Implementing Digital Transformation in Organizations Training ppt
The PowerPoint training deck in-depth covers how organizations can successfully transform themselves digitally for accelerated growth. It has PPT slides on DNA and the characteristics of exponential organizations. It covers planning aspects of digital transformation with maturity assessment and readiness, the leaders role, the digital maturity model, the digital transformation plan, and road mapping. The PPT module covers digital transformation strategic objectives, new digital products and services, value proposition design, benefits of data-driven decision-making, business intelligence in the data age, and project selection and prioritization. It also has steps to start digital transformation initiatives and tips for a successful digital transformation journey. Further, The digital transformation ppt deck has key takeaways and discussion questions to make the training session interactive. It also contains templates on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, energizer activities, client training proposal, and evaluation form.
The PowerPoint training deck in-depth covers how organizations can successfully transform themselves digitally for accelera..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Implementing Digital Transformation in Organizations. This presentation deck contains 117 well researched and uniquely designed slides. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
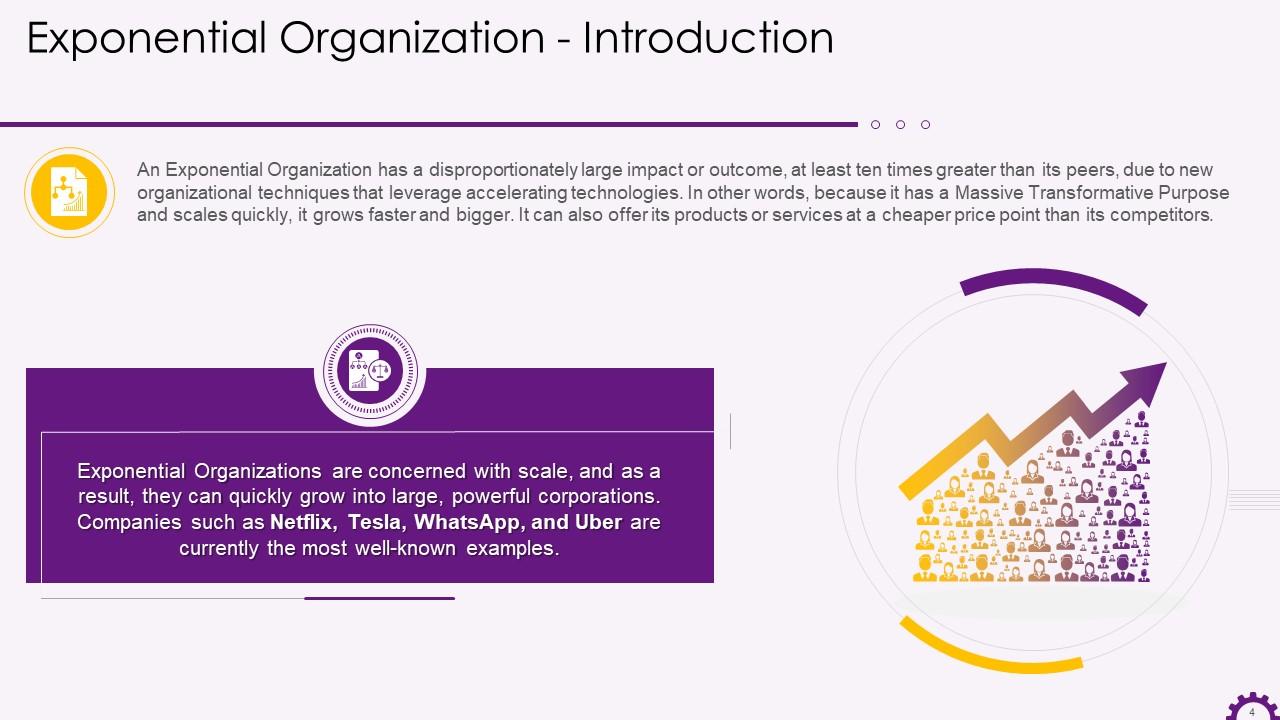
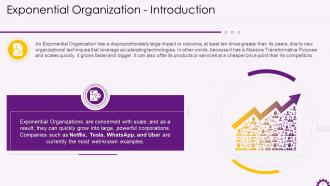
This slide depicts the introduction to exponential organizations. It emphasizes that an exponential organization has a significant impact or outcome due to new techniques that leverage accelerating technologies. They have a massive transformative purpose and scale quickly, allowing them to grow bigger, faster, and cheaper than their competitors. It also mentions well-known examples of exponential organizations such as Netflix, Tesla, WhatsApp, and Uber.
Slide 5
This slide illustrates information about an exponential organization's DNA. Data, disruption, openness, flat structure, small teams, renting rather than owning, and little trust in a five-year plan are all part of it.
Slide 6
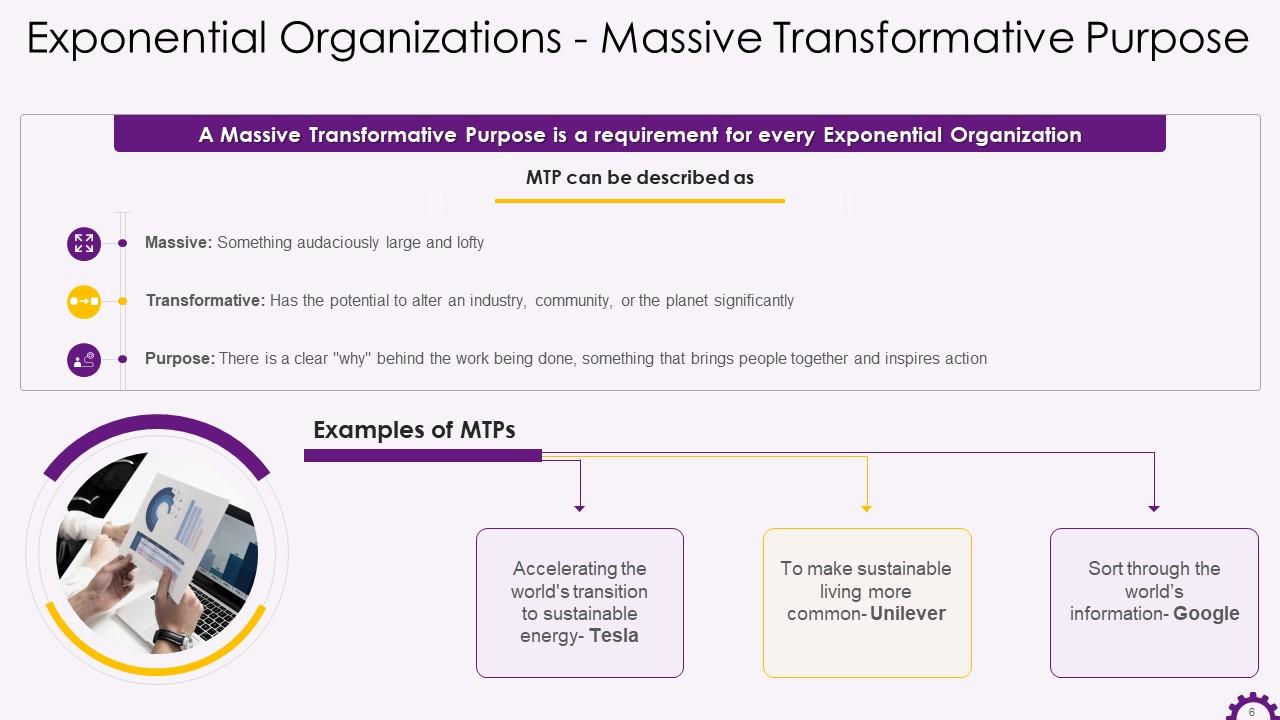
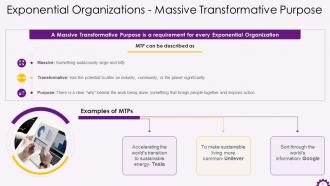
This slide showcases information regarding Massive Transformative Purpose in Exponential Organizations. It highlights that a massive transformative purpose is a need for every exponential organization. It also mentions the examples of MTPs of Tesla, Unilever, and Google.
Slide 7
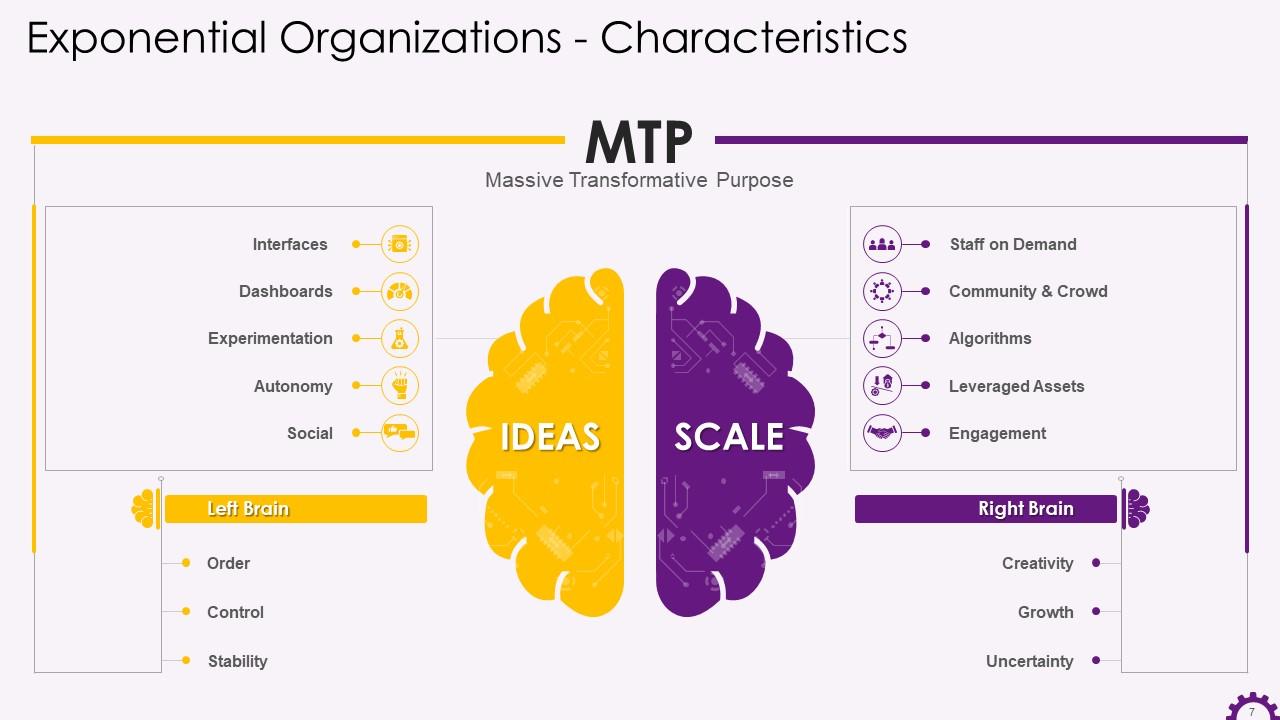
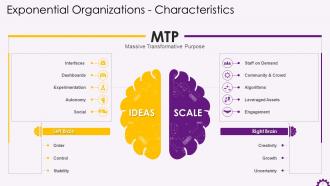
This slide illustrates the characteristics of Exponential Organizations. The characteristics are interfaces, dashboards, experimentation, autonomy, social, staff on demand, community & crowd, algorithms, leveraged assets, and engagement.
Instructor’s Notes:
The characteristics of exponential organizations are:
- Interfaces: Interfaces are the filtering and matching processes that allow an exponential organization to connect SCALE externalities to IDEAS control frameworks. They may start as manual processes before evolving into self-provisioning platforms that allow exponential organizations to scale
- Dashboards: This must provide a real-time picture of the business. Dashboards provide visibility and transparency to a company, shorten feedback loops, reduce the effort required to understand a situation, and allow a company to improve and evolve
- Experimentation: Constant experimentation and process iteration help to reduce risk in an organization. Through fast feedback loops, exponential organizations enable rapid experimentation and process improvement
- Autonomy: The foundation for "permissionless innovation" to support exponential growth in self-organizing, multidisciplinary teams operating with decentralized authority. Autonomy also improves an organization's agility, efficiency, transparency, and accountability
- Social: Even in vertically organized companies, these technologies promote horizontal interactions. Most importantly, they reduce information latency, which shortens the time it takes for an idea to be accepted and implemented. Examples of social technologies are file sharing, telepresence, virtual worlds, and emotional sensing tools
- Staff on Demand: Exponential organizations use external contractors to act quickly and flexibly in a fast-changing world. Companies can fill expertise gaps and ensure a constant flow of fresh ideas by outsourcing as many tasks as possible rather than maintaining a sizeable full-time workforce
- Community & Crowd: Internal staff, partners, vendors, customers, users, and fans comprise an organization's core community. Everyone outside of these core layers constitutes the crowd, and they can all be used to build a community that can provide creativity, innovation, validation, and even funding
- Algorithms: Algorithms power companies like Google, Airbnb, and DHL, allowing for dynamic pricing, credit card fraud detection, traffic optimization, and much more. Exponential organizations use Machine-learning technologies to refine these algorithms
- Leveraged Assets: Renting, sharing, and leveraging assets like office space, machinery, copiers, and even office plants have long been the norm. Businesses are increasingly outsourcing Mission-critical assets. Apple, for example, uses the factories of its manufacturing partner Foxconn for key product lines. The lack of assets increases agility and allows for rapid scaling
- Engagement: User engagement techniques such as incentive prizes and gamification assist exponential organizations and cut time taken to engage markets
Slide 8
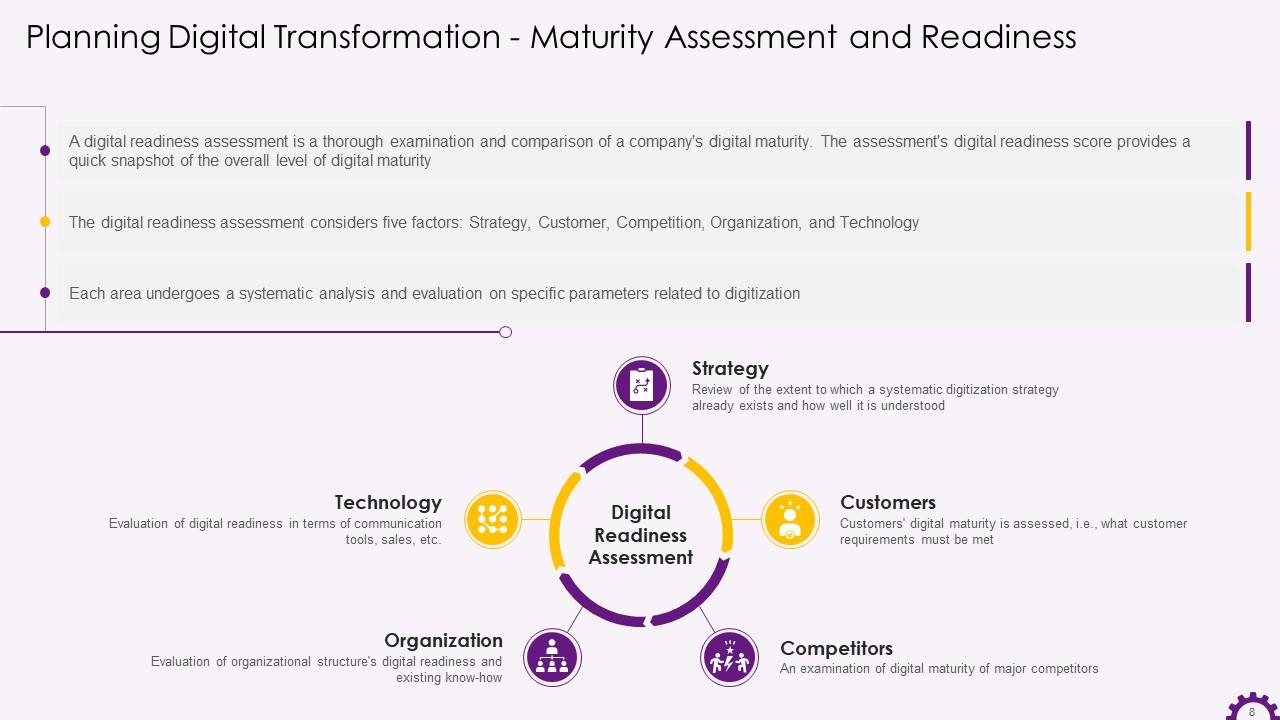
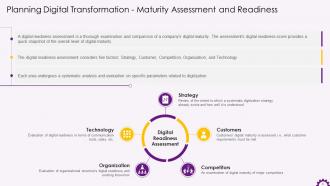
This slide depicts information about maturity assessment and readiness. It emphasizes that a digital readiness assessment is a comprehensive examination and comparison of a company's digital maturity. It also discusses the digital readiness assessment factors of strategy, customer, competition, organization, and technology.
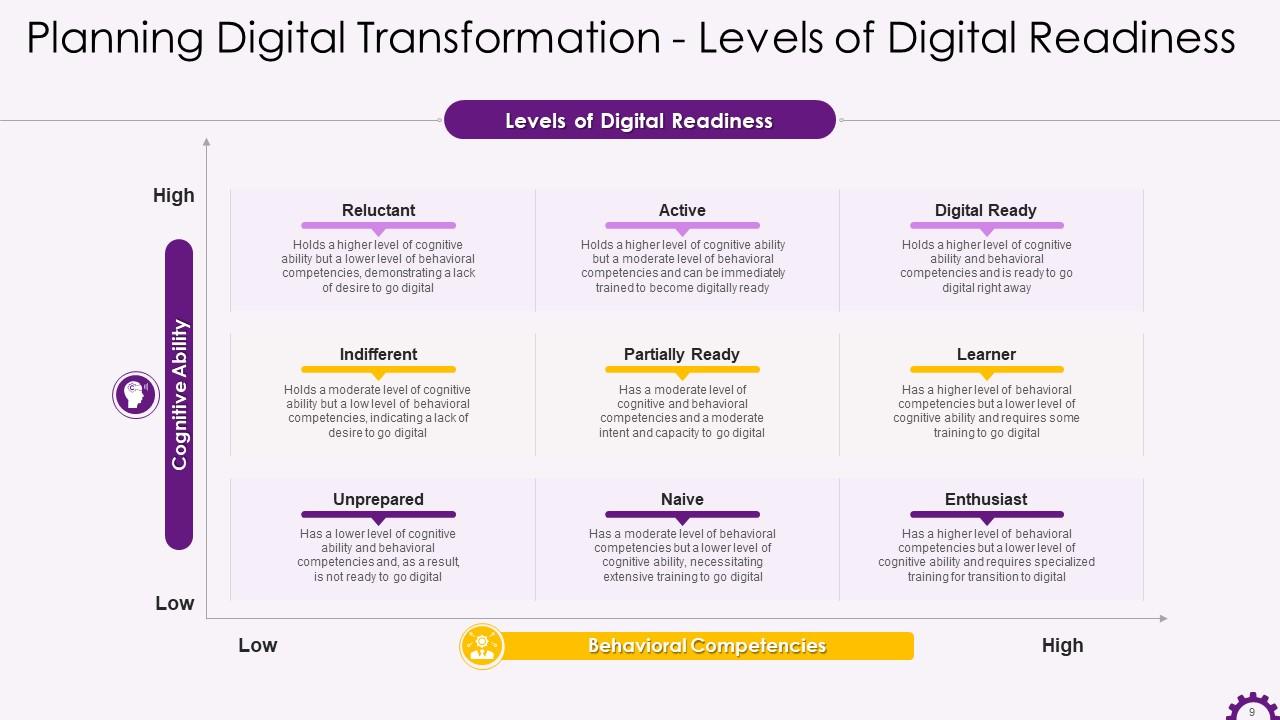
Slide 9
This slide illustrates the various levels of digital readiness. It can be used to assess the digital readiness level of an individual employee or the entire workforce.
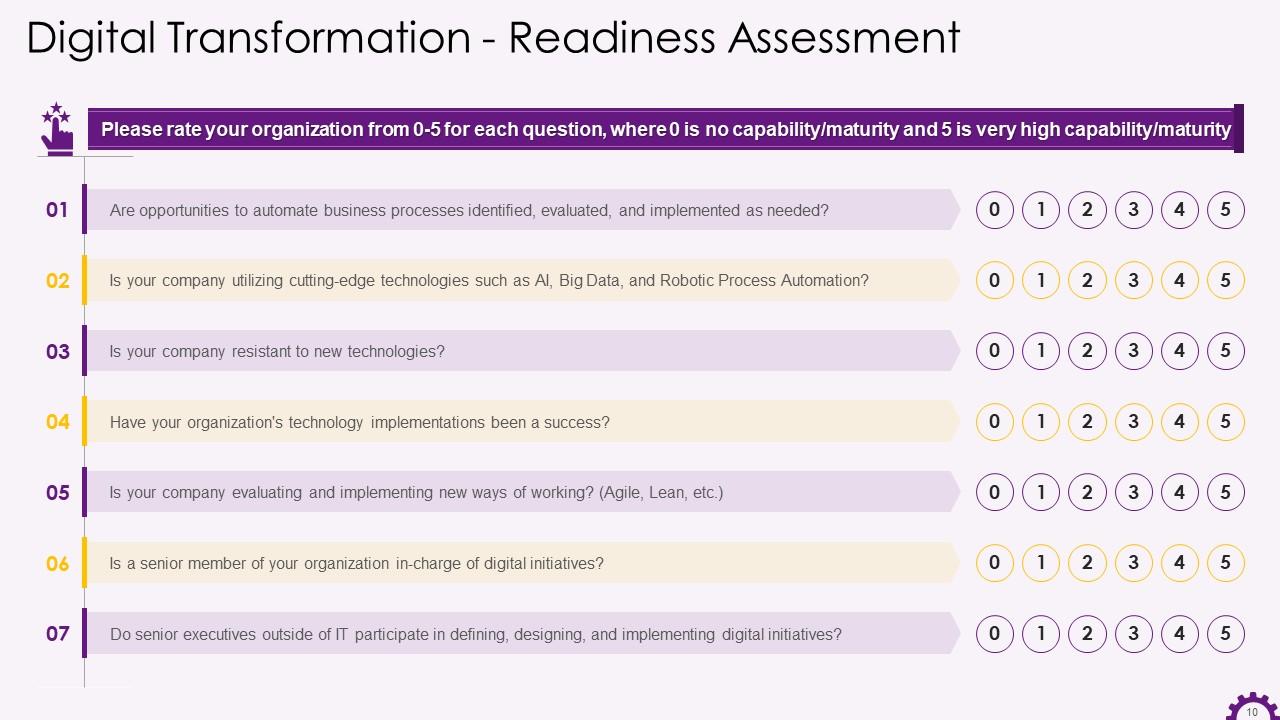
Slide 10
This slide depicts the Digital Transformation Readiness Assessment Exercise. It also emphasizes some statements that can be used to assess an organization's capability or maturity level.
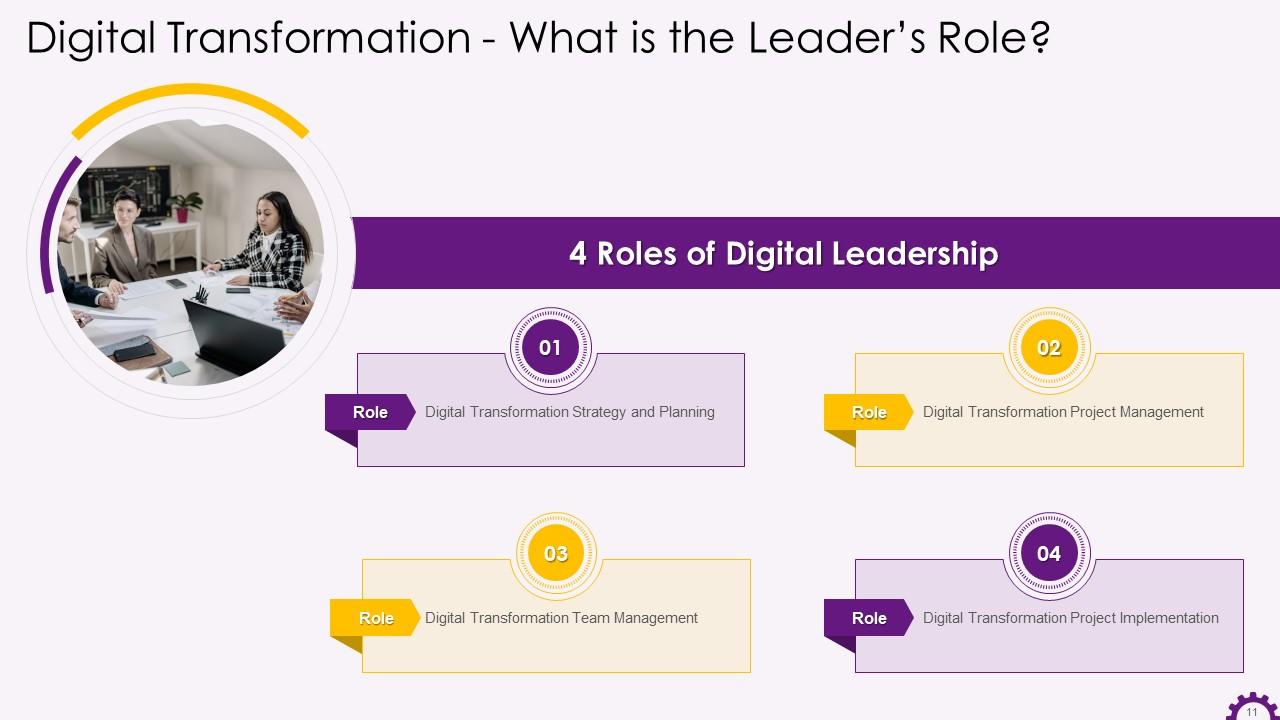
Slide 11
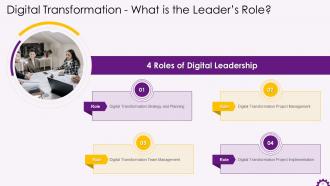
This slide illustrates the roles of a digital leader. The roles are: strategy and planning, project management, team management, and project implementation.
Instructor’s Notes:
The four roles of digital leadership are:
- Digital Transformation Strategy and Planning: A digital transformation plan provides the company with direction and action items on improving customer experience, employee productivity, management capabilities, and company value. This position necessitates strong business acumen, an understanding of the industry, being realistic about the organization's resources, and good planning skills. Without the Planning role, digital projects are haphazard, uncontrolled, and add no value to the company
- Digital Transformation Project Management: Once a plan has been established, the next step is to manage all projects. This requires the company to ensure that it is clear of the scope and has a plan of what it wants to accomplish. Critical digital transformation initiatives will not be completed on time or within budget if a proper project management role is not assigned
- Digital Transformation Team Management: At any given time, every business is working on multiple business improvement initiatives, many of which are related to digital technologies in various shapes and forms. These necessitate management to maintain daily momentum and create accountability to ensure that essential tasks are completed. Without a strong leader, the team becomes disjointed and sidetracked, and the goals are not met
- Digital Transformation Project Implementation: Leaders must sometimes roll up their sleeves and work on projects themselves, rather than just managing the people involved. Typically, technology-related projects necessitate a solid technical foundation to comprehend the implications of decisions
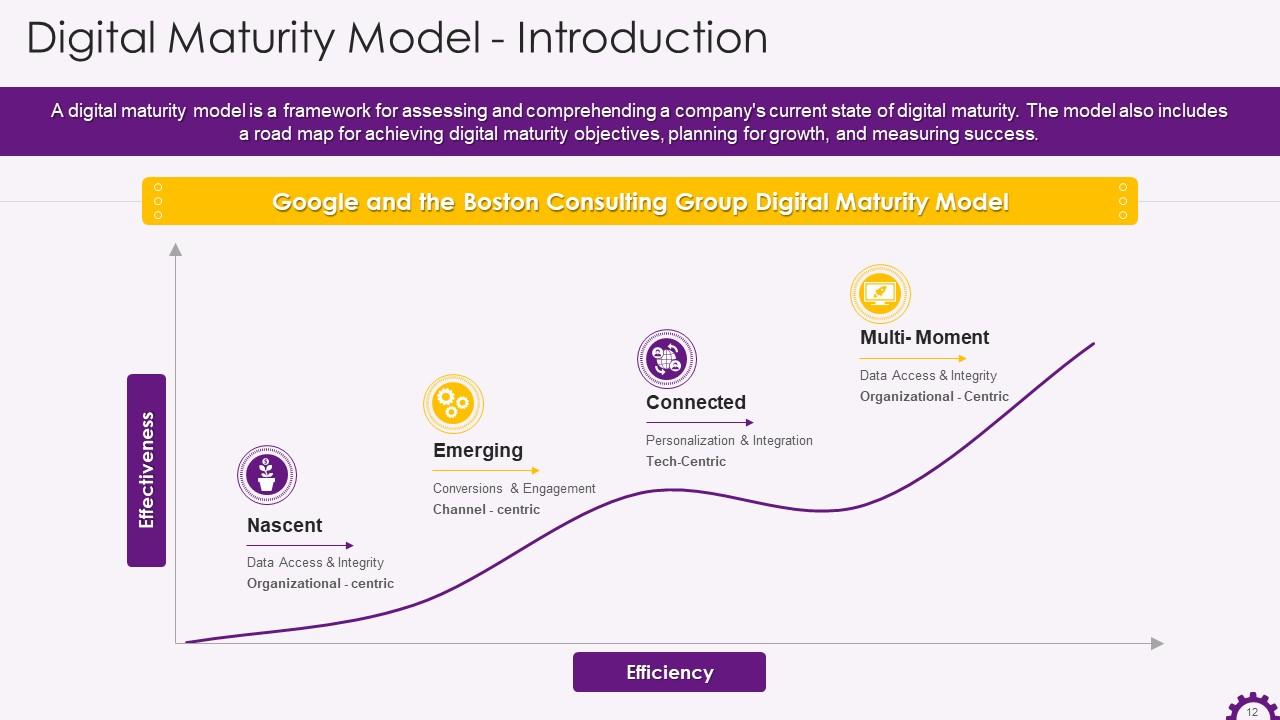
Slide 12
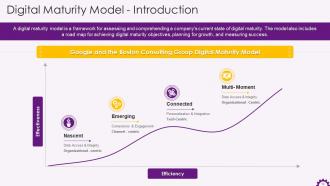
This slide showcases information regarding the digital maturity model. It highlights that a digital maturity model is a framework for assessing and comprehending a company's current state of digital maturity. It also mentions the Google and the Boston Consulting Group Digital Maturity Model.
Instructor’s Notes:
The four stages of digital maturity are:
- Nascent: Data quality creates data silos between departments. Strong leadership buy-in and stakeholder engagement are required
- Emerging: Focused on improving customer experiences, deploying new technology, and developing cross-departmental scaling strategies
- Connected: Utilizes data-driven processes to increase productivity, using offline and online data to drive sales and support company-wide goals
- Multi-Moment: Fully data-driven integrations are used to optimize across all channels, touch points, and departments
Slide 13
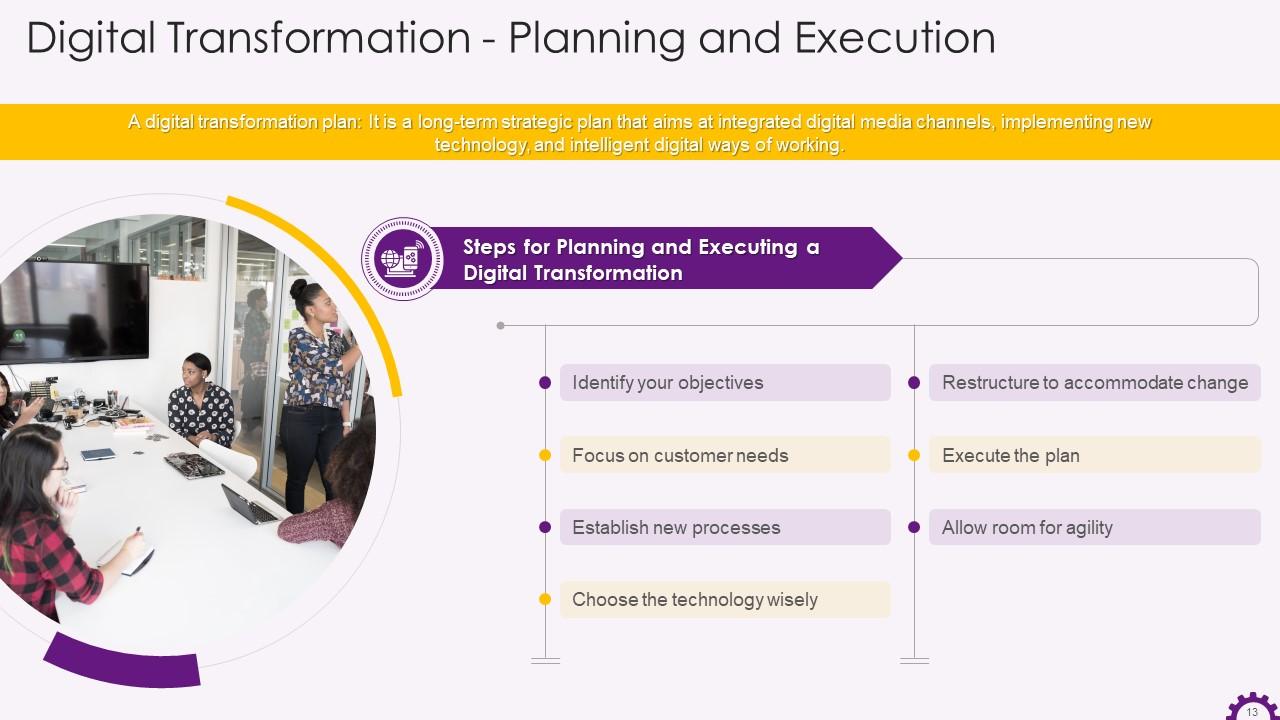
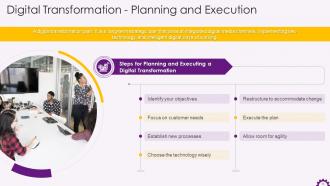
This slide illustrates the introduction to digital transformation plan. It highlights the steps for planning and executing a digital transformation plan.
Instructor’s Notes:
The steps for planning and executing a digital transformation are:
- Identify your objectives: A digital transformation plan should clearly understand your objectives and the steps necessary to achieve them
- Focus on customer needs: Digital transformation aims to increase customer value by utilizing digital tools. To ensure that your digital transformation plan succeeds, everything a company plans should consider its customers' needs
- Establish new processes: The 'business as usual' approach may not always be compatible with your digital transformation initiatives. The involvement of the primary stakeholder is a must. For some businesses, digital transformation will necessitate a complete overhaul of their processes. It is critical to bring employees together to organize this change to ensure that everyone understands the updates, who is responsible for what, and what systems are in place to help the team
- Choose the technology wisely: To successfully implement digital transformation, an organization does not require every technology available. Instead, select a technology that will help the organization optimize the processes they are working on. Finally, the technology that an organization chooses should be aligned with its goals and assist the organization in meeting its objectives
- Restructure to accommodate change: Introducing digital workplace tools that enable change is one of the things organizations do to become more agile and innovative. However, many people recognize that this is insufficient. Some organizations also implement digital literacy programs and related culture change initiatives, while others engage in some restructuring to support the investment in digital workplace tools
- Execute the plan: By executing a plan in manageable chunks, an organization can make continuous and significant improvements without introducing sporadic, overwhelming, and disruptive change
- Allow room for agility: It can take years to complete digitization. An organization can ensure progress with agile methods because you get real-time feedback and correct your course to address issues early. Agility also aids in breaking down silos, increasing transparency within teams, and holding everyone accountable
Slide 14
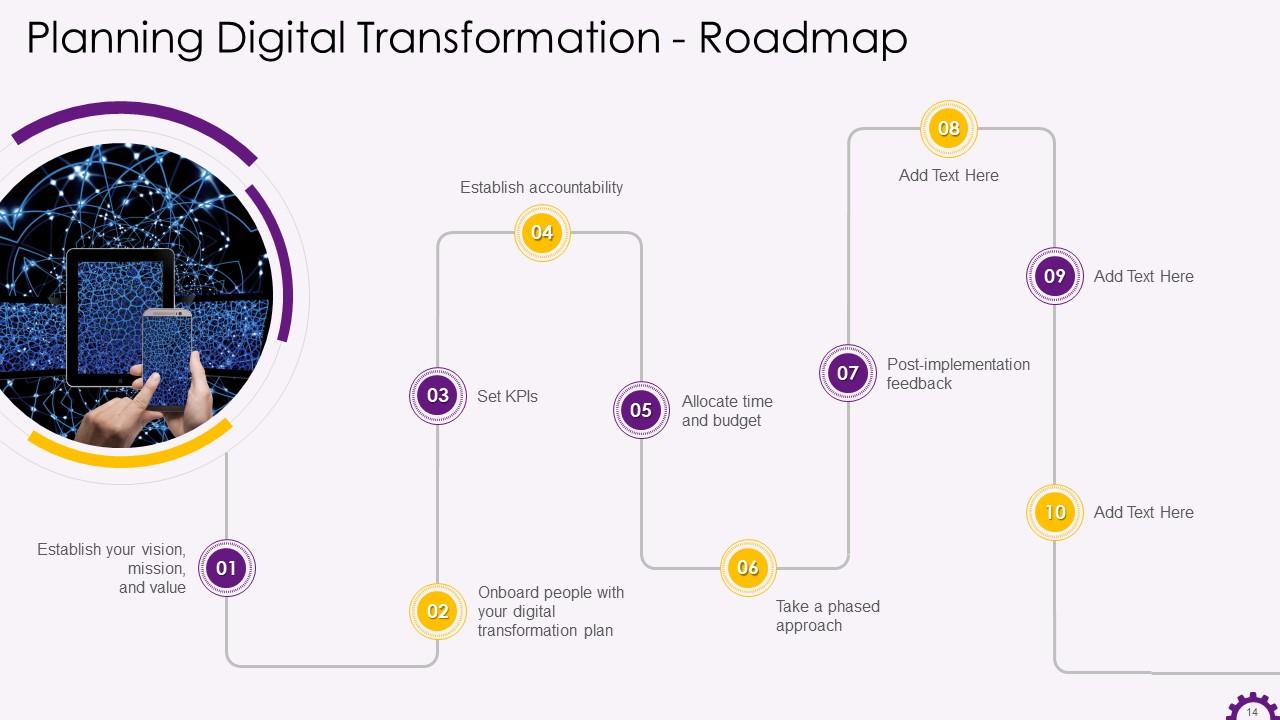
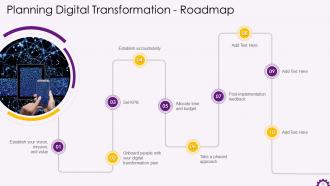
This slide depicts the roadmap for digital transformation. The steps to build a digital transformation roadmap are: Establish your vision, mission, and value, taking people onboard with your digital transformation plan, set KPIs, establish accountability, allocate time and budget, take a phased approach etc.
Slide 16
This slide illustrates an introduction to culture in the digital age. It emphasizes the importance of fostering a corporate culture that encourages innovation and creativity within businesses. It also states that managers and employees must learn digital skills to deal with digital transformation. Furthermore, creating environment that encourages innovation and exchange of ideas will enable team leaders to identify weaknesses in the company or employee.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Management: Directors must believe in digitization and transfer this enthusiasm to the rest of the workforce. Then, the Managers must support the strategy and set an example by being the first to add new tools. They have to upgrade the fastest and control the execution of new technologies. Tracking the results is also a significant step towards a complete digital transformation
- Equipment: Digitization must be tailored to the needs of the teams and provide them with tools to help them work more efficiently. Departments may have very different problems and needs, individual analysis and communication between these will help ensure that business and digital transformation is expedited
- Environment: Businesses must pay attention to their surroundings to identify stumbling blocks that prevent teams from being more productive. More dynamic spaces for their well-being and performance can be created by locating these impediments. When appropriately used, enabling collaborative zones or video conferencing rooms, for example, can improve the functioning of departments
Slide 17
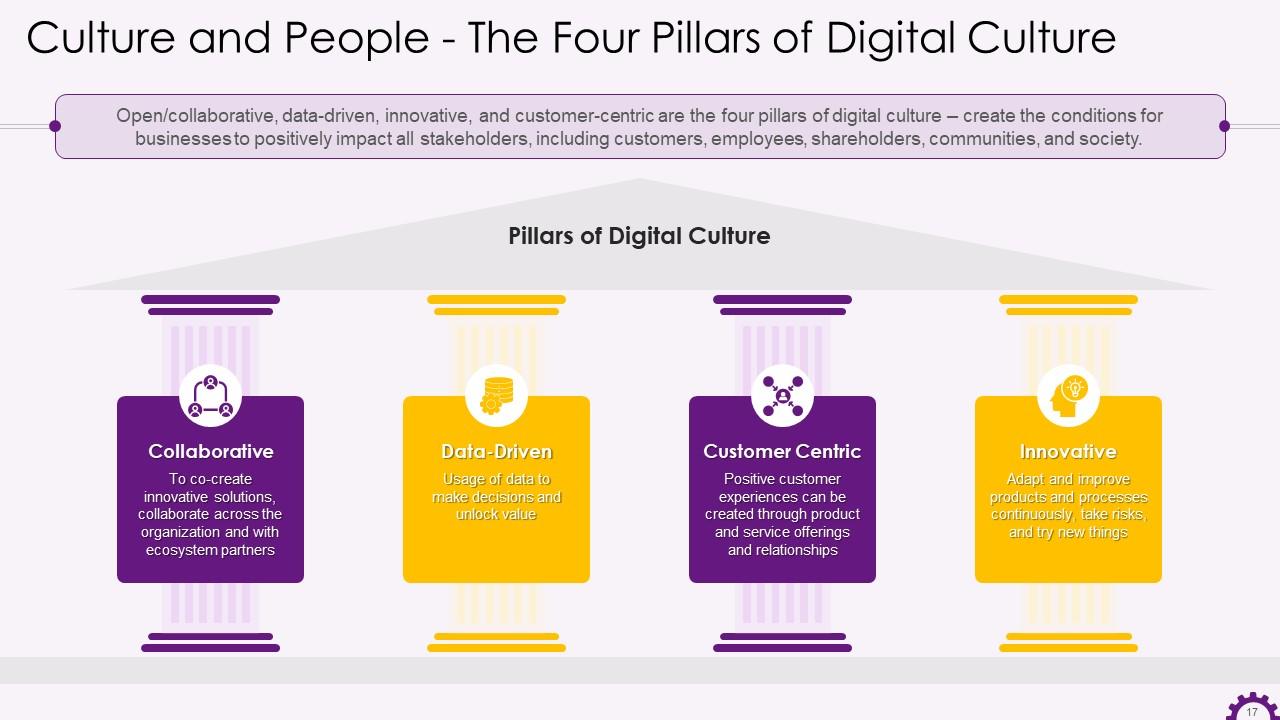
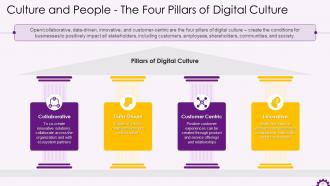
This slide depicts the four pillars of digital culture. The four pillars are collaborative, data-driven, customer centric, and innovative.
Slide 18
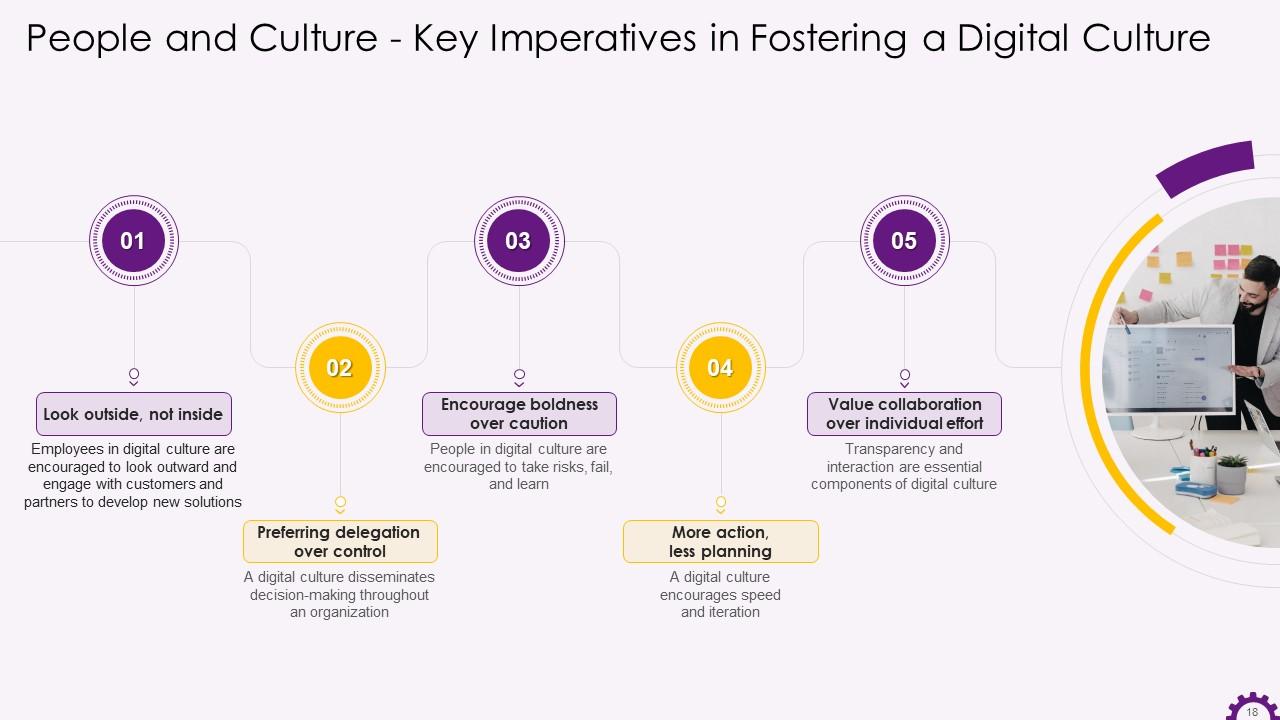
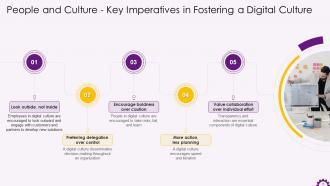
This slide illustrates the critical imperatives in fostering a digital culture such as looking outside, not inside, preferring delegation over control, encouraging boldness over caution, more action, less planning, and value collaboration over individual effort.
Slide 19
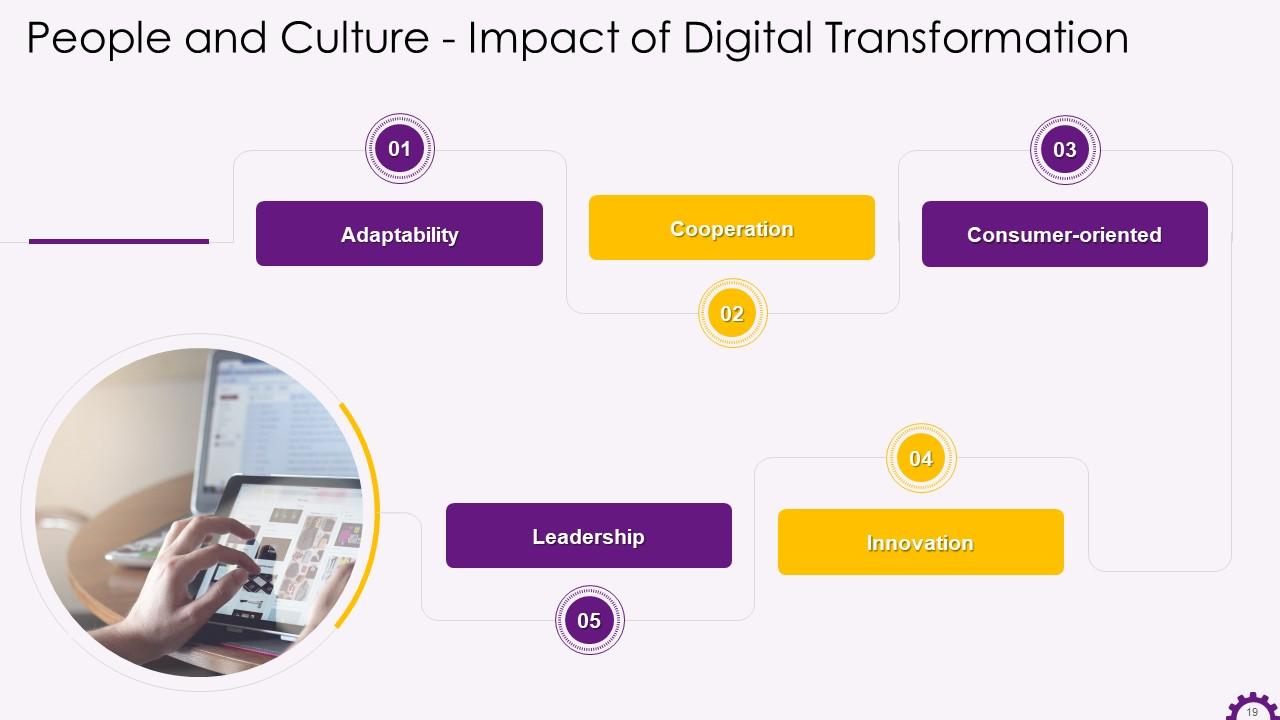
This slide depicts the impact of digital transformation on company culture. The ways through which digital transformation can impact a company’s culture are adaptability, cooperation, consumer-oriented, innovation, and leadership.
Instructor’s Notes:
The ways through which digital transformation can impact a company’s culture are:
- Adaptability: The ability of a company to be effective is linked to its ability to be efficient. Employee efficiency is determined by their ability to identify, integrate, and complete the transformations in sync with the environment. To be successful in this attempt, it is critical to understand the distinctions between the three key concepts listed below. They are as follows:
- Strategic Agility: This implies how a company decides to transform
- Organizational Agility: It means that how a company implements transformational processes
- Operational Agility: It is the speed with which the transformation can take place
- Cooperation: A strong organizational culture assists leaders in rallying employees around a shared vision so that everyone contributes to the development of the business. The importance of collaboration and cooperation cannot be overstated. Furthermore, collaboration with external partners and customers is required to create collaborative eco-systems
- Consumer-oriented: With the rise of "smart" technology, businesses now have access to advanced analytics, providing precise insights into customer behavior. That means businesses can now anticipate customer behavior and handle it in real-time, seamlessly, and efficiently. "Smart" products enable a company to improve its interactions with customers and provide seamless purchasing experiences. Well-established company culture can ensure that employees use these technologies strategically to interact with customers with the most sophisticated levels of insights into individual customers
- Innovation: As consumers crave new technologies, fostering a culture in which creativity is valued and encouraged rather than feared and avoided is also critical. It is crucial to foster an environment that encourages employees to think outside the box, puts them at ease, and allows them to share innovative ideas
- Leadership: The traditional "top to bottom" organizational structure no longer works in today's business world. Information and ideas must be shared fluidly and openly within the organization. Leadership must drive innovation while also understanding that everyone can contribute to innovation and strategy. By adopting this new flexible mindset, companies can create a workplace where individuals can use their skill-set to develop ideas in line with corporate and personal goals
Slide 20
This slide illustrates the challenges faced by organizations while implementing digital culture. The challenges are inertia in abandoning existing processes and cultures, infrastructural costs, resource allocation, inefficient adoption of automation, and up skilling challenges.
Instructor’s Notes:
The digital culture challenges are:
- Inertia in abandoning existing processes and cultures: One of the most perplexing issues business executives face is employees’ resistance to change. A company built on traditional and rigid processes and culture will naturally resist change because sticking to old processes is easier for employees than starting from scratch
- Infrastructural costs: Driving a digital culture is more than just a human endeavor; it needs its own full-fledged infrastructure. This infrastructure includes much more than just hardware and legacy software platforms. It necessitates things such as products, mobile applications, social, cloud, data analytics, and automation, all of which can be expensive for the enterprise and thus act as an impediment
- Resource allocation: Introducing new digital processes into an organization's workflow introduces newer tasks. With the addition of newer operational tasks, there is a need to allocate resources that can navigate the more recent processes tactfully. However, Enterprises are not always prepared to scale-up their resource allocation within that time frame, making digital transformation difficult
- Inefficient adoption of automation: A digital culture places a premium on automation, which entails abandoning manual processes. Most people comfortable in a traditional culture are hesitant to abandon the manual processes they have been using for decades. They are reluctant to get out of their comfort zone and adapt to automation. As a result, enterprise automation is not effectively implemented even when infrastructure processes are in place
- Upskilling challenges: One of the significant impediments to instilling a digital culture is a lack of digital literacy among employees. Employees accustomed to traditional processes will require careful planning of a training module to instill digital competencies. This can be difficult. To ensure success, businesses will need to invest heavily in organizing training sessions and mentorship programs
Slide 21
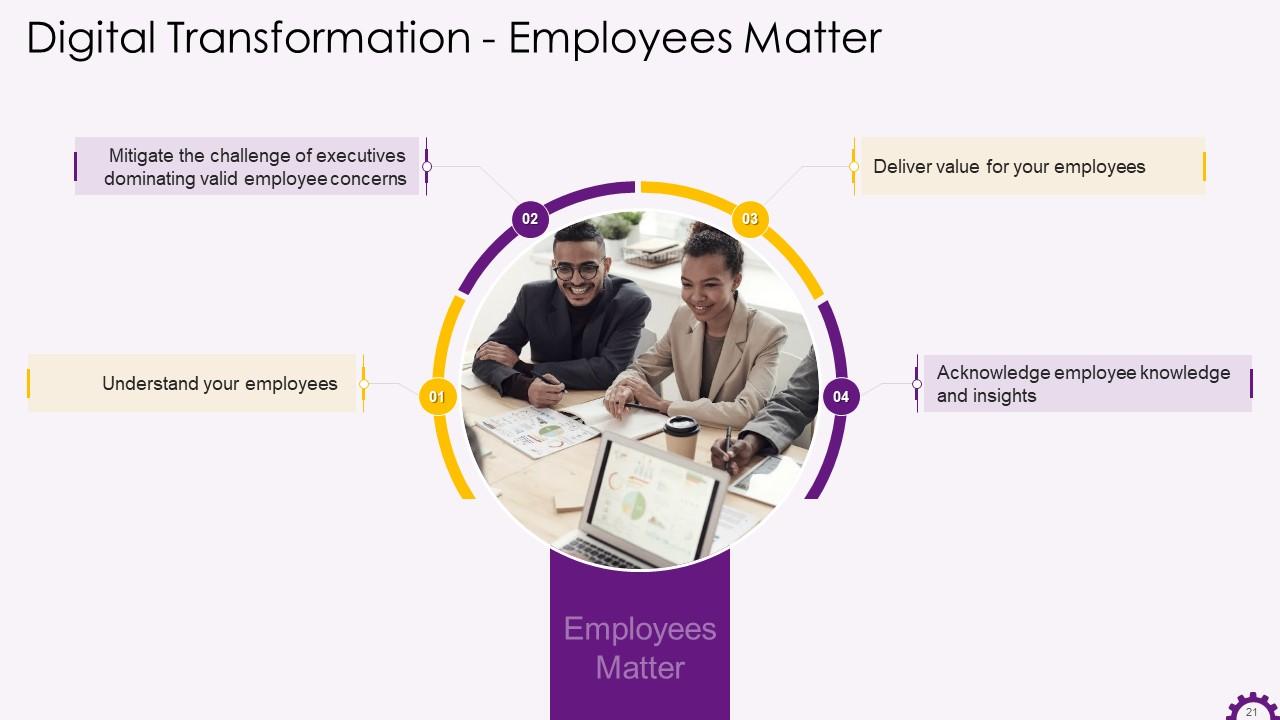
This slide showcases the importance of employees to an organization while implementing digital transformation. It mentions that an organization must understand its employees, deliver value to them, acknowledge their knowledge and insights, etc.
Slide 22
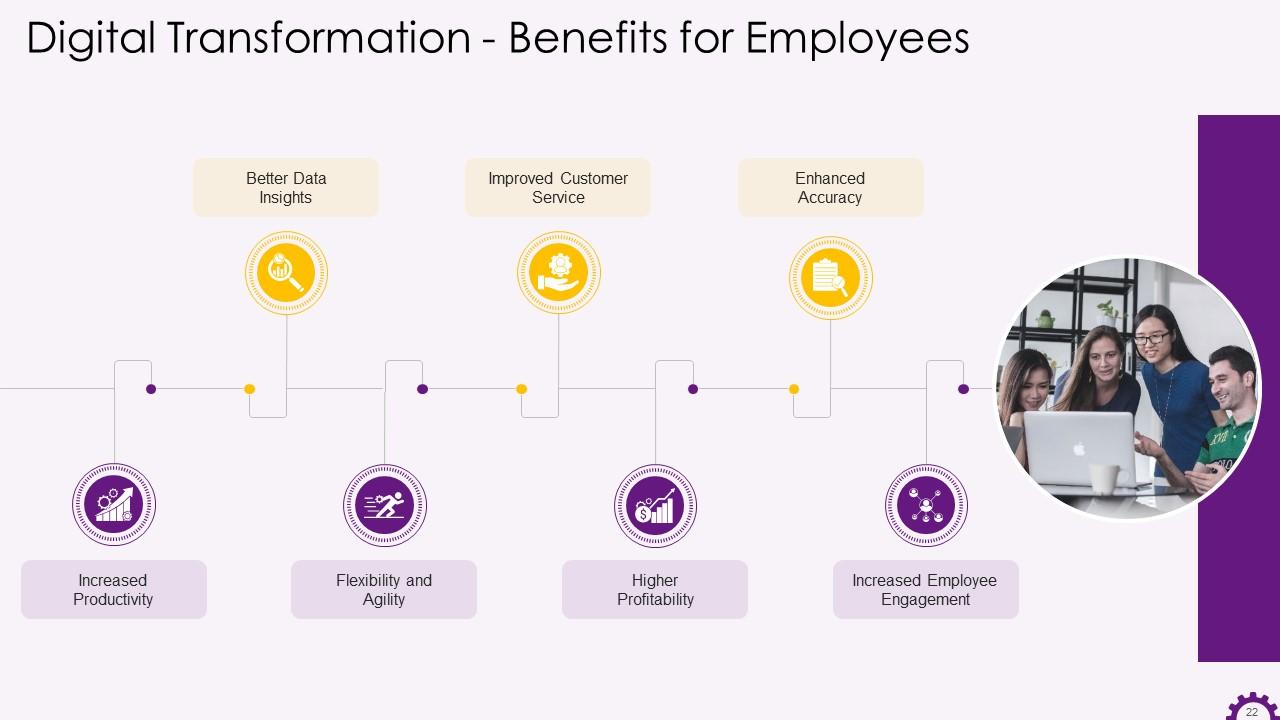
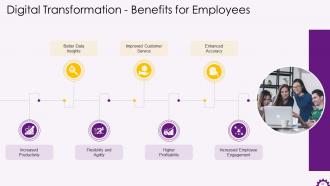
This slide illustrates the benefits of digital transformation for employees. The benefits are increased productivity, better data insights, flexibility and agility, improved customer service, higher profitability, enhanced accuracy, and increased employee engagement.
Instructor’s Notes:
The benefits of digital transformation for employees are:
- Increased Productivity: Employee productivity will rise due to digitizing business operations, streamlining workflows, and improving information flow throughout your organization. Integrating platforms to break down data silos and eliminate manual processes is a significant part of digital transformation
- Better Data Insights: Today data, is the king. Organizations are accumulating more customer data than ever before as the number of online services grows. Many businesses are implementing analytics tools to help them gain powerful insights that will guide intelligent business decisions. Organizations will benefit from greater transparency and informed decision making by structuring data and giving employees the ability to analyze it quickly
- Flexibility and Agility: Another advantage of digital transformation for employees is increased flexibility. Employees can now access the files and systems they need from anywhere, thanks to the fact that many businesses host at least one application or a portion of their computing infrastructure on the cloud. Employee work-life balance has improved due to not being tied to the office and traditional working hours
- Improved Customer Service: Nobody enjoys dealing with dissatisfied customers. Giving employees the tools, they need to respond quickly and automating customer journey elements will improve both the employee and customer experience. While nothing beats human interaction, employees will have more time to help customers who require more in-depth assistance by incorporating elements of automation and client self-service
- Higher Profitability: Digital transformation can deliver measurable RoI as IT becomes more strategic. Many businesses are leveraging technology to provide a competitive advantage, allowing employees to work smarter and provide better customer service. A company that becomes more profitable due to digital transformation is more likely to innovate faster and maintain its market leadership position
- Enhanced Accuracy: Employees may be able to automate specific processes, reduce the burden of paperwork. It helps them combine inputs from disparate systems, improving information accessibility, which is one of the key benefits of upgrading systems. Employees can eliminate the possibility of human error and be confident that they are providing a consistent and accurate service by automating basic processes
- Increased Employee Engagement: Businesses can benefit significantly from digital transformation by upskilling their teams. Employees must be engaged throughout the implementation process and adequately trained to use new technology. By investing in employee development, employees are more likely to feel motivated and valued, resulting in higher employee retention rates
Slide 23
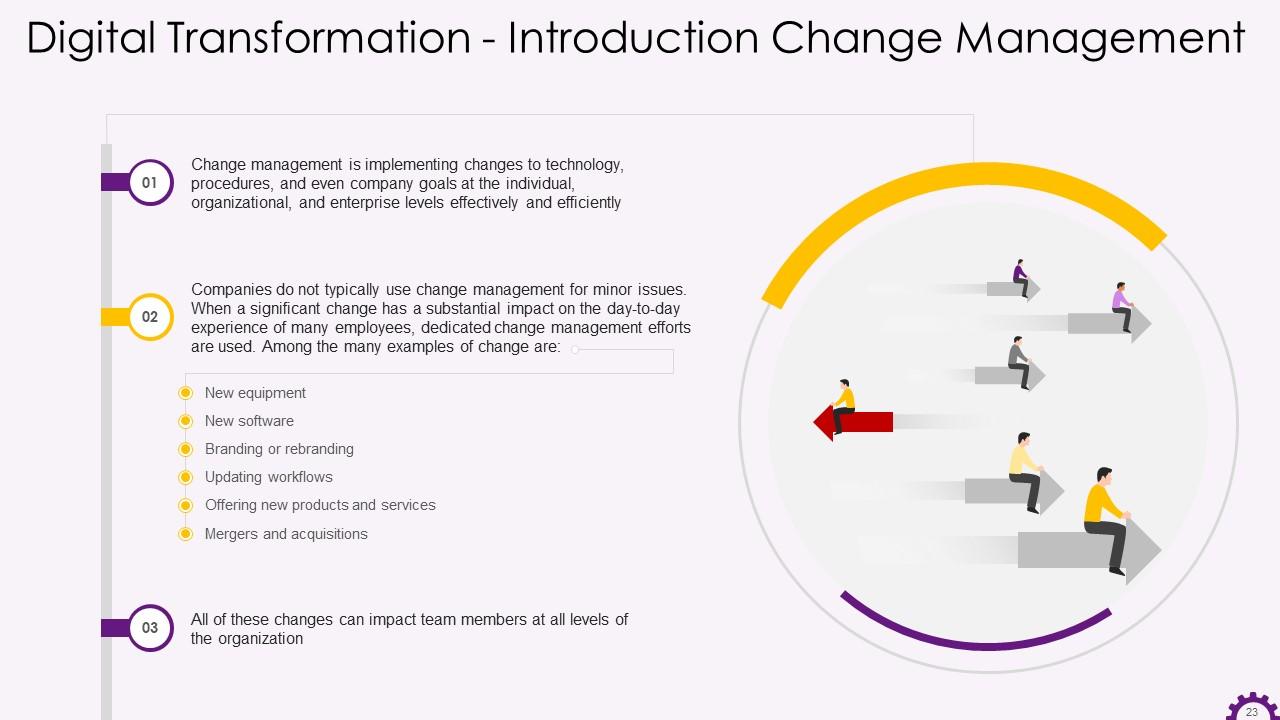
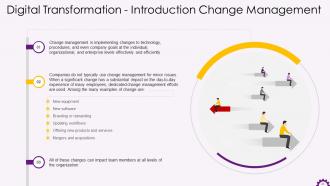
This slide depicts information about change management in the context of digital transformation. It emphasizes that change management is the effective and efficient implementation of changes to technology, procedures, and even company goals at the individual, organizational, and enterprise levels. It also provides examples of organizational changes.
Slide 24
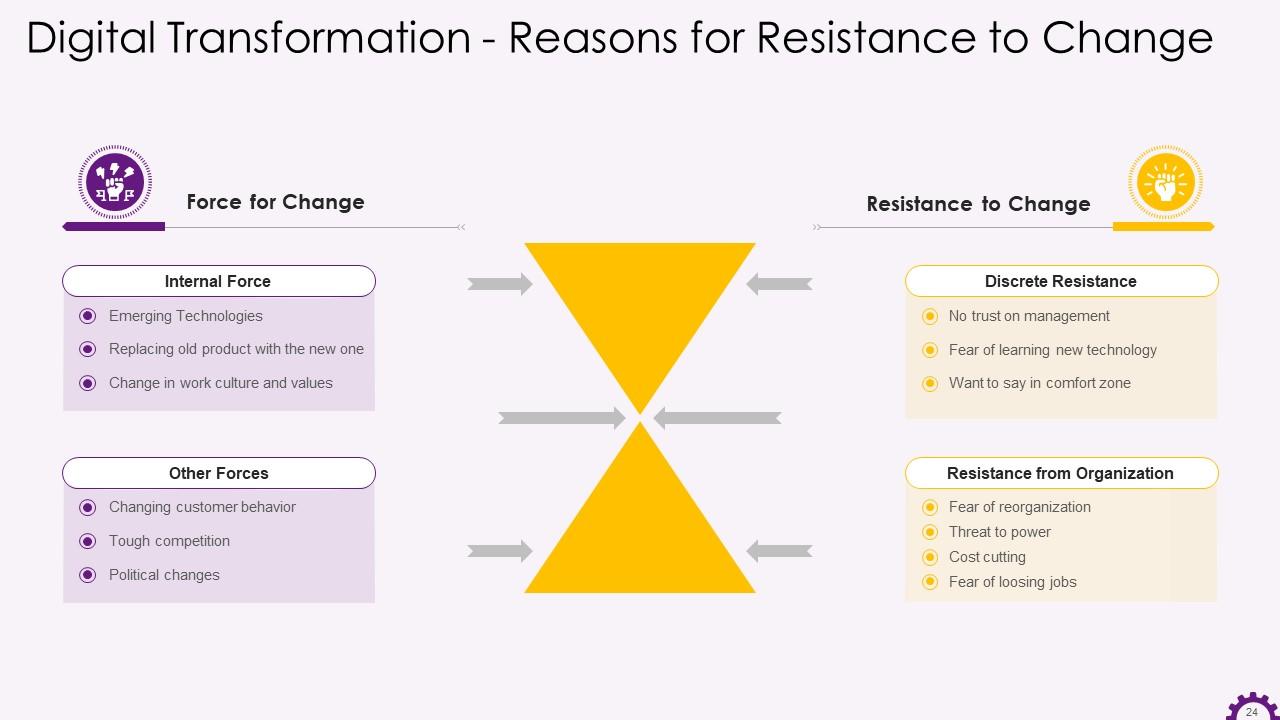
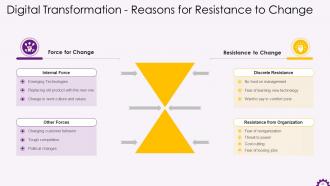
This slide illustrates the reasons for resistance to change when implementing change management. It also discusses the internal and external forces that contribute to organizational change.
Slide 25
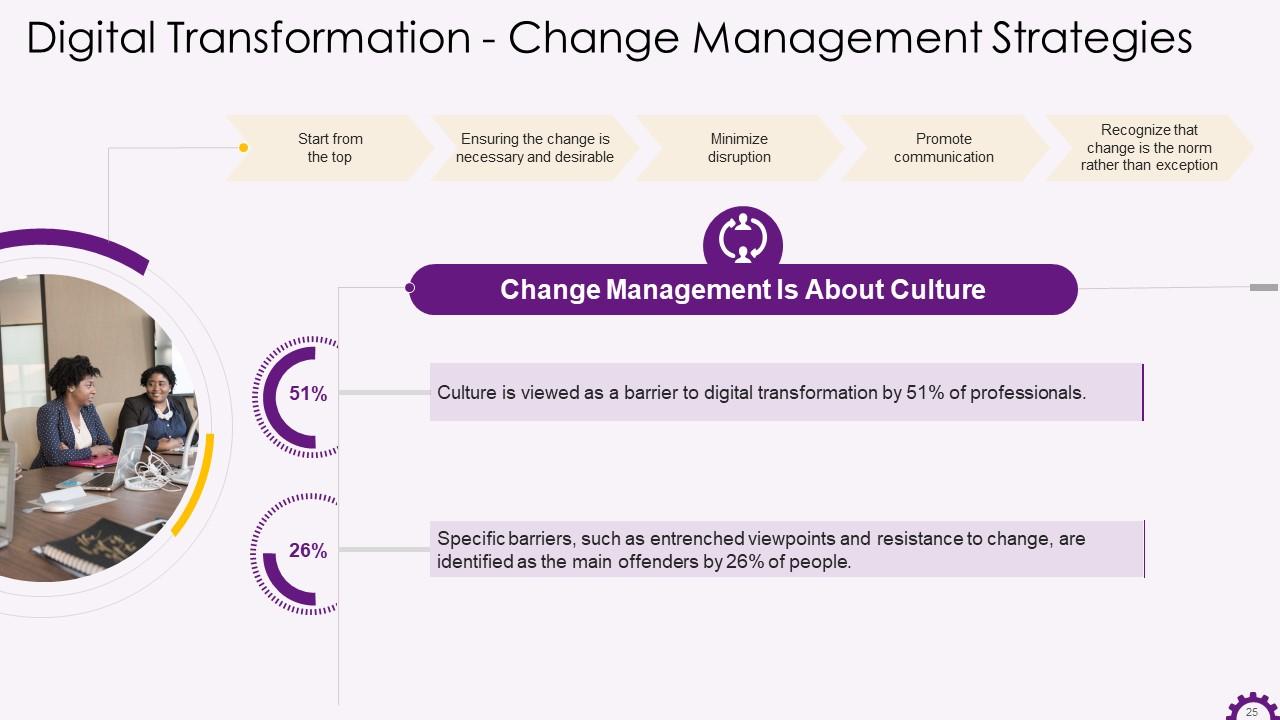
This slide showcases the change management strategies. The strategies include: start from the top, ensuring the change is necessary and desirable, minimizing disruption, promoting communication, recognizing that change is the norm rather than exception.
Instructor’s Notes:
The strategies for change management are:
- Start from the top: Changes that affect the operation aspects of the business will impact the company's culture. As a result, such changes must begin at the top. Leadership's role during times of change is of great importance. For example, research on merger leadership discovered that when leaders took a more active role in change management, the merger process produced a more positive work environment
- Ensuring the change is necessary and desirable: If an organization lacks a solid strategy in place, introducing too much too soon can often be a massive problem down the road. Many digital transformation efforts fail or fall short of expectations. The main reason for this is that decision-makers are not sure of how to approach digital transformation and its impact on their business. Lack of a thorough audit can result in unnecessary solutions for an organization's needs, resulting in additional costs, additional training, and increased unrealistic expectations
- Minimize disruption: Employees transferred to a different position may become enraged, confused, or wonder what went wrong with the previous structure. In both cases, the result is lower morale, unsatisfactory performance, and a brain drain as your best performers flee. Disruption in the workplace can be reduced by:
- Preparing for some disruption and communicating as soon as possible
- Creating a culture that encourages change or transformation
- Giving employees the resources and training they need to adapt to changes
- Promote communication: Communication appears to be one of the underlying factors determining the success or failure of a transition or transformation during organizational change. Effective communication lets everyone on the same page and ensures that those who will bear the brunt of these changes are safe
- Recognize that change is the norm rather than exception: Technology, markets, consumer preferences, and even environmental conditions all rise and fall in the blink of an eye in today's world. Businesses must not only transform their operations to keep up with their customers, they must anticipate change and be prepared to deal with it when it occurs
Slide 26
This slide depicts an overview of the digital employee experience. It emphasizes how effectively people interact with digital tools in the workplace, allowing them to be engaged, proficient, and productive. It also mentions that interacting with technologies is part of the digital employee experience.
Slide 27
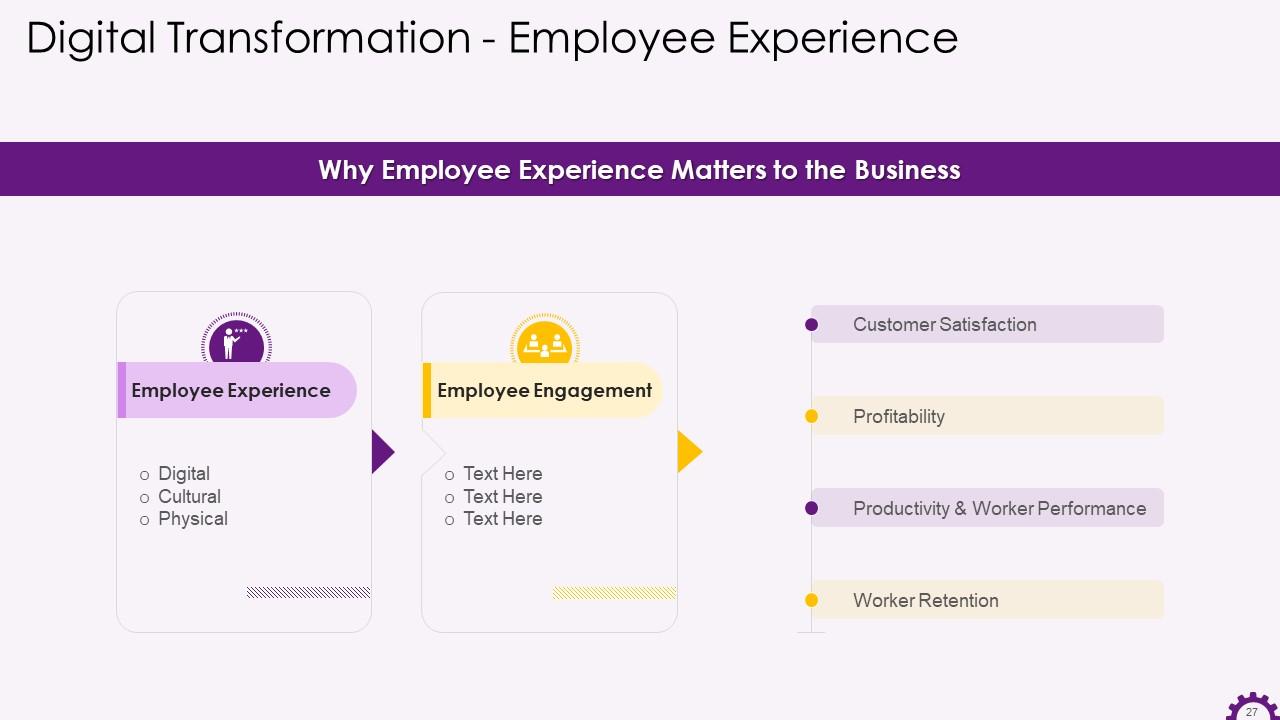
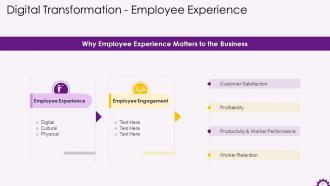
This slide depicts how employee experience affects business. It also highlights that employee engagement leads to customer satisfaction, profitability, productivity, worker performance, etc.
Slide 28
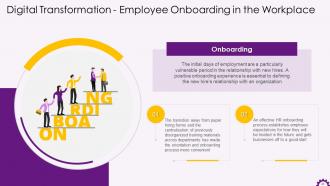
This slide depicts the information regarding employee onboarding in the digital workplace. It highlights that a positive onboarding experience is essential to defining the new hire's relationship with an organization.
Slide 29
This slide illustrates the significance of employee onboarding in a business. It emphasizes that improved employee onboarding performance can increase employee retention, encourage employees to do their best, and help the organization attract top talent.
Slide 30
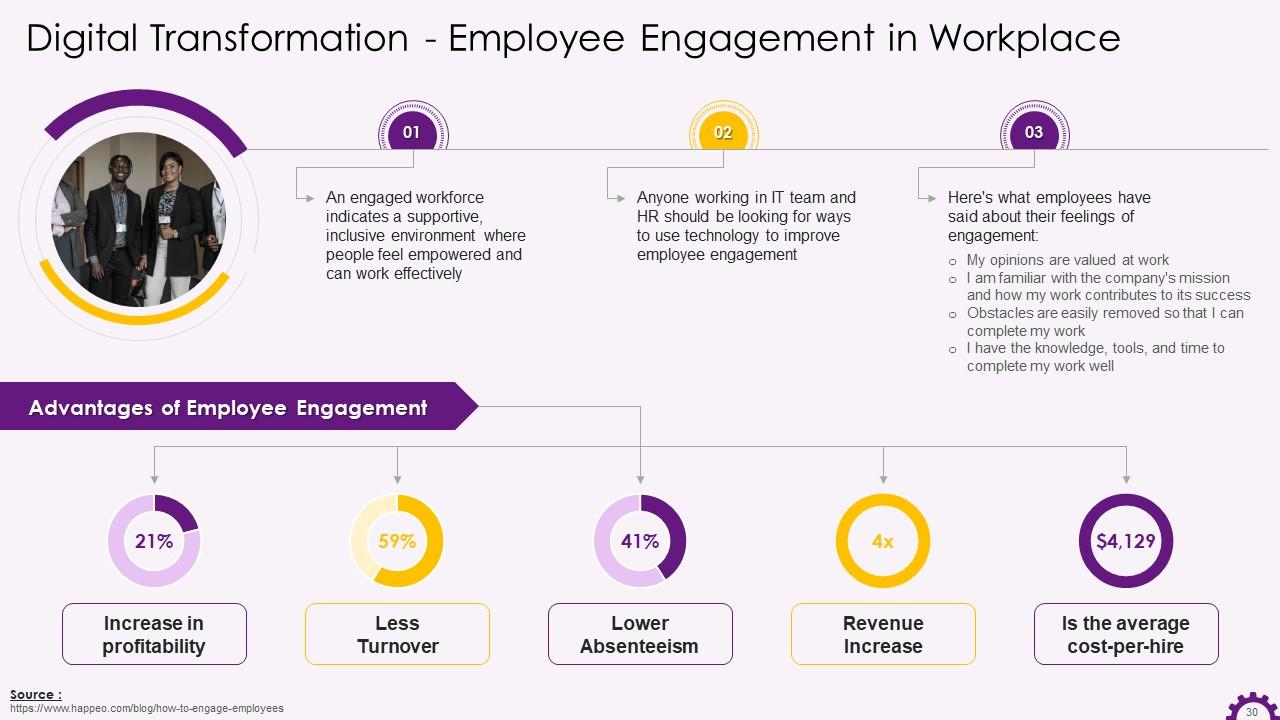
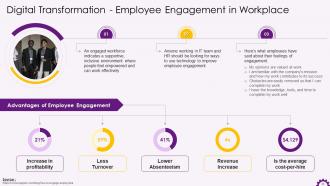
This slide depicts information about employee engagement in a digital workplace. It emphasizes the benefits of employee engagement, such as increased profitability, lower turnover, increased revenue, lower absenteeism, etc.
Slide 32
This slide illustrates information about new digital products and services. It emphasizes that new digital products and services are entirely novel in delivery methods, core value proposition, and unique business model. It also states that Digital Transformation necessitates the creation of smart new products, specifically new products with built-in digital technologies, combining software and hardware to provide new functionality to the customer.
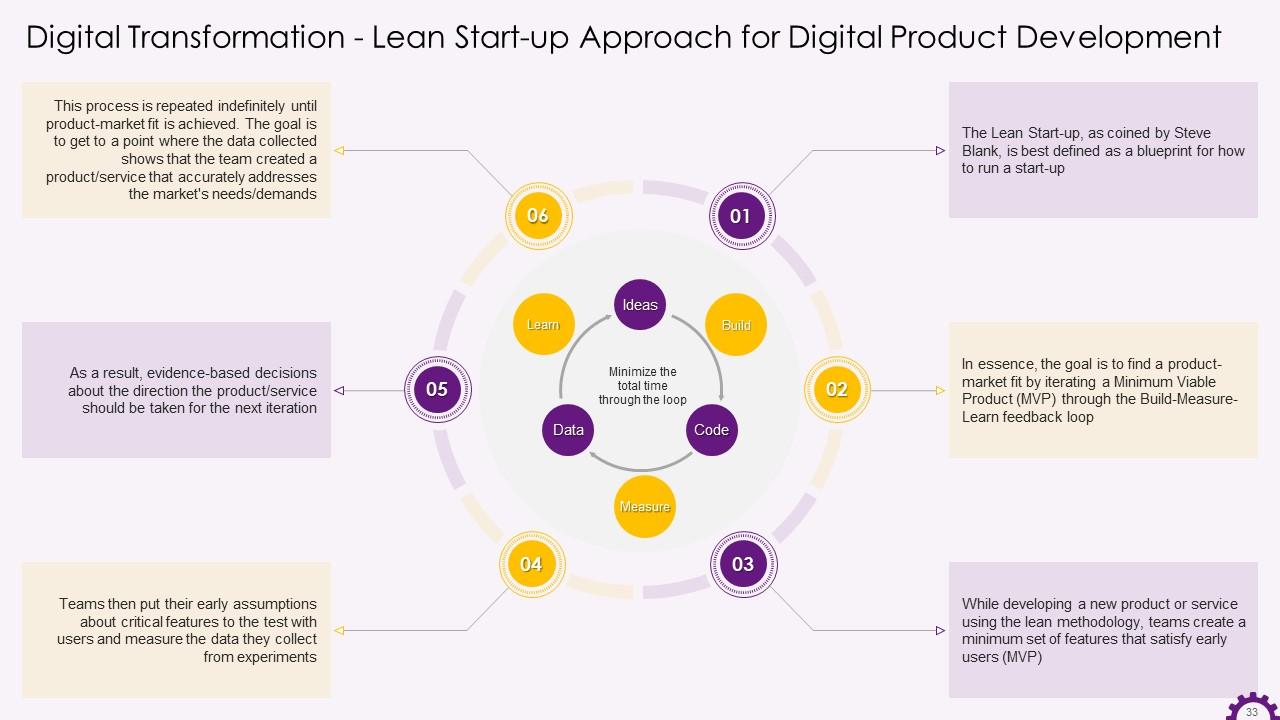
Slide 33
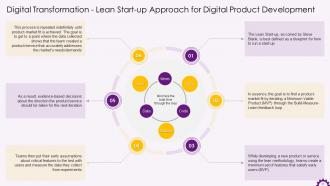
This slide depicts information about the lean start-up methodology. It emphasizes that a lean start-up approach is a road map for running a business. The objective is to find a product-market fit by iterating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) through the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop.
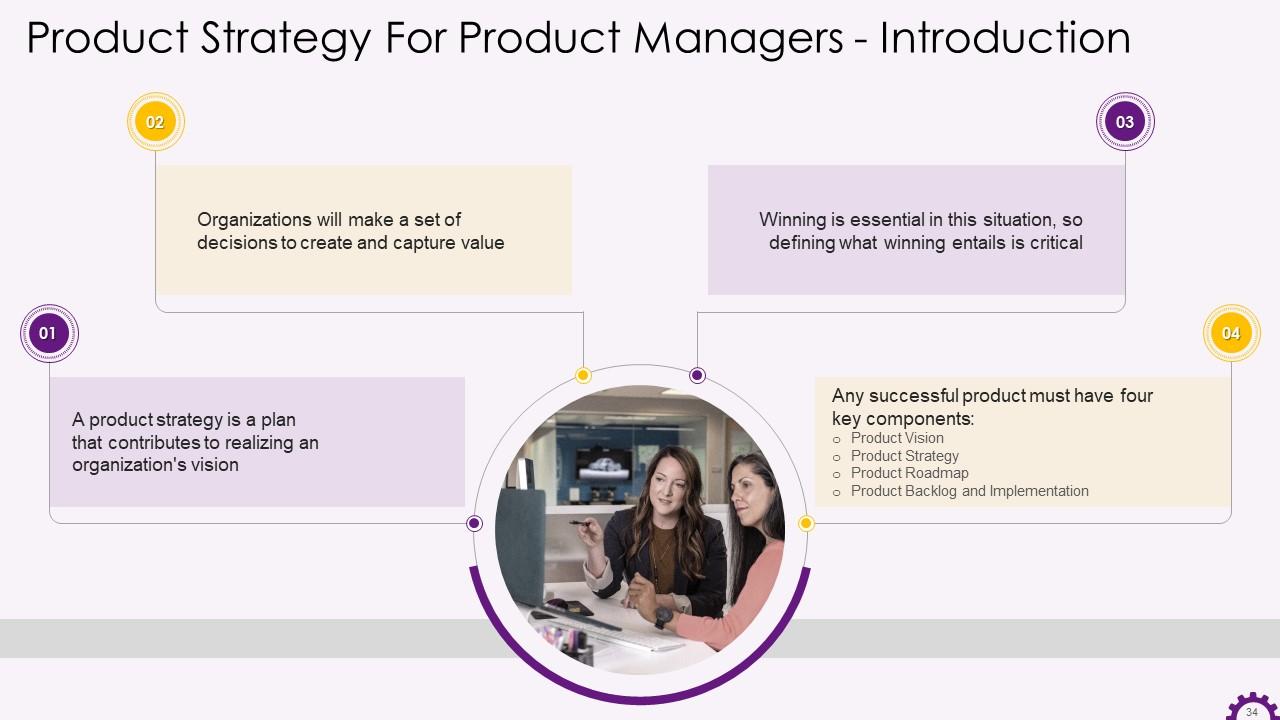
Slide 34
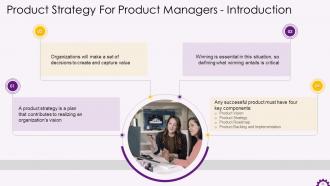
This slide illustrates product strategy information for product managers. It also emphasizes that a product strategy is a plan that helps an organization realize its vision. It also mentions successful product components such as product vision, product strategy, product roadmap, and product backlog and implementation.
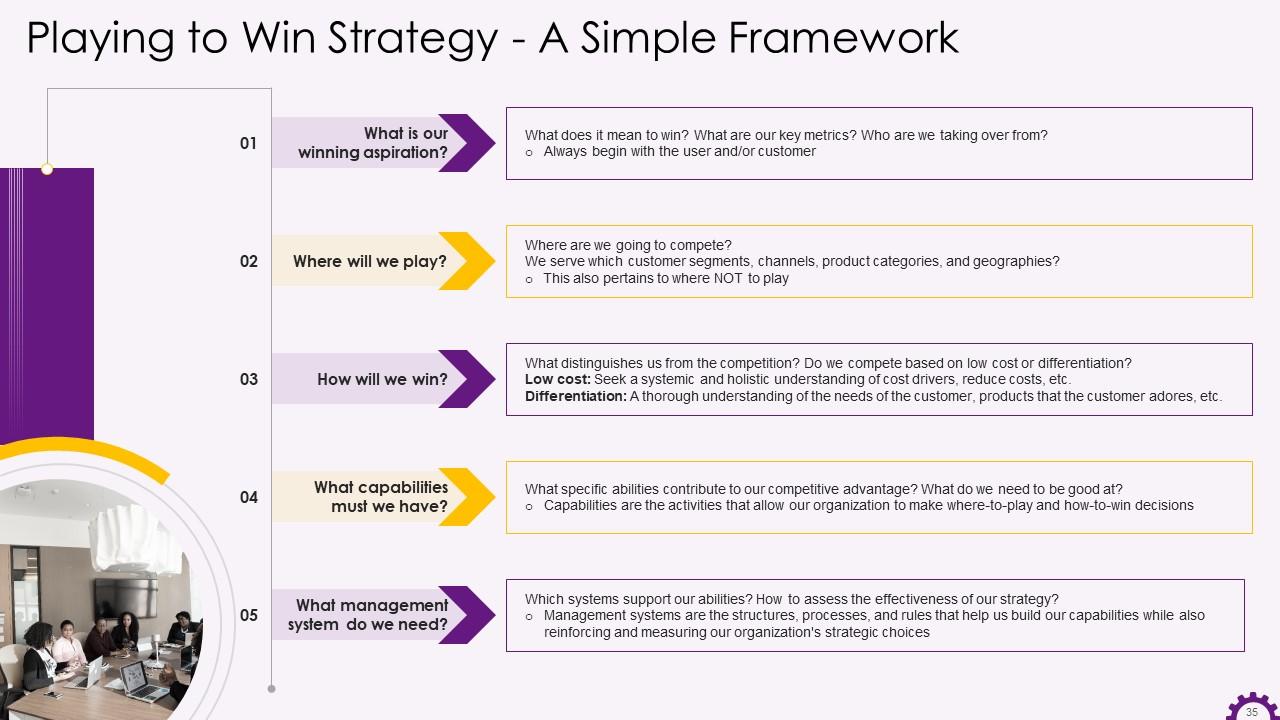
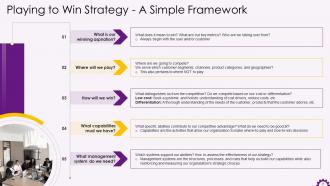
Slide 35
This slide showcases the playing to win strategy framework. The framework's elements are our winning aspiration, where we will play, how we will win, capabilities we must have, and the management systems required.
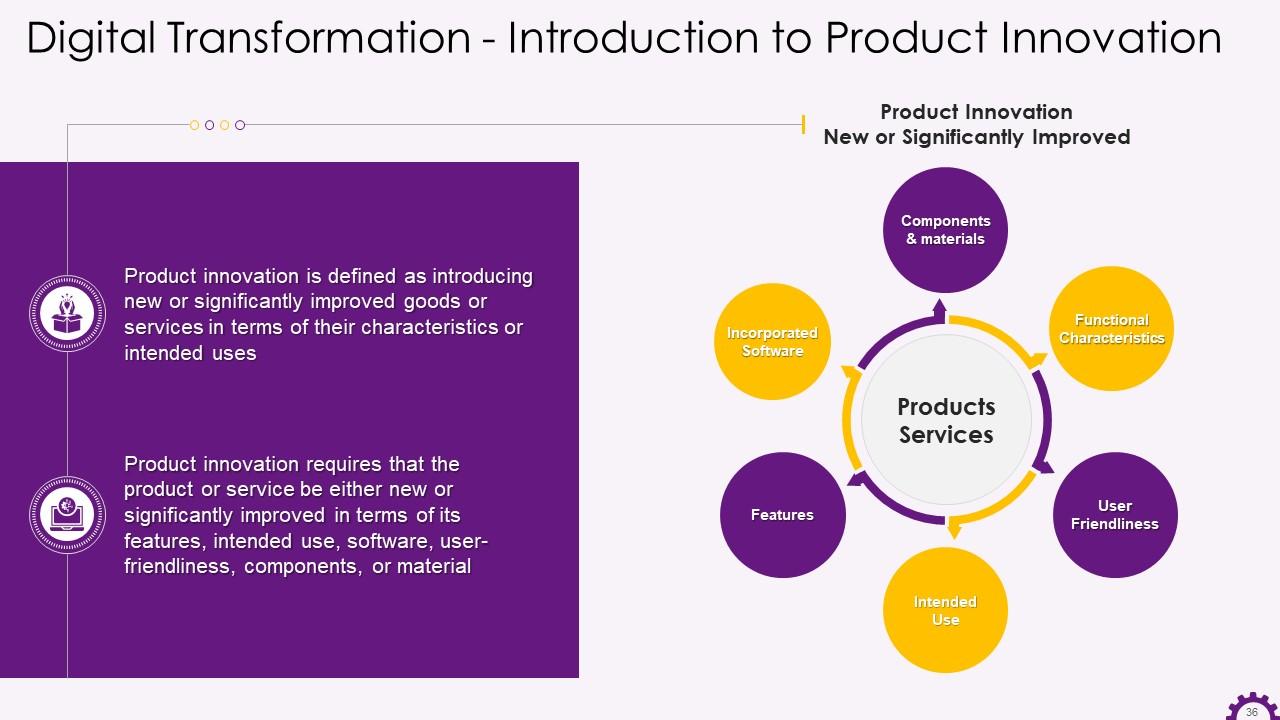
Slide 36
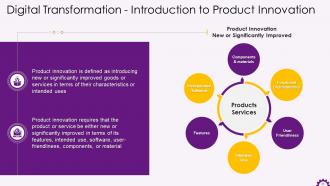
This slide depicts an overview of new product innovation. It emphasizes introducing new or significantly improved goods or services in terms of their characteristics or intended uses. It also states that product innovation necessitates that the product or service be either new or significantly improved in terms of features, intended use, software, usability, components, or material.
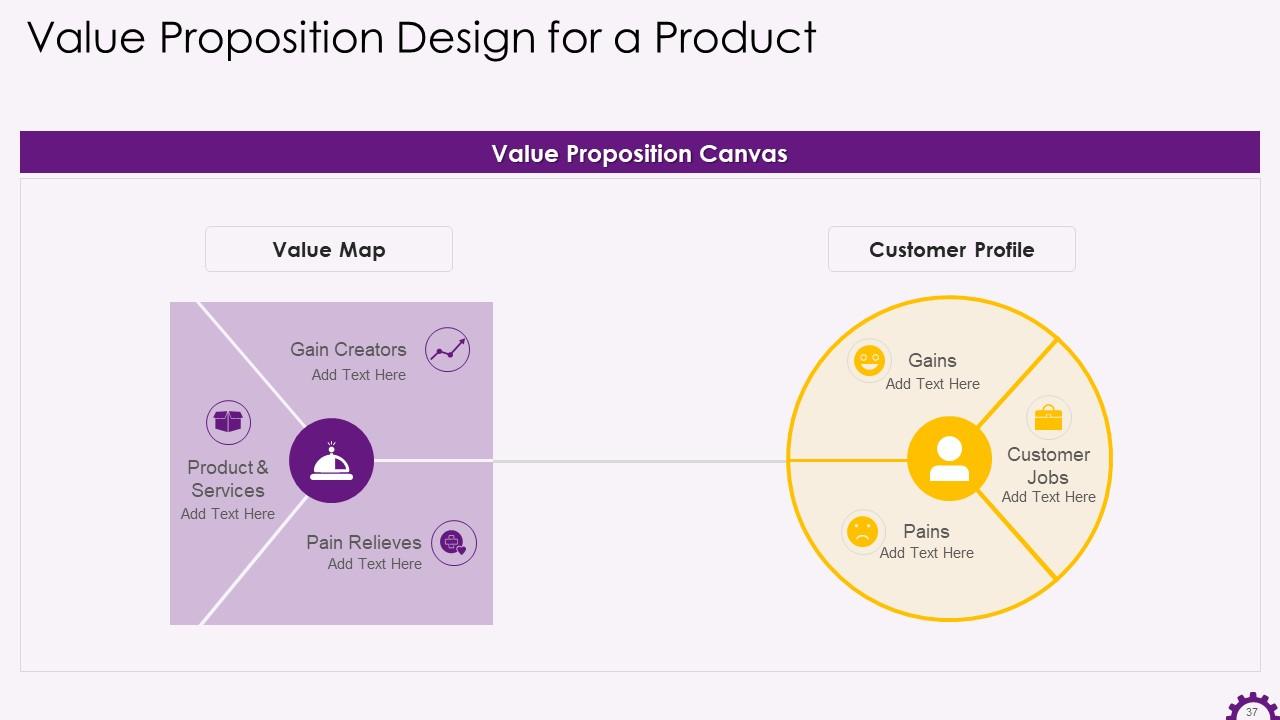
Slide 37
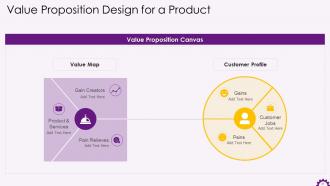
This slide depicts information about a product's value proposition design. The value proposition canvas's components are the value map and the customer profile. It emphasizes that the customer profile consists of the customer's jobs, gains, and pains, and the value map consists of the gain creators, pain relievers, and products & services.
Slide 38
This slide illustrates a value proposition canvas. It highlights how FedEx's value proposition design, including a customer profile and a value map.
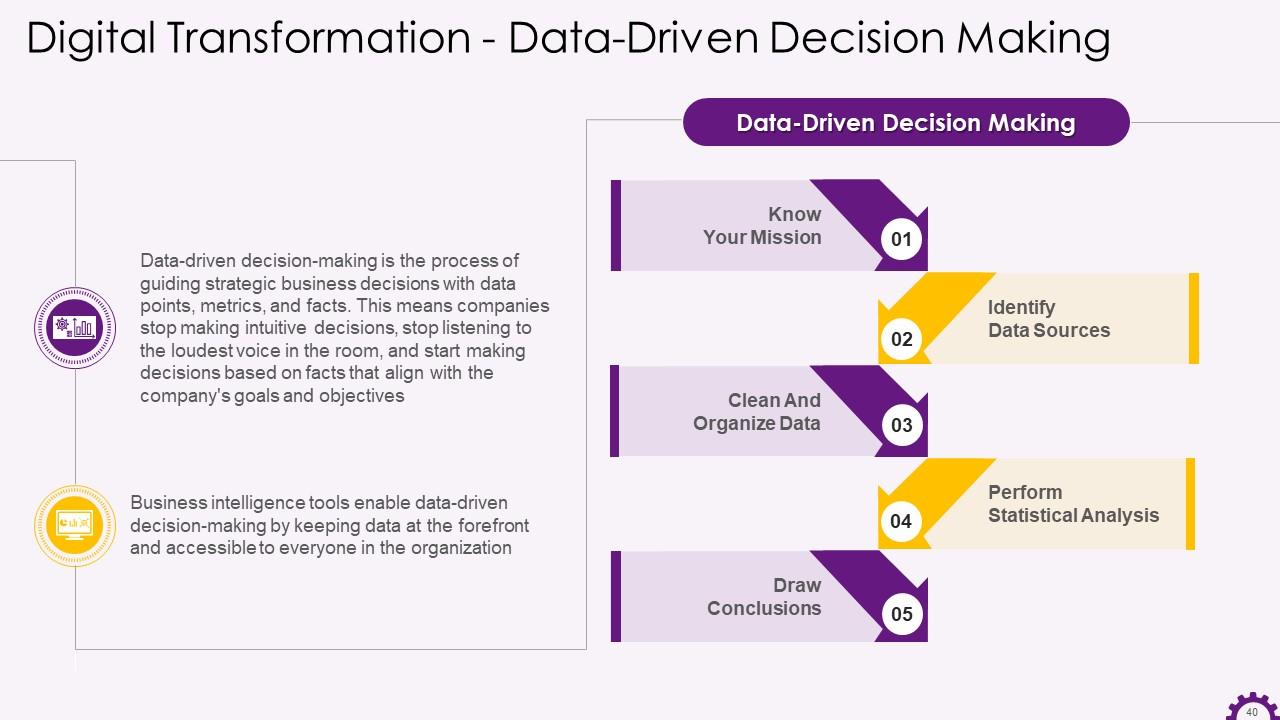
Slide 40
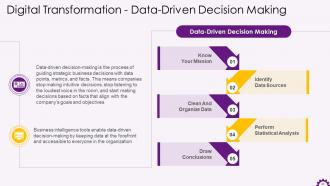
This slide depicts data-driven decision-making information. It emphasizes that data-driven decision-making uses data points, metrics, and facts to guide strategic business decisions. It also mentions that business intelligence tools gives you data, accessible to everyone, that enable decisions to be made.
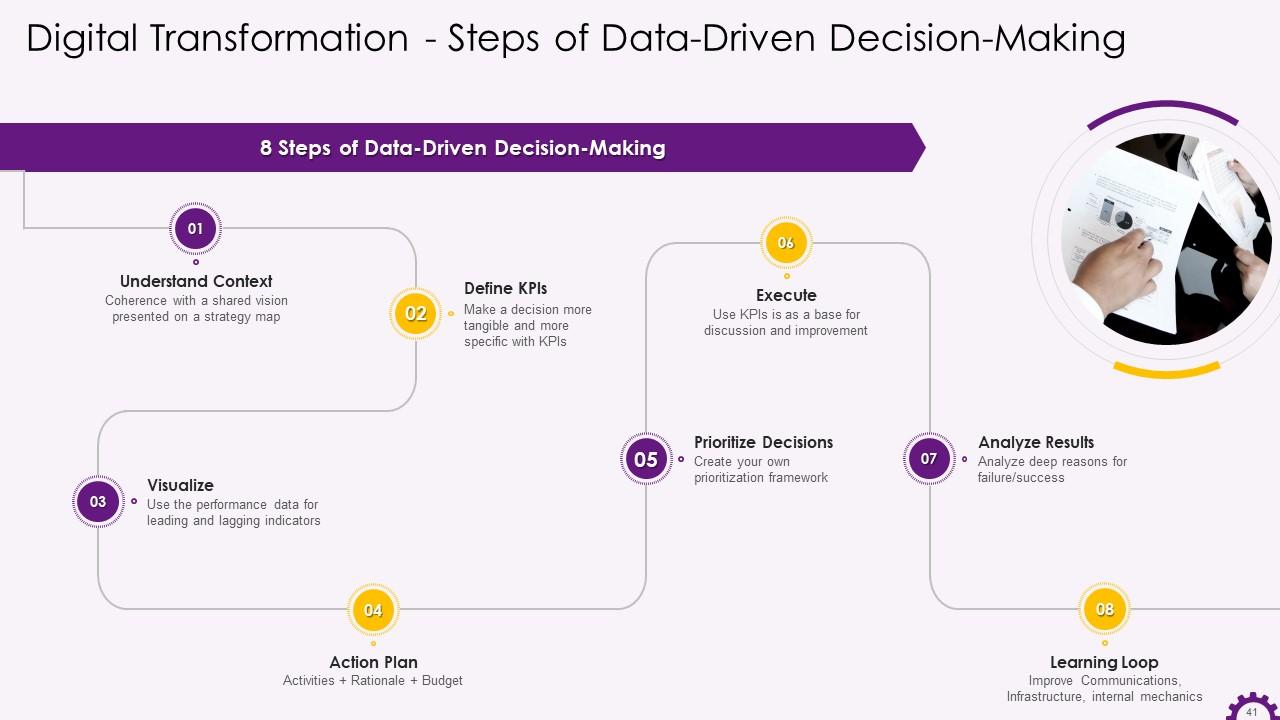
Slide 41
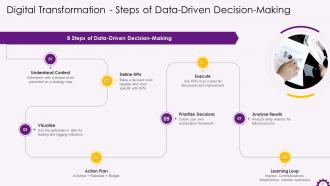
This slide showcases the steps of Data-Driven Decision Making. The steps include understanding context, defining KPIs, visualizing, action plan, prioritizing decision, executing, analyzing results, learning from them and changing your action plan.
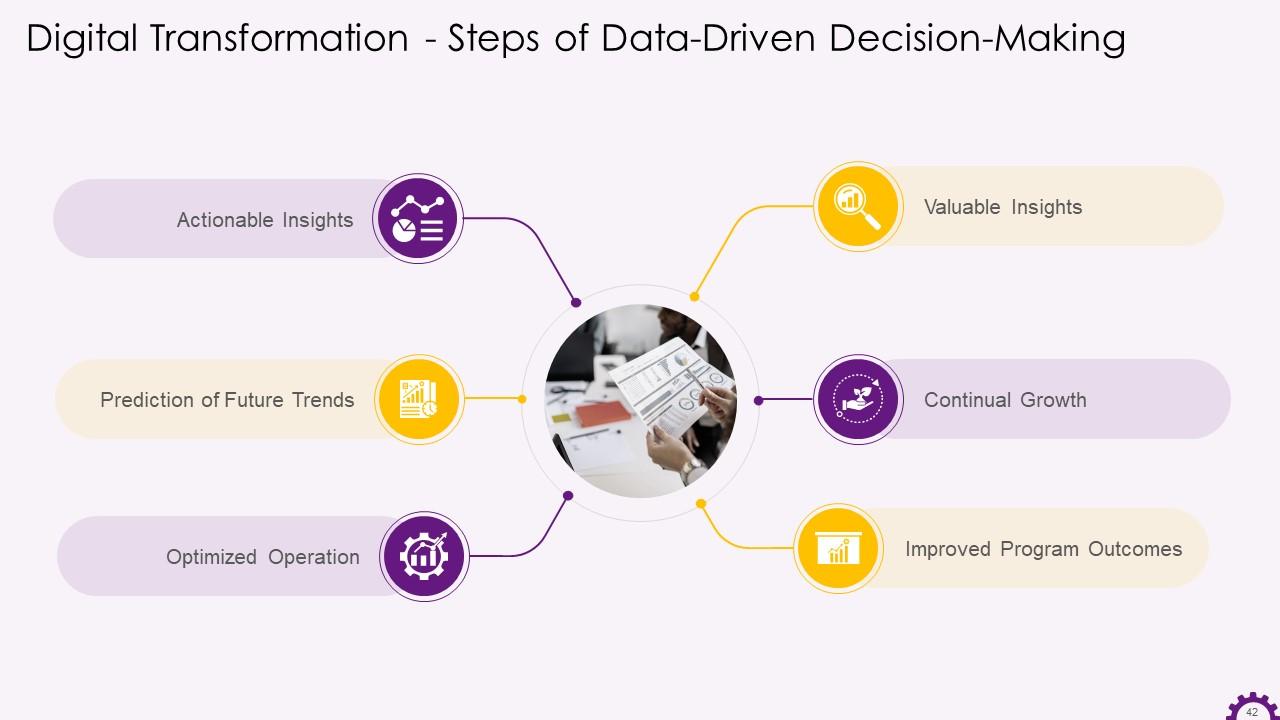
Slide 42
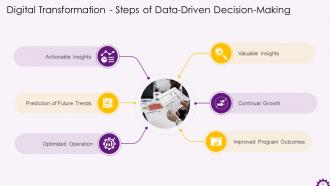
This slide depicts the benefits of data-driven decision-making. The benefits include valuable insights, continuous growth, improved program outcomes, prediction of future trends, and actionable insights.
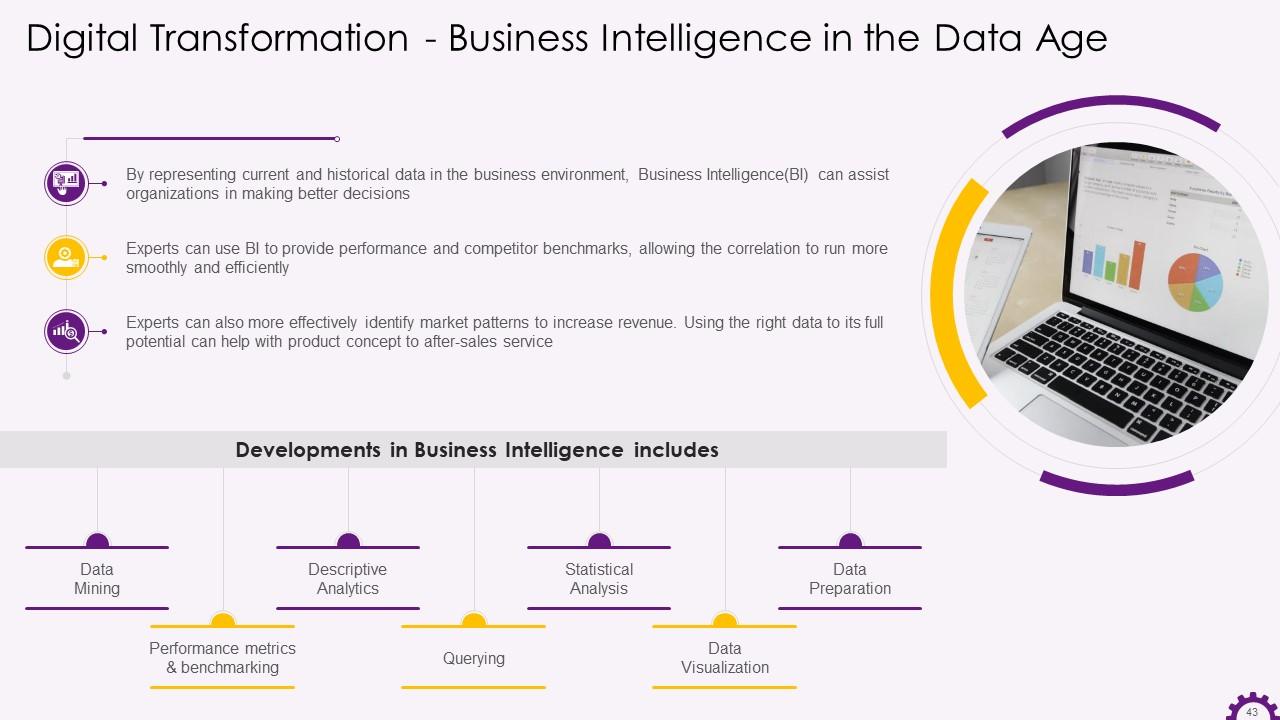
Slide 43
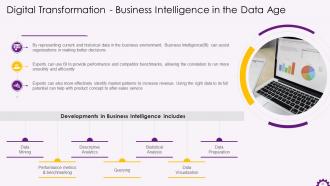
This slide depicts Business Intelligence (BI) in the data age. It highlights that business intelligence can assist organizations in making better decisions. Experts can use business intelligence to provide performance and competitor benchmarks, allowing smoother running of the organization, with improved efficiency.
Instructor’s Notes:
Developments in business intelligence are:
- Data mining: Discovering trends in large datasets using databases, statistics, and machine learning
- Performance metrics and benchmarking: Comparing current performance data to historical data aids in measuring performance against goals, which is typically accomplished through customized dashboards
- Descriptive analytics: Using preliminary data analysis to determine what happened
- Querying: Business intelligence extracts the answers to data-specific questions from the data set
- Statistical analysis: Taking descriptive analytics results and further exploring the data with statistics to determine how and why this trend occurred
- Data visualization: Data analysis is transformed into visual representations such as charts, graphs, and histograms to make data easier to consume
- Visual analysis: Exploration of data through visual storytelling to communicate insights
- Data preparation: Compiling multiple data sources, identifying dimensions and measurements, and preparing the data for analysis
Slide 44
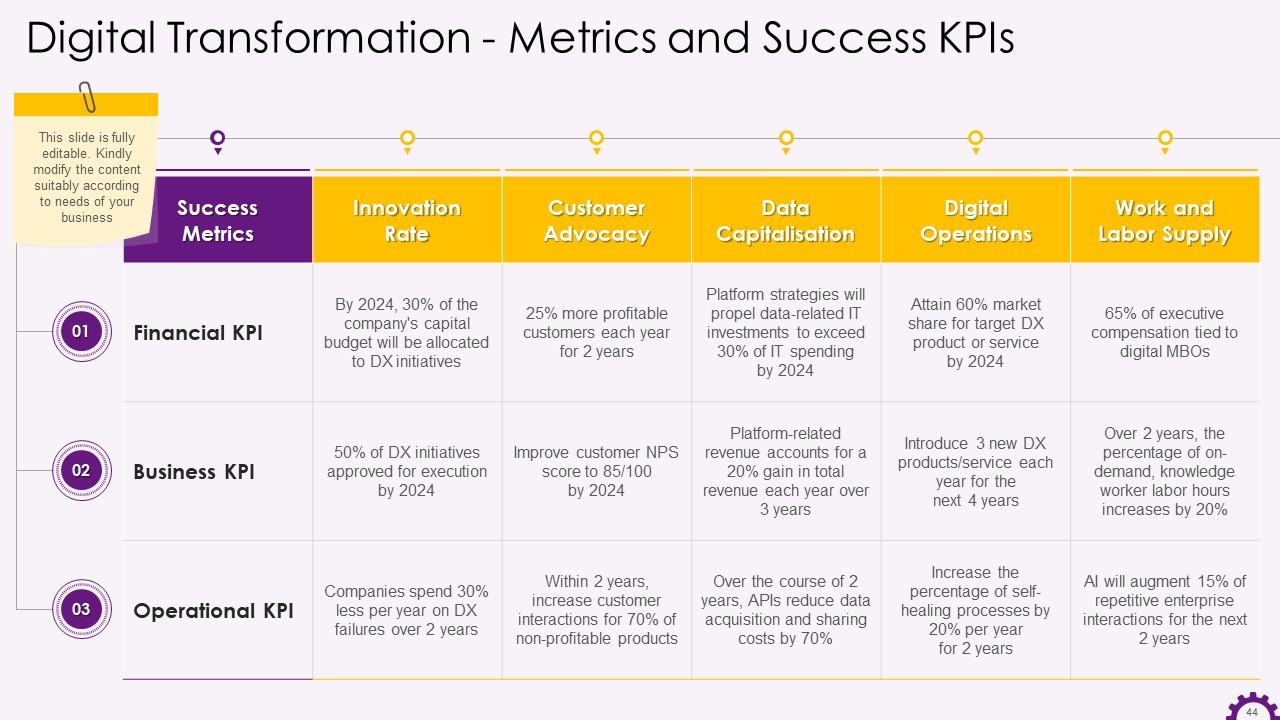
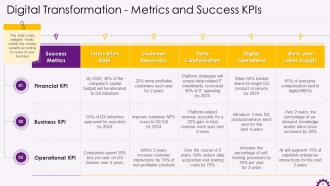
This slide depicts the digital transformation metrics and success KPIs. Success metrics include innovation rate, customer advocacy, data capitalization, digital operations, and work and labor supply. The KPIs are Financial KPI, Business KPI and Operational KPI.
Slide 45
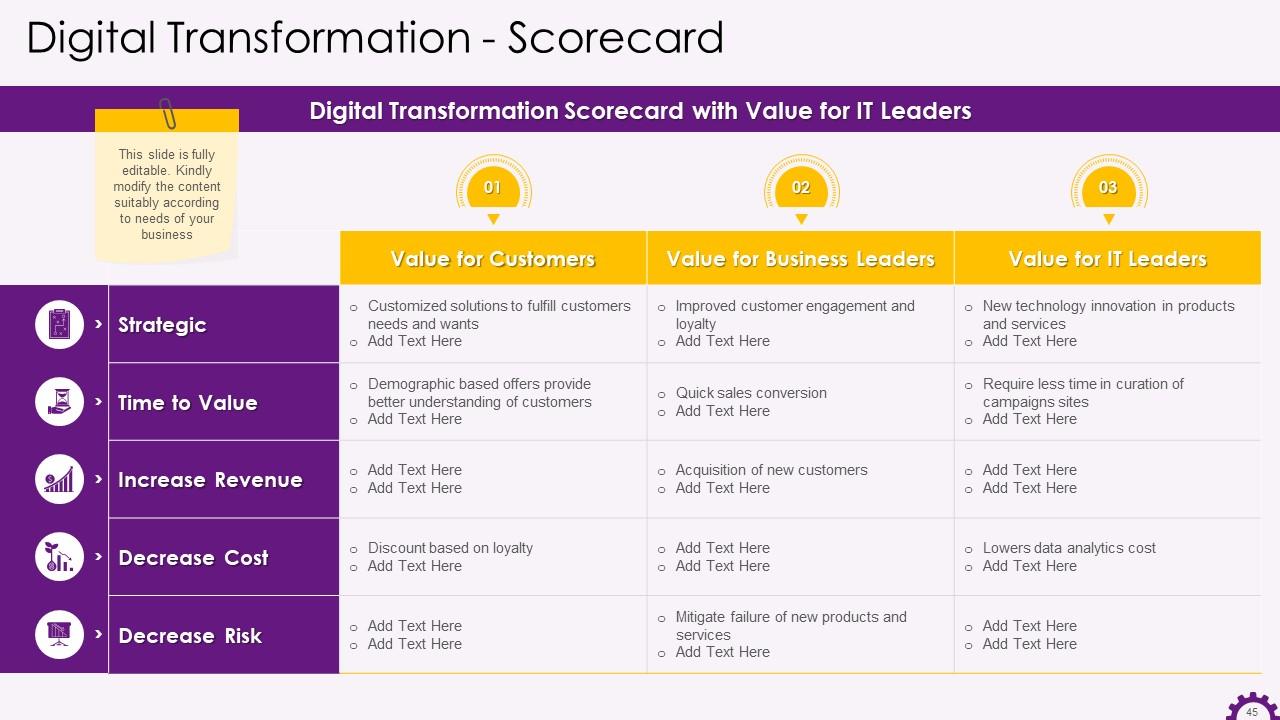
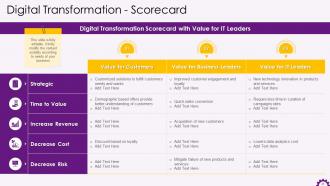
This slide illustrates the digital transformation scorecard. The digital transformation scorecard has values for customers, business leaders, and IT leaders.
Slide 46
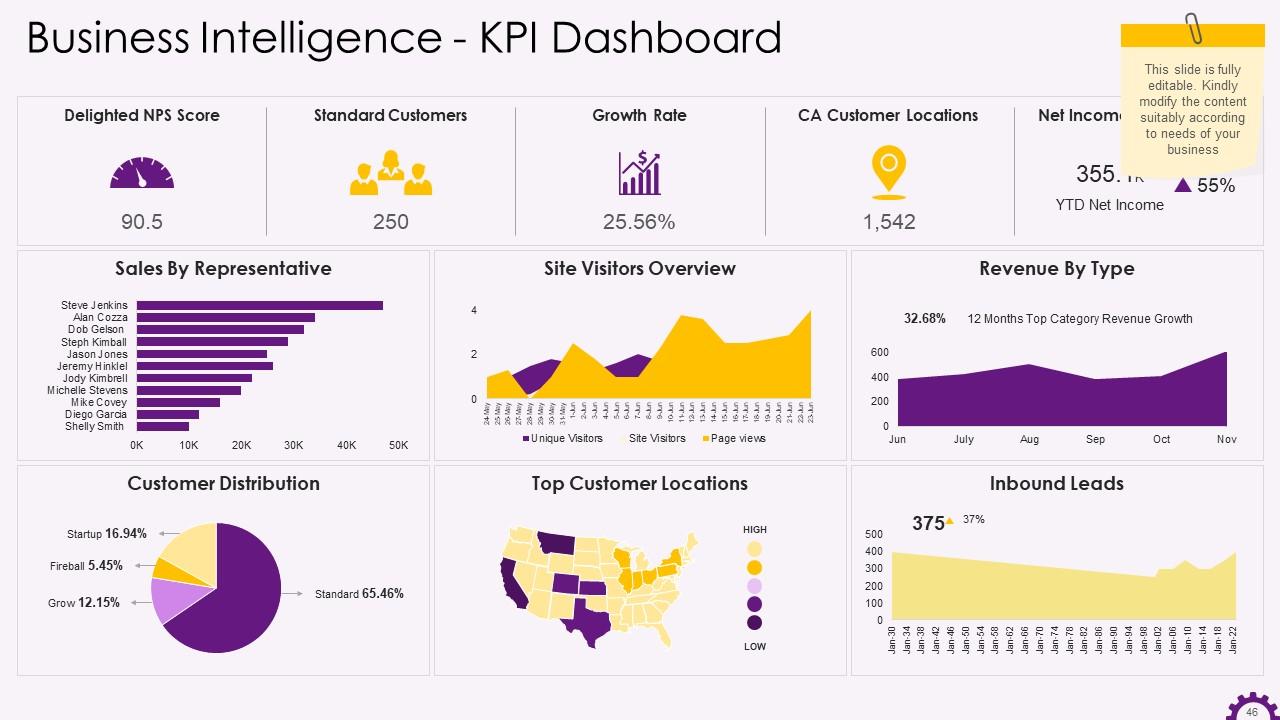
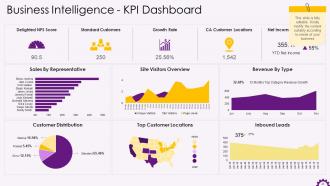
This slide illustrates the business intelligence KPI dashboard with sales by a representative, revenue by type, customer distribution, etc., as its elements.
Slide 47
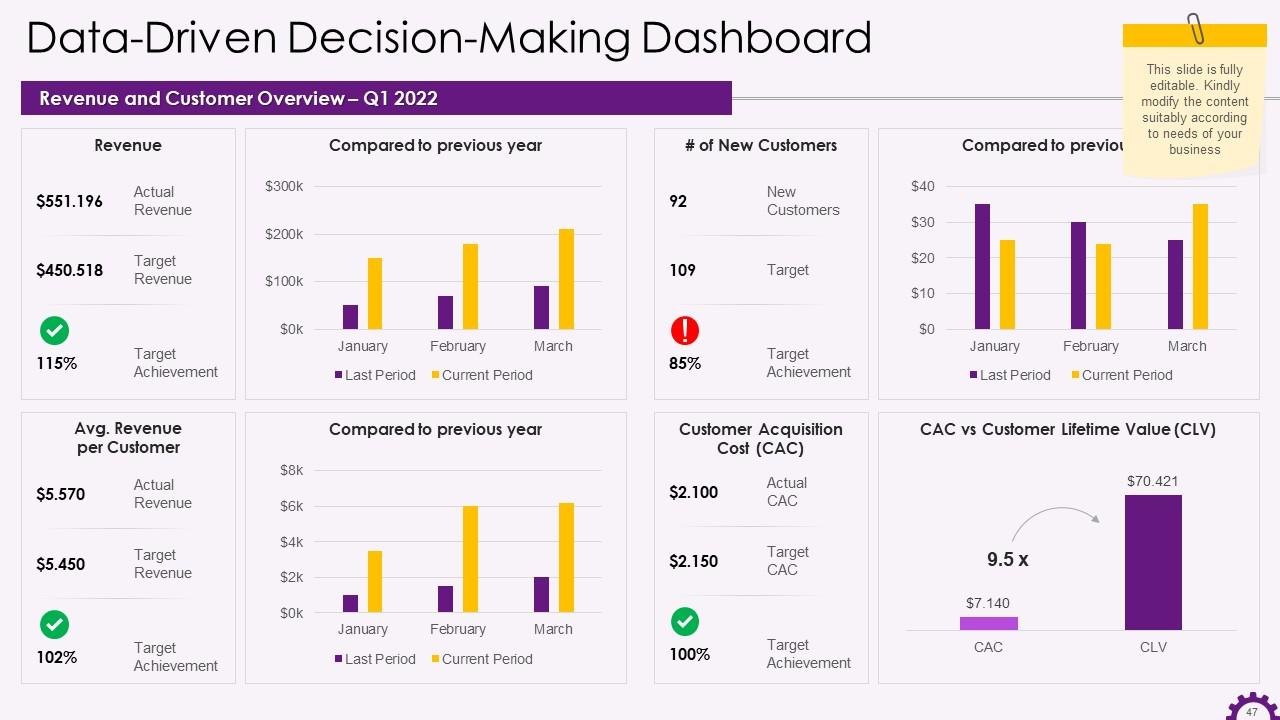
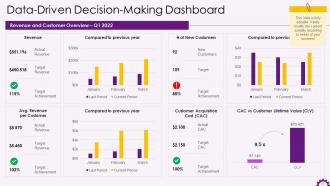
This slide depicts the Data-Driven Decision-Making Dashboard. It highlights the revenue and customer overview for Q1 2022.
Slide 48
This slide depicts the introduction to project and portfolio management for digital transformation. It emphasizes that project portfolio management (PPM) analyses and optimizes all projects and programs' costs, resources, technologies, and processes within a portfolio. It also entails directing the company's energy and workforce toward the common strategic goal of digital transformation.
Slide 49
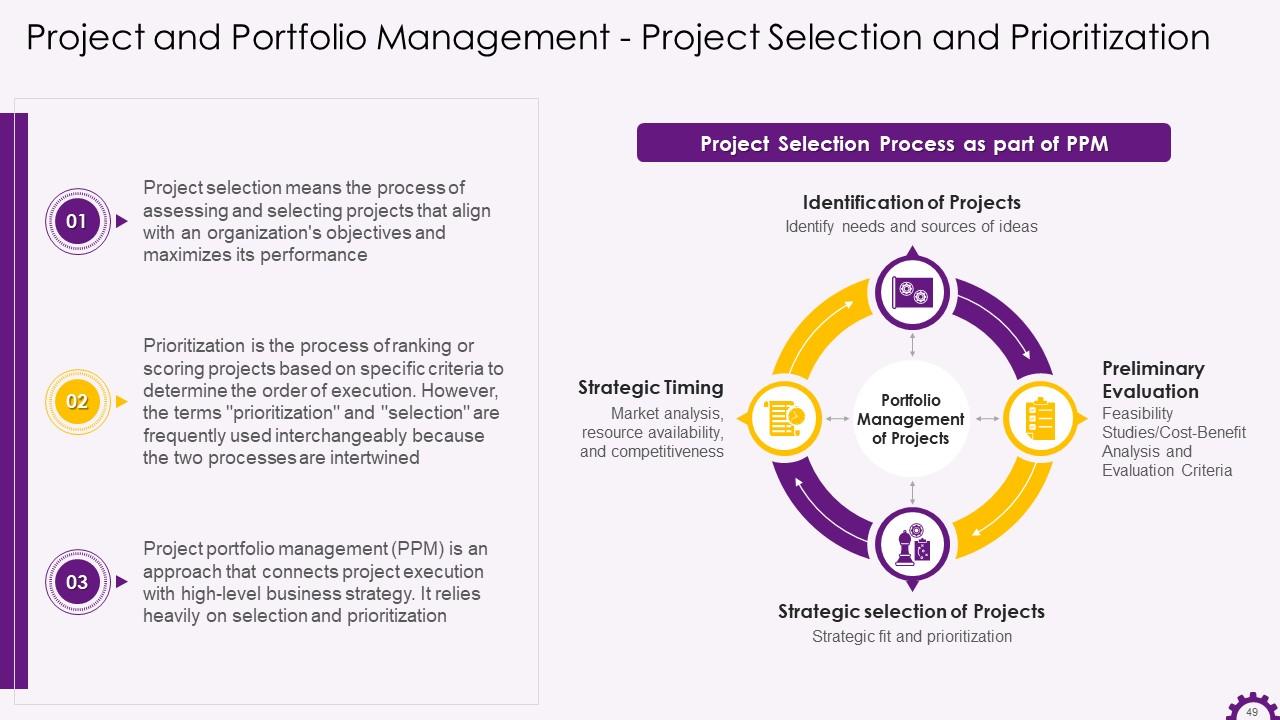
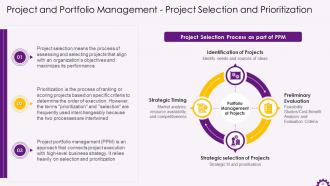
This slide illustrates information regarding project selection and prioritization. It emphasizes that project selection refers to the process of assessing and selecting projects that align with an organization's objectives and maximizes its performance. Prioritization is also defined as the process of ranking or scoring projects based on specific criteria to determine the order of execution. It also mentions the project selection process.
Slide 50
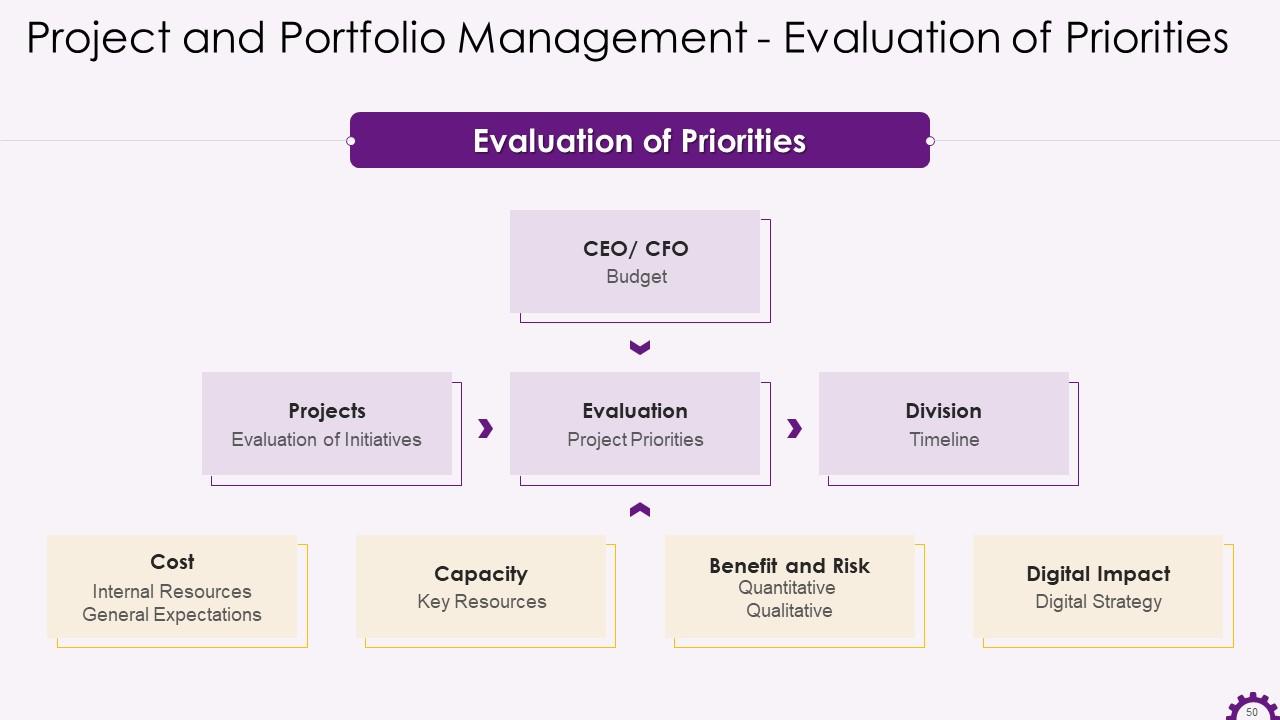
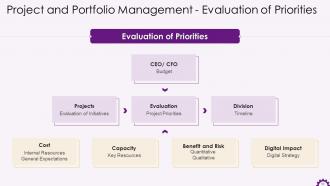
This slide showcases the visual representation of evaluation of priorities in project portfolio management.
Slide 51
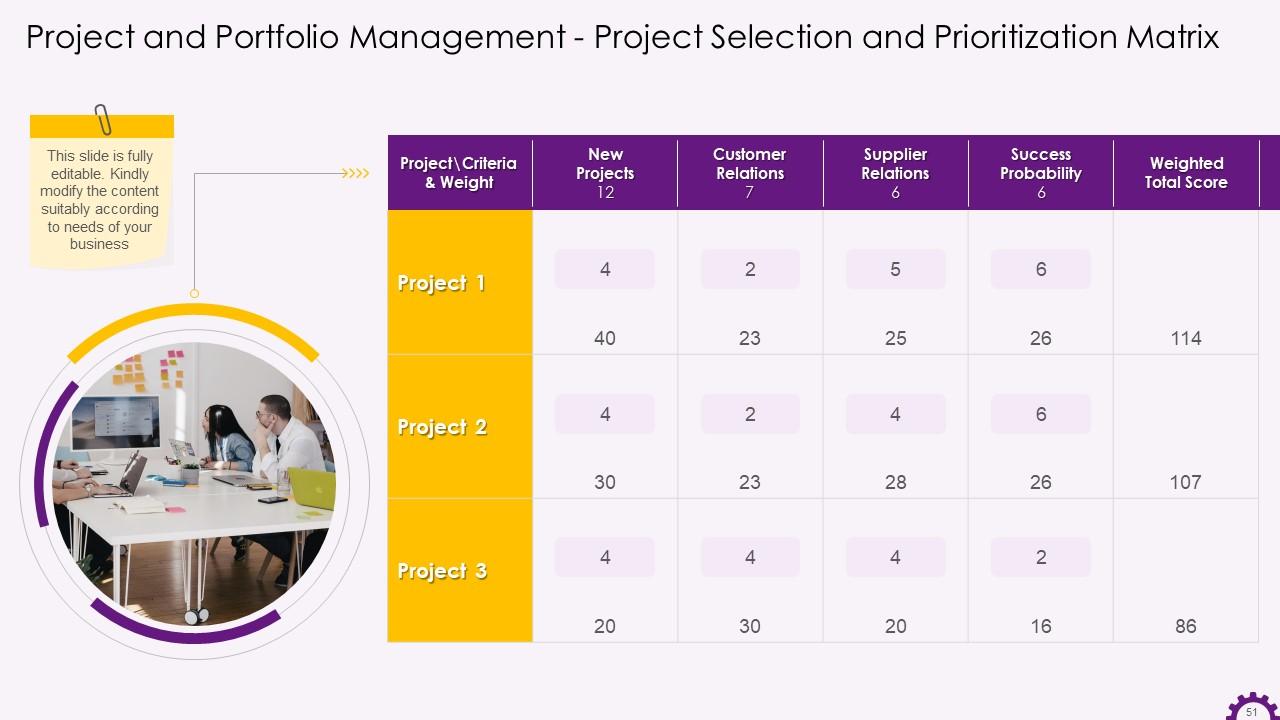
This slide showcases the visual representation of project selection and prioritization matrix. It is based on weighted score. A weighted score is calculated for each project based on the factors decided and weightage allocate to them. In the above table, the number in each box is a simple multiplication of the weight of that criterion and the score of the project based on that particular criterion
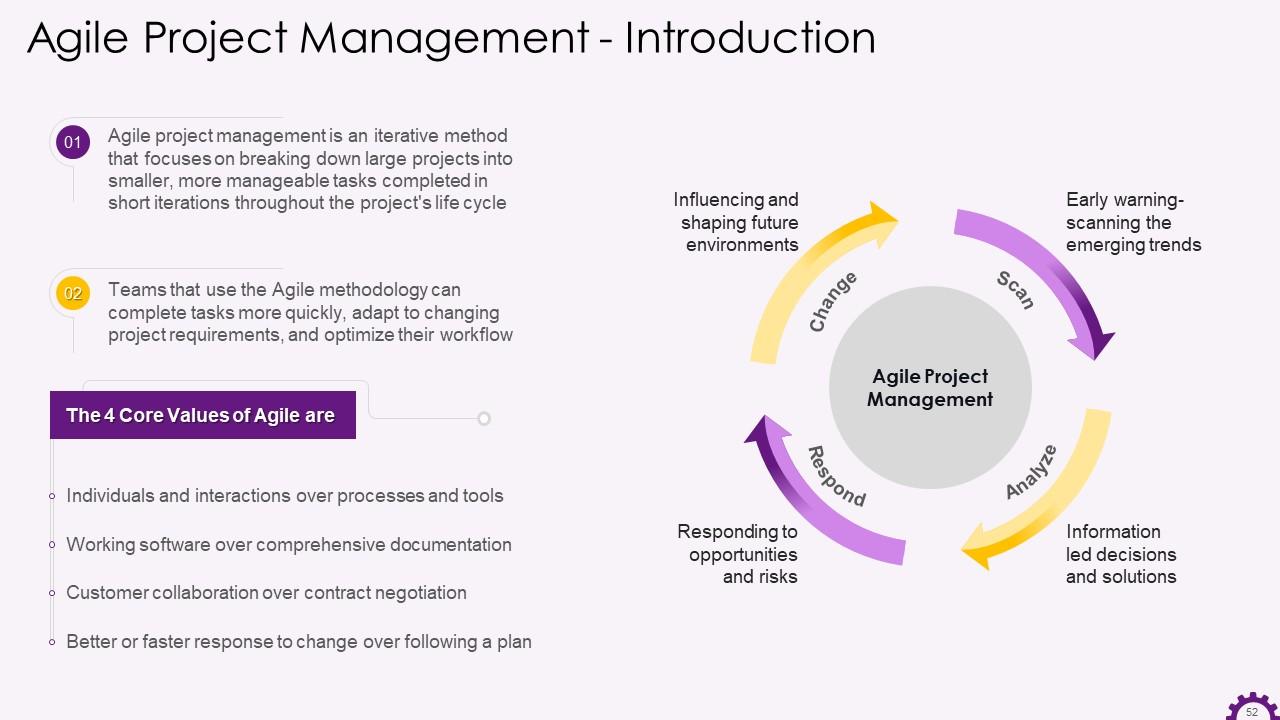
Slide 52
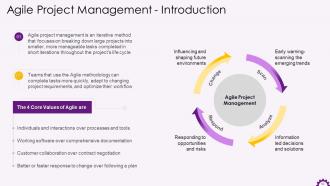
This slide showcases the information regarding agile project management. It emphasizes that agile project management is an iterative method that focuses on breaking down large projects into smaller, more effortless tasks completed in short iterations throughout the project's life cycle. It also emphasizes the four fundamental values of agile project management.
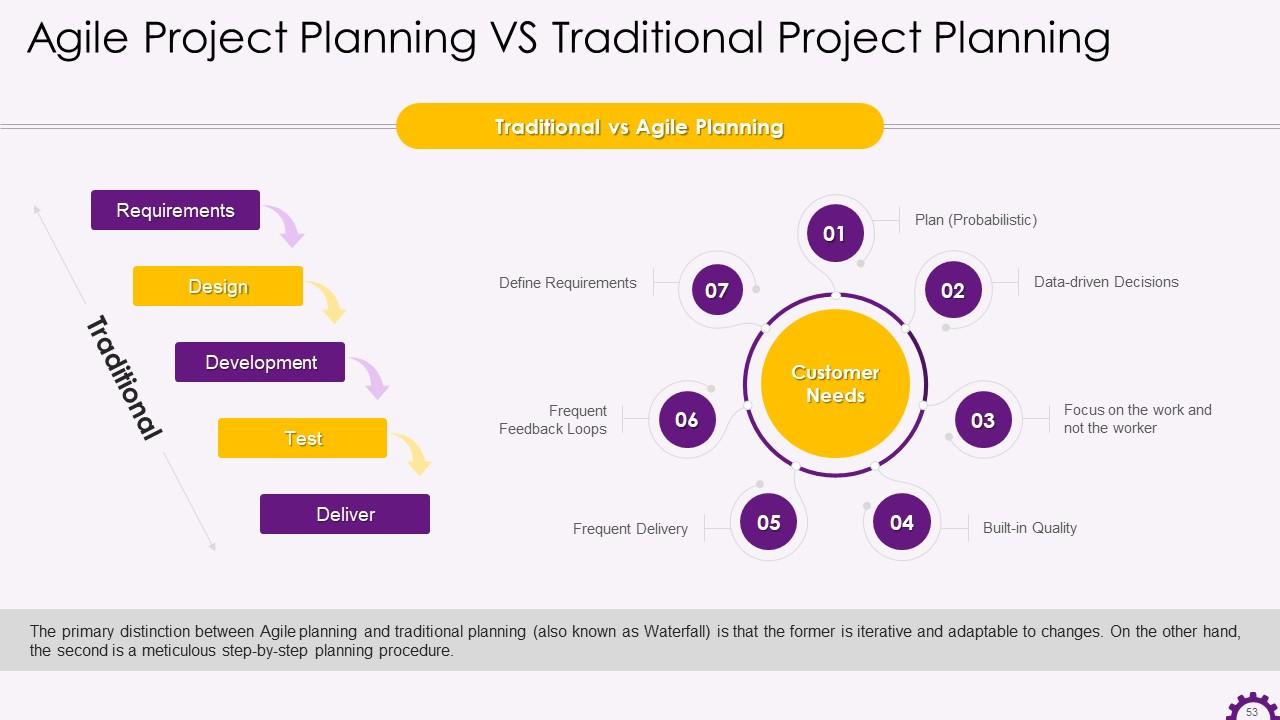
Slide 53
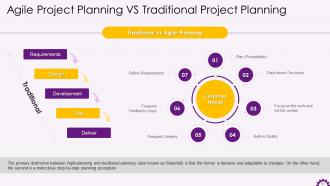
This slide depicts the distinction between agile planning and traditional planning. It highlights that the primary distinction between Agile planning and traditional planning (also known as Waterfall) is that the former is iterative and adaptable to changes. On the other hand, the second is a meticulous step-by-step planning procedure.
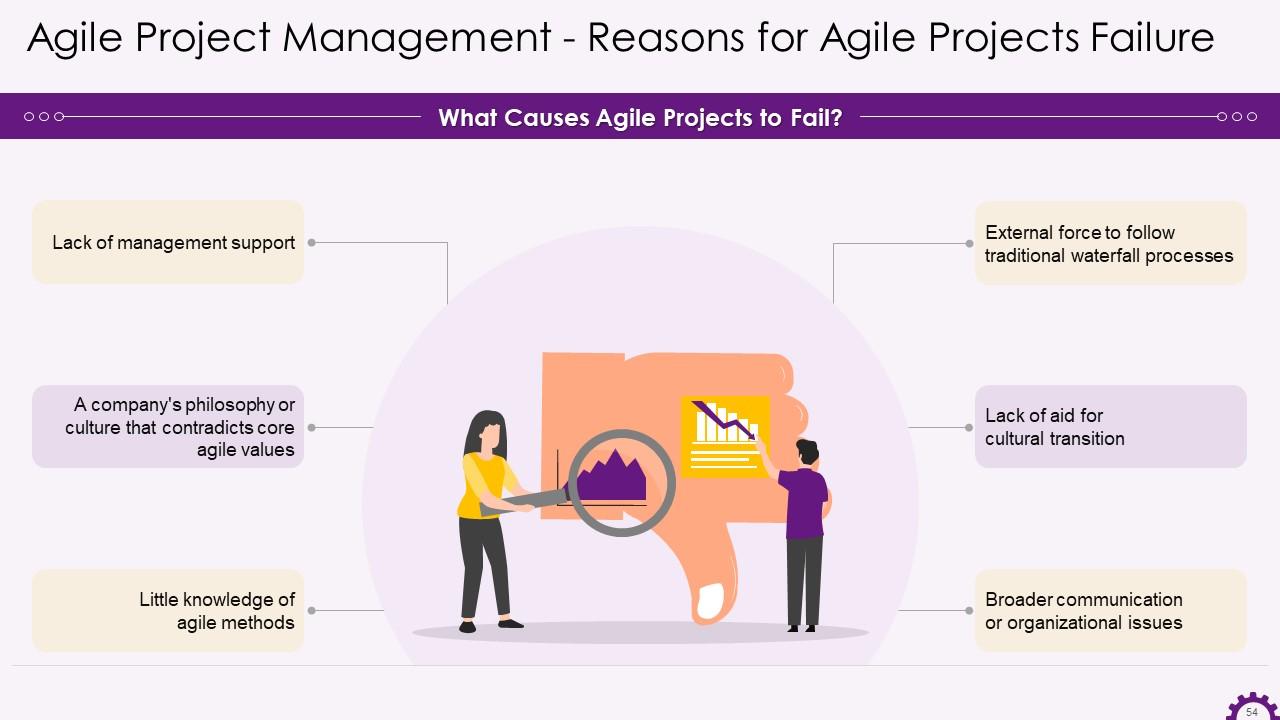
Slide 54
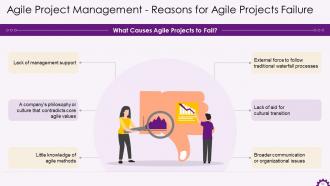
This slide illustrates the reasons that cause agile projects to fail. The reasons are little knowledge of agile methods, company's philosophy or culture that contradicts core agile values, lack of management support, lack of aid for cultural transition, etc.
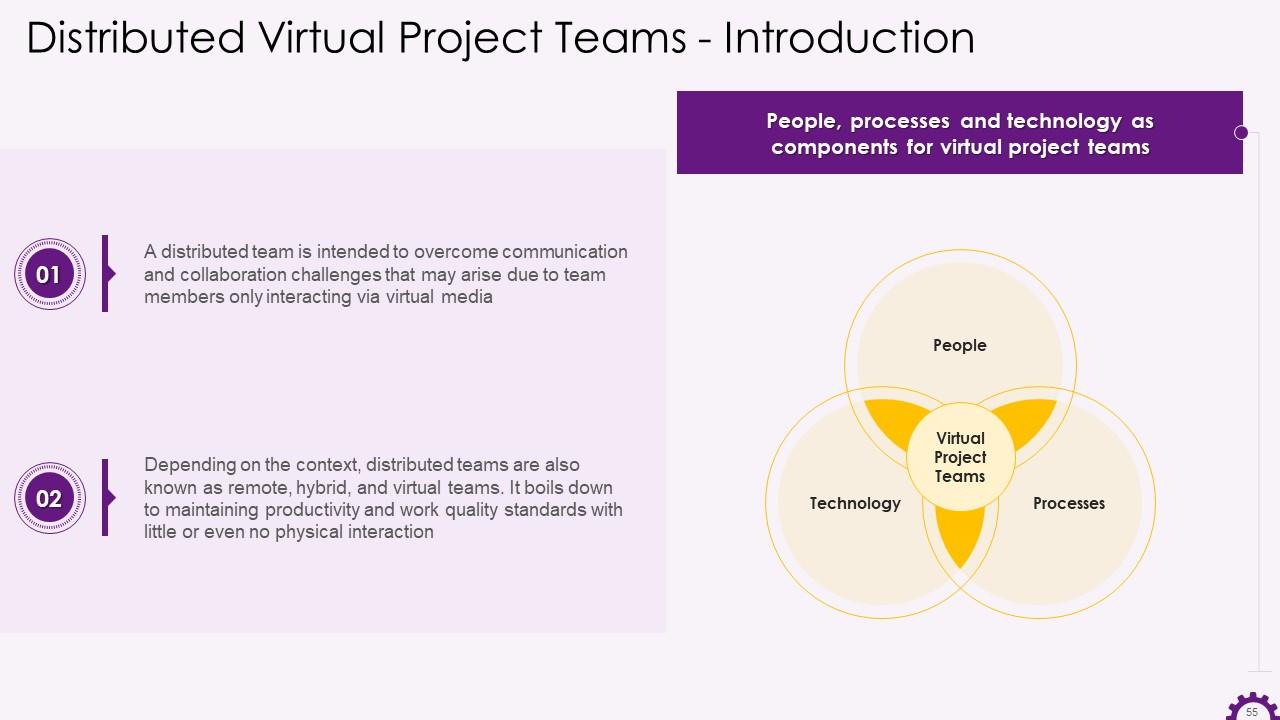
Slide 55
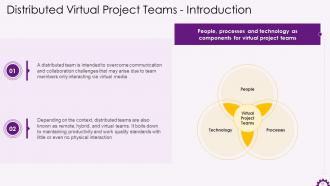
This slide showcases the information regarding distributed teams. It emphasizes that a distributed team is intended to overcome communication and collaboration challenges that may arise due to team members interacting solely through virtual media. Remote, hybrid and virtual teams are examples of distributed teams. It also mentions that the virtual project team's components such as people, processes, and technology.
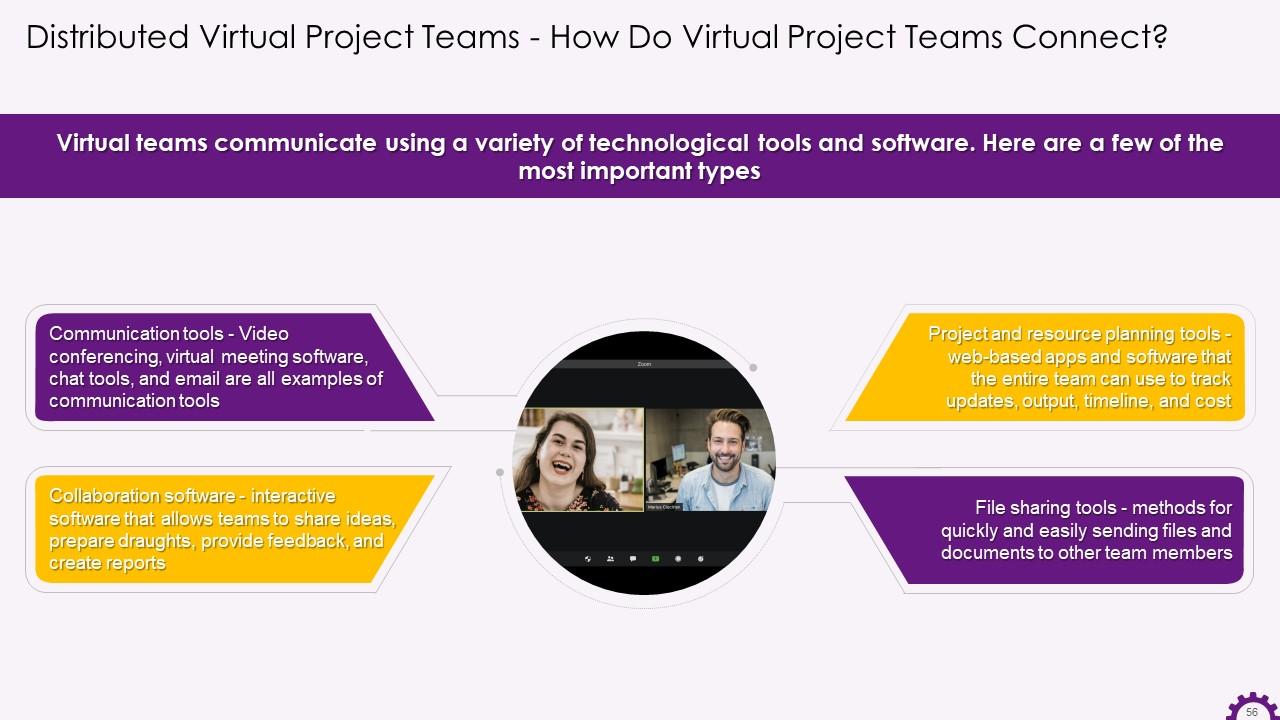
Slide 56
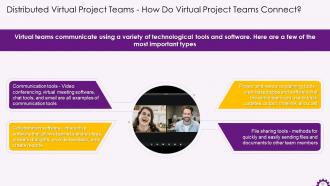
This slide depicts how virtual teams communicate with the help of various technological tools and software. Communication tools, project and resource planning tools, collaboration tools, and file-sharing tools are examples.
Slide 58
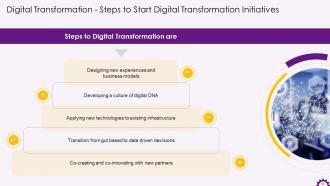
This slide depicts the steps to digital transformation. The steps are designing new experiences and business models, developing a culture of digital DNA, applying new technologies to existing infrastructure, transition from gut to data driven decisions, and co-creating and co-innovating with new partners.
Instructor’s Notes:
The steps to digital transformation are:
- Designing new experiences and business models: Make use of digital designs to create new experiences. Customers want outcomes and experiences while businesses continue to sell goods and services. In the digital world, this disparity in expectations only widens. Successful digital business models both reinforce and promote the brand promise
- Developing a culture of digital DNA: Strong leaders who are not afraid of cannibalizing existing markets and identifying new approaches are required for digital DNA. Organizations must also evaluate their inherent ability to thrive in a digital business environment and cultivate digital artisans. Organizations can instill digital DNA throughout the culture by using a framework for digital proficiency
- Applying new technologies to existing infrastructure: Digital does not imply the abolition of existing technologies. Introducing external data into internal systems generates new patterns, which provide better data for testing new business models. Businesses must take advantage of the opportunity to rethink the technology strategy to align it with the business goals of digital transformation
- Transition from gut based to data driven decisions: The heart of the digital transformation is data. Every touch point, click, and interaction generates a context-rich digital exhaust. Organizations require relevance to be delivered in real-time. The goal is to move from data to decisions by asking the right questions and anticipating future behavior
- Co-creating and co-innovating with new partners: No business can succeed on its own. An ecosystem of co-creation and co-innovation awaits businesses digital transformation. Organizations should participate in industry consortiums and build ecosystems centered on their self-interest
Slide 59
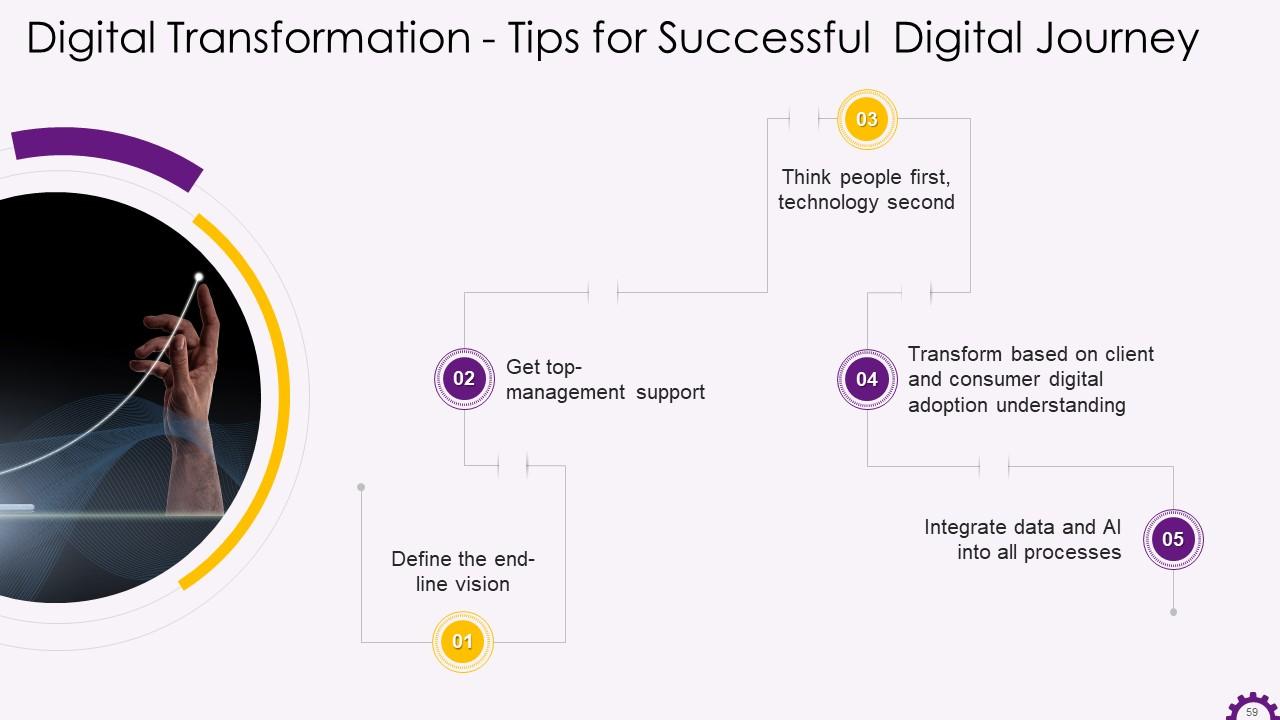
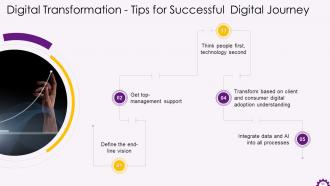
This slide illustrates the tips for a successful digital transformation journey. The recommendations include defining the end-line vision, getting top-management support, thinking people first, technology second, integrating data and AI (Artificial Intelligence) into all processes, etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
The tips for a successful digital transformation journey are:
- Define the End-line Vision: Many organizations fail to leverage new technologies and bridge the digital divide because they do not have a clear vision. They have short-term objectives but no long-term vision. Consequently, minor improvements and process tweaks are made, but the organization is constantly playing catch-up and is vulnerable to disruption from more agile competitors. A clear vision of where the organization must go and specific, measurable goals and objectives should be in place
- Get Top-management Support: Top management commitment is required for successful transformation. The C-suite must demonstrate leadership and communicate objectives and expectations of digital strategies across the organization. Management must champion the digital strategy and demonstrate how the change will benefit stakeholders while also delivering on what has been promised
- Think People First, Technology Second: Simply providing your workforce with new digital tools to work with is insufficient. You must ensure that your team has the necessary skills and knowledge to use the latest digital infrastructure. As with any disruptive initiative, resistance to change must be considered. That is why it is critical to obtain top-level management support and orient the workplace to accept the change
- Transform based on Client and Consumer Digital Adoption Understanding: There is no return to a bygone era. Businesses have to bridge the digital divide to ensure that they can stay relevant, as customers, increasingly, take to digital technology. Organizations should align their transformation goals with their customers' needs and add value throughout the customer journey. This necessitates a thorough understanding of your customers' needs, preferences, the level of digital adoption, and expectations
- Integrate Data and AI into all Processes: Organizations have entered a new era of technological advancement. Previously, new technology was created and deployed to perform a specific function until it needed to be upgraded or replaced. Technology like AI learns and uses data to become more efficient and effective every second. Artificial Intelligence can be integrated with other enterprise software to analyze data and make decisions on a minute-by-minute and day-by-day basis
Slide 60 to 61
These slides illustrate the key takeaways for the session performing digital transformation in organizations.
Slide 62
This slide mentions various questions for discussion on the topic performing digital transformation in organizations.
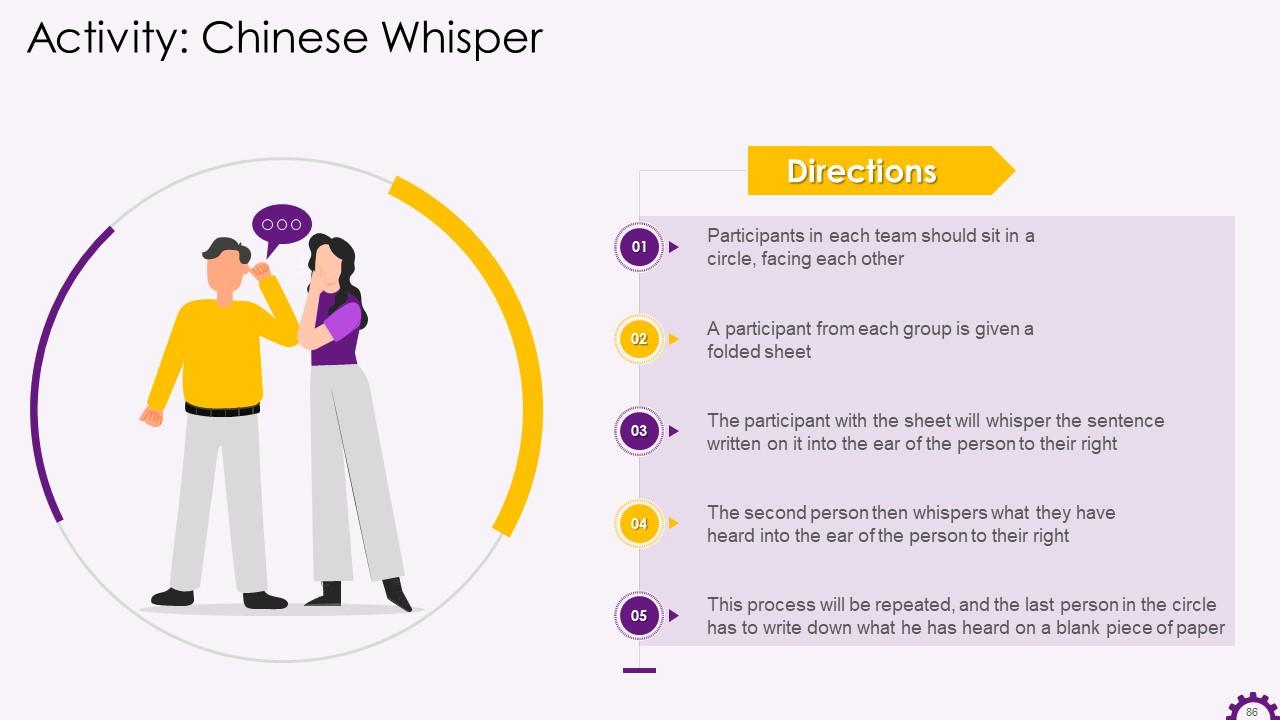
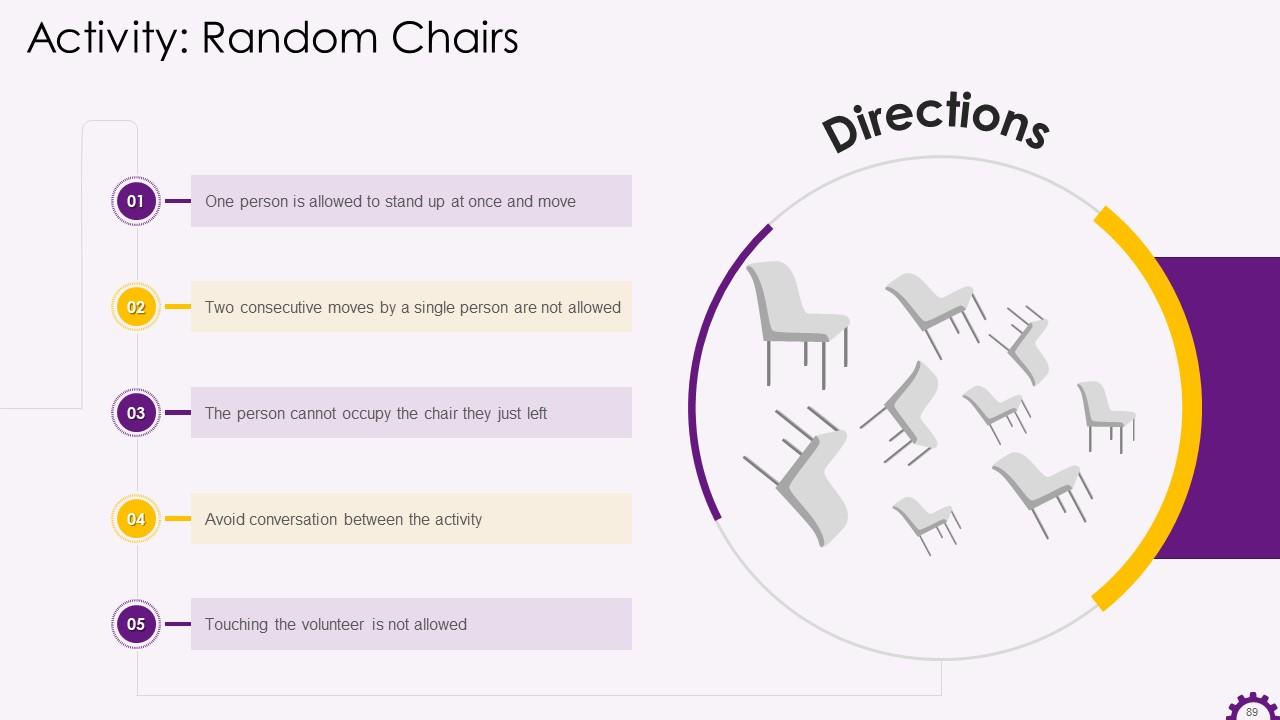
Slide 74 to 89
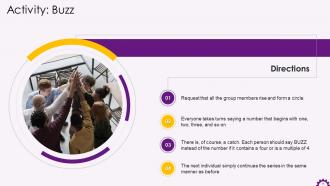
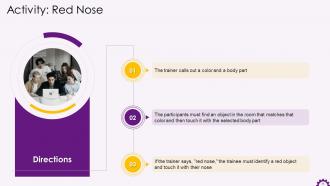
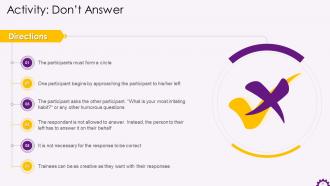
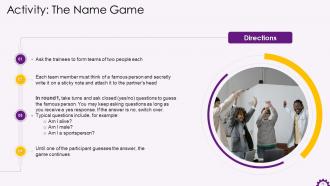
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 90 to 117
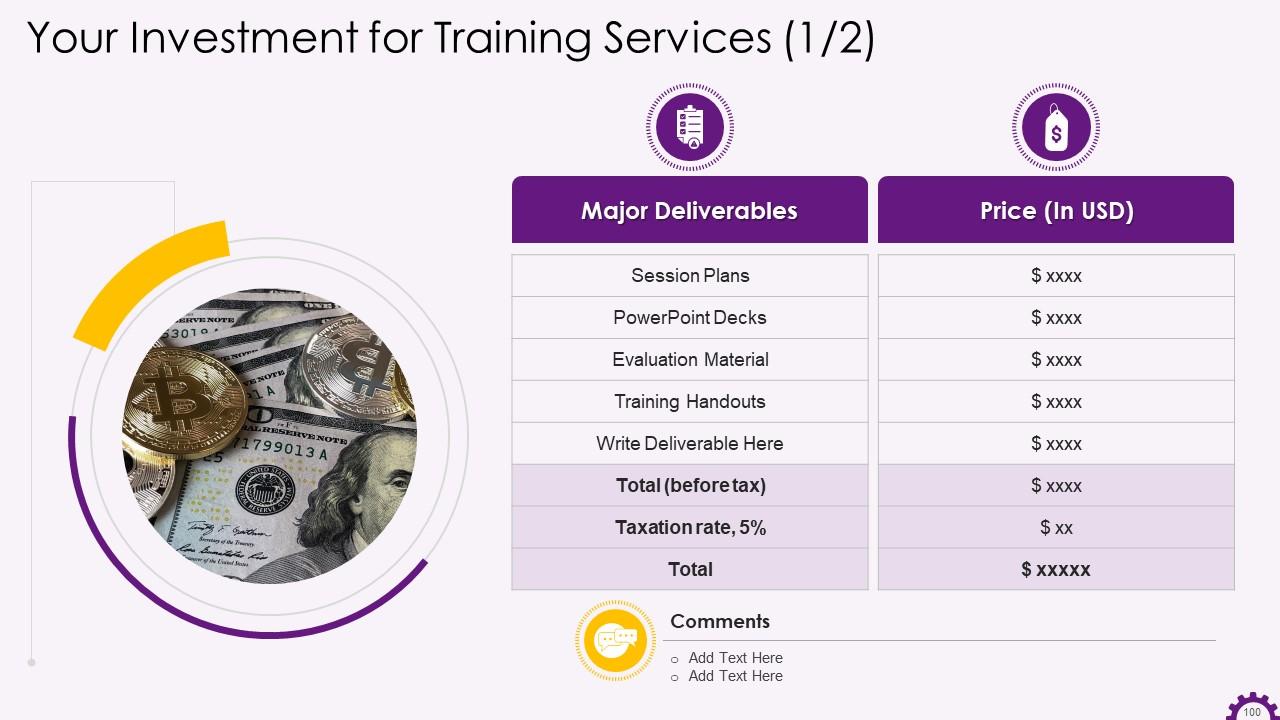
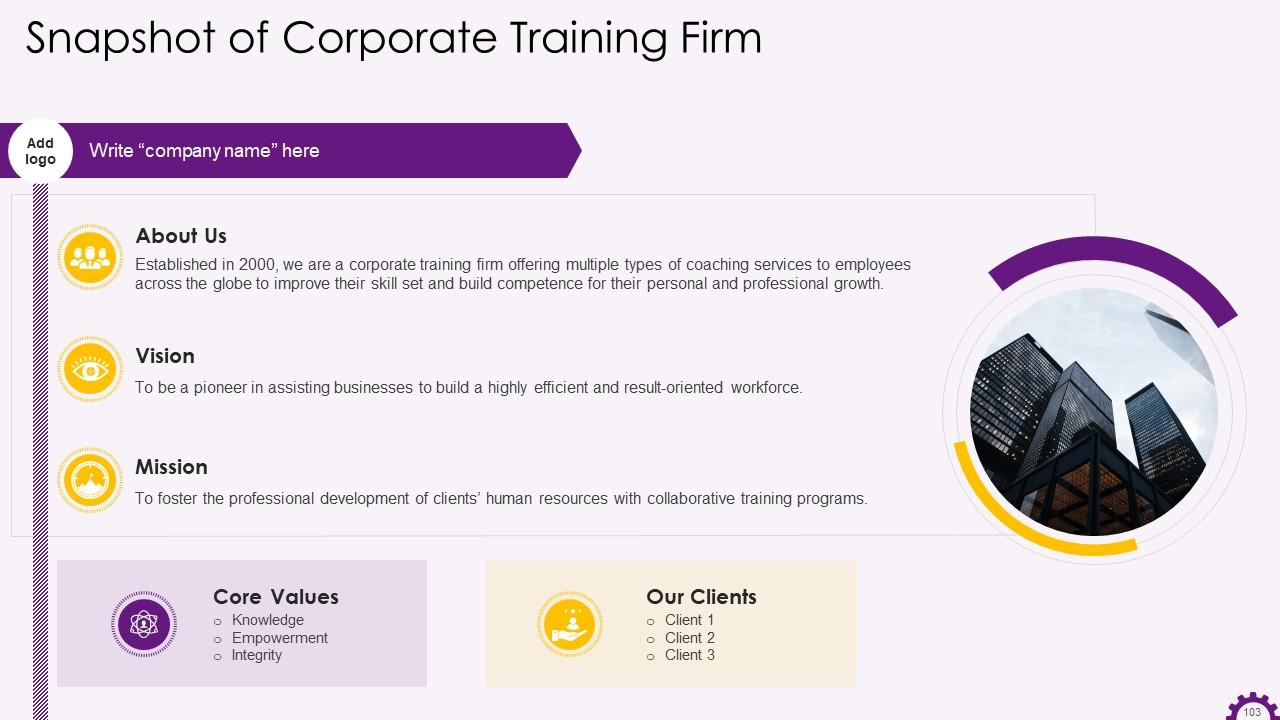
These slides contain a training proposal covering what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
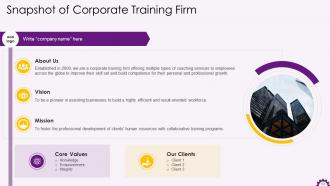
Implementing Digital Transformation in Organizations Training ppt with all 122 slides:
Use our Implementing Digital Transformation in Organizations Training ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Good research work and creative work done on every template.
-
“You have the structure in place that are easy to explore new opportunities.I will be recommending your services to other people.”