Blockchain Technology Applications in Healthcare Industry Training Ppt
This PPT training deck provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology applications in the healthcare industry. The module begins with a brief overview of the healthcare industry in terms of major trends and challenges faced. It includes PPT slides on how blockchain technology provides solutions to medical industry issues with longitudinal patient records, master patient indices, fair claims adjudication, effective supply chain management, and improved interoperability. Further, in detail, it covers the impact of blockchain on multiple domain areas of the healthcare industry, such as healthcare insurance, pharma, drug and devices supply chain, health records, and data exchange. The PowerPoint module also includes case studies, key takeaways, discussion, and MCQs related to the topic to make the training session interactive. The PowerPoint module also includes additional slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, energizer activities, detailed client proposal, and training assessment form.
This PPT training deck provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology applications in the healthcare industry. ..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Session on Blockchain Technology Applications in Healthcare Industry. This presentation deck contains 97 plus well-researched and uniquely designed slides. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees, and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon, and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
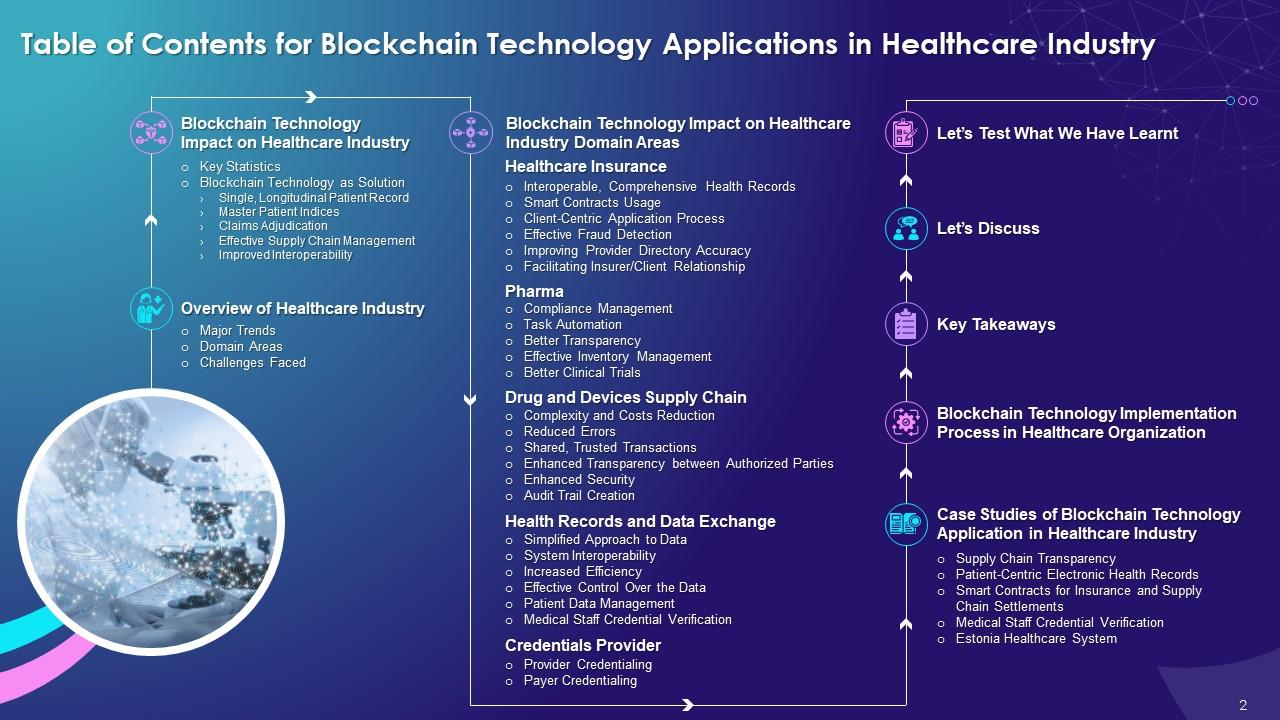
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
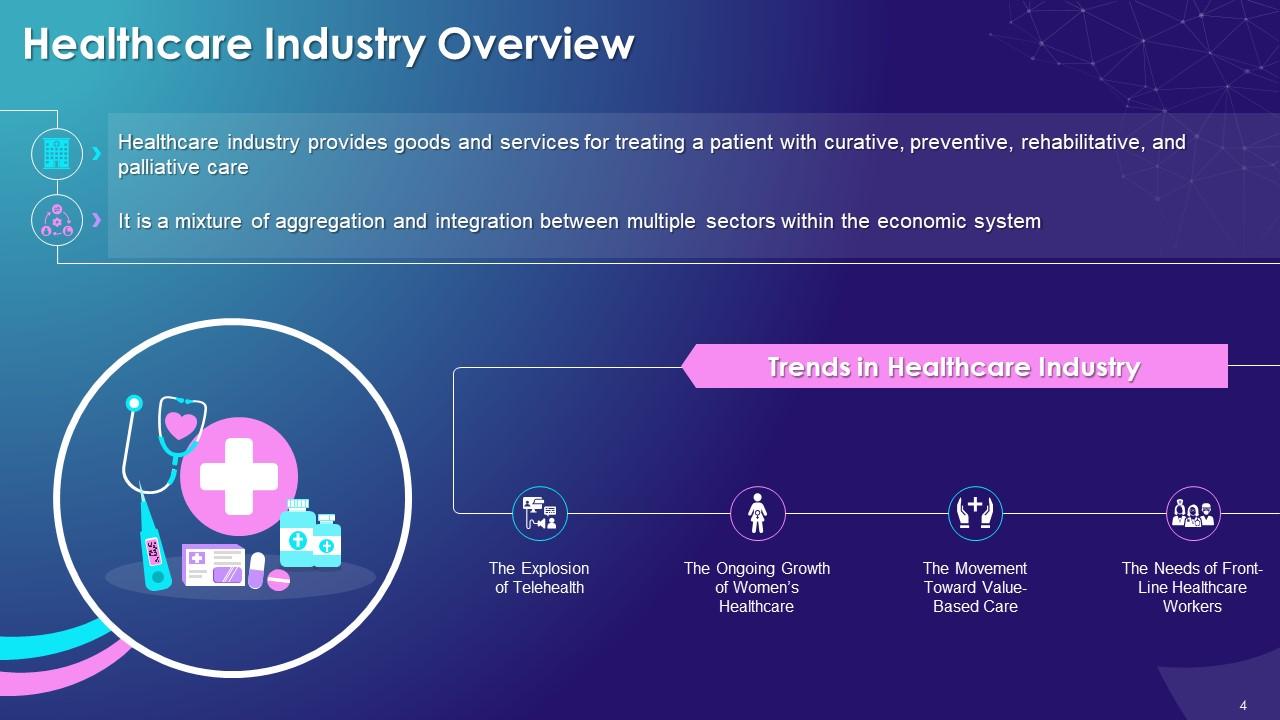
Slide 4
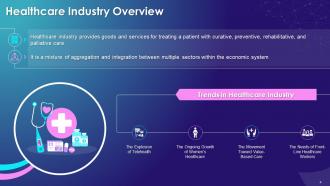
This slide highlights the concept of healthcare. It also highlights key trends in healthcare industry such as the explosion of telehealth, ongoing growth of women's healthcare, movement towards value-based care, and needs of front-line healthcare workers.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple key trends of healthcare industry are as follows:
The Explosion of Telehealth:
- Legal issues, regulatory red tapes, and slow patient adoption held down the growth of telehealth
- A 2019 survey found that 66%of people wanted a telehealth system, but only 8% got the chance to experience it
- By 2020, telehealth services increased to around 59% for the first time
- The usage of telemedicine surged at the onset of the pandemic and declined slightly thereafter
- Telehealth has proved its value and worth to consumers and other business investors
- This increases the interest of investors to invest in telehealth and provide a better experience
The Ongoing Growth of Women’s Healthcare:
- The impact of the pandemic showed its effect on men and women differently
- The working women and mothers have more responsibilities added to their overbooked schedules
- The physiological challenges between men and women must be considered a major issue in women's health
- The investment in women's healthcare has continued over the past two years
- With stress-related ailments like diabetes on the rise, especially in women, this particular healthcare segment could see traction
The Movement Toward Value-Based Care:
- Different health care models such as the Fee-For-Service model and Value-Based-Care model are used in the healthcare industry
- The FFS model depends on profits from high dollar elective procedures to offset the cost of services
- The VBS model rewards providers for improving health outcomes
- VBC is used in women healthcare system to reduce the cost and improve outcomes
The Needs of Front-Line Healthcare Workers:
- Due to the shortage of healthcare workers worldwide, there is a need to hire moreto allow the system to save more lives
- These healthcare workers need support and resources for their requirements in the healthcare industry
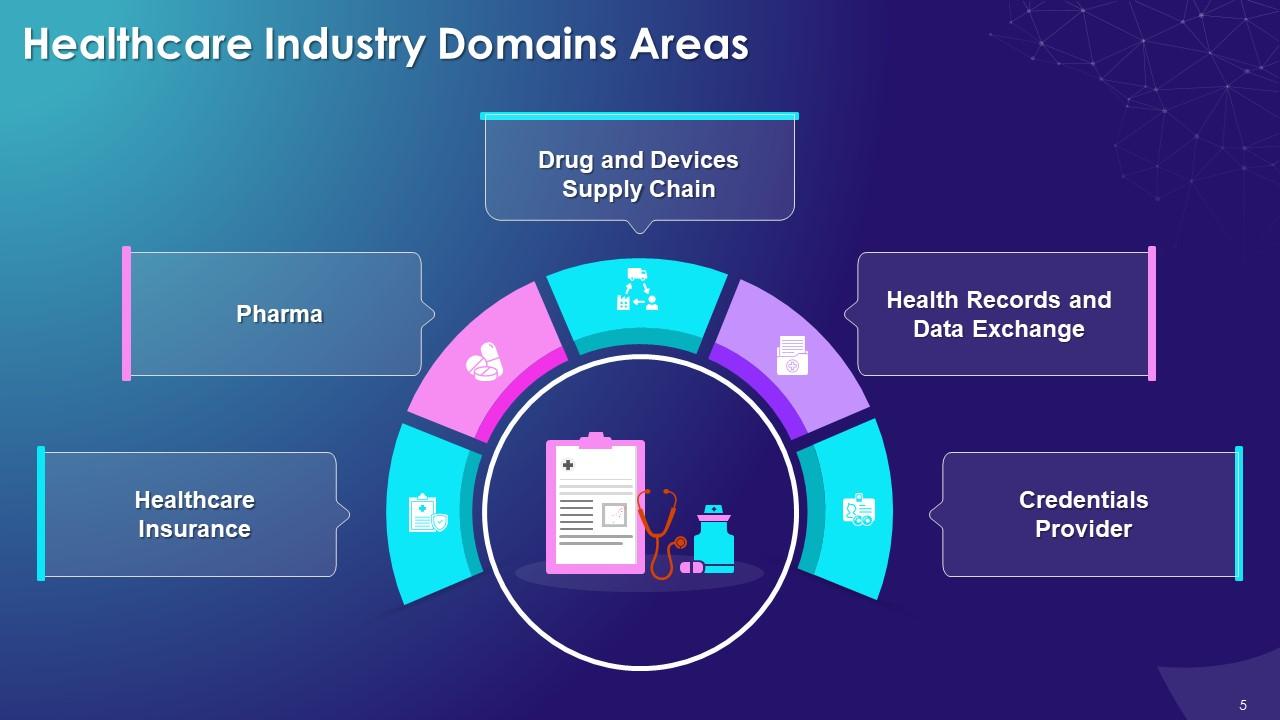
Slide 5
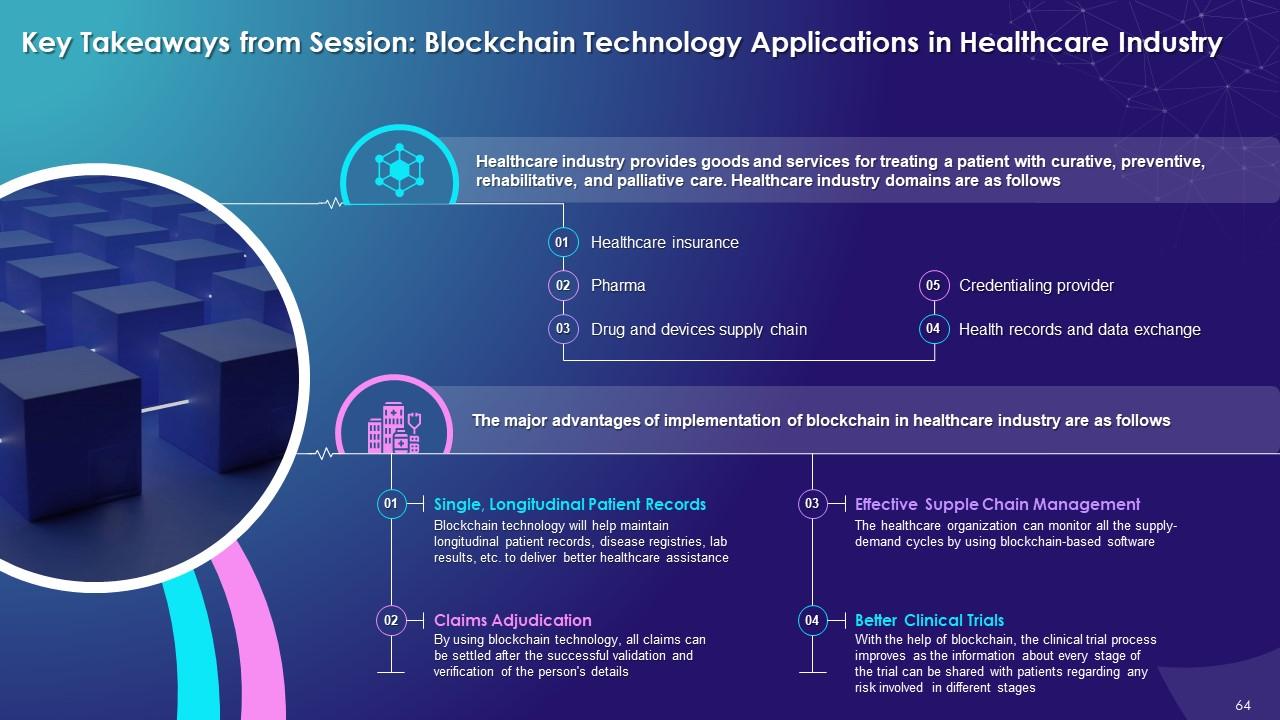
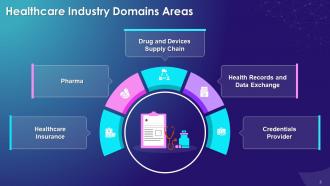
This slide highlights the multiple domain areas in healthcare industry such as healthcare insurance, pharma, drug and devices supply chain, health records and data exchange, and the power to provide or verify credentials.
Instructor’s Notes:
The different domain areas in healthcare industry are as follows:
Healthcare Insurance:
- Health or medical insurance covers either complete or part of the risk of a person's recurring medical expenses
- These medical insurances come in monthly packages with additional benefits attached to them
Pharma:
- This industry helps discover, produce, develop, and market the drugs for medication use
- It is subjected to laws and regulations that govern the patenting, testing, safety, efficacy, and marketing of drugs manufactured
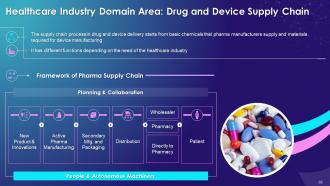
Drug and Devices Supply Chain:
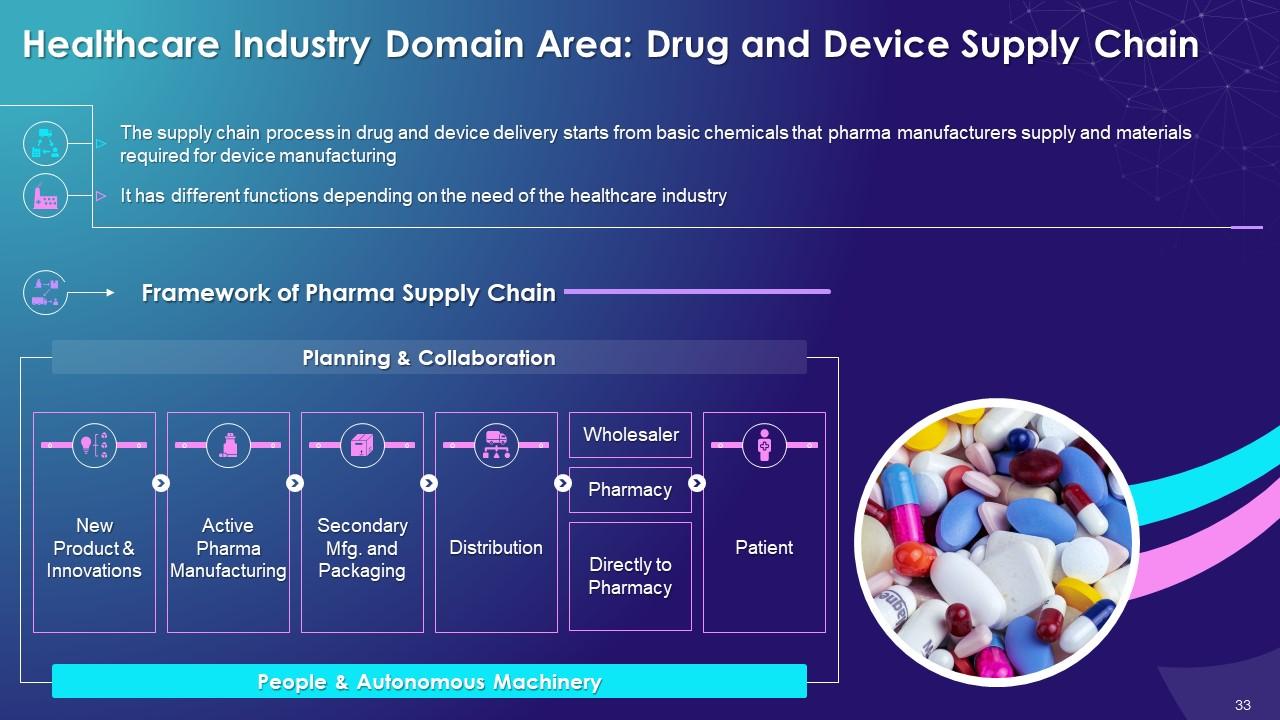
- The supply chain process in drug and device delivery stretches from basic chemicals that pharma makers need and materials required for device manufacturing
- It has functions depending on the need of the healthcare industry
Health Records and Data Exchange:
- Electronic software (HIE) allows doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and patients to share clients' vital medical information in a secure manner
Credentialing Provider:
- The credentialing process helps validate whether the healthcare specialist meets the standards for clinical care
- The client can verify the doctor's education, license, experience, certifications, affiliations, malpractice before investing in any clinical process
Slide 6
This slide illustrates issues in healthcare industry such as maintaining single, longitudinal patient record, problem with master patient indices, management issue in claims adjudication, supply chain management issues, and lack of interoperability.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple issues that healthcare industry faces are as follows:
Issue Maintaining Single, longitudinal patient records:
- It is challenging to secure and store records of patients, such as disease registries, lab results, etc.
- The record-keeping process is not effective, resulting in records being misplaced
Problem with Master patient indices:
- In these indices, an error can be seen in the form of multiple copies added in the name of a single patient
- At the time of retrieving a record, it will be difficult to abstract an old record easily because of the overlap issue in forms
Management issues in Claims adjudication:
- The process of claims adjustments are difficult to handle due to complex verification process
- The different issues during claim adjustments are
- Wrong demographic Information
- Claim not filed on time
- Wrong Current Procedural Terminology codes
Supply chain management issues:
- It is difficult to track supply chain process without proper data management system in the healthcare industry
- The different issues faced by healthcare industry in supply chain system:
- Lack of resilience
- Lack of visibility
- Cost management
Lack of Interoperability:
- Multiple government-certified Electronic Health Record products are used with different clinical terminologies, technical specifications, and functional capabilities
- It becomes challenging to create a specific interoperability format for sharing data
Slide 8
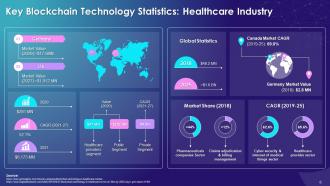
This slide illustrates the statistics on market value of US, Canada and Germany for the from 2020 to 2027. It highlights the CAGR from 2021-2027 up to 52.1% and global statistics for pharma companies. The claims adjudication market is expected to grow from $48.2mn to $1.6bn.
Slide 9
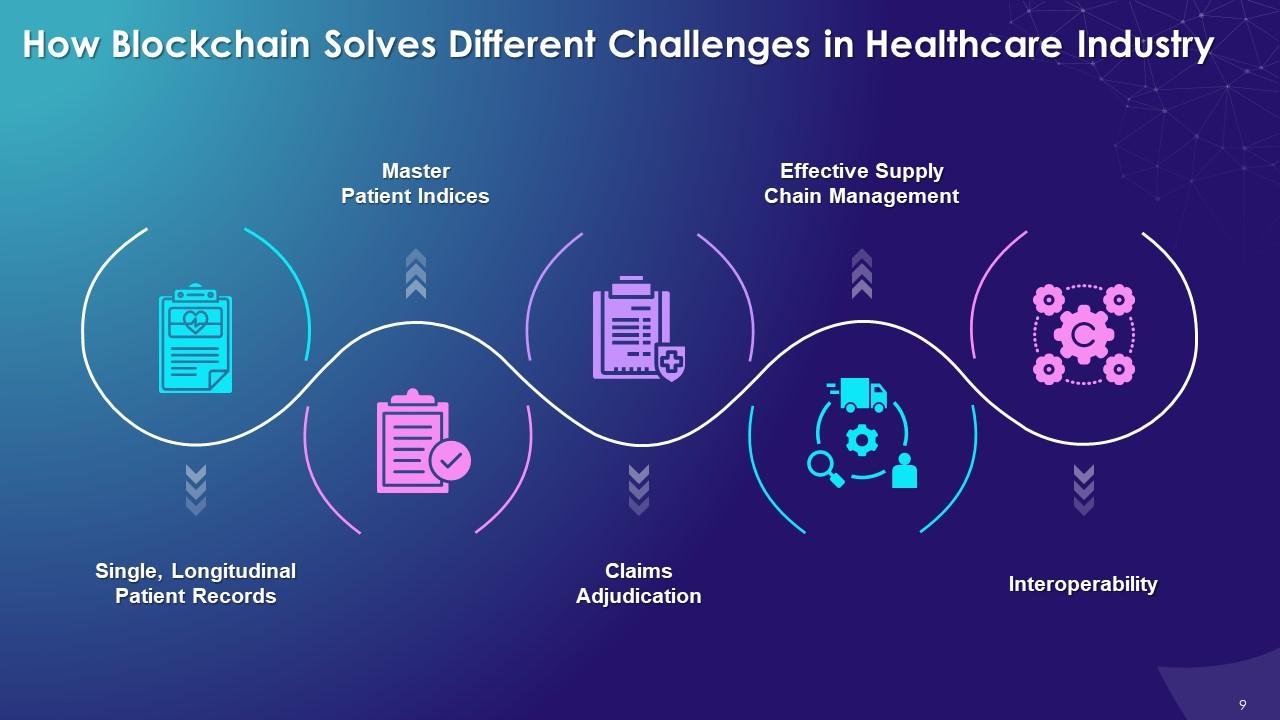
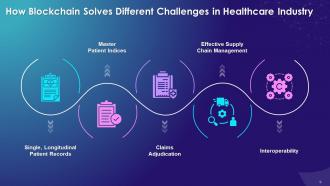
This slide illustrates issues that blockchain technology resolves in healthcare industry such as single, longitudinal patient records, master patient indices, claims adjudication, supply chain management, and interoperability.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple issues blockchain resolves in healthcare industry are as follows:
Single, longitudinal patient records:
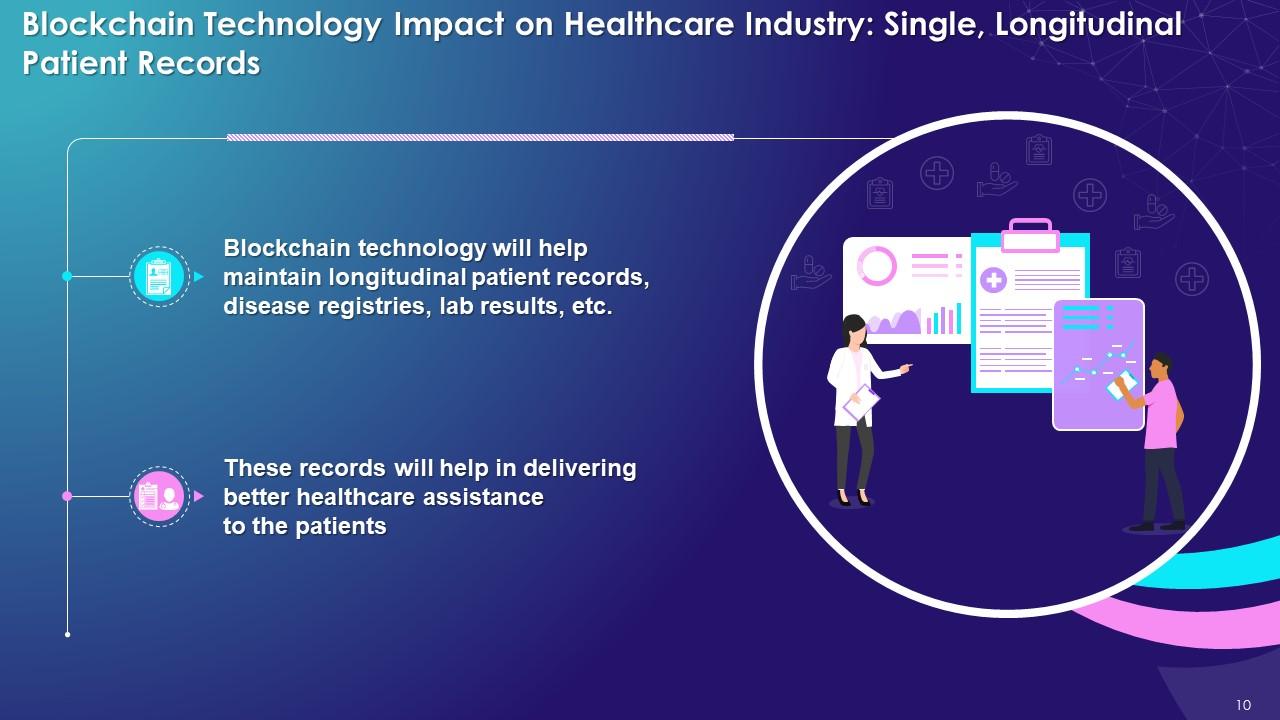
- Blockchain technology will help maintain longitudinal patient records, disease registries, lab results, etc.
- These records will help in delivering better healthcare assistance to the patients
Master patient indices:
- By using blockchain technology, multiple data will be stored in the blocks to avoid any data mismatch or overlapping in the system
- The user only requires a unique hash address to identify the records of a particular patient
Claims adjudication:
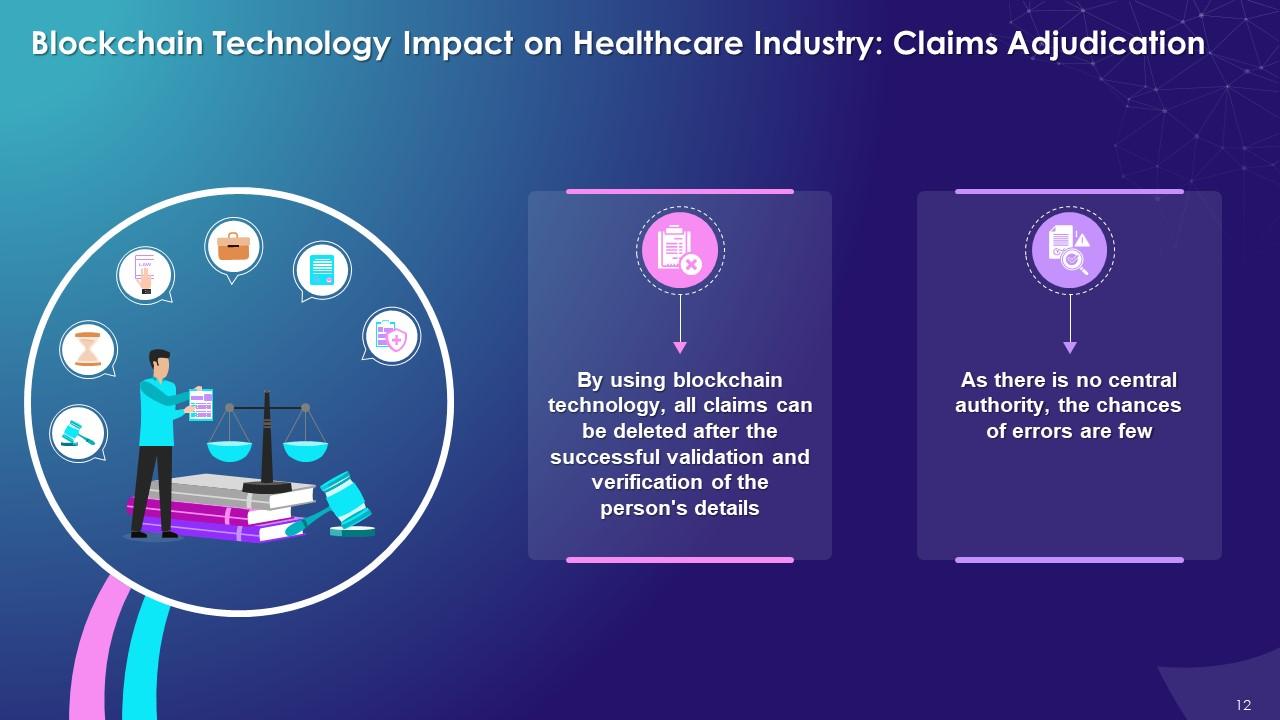
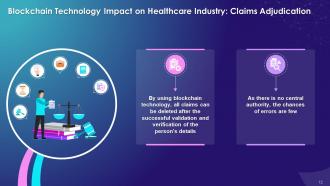
- By using blockchain technology, all claims can be delivered after the successful validation and verification of the person's details
- As there is no central authority, the chances of errors are few
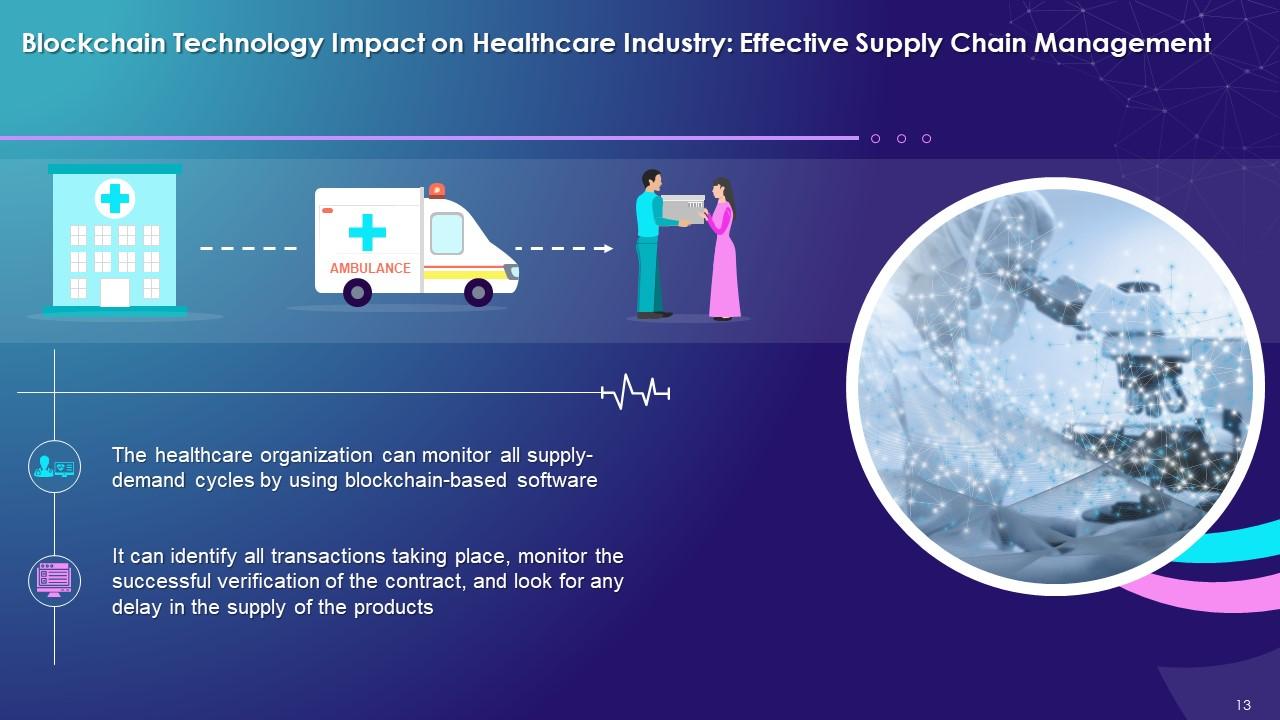
Effective Supply chain management:
- The healthcare organization can monitor all supply-demand cycles by using blockchain-based software
- It can identify all transactions taking place, monitor the successful verification of the contract, and look for any delay in the supply of the products
Interoperability:
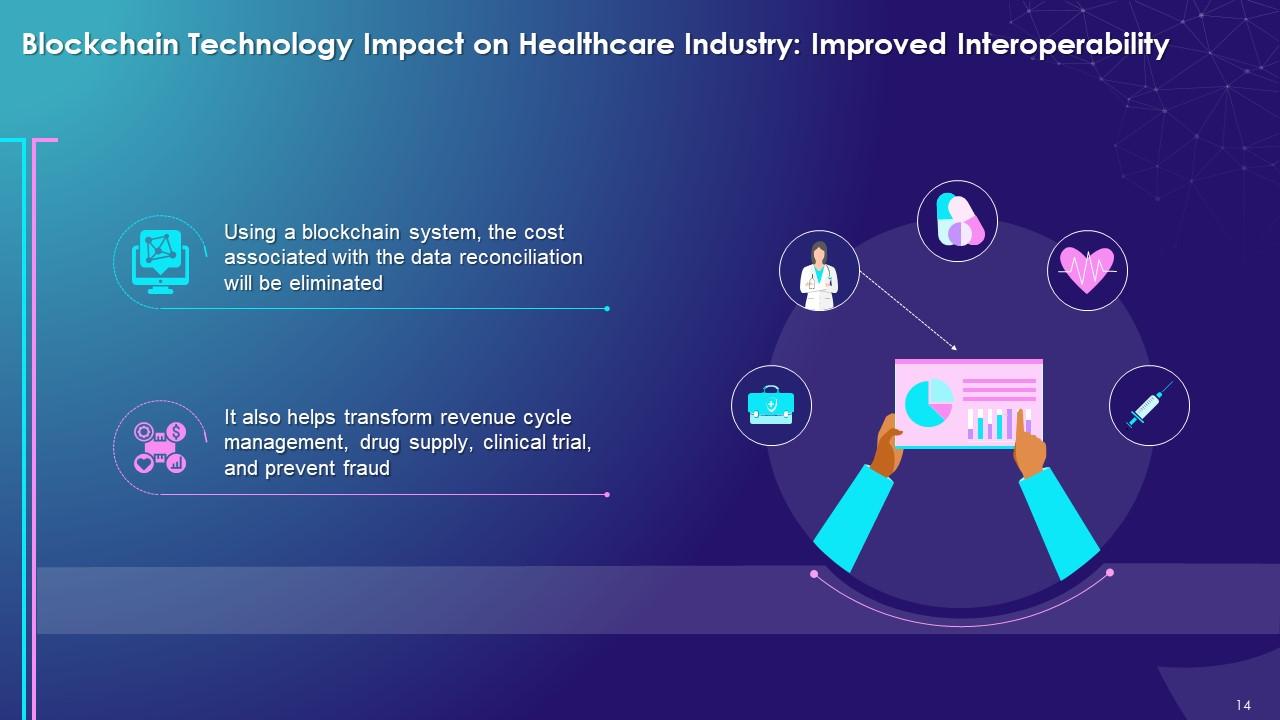
- Using a blockchain system, the cost associated with the data reconciliation will be eliminated
It also helps transform revenue cycle management, drug supply, clinical trial, and prevent fraud
Slide 10
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare industry with single, longitudinal patient records. It explains that with the help of blockchain, longitudinal patient records, disease registries, lab results are recorded. It helps in delivering better healthcare assistance to patients.
Slide 11
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare industry with master patient indices. It explains that using of blockchain technology, multiple data will be stored in the blocks to avoid any data mismatch in the system. It also explains that users only require a unique hash address to identify the records of a particular patient.
Slide 12
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare industry with claims adjudication. It explains that
by using blockchain technology, all the claims can be delivered after the successful validation and verification of the person's details.
Slide 13
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on the healthcare industry in supply chain management. It explains that healthcare organizations can monitor all supply-demand cycles using blockchain-based software. It also identifies all the transactions taking place, monitors the successful verification of the contract, and looks for any delay in the supply of the products.
Slide 14
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare industry with interoperability. It explains that the cost associated with data reconciliation will be eliminated by using the blockchain system. It also helps in transforming revenue cycle management, drug supply, clinical trial, and prevents fraud.
Slide 16
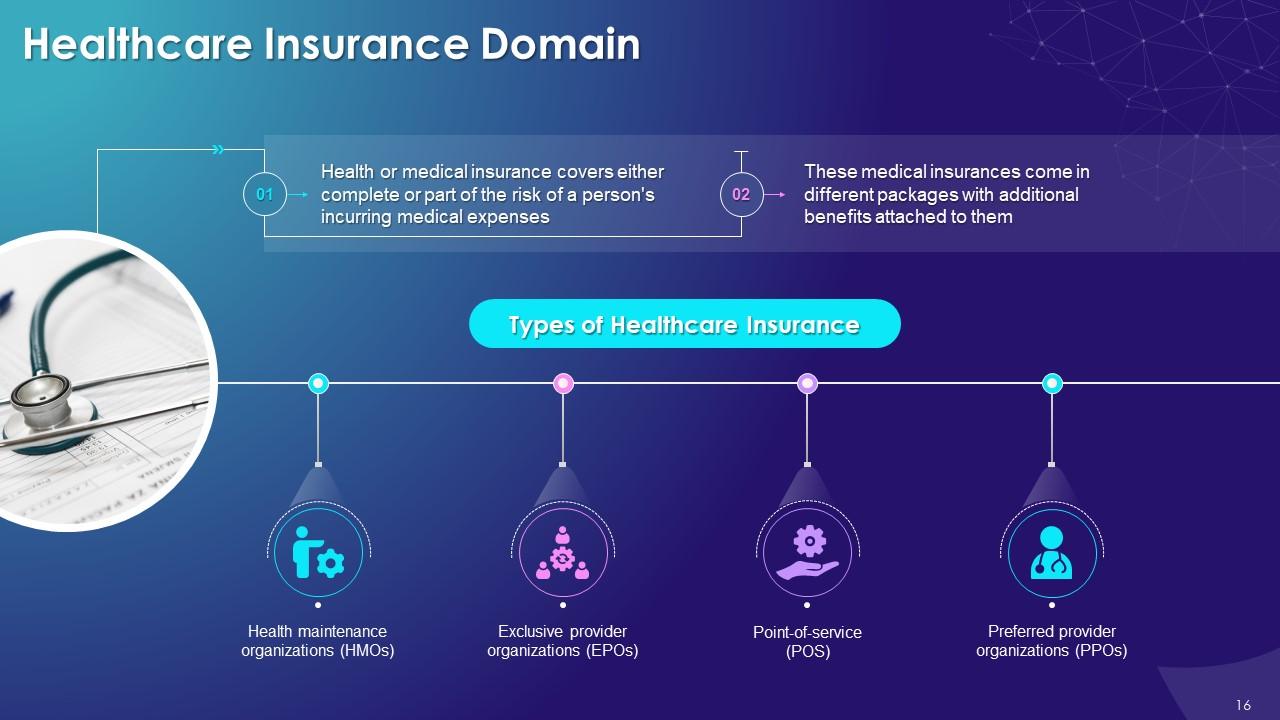
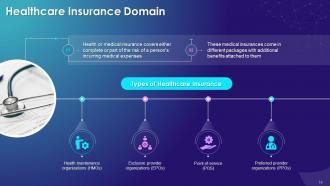
This slide illustrates the concept of medical insurance in healthcare industry. It also determines the different types of healthcare insurances such as health maintenance organizations, exclusive provider organizations, point-of-service, and preferred provider organizations.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple types of healthcare insurance are as follows:
Health maintenance organizations (HMOs):
- This package gives the users access to a local network of participating doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare professionals
- It also provides primary care providers (PCPs) a home-based medical care plan from the network
- It also provides referrals to see a specialist if required
- The cost of an HMO plan is less than other health plans
Exclusive provider organizations (EPOs):
- An EPO consists of a network of participating providers to choose from
- EPO doesn't cover out-of-network care except if there is any emergency case
- If the patient visits the provider with out-of-the-network requirements, then the patient will have to pay the whole service cost
Point-of-service (POS):
- Point-of-service is a combination of both HMO and PPO plans
- In this plan, the users also need to choose a primary care provider from within the plan's network of doctors and other healthcare professionals
- The PCP will get to know your needs and help coordinate all the care needed for a patient
- To see a specialist under this plan, the patient will require a referral
Preferred provider organizations (PPOs):
- PPO also provides an extensive network of doctors, hospitals, and other health care professionals to choose from
- It also covers a certain section of the billing amount when choosing providers outside the plan, but patients still have to pay the majority of the amount from their own pocket
- In this plan, no referral is required for seeing any specialist
Slide 17
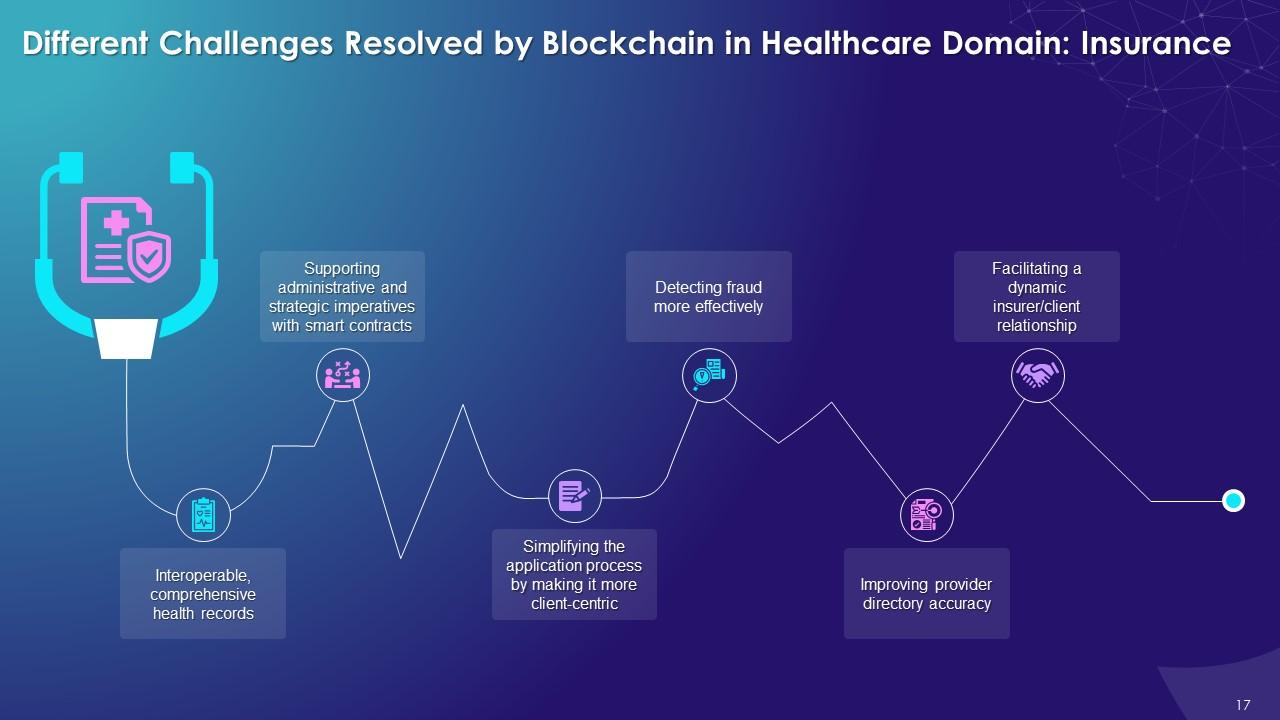
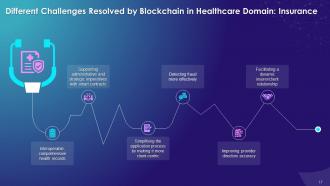
This slide illustrates challenges that the blockchain resolves in health insurance such as interoperability, comprehensive health records, supporting administrative and strategic imperatives with smart contracts. The technology also simplifies the application process, making it more client-centric; detecting fraud more efficiently, improving accuracy and facilitating a dynamic insurer/client relationship.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple issues that blockchain resolves in healthcare insurance industry are as follows:
Interoperable, comprehensive health records:
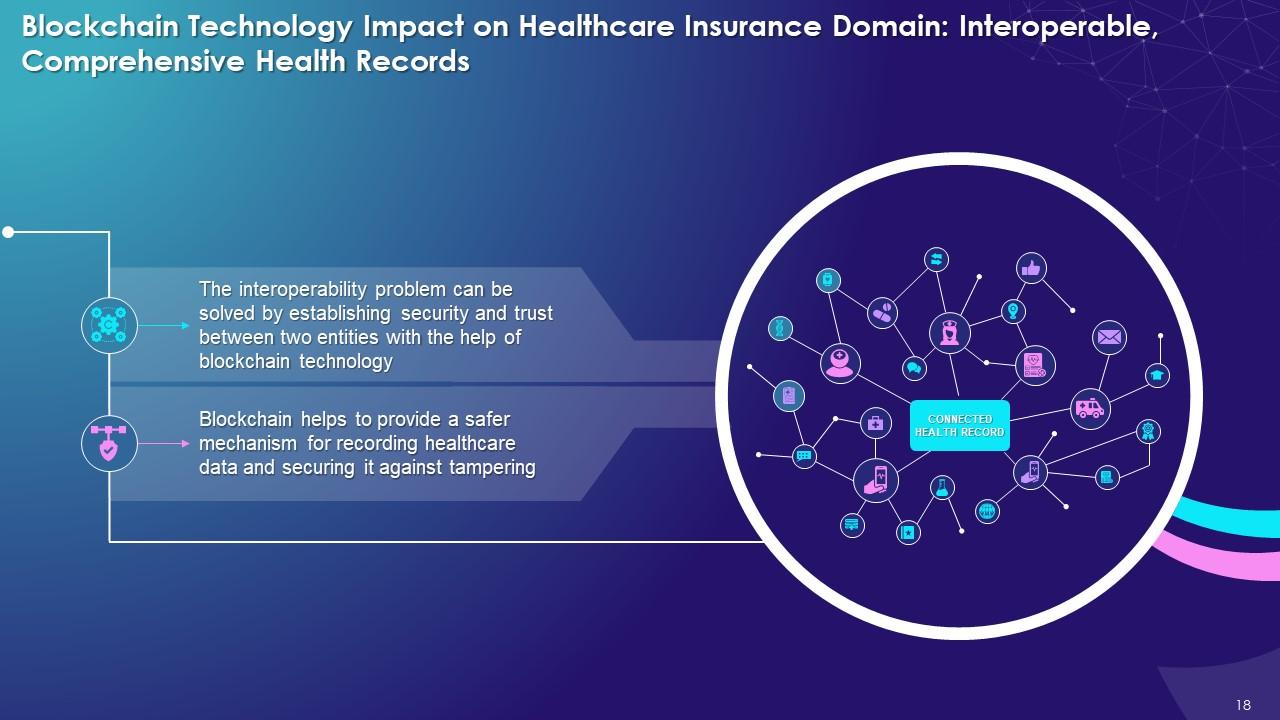
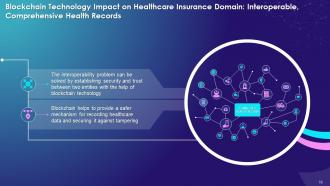
- With the help of blockchain-based software, the interoperability problem can be solved by establishing trust and security within the system
Supporting administrative and strategic imperatives with smart contracts:
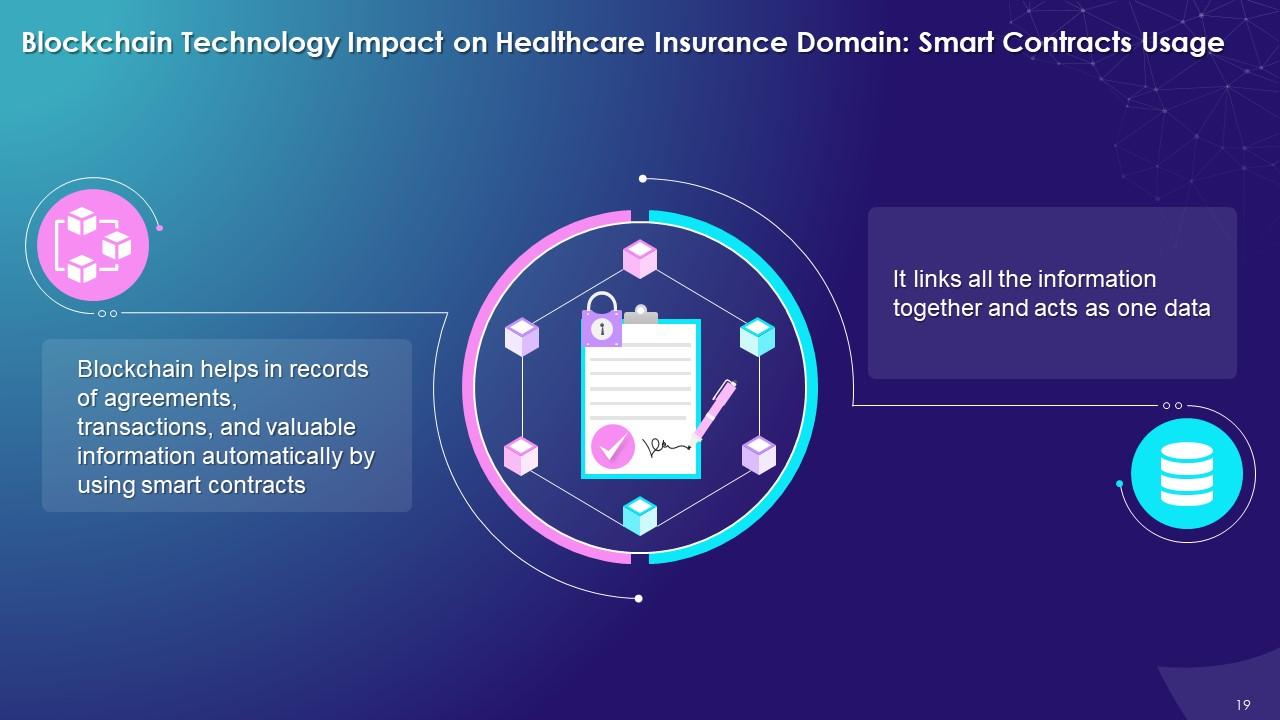
- Using smart contracts, blockchain automatically collects records of agreements, transactions, and valuable information by linking the information together and acting as one data
Simplifying the application process by making it more client-centric:
- The data is recorded in the blockchain-based system, making it easier for the users to find different medical records at the time of need
Detecting fraud more effectively:
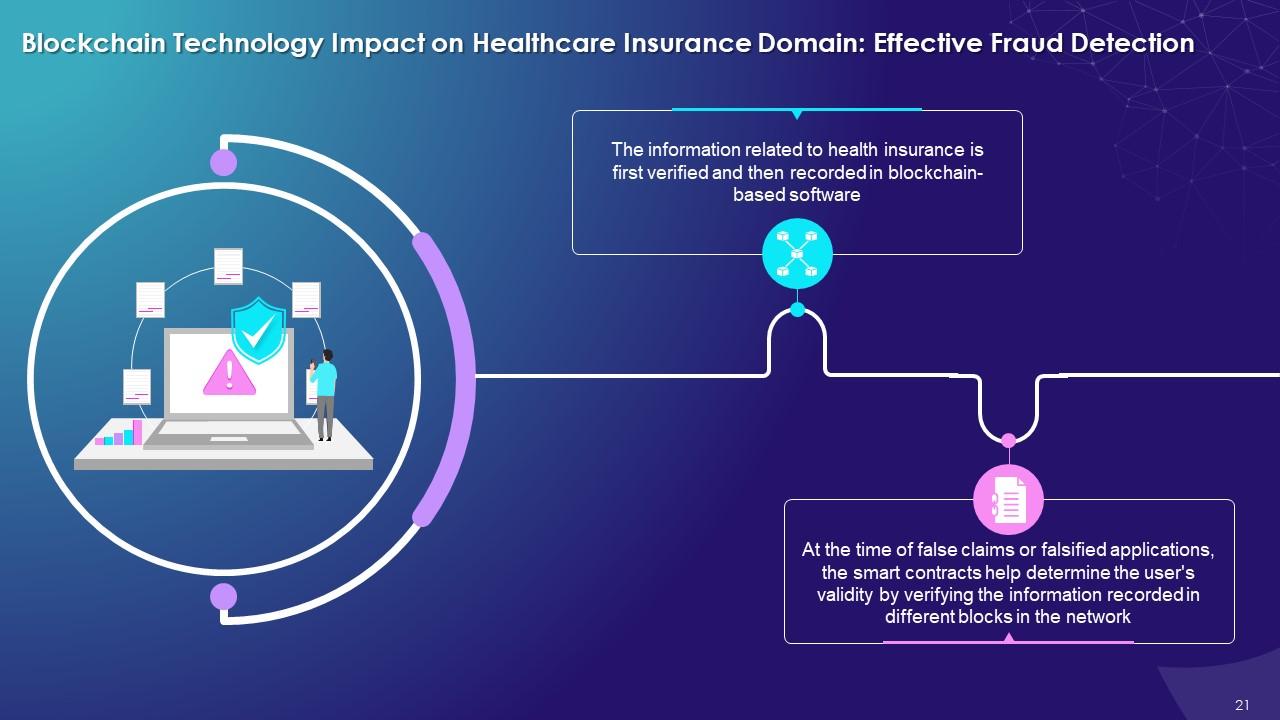
- The information related to health insurance is first verified and then recorded in blockchain-based software
- At the time of false claims or falsified applications, smart contracts help determine the user's validity by verifying the information recorded in different blocks in the network
Improving provider directory accuracy:
- Healthcare providers and insurers can update their listings easily and quickly, owing to the decentralized nature of Blockchain architecture
Facilitating a dynamic insurer/client relationship:
- While securely storing electronic health records in the blockchain, smart contracts can integrate other wellness-related behaviors within the client’s relationship
Slide 18
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare insurance with interoperable, comprehensive health records. It explains that with the help of blockchain, the interoperability problem can be solved by establishing security and trust between two entities.
Slide 19
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on healthcare insurance with supporting administrative and strategic imperatives. It explains that blockchain helps to automatically collect records of agreements, transactions, and valuable information by using smart contracts.
Slide 20
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on healthcare insurance with client centric application process. It explains that blockchain collects data and keeps it in a systematic order within the blocks. At the time of claim adjustments or client treatment, the information can be collected from the blockchain network.
Slide 21
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare insurance with fraud detection process. It explains that blockchain helps to verify the information recorded in the network software. At the time of false claims, smart contracts help determine the user’s validity by verifying the information recorded in different blocks in the network.
Slide 22
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare insurance by improving accuracy. It explains that healthcare providers and insurers can update their listings easily and quickly owing to the decentralized nature of Blockchain architecture.
Slide 23
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on healthcare insurance by facilitating client insurer relationship. It explains that at the time of storing electronic healthcare records in the blockchain, smart contracts integrate the wellness-related behaviors within the client’s relationship.
Slide 25
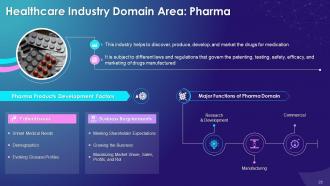
This slide illustrates the concept of Pharma domain in healthcare sector. It also determines the different features such as research and development, manufacturing, commercial, and meeting shareholder expectations that matter in growing the business.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple functions of pharma domain are as follows:
Research and Development:
- Discovery
- Development
- Interaction with Other Departments
Manufacturing:
- Clinical Studies
- Marketed Products
- Interaction with Other Departments
Commercial:
- Product Launch
- Product Marketing
- Sales
- Interaction with Other Departments
Slide 26
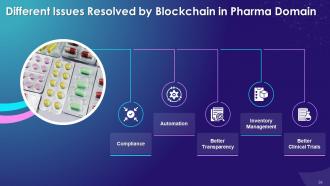
This slide illustrates challenges that the blockchain resolves in pharma domain such as compliance, automation, traceability, inventory management and better clinical trials.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple issues solved by blockchain in pharma domain are as follows:
Compliance:
- Blockchain is used to add governance and compliance to the pharma supply chain
- It is possible due to key features of blockchain, which include immutability, distributed nature, and transparency
Automation:
- Blockchain uses smart contracts to automate tasks on the blockchain
- In the pharma industry, the smart contract executes notifications in case compliance conditions are not met
- After the notification is executed, all the drug-relevant companies are notified
Better Transparency:
- Blockchain technology in the pharma industry makes database operations accessible to the public
- There is no need to verify data with any third-party system as blockchain validates all information before storing it in the blocks
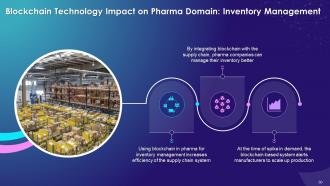
Inventory Management:
- Using blockchain in pharma for inventory management helps the supply chain system
- By integrating blockchain with the supply chain, pharma companies can manage their inventory better
- At the time of spike in demand, the blockchain-based system alerts manufacturing units to stay ready to produce more
Better Clinical Trials:
- With the help of blockchain, the clinical trial process improves as the information about every stage of the trial can be shared with patients
- Stakeholders will also be informed on a daily basis regarding the trial process stages
- Blockchain helps improves overall clinical trials as it provides better consent transparency and traceability
- Consent forms in the blockchain are time-stamped, and no one can tamper with the information once stored
Slide 27
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on pharma domain with compliance. It explains that blockchain is used to add governance and compliance to the pharma supply chain. It also includes key features of blockchain such as immutability, distributed nature, and transparency.
Slide 28
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on pharma domain with automation. It explains that blockchain uses smart contracts to automate tasks. In pharma industry, the smart contract executes notifications in case the compliance conditions are not met and all the drug related companies are notified.
Slide 29
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on pharma domain with better transparency. It explains that blockchain helps in making pharma industry database operations accessible to the public.
Slide 30
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on pharma domain with inventory management. It explains that using blockchain in pharma for inventory management helps the supply chain system. Integrating blockchain with supply chain can help pharma companies to better inventory management.
Slide 31
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on pharma domain with better clinical trials. It highlights that with the help of blockchain, the clinical trial process improves as the information about each stage of trial can be shared with risks involved also explained. Stakeholders will be informed on daily basis regarding the trial process stages. Getting the time consent process is also streamlined, as it is time-stamped and stored as information in a blockchain, which is impossible to tamper with
Slide 33
This slide illustrates the concept of device and drug supply chain in healthcare industry. It also highlights different aspects such as planning and collaboration, new product and innovation, active pharma manufacturing, secondary manufacturing, packaging and distribution.
Slide 34
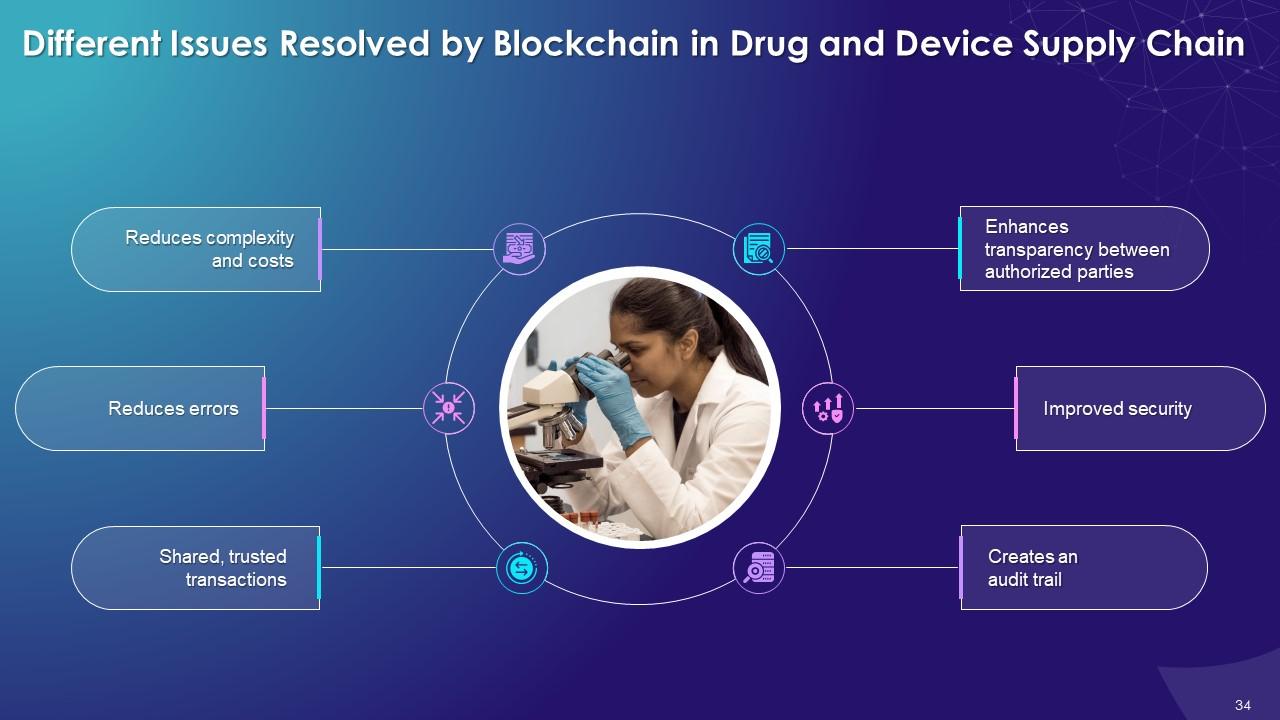
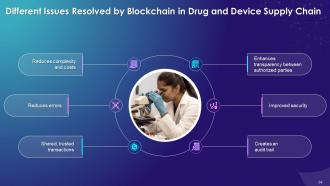
This slide illustrates challenges that blockchain resolves in drug and device supply system. These are lower complexity and costs, reduction in errors, shared trusted transactions, enhanced transparency between authorized parties, improved security, and a clear audit trail.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple issues solved by blockchain in drug and device supply chain are as follows:
Reduces complexity and costs:
- Blockchain helps make the drugs supply chain process traceable, which makes tracking of drugs easier
- It helps in checking the expiry dates of drugs at regular intervals, which improves control and rotation of drugs production and supply
Reduces errors:
- Blockchain technology helps verify the authenticity of the drugs and improves their quality to reduce any harm to patients
Shared, trusted transactions:
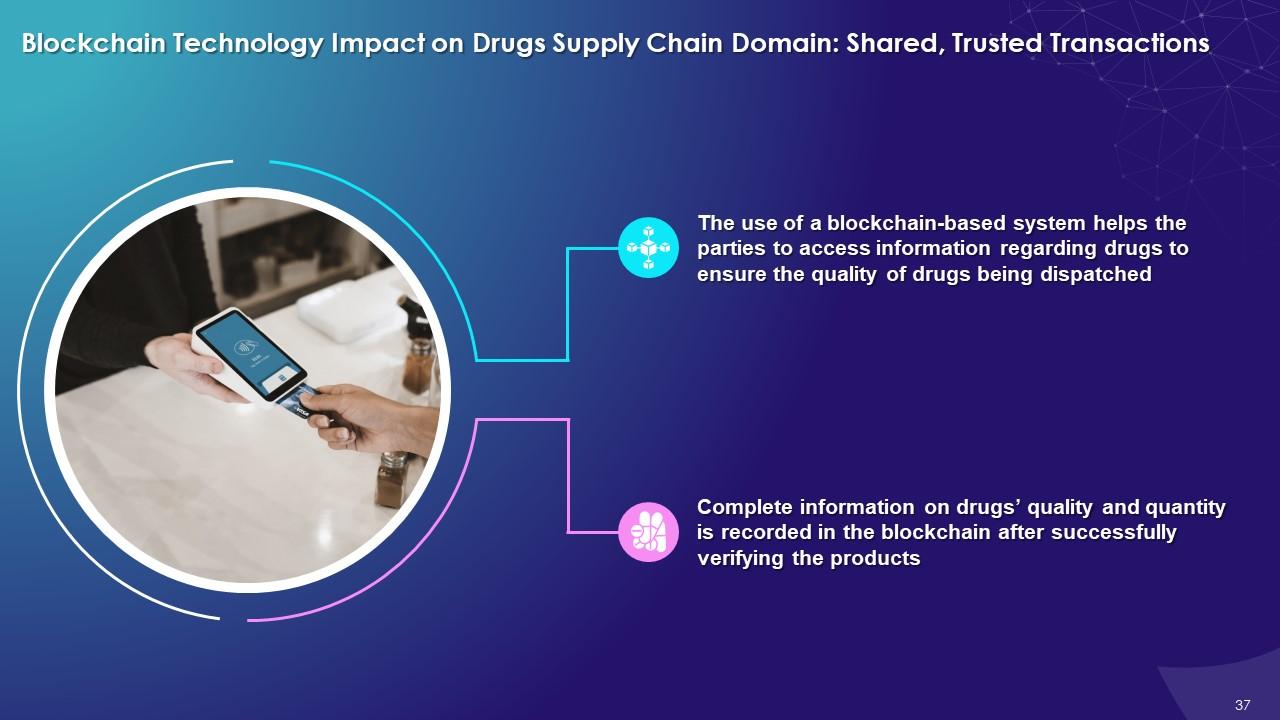
- The use of a blockchain-based system helps the parties access information regarding drugs to ensure the quality of drugs being dispatched
- All information regarding drugs’ quality and quantity is recorded in the blockchain after successful verification of products
Enhances transparency between authorized parties:
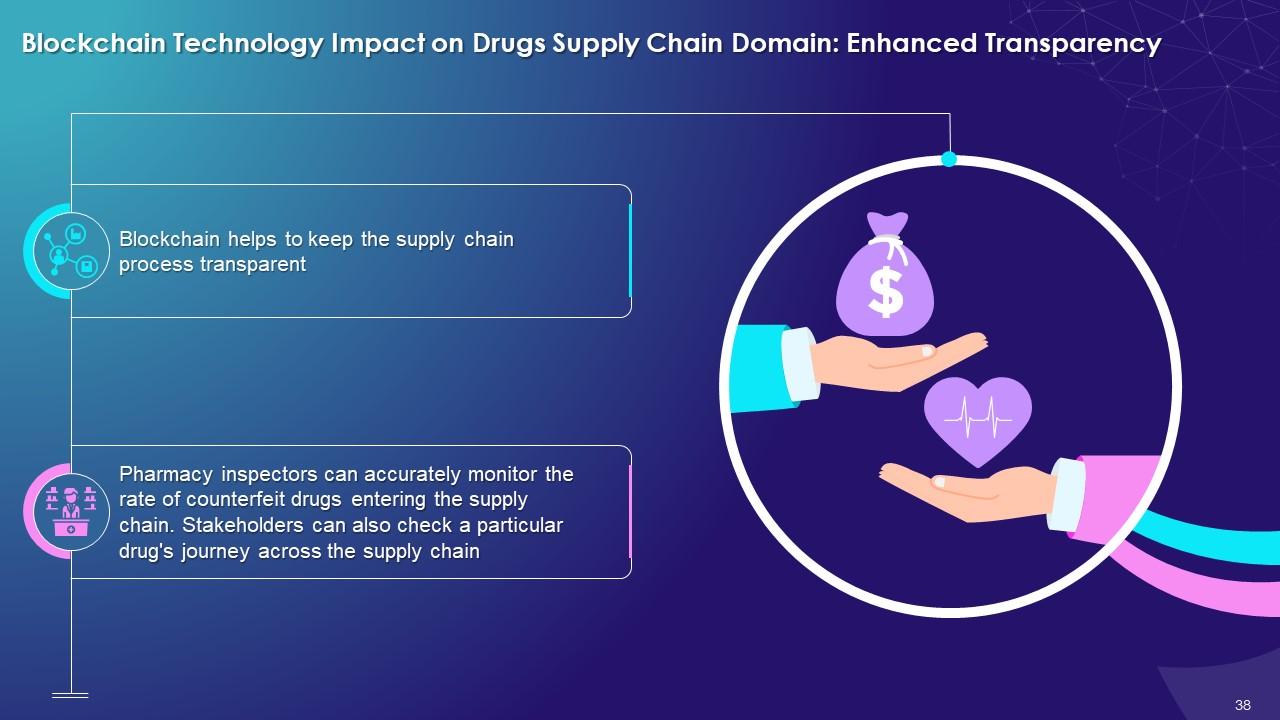
- Blockchain helps to keep the supply chain process transparent
- Pharmacy inspectors can accurately monitor the rate of counterfeit drugs entering the supply chain. Parties can check the drugs’ journey to ensure authenticity
Improved security:
- Blockchain helps to minimize counterfeit drugs
- It also helps to reduce any harm to the patient
- It keeps all data secure in the blocks
Creates an audit trail:
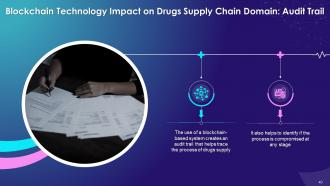
- The use of a blockchain-based system creates an audit trail that helps trace the process of drugs supply
- It also helps to identify if the process has been compromised at any time
Slide 35
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on Drugs supply chain domain by reducing complexity and costs. It explains that blockchain helps make the drugs’ supply chain process traceable, which makes tracking of drugs easier. It also explains that checking the expiry dates of drugs at regular intervals improves control and rotation of drugs production and supply.
Slide 36
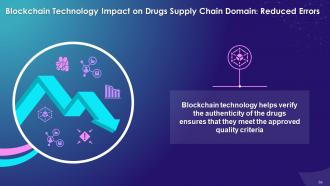
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on Drugs supply chain domain with reduced errors. It explains that blockchain technology helps verify the authenticity of the drugs.
Slide 37
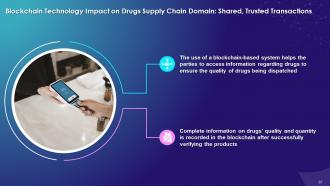
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on drugs’ supply chain domain with shared, trusted transactions. It explains that the use of a blockchain-based system helps parties to access information regarding drugs to ensure the quality of drugs being dispatched. Complete information on drugs’ quality and quantity is recorded in the blockchain after successfully verifying the products.
Slide 38
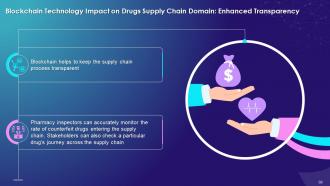
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on Drugs supply chain domain with enhanced transparency between authorized parties. It explains that blockchain helps to keep the supply chain process transparent. The pharmacy inspectors can accurately monitor the rate of counterfeit drugs entering the supply chain. Also, the parties can check the drug journey to ensure authenticity.
Slide 39
This slide highlights the impact of blockchain on Drugs supply chain domain by enhancing security. It explains that blockchain helps to minimize counterfeit drugs, reduce any harm to the patient, and keeps all the data secure in the blocks.
Slide 42
This slide illustrates the concept of health and record exchange of data in healthcare. It highlights that all the records of patients can be accessed by medical specialists securely and electronically which improves the speed, quality, safety, and cost of patient care.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple ways by which health records are exchanged are as follows:
Directed Exchange:
- In this method, all the patient records, such as laboratory test results, patient referrals, discharge papers, etc. can be sent directly to other healthcare professionals
Query-Based Exchange:
- In this exchange process, providers research and discover accessible clinical sources on a patient. This process is used while delivering unplanned care
Consumer-Mediated Exchange:
- This type of process helps the patient access their health information
- It allows patients to manage their health care online the same way as they manage their finance through online banking
Slide 43
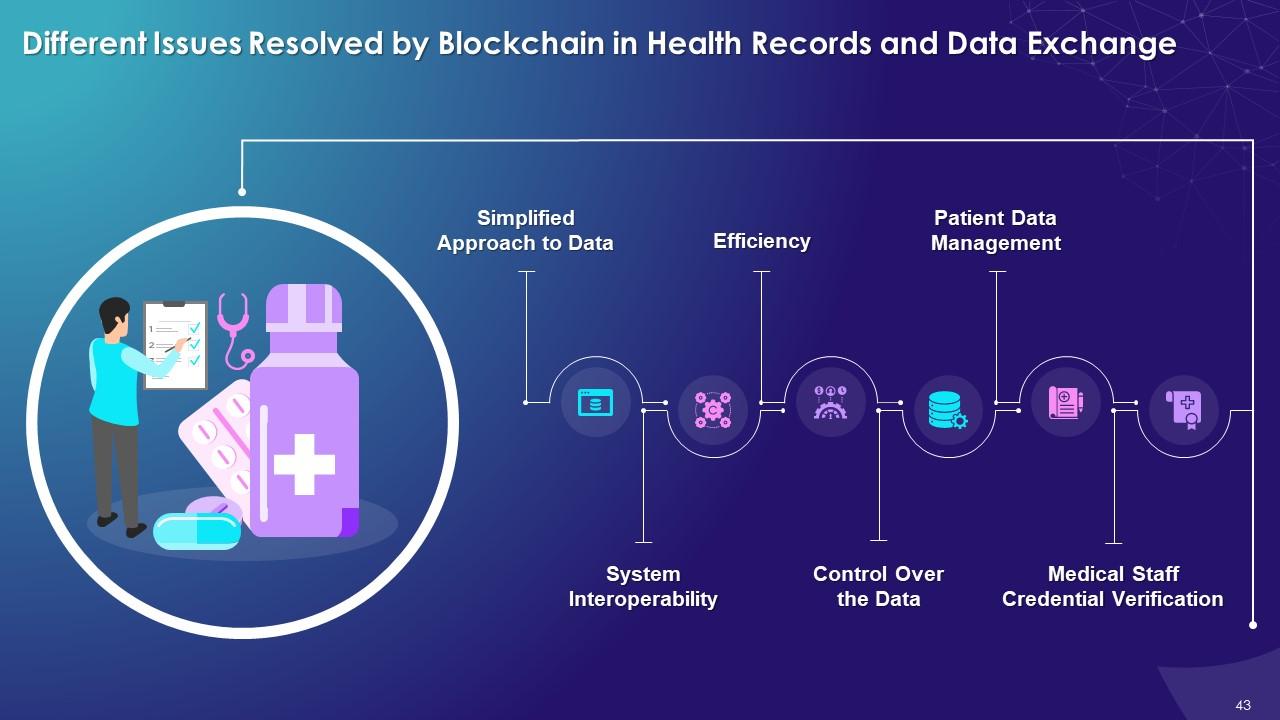
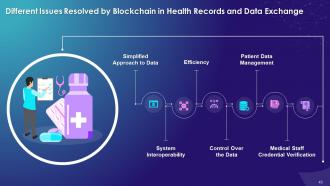
This slide highlights challenges that blockchain resolves in health records and data exchange system. These include a simplified approach to data, system interoperability, efficiency, control over the data, patient data management, and medical staff credential verification.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple issues that blockchain resolves in health records and data exchange system are as follows:
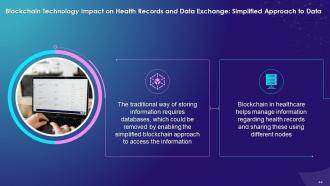
Simplified Approach to Data:
- Blockchain in healthcare helps manage information regarding health records and shares them using different nodes
- The traditional way of storing information requires databases, which could be removed by enabling the simplified blockchain approach to access the information
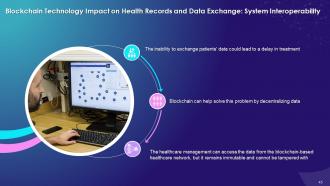
System Interoperability:
- The inability to share/access patients' data could lead to a delay in treatment
- Blockchain helps solve this problem by data decentralization
- The healthcare management can access the data from the blockchain-based healthcare network, but the data remains immutable and cannot be tampered with
Efficiency:
- Blockchain enhances efficiency of the healthcare system via real-time processing
- Blockchain can remove the need for third-party companies and eliminate the delay in data access
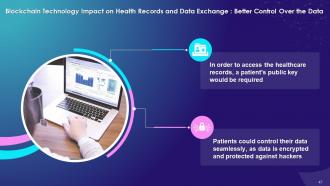
Control Over Data:
- In order to access the healthcare records, a patient's public key would be required
- Patients could control their data seamlessly, as it is encrypted and protected against hacking
Patient Data Management:
- The use of blockchain technology helps healthcare management collect all the data and store in blocks
- Using blockchain for storing health records could help both patients and doctors view the data for an effective understanding of patients' health
Medical Staff Credential Verification:
- The use of blockchain technology in healthcare could help verify the professional records of medical staff members working in the system
- It can ease the hiring process in the healthcare organization
- Due to immutability, the credentials of staff are secure, and the organization has improved transparency
Slide 44
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on health records and data exchange by using simplified approach to data. It explains the use of a blockchain-based system in managing the information regarding health records and sharing these using different nodes in the system.
Slide 45
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on health records and data exchange with system interoperability. It highlights delay in treatment that can happen due to inability to exchange patients' data. It helps in resolving these issues as health data is made interoperable.
Slide 46
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on health records and data exchange with increased efficiency. It highlights that blockchain can turn the healthcare system highly efficient via real-time processing.
Slide 47
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on health records and data exchange by providing control over data. It explains that in order to access the healthcare records, a patient's public key would be required.
Slide 48
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on health records and data exchange by managing patients’ data. It explains that using blockchain technology helps the healthcare management system to collect all data and store it in blocks.
Slide 49
This slide illustrates the impact of blockchain on health records and data exchange for medical staff credential verification. It explains that using blockchain in healthcare could help verify the professional records of medical staff members working in the system. It also explains the use of blockchain for new hiring in the system.
Slide 51
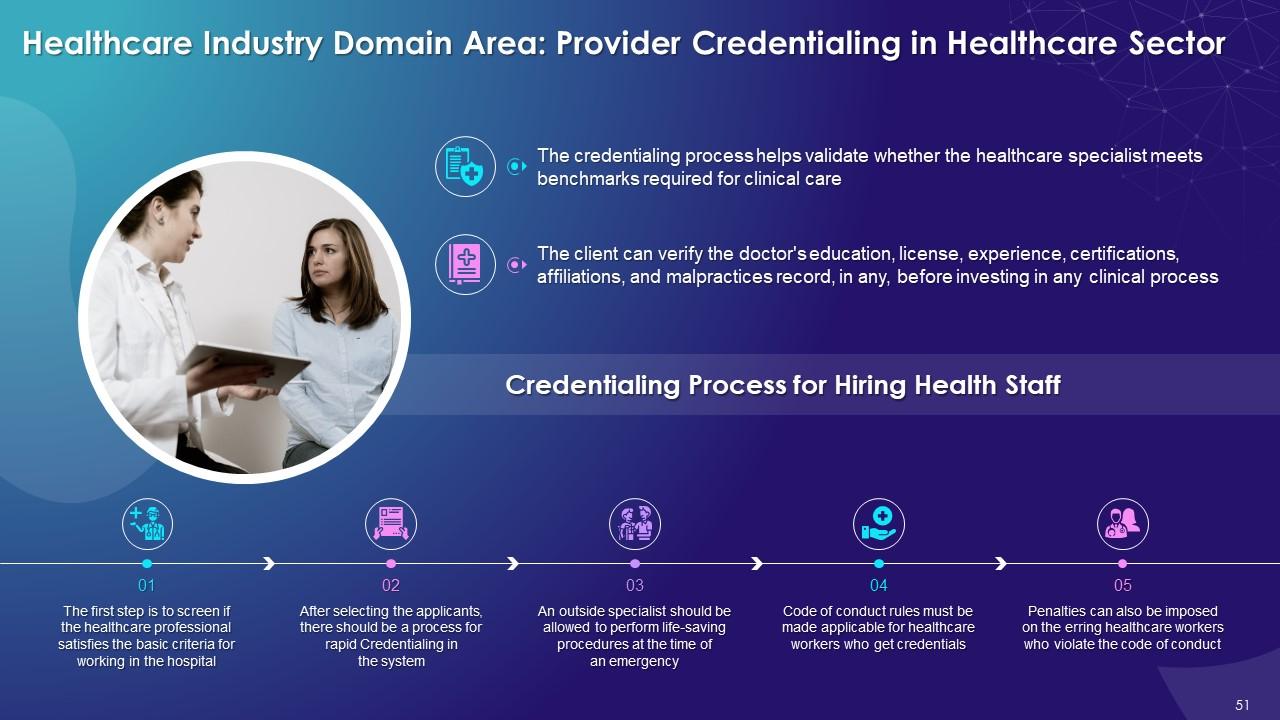
This slide illustrates the concept of credentialing providers in healthcare industry. It also determines the credentialing process for hiring health staff.
Slide 52
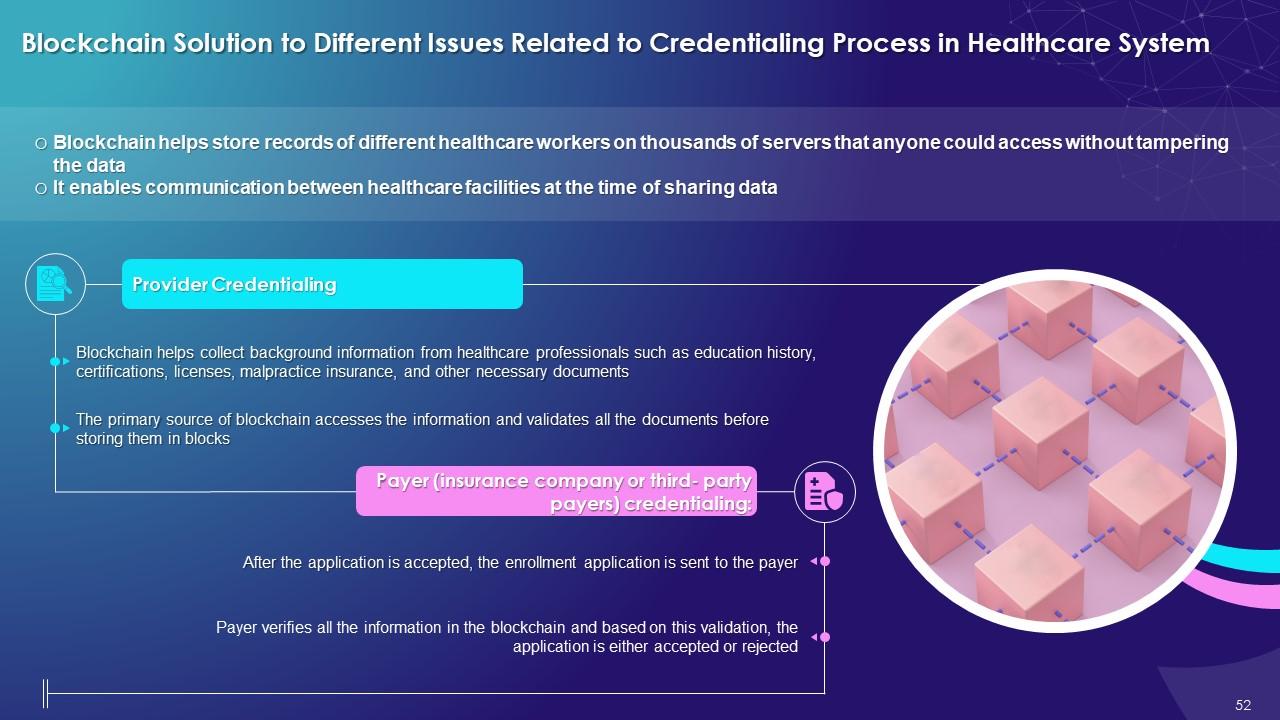
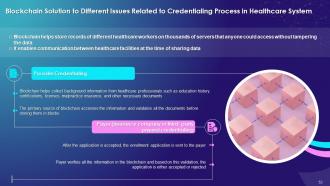
This slide illustrates the challenges that blockchain resolves in the credentialing process. It highlights that blockchain helps store records of different healthcare workers on thousands of servers that anyone could access without tampering with the data and creates communication between healthcare facilities at the time of sharing data.
Slide 54
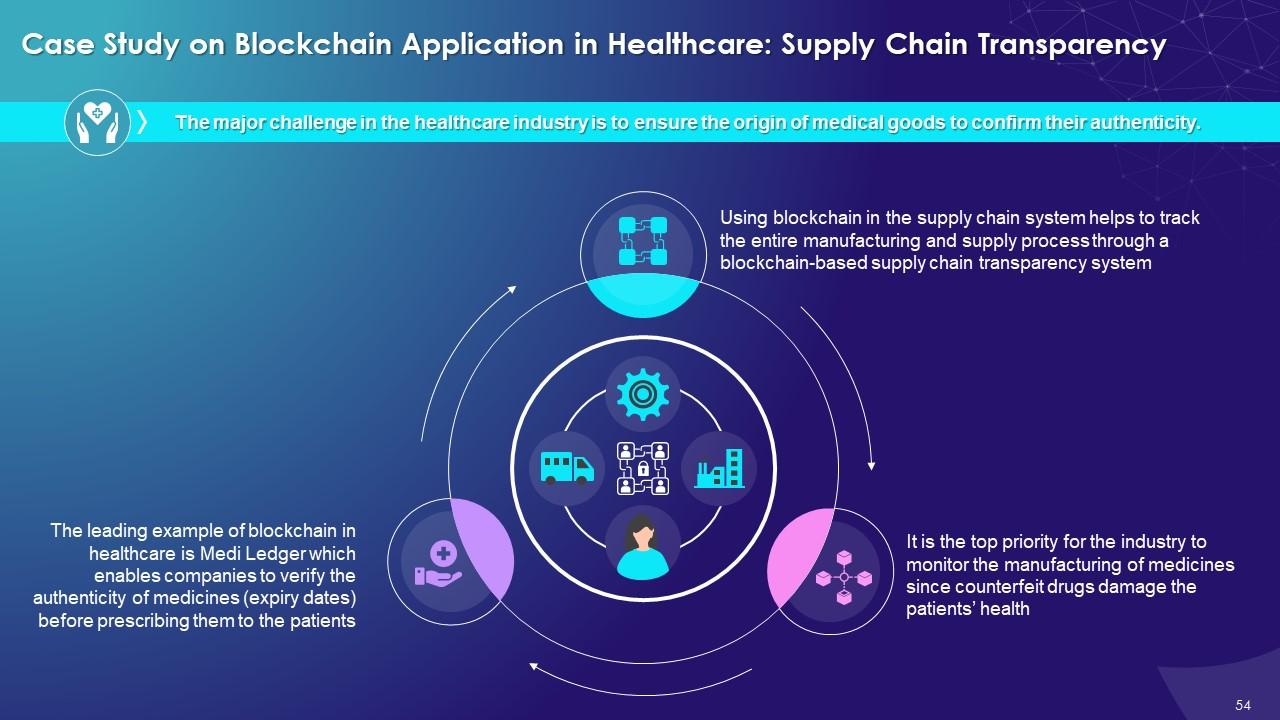
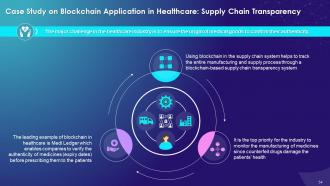
This slide illustrates the use case of supply chain transparency using blockchain technology. It explains that using blockchain in supply chain helps to track the entire manufacturing and supply process through a blockchain-based supply chain transparency system.
Instructor’s Notes:
The key benefits of transparency using blockchain in supply chain are as follows:
Customer confidence:
- It helps to improve customer confidence by letting them track each package's end-to-end provenance, by integration with manufacturing, wholesale, shipping etc.
Compliance:
- By using blockchain-based software, medical device manufacturers and pharmaceuticals can easily ensure patient safety, helping streamline compliance
- It provides automated law enforcement notifications if an alarm is raised over a process or an issue
Supply chain optimization:
- After the data is compiled, companies apply Artificial Intelligence (AI) to predict demand and optimize supply accordingly
Slide 55
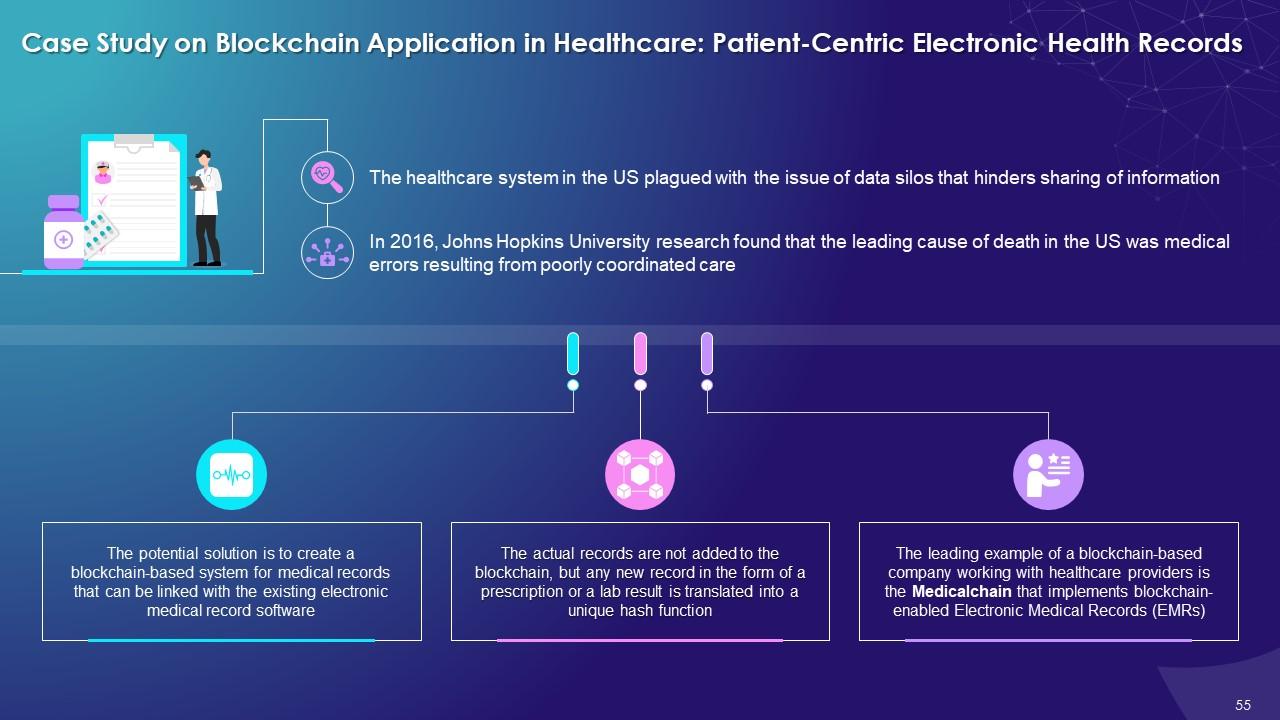
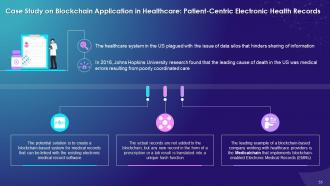
This slide illustrates the use case of patient centric electronic health records by using blockchain technology. It explains that the potential solution is to create a blockchain-based system for medical records that can be linked with the existing electronic medical record software.
Instructor’s Notes:
The key benefits of using blockchain in patient-centric electronic health records are as follows:
Complete Transparency:
- A single medical record source develops trust among patients and enables them to see their records every time they are updated
- Patients can give permission to other healthcare personnel to examine their records and can set time limits on how long a third party can check the data
Fast Validation:
- Insurers can receive immediate validation of healthcare services directly from patients
- Direct validation helps to save time and cost due to the elimination of any intermediary
Slide 57
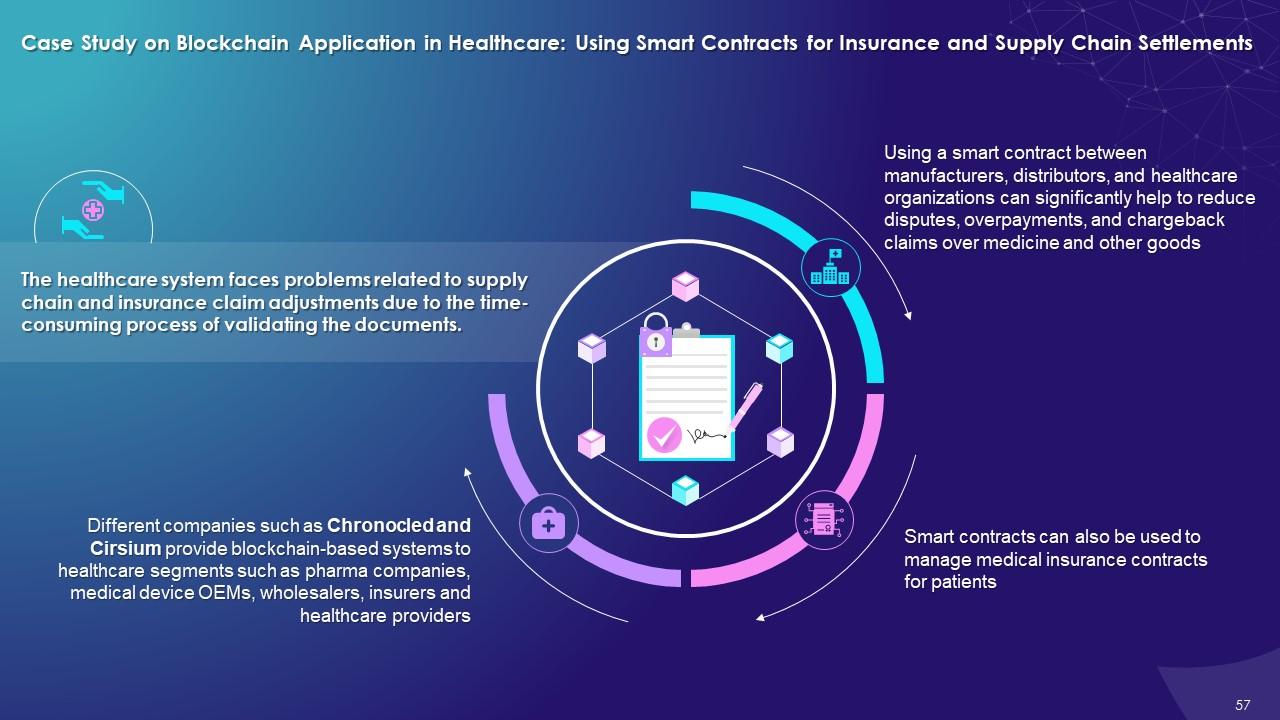
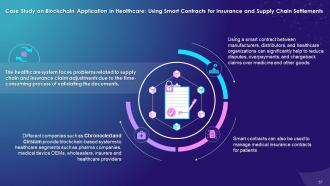
This slide illustrates the use of smart contracts for insurance and supply chain settlements using blockchain technology. It explains that different companies provide blockchain based systems to healthcare segments such as pharma companies, medical device OEMs, Wholesalers, insurers and healthcare providers. It also highlights that using a smart contract between manufacturers, distributors, and healthcare organizations can significantly reduce disputes over payment, chargeback claims over medicines and other goods.
Slide 58
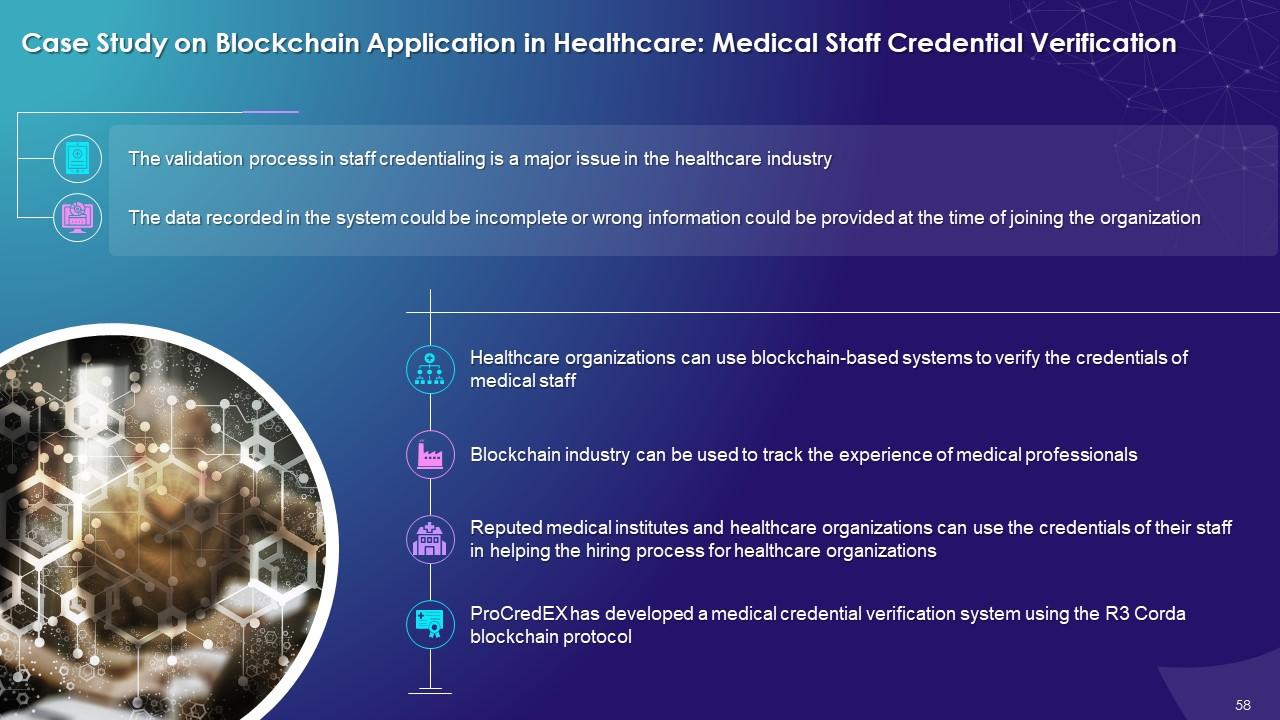
This slide highlights the medical staff credential verification process by using blockchain technology. It explains that healthcare-based systems can be used for verifying the credentials of medical staff. Blockchain based solutions can be used to track the experiences of medical professionals.
Instructor’s Notes:
The key benefits of using blockchain in medical staff credential verification process are as follows:
Faster Credentialing Process:
- Blockchain provides fast credentialing during the hiring process for healthcare organizations
Credential Monetization:
- Blockchain helps to provide an opportunity for healthcare institutes, insurers, and healthcare providers to monetize the credential data of past and existing staff members
Transparency and Reassurance:
- Blockchain helps deliver information to patients on experience of the medical staff who will tend to them. This allows patients to filter out the options regarding healthcare treatment
Slide 60
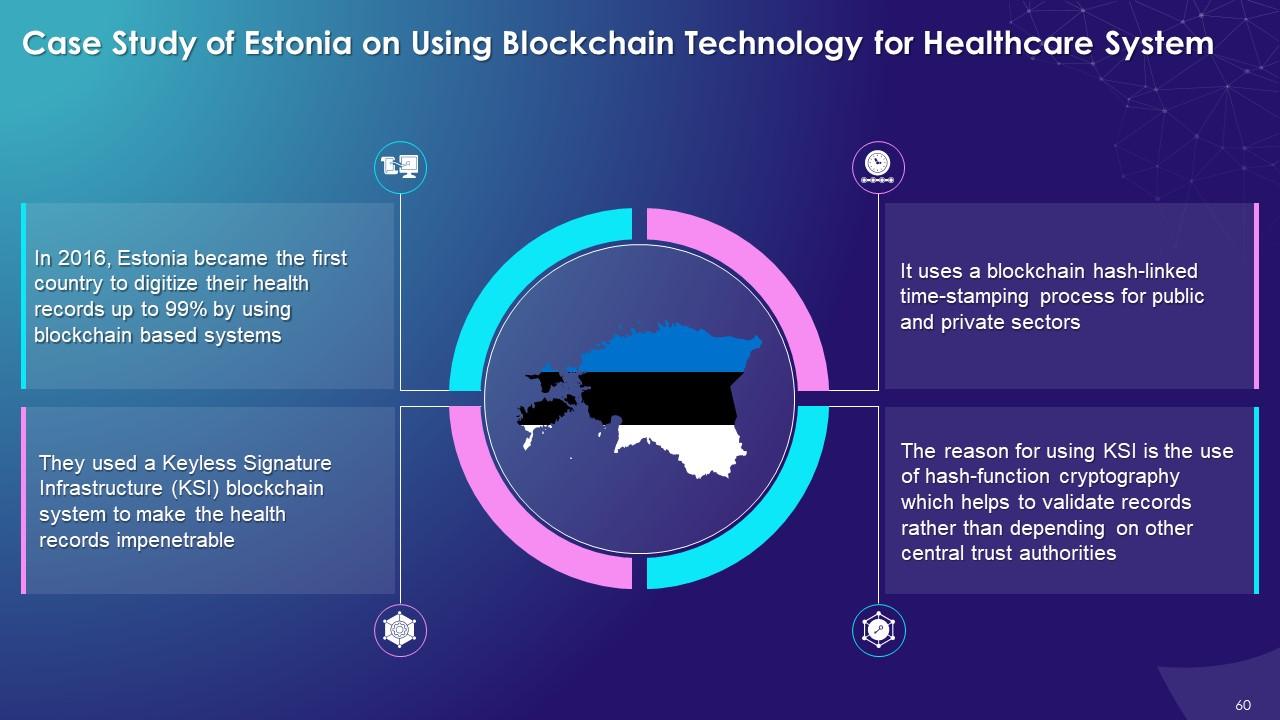
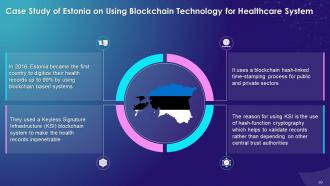
This slide illustrates the use case of Estonia for using blockchain technology for healthcare system. It highlights that in 2016 Estonia became the first country to fully digitize the health records, up to 99%, with the use of a blockchain-based system. It also explains the need to transform the healthcare system into digital healthcare system with the use of blockchain technology.
Slide 61
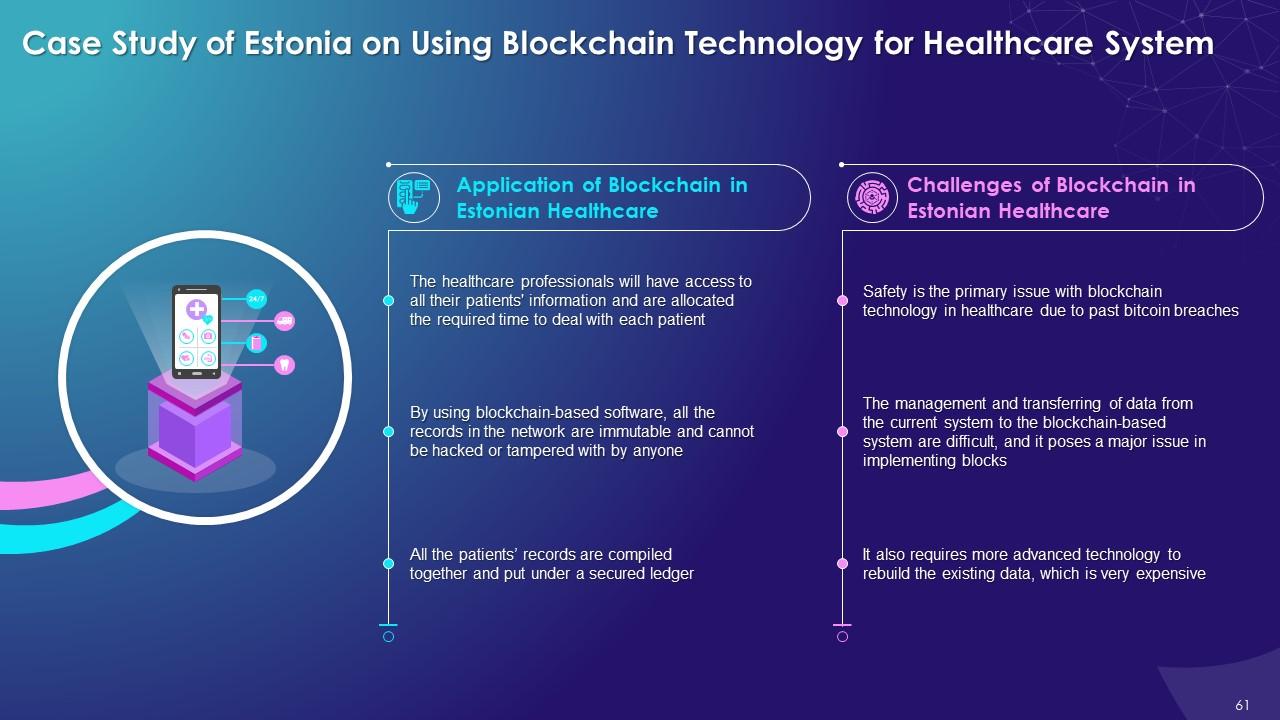
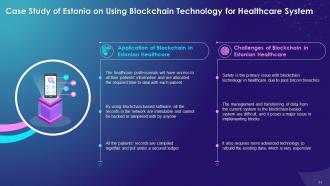
This slide illustrates the different applications of blockchain technology in Estonian healthcare system which states that the healthcare professionals will have access to all their patients' information and are allocated the required time to deal with each patient. It also explains the different challenges of blockchain in Estonian healthcare system such as safety issue, management issue, and transferring the data issue.
Slide 63
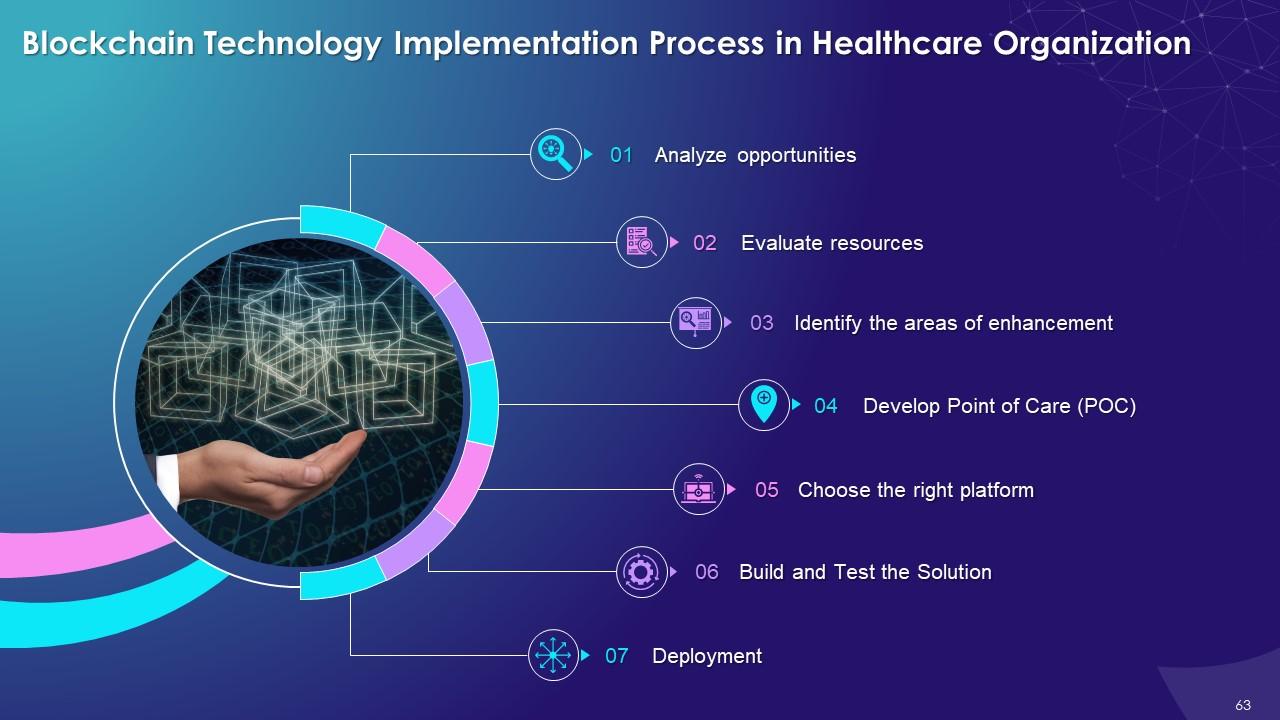
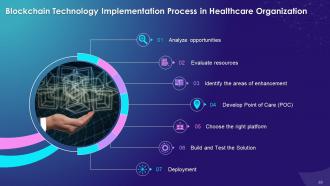
This slide illustrates stages to be cleared for implementation of blockchain in healthcare industry such as analyzing opportunities, evaluating resources, identifying areas of enhancement and developing a Point of Care. It also includes choosing the right platform, building and testing the solution, and development.
Instructor’s Notes
The different stages of implementing blockchain in healthcare organization are as follows:
Analyze opportunities:
- Explore all the options for implementing Blockchain technology. For guidance, you can also reach out to other industries like Banking or Insurance
Evaluate resources:
- For the development and implementation processes, professional knowledge and experiences are required
- The companies that lack these resources hire external teams to help develop platforms for them
- Multiple offshore vendors offer services and can be hired for this platform
- In such cases, the main requirements for the vendors should be reliability, availability of resources, previous portfolios, and references from previous customers
Identify the areas of enhancement:
- It is important to understand which part of the organization needs improvement
- It also requires analyzing and organizing the requirements needed to use the technology
Develop POC:
- Proof of Concept (POC) will help to understand and guide through all the stages of the implementation, and it is important to determine whether it is feasible and functional to execute the task
Choose the right platform:
- Nowadays, multiple networks are available where the users can adopt the technology, which includes Ethereum, Corda, Hyperledger, etc.
Build and Test the Solution:
- It is crucial to test the solution fully and check how it works in the real world
Deployment:
- At the development stage, it is important to establish the solution on the network
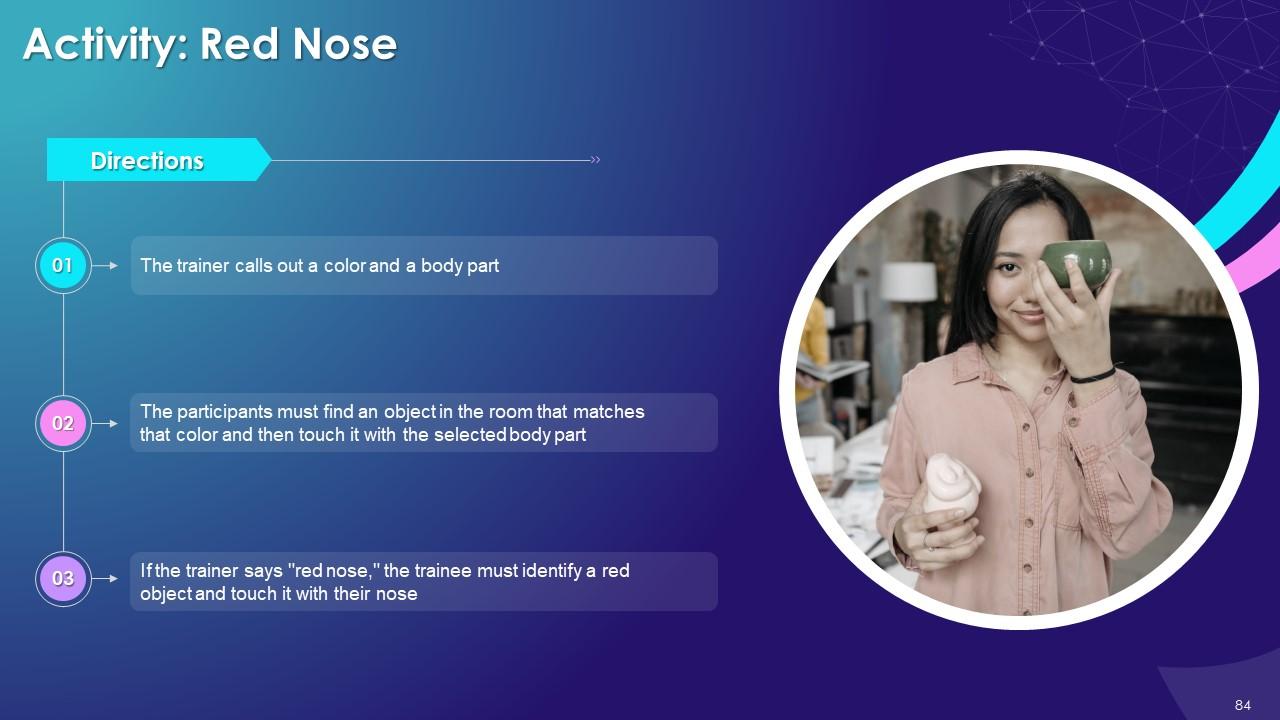
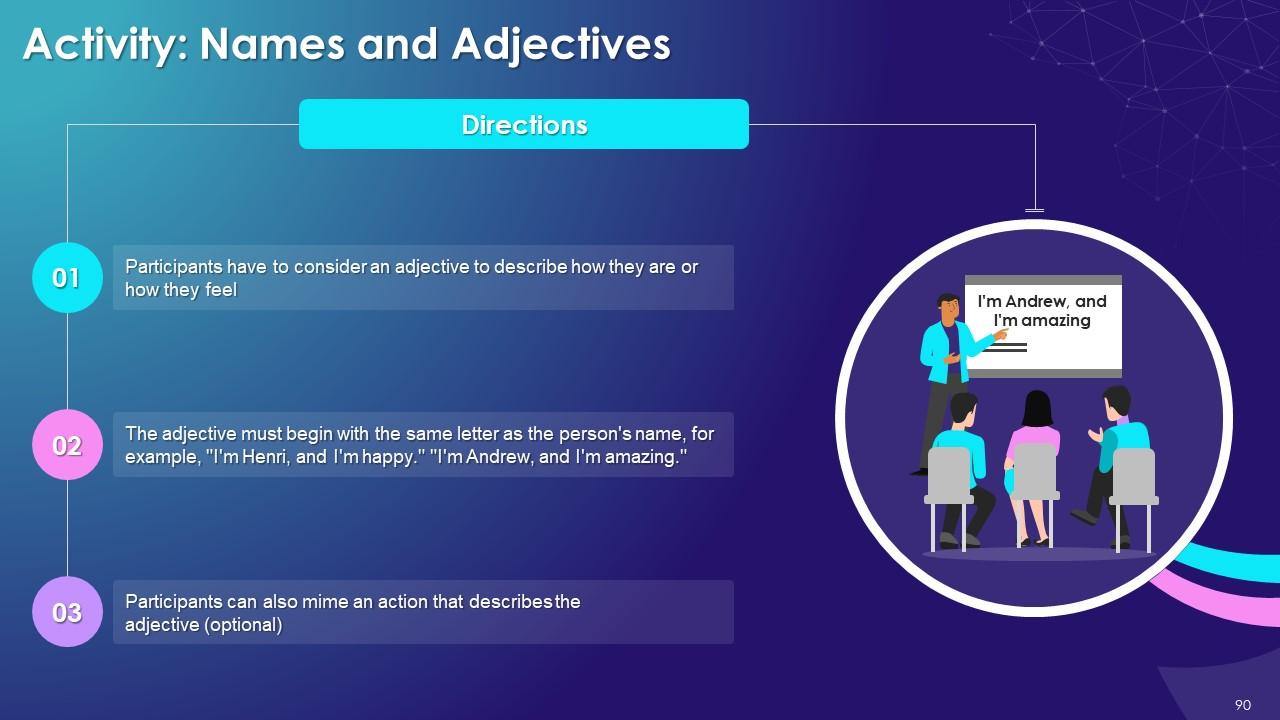
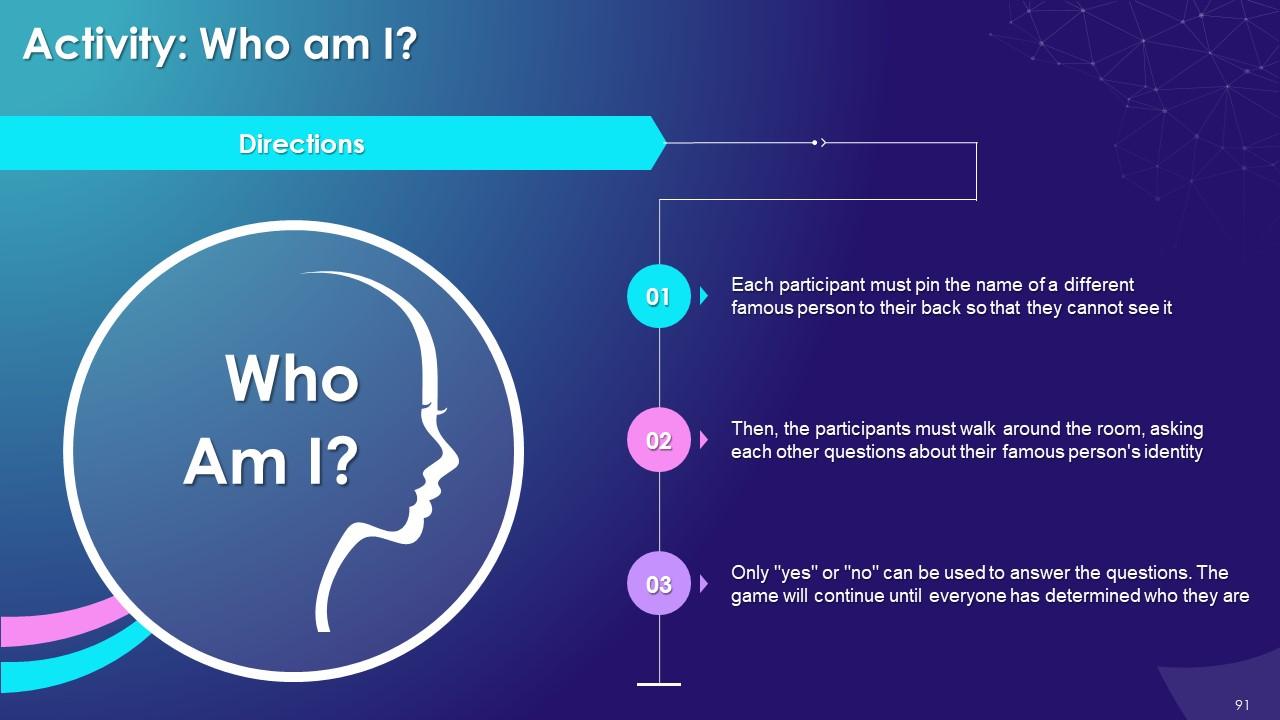
Slide 83 to 97
These slides depict energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Blockchain Technology Applications in Healthcare Industry Training Ppt with all 102 slides:
Use our Blockchain Technology Applications in Healthcare Industry Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
The way SlideTeam professionals work is exceptional. Thanks for being so helpful!
-
Presentation Design is very nice, good work with the content as well.