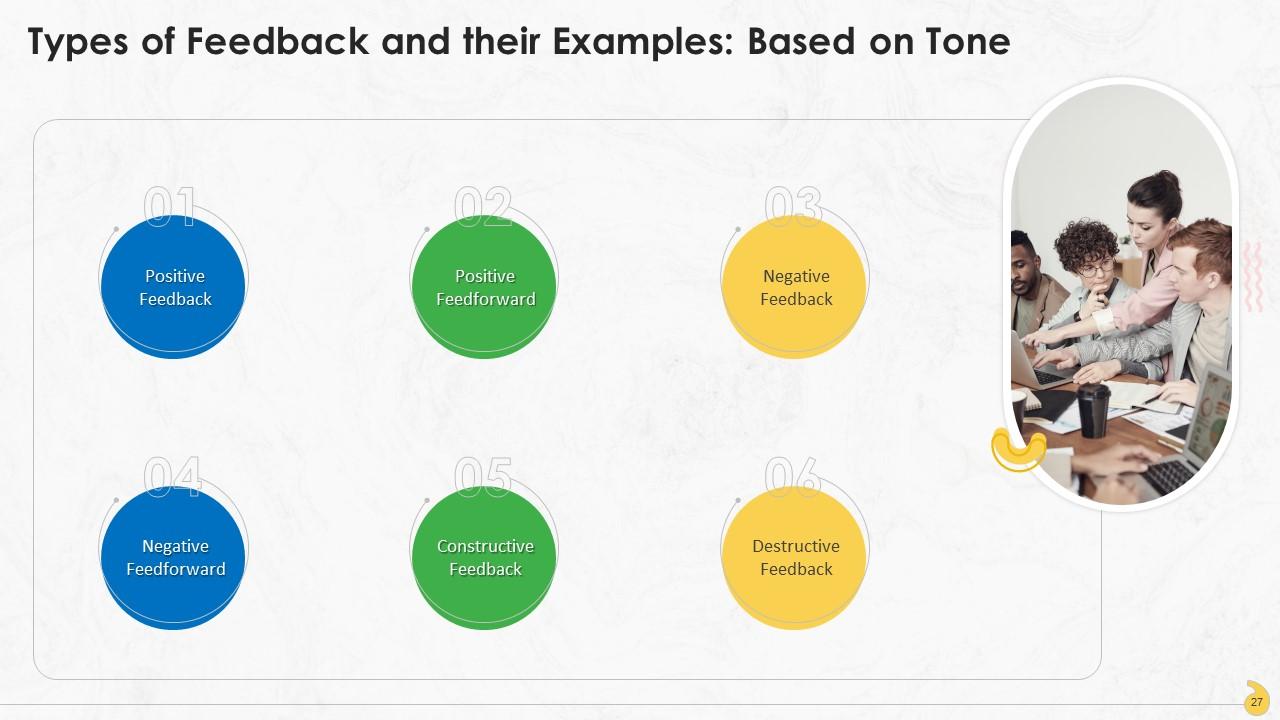
This slide showcases types of feedback based on tone. These are positive feedback, positive feedforward, negative feedback, negative feedforward, constructive feedback, and destructive feedback.
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are types of feedback based on tone:
- Positive Feedback: Positive feedback appreciates particular acts, work or behavior of a person. It helps reinforce good behavior and facilitates professional development
- Positive Feedforward: Positive feedforward focuses on giving comments to affect someone's behavior with the use of affirming words. Negative feedback that may dishearten someone can be avoided by motivating an employee with positive feedforward
- Negative Feedback: Negative feedback is the one that no one wants to hear. Once given, the person concerned might also feel demotivated or misjudged at work. Thus, negative feedback should be strategically used so that it is effective
- Negative Feedforward: Negative feedforward keeps employees on the right path; it also ensures no employee develops habits that hit work performance. Negative feedforward addresses workplace behavior that needs to be shunned at the earliest
- Constructive Feedback: Constructive feedback focuses on the employee's work rather than the person. Made up of positive and negative comments, constructive feedback is based on solid points and observations that benefit the individual concerned
- Destructive Feedback: Destructive feedback being the complete opposite of constructive feedback. It is very personal in nature and focuses only on the individual. It contains little productive advice and tends to point out faults without providing any solutions
Slide 28
This slide highlights the positive feedback that praises a person’s actions, work or behavior at the workplace. Some scenarios for providing positive feedback would be: To acknowledge strong problem-solving skills of an employee, when an employee takes up new responsibilities, and after a particularly productive phase.
Slide 29
This slide provides information on why positive feedback is essential at the workplace. Positive feedback is vital as it leads to: Improved productivity, cost-effectiveness, involved employees, enriched communication, and shapes company culture.
Instructor’s Notes:
Benefits of positive feedback at workplace are:
- Improves Productivity: It's natural that employees when receive constant positive feedback from their superiors, will feel more motivated and inspired to work towards individual and team goals. . Ultimately, all of this is linked to productive and timely achievement of organizational goals
- Cost-Effective: Developing a positive environment can reduce attrition leading to cost-effectiveness. Lack of positive feedback decreases employees' morale, leading to increased turnover. Hiring and developing new talent adds to organizational costs
- Involves Employees: Constant regular feedback leads to more engaged and content employees. They have a sense of purpose and a better understanding of their roles in the organization. Such employees are motivated and more encouraged to share new ideas and opinions
- Enriches Communication: Regular feedback helps keep communication channels open between the one giving feedback and the employee. This enriches communication even more. When employees receive positive feedback about their strengths, it prompts greater discussion and understanding on how to drive organizational growth
- Shapes Company Culture: Positive feedback helps establish a base for good work culture at the organization. Rewarding a few team members with positive feedback would motivates all to excel
Slide 30
This slide contains information about the errors that need to be avoided, while delivering positive feedback at the workplace. These are: Ignoring difficult conversations while forcing positivity, focusing on ability rather than effort, and giving positive feedback in an indirect manner.
Instructor’s Notes:
Mistakes with positive feedback are:
- Ignoring difficult conversations while forcing positivity: One of the biggest mistakes while delivering positive feedback is sugar-coating and avoiding an actual problem and concentrating on just the positive aspects. If it is evident that a problem exists, reinforcing only positive feedback is meaningless. Make sure the problem is addressed
- Focusing on ability rather than effort: Adopting a fixed mindset for measuring employees' capability is a major hindrance, hindrance while providing positive feedback. Giving weightage only to employees' ability rather than their effort can demotivate them. Using words like, "You kept trying and did your best!" contribute to a growth mindset
- Giving positive feedback in an indirect manner: Giving positive feedback in a non-verbal way or in the form of gossip is no good. Making positive comments behind someone's back rarely reach the person concerned. Also, non-verbal feedback given in an indirect way doesn't count as positive feedback
Slide 31
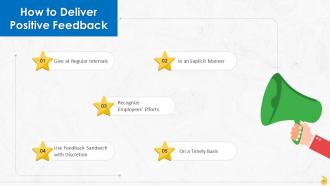
This slide lists tips for delivering positive feedback at work which are: Give at regular intervals, in an explicit manner, recognize employees’ efforts, use feedback sandwiched with discretion, and on a regular basis.
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are the techniques for delivering positive feedback at workplace:
- Give at Regular Intervals: Giving positive feedback at regular intervals indicates that the organization cares about both its as well as employees' personal goals. So, positive feedback should be shared with employees at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, annually)
- In an Explicit Manner: While delivering positive feedback, the person giving feedback should be clear about what he has to say, and vague statements are a big no. The comments/praise should be based on data reflecting legitimate efforts of the employee. This practice will also improve the leadership skills of the feedback giver
- Recognize Employees’ Efforts: Positive feedback directed towards employees' efforts boosts their determination, self-confidence and motivates them. While giving positive feedback, emphasis should be on actions and behaviors rather than the aptitude and personality traits of the employee
- Use Feedback Sandwiched with Discretion: Some managers rely on the "feedback sandwich “approach for giving positive feedback. They begin by providing positive feedback, then talk about areas of improvement, followed by positive feedback. It should be accurately used so that employees can see the true picture of their performance
- On a Timely Basis: Positive feedback should definitely be provided right after the employee has done a deserving task. Waiting for a scheduled performance review or meeting to give positive feedback to employees is usually less impactful; employees might feel their work has gone unrecognized
Slide 32
This slide contains information as to how to give feedback when an employee takes an initiative at the workplace.
Slide 33
This slide contains information as to how to give feedback when an employee meets a goal at the workplace.
Slide 34
This slide contains information as to how to give feedback when an employee overcomes a particular challenge.
Slide 35
This slide contains information as to how to give feedback when an employee helps co-workers.
Slide 36
This slide contains information as to how to give feedback when the employee introduces fresh ideas.
Slide 37
This slide contains information about the negative feedback at workplace, which is focused on pin-pointing employees' behaviors that need to be changed. It strengthens employees' ability to perform their tasks, makes them understand the organization's expectations from them, makes employees feel cared about and supported, and improves the manager's leadership skills.
Slide 38
This slide represents the pointers that explain why negative feedback is essential at the workplace. These are: Enhances team performance, improves manager's skills, betterment of work quality, clears expectations, helps employees feel supported, facilitates questions by the employee, and promotes loyalty.
Instructor’s Notes:
Negative feedback at workplace is vital as it:
- Enhances Team Performance: Negative feedback helps convey to team members or employees their unsatisfactory performance. Employees can improve their performance or meet or exceed the set standards only when critically evaluated
- Improves Manager’s Skills: Once a manager learns how to deliver negative feedback correctly, they feel more confident in their role. It also enhances their capability to tackle resistance from employees while delivering negative feedback
- Betterment of Work Quality: Negative feedback should be such that it doesn't make the team or employees feel that they are doing the job wrong. The goal is to make them perform better. Taking up what they are doing wrong, and an action plan to improve helps employees correct their mistakes
- Clears Expectations: Delivering negative feedback in an effective manner helps in making manager's expectations from the employees' crystal clear. It helps clear confusion, anxiety, or dilemma among employees, as everyone knows how to do their tasks correctly
- Helps Employees Feel Supported: Any feedback, be it positive or negative, is always better than no feedback. It makes employees feel that the organization is paying attention to their growth and that they are being taken care of
- Facilitates Questions by the Employee: Employees can ask questions when negative feedback is given to them. Well-delivered feedback facilitates conversation between the employer and employee where the employee can have a better idea of what is expected and have their queries addressed as well
- Promotes Loyalty: Correctly given negative feedback will make the employees feel seen and supported, making them feel happier and satisfied at work. This implies that employees will be motivated to perform better and are less likely to leave the organization
Slide 39
This slide lists tips on how to deliver negative feedback in a positive manner which are: Keep your emotions balanced, schedule a feedback meeting, center the feedback on behavior, not the employee, omit superficial comments, make sure the feedback is prompt, have a conversation, and create an action plan and follow-up.
Slide 40
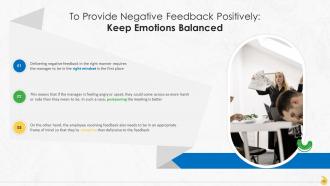
This slide contains information about keeping emotions balanced to deliver negative feedback in a positive manner at the workplace. It is important that the manager’s as well as the employee’s emotions are at on an even keel so that the feedback is effective.
Slide 41
This slide contains information about scheduling a feedback meeting to deliver negative feedback positively. The employer should schedule a meeting well in advance, where both the parties can comfortably have a conversation.
Slide 42
This slide contains information about positioning the negative feedback around employee’s behavior and not the employee. Which, if not done, might result in the employee feeling attacked or embarrassed and dilute the whole purpose of delivering negative feedback.
Slide 43
This slide contains information about omitting superficial comments while providing feedback. Adding superficial statements or compliments make it difficult for the employee to absorb the negative feedback.
Slide 44
This slide contains information about giving negative feedback timely so that its essence doesn’t get lost. Feedback should be given as soon as possible after the behavior that needs to be changed has occurred.
Slide 45
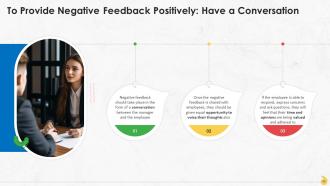
This slide contains information about having a conversational tone while delivering negative feedback. The employee should be given an opportunity to voice their issues and concerns (if there are any).
Slide 46
This slide contains information about creating an action plan and follow-up post negative feedback, wherein specific performance improvement goals and time for reaching those goals are specified.
Slide 47
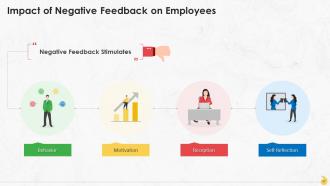
This slide represents the impact of negative feedback on employees’ behavior, their motivation level, their reception towards the feedback, and self-reflection.
Instructor’s Notes:
Negative feedback stimulates the following in employees:
- Behavior: When negative feedback is shared, it helps the employees amend their unacceptable and problematic conduct and also helps elicit new and acceptable conduct at the workplace
- Motivation: Negative feedback not only improves employees' behavior but also acts as a source of motivation. Some employees can take negative feedback as a challenge and use it as a means of improvement, while others would simply be driven to do a better job to avoid it
- Reception: The way employees perceive negative feedback will have a lot of impact on them. If not perceived with right mindset, negative feedback could lower employees' morale or make them dwell upon the negative aspects of the feedback
- Self-reflection: Optimistic employees assess the negative feedback as a learning opportunity and an indication to pay attention to their performance and make it better. Whereas, if employees take it negatively, it will prove as a hindrance in their growth
Slide 48
This slide showcases mistakes that need to be avoided while giving negative feedback at the workplace which are: Sugar-coating negative feedback, initiating conversation by being overly formal, backing down if the person is getting upset, emphasizing on an action plan without first agreeing on the problem, and only giving corrective feedback and ignoring the positive one.
Instructor’s Notes:
The mistakes that managers need to avoid while giving negative feedback are:
- Sugar-coating negative feedback: Sugar-coating negative feedback while being afraid of hurting the other person's feelings or triggering a negative response solves no purpose. Employees will not be able to decipher the information and won't take the feedback seriously. Instead, the manager should try to be direct and honest
- Initiating conversation by being overly formal: Managers often try to be too formal while giving negative feedback to reduce the chances of the situation getting heated up. This, however, may make the employee feel as if they are being scolded or reprimanded. Using a low-key approach involving respect and appreciation proves beneficial
- Backing down if the person is getting upset: Sometimes, negative feedback could trigger an emotional response in employee and they might become defensive or over-sensitive. Here, backing down from giving negative feedback would defeat the whole purpose of feedback and make the situation awkward. Complete feedback should be given, but the employee must be given sufficient time to compose himself/herself (if required)
- Emphasizing on an action plan without first agreeing on the problem: It would be wasteful if the manager focuses on developing the action plan for the problem if the employee, in the first place, is not ready to agree that the problem exists. Without understanding this, the employee won't be committed to an action plan and will focus on the 'perceived' unfair perspective of the manager
- Only giving corrective feedback and ignoring the positive one: Feedback in both its forms, positive and negative, is essential, and focusing on just the negative feedback is a big demotivator for employees. Thus, both of these have to be given appropriately and timely
Slide 49
This slide highlights the meaning and objectives of constructive feedback at the workplace. Constructive feedback is a skill sought to bring out the best in an employee or to maximize the quality of specific output by giving valuable suggestions or comments. The primary objectives of constructive feedback are: To reap results faster, motivate employees, identify weaknesses for improvement, and give new perspectives to situations.
Slide 50
This slide represents the constructive criticism sandwich, which begins with positive feedback and praising the employee, followed by delivering the negative feedback. Later on, motivate the employee with positive feedback and make him/her feel comfortable.
Slide 51
This slide showcases the techniques to be followed while giving constructive feedback at the workplace which are: Set SMART goals, emotional intelligence is key, ground constructive criticism in behavior, make it a continuous process, and have a conversation.
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are the techniques for delivering constructive feedback at the workplace:
- Set SMART Goals: Generally, goals set at the project initiation will be referred to while giving the feedback. The SMART framework, which stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-based, helps establish reference points while giving feedback. For example, while working on a marketing campaign, employees should know the kind of campaign, expected leads, duration, etc.
- Emotional Intelligence is the Key: While delivering constructive feedback, having an emotionally stable state of mind is a must to achieve the desired outcome. The manager has to be aware of their own and the employee's emotions and how the feedback will impact the receiver's and team's productivity
- Ground Constructive Criticism in Behavior: Constructive feedback describes the specific behavior that needs to be changed. Personal attacks on the employee will make him defensive and should always be avoided. For example, instead of saying to an employee that you want them to be more of a "team player," just describe the specific behavior you expect from their end
- Make it a Continuous Process: Constructive feedback should be inculcated in everyday communication. It has several benefits, like greater employee engagement and productivity. Moreover, it facilitates an informal learning process for the employee
Have a Conversation: Rather than just having a one-way conversation by criticizing an employee's work and giving suggestions for improvement, convert the whole thing into a conversation. Here, the manager should encourage equal participation and ask for employees' opinions on the feedback and their suggestions for an action plan
Slide 52
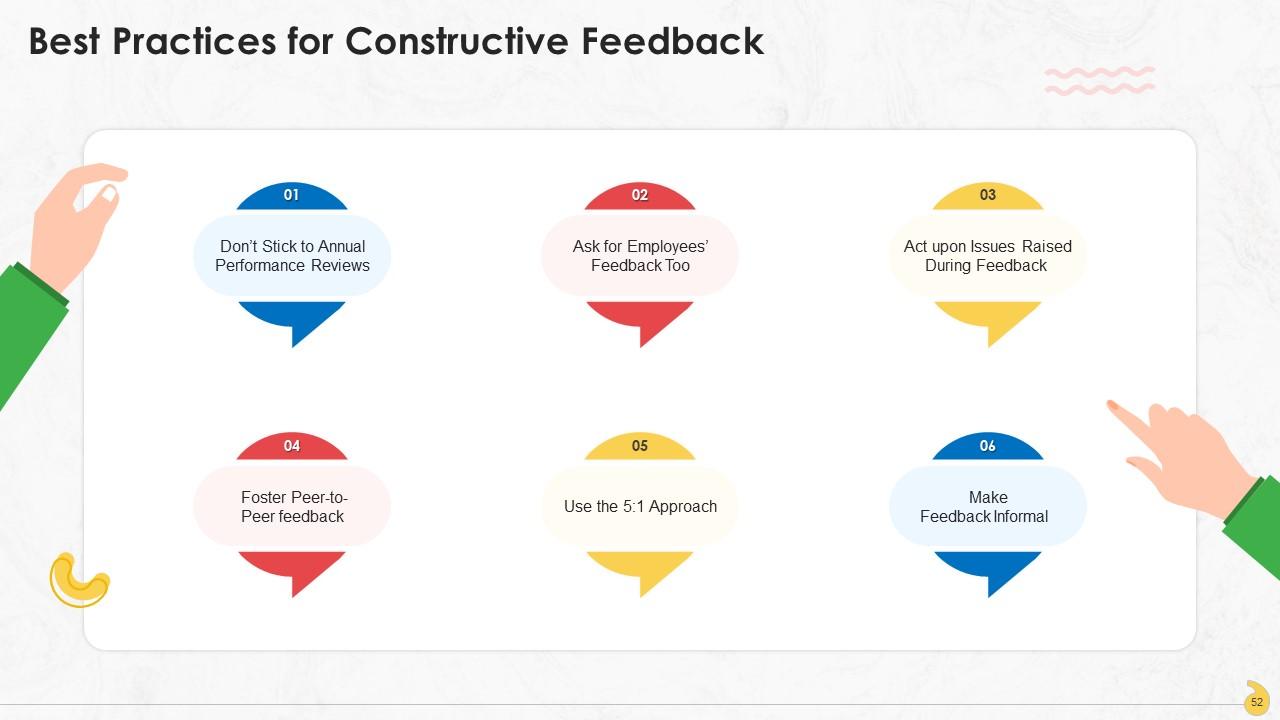
This slide lists constructive feedback best practices to be followed at the workplace which are: Don’t stick to annual performance reviews, ask for employees’ feedback too, act upon issues raised during feedback, foster peer-to-peer feedback, use 5:1 approach, and make feedback informal.
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are the constructive feedback best practices:
- Don’t Stick to Annual Performance Reviews: Employees won’t be able to amend their actions if they receive feedback after months. Avoid giving feedback only at the annual performance review, and give feedback more often
- Ask for Employees’ Feedback Too: Giving feedback becomes easier if the manager continually seeks feedback from the employees too. Reinforce the culture of giving and taking feedback on a company-wide basis
- Act upon Issues Raised During Feedback: Giving and receiving feedback is only relevant if the manager acts upon the issues raised. Not doing so will make the employees think their feedback and growth are unimportant to the manager. Moreover, employees must also be given every opportunity and means to improve their work to enhance the performance to a new level
- Foster Peer-to-Peer feedback: Feedback should not be given only in a top-down manner, but peer-to-peer feedback should also be fostered in the organization. It will help employees feel empowered at work and collaborate and communicate better with each other
- Use the 5:1 Approach: It is essential that employees are applauded for their achievements and accomplishments more often than giving them only negative feedback. The optimal ratio of positive to negative feedback at the workplace is 5:1
- Make Feedback Informal: Gen Y employees prefer informal feedback to formal reviews. It is unnecessary to schedule meetings every time to give feedback to the employees. However, feedback should be specific and goal-related even in an informal setup
Slide 53
This slide contains information about how to give constructive feedback to an unmotivated employee at the workplace.
Slide 54
This slide contains information about how to give constructive feedback to an employee who is not punctual.
Slide 55
This slide contains information about how to give constructive feedback to an employee who does not take initiative at the workplace.
Slide 56
This slide provides information about destructive criticism that may take place at the workplace. It often comes from an emotional outburst or a personal attack that harms, offends, or undermines the recipient. It is vague or non-specific and focused on personal attributes than the employee's actions.
Slide 57
This slide contains information about the consequences of destructive feedback at the workplace which are: Destroys team coherence, causes workplace conflict, affects employee performance, and creates a toxic work environment.
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are the consequences of destructive feedback at the workplace:
- Destroys Team Coherence: When one team member receives destructive feedback from the other, they are likely to be defensive during their next conversation with that person. It affects collaboration and coherence between team members; productivity and efficiency dip
- Causes Workplace Conflict: Destructive feedback may, at times, give rise to workplace conflict. The employee receiving it feels attacked and tends to counterattack, rather than resolving the situation
- Affects Employee Performance: Destructive feedback could prove devastating and can affect the employee's self-worth and confidence, hitting their work performance. The employee may not even try to put in effort into their work after destructive feedback from the manager
- Creates a Toxic Work Environment: Negativity is contagious, so destructive feedback can cause retaliation and negative emotions at the workplace, even if just one team member receives it. This affects the whole team and create a toxic working environment to a great extent
Slide 58
This slide contains tips for managers to deal with destructive feedback that may take place at the workplace. The first tip is to call out the destructive criticism. Then, it is also important to understand the context, assess the situation, and decide what action to take.
Slide 59
This slide highlights differences between constructive and destructive feedback based on intent, delivery, focus and specificity.
Slide 60
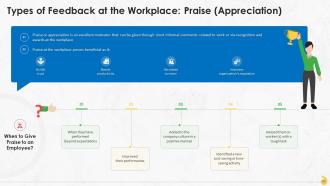
This slide highlights the importance of praise or appreciation at the workplace. It is an excellent motivator that can be given through short informal comments related to work or via recognition and awards. It aids in building trust, boosting productivity, decreasing turnover, and improving organization’s reputation.
Slide 61
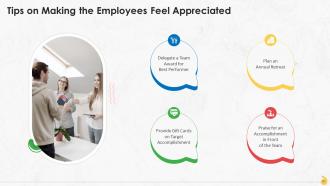
This slide lists tips on making the employees feel appreciated at the workplace. These are: associate tasks with rewards, delegate a team award, create an employee recognition program, plan an annual retreat, provide gift cards, and connect rewards to the organization.
Slide 62
This slide contains information about criticism at the workplace. It is a negative form of feedback used to draw attention to an employee's work that may be below par. Situations of criticizing an employee could be: To talk about areas of improvement, missed deadlines, when an employee lacks time management, and if employee has a negative attitude.
Slide 63
This slide lists tips on criticizing employees effectively at the workplace. The first is to treat criticism as a form of feedback; deliver criticism on an ongoing basis, use positive feed-forward instead of negative feedback. Finally, address the behavior, not the person, and give recommendations for improvement as well.
Slide 64
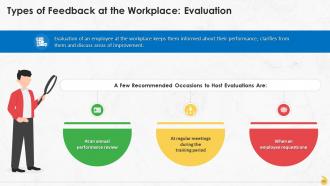
This slide contains information about the meaning and suitable times to host evaluations which are: At an annual performance review, at regular meetings during the training period, and when an employee requests one.
Slide 65
This slide provides tips on evaluating the employees efficiently at the workplace, which are: Have a clear goal to achieve from the feedback, communicate clear expectations to the employees, record of progress and the employees updated, be forthcoming with targets and important details, and don't track metrics just to highlight employee's shortcomings.
Slide 66
This slide contains information about coaching as a type of workplace feedback. It is relevant during the training period of an employee. It involves formal feedback sessions and reviews. It is useful in: Learning a new skill; when an employee is newly hired or promoted; to encourage effective behavior, and to learn a new business process.
Slide 67
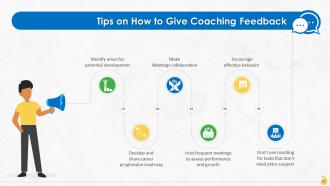
This slide lists tips for giving coaching feedback to employees which are: identify areas for potential development, develop and share career progression road map, make meetings collaborative, host frequent meetings to assess performance and growth, encourage effective behavior, and not using coaching for tasks that are manageable without extra support.
Slide 68
This slide highlights the importance of encouragement as a type of feedback at the workplace. It can be given formally or informally as a part of a performance review or comments on good work that employees have done. It should be used when: when an employee has achieved a new milestone, when the employee has performed beyond expectations, to celebrate success with the team, and when an employee needs motivation.
Slide 69
This slide lists tips on giving encouragement to the employees which are: Use positive feedback to show appreciation, share achievements with the rest of the team, offer responsibility when you feel the employee is ready, and make the encouragement session personal.
Slide 70
This slide highlights the key takeaways from the session on power of feedback. The trainer can use these pointers to highlight vital learnings from the session.
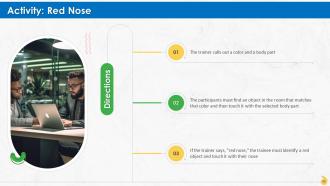
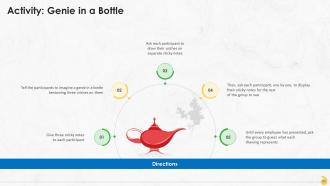
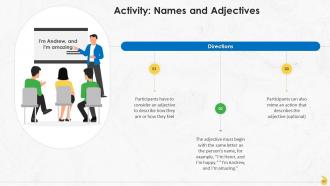
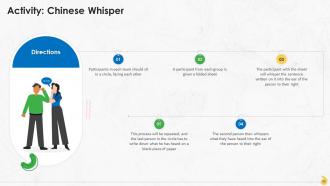
Slide 87 to 101
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Power Of Feedback Training Ppt with all 110 slides:
Use our Power Of Feedback Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Happy to found you SlideTeam. You guys are value for money. Amazing slides.
-
They saved me a lot of time because they had exactly what I was looking for. Couldn’t be happier!