The rise of automation has sparked controversy and lots of debate, with some fearing that machines will soon take over the world. But let's face it; no one wants to spend their days performing monotonous tasks when they can focus on higher-level thinking and innovation. As Dan Schulman, CEO of PayPal, said, “Automation is not about replacing humans. It’s about replacing tasks that are mundane, repetitive, and dangerous.” With that in mind, let's look at some of the latest examples of automation and how they have transformed our lifestyles.
Autonomous Vehicles: Automation transforms our lives by revolutionizing transportation with autonomous vehicles. Companies such as Tesla, Waymo, and Uber are investing heavily in self-driving car technology, which will change how we move around cities and suburbs. Autonomous vehicles are likely to lower the number of accidents, decrease traffic congestion, and allow people to focus on other tasks during their commute.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Chatbots and virtual assistants are already a major part of most customer-facing industries, for their efforts at providing service and support. The experience, so far, is that automation improves customer satisfaction and reduces the workload on human customer support agents, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks. With the development of natural language processing and machine learning, chatbots are becoming more sophisticated and capable of handling complex interactions. This makes them even more valuable.
If you are unsure about the advantages of automation and its profound impact on the world, it is time to get clarity.
To ensure your worldview and business understanding are in sync with the rest of the world, we have curated this all-encompassing guide that will equip you with comprehensive knowledge on the subject. This guide will cover everything from the evolution of automation to its latest breakthroughs and transformations, providing you with a thorough appreciation of the positive effects of automation on our world.
But wait, there's more!
If you're ready to take the plunge and embrace automation in your business, our guide will be a worthy companion, worth its weight in gold. It will serve as the first step towards the successful implementation of automation and moving forward with the world. This indispensable resource will provide you with a roadmap to navigate the automation landscape, enabling you to harness the full potential of this transformative technology.
Let our guide be your guide.
Table of contents
What is Automation
Types of Automation
Benefits of Automation
Automation in Manufacturing
Industries Using Manufacturing Automation
Automation in Business Processes
Use Cases of Business Process Automation(BPA)
Automation in Software Development
Automated Testing
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Potential Impacts of Automation on Society
Conclusion
Before we begin, explore this 95-slide guide on Automation, which covers every crucial element of it such as introduction, types, and advantages. It also discusses challenges, solutions, security, tools, and implementation with visual graphics. Click here to download this editable PowerPoint Presentation.
What is Automation?
Automation involves using cutting-edge technologies to manufacture and distribute goods and services with minimal human involvement. By implementing automation technologies, techniques, and processes, tasks that humans handled have been infused with greater efficiency, reliability, and speed. Automation finds applications across manufacturing, transport, utilities, defense, facilities, operations, and information technology.
Types of Automation
There are three primary types of automation, each with its distinct characteristics:
Fixed Automation: This automation is designed for a specific, repetitive task. The machinery is programmed to perform a single operation, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing. For instance, the production of circuit boards in the semiconductor industry.
Programmable Automation: This automation involves the use of computer-controlled machines that can perform varied tasks. Programmable automation allows machinery to be reprogrammed and adapted to perform many operations, making it more versatile than fixed automation. Examples of programmable automation include robotic assembly lines and CNC machines used in precision machining.
Intelligent Automation: This automation uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning algorithms to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of automated systems. Intelligent automation can handle complex tasks like natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics. Examples of intelligent automation include chatbots used in customer service and automated fraud detection systems in banking.
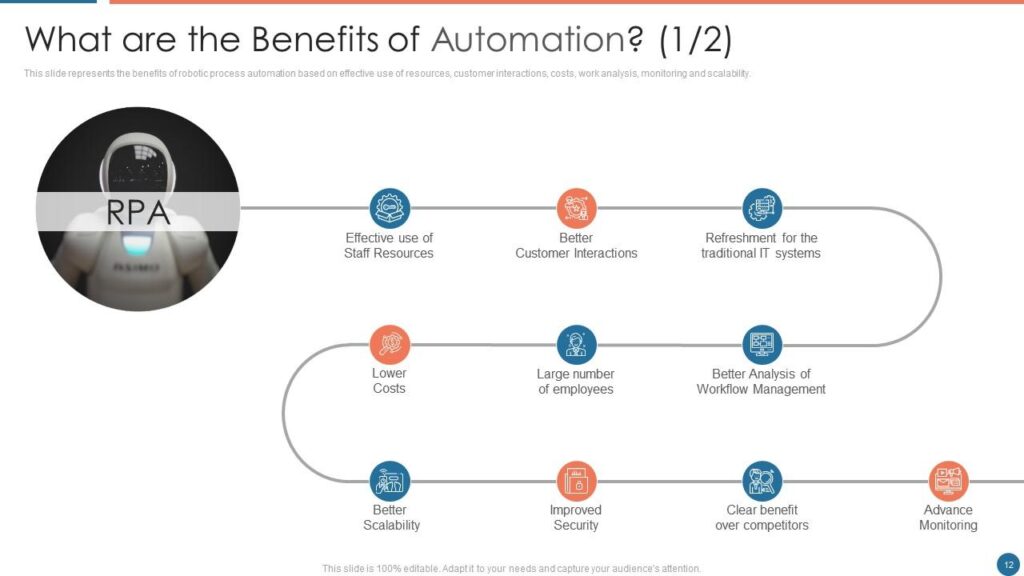
Benefits of Automation
Automation provides advantages across a variety of industries and sectors. Here are some instances:
Click here to download this editable template
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Automation eliminates the requirement of human intervention in repetitive and tedious tasks, allowing employees to focus on more complex activities. This leads to increased efficiency, productivity, and throughput. For example, in manufacturing, automated assembly lines can manufacture products at a much faster rate than manual labor.
Improved Quality and Consistency: Automation minimizes the chance of errors and ensures consistency in output. In food processing, automated systems can measure and mix ingredients accurately, resulting in consistent quality in the end product.
Cost Savings: Automation can reduce labor costs and minimize waste, leading to significant cost savings. For example, in logistics and transportation, automated inventory management systems can reduce the need for manual inventory tracking, minimizing the risk of errors and saving on labor costs.
Enhanced Safety: Automation can replace humans in dangerous tasks such as working in hazardous environments or handling heavy machinery, reducing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries. As an illustration, automated drilling systems can perform high-risk tasks in the oil and gas industry without exposing workers to dangerous conditions.
Improved Data Management: Automation can improve data accuracy, speed, and management. In finance, automated systems can handle significant financial transactions and perform real-time data analysis, enabling quick and informed decision-making.
Automation in Manufacturing
While automation can be traced back to prehistoric times, it gained significant traction during the Second Industrial Revolution, marked by Henry Ford's introduction of the moving assembly line and the establishment of large manufacturing plants.
D.S. Harder, the engineering manager at Ford, coined the term "automation" during the 1940s.
Looking to take your Manufacturing Automation to the next level? We've got you covered with a valuable resource that covers essential aspects you need to enhance your manufacturing process. Click here to download this content-ready PowerPoint Presentation.
In the manufacturing industry, automation refers to using equipment to automate systems or processes, aiming to increase production capacity while reducing costs. Electromechanical systems can be programmed to carry out tasks.
Automation can also be applied to manufacturing business management, as seen with automated inventory scheduling, data analysis for reporting, and handling tasks that may pose a risk to human workers, thereby improving workplace safety.
Industries using Manufacturing Automation
The practice of automation in manufacturing has become ubiquitous across industries, with notable advancements observed in sectors, as illustrated below:
Automotive – Employing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in tandem with human efforts has resulted in increased productivity and enhanced safety in the automotive industry. By automating precise manufacturing processes and reporting and documentation, RPA reduces the risk of human error. Additionally, built-in safety features can be programmed to stop the machine whenever an individual gets too close.
Medical Devices & Pharmaceuticals – The use of automated technology in the medical industry has proved advantageous in the documentation, reporting, and manufacturing of pharmaceutical products and medical devices.
Food & Beverage – Automation guarantees a uniform product for every customer and minimizes human involvement, improving food safety and decreasing recall risks. Automated inventory tracking and tracing, as well as reporting and analytics, can assist with decision-making to reduce food waste or product loss by adjusting scheduling and workflows.
Consumer Products – The consumer goods and products industry relies on automated processes to meet demand without incurring unnecessary costs, particularly during labor shortages. In consumer packaged goods (CPG) manufacturing, automation is visible throughout all stages, from assembly and packaging to material handling, shipping, inspection, testing, scheduling, and reporting.
Electronics & High Technology – In response to increasing demand for electronics and tech products, automated robotics can enhance production speed, eliminate defective products, and maintain optimal manufacturing conditions to create higher quality products at lower production costs.
Packaging – Automation has become a vital component of the packaging industry. It allows manufacturers to maintain product competitiveness and consistency, ensure employee safety, and improve packaging flexibility to accommodate more extensive and diverse product varieties.
Seeking a complete and practical guide to Automation in Logistics? We’ve got you covered with an impressive array of templates, samples, and examples to streamline your logistics operations. Click here to download this content-ready PowerPoint Presentation
The manufacturing industry is benefiting significantly from robotics. The robots are ‘becoming’ more intelligent, allowing them to perform complex tasks more efficiently and with greater consistency while minimizing risks.
The outlook for manufacturing automation appears extremely positive, given the current technological advancements in AI, robotics, machine learning, IoT, and other digital manufacturing technologies that offer better shop floor control.
Automation in Business Process
Business Process Automation (BPA) involves the application of technology to automate routine, repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to concentrate on more essential duties. By automating business processes, costs can be minimized, efficiency can be enhanced, and workflows can be streamlined from the simplest to the most intricate.
It's important to note that business process automation is distinct from business process management, a broader field focused on managing intricate, organization-wide processes.
Get ready to revolutionize your business processes with our cutting-edge PPT Template on Business Process Automation! Say goodbye to tedious manual tasks and hello to increased efficiency, accuracy, and profitability. Click here to download this editable deck on Business Process Automation.
Use Cases of Business Process Automation
Accounts Payable: Business process automation can be leveraged to automate the invoice approval process, from capturing data to routing for approval and processing payments. By eliminating manual intervention, this technology can reduce processing time and errors, freeing up employees to focus on strategic tasks that require human decision-making.
Customer Service: BPA can be used to automate customer service tasks like responding to common inquiries, routing these to the relevant department or team member, and escalating urgent issues to management. This automation can significantly improve response times and enable customer service representatives to focus on more nuanced queries, leading to higher customer satisfaction rates.
Human Resources: Business process automation can be applied to automate HR tasks like employee onboarding, performance management, and benefits administration. By reducing errors and ensuring compliance with company policies and regulations, BPA can increase operational efficiency and employee satisfaction.
Marketing: BPA automates marketing tasks such as lead generation, email marketing, and social media management. By streamlining these processes, BPA can help marketers maximize their efficiency and effectiveness, enabling them to focus on strategic campaigns and initiatives.
Sales: Business process automation automates sales tasks like lead qualification, pipeline management, and sales forecasting. By enhancing sales efficiency and accuracy, BPA can help sales teams build better relationships with prospects and customers, leading to higher conversion rates and revenue growth.
Determining the most appropriate business processes for automation is not limited to a few functions. Some key indicators that warrant automation include high task volume, the involvement of multiple personnel, time-sensitive nature, significant impact on other processes and systems, and the need for compliance and audit trails. Meeting all these criteria signifies that the business process is ripe for automation.
Automation in Software Development
Developing software and systems that supplant repetitive procedures and minimize human intervention is the essence of IT automation. IT automation accelerates the deployment of IT infrastructure and applications by automating tasks that previously required manual effort. This process enables software to configure and replicate instructions, procedures, and policies, leading to streamlining operations. With the rise of virtualized networks and cloud services requiring swift, intricate provisioning, automation has become an integral approach for helping IT teams provide faster, more consistent, and more secure services.
If you are looking for a Presentation focusing on Robotic Process Automation in IT, here’s a handy guide with stunning templates. Click here to download this feature-packed template.
IT automation is a powerful tool that can promote business scalability, generate substantial cost savings, and enable IT staff to concentrate on strategic rather than administrative work. Automating a broad range of data center and cloud operations expedites processes. Thanks to automation, IT environments can expand quickly with fewer errors, becoming more responsive to business needs.
A fully automated environment can reduce the time required to produce production-ready resources from several weeks to less than a day.
There are endless possibilities when it comes to the applications of automation, but some of the most prevalent ones are:
- Automating cloud services
- Automating resource provisioning
- Automating configuration processes
- Automating network management
- Automating security measures, such as monitoring and response.
Automated Testing
In automated testing, software tools, and scripts are used to automatically conduct tests on a software application or system, eliminating the need for human intervention. The primary objective of automated testing is to ensure that the software functions accurately and meets the desired requirements.
Automated testing is an efficient and faster alternative to manual testing as it can run multiple tests without getting tired, enabling developers to identify bugs and defects.
For instance, a website that offers products could use automated testing to test its checkout process. The computerized testing software can replicate customer actions such as adding items to the cart, entering billing and shipping information, and submitting payment. This process can be repeated to confirm the checkout process's correctness and ensure that no bugs or errors hinder customers from purchasing. With automated testing, developers can complete this process in a fraction of the time that manual testing would require, enabling them to concentrate on other aspects of the website's functionality.
If you are looking for reliable assistance on Automation Testing, this PowerPoint Presentation is the best resource. Click here to download this editable presentation now!
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is a software development methodology that integrates code changes and automated testing and continuously delivers changes to production. The goal of CI/CD is to improve the speed, reliability, and quality of software delivery.
Under CI/CD, code changes are merged into a shared repository several times per day. Automated testing ensures that changes work correctly and do not break existing functionality. After successful testing, code changes are automatically deployed to production.
Let's consider an example of a development team working on an e-commerce website. In this case, they could use the CI/CD approach to automate the deployment process for every new code change, enabling fast and reliable delivery of changes. With CI/CD, the code changes could be integrated, tested, and deployed to production within minutes, providing the development team with near real-time feedback and allowing them to make changes rapidly.
This presentation template will walk you through Intelligent Automation and its concepts that can help you build a smart organization. Click here to download this valuable template
Potential Impact of Automation on Society
The potential impacts of automation on society are both positive and negative. Automation technology can automate repetitive and labor-intensive jobs, leading to job losses in specific industries. But it can also create new, higher-skilled jobs, leading to economic growth and higher productivity.
In addition, automation can increase efficiency and productivity across industries by automating mundane tasks, allowing workers to focus on complex and higher-value tasks, leading to increased innovation and competitiveness.
Automation can also improve safety in specific industries by reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. However, automation can also widen the economic gap between those who benefit from it and those who do not.
Those who work in heavily automated industries may experience increased wages and benefits, while those in non-automated industries may experience job losses and decreased wages.
Social and psychological impacts of automation may include increased isolation due to reduced human interaction in specific sectors and increased stress and anxiety among workers who fear job loss due to automation. To ensure that automation benefits everyone, it is crucial to consider these scenarios and be responsible for implementing and regulating technology.
Conclusion
As we gaze into the future of automation, we cannot underestimate its enormous impact. While increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation are undeniable benefits, we cannot turn a blind eye to the negatives of automation.
Job losses and displacement, economic disparities, and ethical dilemmas all pose significant challenges that we must address as a society.
We, however, cannot let these obstacles hinder us with fear or prevent us from embracing the possibilities that automation offers. Together, we must ensure that automation is introduced at a pace that allows for more options for those displaced as well. The focus has to be on creating a future where everyone reaps the rewards.
Let us move forward with unwavering hope and determination, confident that with the right attitude, we can harness the power of automation to usher in a brighter, equitable future for all.
FAQs on Automation
Will automation lead to job loss?
Automation has the potential to revolutionize the job market by eliminating repetitive or labor-intensive tasks in specific industries, which could lead to job losses. But it's essential to recognize that automation also has the potential to create new, innovative jobs that require advanced programming and engineering skills. These new positions could contribute to economic growth and increased productivity. The impact of automation on employment will depend on how we manage the transition and integrate new technologies into the workforce, creating more opportunities for workers to specialize and learn new skills that will benefit both individuals and society.
How can we ensure that automation is implemented responsibly and ethically?
We must take many steps now to ensure the responsible and ethical implementation of automation.
Firstly, we need to establish clear regulations and guidelines for using automation technology, including ethical frameworks and standards to govern the development and deployment of automated systems.
Secondly, we must prioritize transparency and accountability, which involves making decision-making processes behind automated systems traceable and understandable and upholding accountability for any negative impacts.
Thirdly, we should invest in education and training programs to ensure workers have the necessary skills to adapt to an increasingly automated workforce. This may include developing new training programs for individuals at risk of displacement due to automation.
Finally, we must hold open and honest conversations to discuss the potential societal impacts of automation, with a collective focus on finding solutions that prioritize the well-being of all individuals.
Will automation make our lives easier or more difficult?
Automation has the potential to make our lives easier by streamlining tedious and repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more meaningful pursuits. For instance, automation can improve efficiency and productivity in industries such as manufacturing and transportation, reducing human error and improving safety. Automation can also enhance the quality of our lives by providing personalized and seamless experiences, such as in healthcare and entertainment. However, implementing automation must be responsible and ethical, focusing on minimizing negative impacts and prioritizing the well-being of all.




 Customer Reviews
Customer Reviews