Soft Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides
Soft computing comprises various components such as Fuzzy Logic, Neural Networks, Genetic algorithms, Swarm intelligence, and others enabling solving complex problems using uncertain, precise, or incomplete information. Our Decision support systems module titled Soft Computing IT provides an overview of an advanced computational approach. Additionally, our PPT describes Fuzzy Logic that handles vague or uncertain information and allows assigning partial truth values to propositions, making it useful in decision-making processes. It also deals with Neural network systems that imitate the structure of the human brain and can be utilized for tasks like pattern recognition, clustering, and classification. Furthermore, our Pattern Recognition template provides information about Genetic algorithms that draw inspiration from the natural selection and genetic inheritance process. Further, it surveys an evolutionary process involving selecting the most promising individuals, recombining their genetic material, and introducing random mutations to explore new areas of the solution space. Lastly, our Optimization Techniques Deck offers details about Swarm intelligence observed in decentralized, self-organized systems, mainly in social animals like bees, ants, and birds that aim to develop algorithms inspired by the behavior of social insects. Download our 100 percent editable and customizable template, which is also compatible with Google Slides.
Soft computing comprises various components such as Fuzzy Logic, Neural Networks, Genetic algorithms, Swarm intelligence, a..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Deliver this complete deck to your team members and other collaborators. Encompassed with stylized slides presenting various concepts, this Soft Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides is the best tool you can utilize. Personalize its content and graphics to make it unique and thought-provoking. All the ninety nine slides are editable and modifiable, so feel free to adjust them to your business setting. The font, color, and other components also come in an editable format making this PPT design the best choice for your next presentation. So, download now.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1: This slide introduces Soft Computing. State Your Company Name and begin.
Slide 2: This slide is an Agenda slide. State your agendas here.
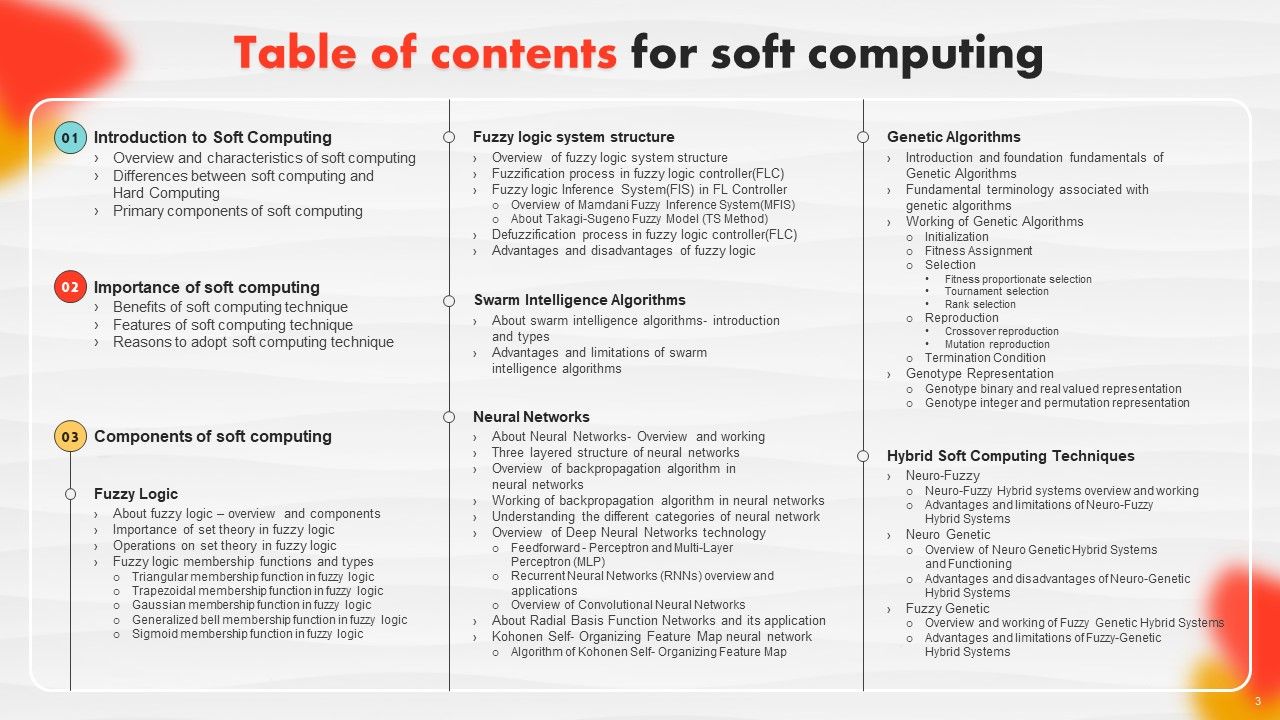
Slide 3: This slide shows a Table of Contents for the presentation.
Slide 4: This slide is in continuation with the previous slide.
Slide 5: This slide introduces Introduction to Soft Computing out of the table of contents.
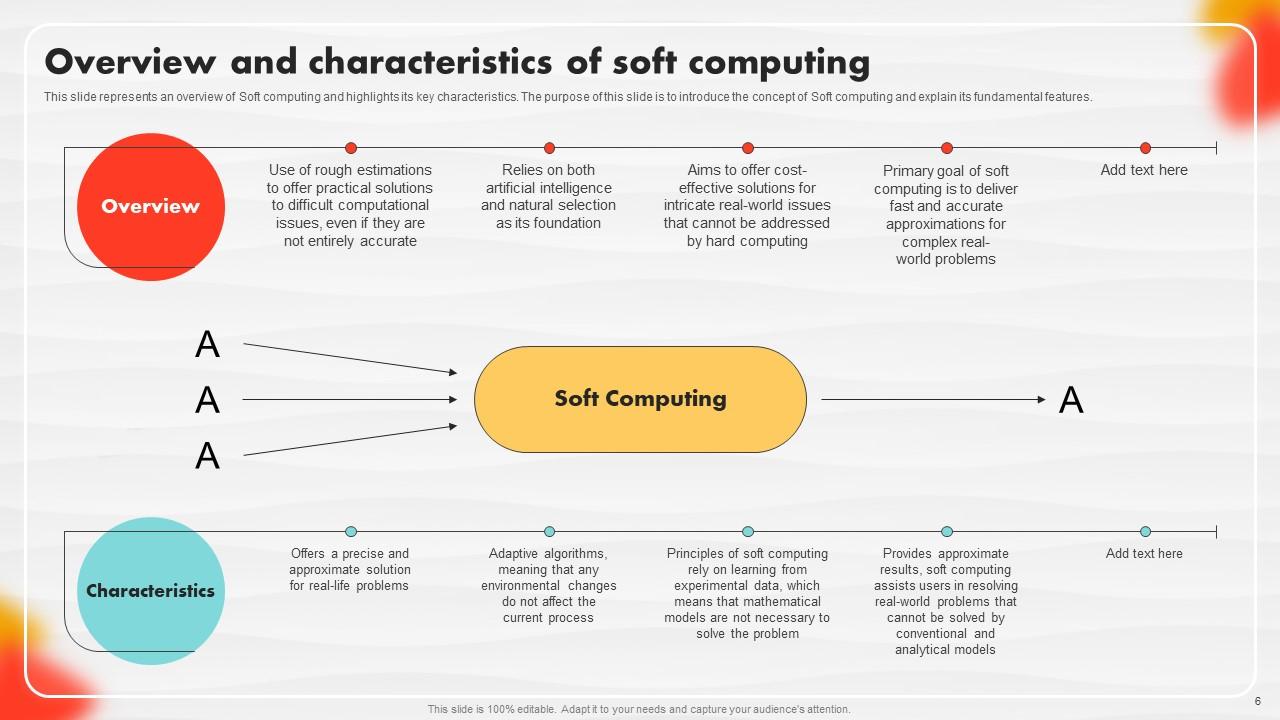
Slide 6: This slide represents an overview of Soft computing and highlights its key characteristics.
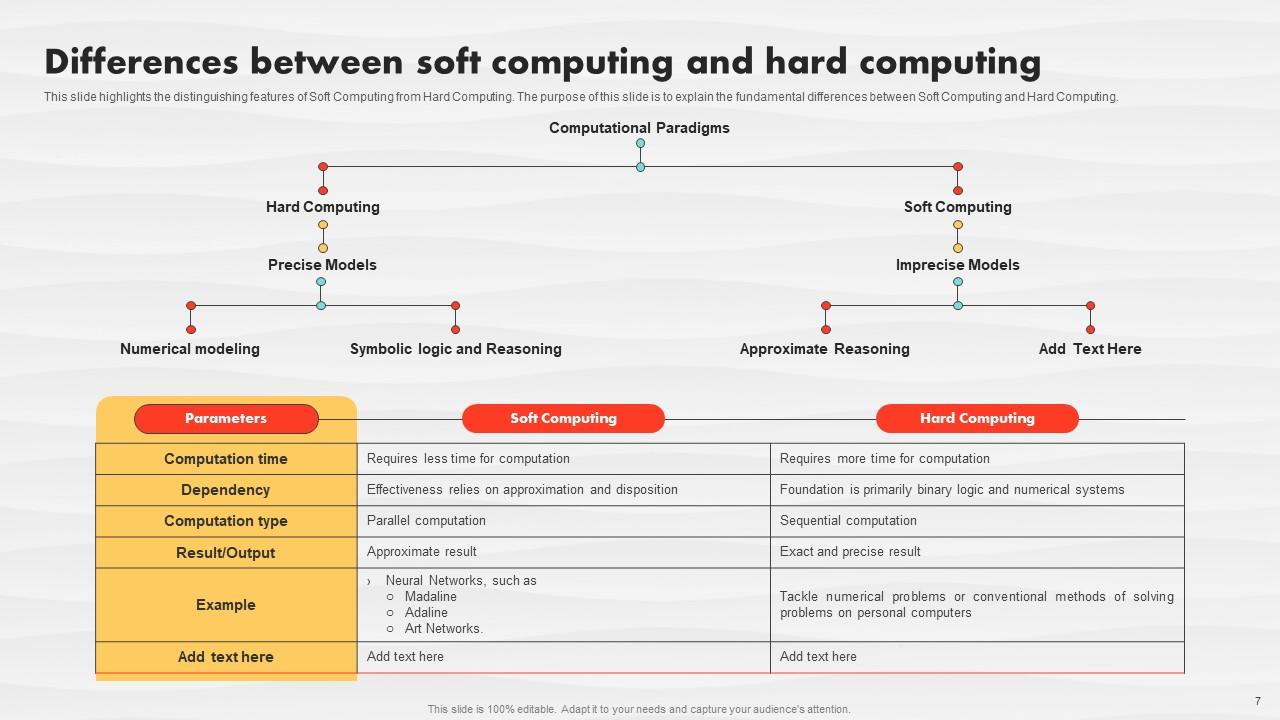
Slide 7: This slide highlights the distinguishing features of Soft Computing from Hard Computing.
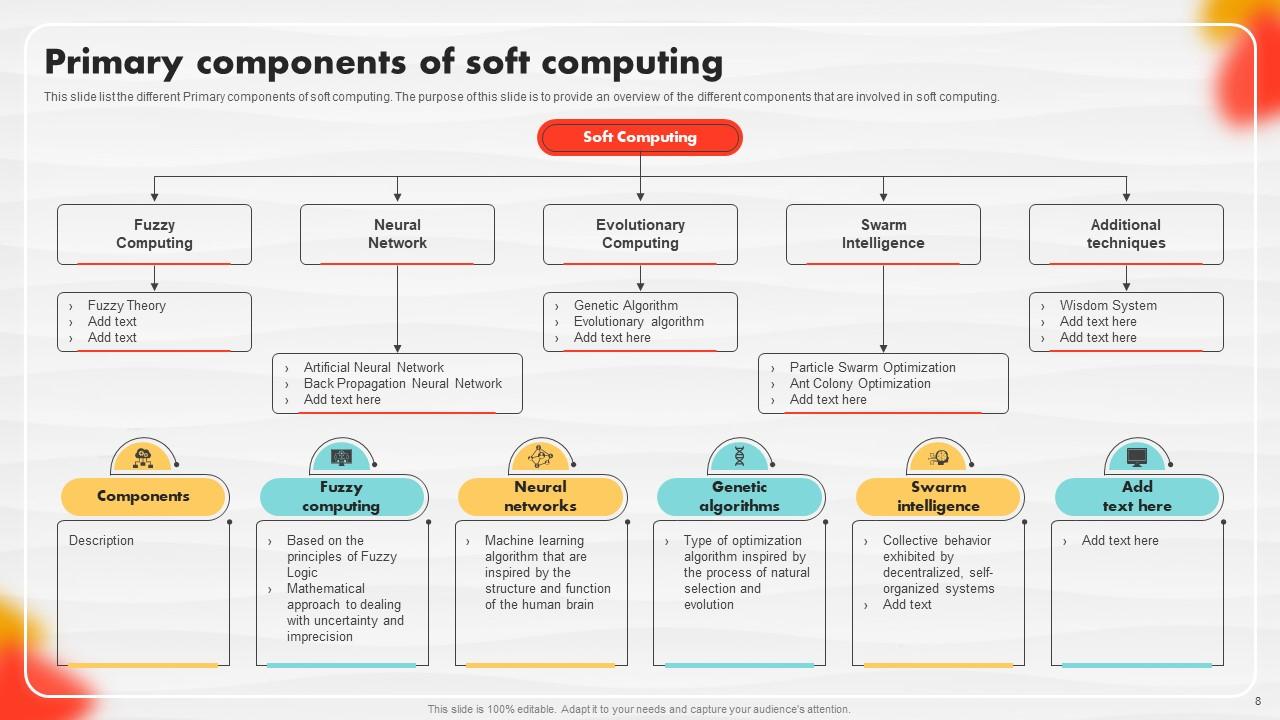
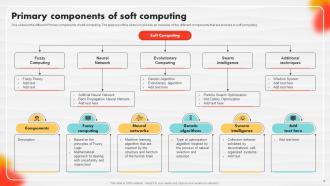
Slide 8: This slide lists the different Primary components of soft computing.
Slide 9: This slide introduces the Importance of soft computing out of the table of contents.
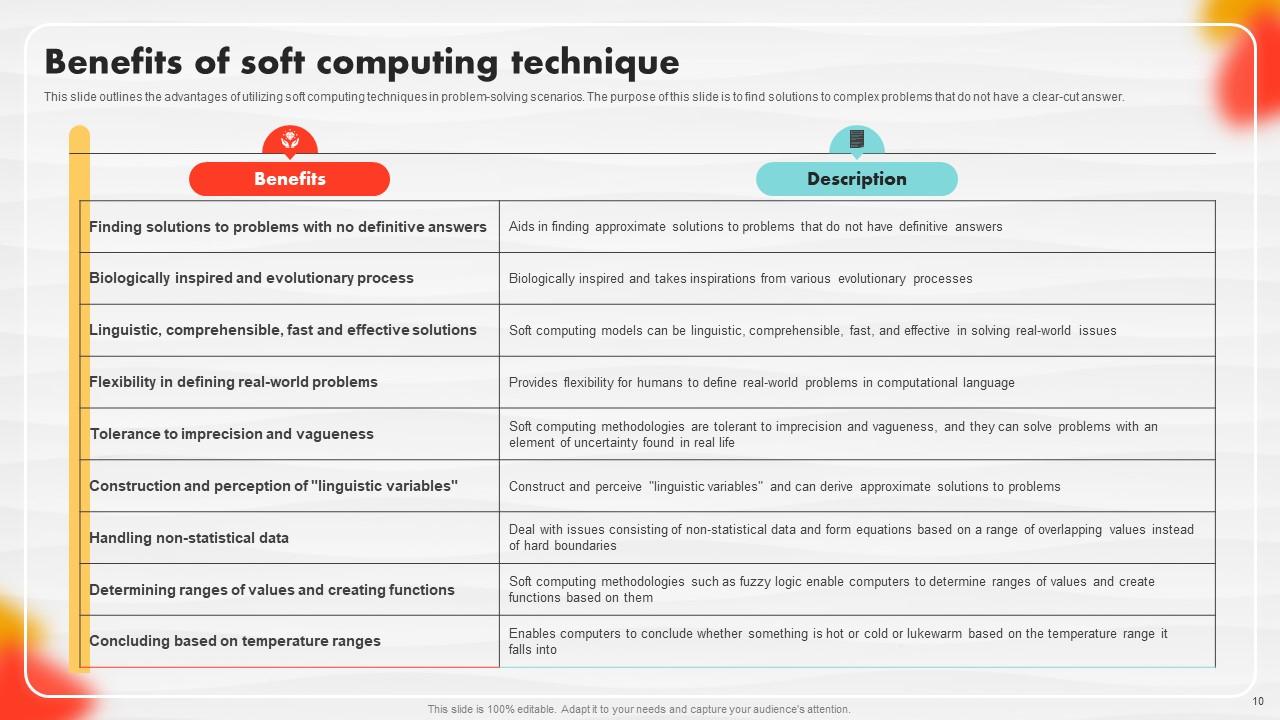
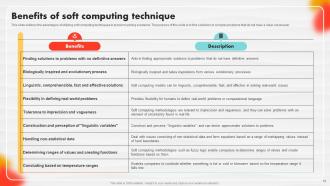
Slide 10: This slide outlines the advantages of utilizing soft computing techniques in problem-solving scenarios.
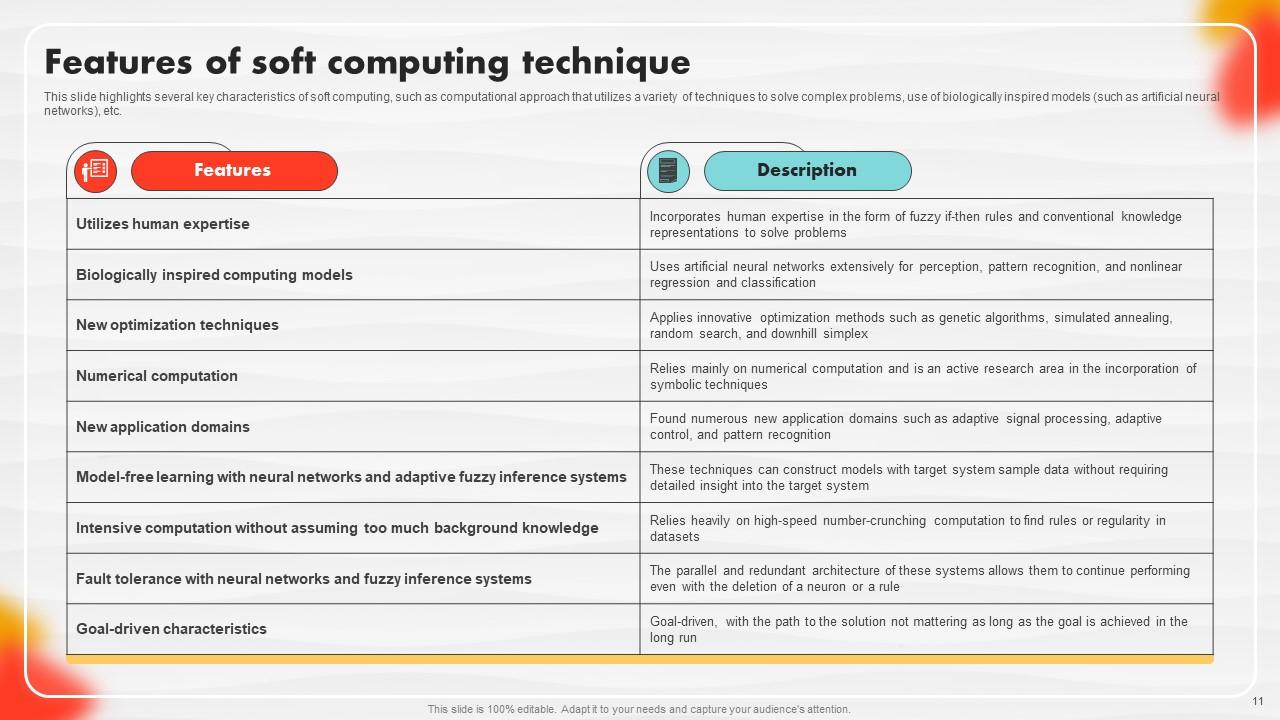
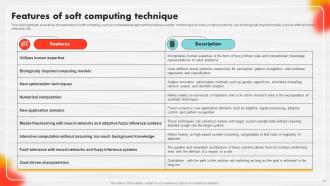
Slide 11: This slide describes Features of soft computing technique.
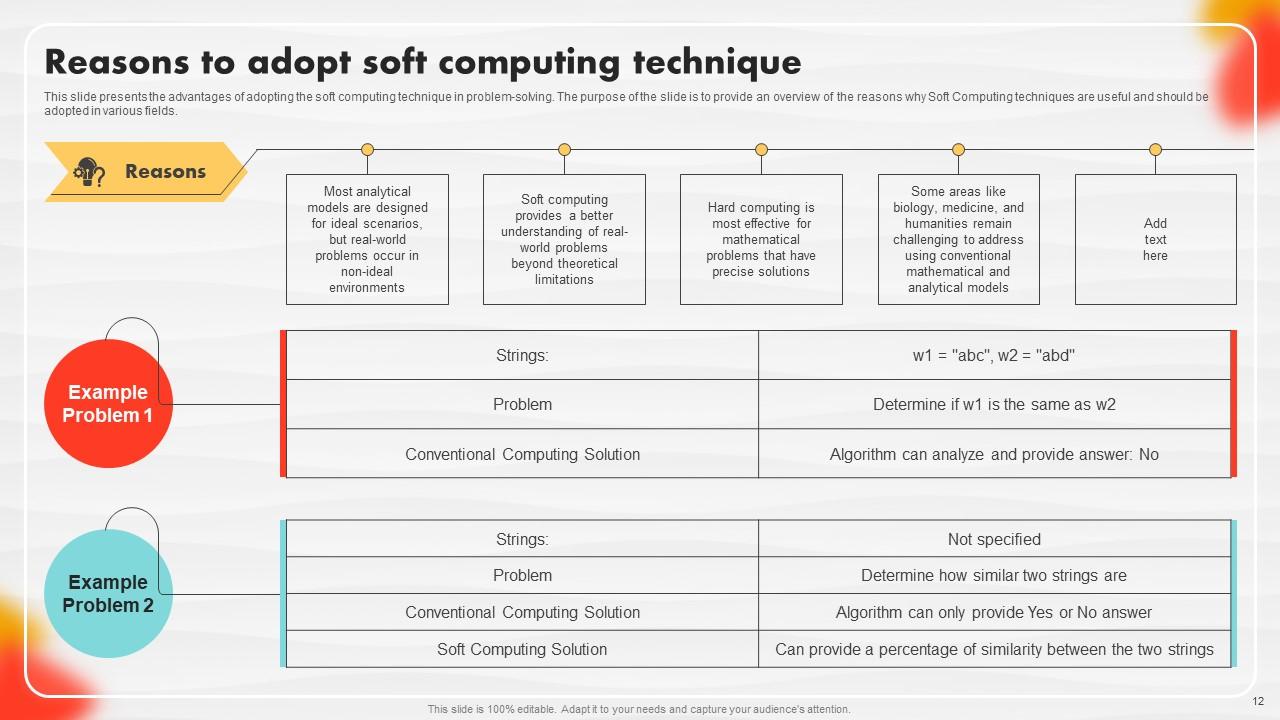
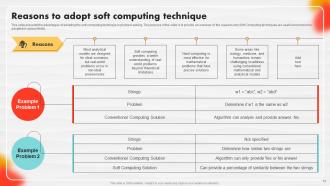
Slide 12: This slide presents the advantages of adopting the soft computing technique in problem-solving.
Slide 13: This slide introduces Components of soft computing out of the table of contents.
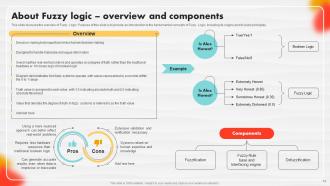
Slide 14: This slide discusses the overview of Fuzzy Logic.
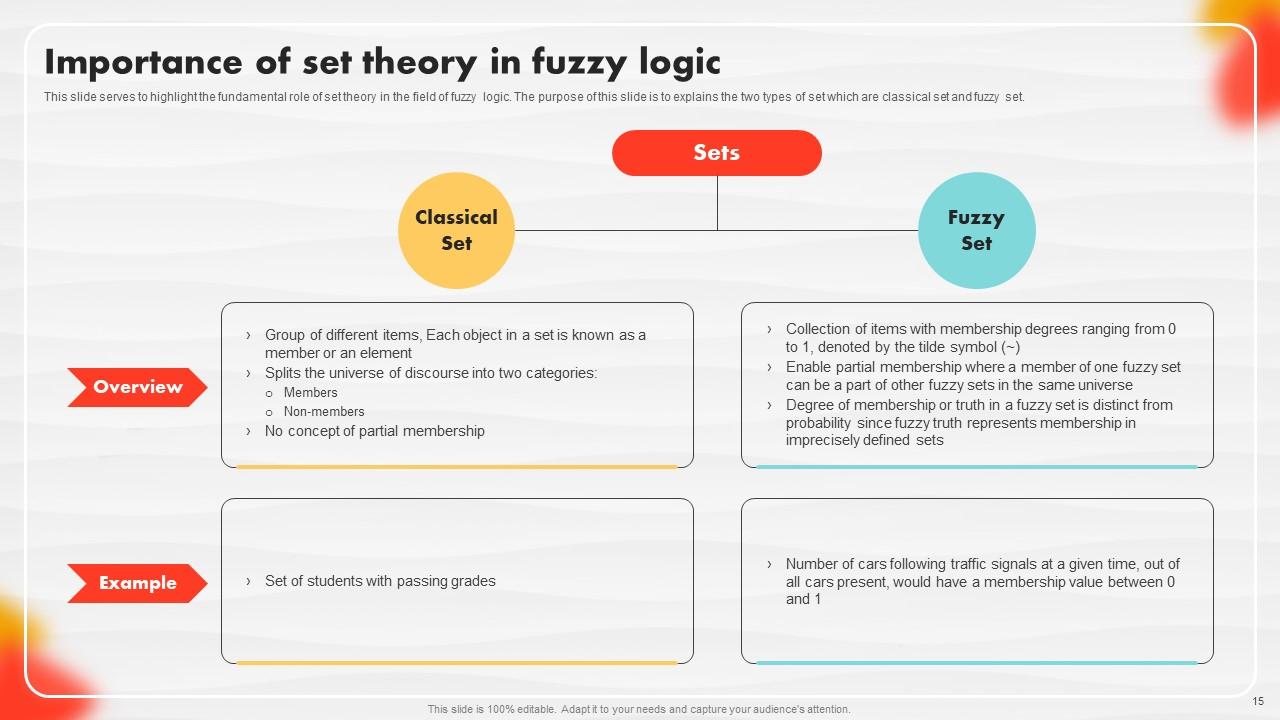
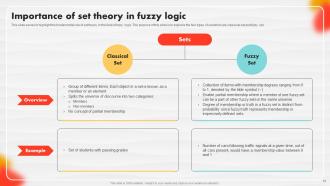
Slide 15: This slide serves to highlight the fundamental role of set theory in the field of fuzzy logic.
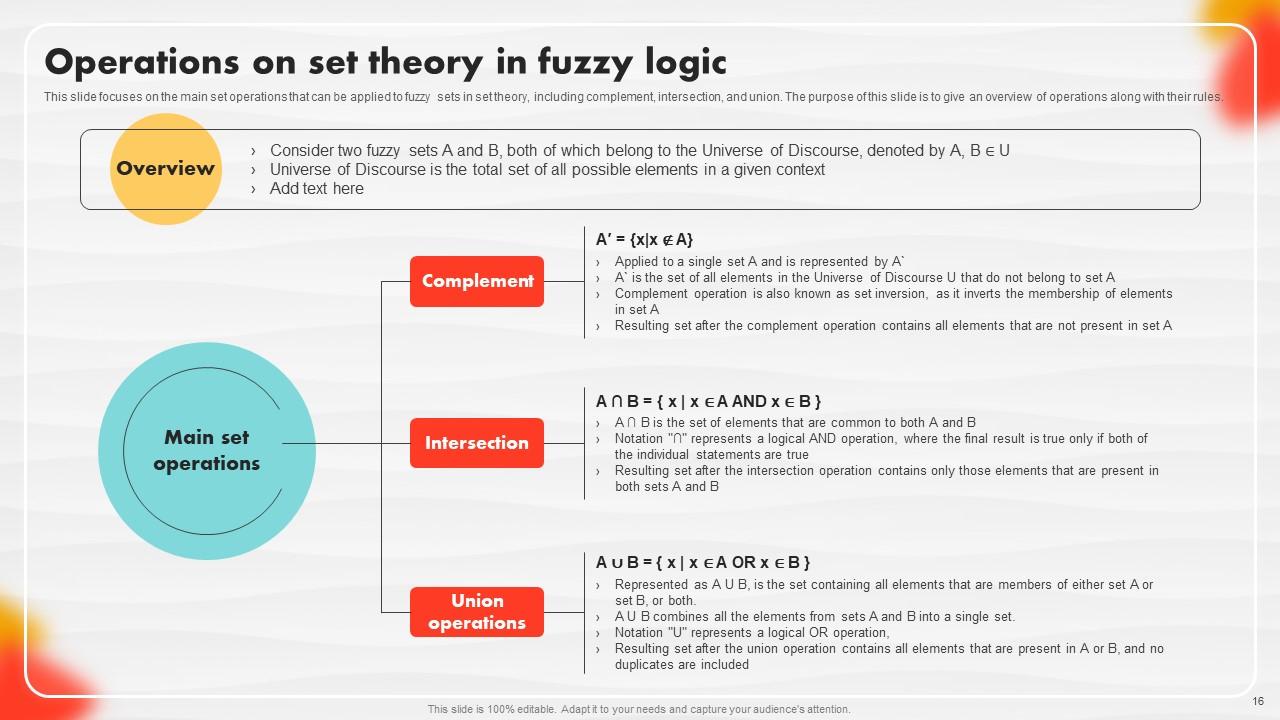
Slide 16: This slide focuses on the main set operations that can be applied to fuzzy sets in set theory.
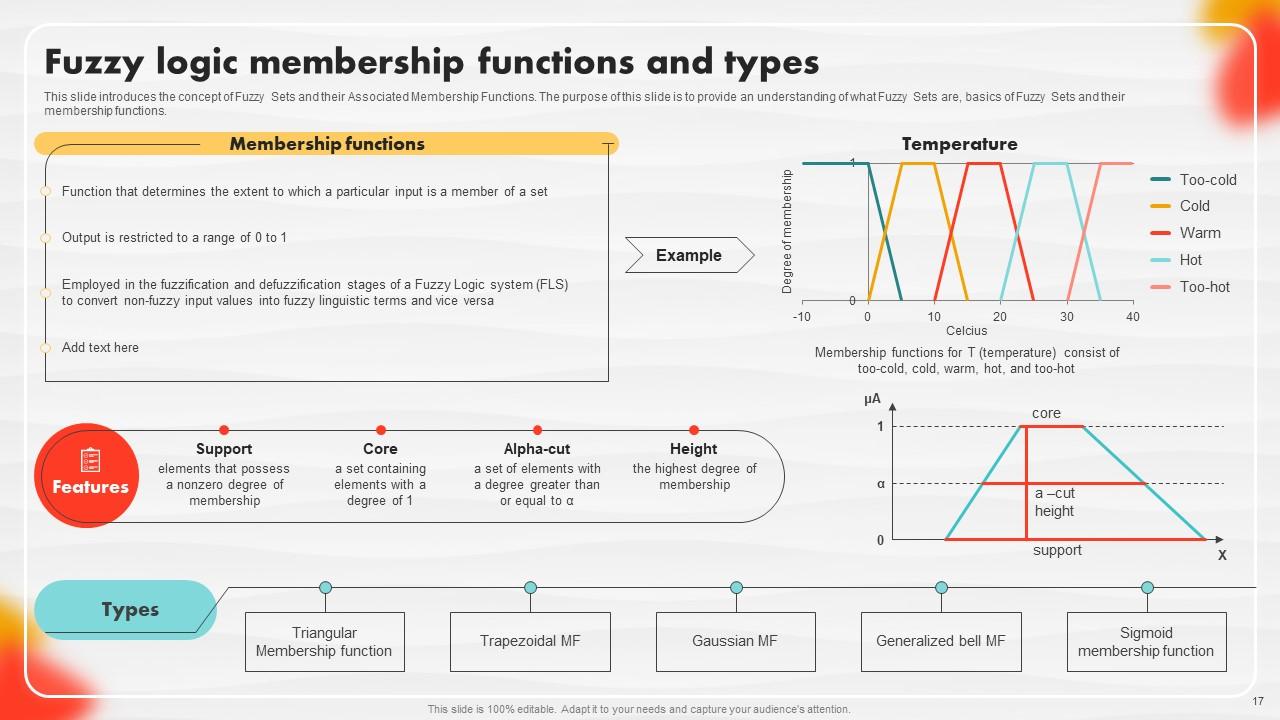
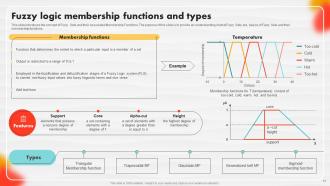
Slide 17: This slide introduces the concept of Fuzzy Sets and their Associated Membership Functions.
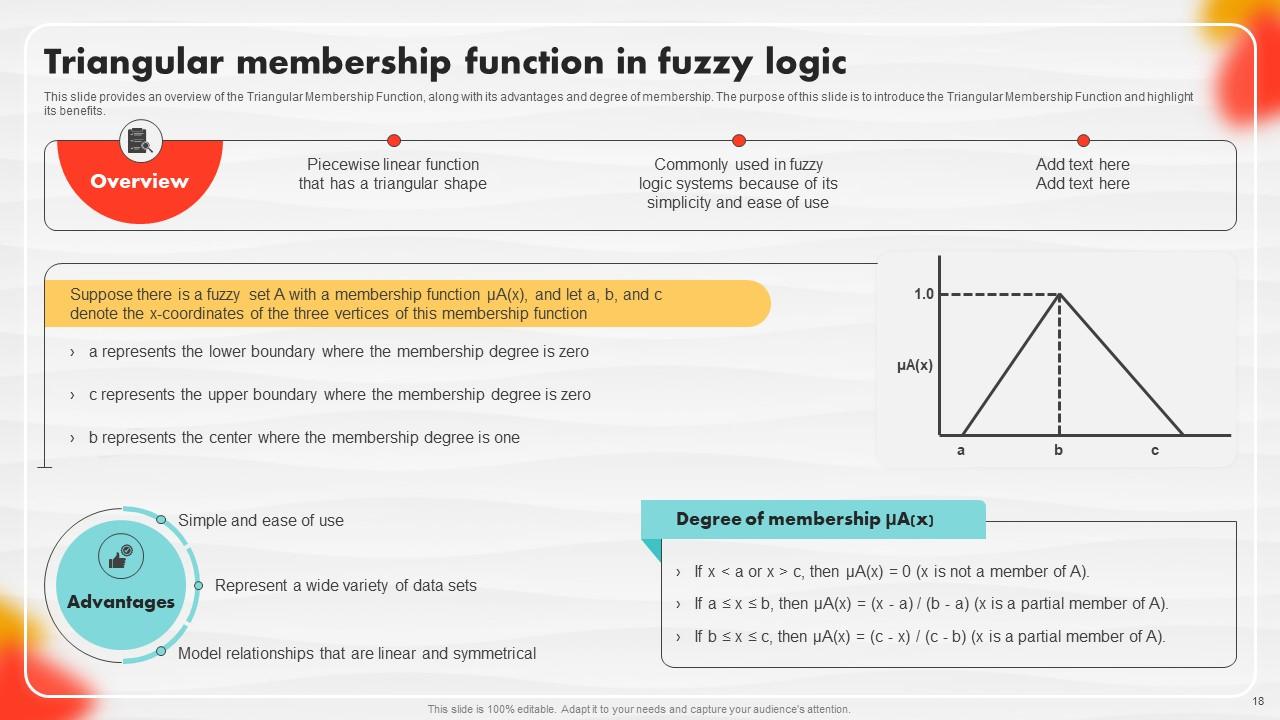
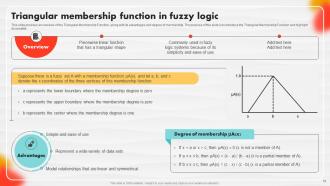
Slide 18: This slide highlights an overview of the Triangular Membership Function, along with its advantages and degree of membership.
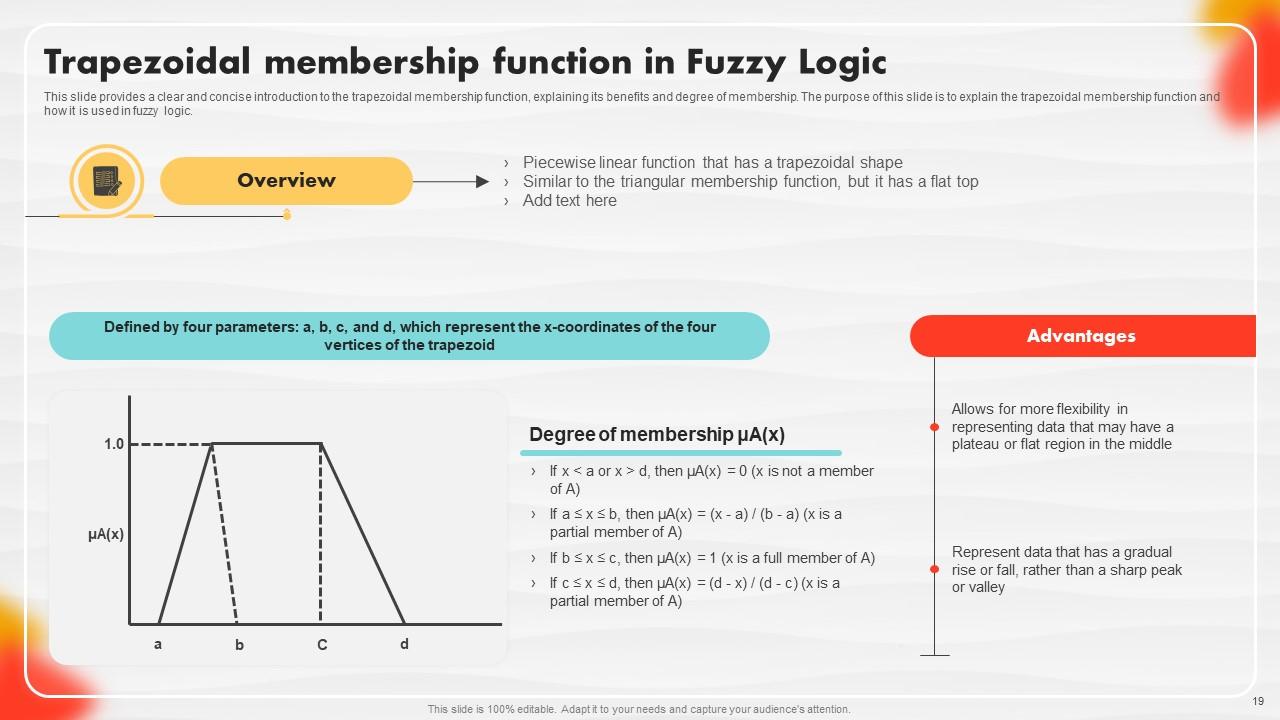
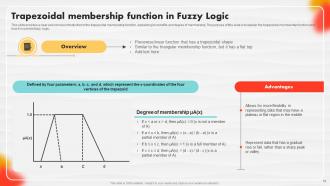
Slide 19: This slide showcases a clear and concise introduction to the trapezoidal membership function.
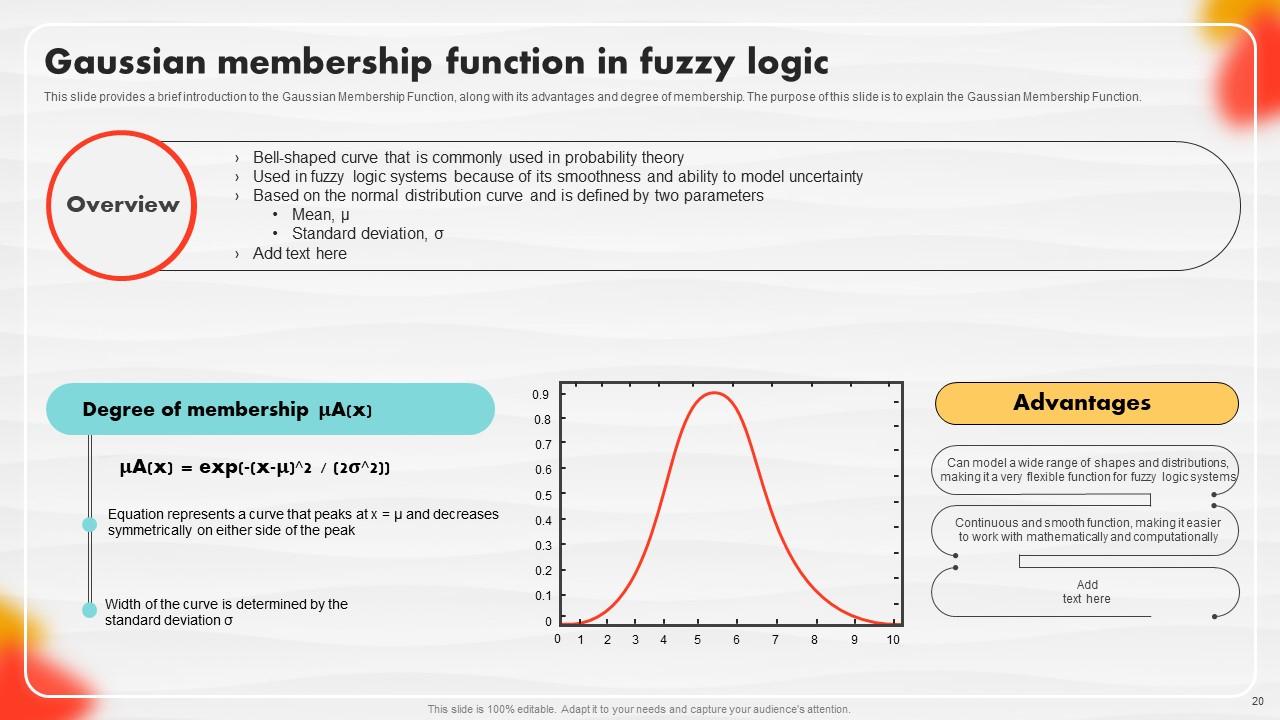
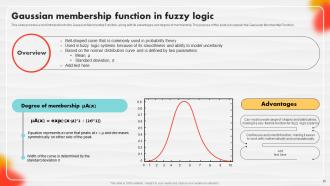
Slide 20: This slide entails a brief introduction to the Gaussian Membership Function, along with its advantages and degree of membership.
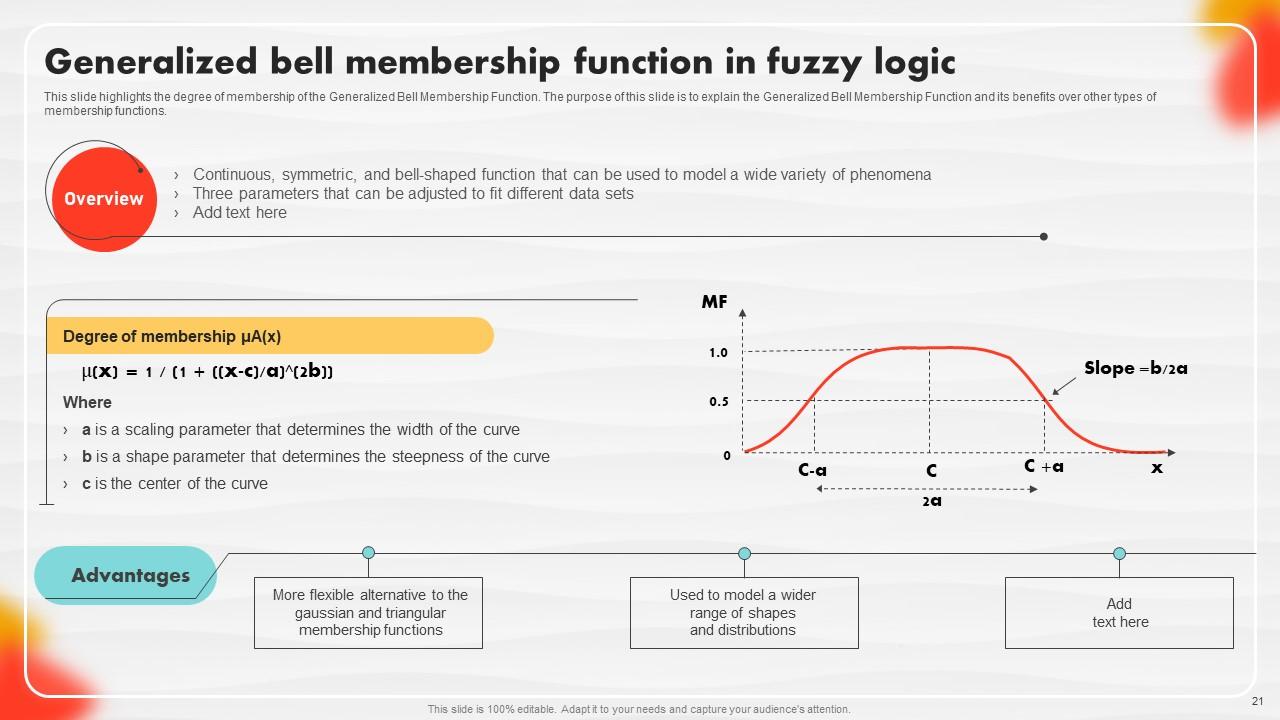
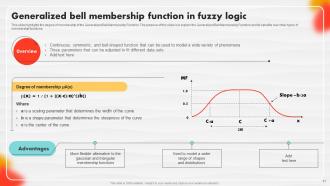
Slide 21: This slide illustrates the degree of membership of the Generalized Bell Membership Function.
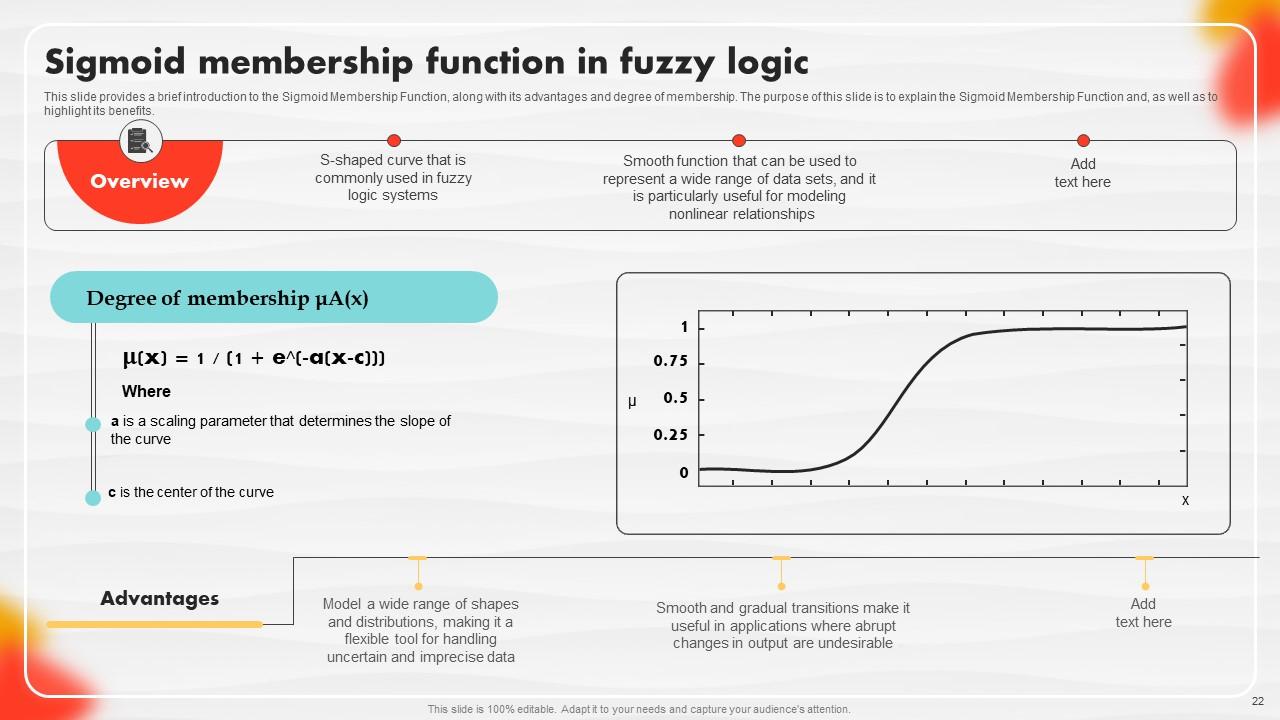
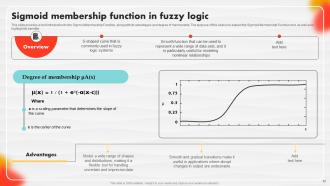
Slide 22: This slide provides a brief introduction to the Sigmoid Membership Function, along with its advantages and degree of
Slide 23: This slide introduces Components of soft computing out of the table of contents and is in continuation.
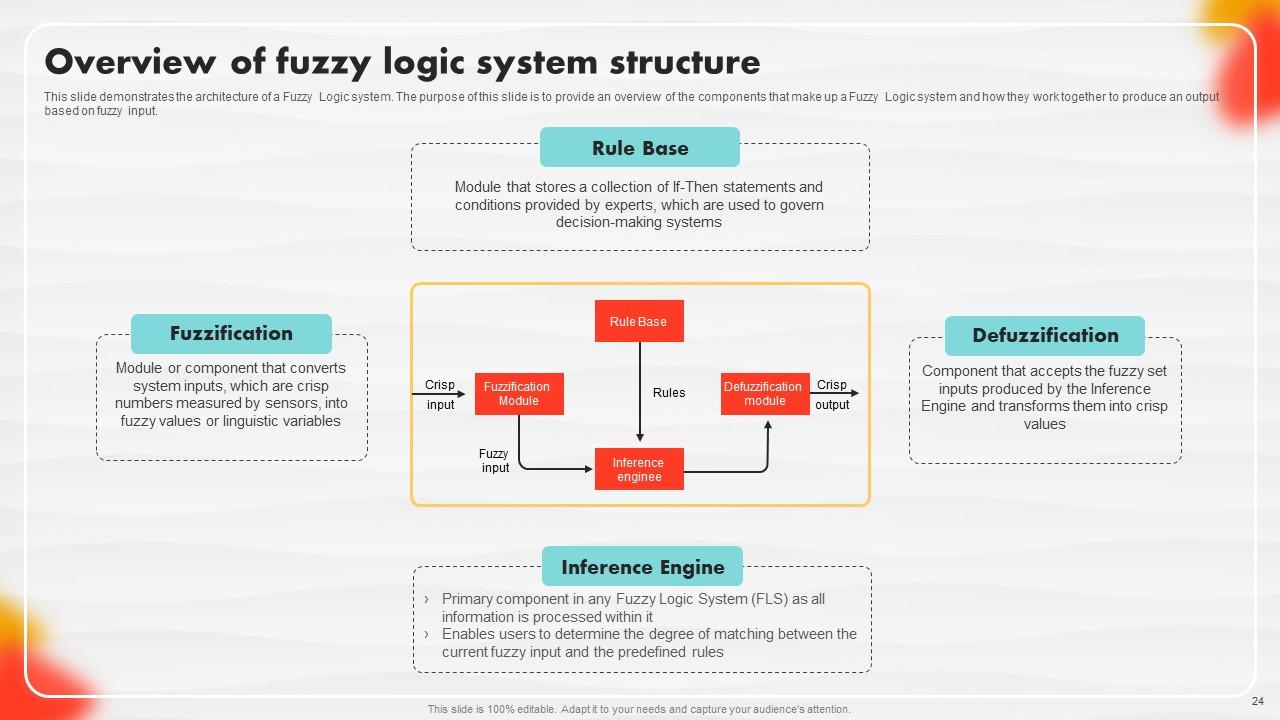
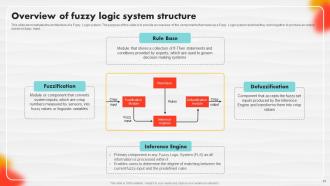
Slide 24: This slide demonstrates the architecture of a Fuzzy Logic system.
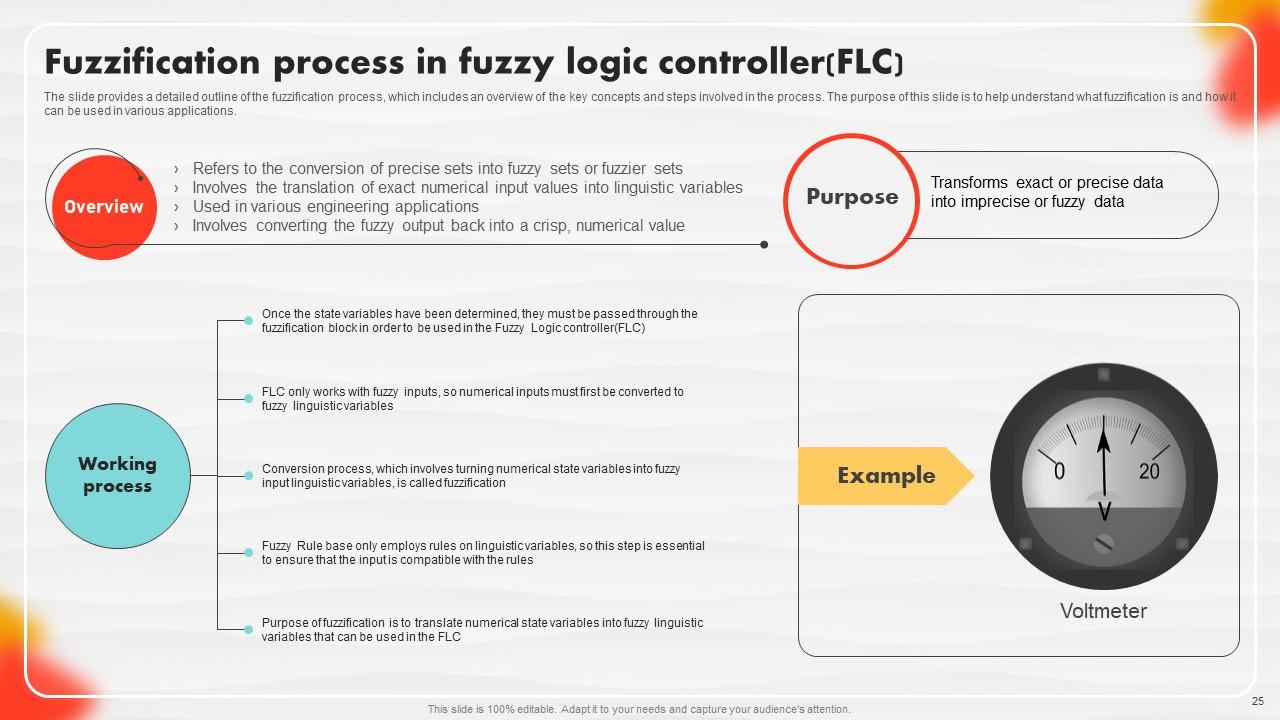
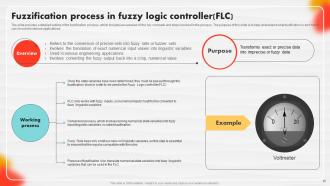
Slide 25: This slide details an outline of the fuzzification process.
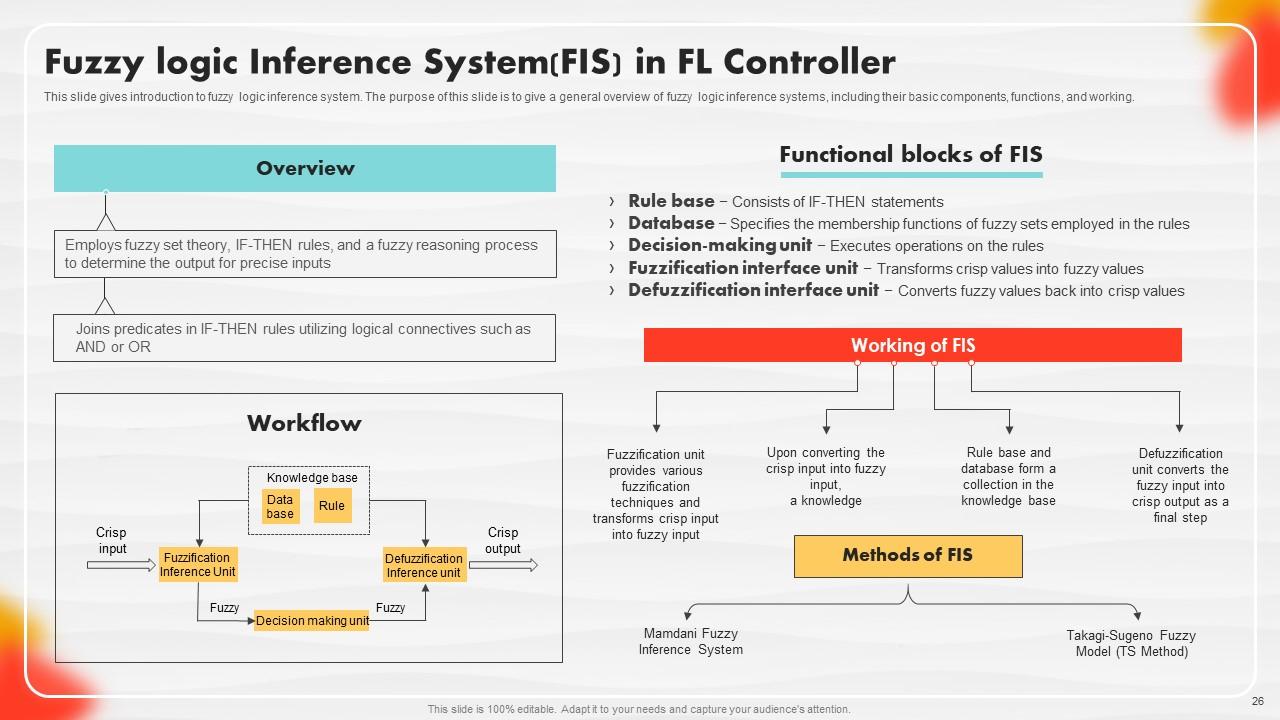
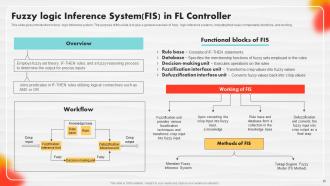
Slide 26: This slide portrays an introduction to a fuzzy logic inference system.
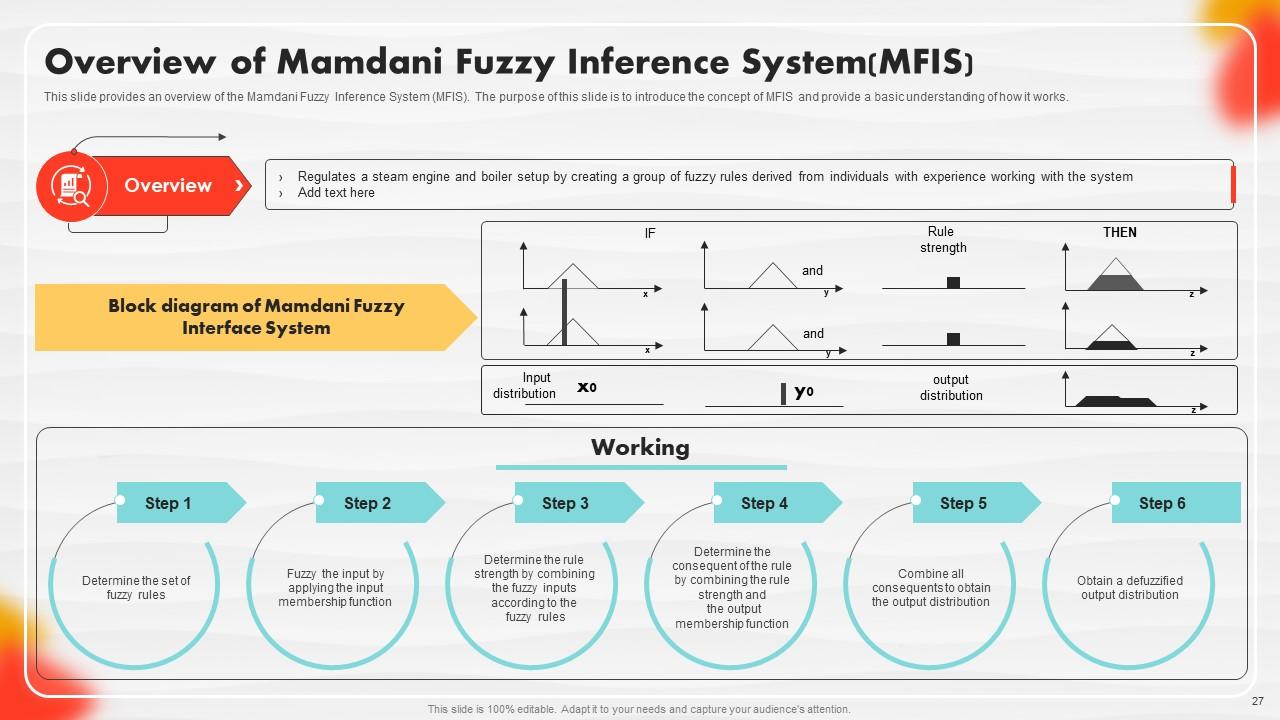
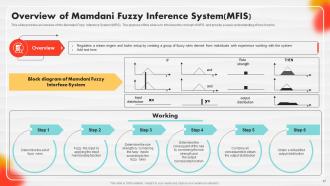
Slide 27: This slide presents an overview of the Mamdani Fuzzy Inference System (MFIS).
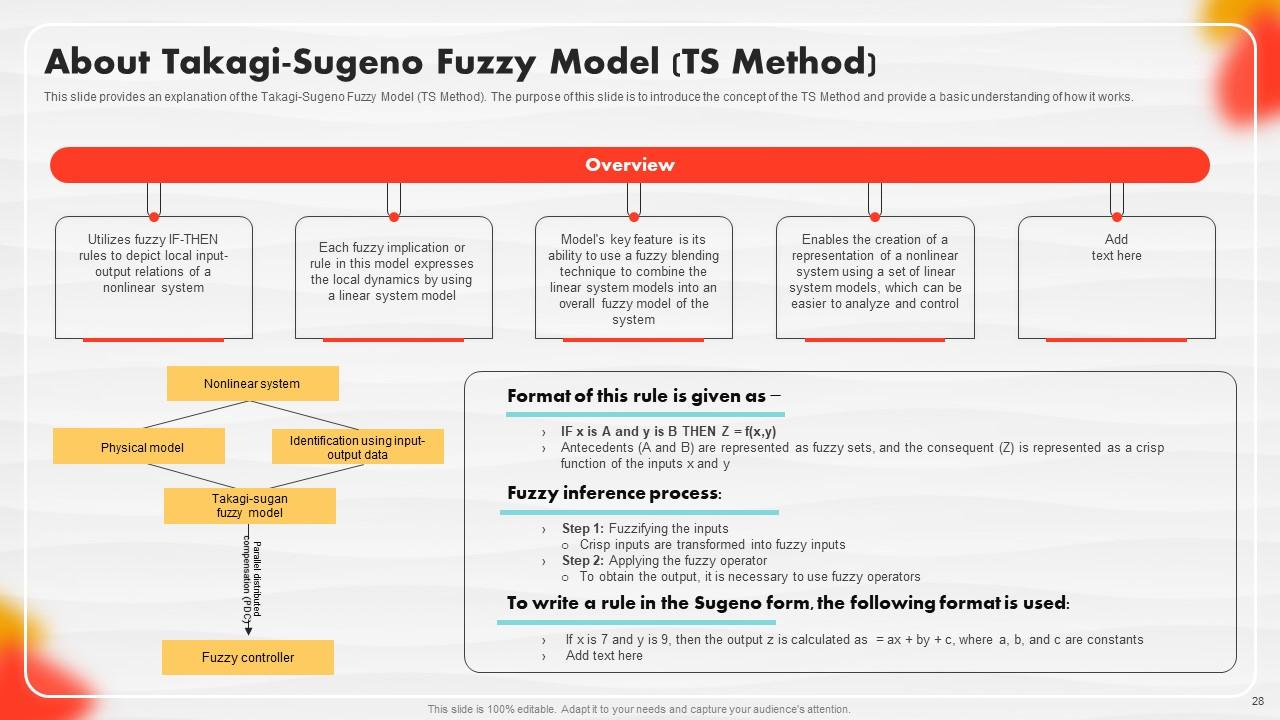
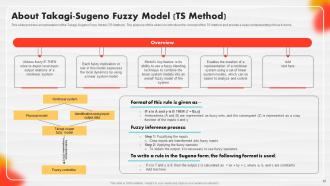
Slide 28: This slide shows an explanation of the Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Model (TS Method).
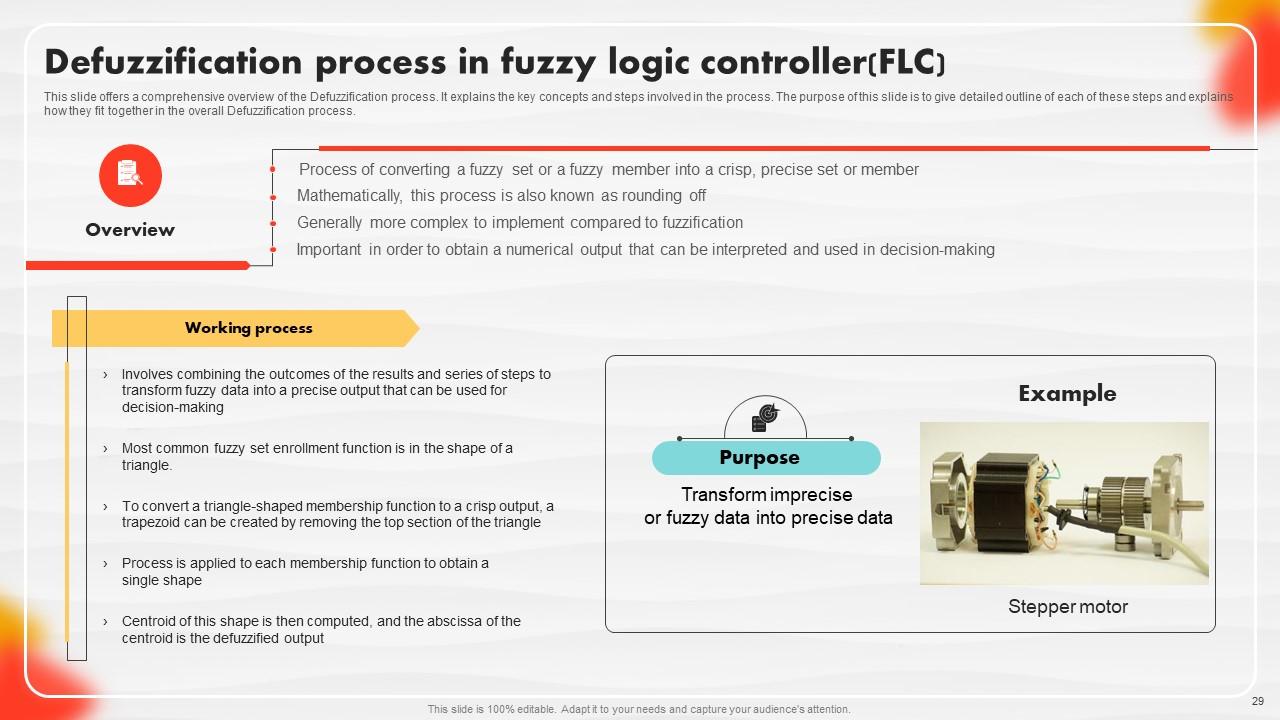
Slide 29: This slide offers a comprehensive overview of the Defuzzification process.
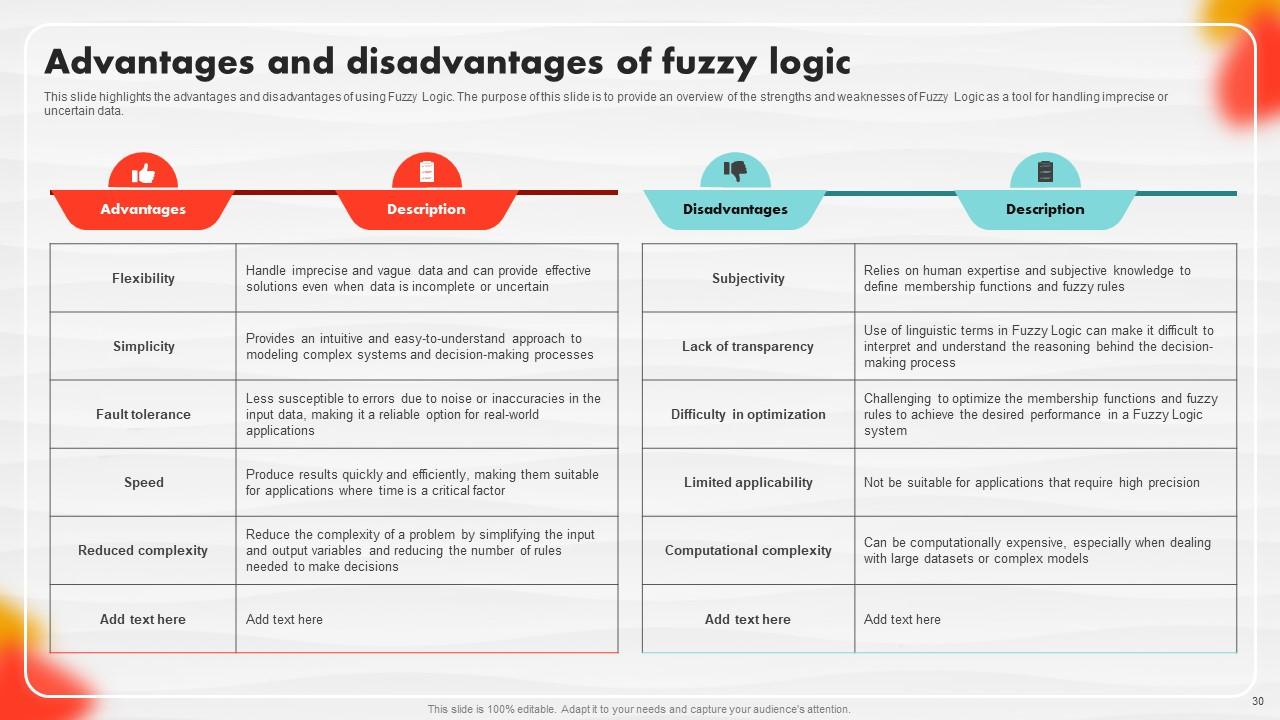
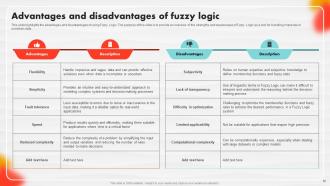
Slide 30: This slide highlights the advantages and disadvantages of using Fuzzy Logic.
Slide 31: This slide introduces Components of soft computing out of the table of contents and is in continuation.
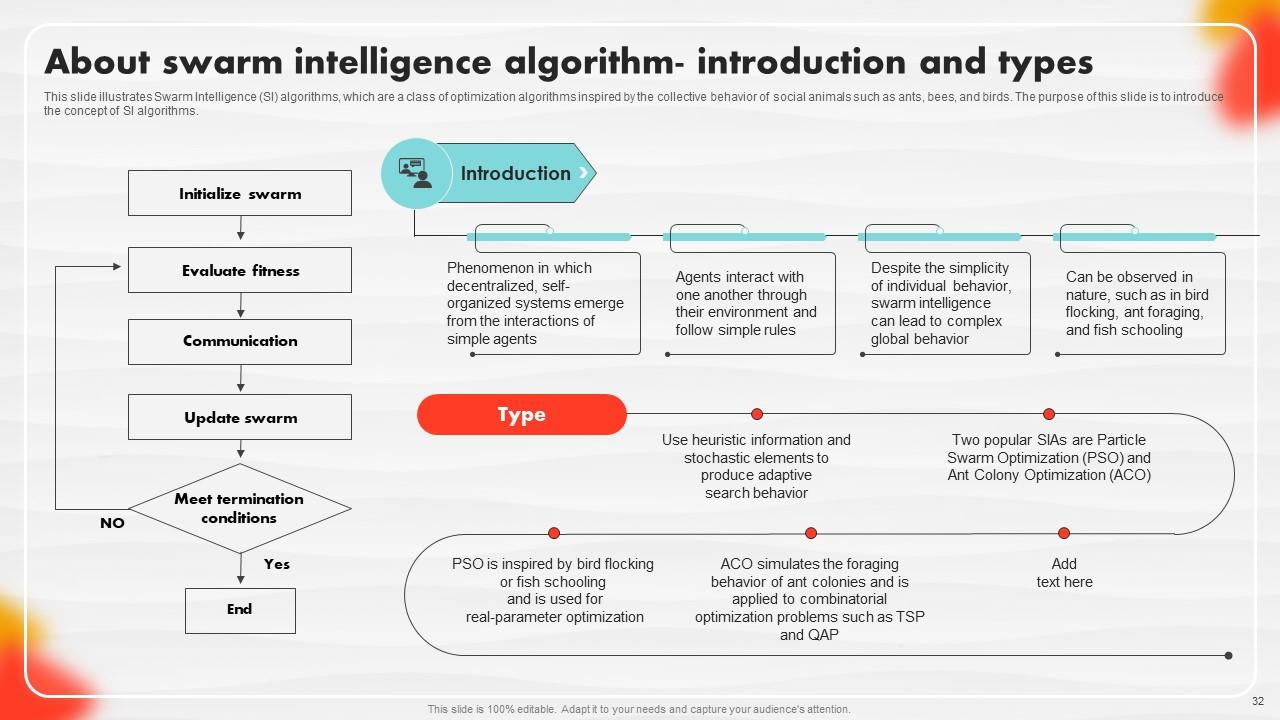
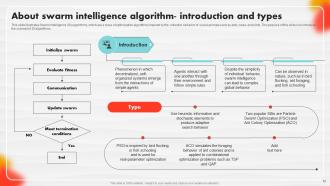
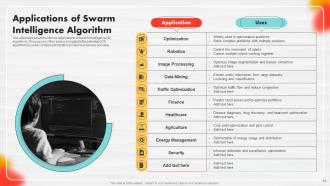
Slide 32: This slide illustrates Swarm Intelligence (SI) algorithms.
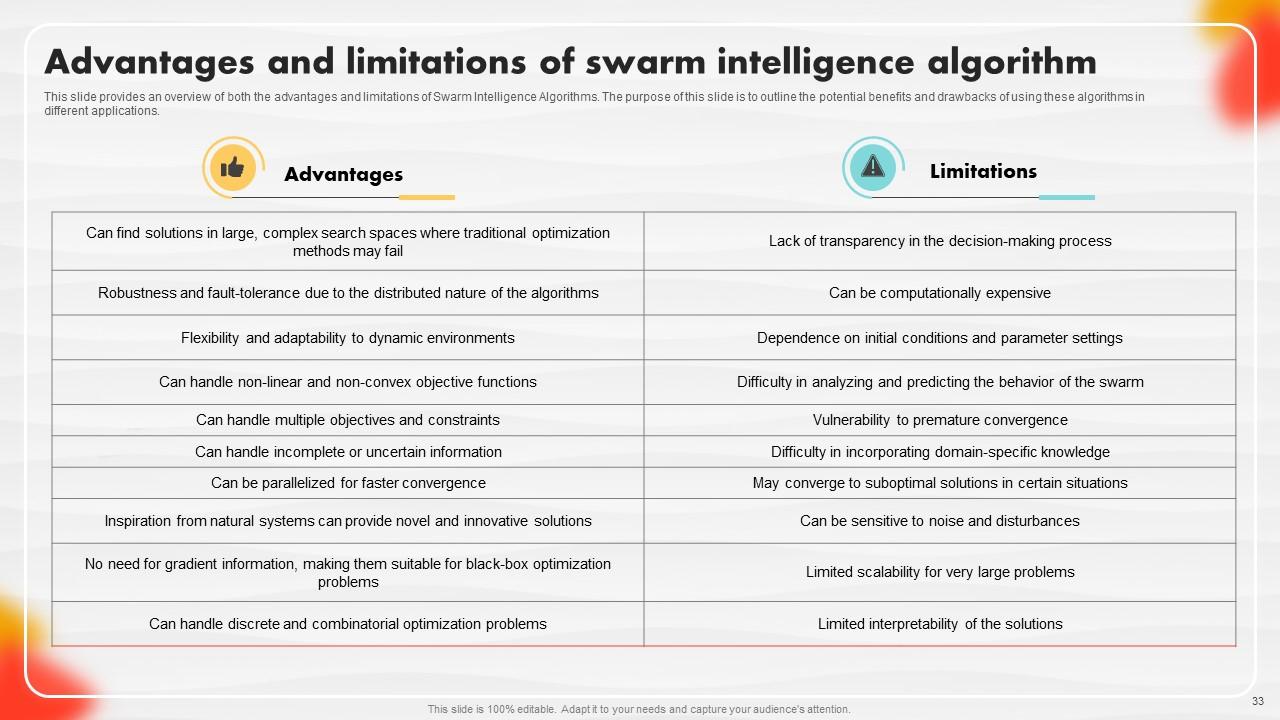
Slide 33: This slide details the benefits of Swarm Intelligence (SI) algorithms.
Slide 34: This slide introduces Components of soft computing out of the table of contents and is in continuation.
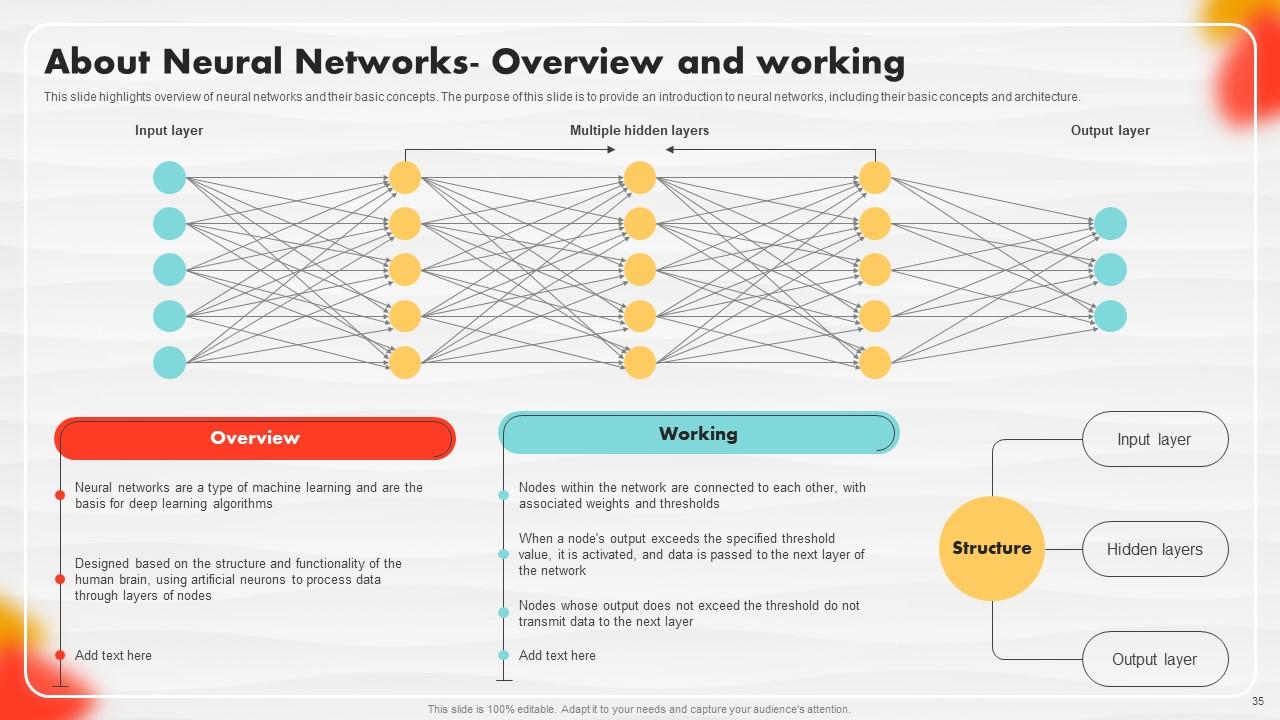
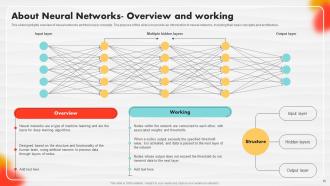
Slide 35: This slide highlights an overview of neural networks and their basic concepts.
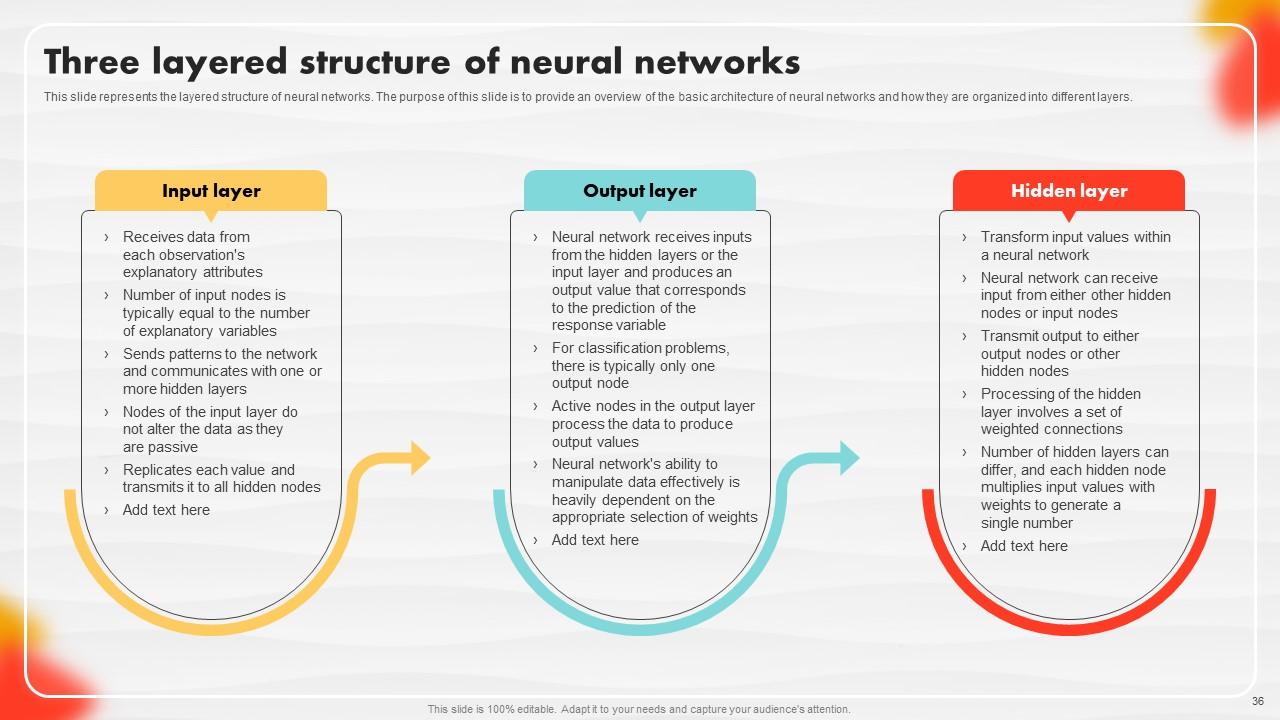
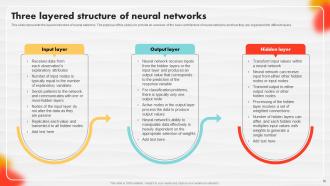
Slide 36: This slide represents the layered structure of neural networks.
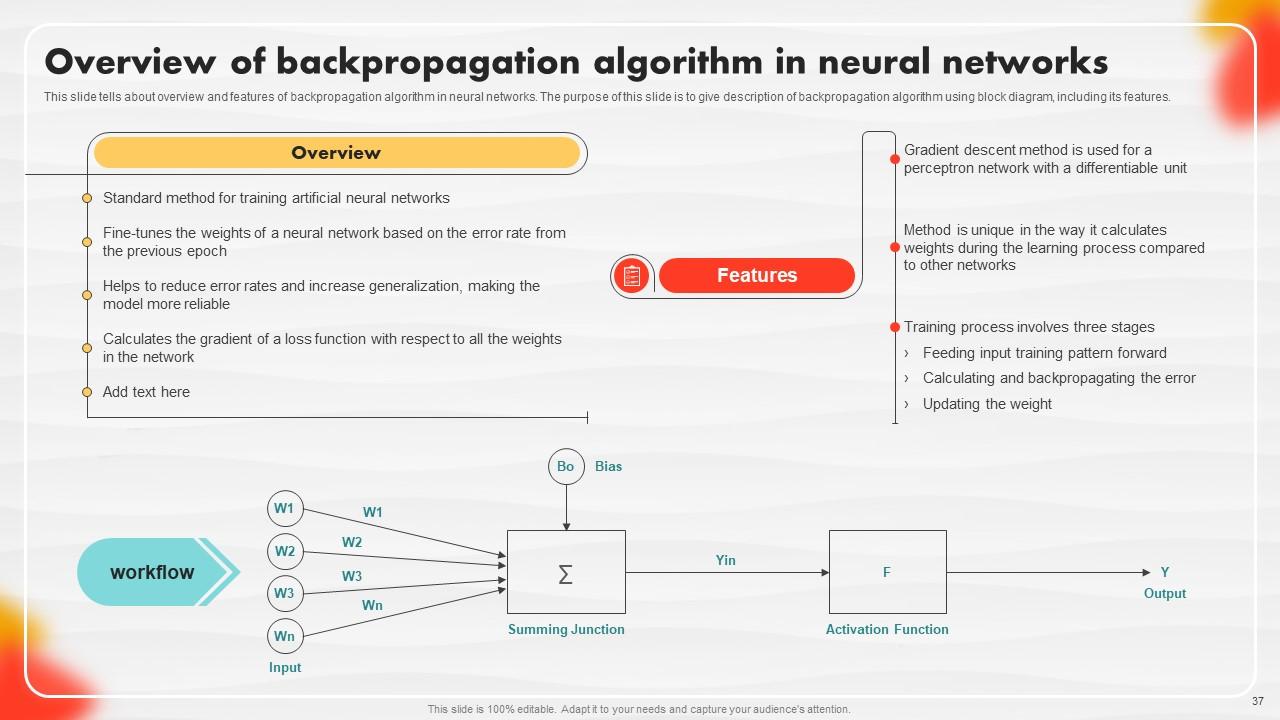
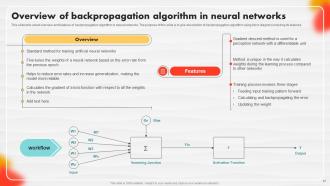
Slide 37: This slide tells about the overview and features of the backpropagation algorithm in neural networks.
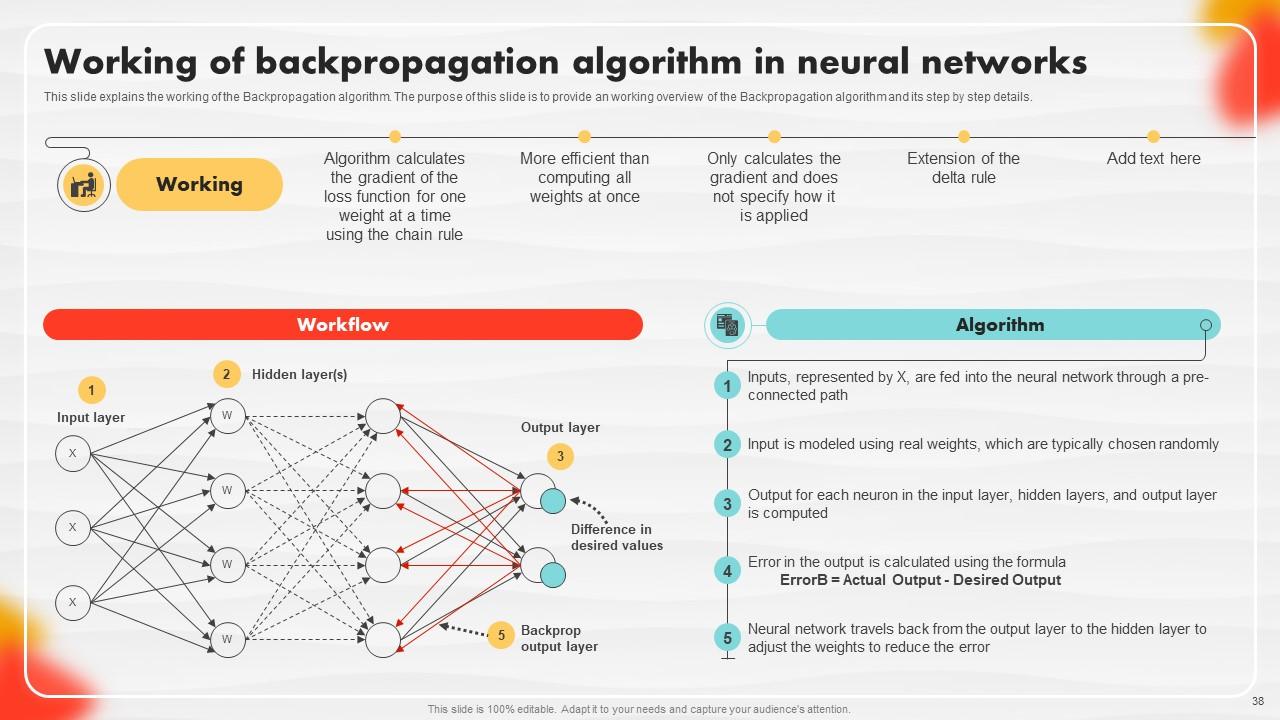
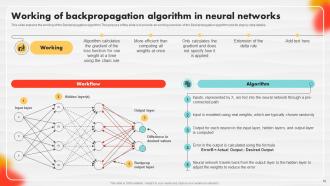
Slide 38: This slide explains the working of the Backpropagation algorithm.
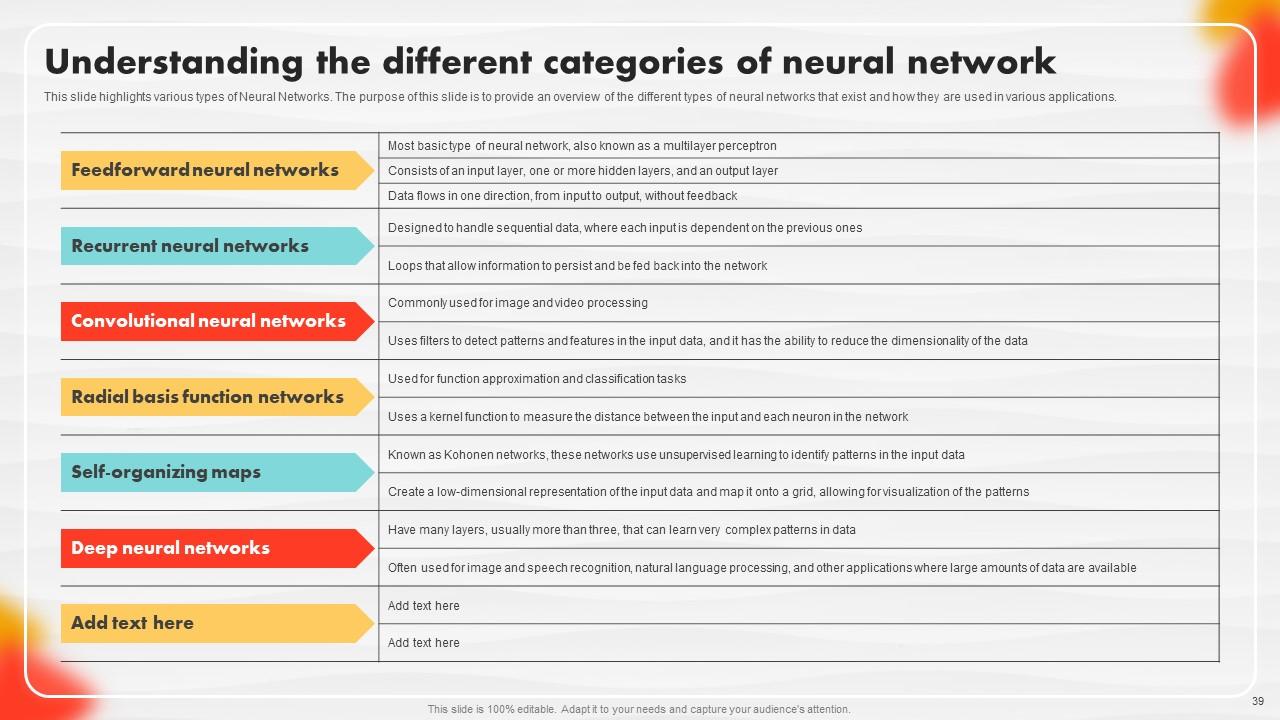
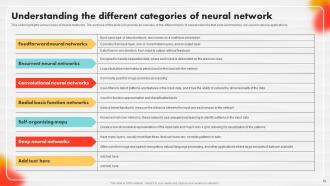
Slide 39: This slide showcases various types of Neural Networks.
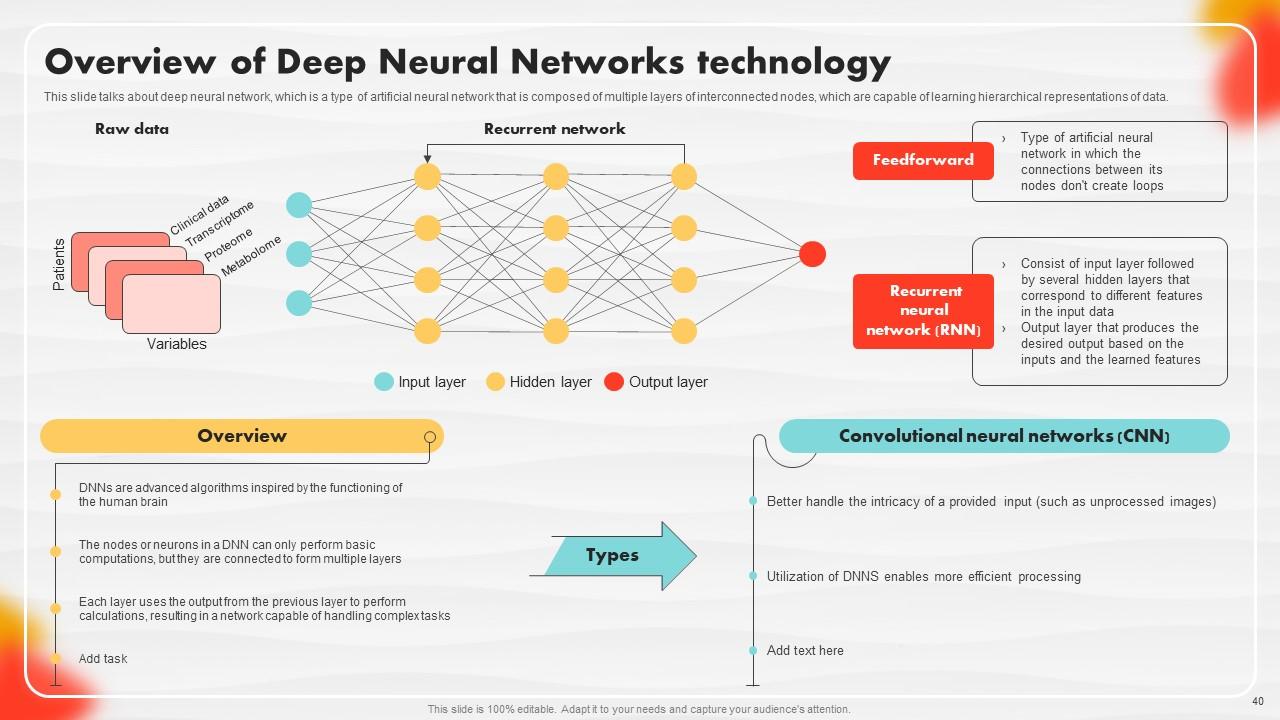
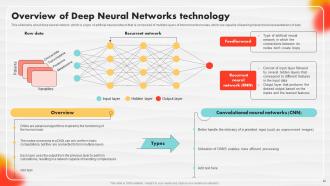
Slide 40: This slide entails about deep neural network.
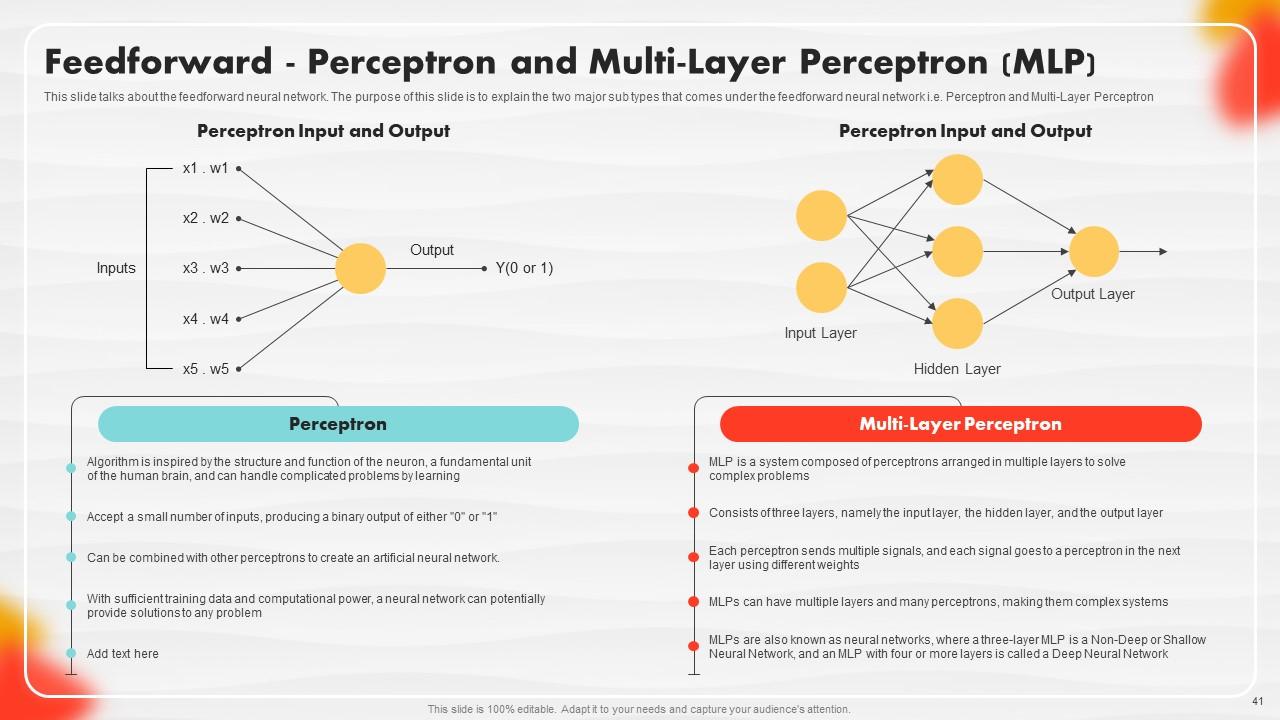
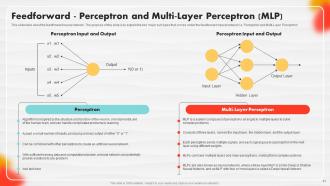
Slide 41: This slide illustrates the feedforward neural network.
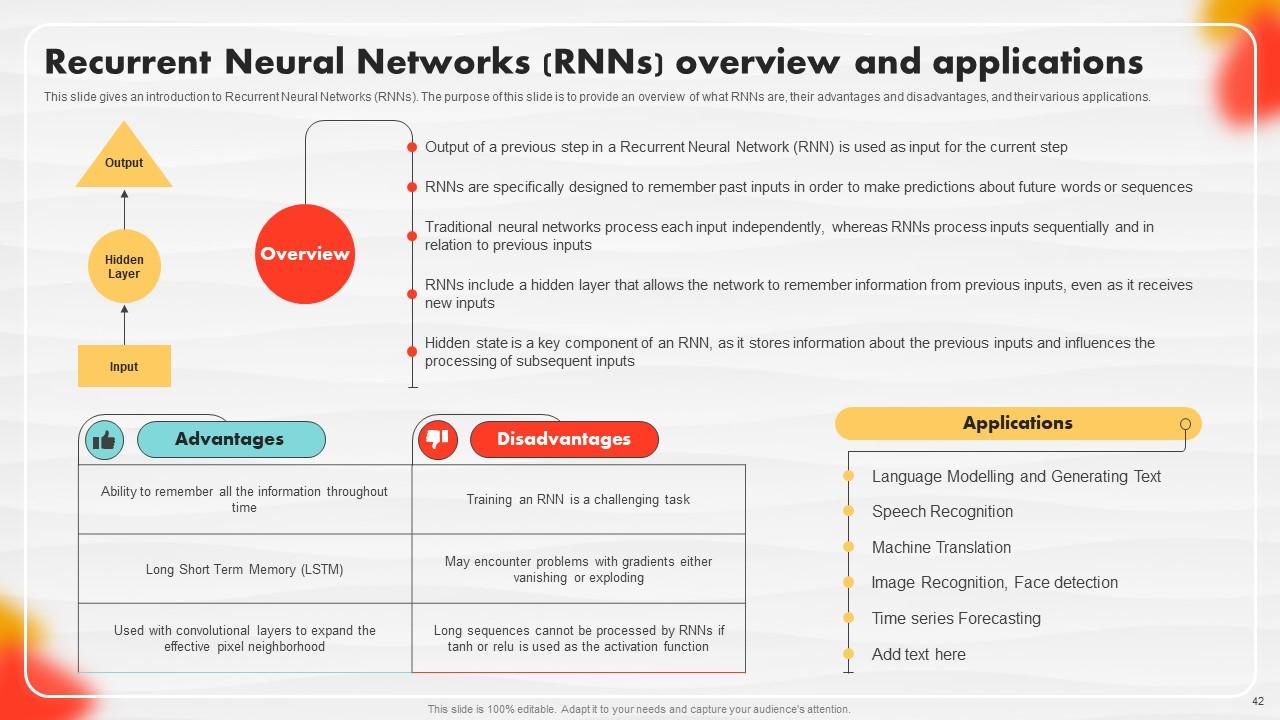
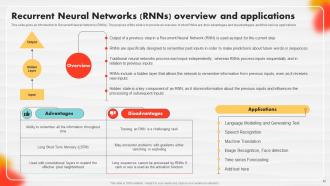
Slide 42: This slide showcases an introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs).
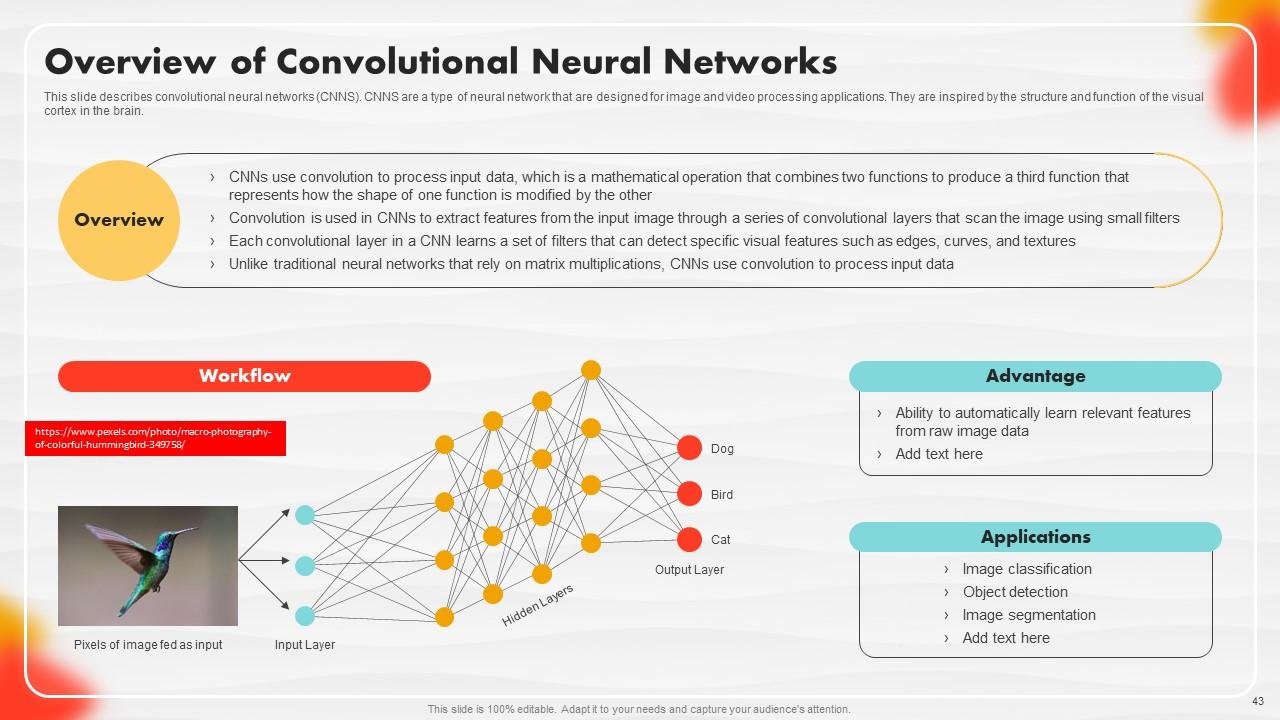
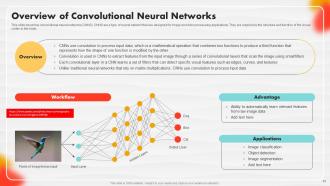
Slide 43: This slide describes convolutional neural networks (CNNS).
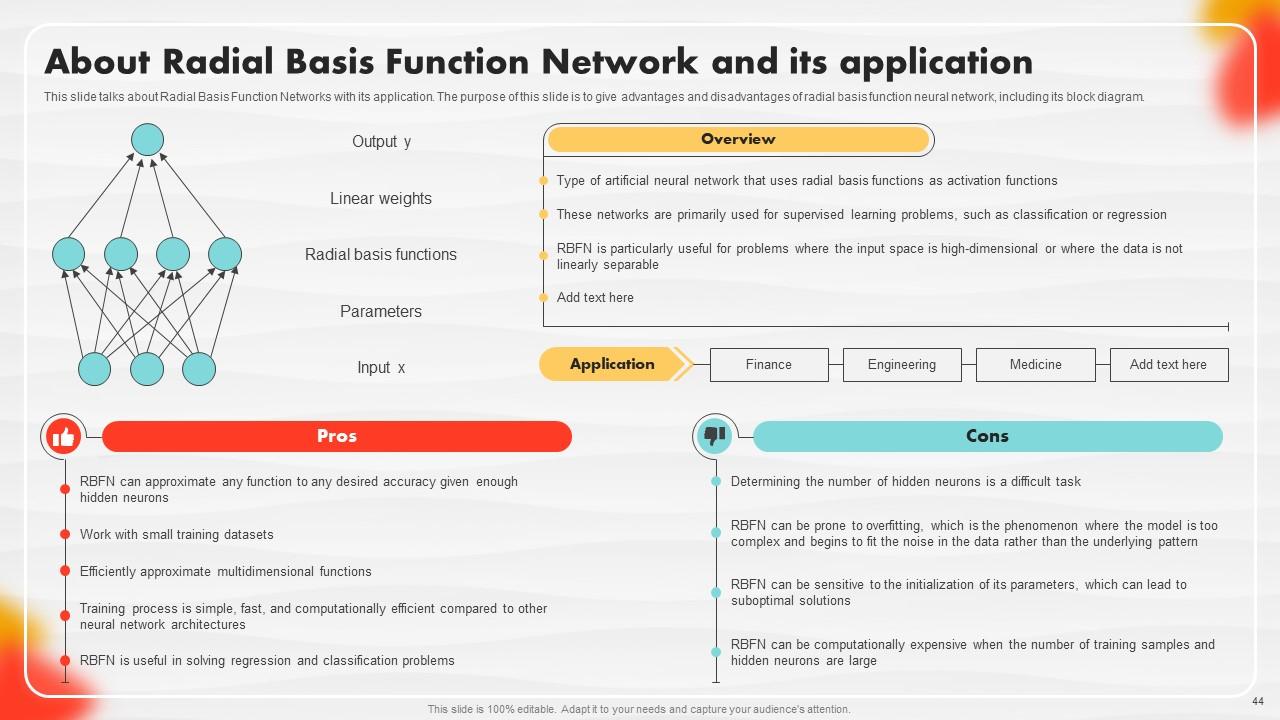
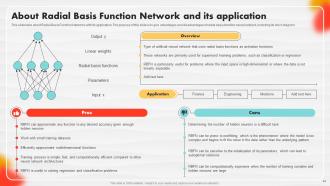
Slide 44: This slide portrays Radial Basis Function Networks with their application.
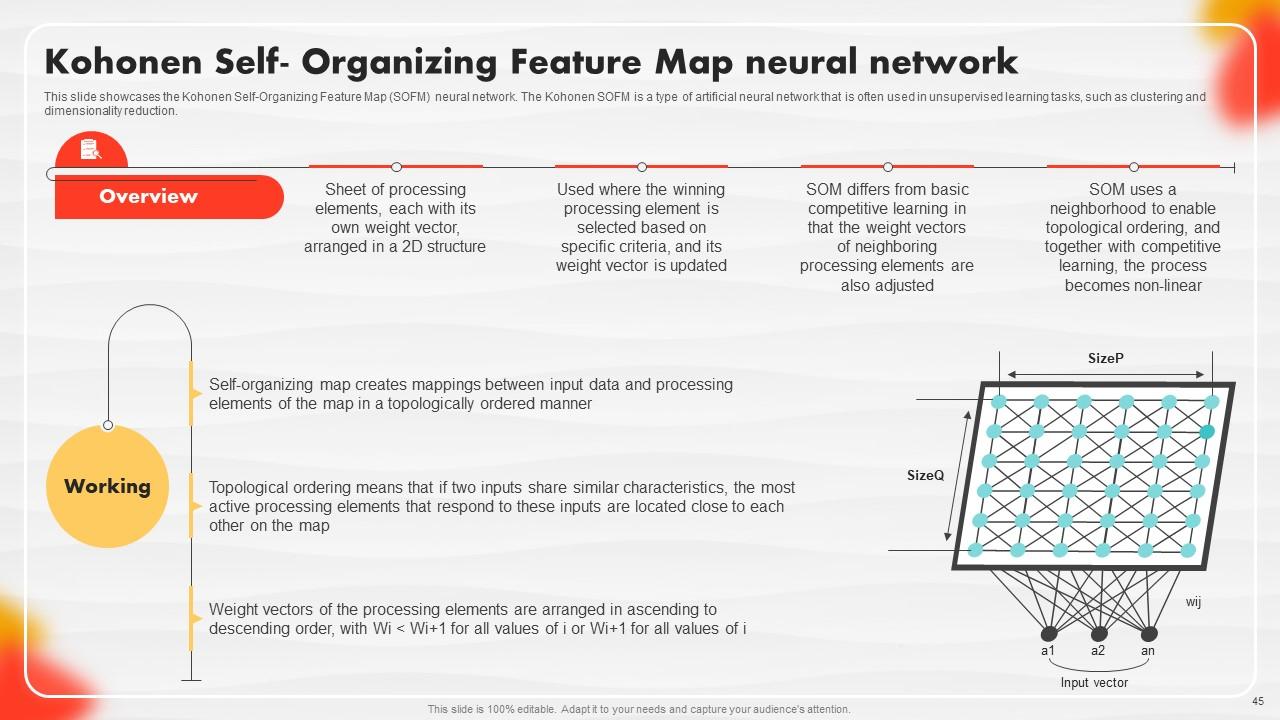
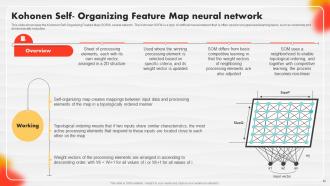
Slide 45: This slide showcases the Kohonen Self-Organizing Feature Map (SOFM) neural network.
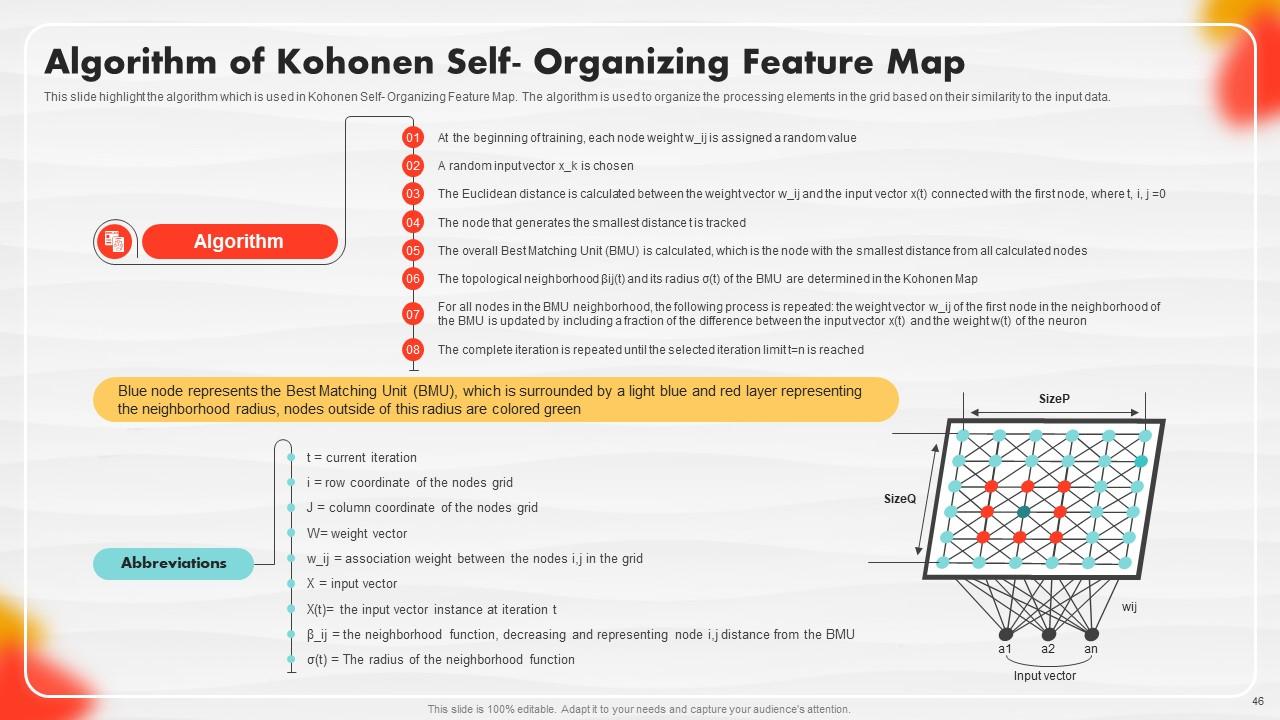
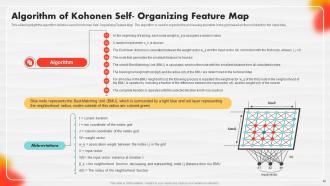
Slide 46: This slide outlines the algorithm that is used in Kohonen Self- Organizing Feature Map.
Slide 47: This slide introduces Components of soft computing out of the table of contents and is in continuation.
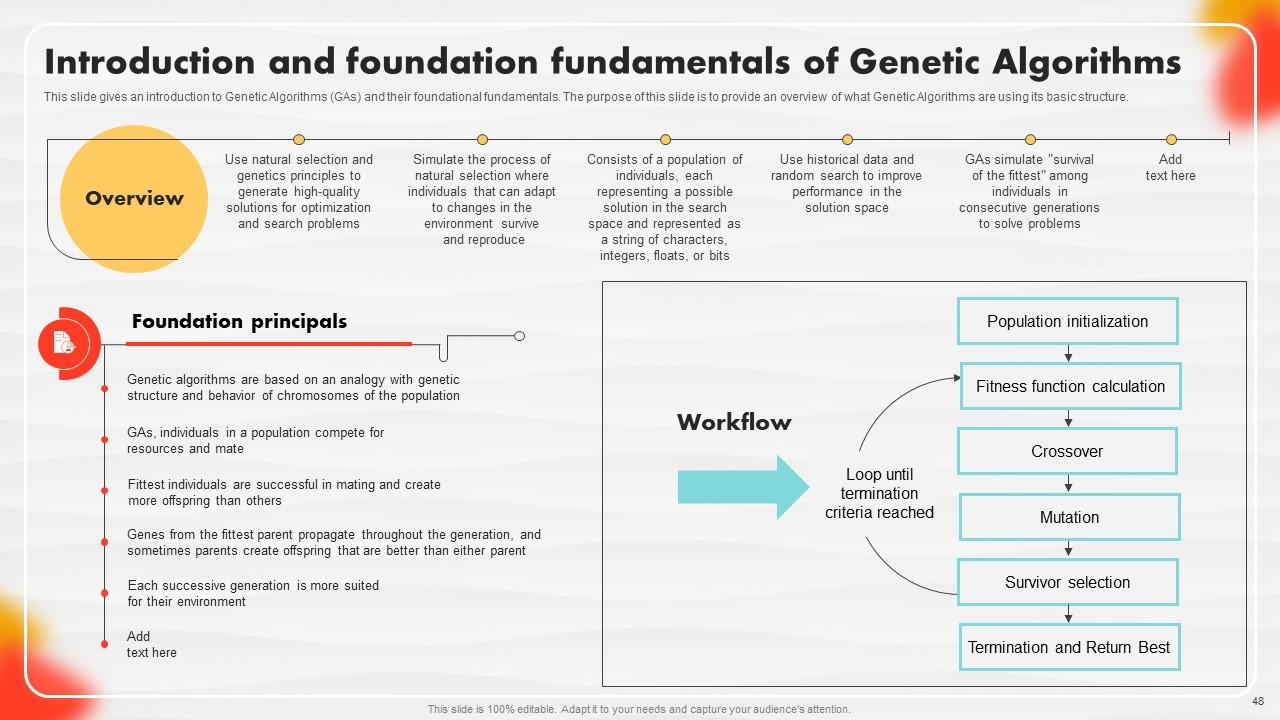
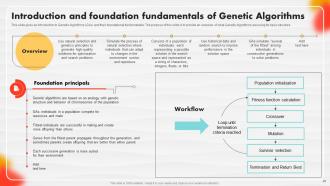
Slide 48: This slide gives an introduction to Genetic Algorithms (GAs) and their foundational fundamentals.
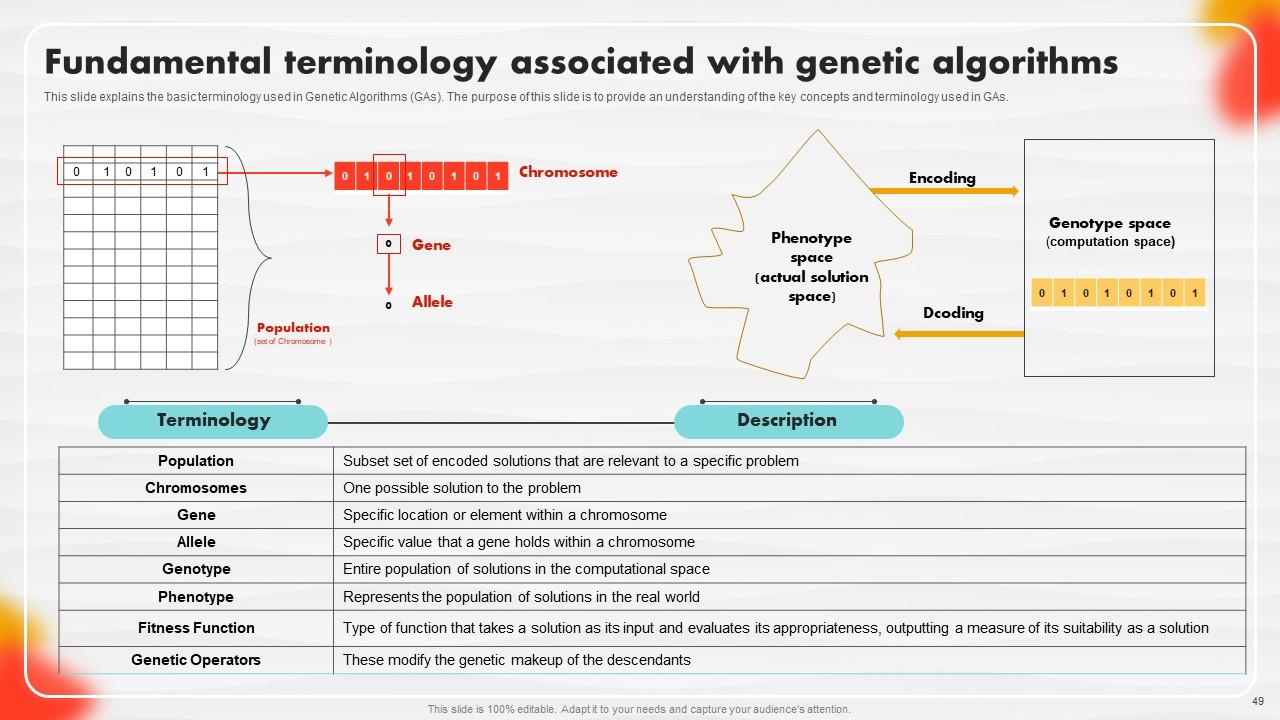
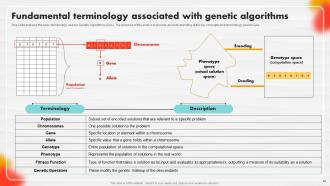
Slide 49: This slide explains the basic terminology used in Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
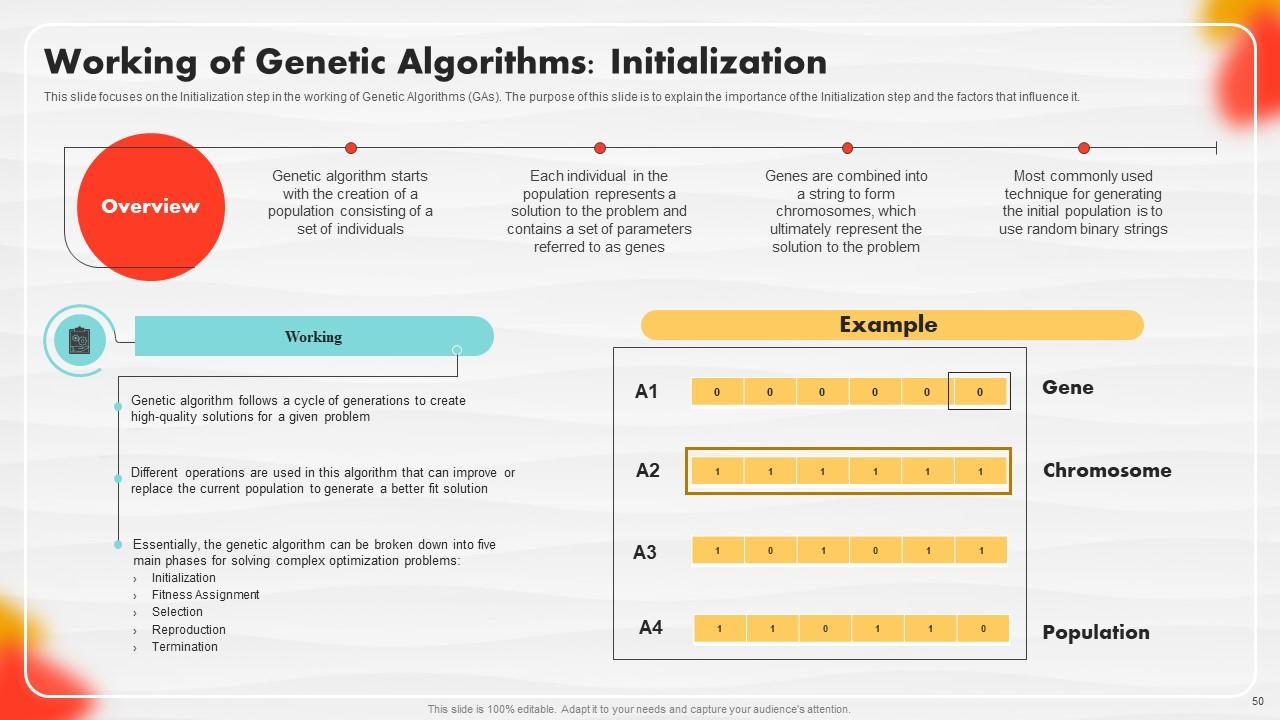
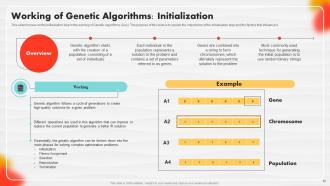
Slide 50: This slide focuses on the Initialization step in the working of Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
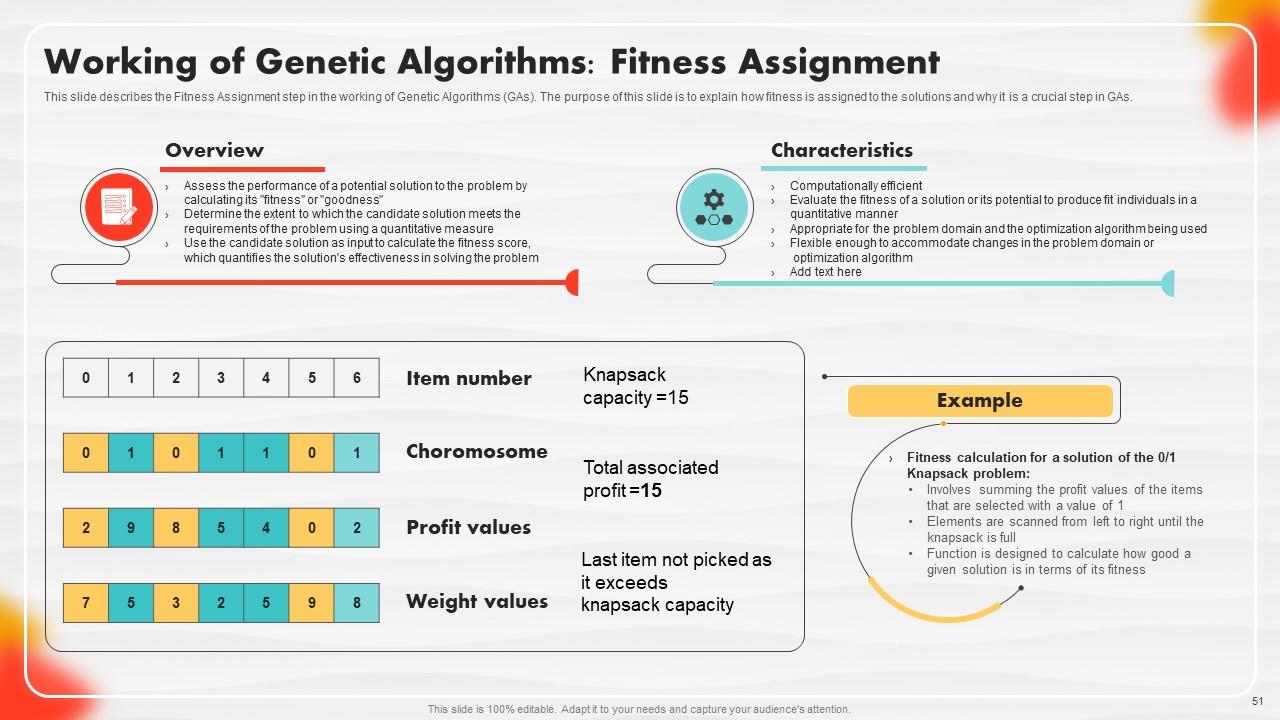
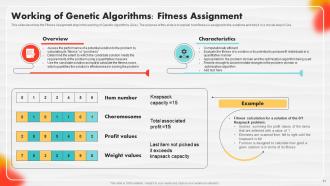
Slide 51: This slide describes the Fitness Assignment step in the working of Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
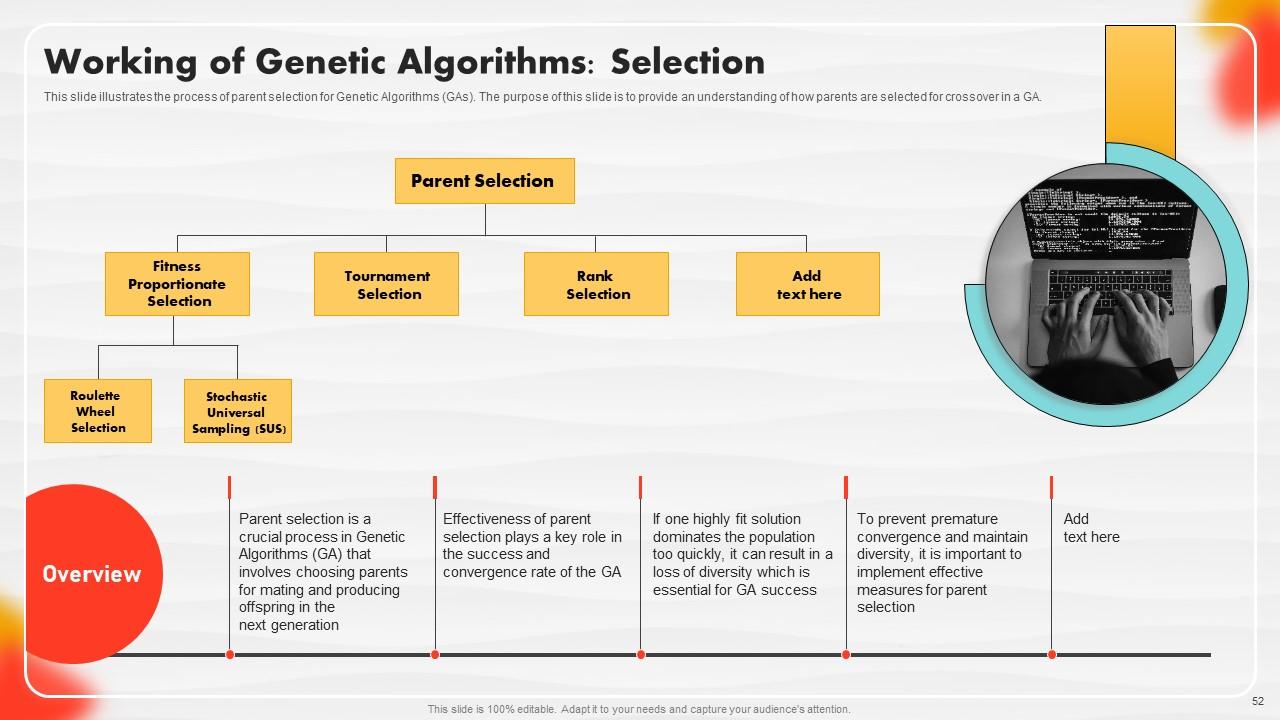
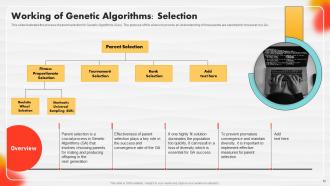
Slide 52: This slide illustrates the process of parent selection for Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
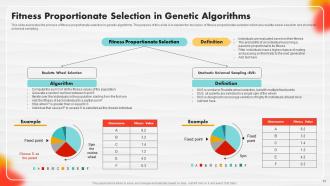
Slide 53: This slide elaborates on the process of fitness proportionate selection in genetic algorithms.
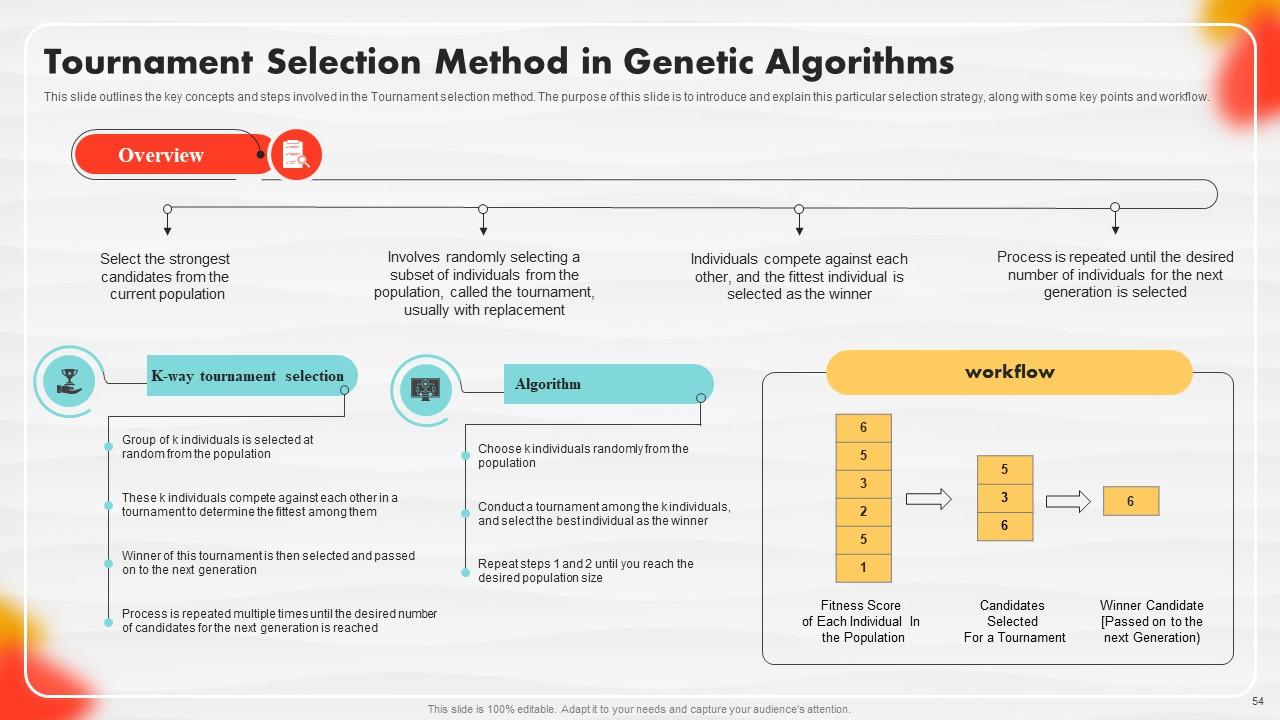
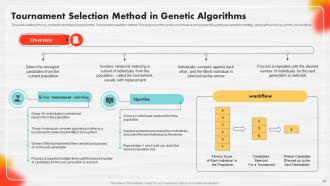
Slide 54: This slide outlines the key concepts and steps involved in the Tournament selection method.
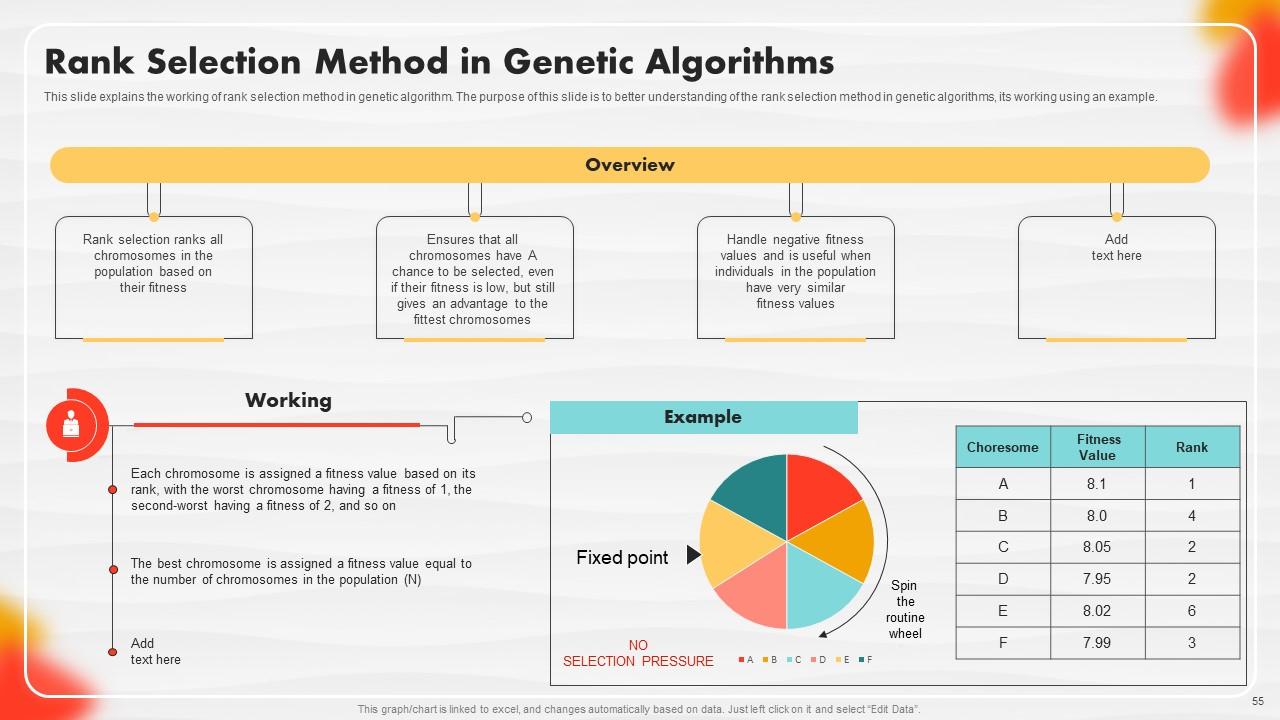
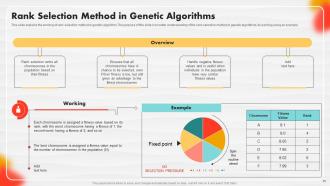
Slide 55: This slide explains the workings of the rank selection method in genetic algorithms. left click on it and select “Edit Data”.
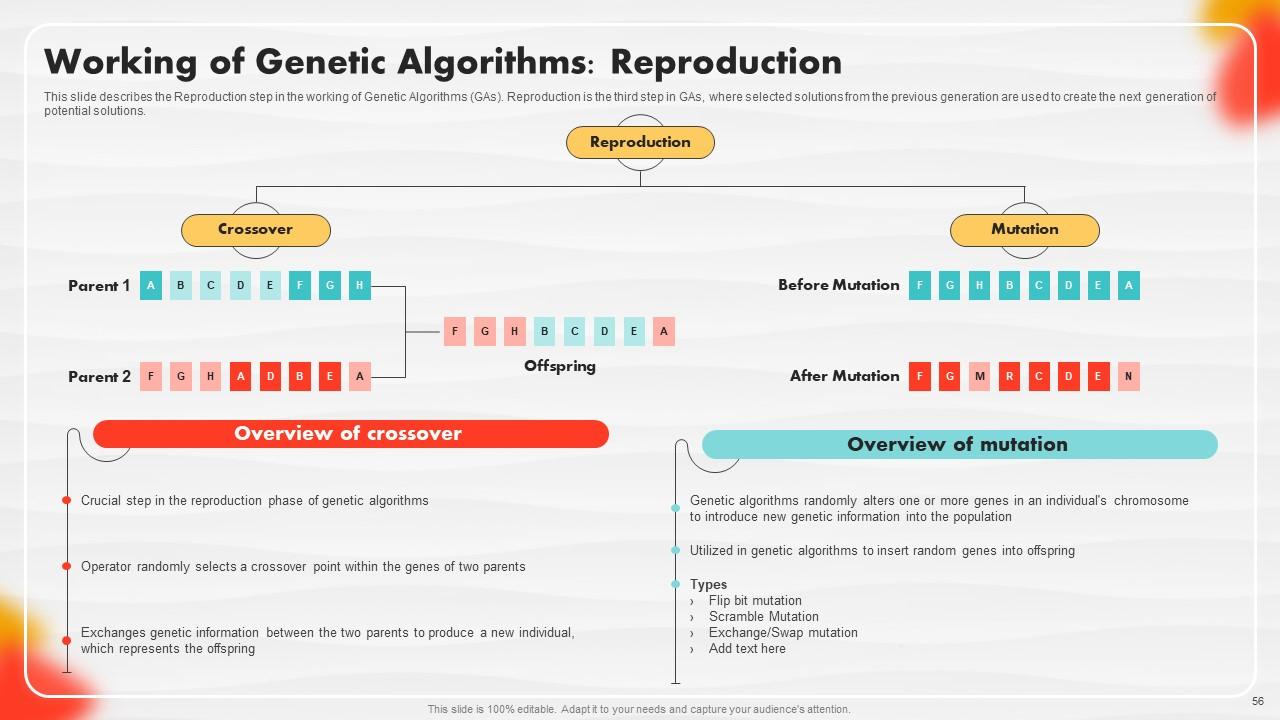
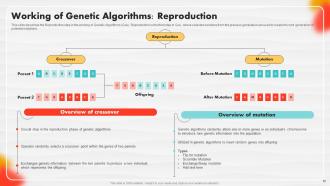
Slide 56: This slide displays the Reproduction step in the working of Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
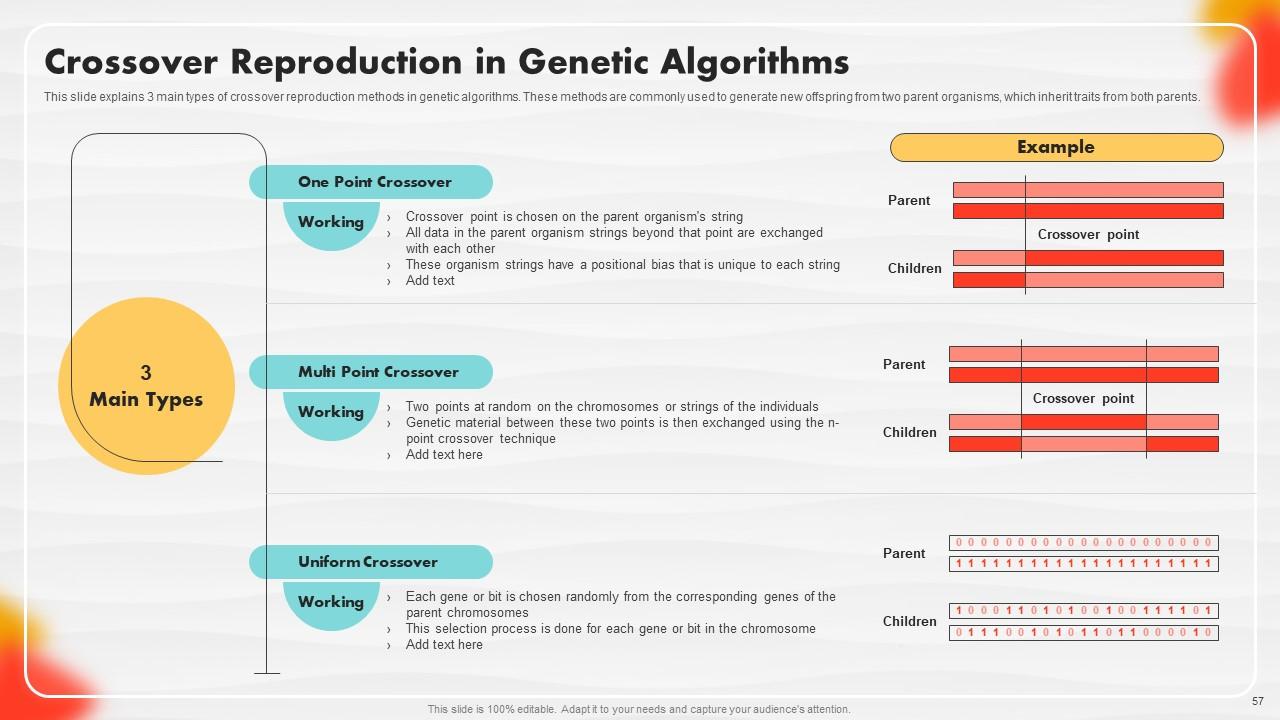
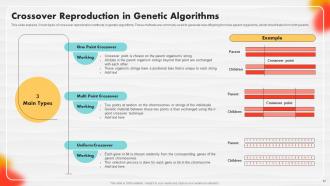
Slide 57: This slide explains 3 main types of crossover reproduction methods in genetic algorithms.
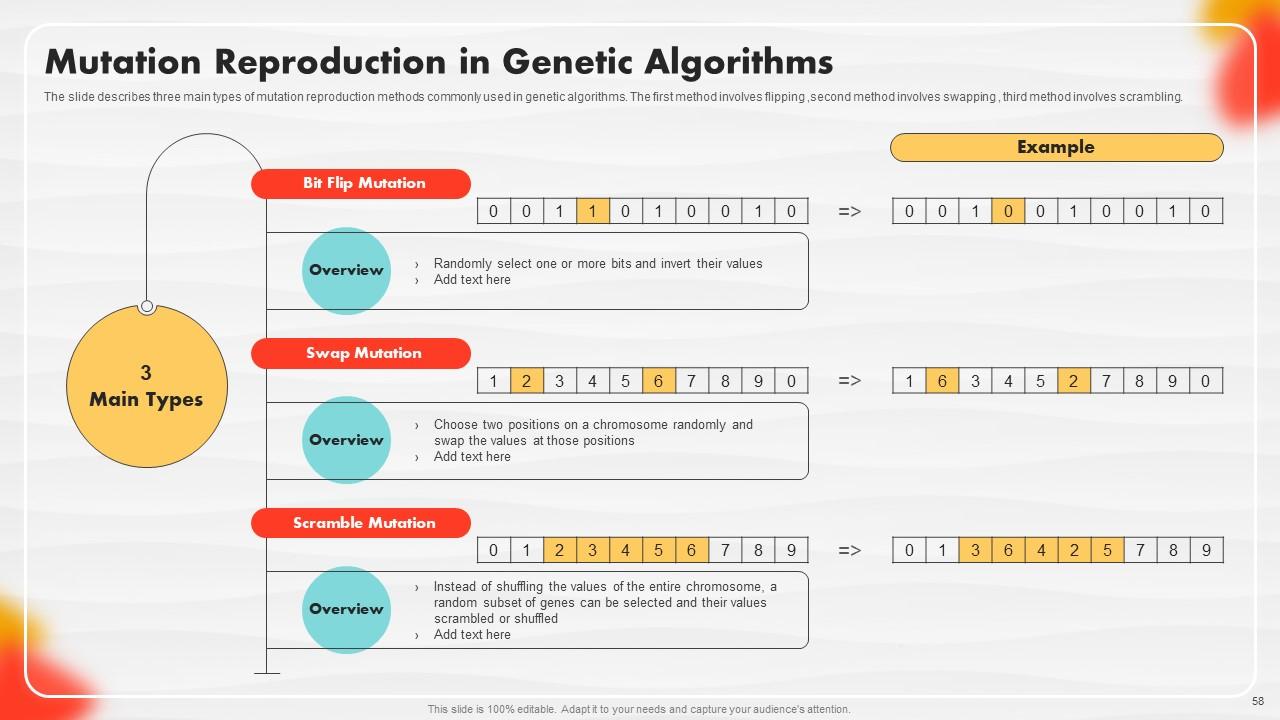
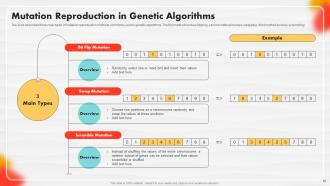
Slide 58: The slide describes three main types of mutation reproduction methods commonly used in genetic algorithms.
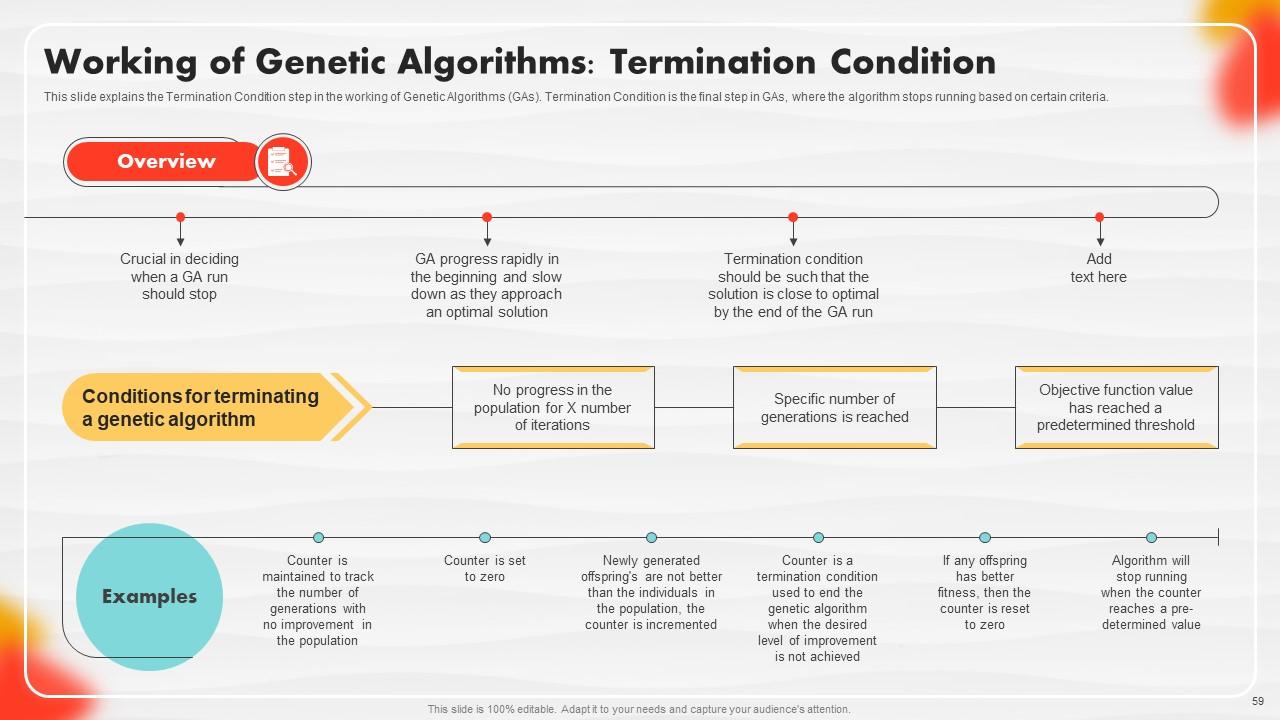
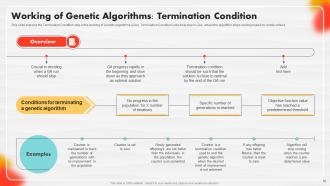
Slide 59: This slide portrays the Termination Condition step in the working of Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
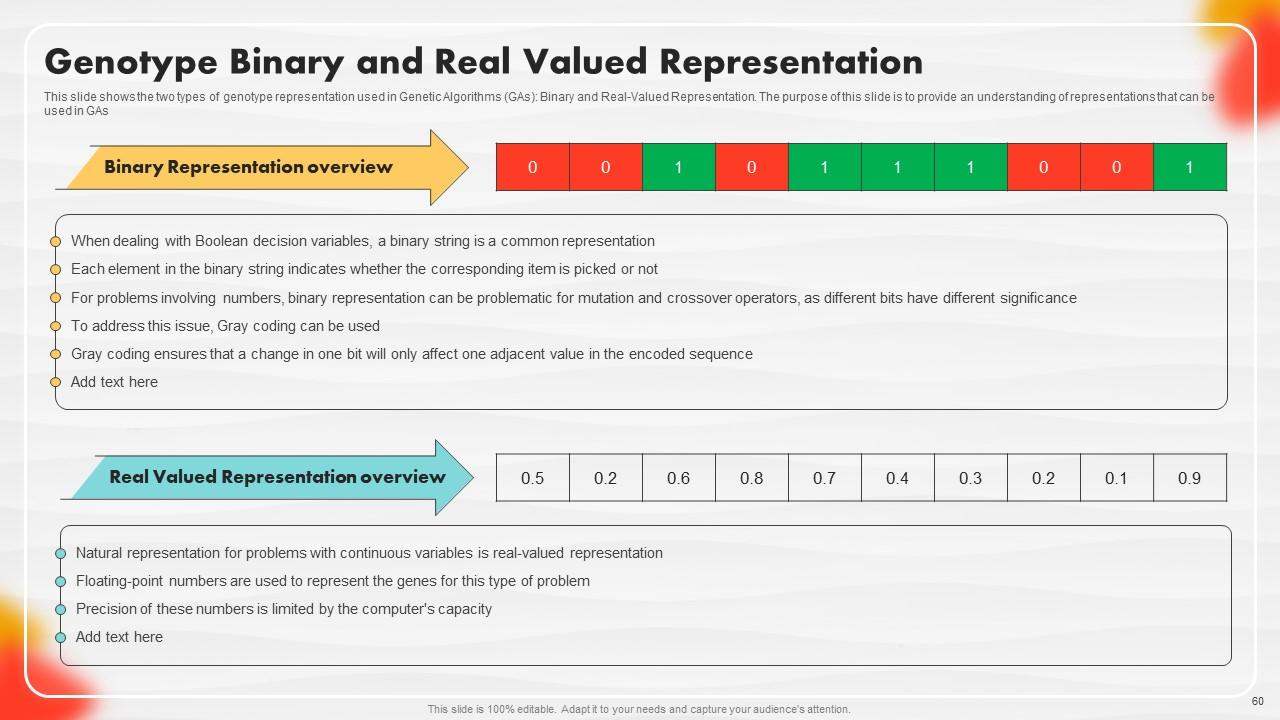
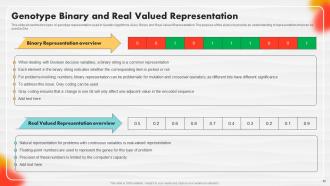
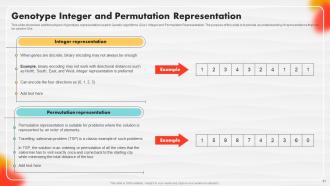
Slide 60: This slide shows the two types of genotype representation used in Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
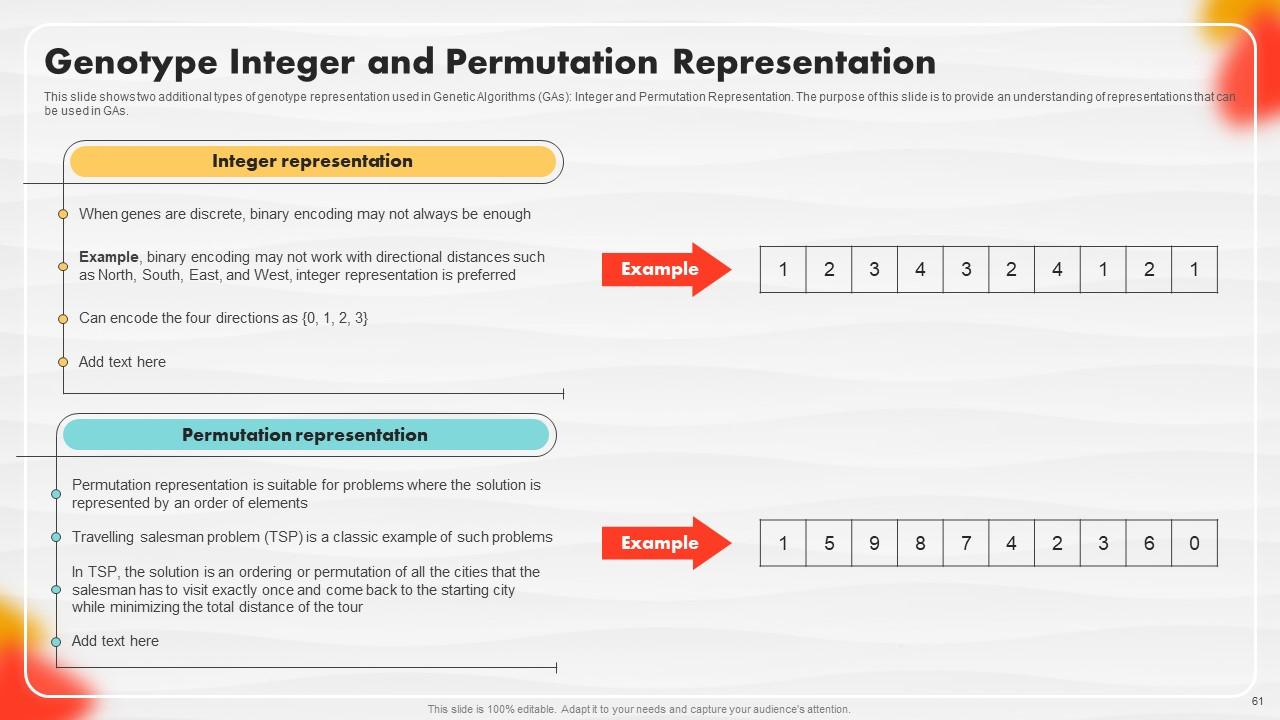
Slide 61: This slide showcases two additional types of genotype representation used in Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
Slide 62: This slide introduces Components of soft computing out of the table of contents and is in continuation.
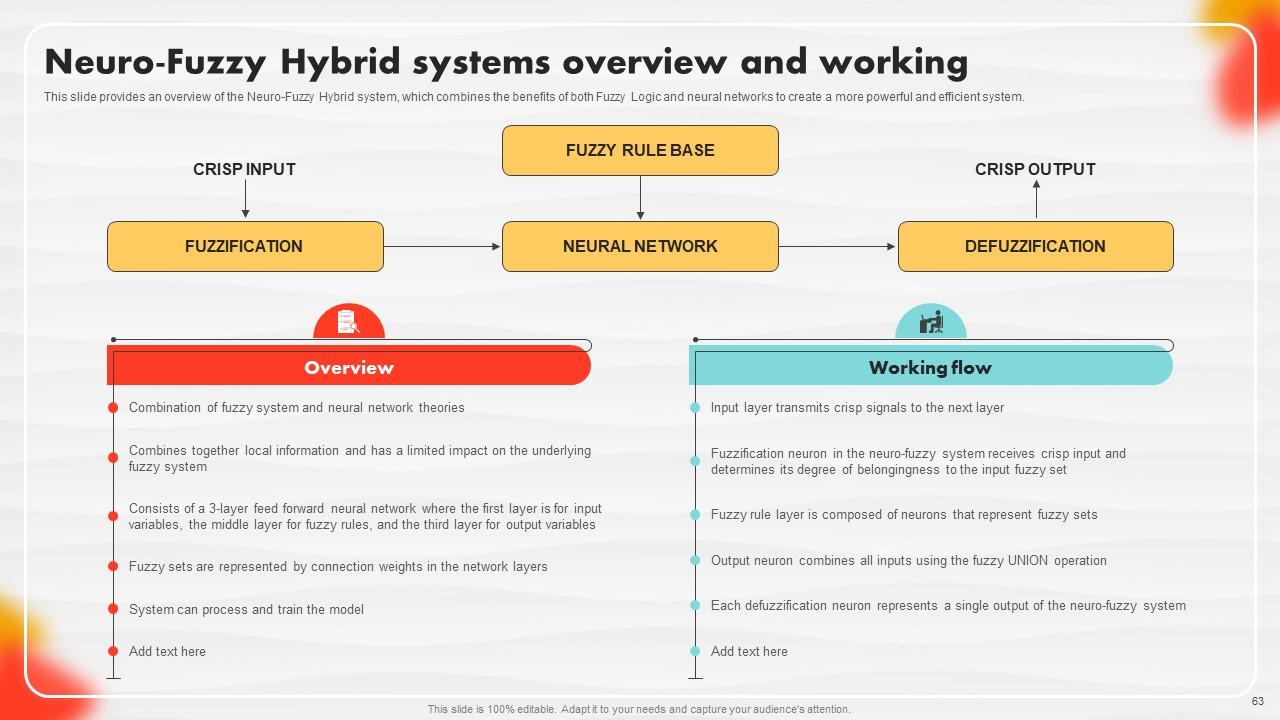
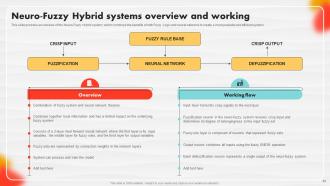
Slide 63: This slide entails a Neuro-Fuzzy Hybrid systems overview and working.
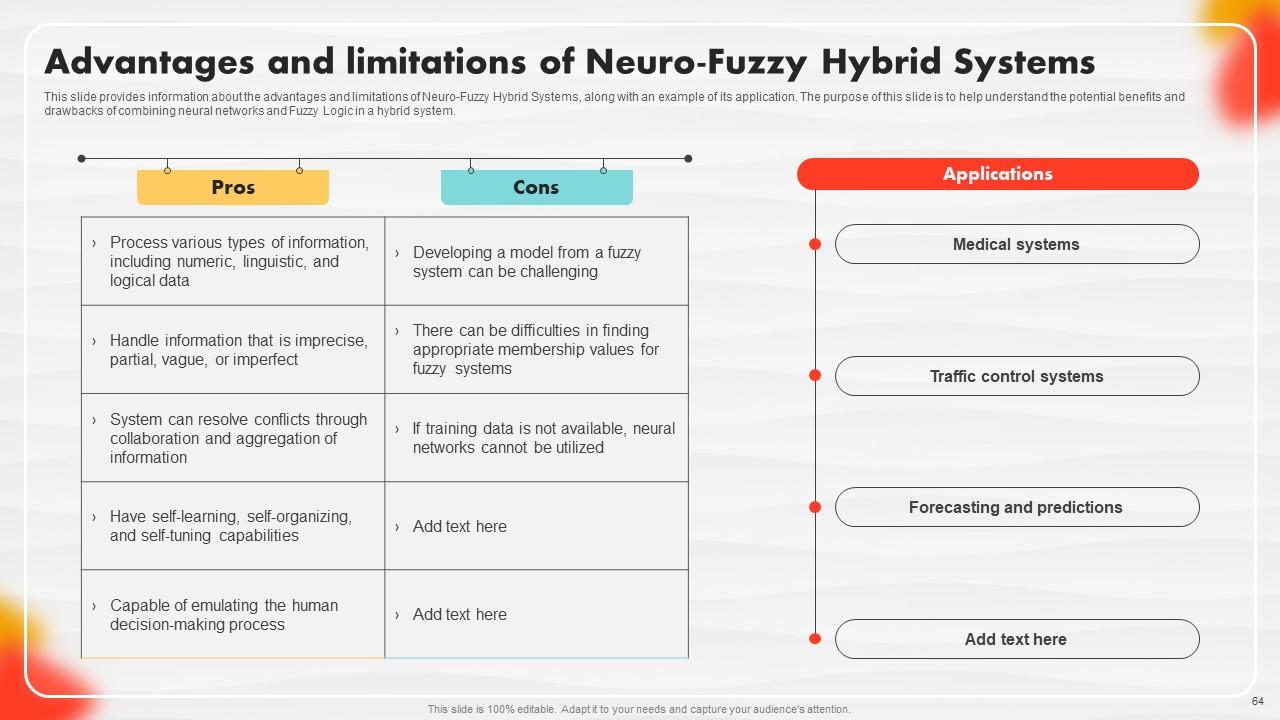
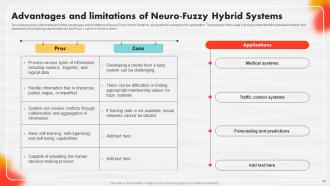
Slide 64: This slide outlines information about the advantages and limitations of Neuro-Fuzzy Hybrid Systems.
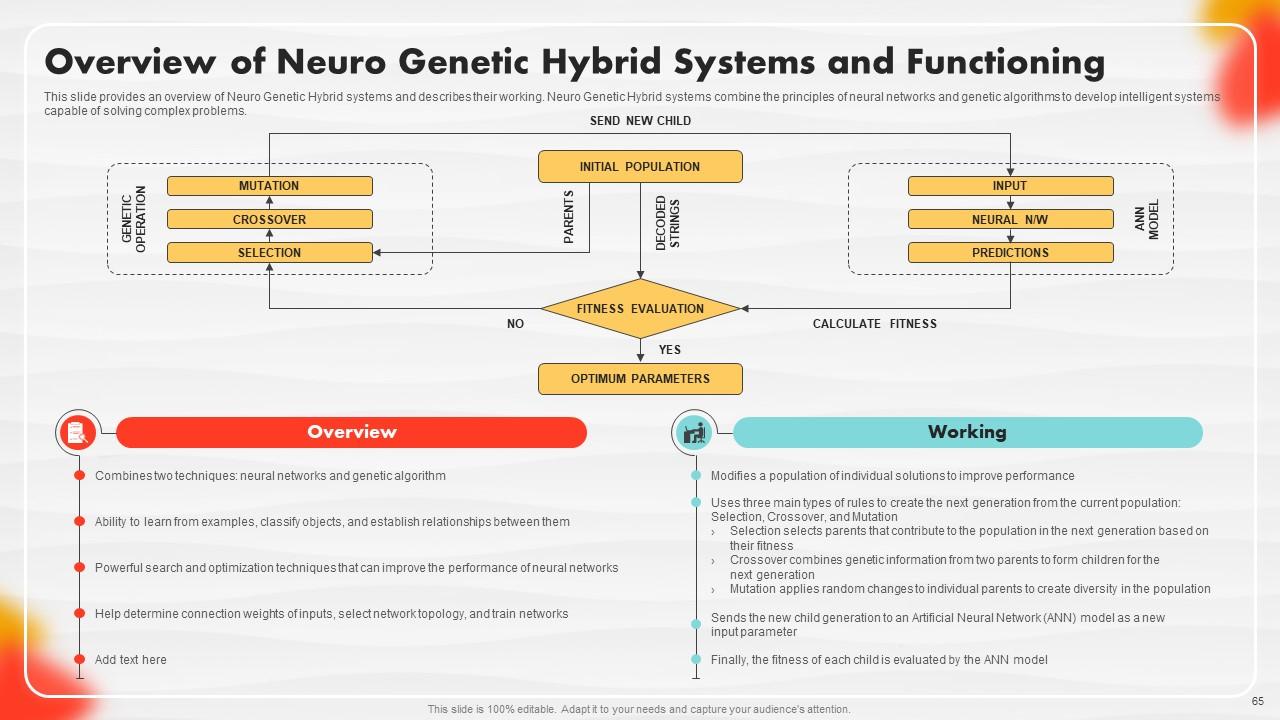
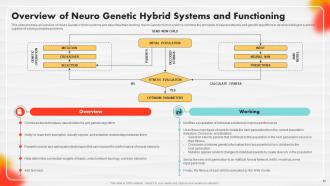
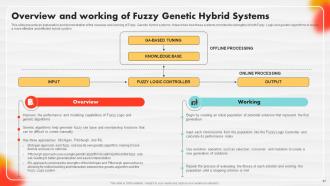
Slide 65: This slide portrays an overview of Neuro Genetic Hybrid systems and describes their working.
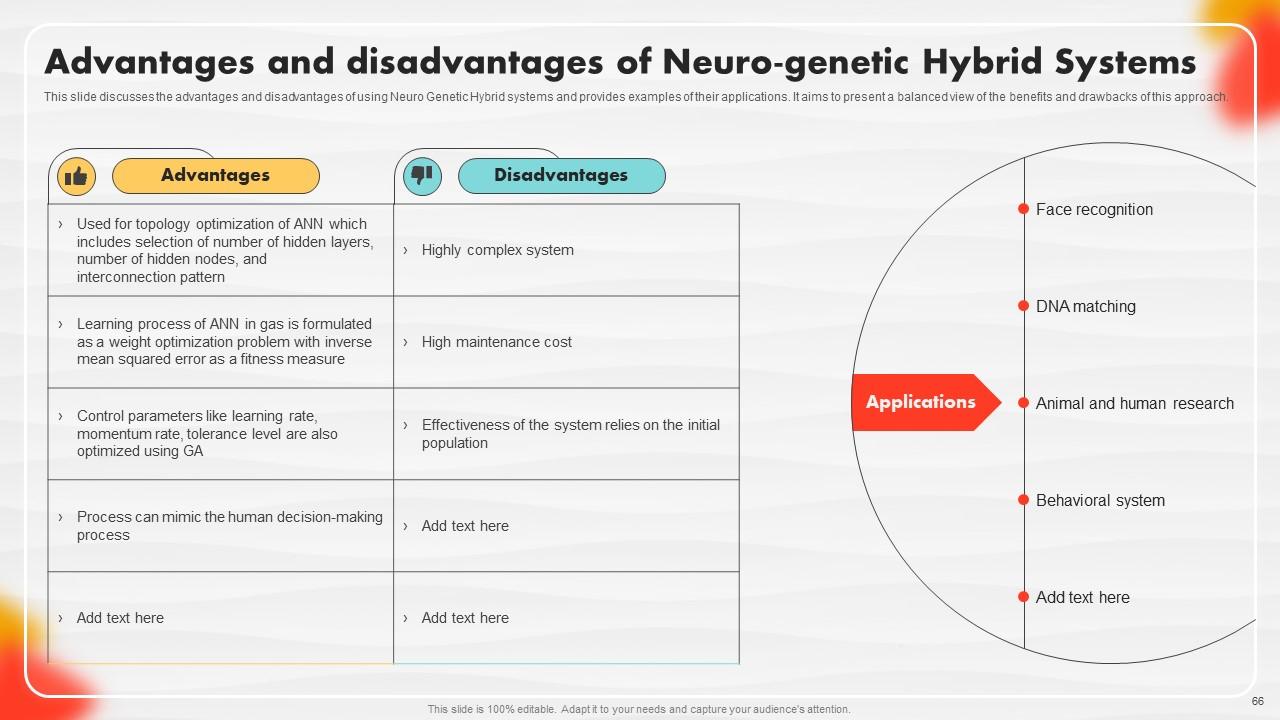
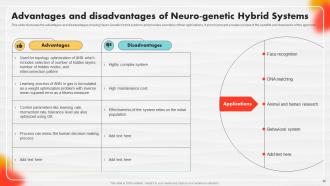
Slide 66: This slide discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using Neuro Genetic Hybrid systems.
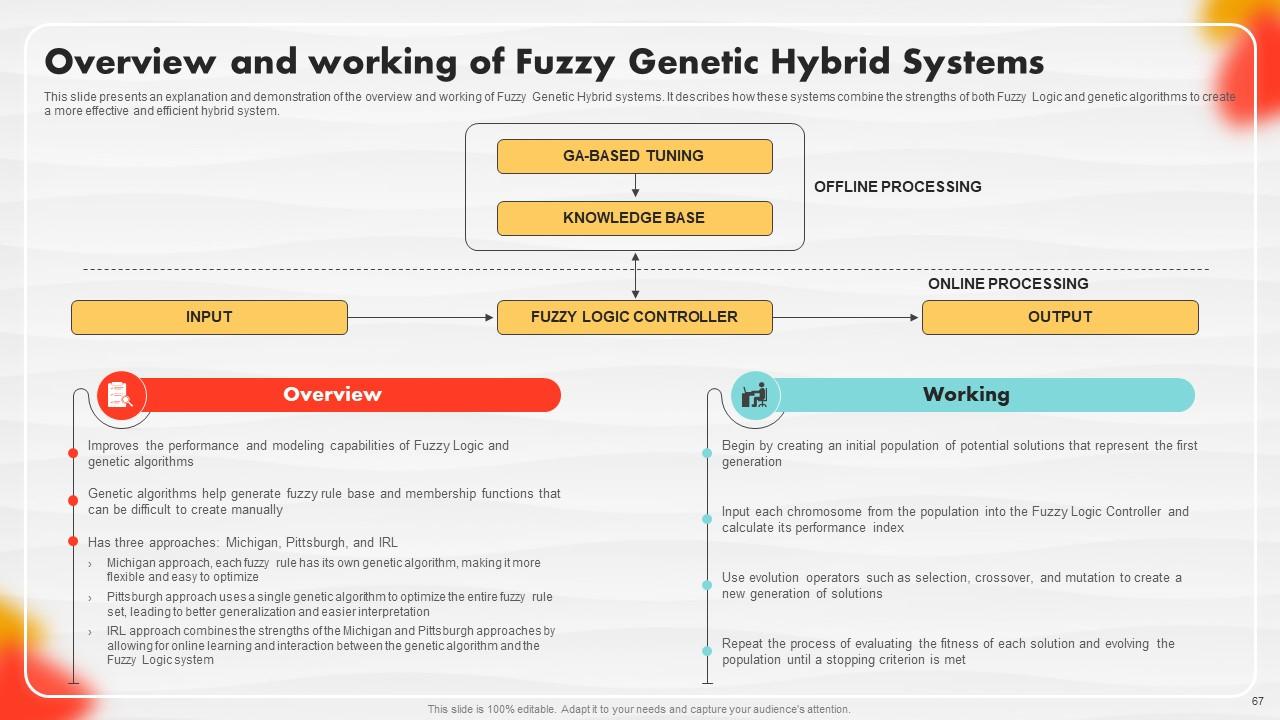
Slide 67: This slide presents an explanation and demonstration of the overview and working of Fuzzy Genetic Hybrid systems. on is met
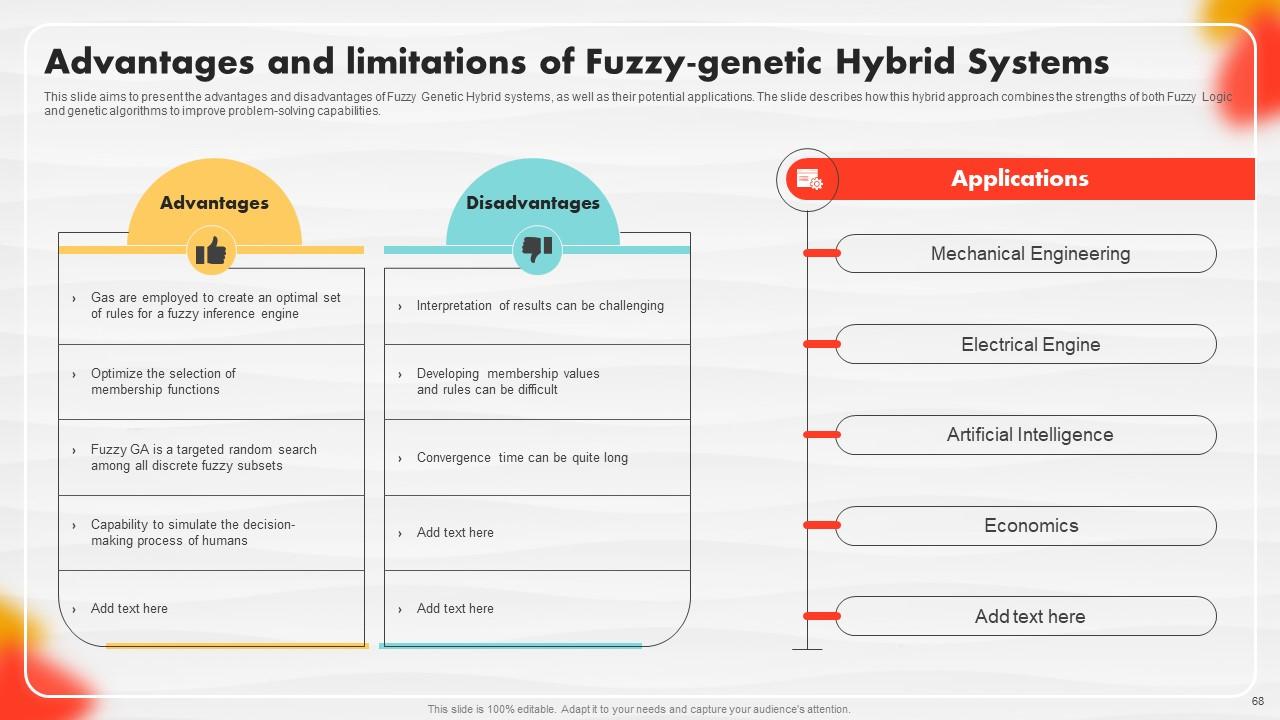
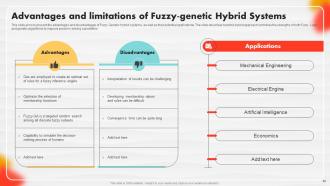
Slide 68: This slide aims to present the advantages and disadvantages of Fuzzy Genetic Hybrid systems.
Slide 69: This slide introduces the Application of soft computing out of the Table of Contents.
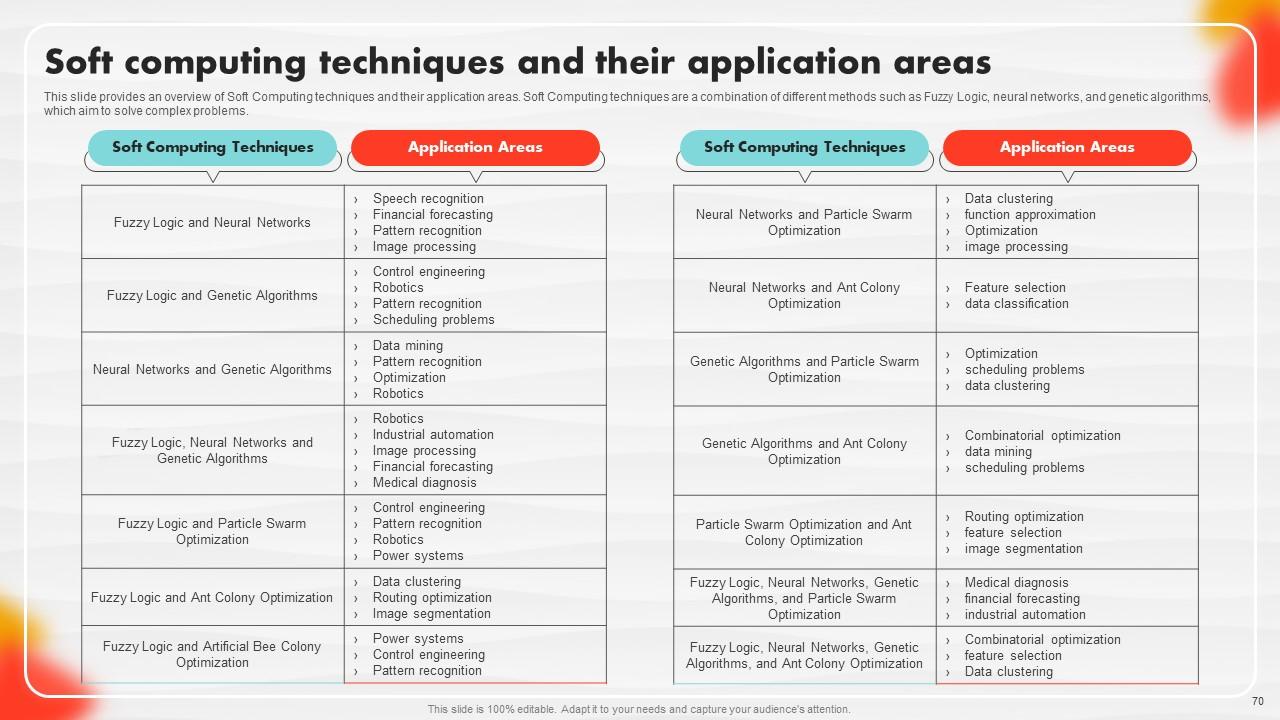
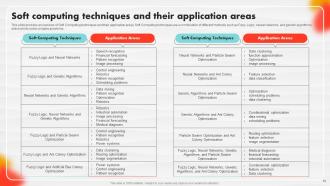
Slide 70: This slide contains an overview of Soft Computing techniques and their application areas.
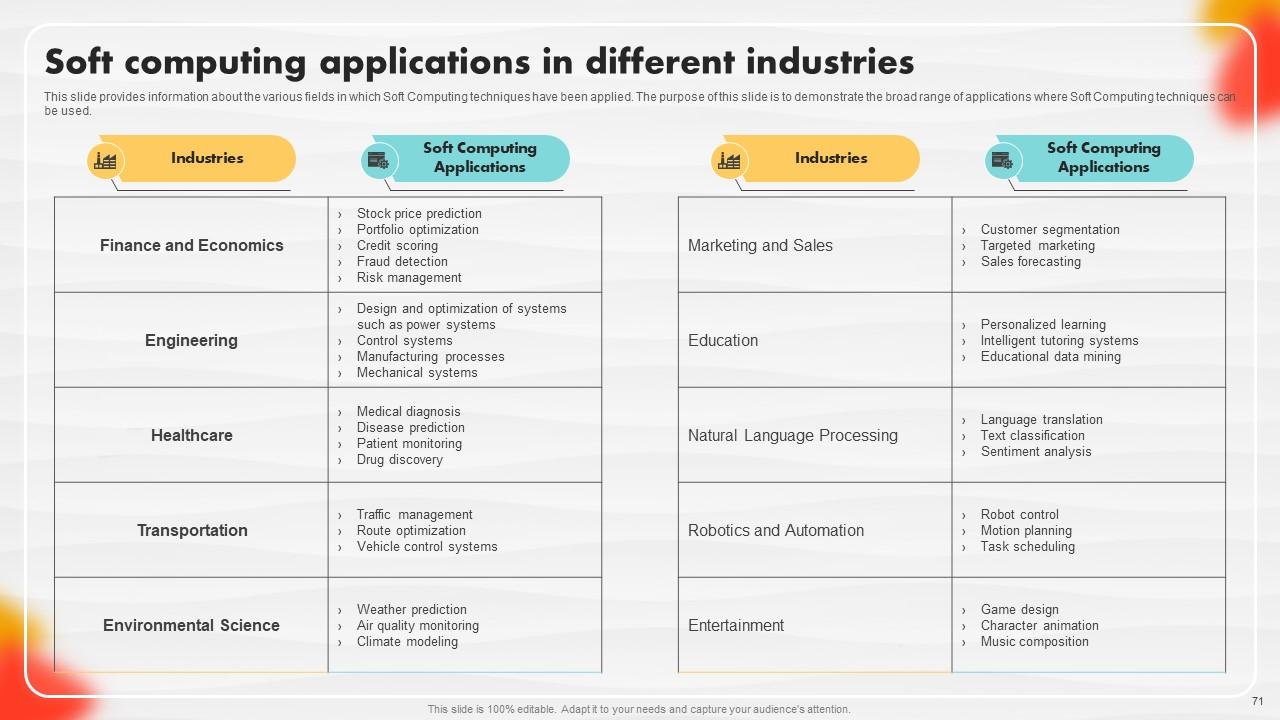
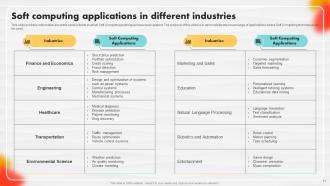
Slide 71: This slide caters to information about the various fields in which Soft Computing techniques have been applied.
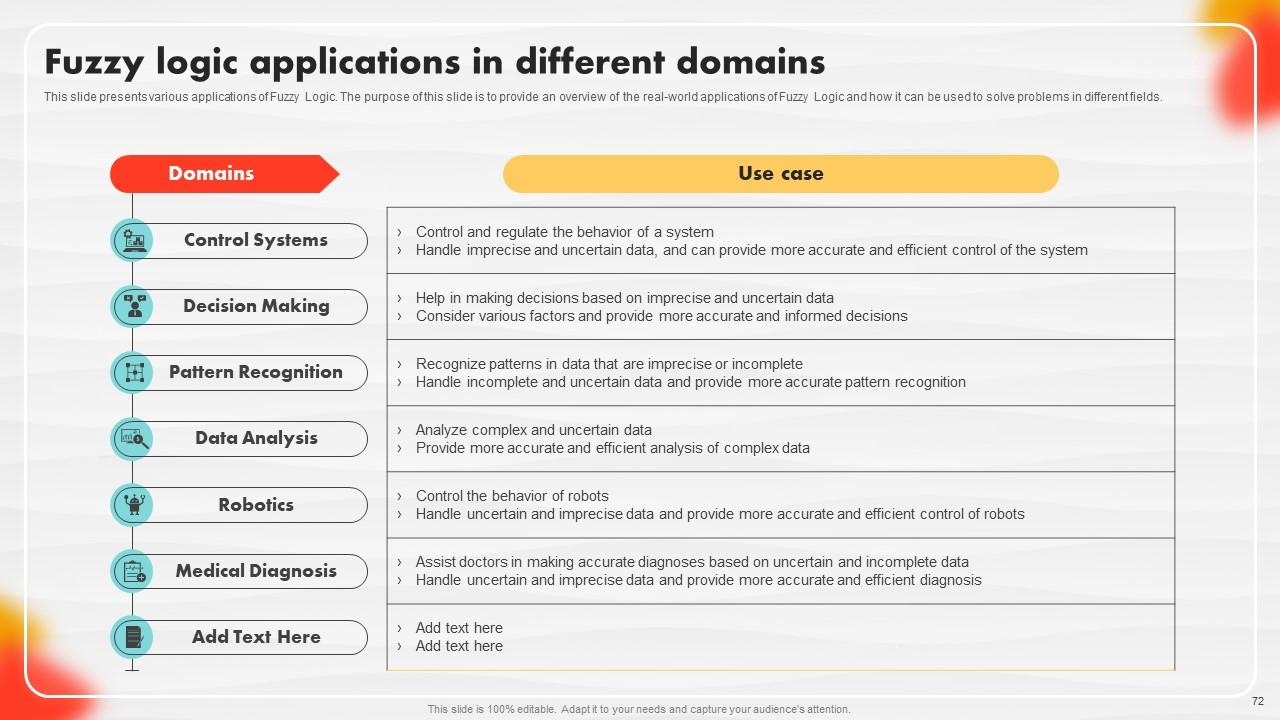
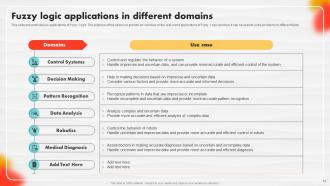
Slide 72: This slide entails various applications of Fuzzy Logic.
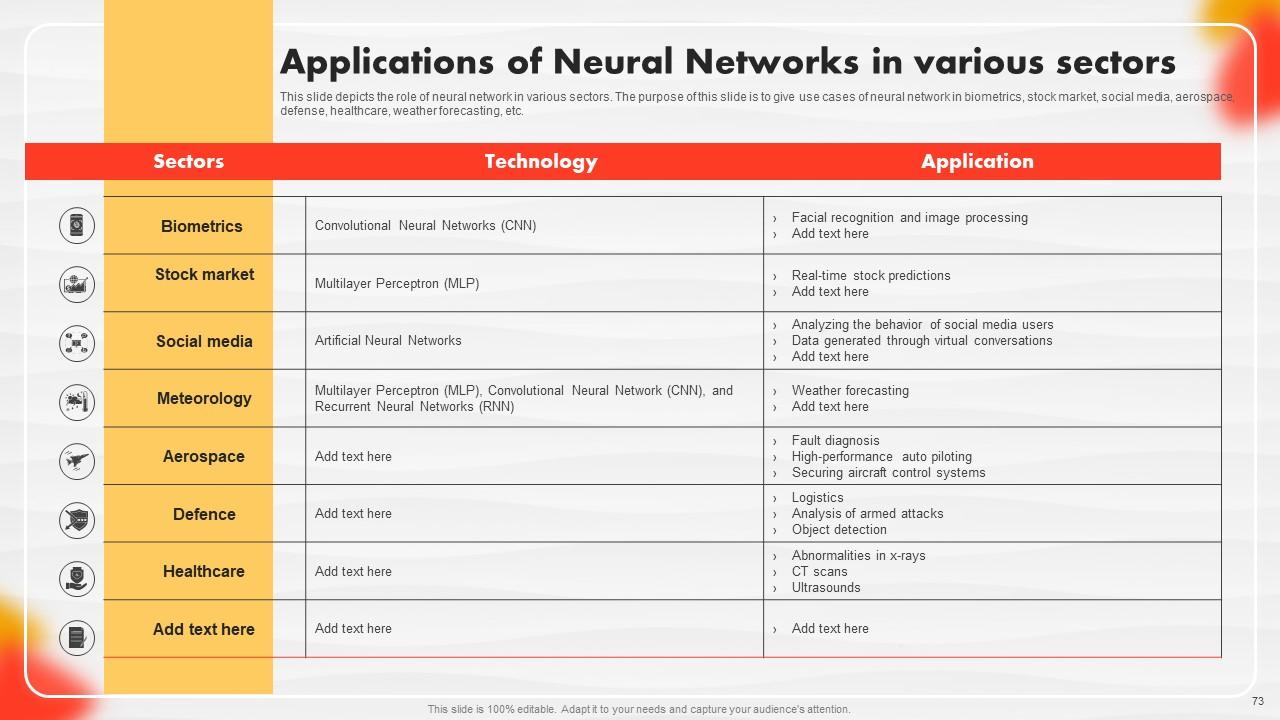
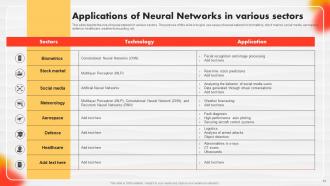
Slide 73: This slide depicts the role of neural networks in various sectors.
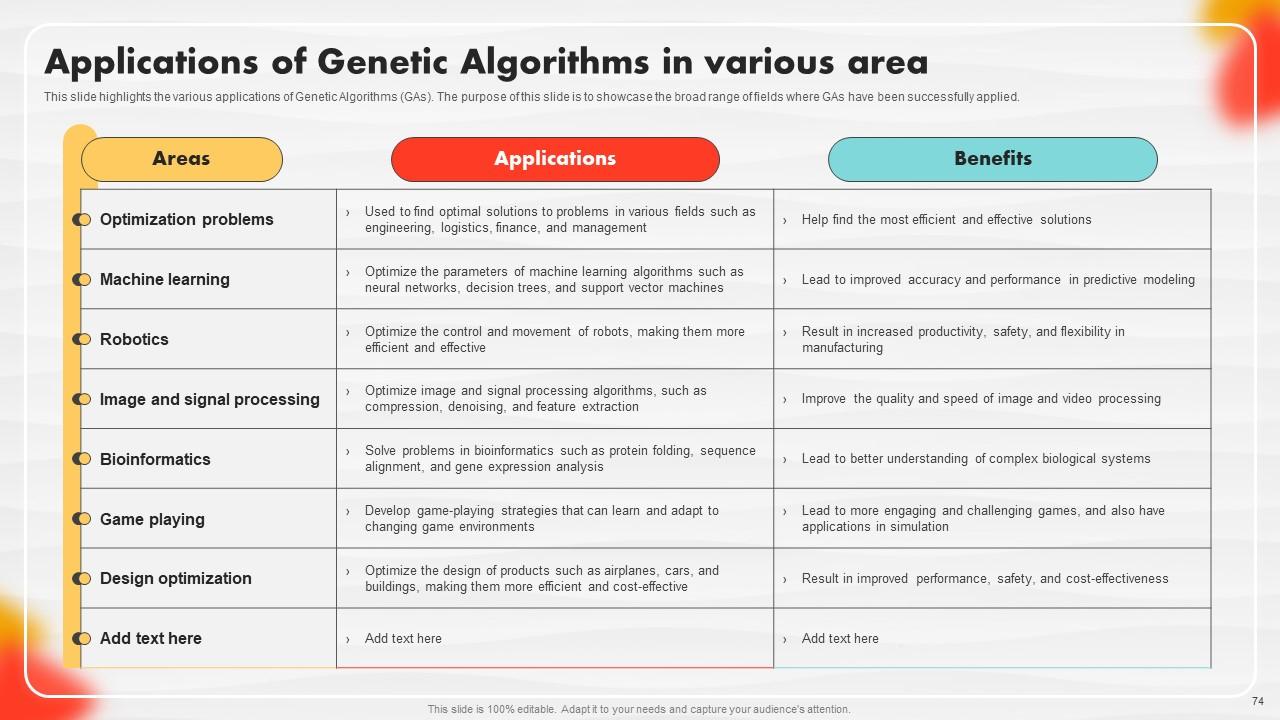
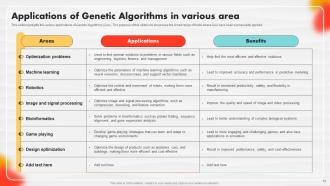
Slide 74: This slide highlights the various applications of Genetic Algorithms (GAs).
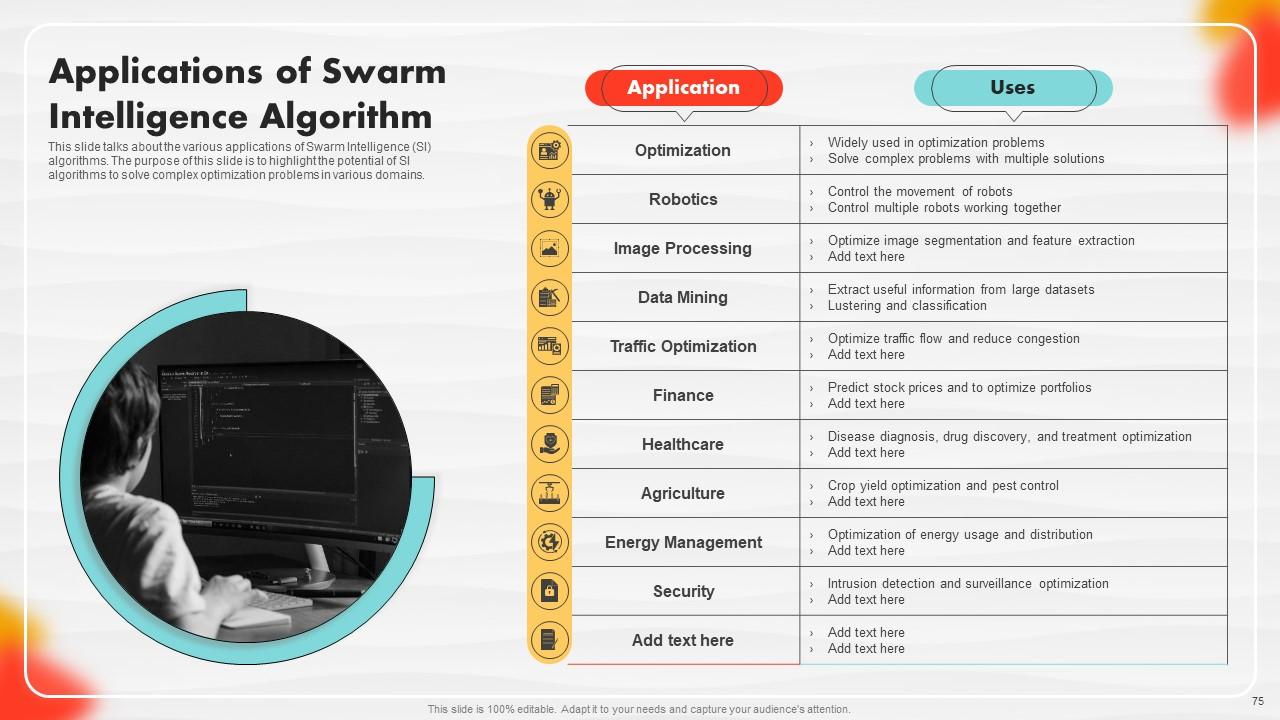
Slide 75: This slide talks about the various applications of Swarm Intelligence (SI) algorithms.
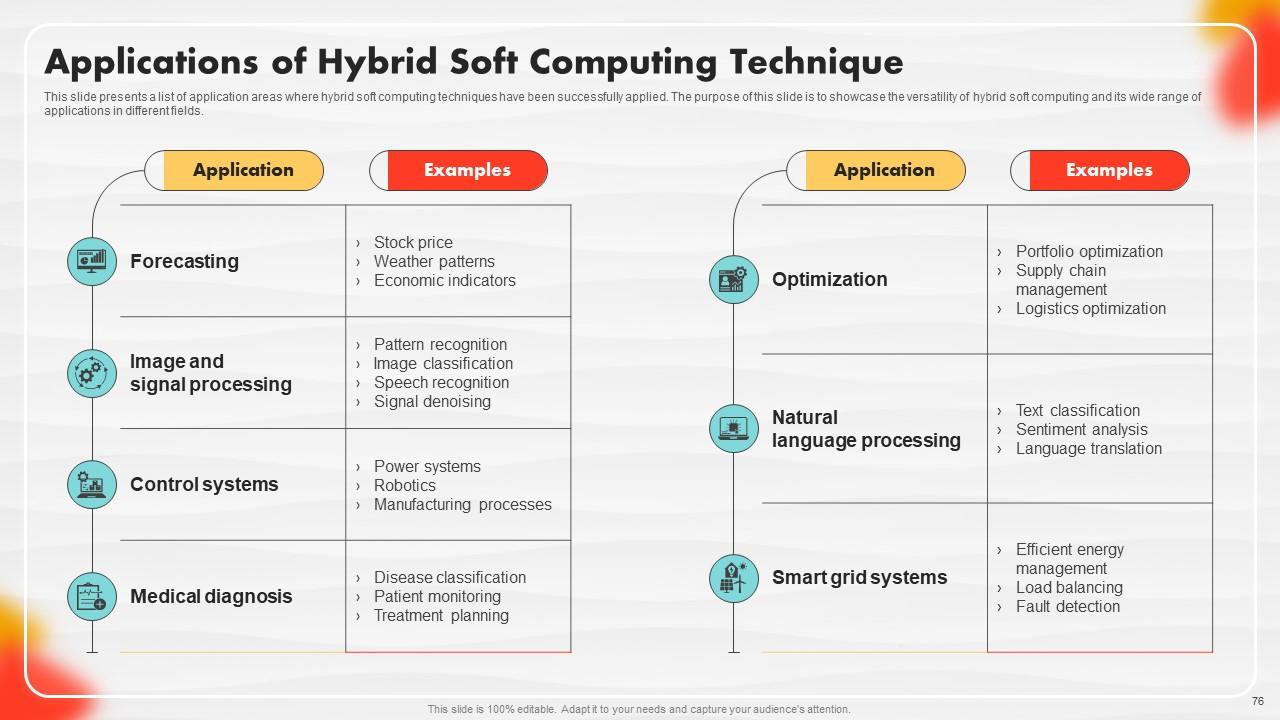
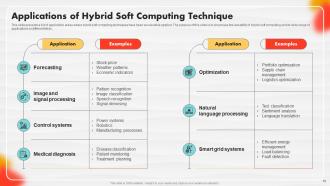
Slide 76: This slide presents a list of application areas where hybrid soft computing techniques have been successfully applied.
Slide 77: This slide introduces the Integration of soft computing out of the Table of Contents.
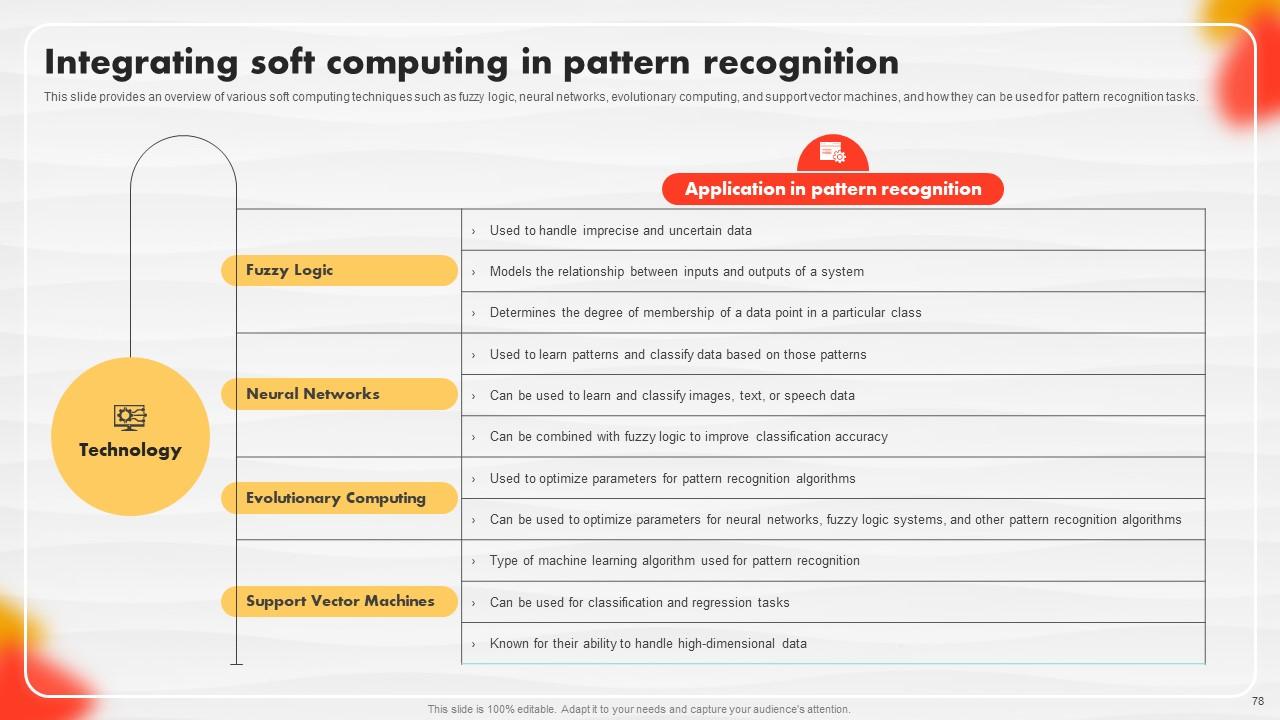
Slide 78: This slide provides an overview of Integrating soft computing in pattern recognition.
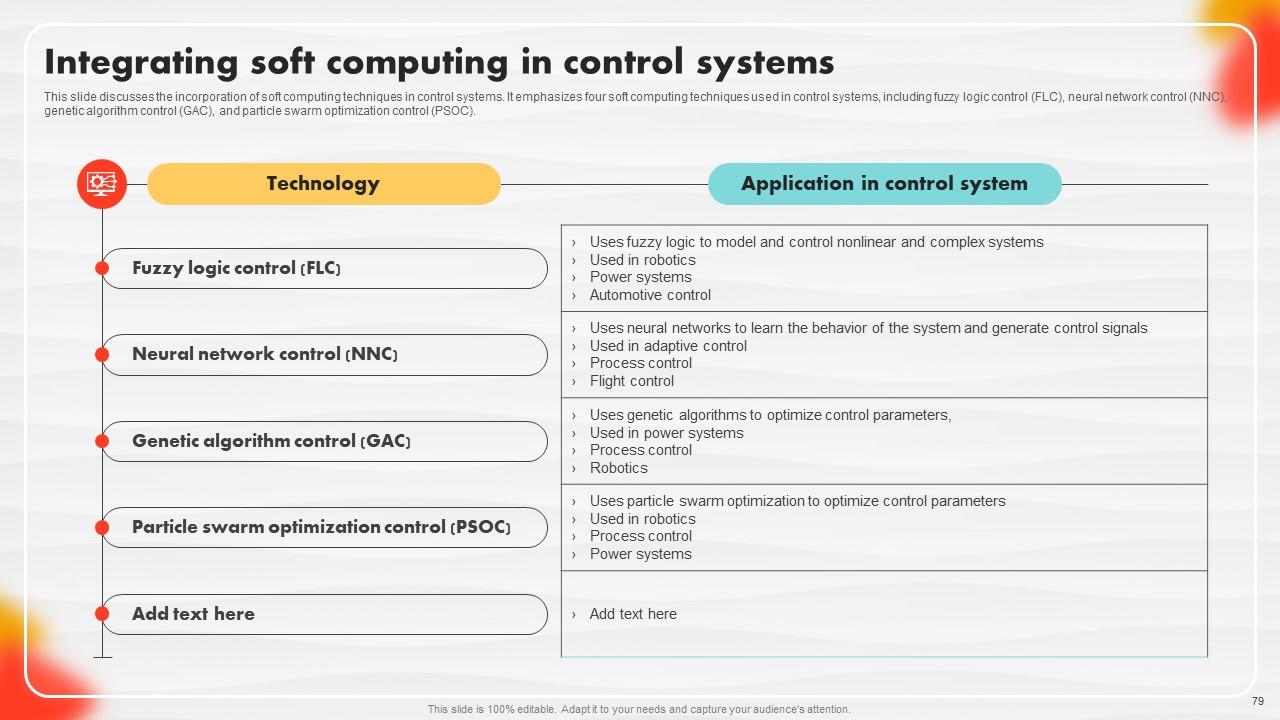
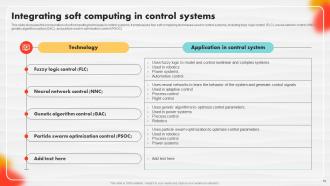
Slide 79: This slide discusses the incorporation of soft computing techniques in control systems.
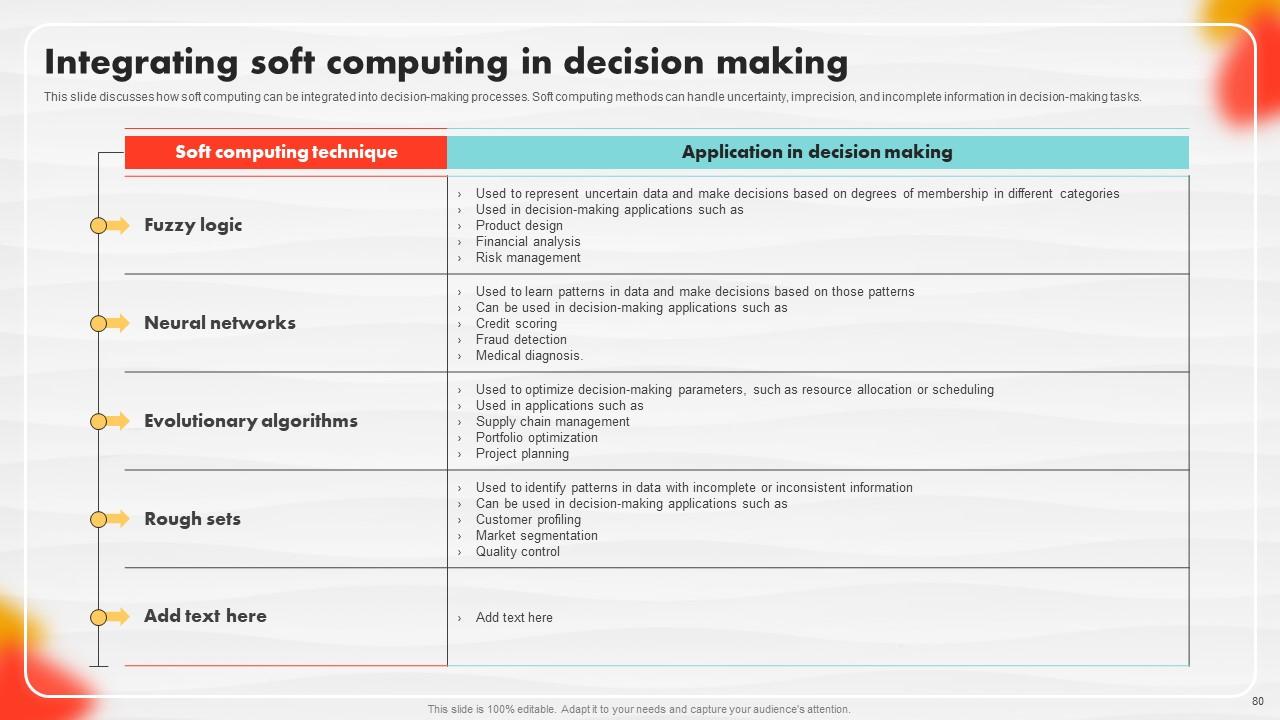
Slide 80: This slide shows how soft computing can be integrated into decision-making processes.
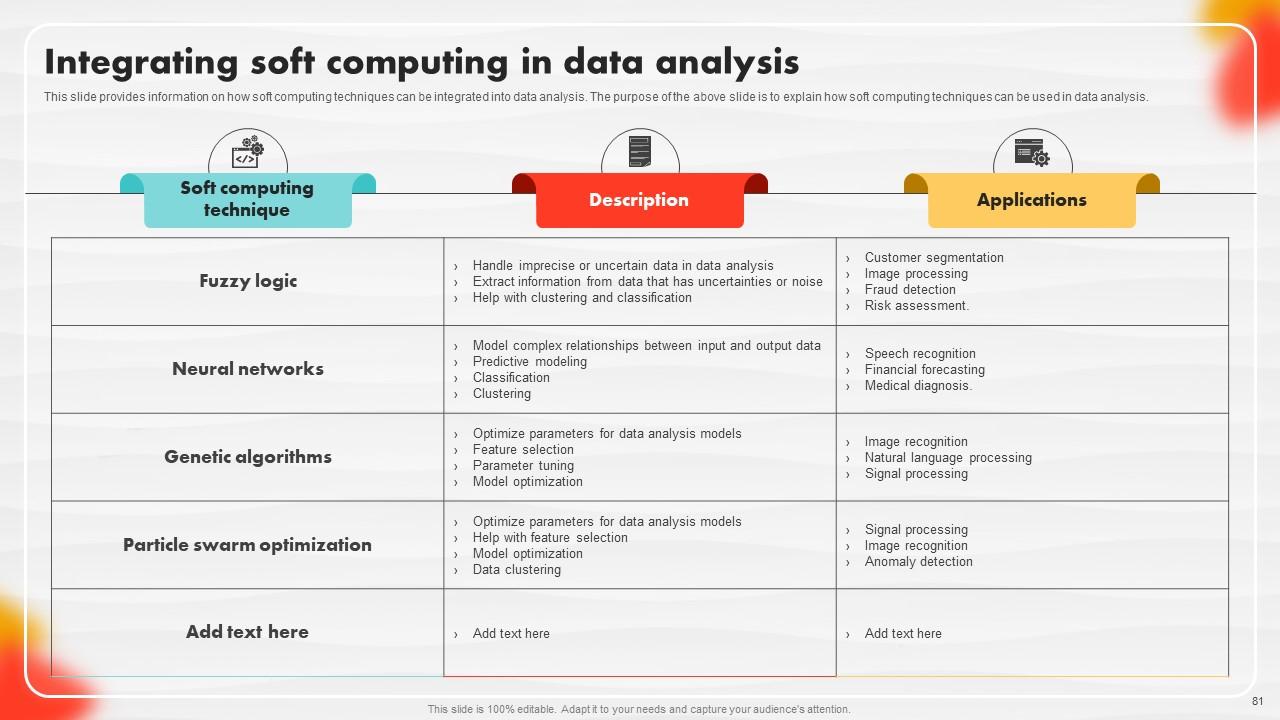
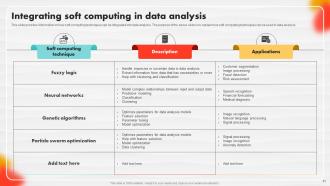
Slide 81: This slide showcases information on how soft computing techniques can be integrated into data analysis.
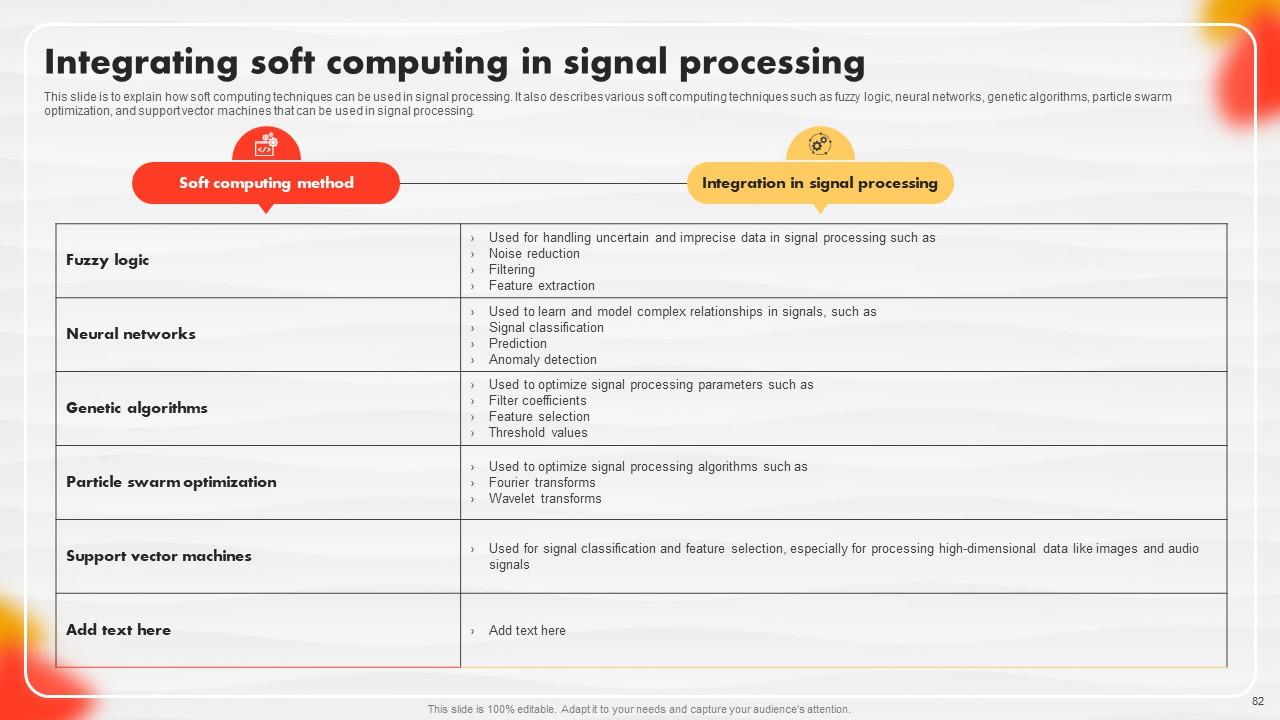
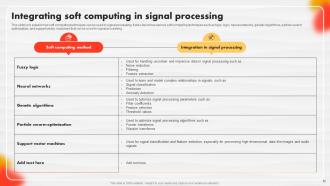
Slide 82: This slide explains how soft computing techniques can be used in signal processing.
Slide 83: This slide introduces Training and budget of soft computing out of the Table of Contents.
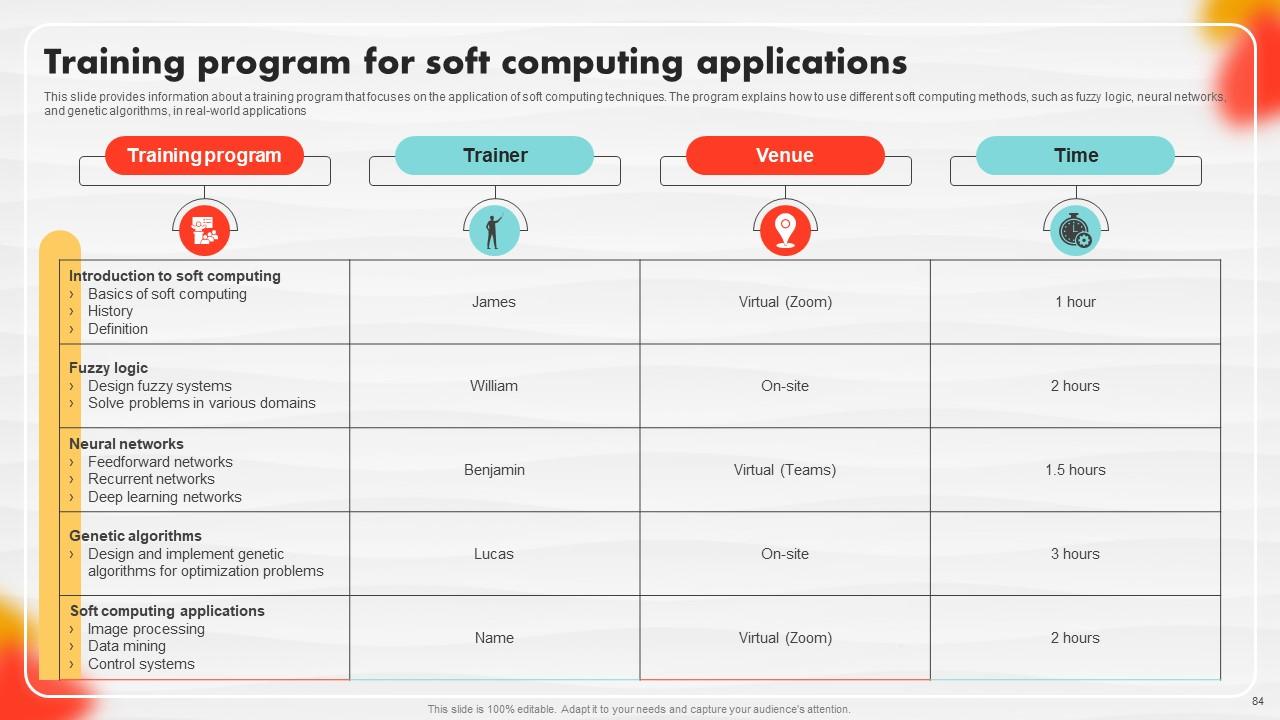
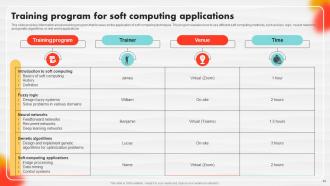
Slide 84: This slide provides information about a training program that focuses on the application of soft computing techniques.
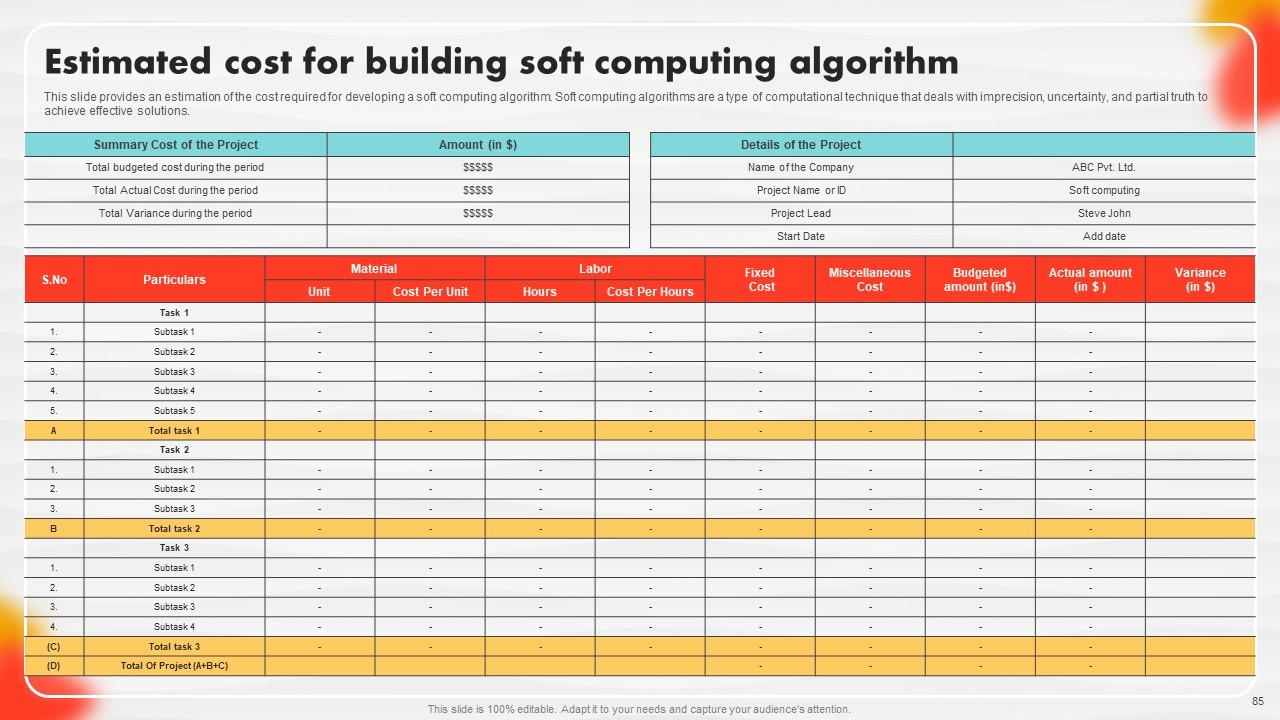
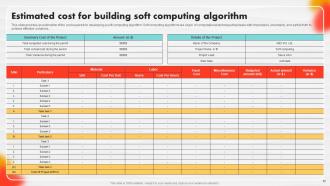
Slide 85: This slide entails an estimation of the cost required for developing a soft computing algorithm.
Slide 86: This slide introduces Challenges and solutions in soft computing problems out of the table of contents.
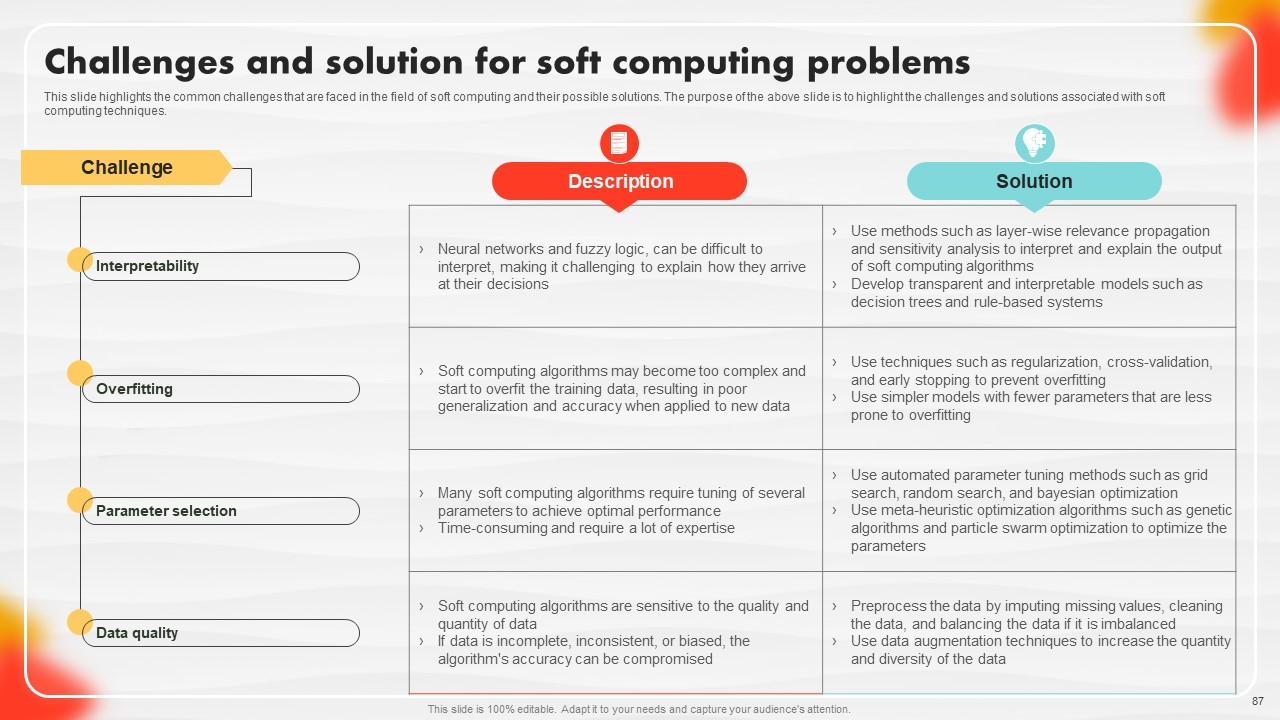
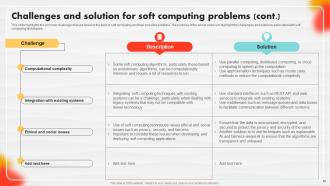
Slide 87: This slide highlights the common challenges that are faced in the field of soft computing and their possible solutions.
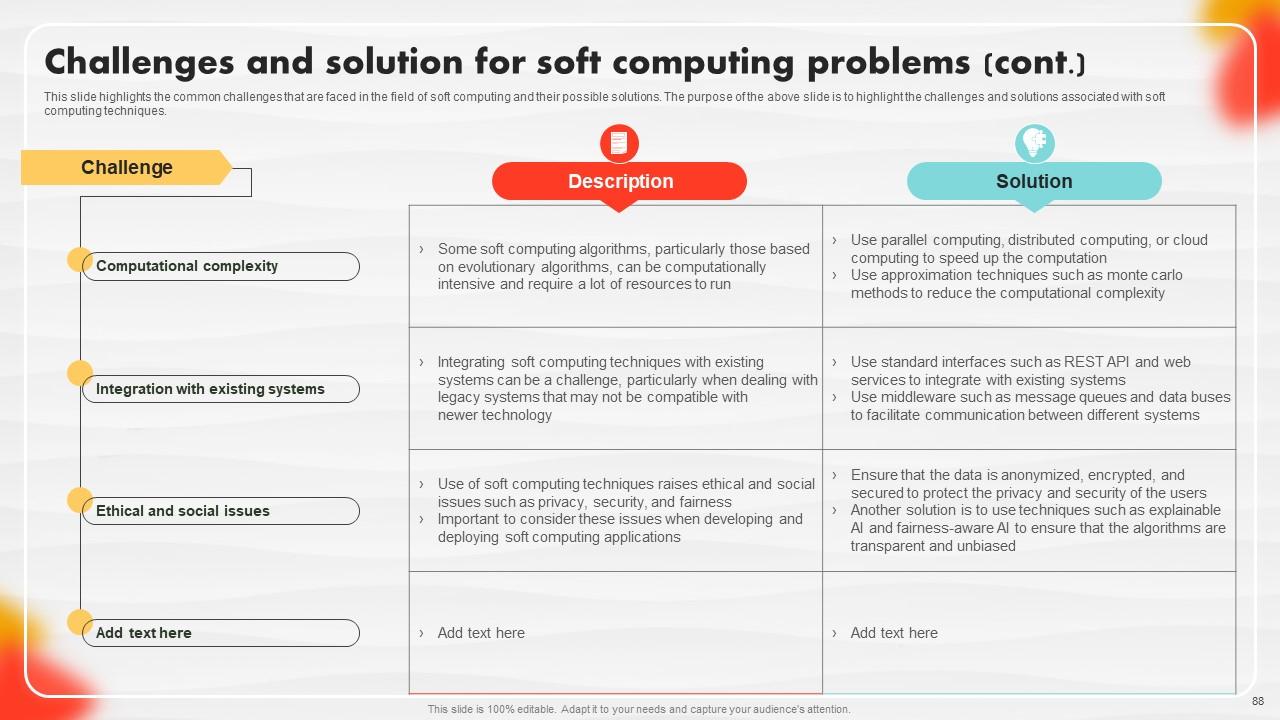
Slide 88: This slide showcases the common challenges that are faced in the field of soft computing and their possible solutions.
Slide 89: This slide introduces Implementing soft computing techniques out of the table of contents.
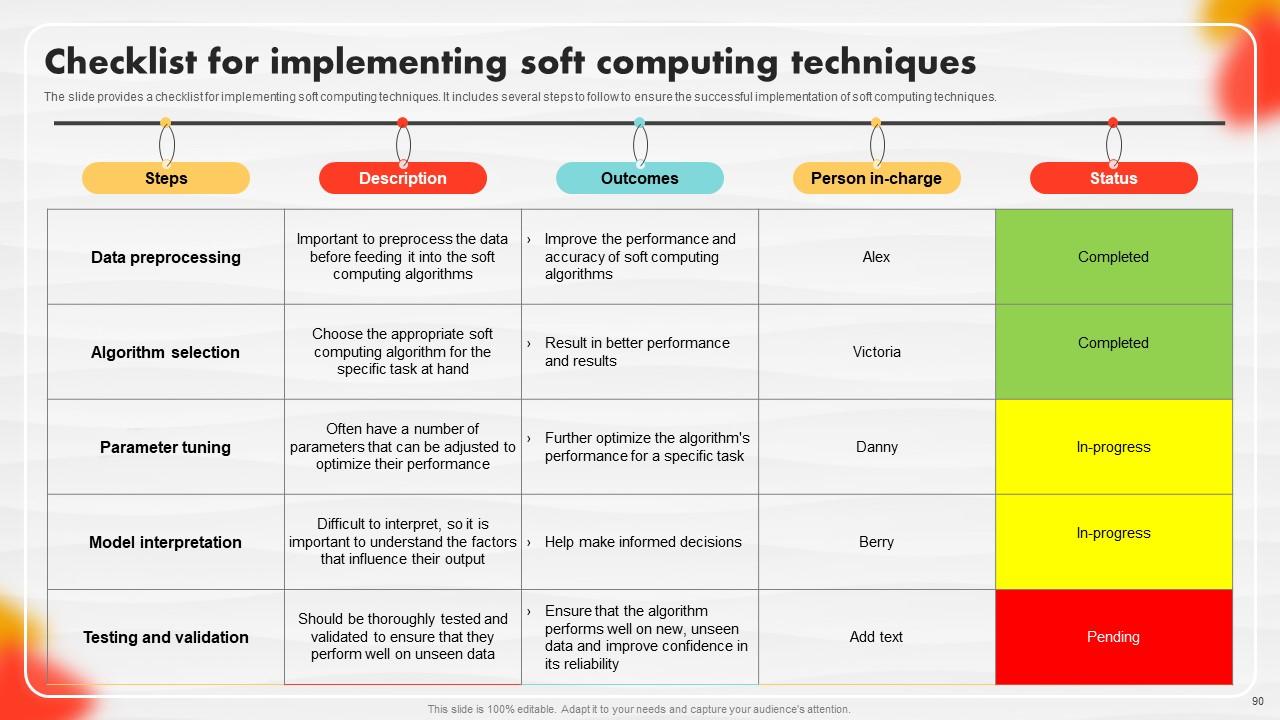
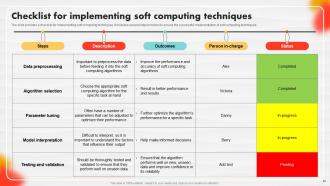
Slide 90: The slide contains a checklist for implementing soft computing techniques.
Slide 91: This slide provides a 30-60-90-day plan with text boxes.
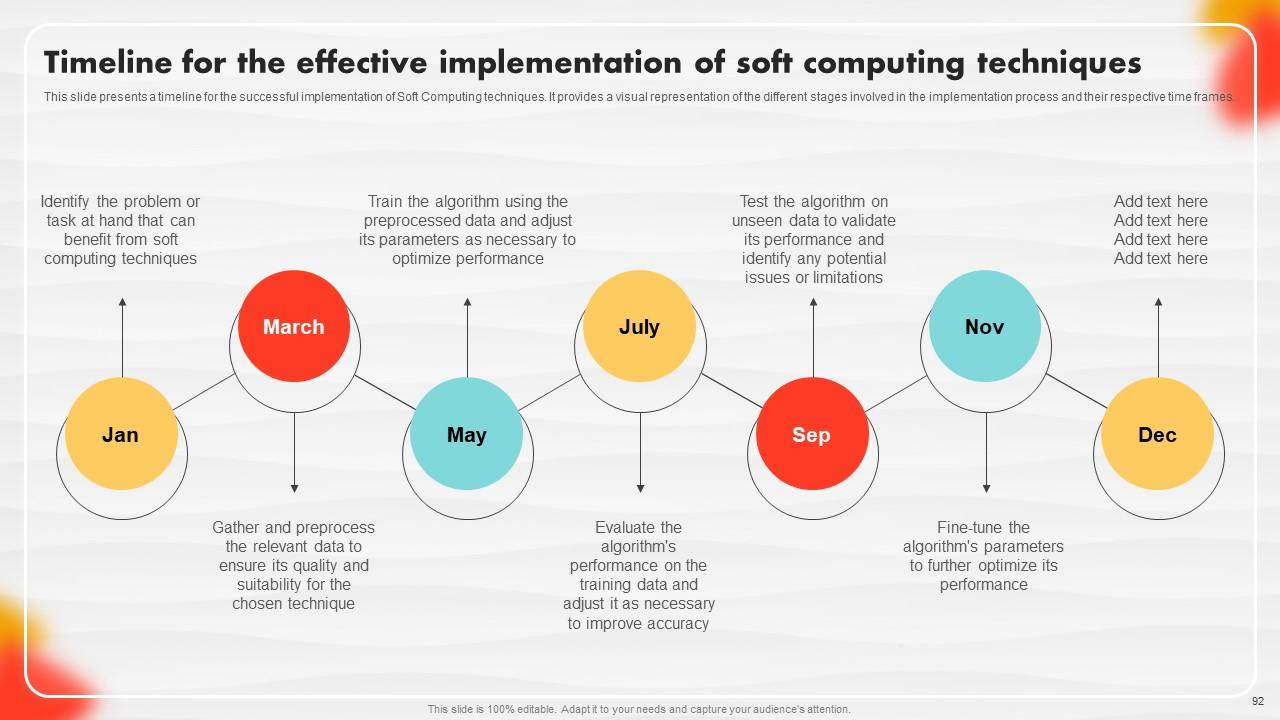
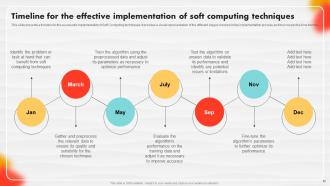
Slide 92: This slide is a Timeline slide. Show data related to time intervals here.
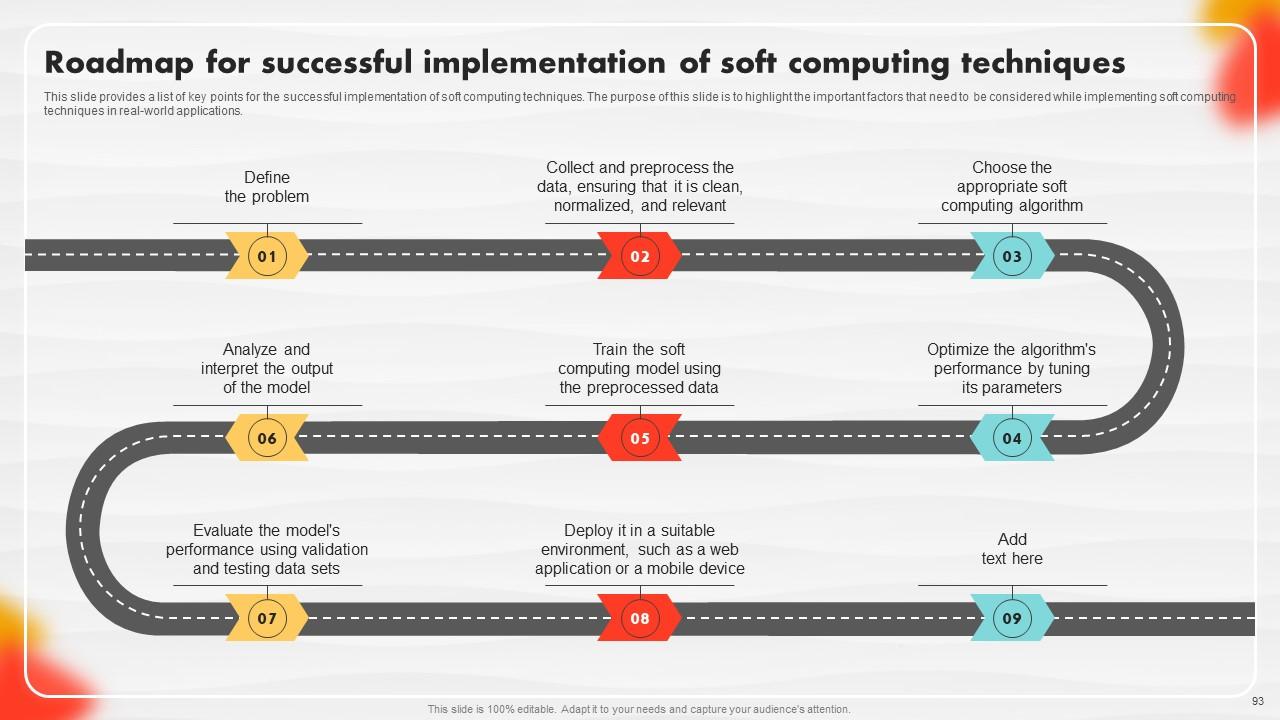
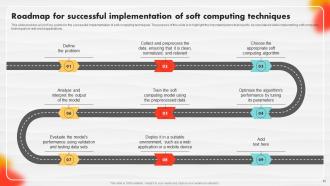
Slide 93: This slide presents a Roadmap with additional text boxes.
Slide 94: This slide introduces Future Directions in soft computing out of the table of contents.
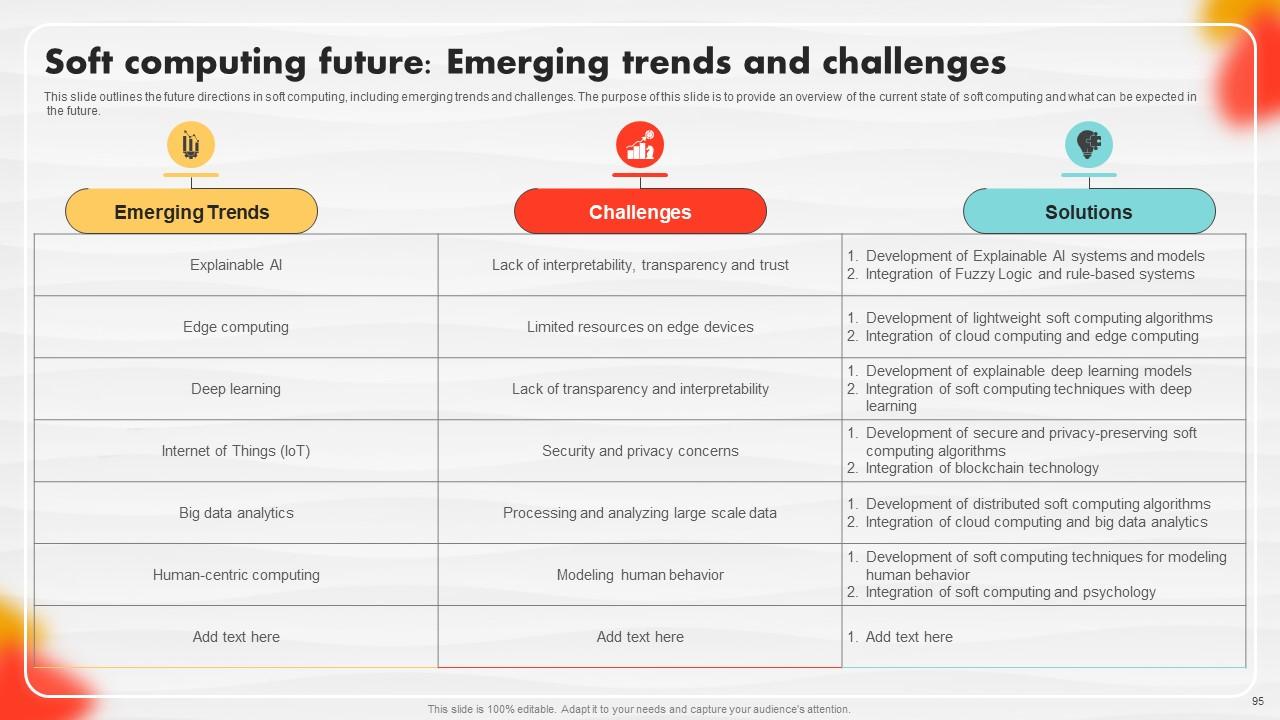
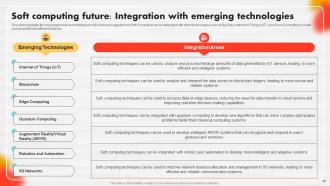
Slide 95: This slide outlines the future directions in soft computing, including emerging trends and challenges.
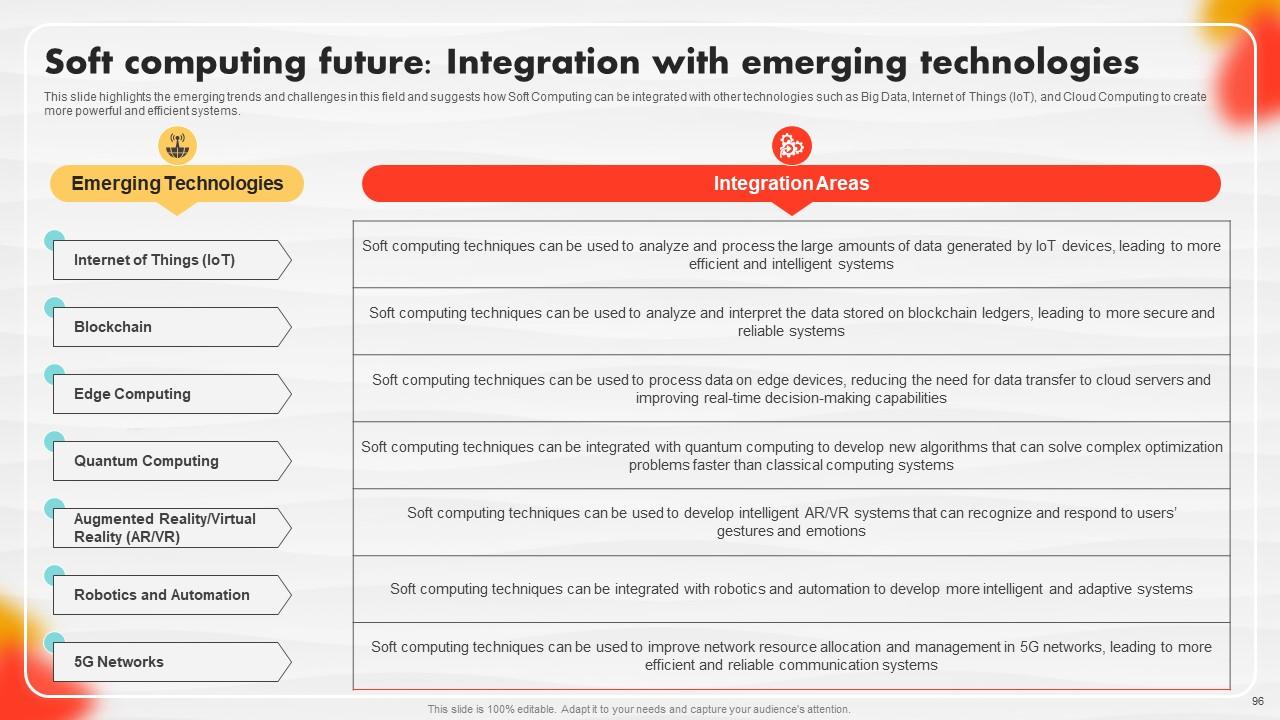
Slide 96: This slide highlights the emerging trends and challenges in this field.
Slide 97: This slide discusses the potential ethical and social implications of Soft Computing as a future direction.
Slide 98: This slide shows all the icons included in the presentation.
Slide 99: This slide is a thank-you slide with address, contact numbers, and email address.
Soft Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 104 slides:
Use our Soft Computing Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
FAQs
Soft computing is a field of computer science that deals with approximate reasoning, uncertainty, and imprecision. It differs from hard computing by focusing on solutions that may not be exact but are more flexible and adaptable to real-world problems.
The primary components of soft computing include fuzzy logic, neural networks, genetic algorithms, and swarm intelligence. These components provide different approaches to modeling and solving complex problems by mimicking human-like thinking, learning, and optimization processes.
Fuzzy logic deals with uncertainty and imprecision by allowing variables to have degrees of membership in linguistic terms. It is applied in problem-solving by providing a structured framework for handling vague and uncertain information, making it suitable for control systems and decision-making.
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the human brain. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes and are used for tasks such as pattern recognition, data analysis, and signal processing. Their applications span various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and image recognition.
Genetic algorithms are optimization techniques inspired by natural selection and genetics. They work by evolving a population of potential solutions to find the best one over successive generations. They are used in various fields, such as engineering and finance, to solve complex optimization problems.
-
The quality of PowerPoint templates I found here is unique and unbeatable. Keep up the good work and continue providing us with the best slides!
-
Based on my personal experience, I would recommend other people to subscribe to SlideTeam. No one can be disappointed here!