Understanding Block And Block Header In Blockchain Training Ppt
This set of slides covers the anatomy of a block in a blockchain. It includes key fields of block in the blockchain, such as block header, block size, transaction counter, and transactions. It also covers the components of the block header, such as block version, previous block hash, Merkle root, timestamp, nonce, and difficulty target.
This set of slides covers the anatomy of a block in a blockchain. It includes key fields of block in the blockchain, such a..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Understanding Block and Block Header in Blockchain. This slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint specialists. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. You can add or delete the content as per your need.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1
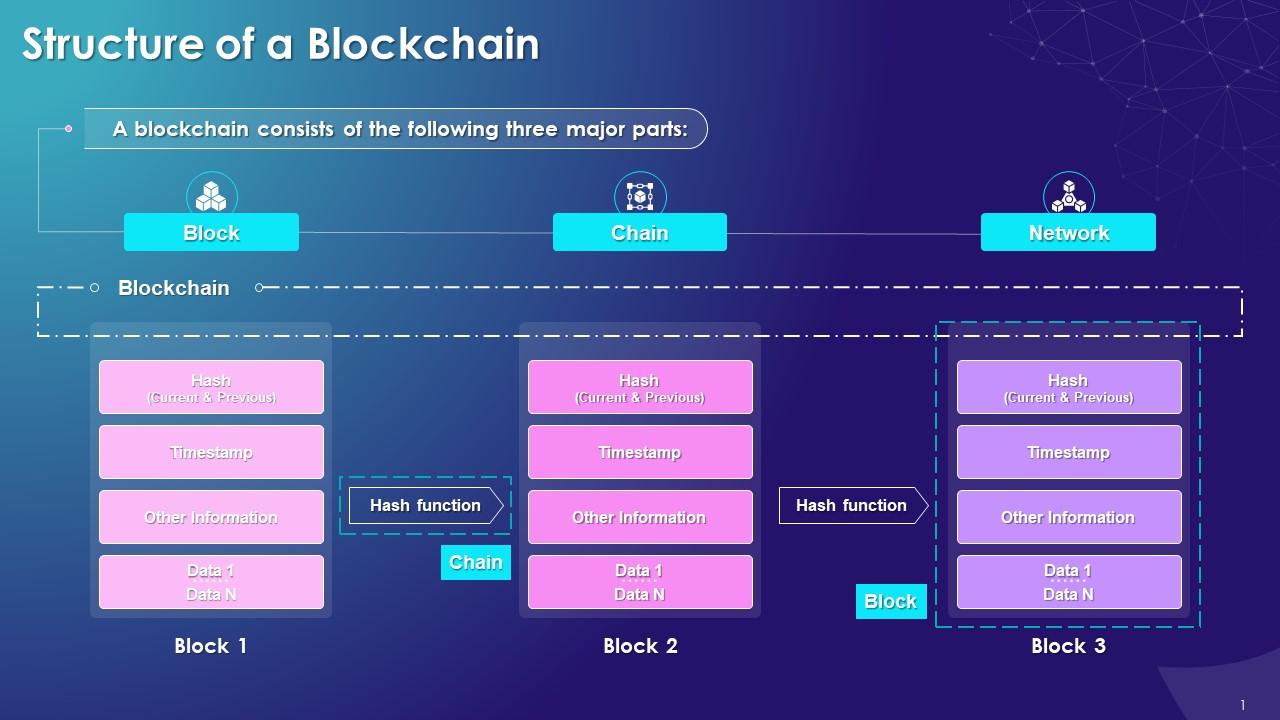
This slide provides an overview of the structure of blockchain, covering the key components such as block, chain, and network.
Instructor’s Notes:
The structure of blockchain is similar to that of linked lists or binary trees in which the linking is done using pointers that point to the previous or next list element on the nodes in the linked list.
The three major parts of blockchain are:
- Block: It contains the list of transactions recorded into a ledger over a time period. For every blockchain, the size, period, and triggering event varies
- Chain: Chain is a hash that glues multiple blocks together in the blockchain and enables trust creation. In the blockchain, the SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm) hashing algorithm is primarily used
- Distributed Network: The network consists of multiple nodes across the globe to achieve the decentralized structure of the blockchain. Each node will contain the complete record of all transactions which have been carried out in the blockchain
Slide 2
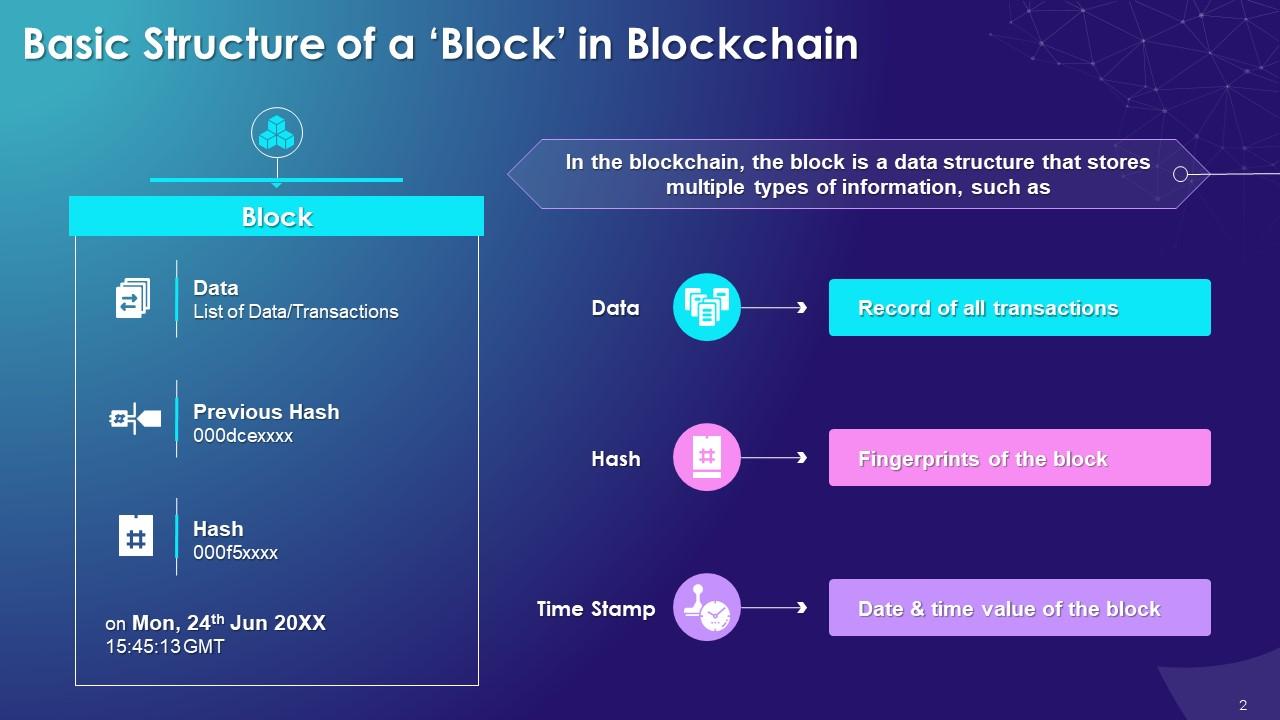
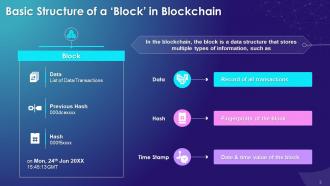
The purpose of this slide is to highlight the key components of a block in the blockchain, which are data, hash, and previous hash. The slide also includes details of timestamp and genesis block.
Instructor’s Notes:
The key components of a block in blockchain are as follows:
- Data: The record of all the transactions. Each block of a blockchain can contain thousands of transaction data. The type of data stored depends upon the use case of blockchain
- Hash: The hash is like a block fingerprint as it helps identify the block and its content. A hash is always unique for each block
- Previous Hash: As the name suggests, it contains the hash information of the preceding block. Its primary function is to create the chain of blocks and make blockchain secure
- Genesis Block: The first block created for any blockchain with the previous hash as “0” is the genesis block
- Timestamp: A timestamp is a date-time value that is stored in a block. It provides information about the time when the block was created. In the blockchain, this value is in the form of a Unix timestamp format
Slide 3
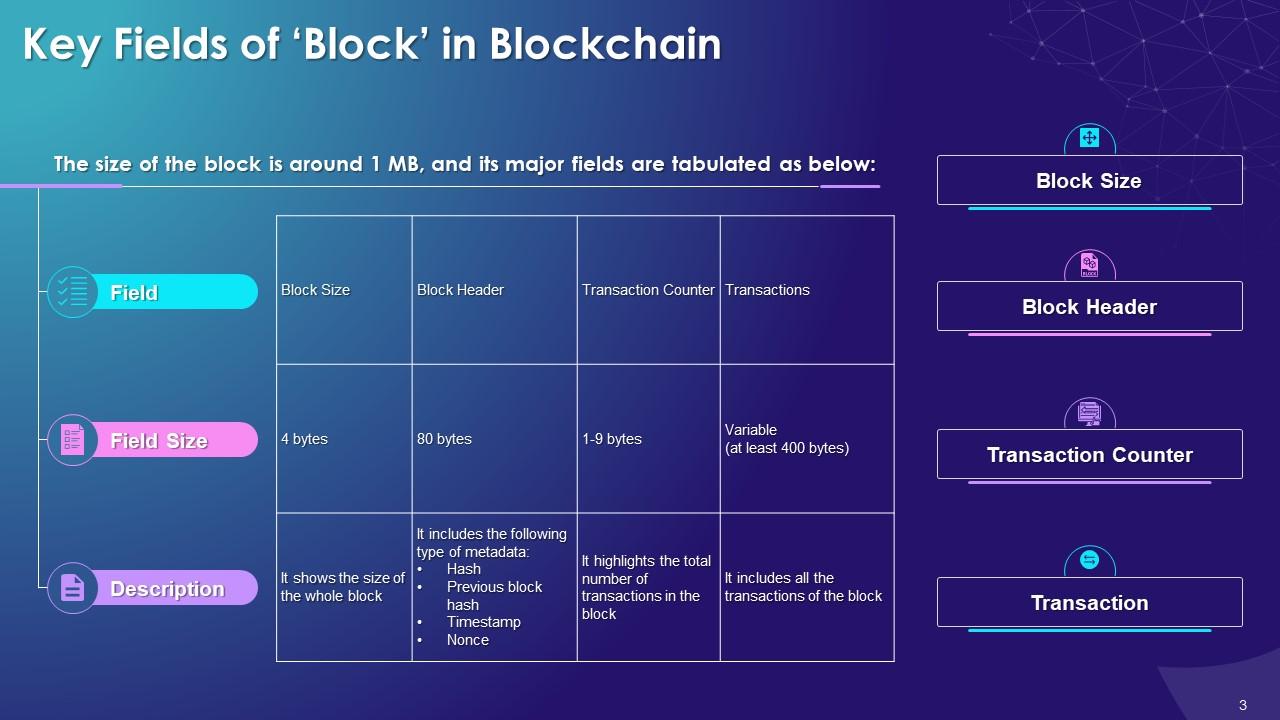
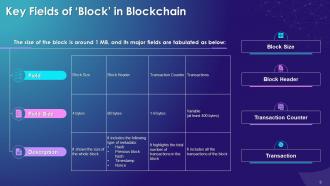
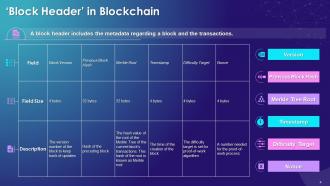
This slide represents the key fields of block in blockchain such as block header, block size, transaction counter and transactions. It also contains information pertaining to field size and content description.
Slide 4
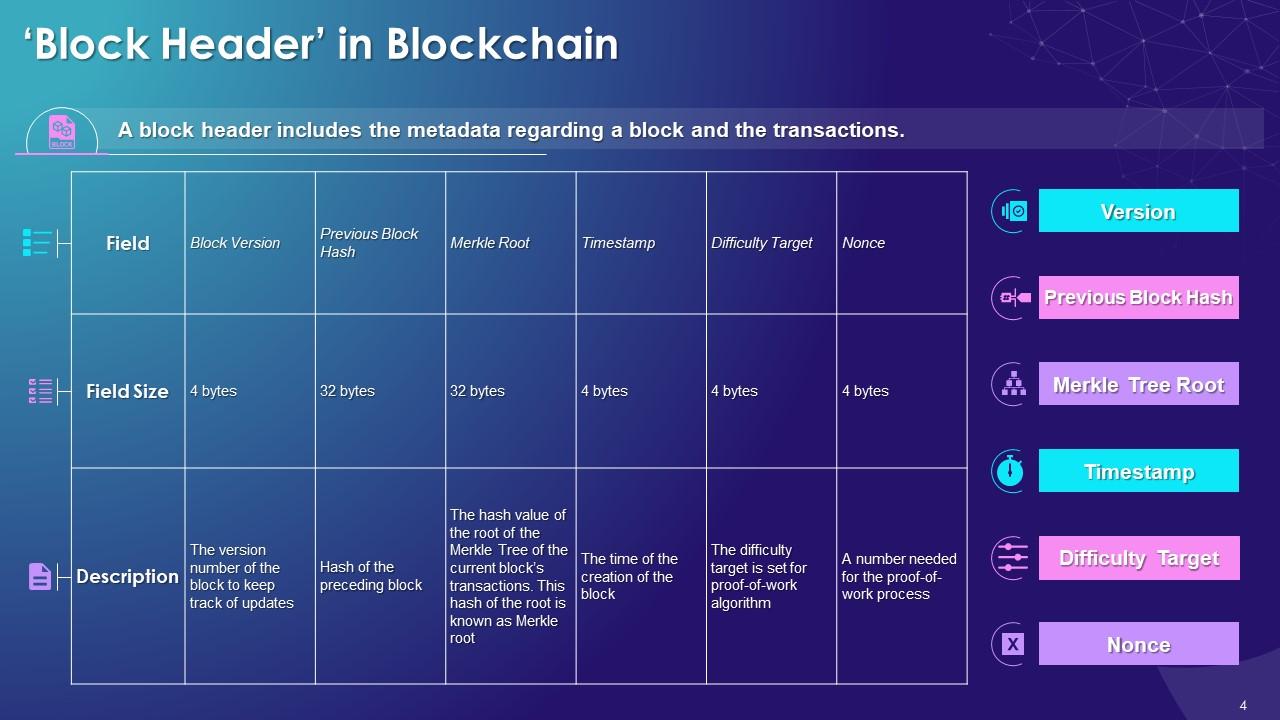
This slide includes the segments of block header such as block version, previous block hash, Merkle root, timestamp, nonce, and difficulty target.
Understanding Block And Block Header In Blockchain Training Ppt with all 20 slides:
Use our Understanding Block And Block Header In Blockchain Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Wonderful ideas and visuals. I'm really pleased with the templates, which are unique and up to date.
-
Content of slide is easy to understand and edit.