Unleashing excellence in your projects starts with the leaders at the helm! Imagine being on a ship navigating through rough waters, where every decision, every move, and every action of the captain determines the safety and success of the journey. Project Quality Management works much in the same way.
Dr. W. Edward Deming, a prominent leader of Total Quality Management, once said, “Quality begins with the intent, which is fixed by the management,” This quote captures the essence of what makes Project Quality Management crucial. It's the top brass that sets the bar for quality and ensures that everyone on the project team is aligned with that standard.
Also, quality isn't just about the work being done, it's about the management of that work. That's why
The Importance of the “Quality of Management” is equal to The Importance of the “Management of Quality.”
When the management is committed to excellence, it's contagious, and everyone on the project team rises to the occasion.
Now is the time to take your projects to new heights with a strong focus on Project Quality Management and watch your team bring home exceptional results!
But here's the catch, intent alone is not enough. The management team must be actively involved in monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments to keep quality at the forefront. That's why effective Project Quality Management requires a proactive approach. It's time for organizations to raise the bar and make quality a critical component of project success. It's time to say goodbye to mediocrity and hello to excellence.
This guide will walk you through the process of Project Quality Management with an actionable plan.
You will learn the following:
1. Analyzing Quality-Related Concerns
2. Implementing a Quality Management Plan
- Assigning Quality Standards
- Project Quality Management Gantt Chart
- Quality Assurance
- Quality Control
- Quality Testing
3. Handling Risk in Project Quality Management
Let’s delve into these topics on a one-on-one basis.
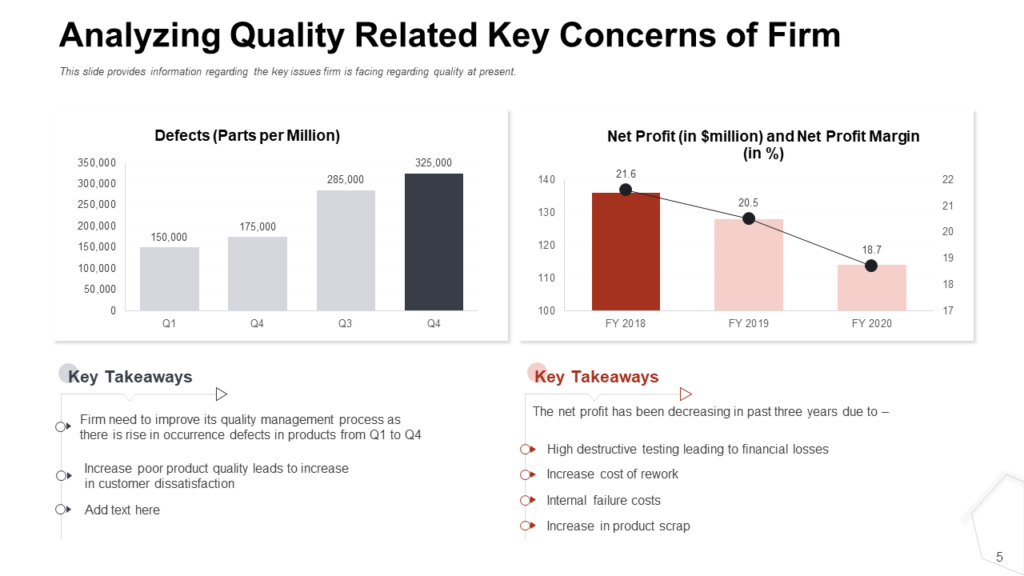
STEP 1: Analyzing Quality-Related Concerns
The initial and paramount step in Project Quality Management is the assessment of key considerations that impinge on quality. This process involves identifying and evaluating issues that could impact the project’s quality and success.
The six real causes of quality issues in a project are:
- Lack of organization: A disorganized project causes confusion and miscommunication, resulting in delays and mistakes.
- Lack of training: A team that lacks proper training may not have the skills and knowledge necessary to produce high-quality work, plaguing the project with errors and mistakes.
- Lack of discipline: A lack of discipline causes chaos. Mistakes and unnecessary delays arise.
- Lack of resources: Paucity of major resources, such as adequate staff or sufficient budget, can limit a team's ability to produce quality.
- Lack of Time: Time constraints can make it challenging to complete the project to a high standard, as there may not be enough time to make necessary revisions or to test the project.
- Lack of Management Support: Without the support of senior management, a project may not receive necessary resources and attention, leading to quality issues and other problems.
One effective way to present your project's quality analysis and impact on your business is using vivid visuals, relatable case studies, or interactive elements that keep your audience engaged and interested.
Remember, the goal is to highlight the importance of addressing these causes of quality issues and emphasize the positive impact a successful quality management plan can have on your project and overall business success. Get creative and make your presentation compelling and informative using this pre-designed template for analyzing quality concerns. Click here to download this editable template.
STEP 2: IMPLEMENTING QUALITY MANAGEMENT PLAN
Executing a Quality Management Plan involves scientific and artistic elements. It requires systematic methodology, data-driven decisions, and effective communication with team members. This section of the guide will assist you in creating high-quality and practical product standards. Let’s begin:
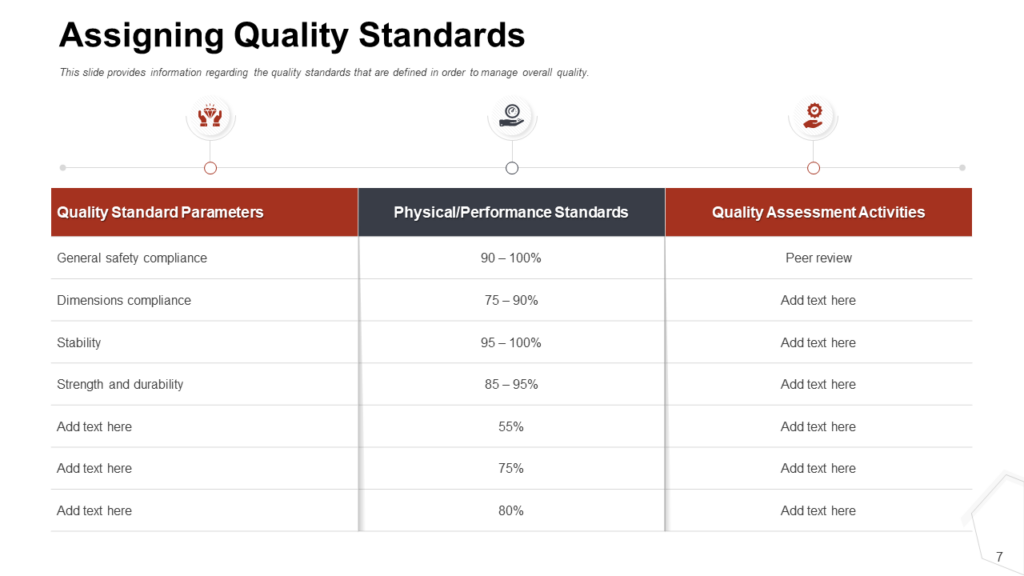
Assigning Quality Standards
This process involves establishing standards that guarantee the desired quality of deliverables. These must be in compliance with industry best practices, company policies, or client requirements. For instance, if the goal of the software project is to create a user-friendly and efficient application, the quality standards might include a response time of less than 2 seconds. An intuitive interface and compatibility across multiple devices are additional quality parameters that must be met. Once these quality standards have been established, they serve as a benchmark for measuring the progress and success of the project.
Here's a sample showcasing a practical way of assigning quality standards. You can use this editable slide as a reference document to ensure that each deliverable meets defined quality criteria. Click here to download this content-ready presentation.
Project Quality Management Gantt Chart
Using Gantt charts can help supervisors track the progress of quality control activities like testing, inspections, and audits. This helps project managers monitor the status of quality-related tasks, ensure on-time completion, and make adjustments.
This convenient Gantt Chart Template provides a comprehensive overview of key tasks such as Analysis, Design, Development, and Testing and their respective sub-tasks. With this template, you can easily track each activity's timeline and the individuals responsible. Ready to simplify your project tracking? Simply click here to download the fully editable slide!
Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) encompasses all aspects of the development process, from inputs to outputs, that enhance the likelihood of a successful outcome.
QA is a proactive approach that eliminates potential bugs (for software products) or defects (physical products) during development. It is integrated into the product or software development lifecycle and requires collaboration between stakeholders, including Business Analysts, Developers, Testers, and Stakeholders. By specifying and establishing requirements for both the development process and quality standards, QA helps improve the efficiency of the project team.
A comprehensive QA strategy for a software product should address the following areas:
- Governance, financial reporting, stakeholder engagement, and risk management
- Assessment of project team skills and training needs
- Communication and collaboration processes
- Methodologies used
- Document control procedures
- Gathering of requirements and definition of non-functional requirements
- The architecture of the application/service
- Testing approach
- Test environments such as QA, Staging, UAT, and production
- Continuous integration and delivery pipelines
- Version control and branching policies
- Design standards and reviews
- Coding standards, code quality assessments, and code reviews.
The sample presented below exhibits an optimal method of organizing your quality assurance endeavors to ensure uniformity. This framework draws all team member's attention to the project's quality benchmarks, the frequency of quality assurance activities, the personnel involved, and any relevant remarks. Click here to download the customizable template.
If you seek a comprehensive guide that centers solely on "Quality Assurance," we highly recommend perusing this enlightening PowerPoint Slide Deck on Quality Assurance Program. It features pre-prepared templates with information on QA concepts such as stages, underlying infrastructure, systematic framework, process flow, and the extent of coverage. This resource is sure to aid you in building a devoted team for your project. Click here to download this PowerPoint Presentation.
Quality Control
Up next, we delve into Quality Control (QC) — a suite of procedures aimed at guaranteeing the excellence of a product or service. The objective of QC is to ensure that the processes outlined in the QA strategy are executed. QC centers around evaluating the quality of the final product, while QA deals with the development process.
The primary focus of QC is to validate that the product adheres to the customer's specifications and requirements. If any issues or problems are detected, these must be rectified before delivery to the customer. This confirms that the product functions as intended.
Testers with specialized expertise perform QC activities, which include Walkthroughs, Testing, Inspection, and Review.
The Importance of Quality Control
The production process is costly, labor-intensive, and potentially hazardous. Lack of quality control measures can lead to the release of faulty products, resulting in liabilities and harm to consumers. Quality control inspectors play a crucial role in identifying and rectifying underlying causes of faults, if any, to ensure the safety and reliability of products.
The methodology for quality control varies depending on the product or industry in question. In the automobile manufacturing industry, for instance, quality control ensures that parts meet established specifications and tolerances. Through rigorous quality control, engines, drive trains, and other mechanical components are guaranteed to operate efficiently, smoothly, safely, and according to their intended design.
In the electronics industry, quality testing encompasses the use of electrical current measurement instruments and stress testing procedures.
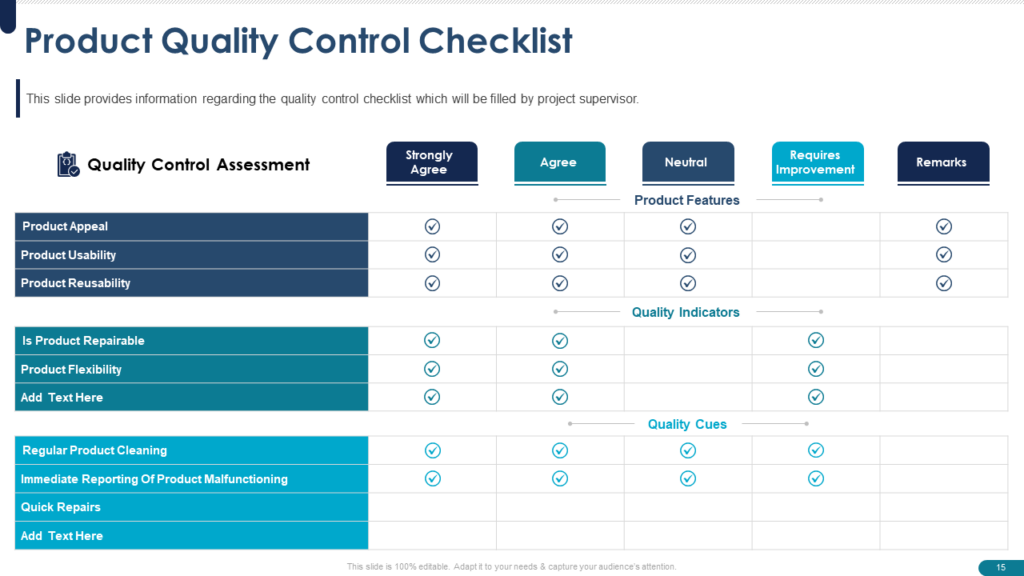
Also, using a Quality Control Checklist is an essential part of any project development. With its use, teams can systematically verify that critical components have been tested and reviewed, reducing the likelihood that important details will be missed.
A checklist template provides a pre-existing framework to check on processes eliminating the need to start from scratch, saving time and effort. It also ensures consistency across projects, standardizes quality control processes, and leads to increased efficiency and reduced risk of defects and errors. You can use this kind of checklist to create one for your project. Click here to download this editable template.
As we have explored the essential aspects of Quality Assurance and Quality Control, it is crucial to mention an informative resource before moving ahead into the next stages. To gain a comprehensive understanding of these critical concepts and ensure the success of your project, we highly recommend exploring this comprehensive PowerPoint Presentation. Click here to download this PPT Presentation entailing complex graphics, charts, and diagrams.
Quality Testing
As the development phase nears its conclusion, what follows is “Testing.” It encompasses functional, non-functional, and acceptance testing, to uncover any software faults or bugs. The objective is not just to detect any issues but also to guarantee that any detected defects are thoroughly remedied, without side-effects.
The testing process includes activities such as planning, test case design, test execution, defect reporting, and test reporting. Combining both automated and manual testing methods is crucial in creating an effective QA process for your product.
While automation has its advantages, it may not always be the best fit for all your testing needs. Supplementing your in-house manual testing with crowd testing can provide you with the benefits of testing on a larger scale in a time-efficient manner.
Below is a consolidated Quality Testing Template that offers a structured approach for testing and ensures clear communication with stakeholders. This template will streamline your quality test process and promote transparency. Click here to download this customizable PPT Template.
Testing Stages
An ideal testing process includes the following stages:
- Test Strategy: A statement outlining the levels, methods, tools, and techniques used for testing the system to meet the organization's needs.
- Test Plan: A plan to verify that the system meets design and functional specifications, detailing objectives, approaches, responsibilities, and procedures needed.
- Test Case Design: Identification of test cases for each module of the system to be tested, with criteria for success.
- Test Procedures: Steps for executing test cases, documented in a separate test procedure specification.
- Test Result Documentation: Recording the number of test cases executed, errors, and nature of errors, assessed against criteria in the test specification.
STEP 3: HANDLING RISK IN PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT
No project is successful without a proper risk assessment.
Imagine this scenario: Your organization has been given a new project, and as the project manager, you have outlined the project charter, scope, and other essential aspects with stakeholders' approval. The project is underway, but suddenly, a critical team member must take an unexpected and extended leave. Without a backup plan in place, the project's deadline is impacted. This leads to rushed hiring, resulting in increased costs and decreased quality. The risk of unexpected absences turned into a problem that could harm the project's progress. With a contingency plan, you would have been better equipped to ensure its success.
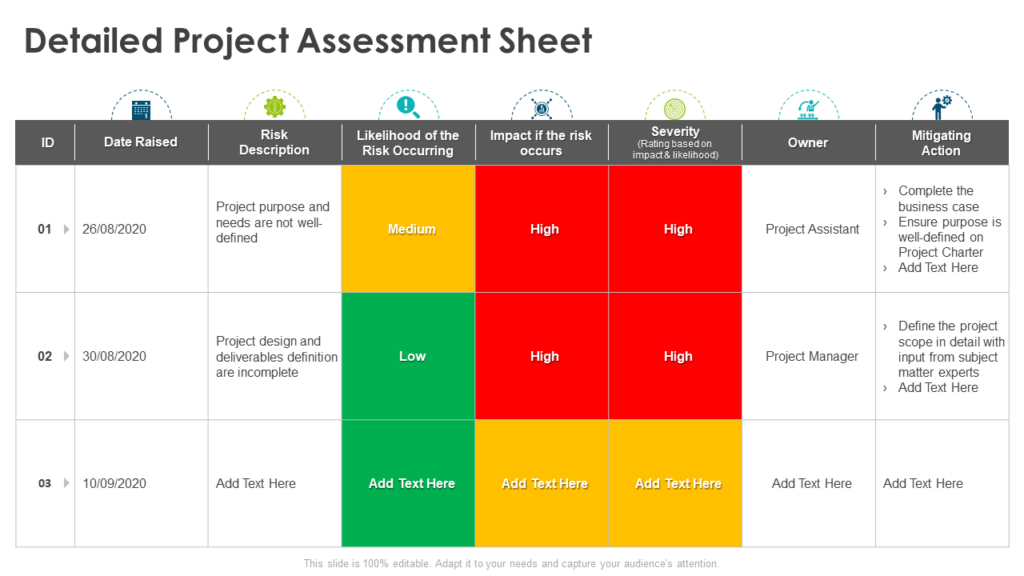
This is where a risk matrix comes in handy. It allows you to identify and evaluate potential risks and the magnitude of their impact on the project. With this information, you can develop the most effective mitigation strategy and take control of the project's outcome.
Here’s a detailed Risk Assessment Matrix Template, a convenient design to evaluate and analyze potential risks and facilitate clear communication. Additionally, it includes a section dedicated to planning for risk mitigation. Click here to download this editable Risk Matrix Template.
STEP 4: QUALITY REVIEW
Project Quality Review is a systematic evaluation to ensure that the project meets the quality standards. Here are five techniques used in a Project Quality Review:
- Maintaining product quality checklist: It is a tool to ensure that all quality checks have been performed.
- Quality check register maintenance: A quality check register is a document that records the results of the quality checks performed on the product.
- Quality check schedule: The schedule should include the frequency of the checks, the items that will be checked, and the personnel responsible.
- Auditing committee for quality review: An auditing committee is a group responsible for conducting quality reviews of the project. The committee should have the expertise to provide recommendations for improvement.
- Frequent communication within the project: It ensures that stakeholders are informed of the progress and that any issues are identified and addressed promptly.
If you are planning to maintain a quality check register for your upcoming project, but are struggling to develop a well-structured layout, then explore this design. Click here to download this customizable Quality Check Template.
STEP 5: QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
The Quality Improvement Initiative addresses challenges and problems arising from quality assurance and control through continuous improvement. This may involve modifications to product specifications, project plans, quality management processes, and other aspects such as control, risk management, and procurement management. The improvement cycle not only enhances the quality of the current project but also sets the stage for future projects with its documentation of the lessons learnt.
STEP 6: TRACKING QUALITY WITH DASHBOARDS
Managing a project's quality without a dashboard is like navigating a road trip blindfolded. You may reach your destination, but the journey is unpredictable, stressful and prone to mistakes. Having a dashboard for quality management is not just a luxury, it's a necessity for ensuring the success of your project and delivering a high-quality final product.
You must develop a dashboard to get real-time, consolidated views of key quality metrics and performance indicators. This allows project managers and stakeholders to quickly assess the health of a project and identify any quality-related issues that need to be addressed.
Dashboards can also help to increase visibility into the quality control process and provide a clear understanding of the status of quality-related tasks and activities. They can be used to track the performance of individual team members, assess the impact of quality improvement initiatives, and monitor compliance with quality standards.
Wondering how to create a dashboard for your next project? We have a fantastic Quality Dashboard Template to share. Click here to download this editable Dashboard Template.
DON'T SETTLE FOR MEDIOCRITY
Embrace Project Quality Management and watch as your team rises to the challenge of excellence. Your projects will benefit from improved planning, better risk management, and increased accountability. The results will speak for themselves: higher quality outcomes, increased customer satisfaction, and greater project success.
The choice is yours. Will you be a leader in the new era of quality-driven projects, or will you be left behind? Invest in Project Quality Management, and unleash the full potential of your projects. The time for action is now, so make a move toward excellence today. Get started by downloading these well-researched templates created by our expert teams.
PS: If you struggle to control your project costs, explore this quick guide on Project Cost Management with templates, samples, and examples.
FAQs on Project Quality Management
What are quality management tools and techniques?
Quality Management Tools and Techniques are used to improve the quality of a project and its outcomes. They are essential components of a comprehensive Project Quality Management approach. Here are a few frequently-used tools and techniques:
Project Quality Metrics: These are measures used to assess the quality of a project and its outputs. Project Quality Metrics can include measures of productivity, cost, customer satisfaction, and compliance with quality standards.
Statistical Process Control: Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a statistical method used to monitor and control a process to ensure it is operating within established limits. This tool is often used in manufacturing, but it can be applied to any process, including project management.
Root Cause Analysis: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a method used to identify the root cause of a problem or issue. This tool can help organizations identify the underlying cause of a quality issue and take steps to prevent recurrence.
Quality Audits: Quality Audits are systematic reviews of a process, product, or service to assess the quality of the output. Quality Audits are performed internally by the project team, or externally by a third-party auditor.
What are the quality standards in a software product?
Here are a few examples of quality standards in software:
ISO/IEC 9126: This is an international standard for software product quality that provides a framework for evaluating software quality in terms of functionality, reliability, usability, efficiency, maintainability, and portability.
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration): This is a process improvement model that provides a structured approach to software development.
SPICE (Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination): This is an international standard for evaluating software development processes and provides a framework for continuous improvement.
Agile: This is a methodology for software development that emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement and helps organizations deliver high-quality software in short development cycles.
These are just a few examples of quality standards in software, and organizations can choose to adopt one or more of these standards, depending on their specific needs and requirements.




 Customer Reviews
Customer Reviews