Strategies For Delivering Effective Feedback Training Ppt
This PPT Training Module on Strategies for Delivering Effective Feedback is a must-have resource for professionals looking to enhance their feedback delivery methods. It begins with a deep dive into the purpose of employee feedback, setting the stage for a detailed exploration of various feedback models such as Prepare-Listen-Act, Observation-Impact-Action, and Start-Stop Continue. Navigate the process of delivering feedback with precision, learning how to identify opportunities for positive and negative feedback in the workplace. The PowerPoint Module covers feedback through redirection and reinforcement. It also covers major feedback blocks and provides guidelines for giving feedback effectively. Additionally, learn the importance of managing non-verbal cues like eye contact, posture, and facial expressions to reinforce your message. The deck concludes with Key Takeaways and Discussion Questions, designed to engage participants in thoughtful reflection and discussion.
This PPT Training Module on Strategies for Delivering Effective Feedback is a must-have resource for professionals looking ..
- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
-
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.
-

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
Compatible With Google Slides

Get This In WideScreen
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
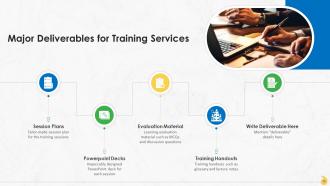
Presenting Training Deck on Strategies for Delivering Effective Feedback. This deck comprises of 44 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 3
This slide provides information on giving employee feedback at the workplace. It is concerned with exchanging information with employees (formally or informally) regarding their work, performance, skills, or ability to work within a team. Its purpose is to promote professional growth, increase job satisfaction, to reinforce positive habits, and aid in continuous learning.
Slide 4
This slide showcases examples of giving positive feedback to employee at workplace.
Slide 5
This slide highlights examples of giving negative feedback to employee at workplace.
Slide 6
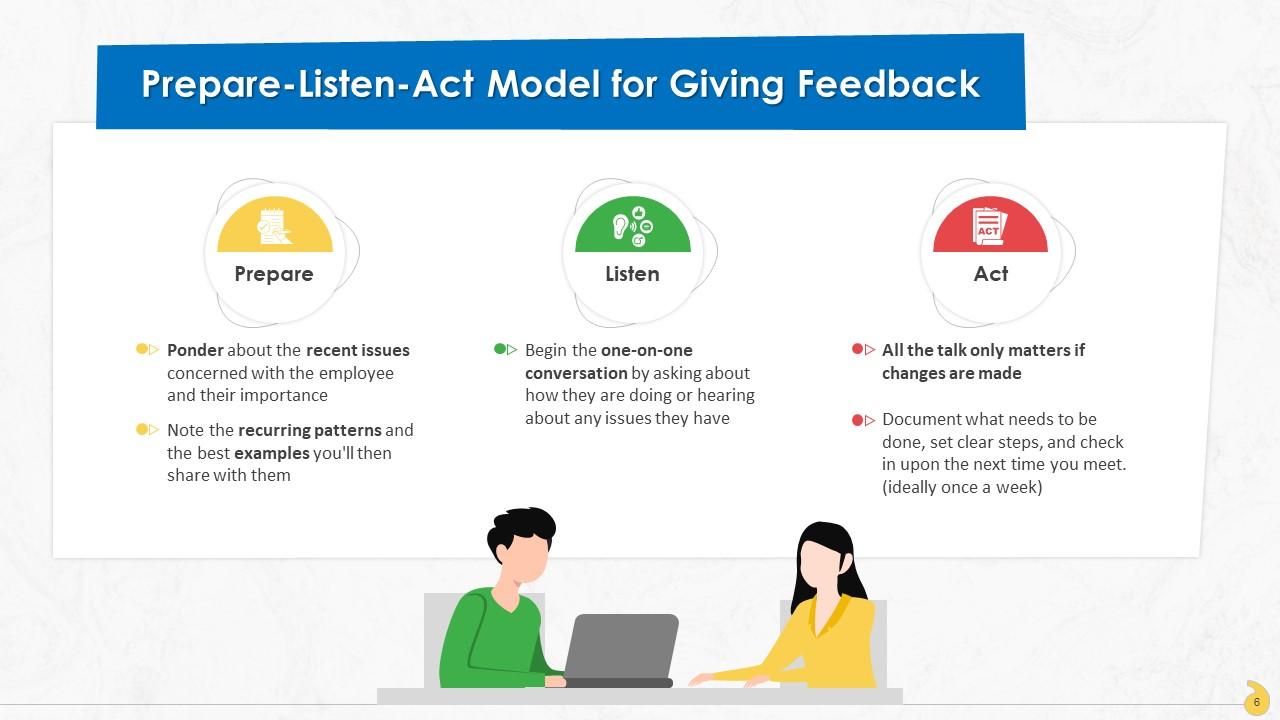
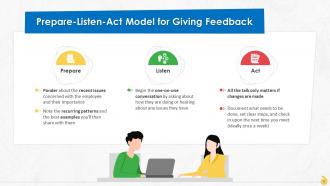
This slide contains information about the prepare-listen-act model for giving effective feedback. In this framework, prepare stage relates to identifying issues concerned with the employee, listen stage is concerned with initiating a one-to-one conversation and hearing from the employee, and act stage is about establishes steps and ways for implementing the changes.
Slide 7
This slide contains information about the perfect way to deliver feedback at the organization which consists of three steps: Observation, impact, and action.
Slide 8
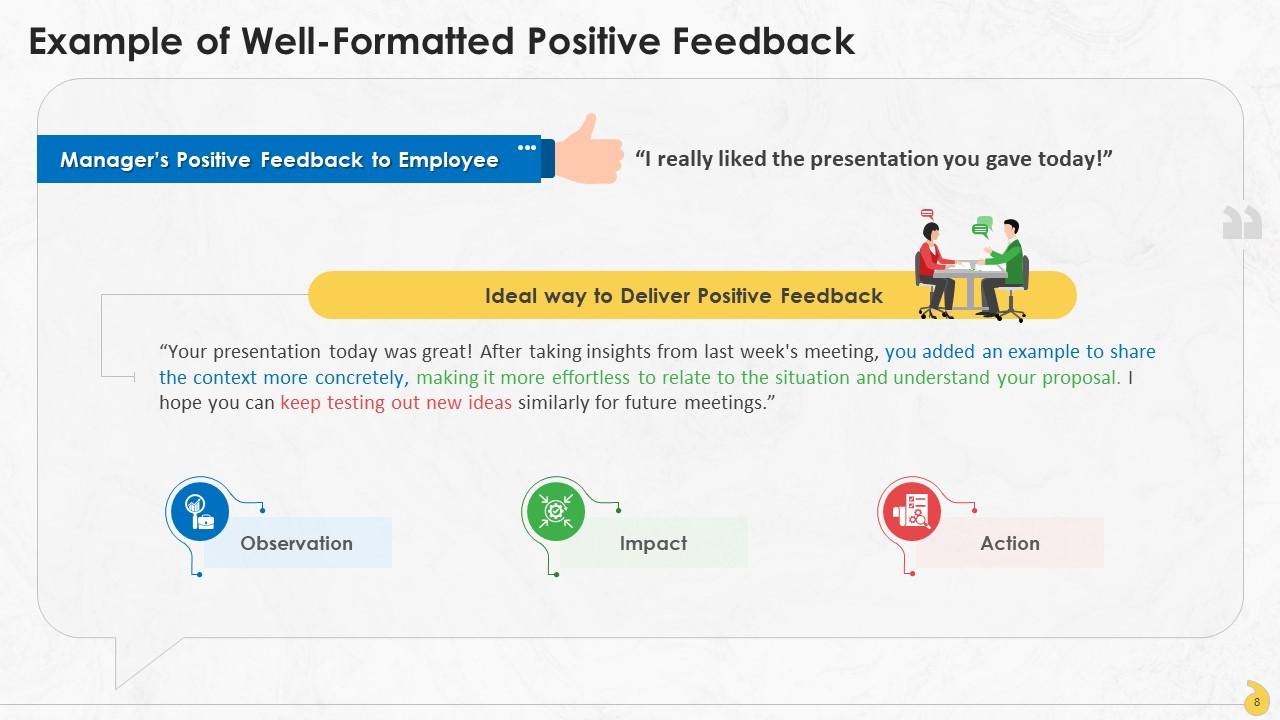
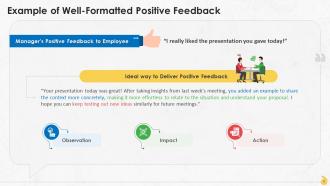
This slide showcases an example of delivering effective positive feedback at workplace by taking into consideration the observation, impact, and action and making this a part of the feedback.
Slide 9
This slide showcases an example of delivering negative feedback at workplace by taking into consideration the observation, impact, and action and inculcating the same in feedback.
Slide 10
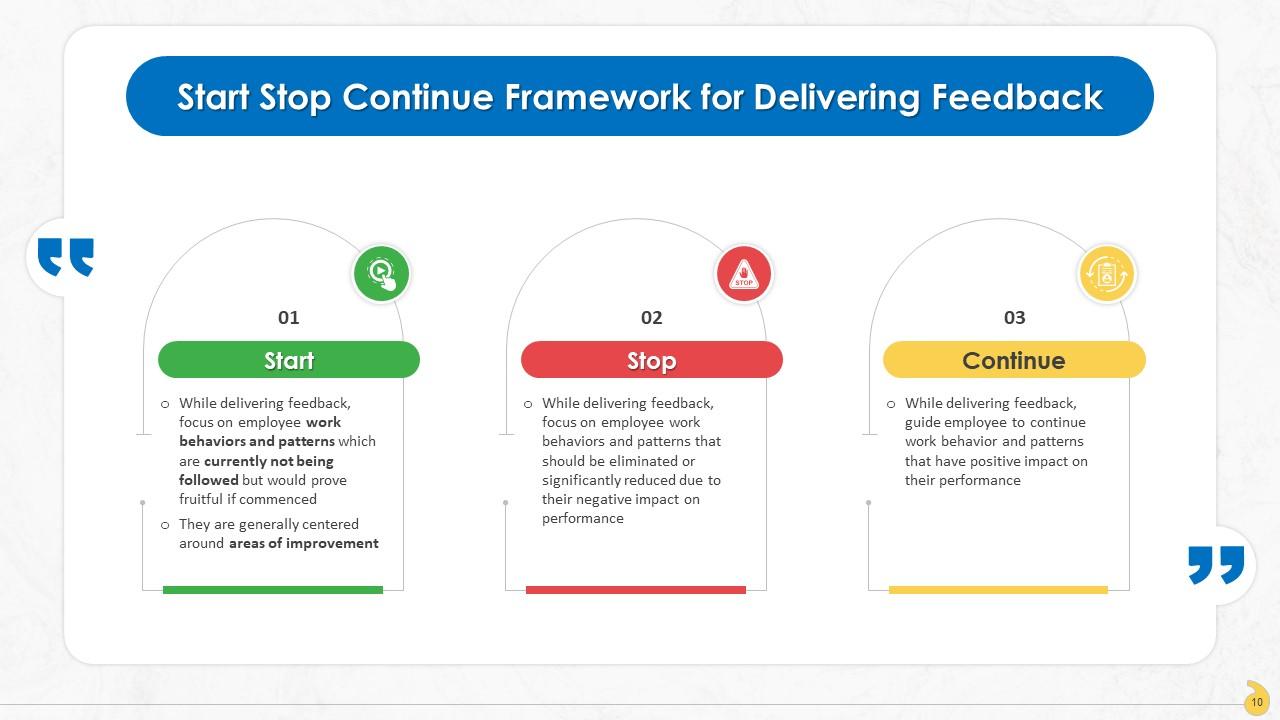
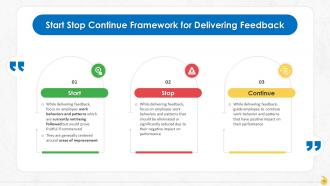
This slide explains the Start-Stop-Continue Model for delivering feedback to employees and its use in the organization. It consists of three elements namely: Start, stop and continue.
Instructor Notes:
Start-Stop-Continue approach can be followed by the manager in following cases:
- When they need to cover all aspects of feedback i.e., areas of improvement, appreciation, and constructive criticism together
- To deliver action-oriented feedback to employee or while writing a performance improvement plan
- For building a personal development plan for the employee
Slide 11
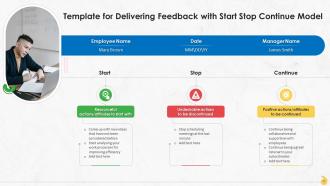
This slide represents the template which can be used for delivering feedback to the employees while following the start stop continue approach.
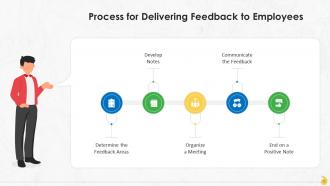
Slide 12
This slide highlights the process for delivering feedback at the workplace. The steps involved are: Determine the feedback areas, develop notes, organize a meeting, communicate the feedback, and end on a positive note.
Instructor’s Notes:
The process for delivering feedback to the employees is:
- Determine the Feedback Areas: Firstly, identify areas for which feedback is to be given to the employee. These could be areas where the employee is already performing well or points for further improvement. Create a list for the same
- Develop Notes: Put together the points in the order in which you plan to provide feedback. It will help you stay focused and ensure necessary information is communicated to the employee. An employee evaluation form can help structure notes
- Organize a Meeting: Schedule a one-on-one meeting with the employee, but give them time to equip for the meeting. Ask them to take note of the areas in which they think they are doing well and the scope for improvements. This practice will help facilitate a constructive conversation and allow the employee to conduct an honest assessment of their work
- Communicate the Feedback: Deliver the feedback in a private meeting. Structure the discussion as a conversation so that employees can voice their thoughts and opinions. Ensure that the input is centered around work performance and professional behavior and not on personal or emotional talks
- End on a Positive Note: Conclude the feedback on a positive notation. It shows the employee they are a valuable addition to the company, and they will be able to have a sense of accomplishment, along with having focus on areas of improvement
Slide 13
This slide lists the situation for giving positive feedback to an employee. This happens when an employee reaches a goal, learned a new skill, has been a team player, learns from a past mistake and goes above and beyond their usual call of duty.
Slide 14
This slide lists the situation for giving negative feedback to an employee. This usually happens when an employee: is low on morale, has unprofessional attitude, delivers a project at a later time, engages in team conflict, is not aligned with business goals, and lacks autonomy during tasks.
Slide 15
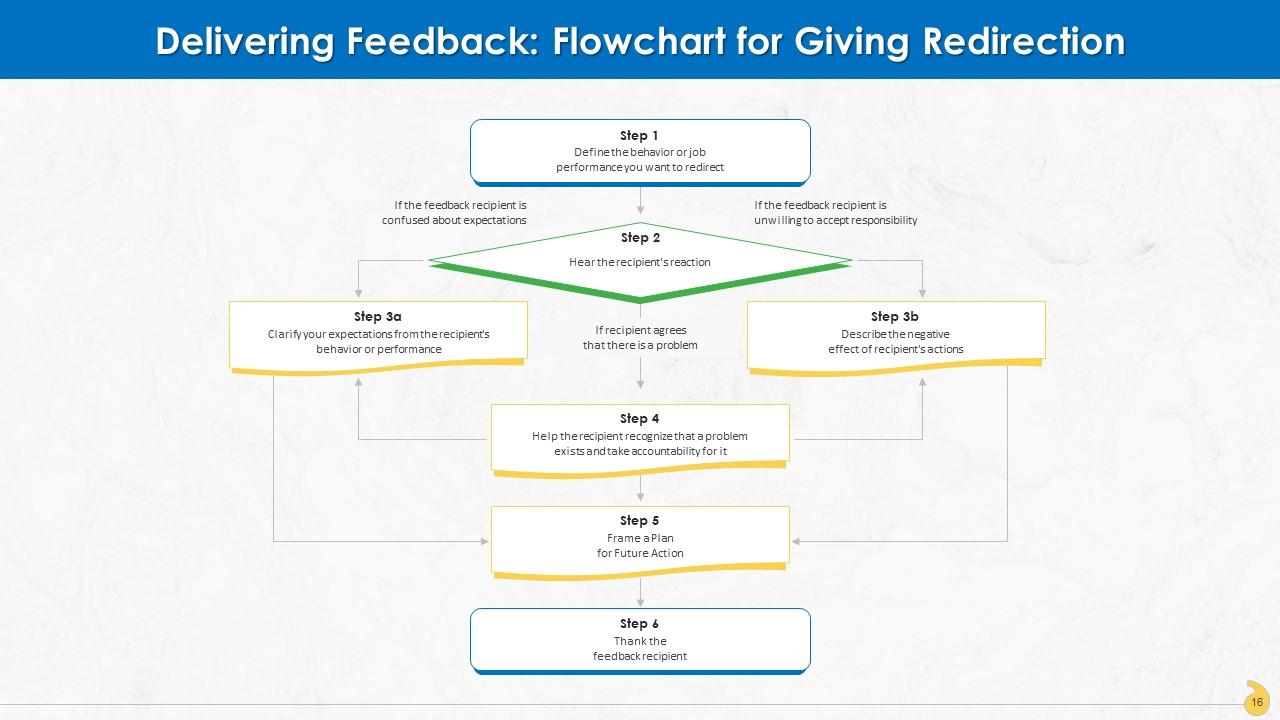
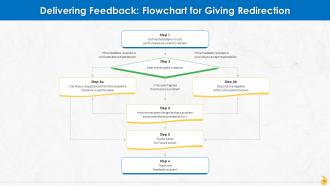
This slide depicts how redirection can aid in accomplishing feedback goals by identifying job-related performance and behaviors that do not contribute toward individual, group, or organizational goals. It also helps develop alternatives to achieve the same.
Slide 16
This slide represents stages involved in redirecting employees for achieving goals at the individual and organizational level.
Slide 17
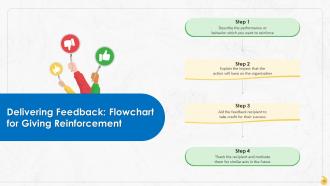
This slide depicts how reinforcement can aid in accomplishing feedback goals by determining job-related patterns and behaviors that contribute toward individual, group, or organizational goals and further encouraging the employee to continue doing so in the future.
Slide 18
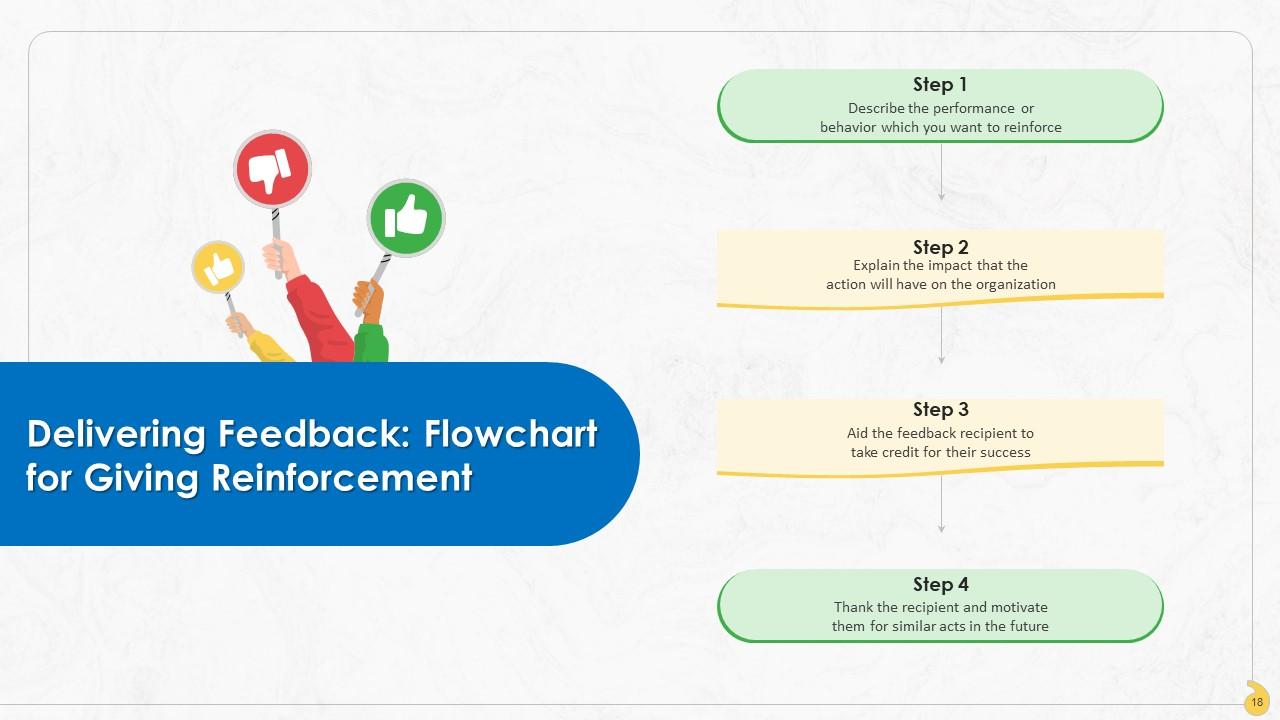
This slide represents stages involved in reinforcing the employees to continue desirable actions that contribute to positive changes at the organization.
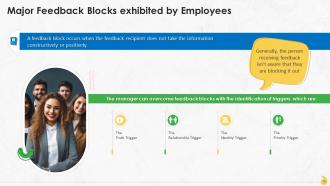
Slide 19
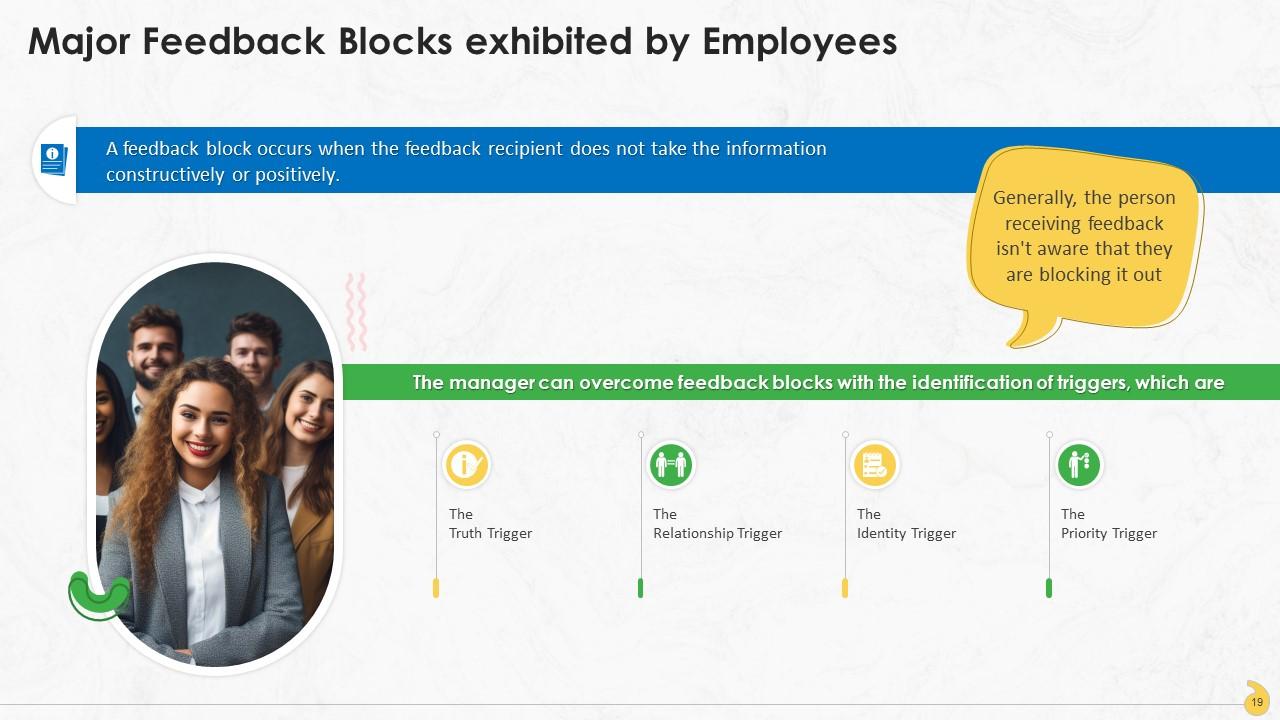
This slide contains information about the challenges that an effective feedback mechanism at the workplace faces. These are: The truth trigger, the relationship trigger, the identity trigger, and the priority trigger.
Slide 20
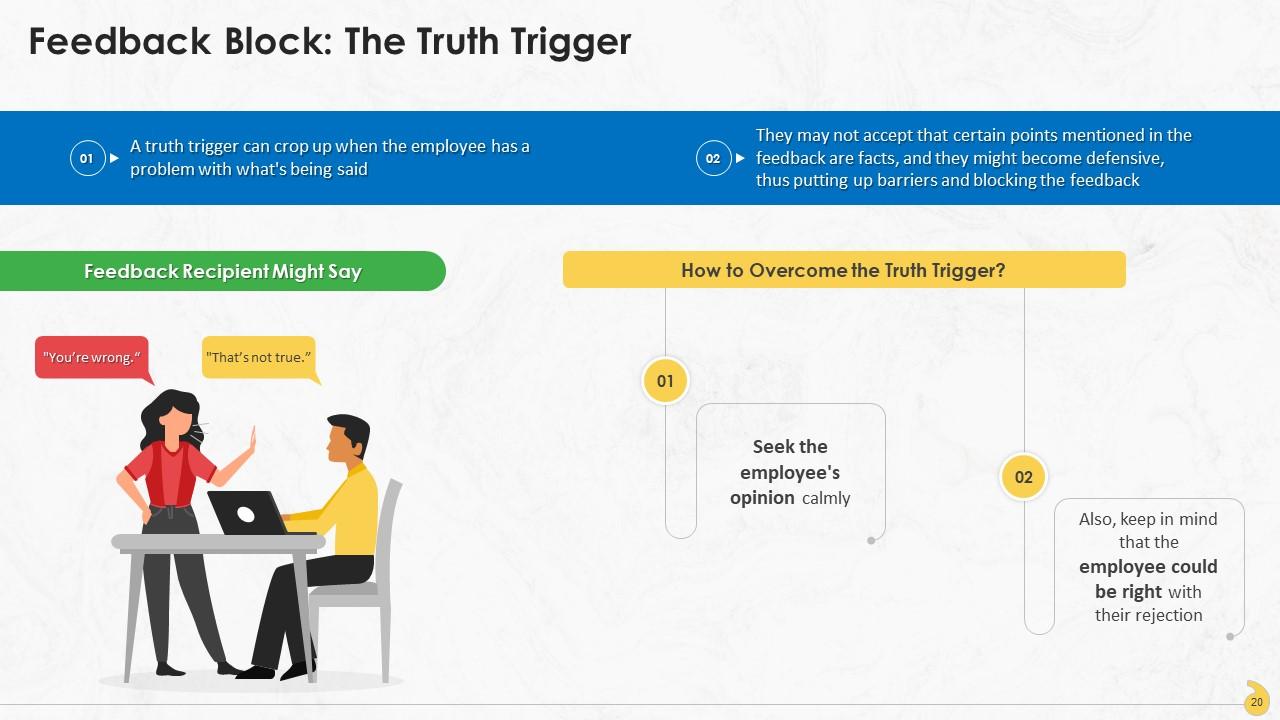
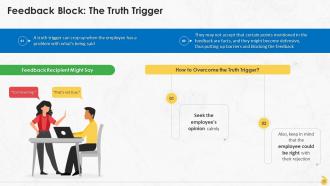
This slide represents the truth trigger as a feedback block at the workplace and the method to deal with such resistance. It can crop up when the employee has a problem with what’s being said.
Slide 21
This slide represents the relationship trigger as a feedback block at the workplace and the method to overcome that. When a manager encounters a relationship trigger, the best he can do is to accept the counter-criticism and communicate to the employee that the issue would be discussed later, soon.
Slide 22
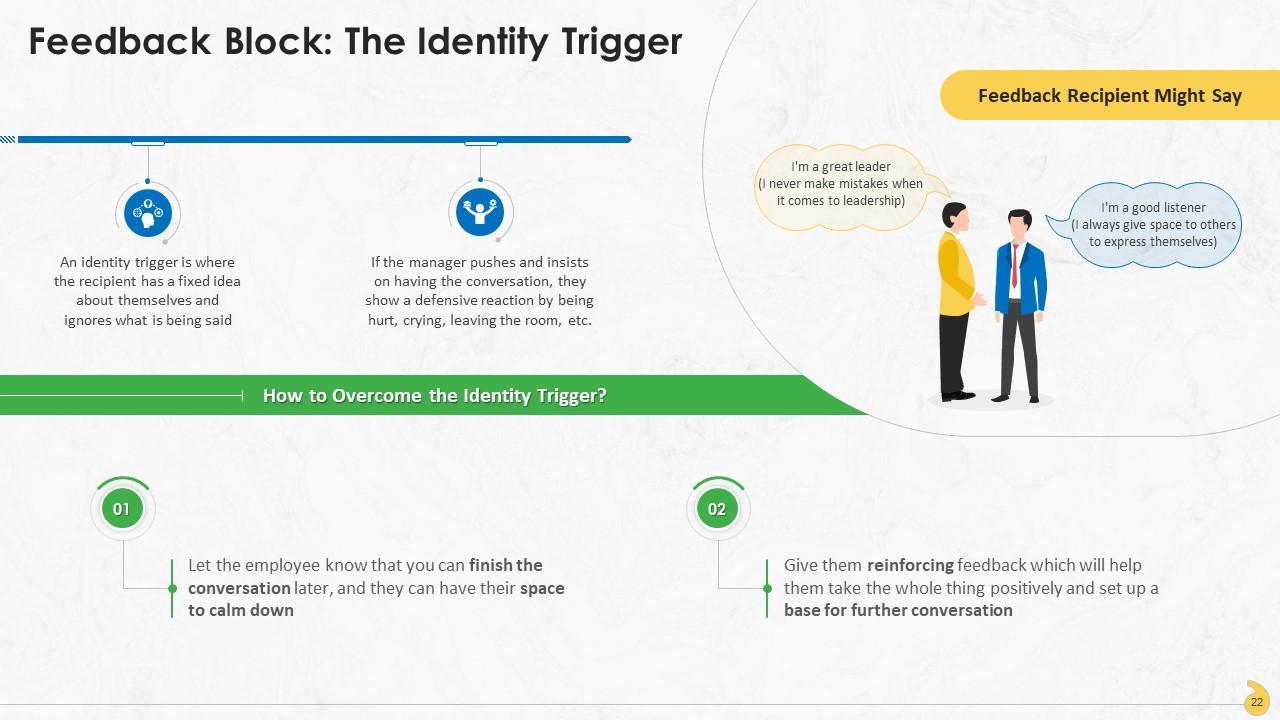
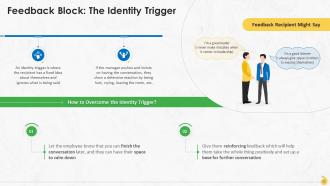
This slide represents the identity trigger as a feedback block at the workplace and the method to overcome it. An identity trigger is where the recipient has a fixed idea about themselves and ignores what is being said.
Slide 23
This slide contains information about priority trigger as a feedback block at the workplace and the method to overcome that. The priority trigger is the one where the recipient finds it hard to allocate attention to the manager’s feedback since they have other tasks which they feel are more important.
Slide 24
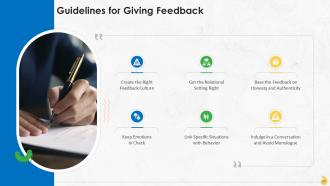
This slide lists the guidelines for giving feedback effectively at the workplace. These are: Create the right feedback culture, get the relational setting right, base the feedback on honesty and authenticity, keep emotions in check, link specific situations with behavior, and indulge in a conversation and avoid the monologue.
Slide 25
This slide contains information about creating the right feedback culture by being transparent about expectations and standards, giving feedback at small intervals, and the manager being open to accepting their own shortcomings.
Slide 26
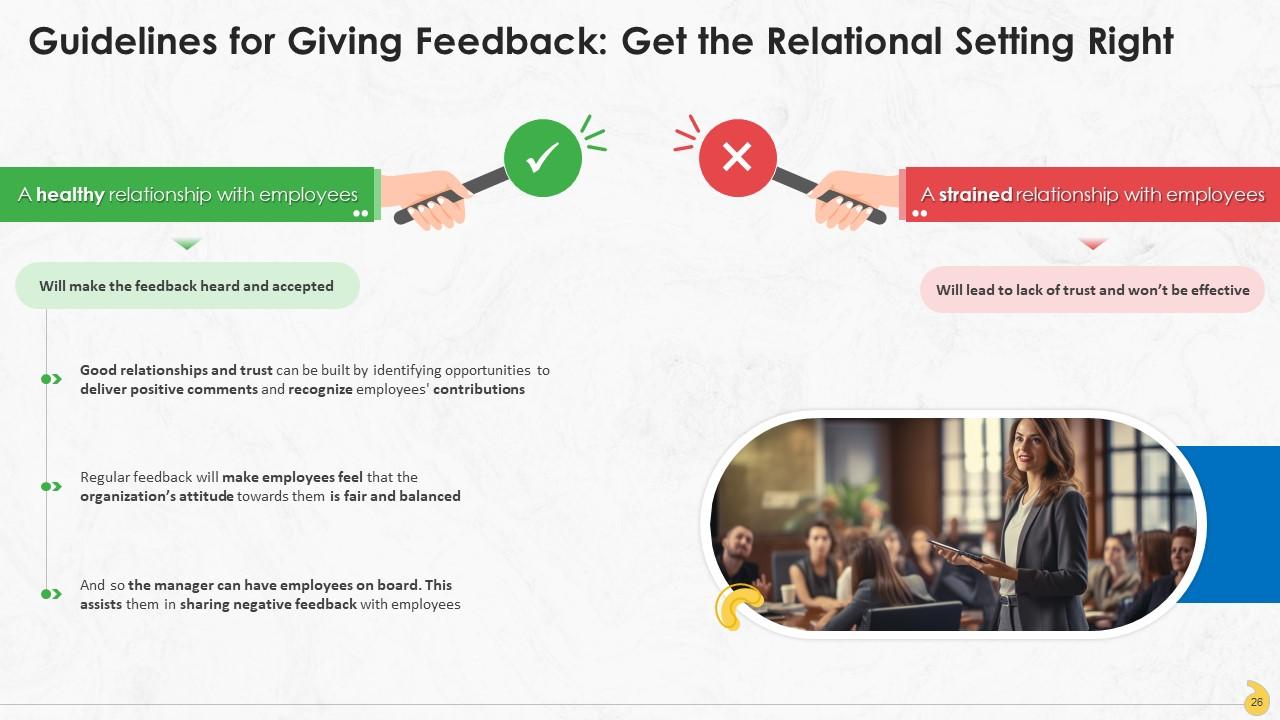
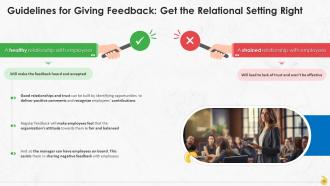
This slide contains information about getting the relational setting with employees right. A positive relationship ensures the feedback is heard and accepted. Building a healthy relationship requires giving sincere praise and positive comments when necessary. This practice will ensure that employees don’t become defensive when negative feedback comes their way.
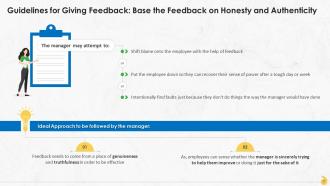
Slide 27
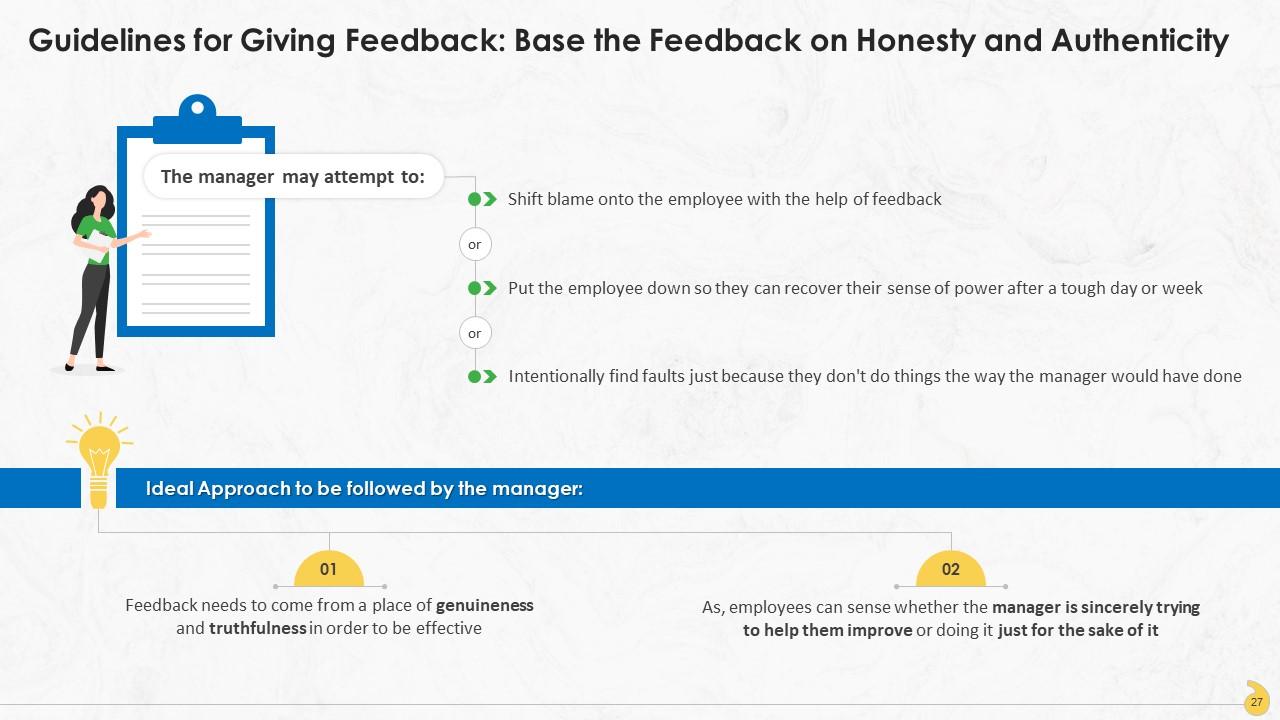
This slide showcases how effective feedback must be based on reality and the honesty of manager. The manager should share feedback only when they are clear about their own truthfulness. Employees can sense whether the manager is sincerely trying to help them improve or doing it just for the sake of it.
Slide 28
This slide highlights the importance of keeping emotions in check on the part of manager by taking into consideration the consequences their actions will bring. Sarcasm, attacking, venting and ranting will threaten employees’ dignity and can make them defensive.
Slide 29
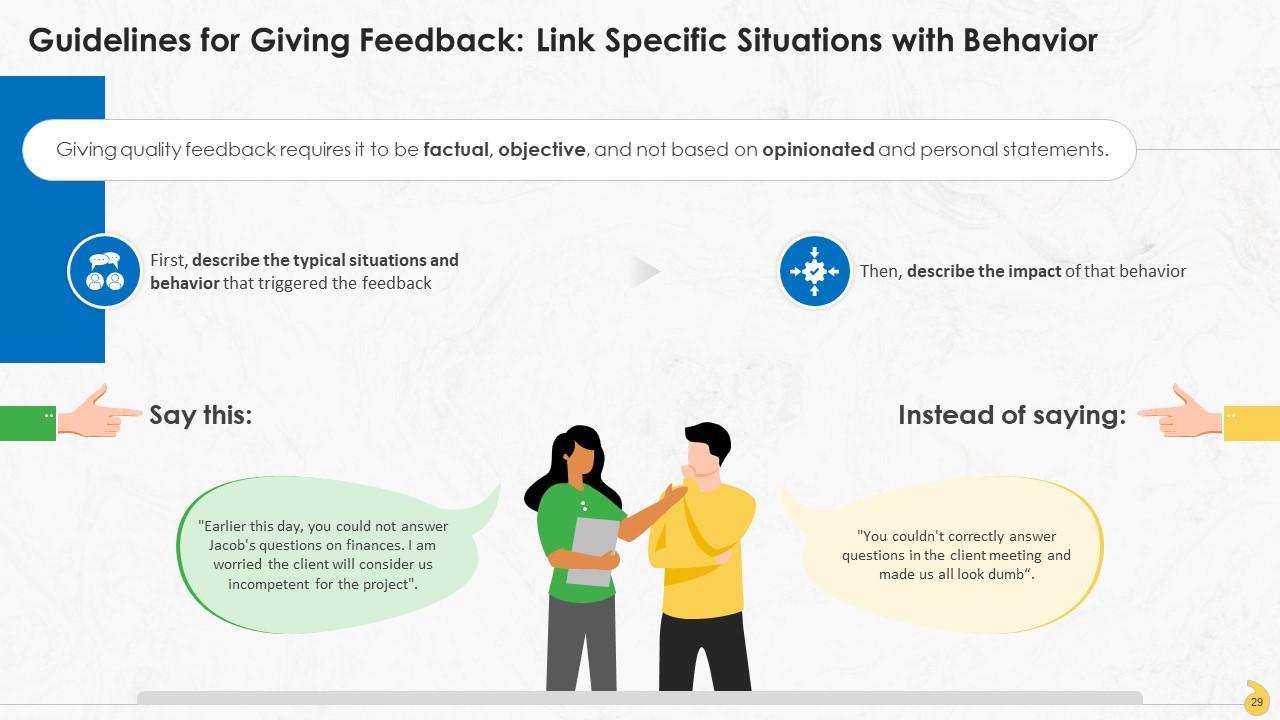
This slide highlights the need of linking specific situations with behavior for giving good, effective employee feedback. It should be factual, objective, and not based on opinionated and personal statements.
Slide 30
This slide contains information about having a conversation and ditching the monologue to give great feedback at the workplace. This ensures that the feedback recipient has interpreted the information correctly and is psychologically ready to change.
Slide 31
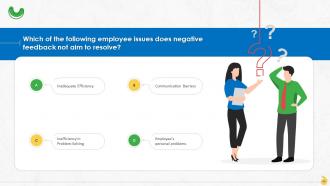
This slide lists issues that negative feedback aims to resolve such as communication barriers, poor interpersonal skills, difficulty aligning with organization, low motivation, inadequate efficiency, and inefficiency in problem-solving.
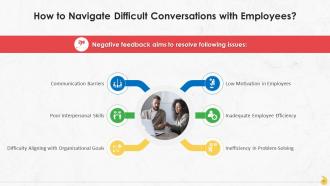
Slide 32
This slide provides information on guidelines that help a manager in having difficult conversations with employees. These are: Avoid using absolutes, communicate in specifics, use the “I” statements, listen actively, consider the conversation layers, prioritize building trust, brainstorm solutions together, and be aware of the tone.
Instructor’s Notes:
Guidelines to keep in mind for difficult conversations with employees are:
- Avoid Using Absolutes: Omit using words like “always” and “never” in the feedback as such words make the employee perceive feedback in a negative manner
- Communicate in Specifics: Present a specific situation or behavior to the employee while giving difficult feedback. Employees see these as the concrete basis on the evidence of which they will be able to amend their behavior or performance
- Use the “I” Statements: Converse using "I" words. For example, "I noticed that you missed the annual meeting”. This provides more personalized feedback to the employee
- Listen Actively: Difficult feedback can be constructively given by giving the recipient an equal chance to clarify their point. It is important to focus on how the other party has interpreted the feedback
- Consider the Conversation Layers: An honest and productive conversation is crucial for difficult feedback. Conversation can be layered by first describing what had happened, then explaining how you (as a manager) felt about what happened, and finally, how the situation or incident caused undesirable circumstances
- Prioritize Building Trust: Cultivating trust should be an ongoing process in the organization which will help the manager gain the trust and confidence of the employees. This practice will make the employees not take difficult feedback with a negative intent
- Brainstorm Solutions Together: Both the feedback giver and recipient should brainstorm solutions together during difficult feedback. It will help surface more robust solutions for the problem
- Be Aware of the Tone: It is essential to take extra care of the tone, while delivering feedback. Avoid being judgmental, arrogant, or sarcastic else it will dilute the whole purpose of feedback
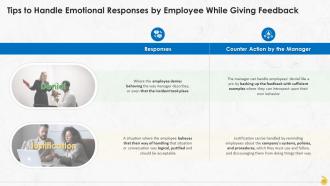
Slide 33
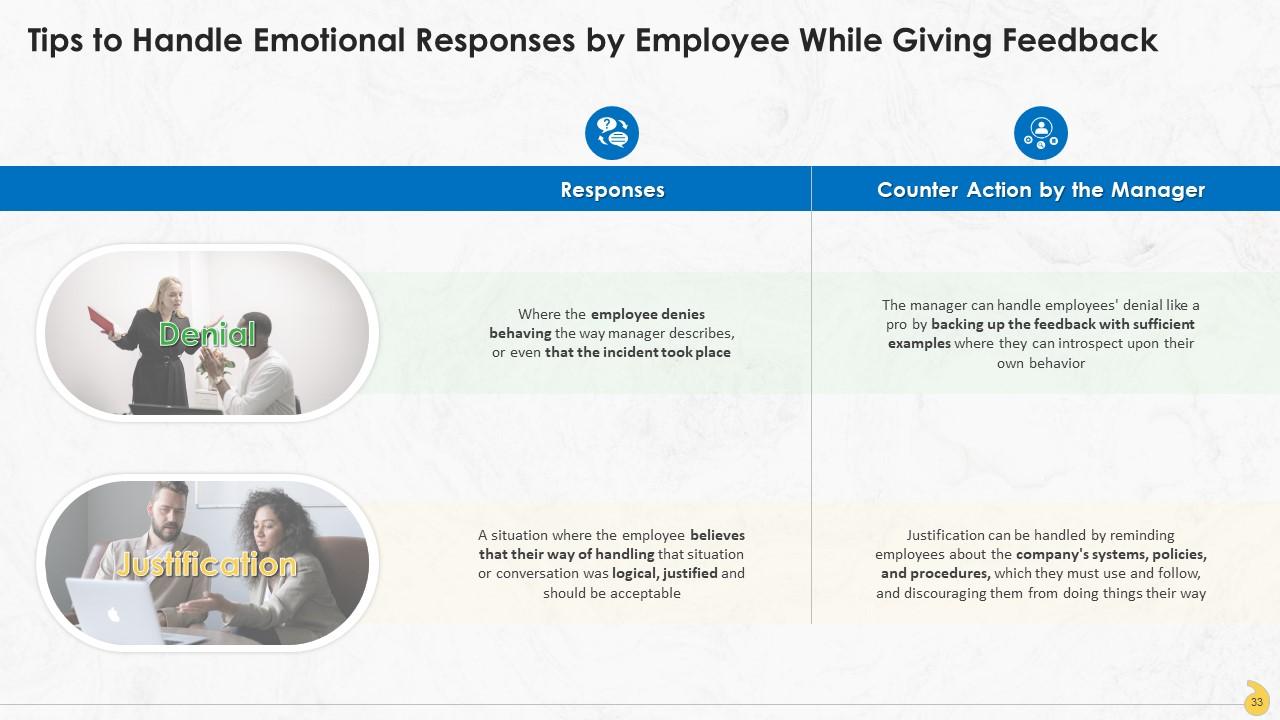
This slide contains information about the employees’ responses to feedback. This mostly takes the form of denial and justification. Also, the manner by which the manager can handle those responses is explained. Denial can be handled by backing up the feedback with sufficient examples where they can introspect upon their own behavior. Whereas, justification can be handled by reminding employees about the company's systems, policies, and procedures, which they must use and follow, and discouraging them from doing things their way.
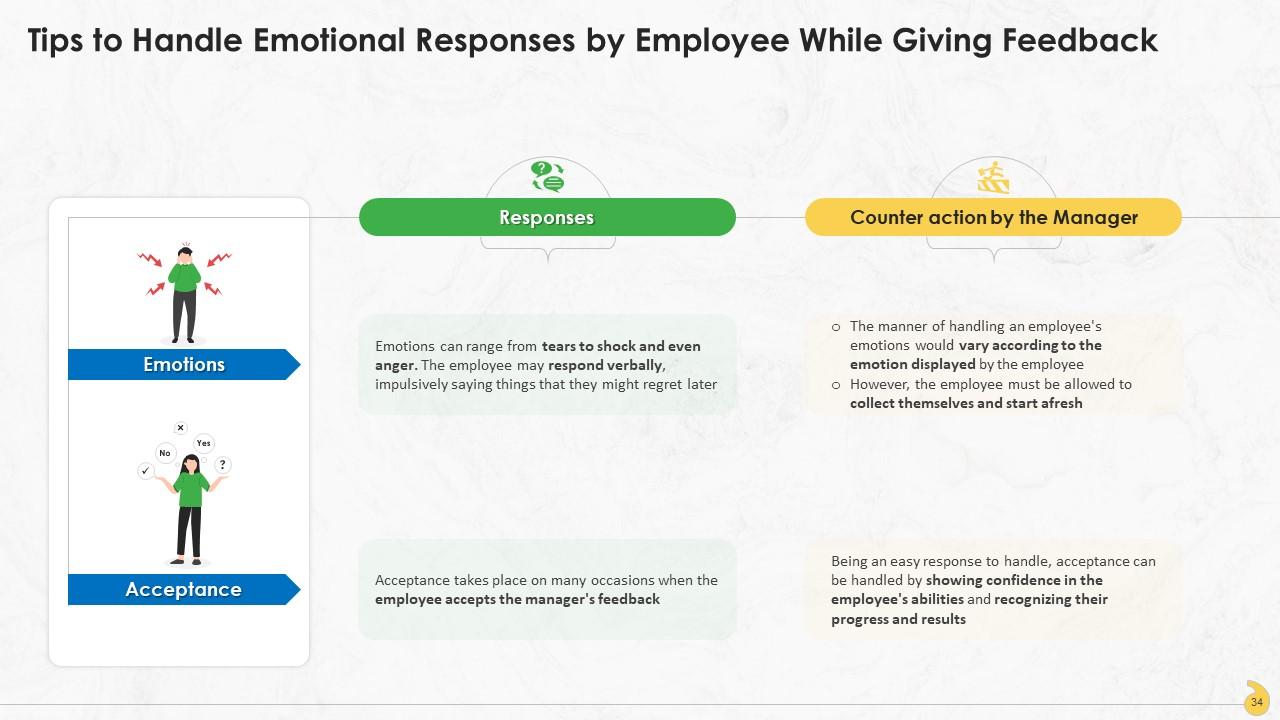
Slide 34
This slide highlights the situations of display of emotions and acceptance by the employee. Emotions can range from tears to shock and even anger. The employee may respond verbally, impulsively saying things that they might regret later. Acceptance, on the other hand, takes place on many occasions when the employee accepts the manager's feedback.
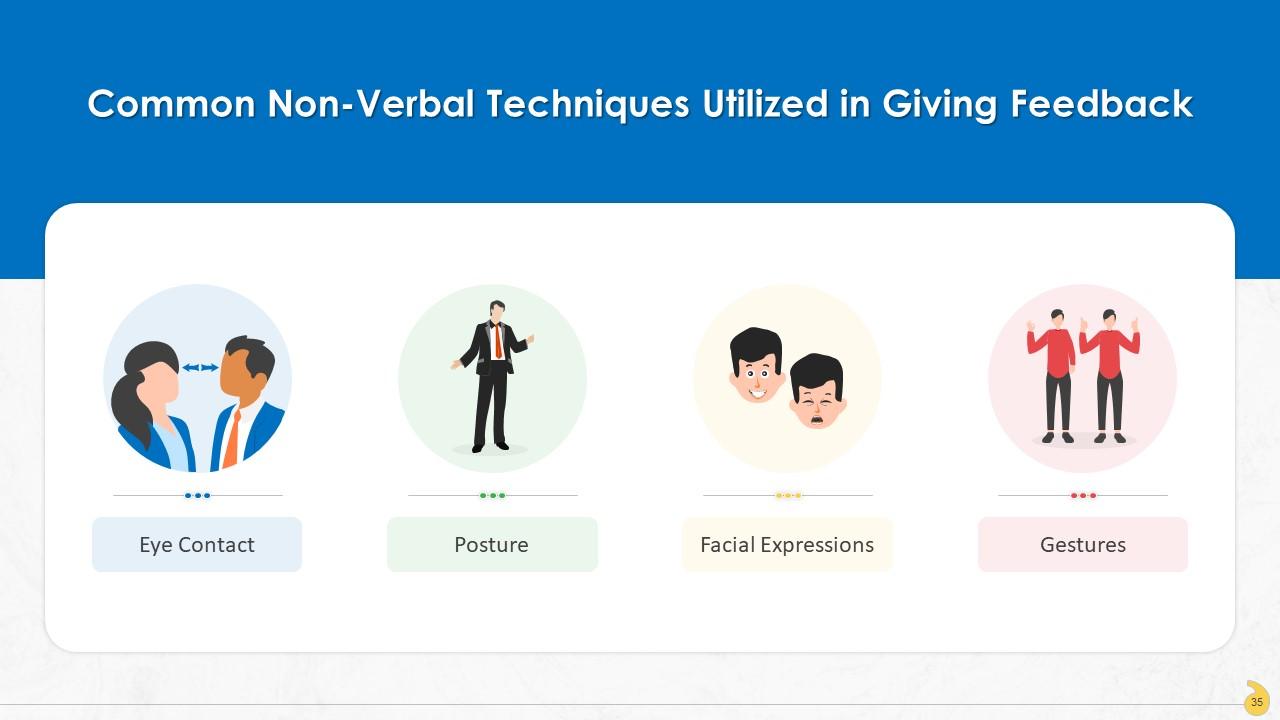
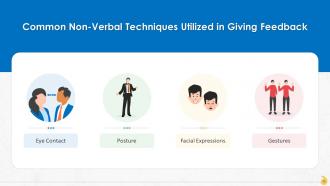
Slide 35
This slide lists non-verbal emotions that play a major role in delivering feedback to the employees. These are: Eye contact, posture, facial expressions, and gestures.
Slide 36
This slide highlights the importance of eye contact, while giving feedback to the employee. Eye contact associates a higher degree of intellect with the recipient, and flickering eyes or lack of eye contact undermines the impact of what is being said to the feedback recipient.
Slide 37
This slide contains information about the correct posture to be followed while giving feedback. An open posture, while facing the employee directly is considered right and makes the employee comfortable.
Slide 38
This slide represents how facial expressions contribute toward displaying manager’s emotions while giving feedback. The feedback recipient tends to unconsciously copy facial expressions of the manager, which is why it is important to have welcoming and pleasant facial expressions.
Slide 39
This slide contains information about gestures as playing a strong role in giving feedback to the employee. The common gestures to avoid are: finger-pointing, playing with hair, tapping, fidgeting, and wringing hands.
Slide 40
This slide represents a form for delivering feedback to the employee at the workplace that evaluates an employee on the basis of quality of work, attendance and punctuality, reliability/dependability, and their decision-making power.
Slide 41
This slide represents important pointers from the session: Strategies for delivering effective feedback. The trainer can use these to emphasize upon vital learnings from the session.
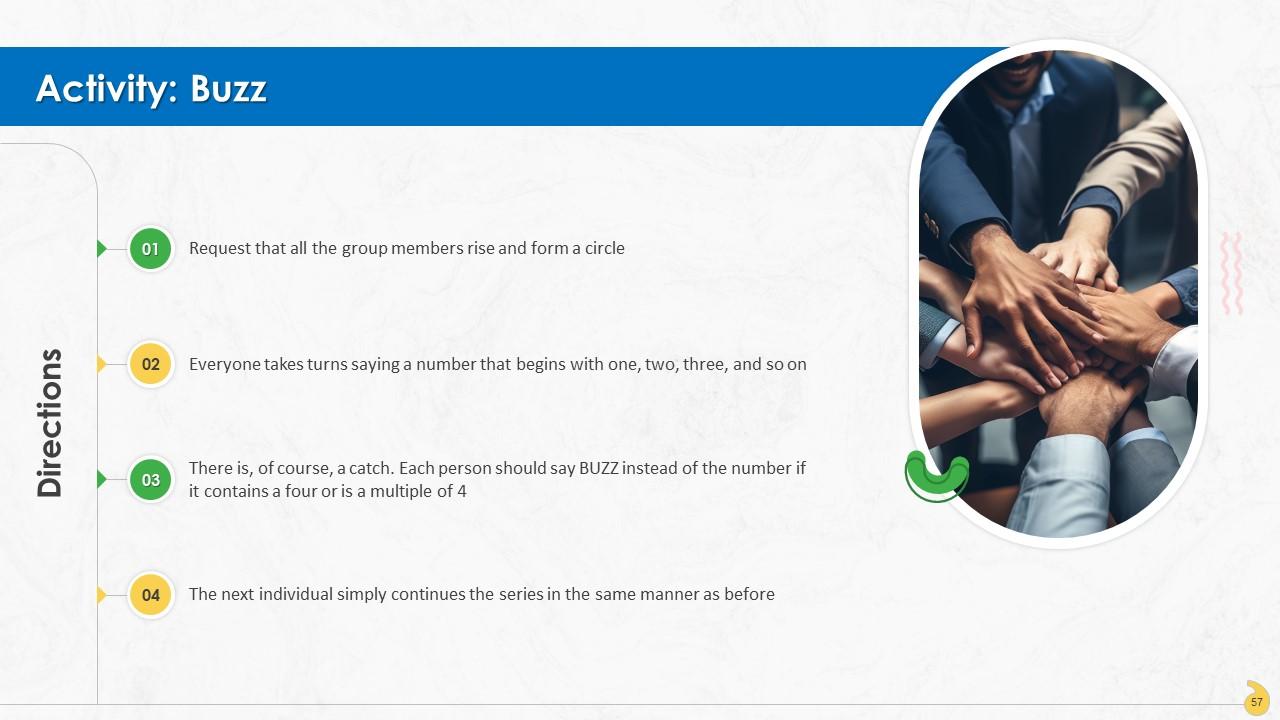
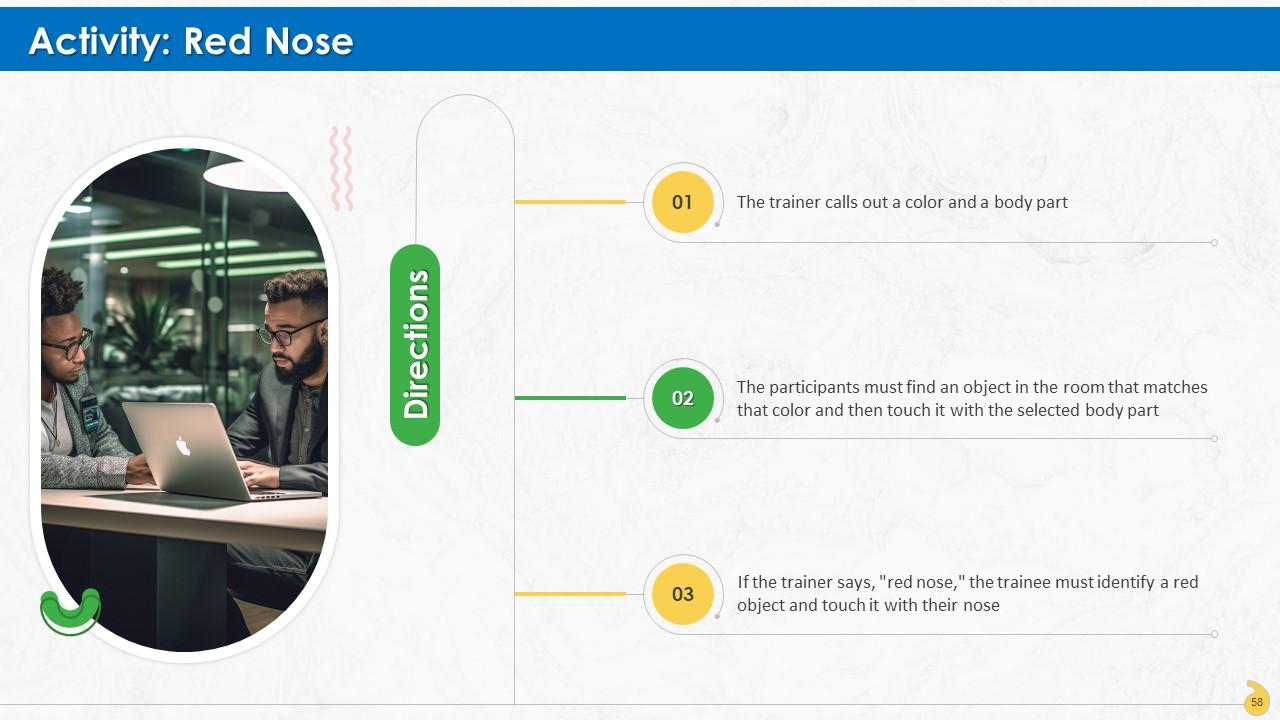
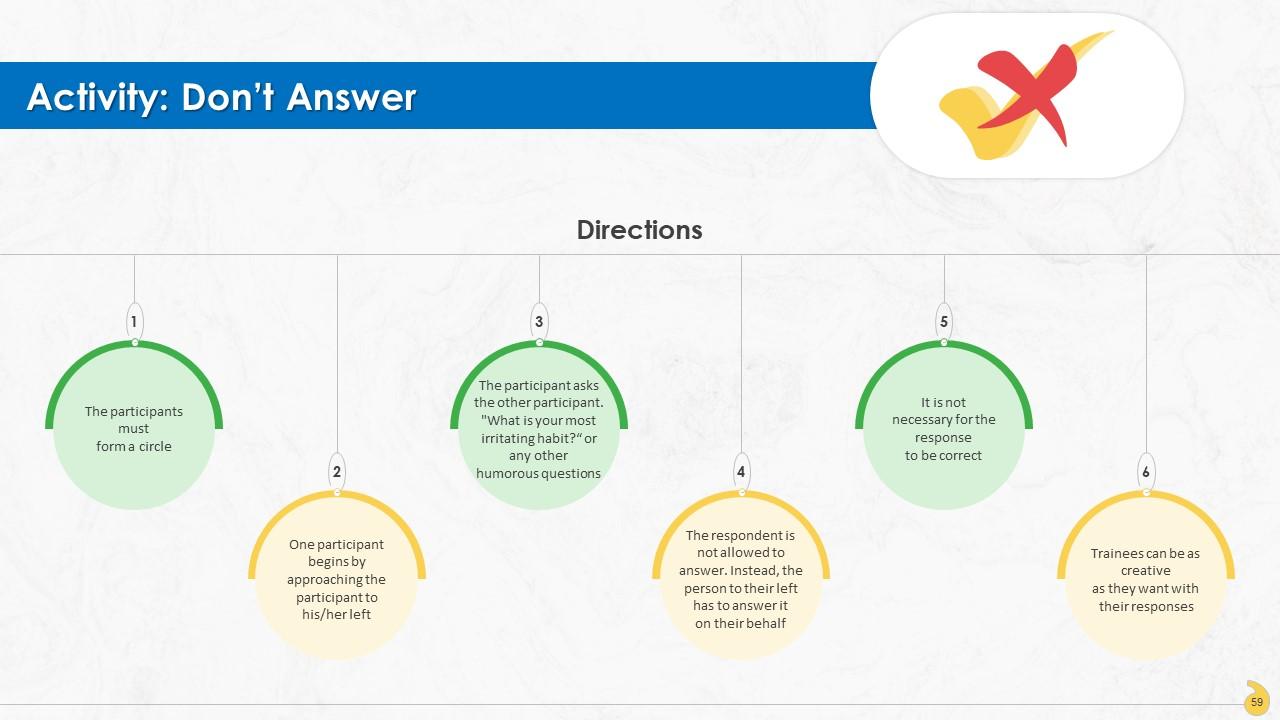
Slide 56 to 71
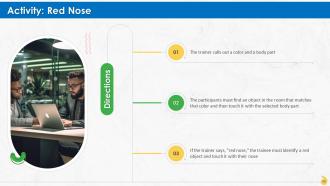
These slides contain energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 72 to 99
These slides contain a training proposal covering what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
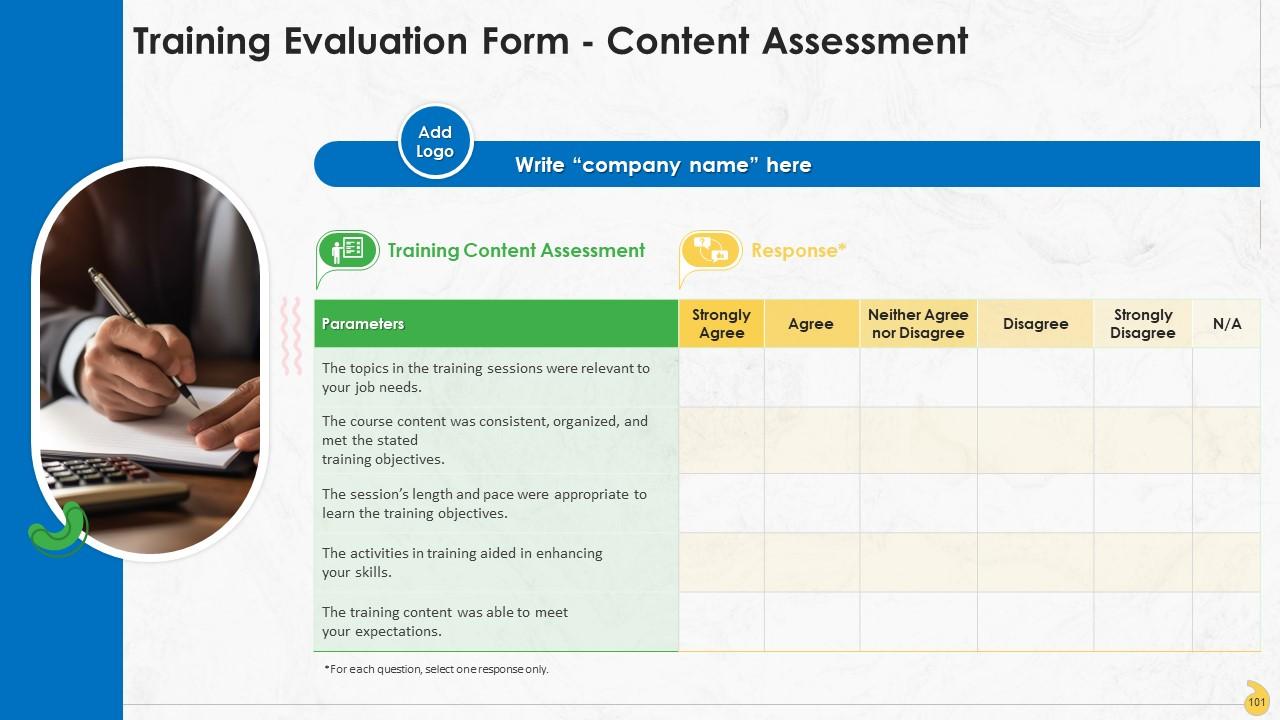
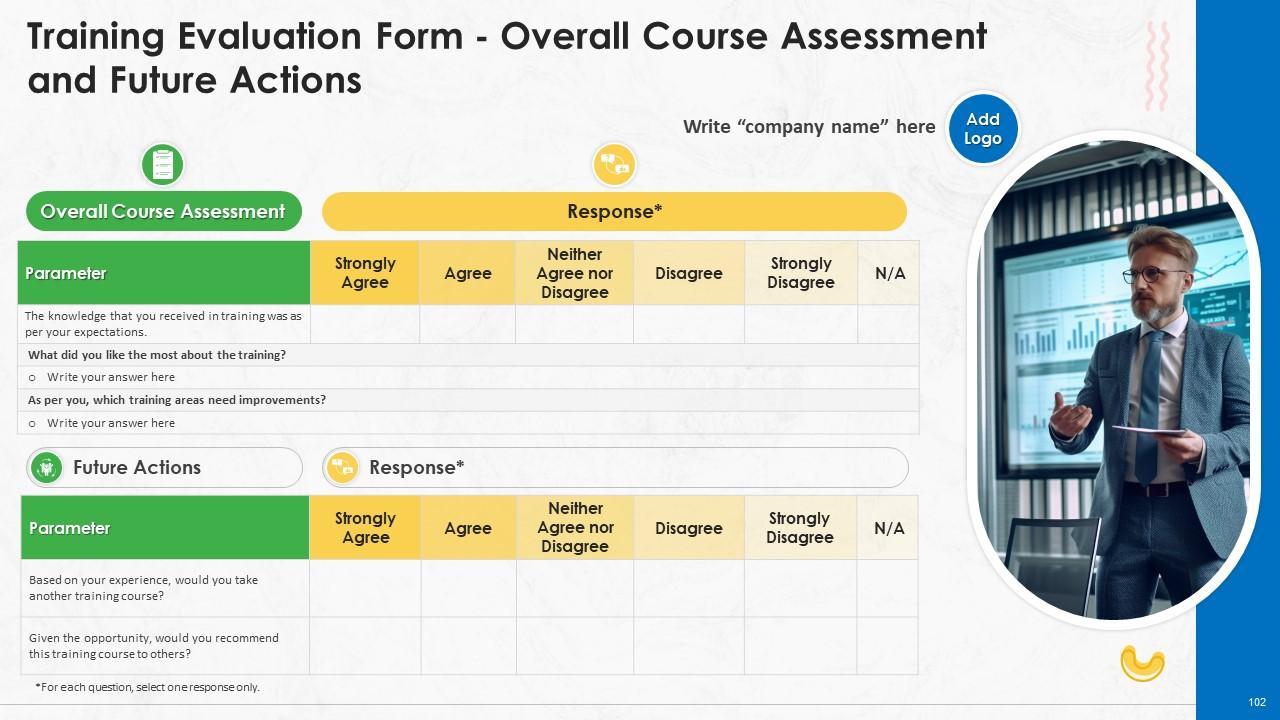
Slide 100 to 102
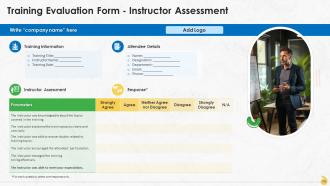
These slides include a training evaluation form for instructor, content and course assessment.
Strategies For Delivering Effective Feedback Training Ppt with all 111 slides:
Use our Strategies For Delivering Effective Feedback Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
The customer care of SlideTeam is very responsive. I was having a payment issue and they fixed it for me in no time.
-
Well-designed and informative templates. Absolutely brilliant!